



生物多样性 ›› 2014, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (2): 141-156. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2014.13195 cstr: 32101.14.SP.J.1003.2014.13195
王斌, 黄俞淞, 李先琨*( ), 向悟生, 丁涛, 黄甫昭, 陆树华, 韩文衡, 文淑均, 何兰军
), 向悟生, 丁涛, 黄甫昭, 陆树华, 韩文衡, 文淑均, 何兰军
收稿日期:2013-08-30
接受日期:2013-10-25
出版日期:2014-03-20
发布日期:2014-04-03
通讯作者:
李先琨
基金资助:
Bin Wang, Yusong Huang, Xiankun Li*( ), Wusheng Xiang, Tao Ding, Fuzhao Huang, Shuhua Lu, Wenheng Han, Shujun Wen, Lanjun He
), Wusheng Xiang, Tao Ding, Fuzhao Huang, Shuhua Lu, Wenheng Han, Shujun Wen, Lanjun He
Received:2013-08-30
Accepted:2013-10-25
Online:2014-03-20
Published:2014-04-03
Contact:
Li Xiankun
摘要:
北热带喀斯特季节性雨林(northern tropical karst seasonal rain forest)是在我国热带北缘喀斯特地区分布的典型森林植被类型之一。由于富钙偏碱的地球化学背景及多样性的生境类型, 同时受季风气候影响, 该森林呈现群落结构多样、树种组成丰富、特有成分突出等特点。基于大型固定监测样地对该森林树种组成与空间分布进行的研究, 是探明该区域生物多样性形成与维持机制的基础。我们于2011年底建立了广西弄岗北热带喀斯特季节性雨林15 ha监测样地, 依照CTFS (Center for Tropical Forest Science)全球森林生物多样性监测规范, 定位并调查了样地内每一棵胸径≥1 cm的木本植物。结果表明: (1)样地内有监测树种223种, 隶属于56科157属; 独立个体总数为68,010株(含分枝为95,471株), 平均胸径为4.84 cm; (2)树种科、属的区系均以热带成分为主, 大戟科、马鞭草科、梧桐科等为优势科; (3)个体数最多的11个树种的个体数之和占到总个体数的51.64%, 前58个树种的占90.19%; 稀有种有75种, 占总树种数的33.63%; (4)群落结构稳定且更新良好, 主要优势种的径级结构均呈倒“J”形, 无明显断层; (5)树种分布在空间上表现出明显差异, 黄梨木(Boniodendron minus)等强耐旱型树种分布于山顶周围; 蚬木(Excentrodendron tonkinense)等树种分布于山坡中部; 对叶榕(Ficus hispida)等喜湿耐荫型树种分布于山谷周围; (6)胸径>20 cm的个体较多分布在山坡中下部, 极少分布在山顶周围; 胸径10–20 cm的个体较均匀分布于整个样地; 分枝和萌枝较多分布在山顶周围; (7)种–面积散点图在2–7 ha的取样面积下分化形成两条曲线, 表明了树种数量组成在空间上具有强烈异质性。研究初步认为: 强烈生境异质性及独特地质背景可能是影响该喀斯特森林物种组成及空间分布的重要因素。
