



生物多样性 ›› 2017, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (5): 464-480. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2017024 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2017024
斯幸峰, 赵郁豪, 陈传武, 任鹏, 曾頔, 吴玲兵, 丁平*( )
)
收稿日期:2017-01-24
接受日期:2017-05-13
出版日期:2017-05-20
发布日期:2017-06-06
通讯作者:
丁平
基金资助:
Xingfeng Si, Yuhao Zhao, Chuanwu Chen, Peng Ren, Di Zeng, Lingbing Wu, Ping Ding*( )
)
Received:2017-01-24
Accepted:2017-05-13
Online:2017-05-20
Published:2017-06-06
Contact:
Ding Ping
摘要:
Beta多样性是指不同群落间物种组成的差异, 由物种周转(或物种替换)和嵌套(或丰富度差异)这两种过程决定。Beta多样性分解是将这两种过程对总体beta多样性的作用进行拆分, 然后分别探讨这两种过程对群落间物种组成差异的影响。2010年之后, 人们提出了beta多样性分解的方法, 其中占据主导地位的是由Andrés Baselga于2010年提出的BAS法(总体beta多样性分解为物种周转和嵌套组分)和由János Podani和Dénes Schmera于2011年以及José C. Carvalho等于2012年提出的POD法(总体beta多样性分解为物种替换和丰富度差异组分)。这两种分解方法引起了持续的争论, 促进了该领域的快速发展。作者归纳分析了2010年后有关beta多样性分解的文献后发现, 使用BAS法的论文无论在发表量和引用次数上都多于POD法(75% vs. 20%)。Beta多样性分解的研究主要集中在欧洲(45%), 研究类群则以动物(64%)为主。本文在回顾beta多样性分解方法的提出及其发展过程的基础上, 从时空维度(纬度梯度、海拔梯度、生境片断化过程以及季节和年际动态)、多样性的不同方面(物种、功能和谱系多样性)和不同生物类群之间的比较等研究角度出发, 进一步阐述了beta多样性分解方法在探讨生物多样性分布格局以及形成机制中的应用。对于beta多样性分解的研究, 我们认为需要深入探讨的问题有: (1) beta多样性分解方法的比较分析和整合; (2)结合物种多度信息探讨beta多样性及其组分的分布格局; (3)对大尺度下beta多样性分解的结果进行普适性验证。
斯幸峰, 赵郁豪, 陈传武, 任鹏, 曾頔, 吴玲兵, 丁平 (2017) Beta多样性分解: 方法、应用与展望. 生物多样性, 25, 464-480. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2017024.
Xingfeng Si, Yuhao Zhao, Chuanwu Chen, Peng Ren, Di Zeng, Lingbing Wu, Ping Ding (2017) Beta-diversity partitioning: methods, applications and perspectives. Biodiversity Science, 25, 464-480. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2017024.
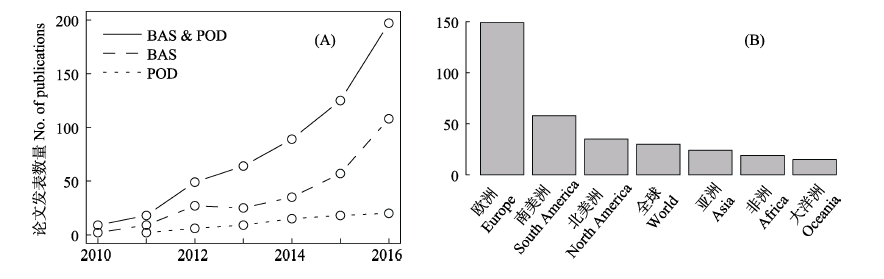
图1 2010-2016年间beta多样性分解研究领域的论文发表状况。(A)引用BAS法和POD法的年度论文发表数量,以及使用BAS法或POD法分析数据的年度论文发表数量; (B)地区分布
Fig. 1 Publications for studies in the field of beta-diversity partitioning from 2010 to 2016. (A) Number of annual publications cited BAS and POD methods, and using BAS or POD method to analyze the data; (B) Distribution of research areas
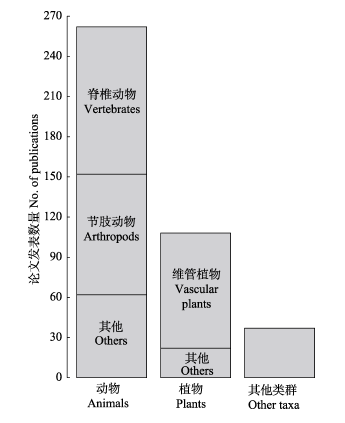
图2 2010-2016年间beta多样性分解论文所涉及的生物门类及相应发表论文数量
Fig. 2 Number of publications for each biological taxon in the field of beta-diversity partitioning from 2010 to 2016
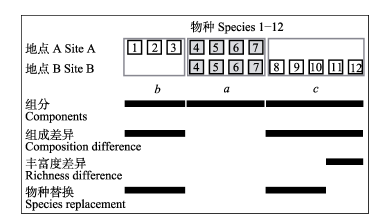
图3 两个研究地点间物种组成示意图。a为共有物种数, b和c分别是两个地点各自特有的物种数。两个研究地点间物种的组成差异为b + c, 丰富度差异为|b - c|, 以及物种替换为2 min (b, c)。
Fig. 3 Demonstration of species compositions between two sites. a is the number of shared species, b and c are the species exclusive to each site. The number of compositional differences between two sites is b + c. Richness difference is |b - c|, and species replacement is given by 2 min (b, c).
| [1] | Almeida-Neto M, Frensel D, Ulrich W (2012) Rethinking the relationship between nestedness and beta diversity: a comment on Baselga (2010). Global Ecology and Biogeography, 21, 772-777. |
| [2] | Almeida-Neto M, Guimarães P, Guimarães PR, Loyola RD, Ulrich W (2008) A consistent metric for nestedness analysis in ecological systems: reconciling concept and measurement. Oikos, 117, 1227-1239. |
| [3] | Anderson MJ, Crist TO, Chase JM, Vellend M, Inouye BD, Freestone AL, Sanders NJ, Cornell HV, Comita LS, Davies KF (2011) Navigating the multiple meanings of β diversity: a roadmap for the practicing ecologist. Ecology Letters, 14, 19-28. |
| [4] | Andrew ME, Wulder MA, Coops NC, Baillargeon G (2012) Beta-diversity gradients of butterflies along productivity axes. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 21, 352-364. |
| [5] | Angeler DG (2013) Revealing a conservation challenge through partitioned long-term beta diversity: increasing turnover and decreasing nestedness of boreal lake metacommunities. Diversity and Distributions, 19, 772-781. |
| [6] | Atmar W, Patterson BD (1993) The measure of order and disorder in the distribution of species in fragmented habitat. Oecologia, 96, 373-382. |
| [7] | Baselga A (2010) Partitioning the turnover and nestedness components of beta diversity. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 19, 134-143. |
| [8] | Baselga A (2012) The relationship between species replacement, dissimilarity derived from nestedness, and nestedness. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 21, 1223-1232. |
| [9] | Baselga A (2013a) Multiple site dissimilarity quantifies compositional heterogeneity among several sites, while average pairwise dissimilarity may be misleading. Ecography, 36, 124-128. |
| [10] | Baselga A (2013b) Separating the two components of abundance-based dissimilarity: balanced changes in abundance vs. abundance gradients. Methods in Ecology and Evolution, 4, 552-557. |
| [11] | Baselga A (2017) Partitioning abundance-based multiple-site dissimilarity into components: balanced variation in abundance and abundance gradients. Methods in Ecology and Evolution, 8, doi: 10.1111/2041-1210X.12693. |
| [12] | Baselga A, Bonthoux S, Balent G (2015) Temporal beta diversity of bird assemblages in agricultural landscapes: land cover change vs. stochastic processes. PLoS ONE, 10, e0127913. |
| [13] | Baselga A, Gómez-Rodríguez C, Lobo JM (2012) Historical legacies in world amphibian diversity revealed by the turnover and nestedness components of beta diversity. PLoS ONE, 7, e32341. |
| [14] | Baselga A, Jiménez-Valverde A, Niccolini G (2007) A multiple-site similarity measure independent of richness. Biology Letters, 3, 642-645. |
| [15] | Baselga A, Leprieur F (2015) Comparing methods to separate components of beta diversity. Methods in Ecology and Evolution, 6, 1069-1079. |
| [16] | Baselga A, Orme CDL (2012) betapart: an R package for the study of beta diversity. Methods in Ecology and Evolution, 3, 808-812. |
| [17] | Bellier E, Grøtan V, Engen S, Schartau AK, Herfindal I, Finstad AG (2014) Distance decay of similarity, effects of environmental noise and ecological heterogeneity among species in the spatio-temporal dynamics of a dispersal-limited community. Ecography, 37, 172-182. |
| [18] | Benedick S, Hill JK, Mustaffa N, Chey VK, Maryati M, Searle JB, Schilthuizen M, Hamer KC (2006) Impacts of rain forest fragmentation on butterflies in northern Borneo: species richness, turnover and the value of small fragments. Journal of Applied Ecology, 43, 967-977. |
| [19] | Beng KC, Tomlinson KW, Shen XH, Surget-Groba Y, Hughes AC, Corlett RT, Slik JWF (2016) The utility of DNA metabarcoding for studying the response of arthropod diversity and composition to land-use change in the tropics. Scientific Reports, 6, 24965. |
| [20] | Bishop TR, Robertson MP, Rensburg BJ, Parr CL (2015) Contrasting species and functional beta diversity in montane ant assemblages. Journal of Biogeography, 42, 1776-1786. |
| [21] | Boieiro M, Carvalho JC, Cardoso P, Aguiar CAS, Rego C, de Faria e Silva I, Amorim IR, Pereira F, Azevedo EB, Borges PAV, Serrano ARM (2013) Spatial factors play a major role as determinants of endemic ground beetle beta diversity of Madeira Island Laurisilva. PLoS ONE, 8, e64591. |
| [22] | Brown JH (2001) Mammals on mountainsides: elevational patterns of diversity. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 10, 101-109. |
| [23] | Bryant JA, Lamanna C, Morlon H, Kerkhoff AJ, Enquist BJ, Green JL (2008) Microbes on mountainsides: contrasting elevational patterns of bacterial and plant diversity. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 105, 11505-11511. |
| [24] | Buckley LB, Jetz W (2008) Linking global turnover of species and environments. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 105, 17836-17841. |
| [25] | Calderón-Patrón JM, Moreno CE, Pineda-López R, Sánchez- Rojas G, Zuria I (2013) Vertebrate dissimilarity due to turnover and richness differences in a highly beta-diverse region: the role of spatial grain size, dispersal ability and distance. PLoS ONE, 8, e82905. |