王斌, 黄俞淞, 李先琨, 向悟生, 丁涛, 黄甫昭, 陆树华, 韩文衡, 文淑均, 何兰军 (2014) 弄岗北热带喀斯特季节性雨林15 ha监测样地的树种组成与空间分布. 生物多样性, 22, 141-156. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2014.13195.
Bin Wang,Yusong Huang,Xiankun Li,Wusheng Xiang,Tao Ding,Fuzhao Huang,Shuhua Lu,Wenheng Han,Shujun Wen,Lanjun He (2014) Species composition and spatial distribution of a 15 ha northern tropical karst seasonal rain forest dynamics study plot in Nonggang, Guangxi, southern China. Biodiversity Science, 22, 141-156. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2014.13195.
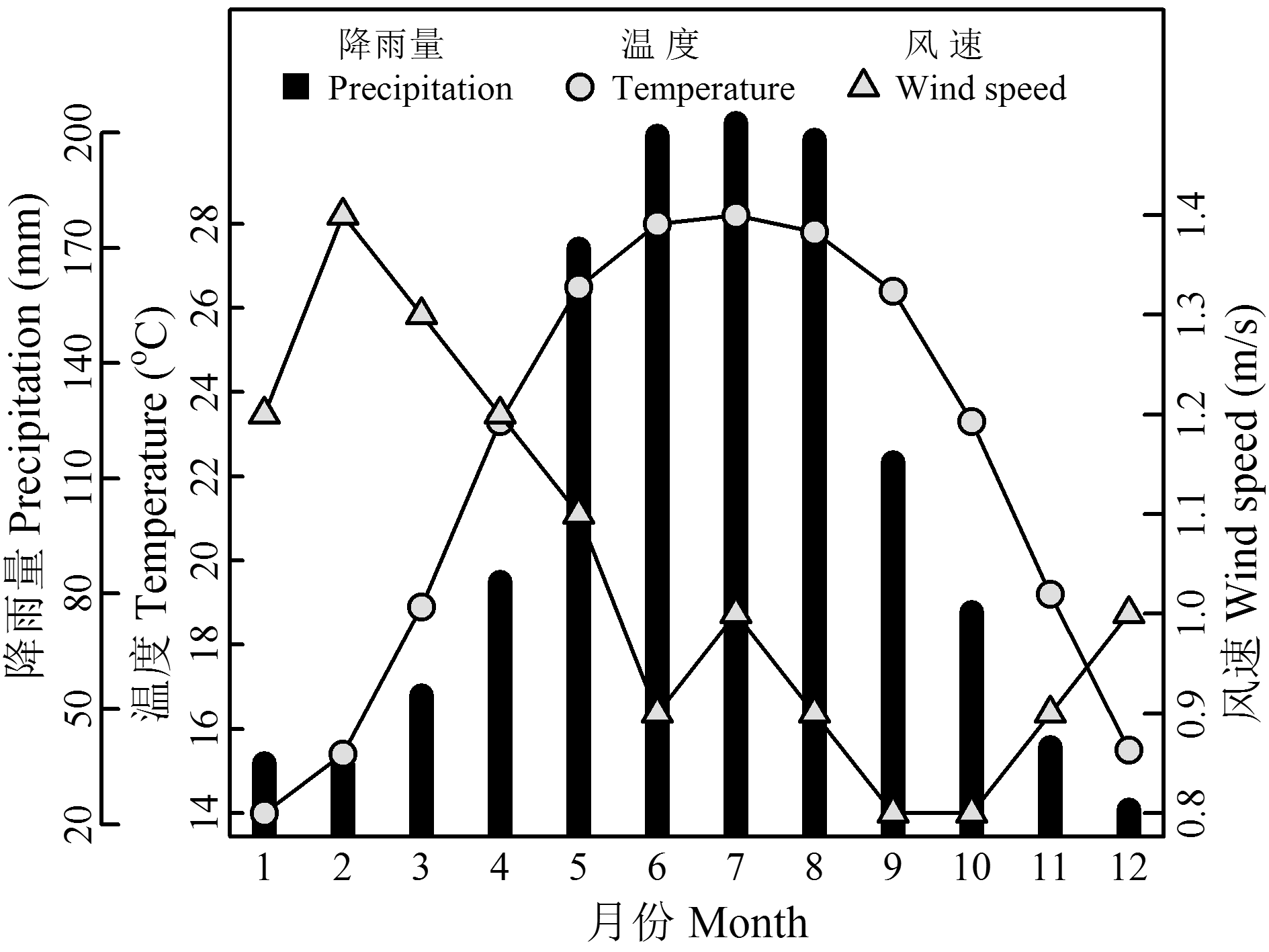
图1 弄岗自然保护区1971–2000年的月平均降雨量、气温、风速的变化
Fig. 1 Monthly variations of rainfall, air temperature and wind speed between 1971 and 2000 in the Nonggang Nature Reserve
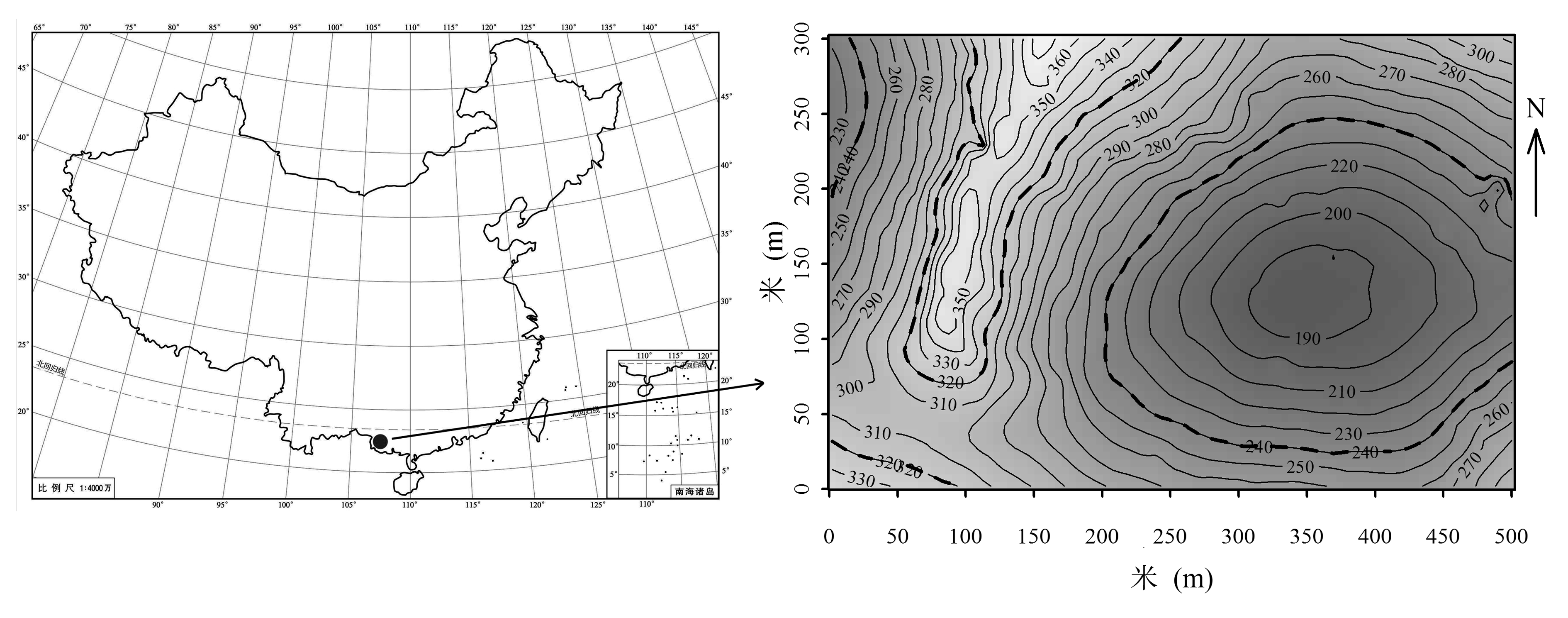
图2 弄岗样地地形图及其在中国的地理位置。根据植被及土壤分布规律, 弄岗样地初步可分3种生境类型: (1)海拔>320 m的山顶类型; (2)海拔位于240–320 m之间的山坡类型; (3)海拔<240 m的洼地类型。
Fig. 2 The location and contour map of the 15-ha Nonggang forest plot, China. According to the vegetation and soil distribution, the Nonggang forest plot was basically divided into three habitat types: (1) Mountain peak type at the altitude > 320 m; (2) Mountain slope type at the altitude between 240 and 320 m; (3) Valley bottom type at the altitude < 240 m.