| [26] | Cardoso P, Borges PAV, Veech JA (2009) Testing the performance of beta diversity measures based on incidence data: the robustness to undersampling. Diversity and Distributions, 15, 1081-1090. |
| [27] | Cardoso P, Rigal F, Carvalho JC (2015) BAT—biodiversity assessment tools, an R package for the measurement and estimation of alpha and beta taxon, phylogenetic and functional diversity. Methods in Ecology and Evolution, 6, 232-236. |
| [28] | Cardoso P, Rigal F, Carvalho JC, Fortelius M, Borges PAV, Podani J, Schmera D (2014) Partitioning taxon, phylogenetic and functional beta diversity into replacement and richness difference components. Journal of Biogeography, 41, 749-761. |
| [29] | Carvalho JC, Cardoso P, Borges PAV, Schmera D, Podani J (2013) Measuring fractions of beta diversity and their relationships to nestedness: a theoretical and empirical comparison of novel approaches. Oikos, 122, 825-834. |
| [30] | Carvalho JC, Cardoso P, Crespo LC, Henriques S, Carvalho R, Gomes P (2011) Determinants of beta diversity of spiders in coastal dunes along a gradient of mediterraneity. Diversity and Distributions, 17, 225-234. |
| [31] | Carvalho JC, Cardoso P, Gomes P (2012) Determining the relative roles of species replacement and species richness differences in generating beta-diversity patterns. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 21, 760-771. |
| [32] | Cavender-Bares J, Kozak KH, Fine PVA, Kembel SW (2009) The merging of community ecology and phylogenetic biology. Ecology Letters, 12, 693-715. |
| [33] | Chen SB, Ouyang ZY, Xu WH, Xiao Y (2010) A review of beta diversity studies. Biodiversity Science, 18, 323-335. |
| (in Chinese with English abstract) [陈圣宾, 欧阳志云, 徐卫华, 肖燚 (2010) Beta多样性研究进展. 生物多样性, 18, 323-335.] | |
| [34] | Cody ML (1975) Towards a theory of continental species diversities: bird distributions over Mediterranean habitat gradients. In: Ecology and Evolution of Communities (eds Cody ML, Diamond JM), pp. 214-257. Harvard University Press, Cambridge. |
| [35] | Colwell RK, Coddington JA (1994) Estimating terrestrial biodiversity through extrapolation. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London, Series B: Biological Sciences, 345, 101-118. |
| [36] | Colwell RK, Gotelli NJ, Ashton LA, Beck J, Brehm G, Fayle TM, Fiedler K, Forister ML, Kessler M, Kitching RL (2016) Midpoint attractors and species richness: modelling the interaction between environmental drivers and geometric constraints. Ecology Letters, 19, 1009-1022. |
| [37] | Colwell RK, Lees DC (2000) The mid-domain effect: geometric constraints on the geography of species richness. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 15, 70-76. |
| [38] | Devictor V, Mouillot D, Meynard C, Jiguet F, Thuiller W, Mouquet N (2010) Spatial mismatch and congruence between taxonomic, phylogenetic and functional diversity: the need for integrative conservation strategies in a changing world. Ecology Letters, 13, 1030-1040. |
| [39] | Diserud OH, Ødegaard F (2007) A multiple-site similarity measure. Biology Letters, 3, 20-22. |
| [40] | Dobrovolski R, Melo AS, Cassemiro FAS, Diniz-Filho JAF (2012) Climatic history and dispersal ability explain the relative importance of turnover and nestedness components of beta diversity. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 21, 191-197. |
| [41] | Ensing DJ, Pither J (2015) A novel multiple-site extension to pairwise partitioned taxonomic beta diversity. Ecological Complexity, 21, 62-69. |
| [42] | Fahrig L (2017) Ecological responses to habitat fragmentation per se. Annual Review of Ecology, Evolution, and Systematics, 48, doi: 10.1146/annurev-ecolsys-110316-022612. |
| [43] | Faith DP (1992) Conservation evaluation and phylogenetic diversity. Biological Conservation, 61, 1-10. |
| [44] | Fernandez LD, Fournier B, Rivera R, Lara E, Mitchell EAD, Hernandez CE (2016) Water-energy balance, past ecological perturbations and evolutionary constraints shape the latitudinal diversity gradient of soil testate amoebae in south- western South America. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 25, 1216-1227. |
| [45] | Foord SH, Dippenaar-Schoeman AS (2016) The effect of elevation and time on mountain spider diversity: a view of two aspects in the Cederberg mountains of South Africa. Journal of Biogeography, 43, 2354-2365. |
| [46] | Fukami T (2015) Historical contingency in community assembly: integrating niches, species pools, and priority effects. Annual Review of Ecology, Evolution, and Systematics, 46, 1-23. |
| [47] | Fukami T, Bezemer TM, Mortimer SR, Putten WH (2005) Species divergence and trait convergence in experimental plant community assembly. Ecology Letters, 8, 1283-1290. |
| [48] | Gibson L, Lynam AJ, Bradshaw CJA, He F, Bickford DP, Woodruff DS, Bumrungsri S, Laurance WF (2013) Near-complete extinction of native small mammal fauna 25 years after forest fragmentation. Science, 341, 1508-1510. |
| [49] | Graham CH, Fine PV (2008) Phylogenetic beta diversity: linking ecological and evolutionary processes across space in time. Ecology Letters, 11, 1265-1277. |
| [50] | Guadagnin DL, Peter ÂS, Perello LFC, Maltchik L (2005) Spatial and temporal patterns of waterbird assemblages in fragmented wetlands of southern Brazil. Waterbirds, 28, 261-272. |
| [51] | Gutiérrez-Cánovas C, Millán A, Velasco J, Vaughan IP, Ormerod SJ (2013) Contrasting effects of natural and anthropogenic stressors on beta diversity in river organisms. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 22, 796-805. |
| [52] | Habel JC, Segerer A, Ulrich W, Torchyk O, Weisser WW, Schmitt T (2016) Butterfly community shifts over 2 centuries. Conservation Biology, 30, 754-762. |
| [53] | Halley JM, Iwasa Y (2011) Neutral theory as a predictor of avifaunal extinctions after habitat loss. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 108, 2316-2321. |
| [54] | Harrison S, Ross SJ, Lawton JH (1992) Beta diversity on geographic gradients in Britain. Journal of Animal Ecology, 61, 151-158. |
| [55] | Herzog SK, Kessler M, Bach K (2005) The elevational gradient in Andean bird species richness at the local scale: a foothill peak and a high-elevation plateau. Ecography, 28, 209-222. |
| [56] | Hillebrand H (2004) On the generality of the latitudinal diversity gradient. The American Naturalist, 163, 192-211. |
| [57] | Hortal J, Diniz-Filho JAF, Bini LM, Angel Rodriguez M, Baselga A, Nogues-Bravo D, Rangel TF, Hawkins BA, Lobo JM (2011) Ice age climate, evolutionary constraints and diversity patterns of European dung beetles. Ecology Letters, 14, 741-748. |
| [58] | James A, Pitchford JW, Plank MJ (2012) Disentangling nestedness from models of ecological complexity. Nature, 487, 227-230. |
| [59] | Jankowski JE, Ciecka AL, Meyer NY, Rabenold KN (2009) Beta diversity along environmental gradients: implications of habitat specialization in tropical montane landscapes. Journal of Animal Ecology, 78, 315-327. |
| [60] | Jetz W, Thomas G, Joy J, Hartmann K, Mooers A (2012) The global diversity of birds in space and time. Nature, 491, 444-448. |
| [61] | Kattan GH, Franco P, Saavedra-Rodríguez CA, Valderrama C, Rojas V, Osorio D, Martínez J (2006) Spatial components of bird diversity in the Andes of Colombia: implications for designing a regional reserve system. Conservation Biology, 20, 1203-1211. |
| [62] | Koleff P, Gaston KJ, Lennon JJ (2003a) Measuring beta diversity for presence-absence data. Journal of Animal Ecology, 72, 367-382. |
| [63] | Koleff P, Lennon JJ, Gaston KJ (2003b) Are there latitudinal gradients in species turnover? Global Ecology and Biogeography, 12, 483-498. |
| [64] | Kraft NJB, Comita LS, Chase JM, Sanders NJ, Swenson NG, Crist TO, Stegen JC, Vellend M, Boyle B, Anderson MJ (2011) Disentangling the drivers of β diversity along latitudinal and elevational gradients. Science, 333, 1755-1758. |
| [65] | Krauss J, Bommarco R, Guardiola M, Heikkinen RK, Helm A, Kuussaari M, Lindborg R, Öckinger E, Pärtel M, Pino J, Pöyry J, Raatikainen KM, Sang A, Stefanescu C, Teder T, Zobel M, Steffan-Dewenter I (2010) Habitat fragmentation causes immediate and time-delayed biodiversity loss at different trophic levels. Ecology Letters, 13, 597-605. |
| [66] | Lamy T, Legendre P, Chancerelle Y, Siu G, Claudet J (2015) Understanding the spatio-temporal response of coral reef fish communities to natural disturbances: insights from beta-diversity decomposition. PLoS ONE, 10, e0138696. |
| [67] | Legendre P (2014) Interpreting the replacement and richness difference components of beta diversity. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 23, 1324-1334. |
| [68] | Legendre P, De Cáceres M (2013) Beta diversity as the variance of community data: dissimilarity coefficients and partitioning. Ecology Letters, 16, 951-963. |
| [69] | Lennon JJ, Koleff P, Greenwood J, Gaston KJ (2001) The geographical structure of British bird distributions: diversity, spatial turnover and scale. Journal of Animal Ecology, 70, 966-979. |
| [70] | Leprieur F, Albouy C, De Bortoli J, Cowman PF, Bellwood DR, Mouillot D (2012) Quantifying phylogenetic beta diversity: distinguishing between ‘true’ turnover of lineages and phylogenetic diversity gradients. PLoS ONE, 7, e42760. |
| [71] | Leprieur F, Oikonomou A (2014) The need for richness-independent measures of turnover when delineating biogeographical regions. Journal of Biogeography, 41, 417-420. |
| [72] | Leprieur F, Tedesco PA, Hugueny B, Beauchard O, Dürr HH, Brosse S, Oberdorff T (2011) Partitioning global patterns of freshwater fish beta diversity reveals contrasting signatures of past climate changes. Ecology Letters, 14, 325-334. |
| [73] | Lewis RJ, Marrs RH, Pakeman RJ, Milligan G, Lennon JJ (2016) Climate drives temporal replacement and nested-resultant richness patterns of Scottish coastal vegetation. Ecography, 39, 754-762. |
| [74] | Li SP, Cadotte MW, Meiners SJ, Pu Z, Fukami T, Jiang L (2016) Convergence and divergence in a long-term old-field succession: the importance of spatial scale and species abundance. Ecology Letters, 19, 1101-1109. |