| 分布区类型 Areal types | 科数 No. of families | 科的比例 % | 属数 No. of genera | 属的比例 % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. 世界广布 Cosmopolitan | 12 | – | 2 | – |
| 2. 泛热带 Pantropic | 31 | 70.45 | 36 | 23.23 |
| 3. 热带亚洲及热带美洲间断 Tropical Asia and South Tropical America disjuncted | 5 | 11.36 | 6 | 3.87 |
| 4. 旧世界热带 Old World Tropic | 2 | 4.54 | 23 | 14.84 |
| 5. 热带亚洲至热带大洋洲 Tropical Asia to Tropical Australasia Oceania | 0 | 0 | 18 | 11.61 |
| 6. 热带亚洲至热带非洲 Tropical Asia to Tropical Africa | 0 | 0 | 9 | 5.81 |
| 7. 热带亚洲 Tropical Asia | 1 | 2.27 | 45 | 29.03 |
| 8. 北温带 North Temperate | 4 | 9.09 | 5 | 3.23 |
| 9. 东亚和北美洲间断 East Asia and North America disjuncted | 1 | 2.27 | 7 | 4.52 |
| 11. 温带亚洲 Temperate Asia | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0.65 |
| 12. 地中海区、西亚至中亚 Mediterranean, West Asia to Central Asia | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0.65 |
| 14. 东亚 East Asia | 0 | 0 | 4 | 2.58 |
| 合计 Total | 56 | 100 | 157 | 100 |
表1 弄岗森林样地木本植物区系类型
Table 1 The areal-types of woody plants in the Nonggang forest plot, Guangxi
| 分布区类型 Areal types | 科数 No. of families | 科的比例 % | 属数 No. of genera | 属的比例 % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. 世界广布 Cosmopolitan | 12 | – | 2 | – |
| 2. 泛热带 Pantropic | 31 | 70.45 | 36 | 23.23 |
| 3. 热带亚洲及热带美洲间断 Tropical Asia and South Tropical America disjuncted | 5 | 11.36 | 6 | 3.87 |
| 4. 旧世界热带 Old World Tropic | 2 | 4.54 | 23 | 14.84 |
| 5. 热带亚洲至热带大洋洲 Tropical Asia to Tropical Australasia Oceania | 0 | 0 | 18 | 11.61 |
| 6. 热带亚洲至热带非洲 Tropical Asia to Tropical Africa | 0 | 0 | 9 | 5.81 |
| 7. 热带亚洲 Tropical Asia | 1 | 2.27 | 45 | 29.03 |
| 8. 北温带 North Temperate | 4 | 9.09 | 5 | 3.23 |
| 9. 东亚和北美洲间断 East Asia and North America disjuncted | 1 | 2.27 | 7 | 4.52 |
| 11. 温带亚洲 Temperate Asia | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0.65 |
| 12. 地中海区、西亚至中亚 Mediterranean, West Asia to Central Asia | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0.65 |
| 14. 东亚 East Asia | 0 | 0 | 4 | 2.58 |
| 合计 Total | 56 | 100 | 157 | 100 |
| 科名 Family | 分布区类型 Areal types | 属数 No. of genera | 树种数 No. of species | 个体数 No. of stems | 断面积之和 Basal area (m2) | 重要值IV |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 大戟科 Euphorbiaceae | 泛热带 Pantropic | 21 | 36 | 23,181 | 61.6 | 19.78 |
| 马鞭草科 Verbenaceae | 热带亚洲及热带南美间断 Tropical Asia and North America disjuncted | 4 | 9 | 6,985 | 48.1 | 8.67 |
| 梧桐科 Sterculiaceae | 泛热带 Pantropic | 4 | 5 | 11,514 | 37.81 | 8.62 |
| 桑科 Moraceae | 世界广布 Cosmopolitan | 6 | 18 | 5,667 | 16.42 | 6.36 |
| 椴树科 Tiliaceae | 泛热带 Pantropic | 3 | 3 | 4,007 | 27.39 | 4.63 |
| 茜草科 Rubiaceae | 世界广布 Cosmopolitan | 9 | 11 | 2,578 | 7.81 | 3.35 |
| 楝科 Meliaceae | 世界广布 Cosmopolitan | 8 | 9 | 3,397 | 6.82 | 3.24 |
| 番荔枝科 Annonaceae | 泛热带 Pantropic | 6 | 7 | 3,531 | 2.54 | 2.55 |
| 无患子科 Sapindaceae | 泛热带 Pantropic | 6 | 6 | 1,791 | 9.86 | 2.53 |
| 蝶形花科 Fabaceae | 世界广布 Cosmopolitan | 4 | 4 | 323 | 17.22 | 2.46 |
| 柿树科 Ebenaceae | 泛热带 Pantropic | 1 | 4 | 3,394 | 5.61 | 2.36 |
| 紫葳科 Bignoniaceae | 泛热带 Pantropic | 4 | 6 | 764 | 8.47 | 2.03 |
表2 弄岗森林样地重要值排名前12位的科
Table 2 Top 12 families with the highest importance values in the Nonggang forest plot, Guangxi
| 科名 Family | 分布区类型 Areal types | 属数 No. of genera | 树种数 No. of species | 个体数 No. of stems | 断面积之和 Basal area (m2) | 重要值IV |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 大戟科 Euphorbiaceae | 泛热带 Pantropic | 21 | 36 | 23,181 | 61.6 | 19.78 |
| 马鞭草科 Verbenaceae | 热带亚洲及热带南美间断 Tropical Asia and North America disjuncted | 4 | 9 | 6,985 | 48.1 | 8.67 |
| 梧桐科 Sterculiaceae | 泛热带 Pantropic | 4 | 5 | 11,514 | 37.81 | 8.62 |