| [75] | Liu C, Dudley KL, Xu Z-H, Economo EP (2017) Mountain metacommunities: climate and spatial connectivity shape ant diversity in a complex landscape. Ecography, 40, doi: 10.1111/ecog.03067. |
| [76] | Liu YN, Tang ZY, Fang JY (2015) Contribution of environmental filtering and dispersal limitation to species turnover of temperate deciduous broad-leaved forests in China. Applied Vegetation Science, 18, 34-42. |
| [77] | Loiseau N, Legras G, Gaertner JC, Verley P, Chabanet P, Mérigot B (2017) Performance of partitioning functional beta-diversity indices: influence of functional representation and partitioning methods. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 26, doi: 10.1111/geb.12581. |
| [78] | Lomolino M (2001) Elevation gradients of species-density: historical and prospective views. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 10, 3-13. |
| [79] | Losos JB (1996) Phylogenetic perspectives on community ecology. Ecology, 77, 1344-1354. |
| [80] | Marini L, Bertolli A, Bona E, Federici G, Martini F, Prosser F, Bommarco R (2013) Beta-diversity patterns elucidate mechanisms of alien plant invasion in mountains. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 22, 450-460. |
| [81] | Martiny JBH, Bohannan BJ, Brown JH, Colwell RK, Fuhrman JA, Green JL, Horner-Devine MC, Kane M, Krumins JA, Kuske CR (2006) Microbial biogeography: putting microorganisms on the map. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 4, 102-112. |
| [82] | McCain CM (2009) Global analysis of bird elevational diversity. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 18, 346-360. |
| [83] | McCain CM, Beck J (2016) Species turnover in vertebrate communities along elevational gradients is idiosyncratic and unrelated to species richness. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 25, 299-310. |
| [84] | McGill BJ, Enquist BJ, Weiher E, Westoby M (2006) Rebuilding community ecology from functional traits. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 21, 178-185. |
| [85] | McKnight MW, White PS, McDonald RI, Lamoreux JF, Sechrest W, Ridgely RS, Stuart SN (2007) Putting beta-diversity on the map: broad-scale congruence and coincidence in the extremes. PLoS Biology, 5, e272. |
| [86] | Melo AS, Rangel TFL, Diniz-Filho JAF (2009) Environmental drivers of beta-diversity patterns in New-World birds and mammals. Ecography, 32, 226-236. |
| [87] | Mori AS, Shiono T, Haraguchi TF, Ota AT, Koide D, Ohgue T, Kitagawa R, Maeshiro R, Aung TT, Nakamori T, Hagiwara Y, Matsuoka S, Ikeda A, Hishi T, Hobara S, Mizumachi E, Frisch A, Thor G, Fujii S, Osono T, Gustafsson L (2015) Functional redundancy of multiple forest taxa along an elevational gradient: predicting the consequences of non-random species loss. Journal of Biogeography, 42, 1383-1396. |
| [88] | Mori AS, Shiono T, Koide D, Kitagawa R, Ota AT, Mizumachi E (2013) Community assembly processes shape an altitudinal gradient of forest biodiversity. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 22, 878-888. |
| [89] | Mouillot D, De Bortoli J, Leprieur F, Parravicini V, Kulbicki M, Bellwood DR (2013) The challenge of delineating biogeographical regions: nestedness matters for Indo-Pacific coral reef fishes. Journal of Biogeography, 40, 2228-2237. |
| [90] | Nekola JC, White PS (1999) The distance decay of similarity in biogeography and ecology. Journal of Biogeography, 26, 867-878. |
| [91] | Orrock JL, Watling JI (2010) Local community size mediates ecological drift and competition in metacommunities. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London B: Biological Sciences, 277, 2185-2191. |
| [92] | Patterson BD, Atmar W (1986) Nested subsets and the structure of insular mammalian faunas and archipelagos. Biological Journal of the Linnean Society, 28, 65-82. |
| [93] | Petchey OL, Gaston KJ (2002) Functional diversity (FD), species richness and community composition. Ecology Letters, 5, 402-411. |
| [94] | Petchey OL, Gaston KJ (2006) Functional diversity: back to basics and looking forward. Ecology Letters, 9, 741-758. |
| [95] | Pianka ER (1966) Latitudinal gradients in species diversity: a review of concepts. The American Naturalist, 100, 33-46. |
| [96] | Pimm SL, Diamond J, Reed TM, Russell GJ, Verner J (1993) Times to extinction for small populations of large birds. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 90, 10871-10875. |
| [97] | Pimm SL, Jenkins CN, Abell R, Brooks TM, Gittleman JL, Joppa LN, Raven PH, Roberts CM, Sexton JO (2014) The biodiversity of species and their rates of extinction, distribution, and protection. Science, 344, 987-997. |
| [98] | Podani J, Ricotta C, Schmera D (2013) A general framework for analyzing beta diversity, nestedness and related community-level phenomena based on abundance data. Ecological Complexity, 15, 52-61. |
| [99] | Podani J, Schmera D (2011) A new conceptual and methodological framework for exploring and explaining pattern in presence-absence data. Oikos, 120, 1625-1638. |