| 桑科 Moraceae | 世界广布 Cosmopolitan | 6 | 18 | 5,667 | 16.42 | 6.36 |
| 椴树科 Tiliaceae | 泛热带 Pantropic | 3 | 3 | 4,007 | 27.39 | 4.63 |
| 茜草科 Rubiaceae | 世界广布 Cosmopolitan | 9 | 11 | 2,578 | 7.81 | 3.35 |
| 楝科 Meliaceae | 世界广布 Cosmopolitan | 8 | 9 | 3,397 | 6.82 | 3.24 |
| 番荔枝科 Annonaceae | 泛热带 Pantropic | 6 | 7 | 3,531 | 2.54 | 2.55 |
| 无患子科 Sapindaceae | 泛热带 Pantropic | 6 | 6 | 1,791 | 9.86 | 2.53 |
| 蝶形花科 Fabaceae | 世界广布 Cosmopolitan | 4 | 4 | 323 | 17.22 | 2.46 |
| 柿树科 Ebenaceae | 泛热带 Pantropic | 1 | 4 | 3,394 | 5.61 | 2.36 |
| 紫葳科 Bignoniaceae | 泛热带 Pantropic | 4 | 6 | 764 | 8.47 | 2.03 |
| 树种名 Species | 科名 Families | 个体数 No. of stems | 分枝数 No. of ramifications | 平均断面积Mean basal area (cm2) | 相对频度Relative frequency | 重要值IV | 偏好生境Preferred habitats |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 闭花木 Cleistanthus sumatranus | Euphorbiaceae | 9,977 | 2,005 | 30.13 | 1.50 | 9.05 | 中上坡 H-2 |
| 苹婆 Sterculia monosperma | Sterculiaceae | 6,328 | 2,738 | 37.76 | 2.79 | 7.47 | 中下坡 H-4 |
| 广西牡荆 Vitex kwangsiensis | Verbenaceae | 2,470 | 2,933 | 87.75 | 2.63 | 6.86 | 中下坡 H-4 |
| 蚬木 Excentrodendron tonkinense | Tiliaceae | 1,502 | 369 | 76.87 | 1.82 | 2.79 | 中上坡 H-2 |
| 海南椴 Diplodiscus trichosperma | Tiliaceae | 1,126 | 856 | 65.30 | 1.76 | 2.44 | 中上坡 H-2 |
| 劲直刺桐 Erythrina stricta | Fabaceae | 316 | 2 | 541.58 | 1.29 | 2.32 | 谷底 H-5 |
| 海南大风子 Hydnocarpus hainanensis | Flacourtiaceae | 2,260 | 333 | 14.21 | 2.41 | 2.28 | 中下坡 H-4 |
| 日本五月茶 Antidesma japonicum | Euphorbiaceae | 2,535 | 373 | 10.48 | 1.91 | 2.18 | 谷底 H-5 |
| 对叶榕 Ficus hispida | Moraceae | 2,989 | 188 | 14.11 | 0.68 | 2.14 | 谷底 H-5 |
| 金丝李 Garcinia paucinervis | Guttiferae | 1,684 | 258 | 21.96 | 2.60 | 2.12 | 中上坡 H-2 |
| 茎花山柚 Champereia manillana | Opiliaceae | 1,340 | 138 | 22.76 | 2.39 | 1.79 | 中坡 H-3 |
| 假玉桂 Celtis timorensis | Ulmaceae | 1,122 | 27 | 42.65 | 2.11 | 1.74 | 中下坡 H-4 |
| 细叶谷木 Memecylon scutellatum | Melastomataceae | 1,221 | 974 | 21.60 | 2.00 | 1.74 | 山顶 H-1 |
| 截裂翅子树 Pterospermum truncatolobatum | Sterculiaceae | 1,604 | 721 | 13.98 | 1.75 | 1.69 | 中坡 H-3 |
| 山榄叶柿 Diospyros siderophylla | Ebenaceae | 1,592 | 531 | 17.83 | 1.30 | 1.59 | 山顶 H-1 |
| 三角车 Rinorea bengalensis | Violaceae | 2,178 | 476 | 9.38 | 0.77 | 1.57 | 中坡 H-3 |
| 黄梨木 Boniodendron minus | Sapindaceae | 694 | 406 | 75.20 | 1.15 | 1.55 | 山顶 H-1 |
| 割舌树 Walsura robusta | Meliaceae | 1,315 | 246 | 18.69 | 1.67 | 1.49 | 中坡 H-3 |
| 肥牛树 Cephalomappa sinensis | Euphorbiaceae | 917 | 919 | 33.66 | 0.78 | 1.33 | 中上坡 H-2 |
| 网脉核果木 Drypetes perreticulata | Euphorbiaceae | 631 | 99 | 60.84 | 1.47 | 1.24 | 中坡 H-3 |
| 其他 Other | – | 24,209 | 12,869 | – | 65.22 | 44.62 | – |
| 总计 Total | – | 68,010 | 27,461 | – | 100 | 100 | – |
表3 弄岗森林样地重要值排名前20位树种的组成及偏好生境
Table 3 Composition and preferred habitats of top 20 species with the highest important values in the Nonggang forest plot, Guangxi
| 树种名 Species | 科名 Families | 个体数 No. of stems | 分枝数 No. of ramifications | 平均断面积Mean basal area (cm2) | 相对频度Relative frequency | 重要值IV | 偏好生境Preferred habitats |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 闭花木 Cleistanthus sumatranus | Euphorbiaceae | 9,977 | 2,005 | 30.13 | 1.50 | 9.05 | 中上坡 H-2 |
| 苹婆 Sterculia monosperma | Sterculiaceae | 6,328 | 2,738 | 37.76 | 2.79 | 7.47 | 中下坡 H-4 |
| 广西牡荆 Vitex kwangsiensis | Verbenaceae | 2,470 | 2,933 | 87.75 | 2.63 | 6.86 | 中下坡 H-4 |
| 蚬木 Excentrodendron tonkinense | Tiliaceae | 1,502 | 369 | 76.87 | 1.82 | 2.79 | 中上坡 H-2 |
| 海南椴 Diplodiscus trichosperma | Tiliaceae | 1,126 | 856 | 65.30 | 1.76 | 2.44 | 中上坡 H-2 |
| 劲直刺桐 Erythrina stricta | Fabaceae | 316 | 2 | 541.58 | 1.29 | 2.32 | 谷底 H-5 |
| 海南大风子 Hydnocarpus hainanensis | Flacourtiaceae | 2,260 | 333 | 14.21 | 2.41 | 2.28 | 中下坡 H-4 |
| 日本五月茶 Antidesma japonicum | Euphorbiaceae | 2,535 | 373 | 10.48 | 1.91 | 2.18 | 谷底 H-5 |
| 对叶榕 Ficus hispida | Moraceae | 2,989 | 188 | 14.11 | 0.68 | 2.14 | 谷底 H-5 |
| 金丝李 Garcinia paucinervis | Guttiferae | 1,684 | 258 | 21.96 | 2.60 | 2.12 | 中上坡 H-2 |
| 茎花山柚 Champereia manillana | Opiliaceae | 1,340 | 138 | 22.76 | 2.39 | 1.79 | 中坡 H-3 |
| 假玉桂 Celtis timorensis | Ulmaceae | 1,122 | 27 | 42.65 | 2.11 | 1.74 | 中下坡 H-4 |
| 细叶谷木 Memecylon scutellatum | Melastomataceae | 1,221 | 974 | 21.60 | 2.00 | 1.74 | 山顶 H-1 |
| 截裂翅子树 Pterospermum truncatolobatum | Sterculiaceae | 1,604 | 721 | 13.98 | 1.75 | 1.69 | 中坡 H-3 |
| 山榄叶柿 Diospyros siderophylla | Ebenaceae | 1,592 | 531 | 17.83 | 1.30 | 1.59 | 山顶 H-1 |
| 三角车 Rinorea bengalensis | Violaceae | 2,178 | 476 | 9.38 | 0.77 | 1.57 | 中坡 H-3 |
| 黄梨木 Boniodendron minus | Sapindaceae | 694 | 406 | 75.20 | 1.15 | 1.55 | 山顶 H-1 |
| 割舌树 Walsura robusta | Meliaceae | 1,315 | 246 | 18.69 | 1.67 | 1.49 | 中坡 H-3 |
| 肥牛树 Cephalomappa sinensis | Euphorbiaceae | 917 | 919 | 33.66 | 0.78 | 1.33 | 中上坡 H-2 |
| 网脉核果木 Drypetes perreticulata | Euphorbiaceae | 631 | 99 | 60.84 | 1.47 | 1.24 | 中坡 H-3 |
| 其他 Other | – | 24,209 | 12,869 | – | 65.22 | 44.62 | – |
| 总计 Total | – | 68,010 | 27,461 | – | 100 | 100 | – |
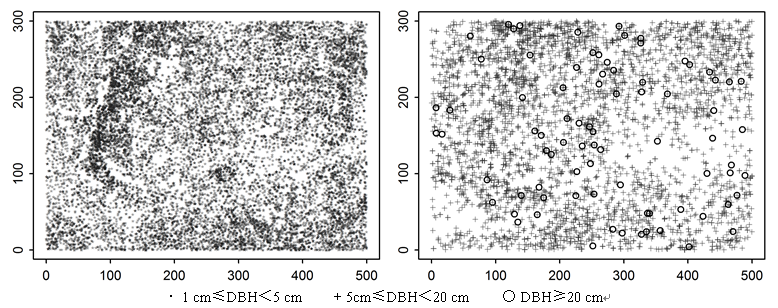
图9 弄岗样地所有分枝和萌枝在3个不同径级的空间分布图
Fig. 9 Spatial distribution maps of tree ramifications and sprouts at three different DBH classes in the Nonggang forest plot
| 样地名称 Forest plot | 地理坐标 Coordinates | 面积 Size (ha) | 科 Family | 属 Genus | 种 Species | 个体数 Stem (株/ha) | 胸高断面积 BA (m2/ha) | 稀有种 Rare (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 长白山–阔叶红松林 | 42.38° N, 128.08° E | 25 | 18 | 32 | 52 | 1,556 | 43.23 | 34.60 |
| 2 天童山–中亚热带常绿阔叶林 | 29.81° N, 121.77° E | 20 | 50 | 91 | 153 | 4,730 | 38.98 | 36.20 |
| 3 古田山–中亚热带常绿阔叶林 | 29.25° N, 118.12° E | 24 | 49 | 104 | 159 | 5,863 | 36.90 | 37.10 |
| 4 鼎湖山–南亚热带常绿阔叶林 | 23.10° N, 112.32° E | 20 | 56 | 119 | 210 | 3,581 | 30.17 | 52.38 |
| 5 弄岗–北热带喀斯特季节性雨林 | 22.43° N, 106.95° E | 15 | 56 | 157 | 223 | 4,534 | 22.08 | 33.63 |
| 6 垦丁–热带高位珊瑚礁季雨林 | 21.95° N, 120.82° E | 10 | 34 | 74 | 95 | 3,909 | 45.15 | 28.42 |
| 7 西双版纳–热带雨林 | 21.61° N, 101.57° E | 20 | 70 | 213 | 468 | 4,792 | 42.34 | 49.14 |
表4 不同植被类型森林监测样地的地理坐标、面积以及树种组成(郝占庆等, 2008; 兰国玉等, 2008; 叶万辉等, 2008; 祝燕等, 2008; Wu et al., 2011; 杨庆松等, 2011)
Table 4 Location, size and species composition of stem-mapping forest plots with different vegetation types
| 样地名称 Forest plot | 地理坐标 Coordinates | 面积 Size (ha) | 科 Family | 属 Genus | 种 Species | 个体数 Stem (株/ha) | 胸高断面积 BA (m2/ha) | 稀有种 Rare (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 长白山–阔叶红松林 | 42.38° N, 128.08° E | 25 | 18 | 32 | 52 | 1,556 | 43.23 | 34.60 |
| 2 天童山–中亚热带常绿阔叶林 | 29.81° N, 121.77° E | 20 | 50 | 91 | 153 | 4,730 | 38.98 | 36.20 |
| 3 古田山–中亚热带常绿阔叶林 | 29.25° N, 118.12° E | 24 | 49 | 104 | 159 | 5,863 | 36.90 | 37.10 |
| 4 鼎湖山–南亚热带常绿阔叶林 | 23.10° N, 112.32° E | 20 | 56 | 119 | 210 | 3,581 | 30.17 | 52.38 |
| 5 弄岗–北热带喀斯特季节性雨林 | 22.43° N, 106.95° E | 15 | 56 | 157 | 223 | 4,534 | 22.08 | 33.63 |
| 6 垦丁–热带高位珊瑚礁季雨林 | 21.95° N, 120.82° E | 10 | 34 | 74 | 95 | 3,909 | 45.15 | 28.42 |
| 7 西双版纳–热带雨林 | 21.61° N, 101.57° E | 20 | 70 | 213 | 468 | 4,792 | 42.34 | 49.14 |
| [1] | Barot S, Gignoux J (2004) Mechanism promoting plant coexistence: can all the proposed processes be reconciled? Oikos, 106, 185–192. |