| [100] | Podani J, Schmera D (2016) Once again on the components of pairwise beta diversity. Ecological Informatics, 32, 63-68. |
| [101] | Ponisio LC, M’Gonigle LK, Kremen C (2016) On-farm habitat restoration counters biotic homogenization in intensively managed agriculture. Global Change Biology, 22, 704-715. |
| [102] | Qian H (2009) Beta diversity in relation to dispersal ability for vascular plants in North America. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 18, 327-332. |
| [103] | Qian H, Chen SB, Mao LF, Ouyang ZY (2013) Drivers of β-diversity along latitudinal gradients revisited. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 22, 659-670. |
| [104] | Qian H, Ricklefs RE (2007) A latitudinal gradient in large-scale beta diversity for vascular plants in North America. Ecology Letters, 10, 737-744. |
| [105] | Rahbek C (1995) The elevational gradient of species richness: a uniform pattern? Ecography, 18, 200-205. |
| [106] | Rahbek C (2005) The role of spatial scale and the perception of large-scale species-richness patterns. Ecology Letters, 8, 224-239. |
| [107] | Ricklefs RE (1987) Community diversity: relative roles of local and regional processes. Science, 235, 167-171. |
| [108] | Ricotta C, Carranza ML, Avena G (2002) Computing β-diversity from species-area curves. Basic and Applied Ecology, 3, 15-18. |
| [109] | Ricotta C, Pavoine S (2015) A multiple-site dissimilarity measure for species presence/absence data and its relationship with nestedness and turnover. Ecological Indicators, 54, 203-206. |
| [110] | Rosenzweig ML (1995) Species Diversity in Space and Time. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge. |
| [111] | Schmera D, Podani J (2011) Comments on separating components of beta diversity. Community Ecology, 12, 153-160. |
| [112] | Sheldon KS, Yang S, Tewksbury JJ (2011) Climate change and community disassembly: impacts of warming on tropical and temperate montane community structure. Ecology Letters, 14, 1191-1200. |
| [113] | Shimadzu H, Dornelas M, Magurran AE (2015) Measuring temporal turnover in ecological communities. Methods in Ecology and Evolution, 6, 1384-1394. |
| [114] | Si XF (2014) Species Turnover and Beta Diversity of Breeding Bird Communities in Fragmented Habitats. PhD Dissertation, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou. |
| (in Chinese with English abstract) [斯幸峰 (2014) 片段化生境中繁殖鸟类群落的物种周转和β多样性. 博士学位论文, 浙江大学, 杭州.] | |
| [115] | Si XF, Baselga A, Ding P (2015) Revealing beta-diversity patterns of breeding bird and lizard communities on inundated land-bridge islands by separating the turnover and nestedness components. PLoS ONE, 10, e0127692. |
| [116] | Si XF, Baselga A, Leprieur F, Song X, Ding P (2016) Selective extinction drives taxonomic and functional alpha and beta diversities in island bird assemblages. Journal of Animal Ecology, 85, 409-418. |
| [117] | Si XF, Cadotte MW, Zeng D, Baselga A, Zhao YH, Li JQ, Wu YR, Wang SY, Ding P (2017) Functional and phylogenetic structure of island bird communities. Journal of Animal Ecology, 86, 532-542. |
| [118] | Si XF, Ding P (2011) History, status of monitoring land birds in Europe and American and countermeasures of China. Biodiversity Science, 19, 303-310. |
| (in Chinese with English abstract) [斯幸峰, 丁平 (2011) 欧美陆地鸟类监测的历史、现状与我国的对策. 生物多样性, 19, 303-310.] | |
| [119] | Si XF, Pimm SL, Russell GJ, Ding P (2014) Turnover of breeding bird communities on islands in an inundated lake. Journal of Biogeography, 41, 2283-2292. |
| [120] | Siefert A, Ravenscroft C, Weiser MD, Swenson NG (2013) Functional beta-diversity patterns reveal deterministic community assembly processes in eastern North American trees. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 22, 682-691. |
| [121] | Socolar JB, Gilroy JJ, Kunin WE, Edwards DP (2016) How should beta-diversity inform biodiversity conservation? Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 31, 67-80. |
| [122] | Sodhi NS, Wilcove DS, Lee TM, Sekercioglu CH, Subaraj R, Bernard H, Yong DL, Lim SLH, Prawiradilaga DM, Brook BW (2010) Deforestation and avian extinction on tropical landbridge islands. Conservation Biology, 24, 1290-1298. |
| [123] | Soininen J, McDonald R, Hillebrand H (2007) The distance decay of similarity in ecological communities. Ecography, 30, 3-12. |
| [124] | Staniczenko PP, Kopp JC, Allesina S (2013) The ghost of nestedness in ecological networks. Nature Communications, 4, 1391. |
| [125] | Stegen JC, Hurlbert AH (2011) Inferring ecological processes from taxonomic, phylogenetic and functional trait beta-diversity. PLoS ONE, 6, e20906. |
| [126] | Steinitz O, Heller J, Tsoar A, Rotem D, Kadmon R (2006) Environment, dispersal and patterns of species similarity. Journal of Biogeography, 33, 1044-1054. |
| [127] | Su G, Xu J, Akasaka M, Molinos JG, Shin-ichiro SM (2015) Human impacts on functional and taxonomic homogenization of plateau fish assemblages in Yunnan, China. Global Ecology and Conservation, 4, 470-478. |