| [2] | Cao JH (曹建华), Yuan DX (袁道先), Pan GX (潘根兴), Lin YS (林玉石) (2001) Preliminary study on biological action in karst dynamic system. Earth Science Frontiers(地学前缘), 8(1), 203–209. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [3] | Chen P (陈平) (1988) A report on the soil investigation of the Longgang Natural Reserve. Guihaia(广西植物) (Suppl. 1), 52–73. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [4] | Condit R (1995) Research in large, long-term tropical forest plots. Trends in Ecology and Evolution, 10, 18–23. |
| [5] | Condit R, Ashton P, Baker P, Bunyavejchewin S, Gunatilleke S, Gunatilleke N, Hubbell SP, Foster RB, Itoh A, Lafrankie JV, Lee HS, Losos E, Manokaran N, Sukumar R, Yamakura T (2000) Spatial patterns in the distribution of tropical tree species. Science, 288, 1414–1418. |
| [6] | Guo K (郭柯), Liu CC (刘长成), Dong M (董鸣) (2011) Ecological adaptation of plants and control of rocky- desertification on karst region of Southwest China. Journal of Plant Ecology (Chinese version) (植物生态学报), 35, 991–999. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [7] | Hao ZQ (郝占庆), Li BH (李步杭), Zhang J (张健), Wang XG (王绪高), Ye J (叶吉), Yao XL (姚晓琳) (2008) Broad- leaved Korean pine (Pinus koraiensis) mixed forest plot in Changbaishan (CBS) of China: community composition and structure. Journal of Plant Ecology (Chinese version) (植物生态学报), 32, 238–250. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [8] | He FL, Hubbell SP (2011) Species–area relationships always overestimate extinction rates from habitat loss. Nature, 473, 368–371. |
| [9] | Huang YS (黄俞淞), Wu WH (吴望辉), Jiang RH (蒋日红), Liu SY (刘晟源), Liu Y (刘演), Li XK (李先琨) (2013) Primary study on species diversity of plant in Longgang National Nature Reserve of Guangxi. Guihaia(广西植物), 33, 346–355. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [10] | Hubbell SP (2001) The United Neutral Theory of Biodiversity and Biography. Princeton University Press, Princeton, New Jersey. |
| [11] | Hubbell SP, Foster RB (1986) Commonness and rarity in a neotropical forest: implications for tropical tree conserva- tion. In: Conservation Biology: Science of Scarcity and Diversity (ed. Soule ME), pp. 205–231. Sinauer Press, Sunderland, UK. |
| [12] | Janzen DH (1970) Herbivorous and number of tree species in tropical forests. The American Naturalist, 104, 501–528. |
| [13] | Lan GY (兰国玉), Hu YH (胡跃华), Cao M (曹敏), Zhu H (朱华), Wang H (王洪), Zhou SS (周仕顺), Deng XB (邓晓保), Cui JY (崔景云), Huang JG (黄建国), Liu LY (刘林云), Xu HL (许海龙), Song JP (宋军平), He YC (何有才) (2008) Establishment of Xishuangbanna tropical forest dynamic plot: species compositions and spatial distribution patterns. Journal of Plant Ecology (Chinese version) (植物生态学报), 32, 287–298. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [14] | Li KY (李克因) (1988) Primary exploration of the geomor- phological districts and the development of surface forms in the Longgang Nature Reserve. Guihaia(广西植物), (Suppl. 1), 33–51. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [15] | Li XK (李先琨), Jiang ZC (蒋忠诚), Huang YQ (黄玉清), Xiang WS (向悟生), Lü SH (吕仕洪), Ye D (叶铎), Su ZM (苏宗明) (2008) Dynamics of dominant population and its influence on karstification in Southwest Guangxi, China. Acta Geoscientica Sinica(地球学报), 29, 253–259. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [16] | Li XK (李先琨), Su ZM (苏宗明), Lü SH (吕仕洪), Ou ZL (欧祖兰), Xiang WS (向悟生), Ou Z (区智), Lu SH (陆树华) (2003) The spatial pattern of natural vegetation in the karst regions of Guangxi and the ecological signality for ecosystem rehabilitation and reconstruction. Journal of Mountain Science(山地学报), 21(2), 129–139. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [17] | Liang CF (梁畴芬), Liang JY (梁建英), Liu LF (刘兰芳), Mo XL (莫新礼) (1988) A report on the floristic survey on the Longgang Natural Reserve. Guihaia(广西植物) (Suppl. 1), 83–184. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [18] | Lin YC, Chang LW, Yang KC, Wang HH, Sun IF (2011) Point patterns of tree distribution determined by habitat heterogeneity and dispersal limitation. Oecologia, 165, 175–184. |
| [19] | Linares PR, Alvarez SIP (2005) Tree community patterns in seasonally dry tropical forests in the Cerros de Amotape Cordillera, Tumbes, Peru. Forest Ecology and Management, 209, 261–272. |
| [20] | Liu YG (刘玉国), Liu CC (刘长成), Li GQ (李国庆), Wei YF (魏雅芬), Liu YG (刘永刚), Guo K (郭柯) (2011) Litter mass of five karst forests and their hydrological effects in Guizhou. Scientia Silvae Sinicae(林业科学), 47(3), 82–88. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [21] | Liu ZH, Dreybrodt W, Wang HJ (2010) A new direction in effective accounting for the atmospheric CO2 budget: considering the combined action of carbonate dissolution, the global water cycle and photosynthetic uptake of DIC by aquatic organisms. Earth Science Reviews, 99, 162–172. |
| [22] | Ma KP (马克平) (2008) Large scale permanent plots: impor- tant platform for long term research on biodiversity in forest ecosystem. Journal of Plant Ecology (Chinese version) (植物生态学报), 32, 237. (in Chinese) |
| [23] | Nathan R (2006) Long-distance dispersal of plants. Science, 313, 786–788. |
| [24] | Qin HN (覃海宁), Liu Y (刘演) (2010) A Checklist of Vascular Plants of Guangxi (广西植物名录). Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [25] | R Core Team (2013) R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. R Foundation for Statistical Compu- ting, Vienna, Austria. . |
| [26] | Su ZM (苏宗明), Li XK (李先琨) (2003) The types of natural vegetation in karst region of Guangxi and its classified system. Guihaia(广西植物), 23, 289–293. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [27] | Su ZM (苏宗明), Zhao TL (赵天林), Huang QC (黄庆昌) (1988) The vegetation of Longgang Natural Reserve in Guangxi. Guihaia(广西植物), (Suppl. 1), 188–214. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [28] | Wang HH (王相华), Sun IF (孙义方), Chien CT (简庆德), Pan FJ (潘富俊), Kuo CF (郭纪凡), Yu MH (游孟雪), Ku HL (古心兰), Wu SH (伍淑惠), Cheng YP (程俞斌), Chen SY (陈舜英), Kao YC (高瑞卿) (2004) Tree species com- position and habitat types of a karst forest in Kenting, Southern Taiwan. Taiwan Journal of Forest Science(台湾林业科学), 19, 323–335. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [29] | Wu SH, Hseu ZY, Shih YT, Sun IF, Wang HH, Sen YC (2011) Kenting Karst Forest Dynamics Plot: Tree Species Charac- teristics and Distribution Patterns. Taiwan Forestry Research Institute, Taipei. |
| [30] | Wu ZY (吴征镒) (1991) The areal-types of Chinese genera of seed plants. Acta Botanica Yunnanica(云南植物研究), 13(Suppl. IV), 1–139. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [31] | Wu ZY (吴征镒), Zhou ZK (周浙昆), Li DZ (李德铢), Peng H (彭华), Sun H (孙航) (2003) The areal-types of the world families of seed plants. Acta Botanica Yunnanica(云南植物研究), 25, 245–257. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [32] | Yang QS (杨庆松), Ma ZP (马遵平), Xie YB (谢玉彬), Zhang ZG (张志国), Wang ZH (王樟华), Liu HM (刘何铭), Li P (李萍), Zhang N (张娜), Wang DL (王达力), Yang HB (杨海波), Fang XF (方晓峰), Yan ER (阎恩荣), Wang XH (王希华) (2011) Community structure and species composition of an evergreen broad-leaved forest in Tiantong’s 20 ha dynamic plot, Zhejiang Province, eastern China. Biodiver- sity Science(生物多样性), 19, 215–223. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [33] | Ye WH (叶万辉), Cao HL (曹洪麟), Huang ZL (黄忠良), Lian JY (练琚愉), Wang ZG (王志高), Li L (李林), Wei SG (魏识广), Wang ZM (王章明) (2008) Community structure of a 20 ha lower subtropical evergreen broadleaved forest plot in Dinghushan, China. Journal of Plant Ecology (Chinese version) (植物生态学报), 32, 274–286. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [34] | Yuan DX (袁道先) (2001) World correlation of karst ecosystem: objectives and implementation plan. Advance in Earth Sciences(地球科学进展), 16, 462–466. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [35] | Yuan DX (袁道先), Zhang C (章程) (2008) Karst dynamics theory in China and its practice. Acta Geoscientica Sinica(地球学报), 29, 355–365. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [36] | Zhang ZH, Hu G, Zhu JD, Luo DH, Ni J (2010) Spatial patterns and interspecific associations of dominant tree species in two old-growth karst forests, SW China. Ecological Research, 25, 1151–1160. |
| [37] | Zhu SQ (朱守谦) (1993) Ecological Research on Karst Forest (I) (喀斯特森林生态研究I). Guizhou Science and Technology Press, Guiyang. (in Chinese) |
| [38] | Zhu Y (祝燕), Zhao GF (赵谷风), Zhang LW (张俪文), Shen GC (沈国春), Mi XC (米湘成), Ren HB (任海保), Yu MJ (于明坚), Chen JH (陈建华), Chen SW (陈声文), Fang T (方腾), Ma KP (马克平) (2008) Community composition and structure of Gutianshan forest dynamic plot in a mid-subtropical evergreen broad-leaved forest, east China. Journal of Plant Ecology (Chinese version) (植物生态学报), 32, 262–273. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [1] | 马文俊, 刘思嘉, 李柯懋, 简生龙, 薛长安, 韩庆祥, 魏金良, 陈生学, 牛依萌, 崔洲平, 隋瑞臣, 田菲, 赵凯. 青海省长江源区鱼类分布及多样性格局[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24494-. |
| [2] | 李艳朋, 陈洁, 卢春洋, 许涵. 海南尖峰岭热带山地雨林64 ha次生林动态监测样地群落结构特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24445-. |
| [3] | 何泽嵘, 叶鹏, 王舒婷, 关永鑫, 闫淑君, 洪心茹. 中国城市草坪的杂草优势种组成及空间分布[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(1): 24133-. |
| [4] | 舒为杰, 何花, 曾罗, 谷志容, 谭敦炎, 杨晓琛. 雌雄异株物种一把伞南星雌雄株空间分布及性别二态性[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(6): 24084-. |
| [5] | 吴芳芳, 刘娜, 何春梅, 原作强, 郝占庆, 尹秋龙. 秦岭山地木本植物群落结构及多样性的海拔梯度格局[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(12): 24239-. |
| [6] | 杨俊毅, 关潇, 李俊生, 刘晶晶, 郝颢晶, 王槐睿. 乌江流域生物多样性与生态系统服务的空间格局及相互关系[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(7): 23061-. |
| [7] | 李佳奇, 郭屹立, 李冬兴, 王斌, 向悟生, 黄甫昭, 陆芳, 文淑均, 李健星, 陆树华, 李先琨. 桂西南北热带喀斯特季节性雨林土壤钾、钙、镁空间分布特征及其影响因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(2): 22352-. |
| [8] | 林木青, 张应明, 欧阳芳, 束祖飞, 朱朝东, 肖治术. 广东车八岭国家级自然保护区独栖性胡蜂多样性空间分布特征及其对环境因子的响应[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(2): 22310-. |
| [9] | 马瑞霞, 郭屹立, 李冬兴, 王斌, 向悟生, 黄甫昭, 陆芳, 文淑均, 李健星, 陆树华, 李先琨. 桂西南喀斯特季节性雨林幼树更新的空间分布格局及机制[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(2): 22251-. |
| [10] | 刘文聪, 田希, 杨涛, 饶杰生, 王晓凤, 钱恒君, 涂梦灵, 单子铭, 欧晓昆, 沈泽昊. 云南鸡足山半湿润常绿阔叶林优势树种的种群结构与更新特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(11): 23251-. |
| [11] | 崔家鹤, 李智勇, 王宇池, 孙蔷, 莎娜, 李紫晶, 武艳涛, 史亚博, 韩瀛, 李明乐, 王立新, 赵利清, 梁存柱. 垫状驼绒藜群落特征及地理分布数据集[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(10): 23172-. |
| [12] | 鲁梦珍, 曾馥平, 宋同清, 彭晚霞, 张浩, 苏樑, 刘坤平, 谭卫宁, 杜虎. 喀斯特常绿落叶阔叶林死亡个体空间分布格局及生境关联[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(4): 21340-. |
| [13] | 王雅婷, 张定海, 张志山. 古尔班通古特沙漠固定沙丘上白梭梭和梭梭的空间分布及种间关联性[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(3): 21280-. |
| [14] | 王重阳, 赵联军, 孟世勇. 王朗国家级自然保护区滑坡体兰科植物分布格局及其保护策略[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(2): 21313-. |
| [15] | 刘璐, 迟瑶, 吴朝宁, 钱天陆, 王结臣. 陆栖哺乳动物的地理隔离研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(8): 1134-1145. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn
![]()