| [128] | Svenning J-C, Fløjgaard C, Baselga A (2011) Climate, history and neutrality as drivers of mammal beta diversity in Europe: insights from multiscale deconstruction. Journal of Animal Ecology, 80, 393-402. |
| [129] | Swenson NG, Anglada-Cordero P, Barone JA (2011a) Deterministic tropical tree community turnover: evidence from patterns of functional beta diversity along an elevational gradient. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 278, 877-884. |
| [130] | Swenson NG, Stegen JC, Davies SJ, Erickson DL, Forero-Montaña J, Hurlbert AH, Kress WJ, Thompson J, Uriarte M, Wright SJ, Zimmerman JK (2011b) Temporal turnover in the composition of tropical tree communities: functional determinism and phylogenetic stochasticity. Ecology, 93, 490-499. |
| [131] | Tang ZY, Fang JY, Chi XL, Feng JM, Liu YN, Shen Z-H, Wang XP, Wang Z-H, Wu XP, Zheng CY (2012) Patterns of plant beta-diversity along elevational and latitudinal gradients in mountain forests of China. Ecography, 35, 1083-1091. |
| [132] | Terborgh JW (2015) Toward a trophic theory of species diversity. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 112, 11415-11422. |
| [133] | Thorn S, Bässler C, Bernhardt-Römermann M, Cadotte M, Heibl C, Schäfer H, Seibold S, Müller J (2016) Changes in the dominant assembly mechanism drive species loss caused by declining resources. Ecology Letters, 19, 163-170. |
| [134] | Tilman D (2001) Functional diversity. In: Encyclopedia of Biodiversity (ed. Levin SA), pp. 109-120. Academic Press, San Diego. |
| [135] | Tuomisto H (2010a) A diversity of beta diversities: straightening up a concept gone awry. Part 1. Defining beta diversity as a function of alpha and gamma diversity. Ecography, 33, 2-22. |
| [136] | Tuomisto H (2010b) A diversity of beta diversities: straightening up a concept gone awry. Part 2. Quantifying beta diversity and related phenomena. Ecography, 33, 23-45. |
| [137] | Uchida K, Ushimaru A (2015) Land abandonment and intensification diminish spatial and temporal β-diversity of grassland plants and herbivorous insects within paddy terraces. Journal of Applied Ecology, 52, 1033-1043. |
| [138] | Ulrich W, Almeida-Neto M, Gotelli NJ (2009) A consumer’s guide to nestedness analysis. Oikos, 118, 3-17. |
| [139] | Umaña MN, Zhang C, Cao M, Lin L, Swenson NG (2015) Commonness, rarity, and intraspecific variation in traits and performance in tropical tree seedlings. Ecology Letters, 18, 1329-1337. |
| [140] | Urban MC (2015) Accelerating extinction risk from climate change. Science, 348, 571-573. |
| [141] | Villéger S, Grenouillet G, Brosse S (2013) Decomposing functional β-diversity reveals that low functional β-diversity is driven by low functional turnover in European fish assemblages. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 22, 671-681. |
| [142] | Villéger S, Mason NW, Mouillot D (2008) New multidimensional functional diversity indices for a multifaceted framework in functional ecology. Ecology, 89, 2290-2301. |
| [143] | Villéger S, Miranda JR, Hernandez DF, Mouillot D (2012) Low functional β-diversity despite high taxonomic β-diversity among tropical estuarine fish communities. PLoS ONE, 7, e40679. |
| [144] | Wang GM, Zuo JC, Li XR, Liu YH, Yu JB, Shao HB, Li YZ (2014) Low plant diversity and floristic homogenization in fast-urbanizing towns in Shandong Peninsular, China: effects of urban greening at regional scale for ecological engineering. Ecological Engineering, 64, 179-185. |
| [145] | Wang J, Meier S, Soininen J, Casamayor EO, Pan F, Tang X, Yang X, Zhang Y, Wu Q, Zhou J, Shen J (2017) Regional and global elevational patterns of microbial species richness and evenness. Ecography, 40, 393-402. |
| [146] | Wang J, Pan F, Soininen J, Heino J, Shen J (2016) Nutrient enrichment modifies temperature-biodiversity relationships in large-scale field experiments. Nature Communications, 7, 13960. |
| [147] | Wang J, Soininen J, Zhang Y, Wang B, Yang X, Shen J (2012) Patterns of elevational beta diversity in micro- and macroorganisms. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 21, 743-750. |
| [148] | Wang SX, Wang XA, Guo H (2013) Change patterns of beta-diversity in the succession process of plant communities on Loess Plateau of Northwest China. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 32, 1135-1140. |
| (in Chinese with English abstract) [王世雄, 王孝安, 郭华 (2013) 黄土高原植物群落演替过程中的β多样性变化. 生态学杂志, 32, 1135-1140.] | |
| [149] | Wang SX, Zhao L, Li N, Guo H, Wang XA, Duan RY (2016) Community heterogeneity of undergrowth vegetation in Pinus tabuliformis forest on the Loess Plateau of Northwest China. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 35, 1197-1203. |
| (in Chinese with English abstract) [王世雄, 赵亮, 李娜, 郭华, 王孝安, 段仁燕 (2016) 黄土高原油松林林下群落异质性分析. 生态学杂志, 35, 1197-1203.] | |
| [150] | Wang YP, Bao YX, Yu MJ, Xu GF, Ding P (2010) Nestedness for different reasons: the distributions of birds, lizards and small mammals on islands of an inundated lake. Diversity and Distributions, 16, 862-873. |
| [151] | Webb CO (2000) Exploring the phylogenetic structure of ecological communities: an example for rain forest trees. The American Naturalist, 156, 145-155. |
| [152] | Webb CO, Ackerly DD, McPeek MA, Donoghue MJ (2002) Phylogenies and community ecology. Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics, 33, 475-505. |
| [153] | Wen ZX, Yang QS, Quan Q, Xia L, Ge DY, Lü X (2016) Multiscale partitioning of small mammal β-diversity provides novel insights into the Quaternary faunal history of Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau and Hengduan Mountains. Journal of Biogeography, 43, 1412-1424. |
| [154] | Whittaker RH (1960) Vegetation of the Siskiyou Mountains, Oregon and California. Ecological Monographs, 30, 279-338. |
| [155] | Whittaker RH (1972) Evolution and measurement of species diversity. Taxon, 21, 213-251. |
| [156] | Wiersma YF, Urban DL (2005) Beta diversity and nature reserve system design in the Yukon, Canada. Conservation Biology, 19, 1262-1272. |
| [157] | Wilcove DS, Rothstein D, Jason D, Phillips A, Losos E (1998) Quantifying threats to imperiled species in the United States. BioScience, 48, 607-615. |
| [158] | Williams PH (1996) Mapping variations in the strength and breadth of biogeographic transition zones using species turnover. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London, Series B: Biological Sciences, 263, 579-588. |
| [159] | Willig MR, Kaufman DM, Stevens RD (2003) Latitudinal gradients of biodiversity: pattern, process, scale, and synthesis. Annual Review of Ecology, Evolution, and Systematics, 34, 273-309. |
| [160] | Wilson MC, Chen XY, Corlett RT, Didham RK, Ding P, Holt RD, Holyoak M, Hu G, Hughes AC, Jiang L, Laurance WF, Liu JJ, Pimm SL, Robinson SK, Russo SE, Si XF, Wilcove DS, Wu JG, Yu MJ (2016) Habitat fragmentation and biodiversity conservation: key findings and future challenges. Landscape Ecology, 31, 219-227. |
| [161] | Wu LB, Si XF, Didham RK, Ge DP, Ding P (2017) Dispersal modality determines the relative partitioning of beta diversity in spider assemblages on subtropical land-bridge islands. Journal of Biogeography, 44, doi: 10.1111/ jbi.13007. |
| [162] | Wu YJ, Lei FM (2013) Species richness patterns and mechanisms along the elevational gradients. Chinese Journal of Zoology, 48, 797-807. |
| (in Chinese with English abstract) [吴永杰, 雷富民 (2013) 物种丰富度垂直分布格局及影响机制. 动物学杂志, 48, 797-807.] | |
| [163] | Xu J, Su GH, Xiong Y, Akasaka M, Molinos JG, Shin-ichiro SM, Zhang M (2015a) Complimentary analysis of metacommunity nestedness and diversity partitioning highlights the need for a holistic conservation strategy for highland lake fish assemblages. Global Ecology and Conservation, 3, 288-296. |
| [164] | Xu WB, Chen GK, Liu CR, Ma KP (2015b) Latitudinal differences in species abundance distributions, rather than spatial aggregation, explain beta-diversity along latitudinal gradients. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 24, 1170-1180. |
| [165] | Zhang Q, Hou X, Li FY, Niu J, Zhou Y, Ding Y, Zhao L, Li X, Ma W, Kang S (2014) Alpha, beta and gamma diversity differ in response to precipitation in the Inner Mongolia grassland. PLoS ONE, 9, e93518. |
| [1] | 祝晓雨, 王晨灏, 王忠君, 张玉钧. 城市绿地生物多样性研究进展与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 25027-. |
| [2] | 王欣, 鲍风宇. 基于鸟类多样性提升的南滇池国家湿地公园生态修复效果分析[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24531-. |
| [3] | 明玥, 郝培尧, 谭铃千, 郑曦. 基于城市绿色高质量发展理念的中国城市生物多样性保护与提升研究[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24524-. |
| [4] | 卢晓强, 董姗姗, 马月, 徐徐, 邱凤, 臧明月, 万雅琼, 李孪鑫, 于赐刚, 刘燕. 前沿技术在生物多样性研究中的应用现状、挑战与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24440-. |
| [5] | 赵维洋, 王伟, 马冰然. 其他有效的区域保护措施(OECMs)研究进展与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(3): 24525-. |
| [6] | 周志华, 金效华, 罗颖, 李迪强, 岳建兵, 刘芳, 何拓, 李希, 董晖, 罗鹏. 中国林草部门落实《昆明-蒙特利尔全球生物多样性框架》的机制、成效分析及建议[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(3): 24487-. |
| [7] | 刘立, 臧明月, 马月, 万雅琼, 胡飞龙, 卢晓强, 刘燕. 央地协同推动国家生物多样性战略和行动计划执行的措施、进展与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(3): 24532-. |
| [8] | 刘志祥, 谢华, 张慧, 黄晓磊. 表皮碳氢化合物在社会性昆虫中的功能多样性及其调控[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24302-. |
| [9] | 宋阳, 柳军, 何少林, 徐薇, 程琛, 刘博, 余绩庆. 我国能源企业生物多样性保护主流化管理路径[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(1): 24345-. |
| [10] | 苏荣菲, 陈睿山, 俞霖琳, 吴婧彬, 康燕. 基于红外相机调查的上海市长宁区社区生境花园生物多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(8): 24068-. |
| [11] | 蔡颖莉, 朱洪革, 李家欣. 中国生物多样性保护政策演进、主要措施与发展趋势[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(5): 23386-. |
| [12] | 鄢德奎. 中国生物多样性保护政策的共同要素、不足和优化建议[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(5): 23293-. |
| [13] | 郑梦瑶, 李媛, 王雪蓉, 张越, 贾彤. 芦芽山不同植被类型土壤原生动物群落构建机制[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(4): 23419-. |
| [14] | 刘荆州, 钱易鑫, 张燕雪丹, 崔凤. 基于潜在迪利克雷分布(LDA)模型的旗舰物种范式研究进展与启示[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(4): 23439-. |
| [15] | 曲锐, 左振君, 王有鑫, 张良键, 吴志刚, 乔秀娟, 王忠. 基于元素组的生物地球化学生态位及其在不同生态系统中的应用[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(4): 23378-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2026 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn
![]()