



生物多样性 ›› 2021, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (7): 865-874. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2020485 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2020485
所属专题: 生物入侵
• 研究报告: 植物多样性 • 下一篇
陈旭1,2, 王国严1,2*( ), 彭培好1,2*(
), 彭培好1,2*( ), 李景吉1,3, 石松林1,2, 张廷斌1,4
), 李景吉1,3, 石松林1,2, 张廷斌1,4
收稿日期:2020-12-30
接受日期:2021-06-04
出版日期:2021-07-20
发布日期:2021-06-29
通讯作者:
* E-mail: peihaop@163.com; wangguoyan@yeah.net
基金资助:
Xu Chen1,2, Guoyan Wang1,2*( ), Peihao Peng1,2*(
), Peihao Peng1,2*( ), Jingji Li1,3, Songlin Shi1,2, Tingbin Zhang1,4
), Jingji Li1,3, Songlin Shi1,2, Tingbin Zhang1,4
Received:2020-12-30
Accepted:2021-06-04
Online:2021-07-20
Published:2021-06-29
Contact:
* E-mail: peihaop@163.com; wangguoyan@yeah.net
摘要:
外来植物入侵严重威胁着入侵地本土植物多样性和生态系统功能, 认识外来物种的入侵机制有助于提高对入侵植物的防控能力。本文以攀西地区云南松(Pinus yunnanensis)林下外来入侵植物紫茎泽兰(Ageratina adenophora)为研究对象, 基于大量野外群落调查, 从群落可入侵性入手, 分析了环境因子和群落物种多样性、谱系多样性等群落生态学特征对紫茎泽兰入侵的影响。结果表明: 海拔、坡向和火烧强度等环境因子和冠层郁闭度、灌木层盖度等生物因子对研究区紫茎泽兰入侵强度没有显著影响(P > 0.05); 但群落灌木层物种多样性和草本层组分种与紫茎泽兰的亲缘关系显著影响紫茎泽兰的入侵强度(P < 0.05), 说明灌木层对光照等环境资源的占用和草本层(同层)物种对相似资源的竞争能够在很大程度上抑制紫茎泽兰的入侵。
陈旭, 王国严, 彭培好, 李景吉, 石松林, 张廷斌 (2021) 四川攀西地区云南松群落物种多样性和谱系多样性对紫茎泽兰入侵的影响. 生物多样性, 29, 865-874. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2020485.
Xu Chen, Guoyan Wang, Peihao Peng, Jingji Li, Songlin Shi, Tingbin Zhang (2021) Effects of taxonomic and phylogenetic diversity of resident Pinus yunnanensis communities on Ageratina adenophora invasion in the Panxi region, Sichuan Province. Biodiversity Science, 29, 865-874. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2020485.
| 环境变量 Environmental variables | PC1 | PC2 |
|---|---|---|
| 海拔 Altitude | 0.29 | -0.43 |
| 纬度 Latitude | -0.42 | -0.13 |
| 坡向 Aspect | 0.25 | -0.21 |
| 坡度 Slope | -0.26 | 0.34 |
| 土壤温度 Soil temperature | 0.51 | - |
| 土壤湿度 Soil moisture | 0.53 | - |
| 火烧强度 Fire intensity | 0.17 | 0.36 |
| 冠层郁闭度 Canopy closure | - | -0.46 |
| 灌木层盖度 Shrub coverage | - | -0.25 |
| 草本层盖度 Herb coverage | 0.17 | 0.47 |
| 变异解释量 Proportion of variance (%) | 57.85 | 23.46 |
表1 云南松群落环境变量在2个主成分上的载荷值
Table 1 Environmental variables loadings on the first two principal components (PC) in Pinus yunnanensis communities
| 环境变量 Environmental variables | PC1 | PC2 |
|---|---|---|
| 海拔 Altitude | 0.29 | -0.43 |
| 纬度 Latitude | -0.42 | -0.13 |
| 坡向 Aspect | 0.25 | -0.21 |
| 坡度 Slope | -0.26 | 0.34 |
| 土壤温度 Soil temperature | 0.51 | - |
| 土壤湿度 Soil moisture | 0.53 | - |
| 火烧强度 Fire intensity | 0.17 | 0.36 |
| 冠层郁闭度 Canopy closure | - | -0.46 |
| 灌木层盖度 Shrub coverage | - | -0.25 |
| 草本层盖度 Herb coverage | 0.17 | 0.47 |
| 变异解释量 Proportion of variance (%) | 57.85 | 23.46 |
| 因子 Factor | 数值范围 Numerical ranges | χ2 | P |
|---|---|---|---|
| 第一主成分 First principal component | -3.35 to 3.16 | 0.23 | 0.63 |
| 第二主成分 Second principal component | -3.02 to 3.43 | 0.72 | 0.39 |
| 灌木层Shannon-Wiener指数 Shannon-Wiener index of shrub layer | 0.14-2.26 | 4.06 | 0.04* |
| 灌木层净种间亲缘关系指数 Net relatedness index of shrub layer | -1.27 to 3.11 | 0.46 | 0.49 |
| 灌木层目标物种净种间亲缘关系指数 Net relatedness index of shrub layer to the target species | -1.29 to 2.39 | 0.05 | 0.81 |
| 草本层Shannon-Wiener指数 Shannon-Wiener index of herb layer | 0.93-2.37 | 1.99 | 0.15 |
| 草本层群落净种间亲缘关系指数 Net relatedness index of herb layer | -1.32 to 1.31 | 3.21 | 0.07 |
| 草本层目标物种净种间亲缘关系指数 Net relatedness index of herb layer to the target species | -1.74 to 1.44 | 4.28 | 0.03* |
表2 攀西地区云南松林环境因子和生物因子对紫茎泽兰入侵强度的影响
Table 2 Effects of environmental and biological factors on the invasion of Ageratina adenophora in Pinus yunnanensis forests in Panxi region
| 因子 Factor | 数值范围 Numerical ranges | χ2 | P |
|---|---|---|---|
| 第一主成分 First principal component | -3.35 to 3.16 | 0.23 | 0.63 |
| 第二主成分 Second principal component | -3.02 to 3.43 | 0.72 | 0.39 |
| 灌木层Shannon-Wiener指数 Shannon-Wiener index of shrub layer | 0.14-2.26 | 4.06 | 0.04* |
| 灌木层净种间亲缘关系指数 Net relatedness index of shrub layer | -1.27 to 3.11 | 0.46 | 0.49 |
| 灌木层目标物种净种间亲缘关系指数 Net relatedness index of shrub layer to the target species | -1.29 to 2.39 | 0.05 | 0.81 |
| 草本层Shannon-Wiener指数 Shannon-Wiener index of herb layer | 0.93-2.37 | 1.99 | 0.15 |
| 草本层群落净种间亲缘关系指数 Net relatedness index of herb layer | -1.32 to 1.31 | 3.21 | 0.07 |
| 草本层目标物种净种间亲缘关系指数 Net relatedness index of herb layer to the target species | -1.74 to 1.44 | 4.28 | 0.03* |
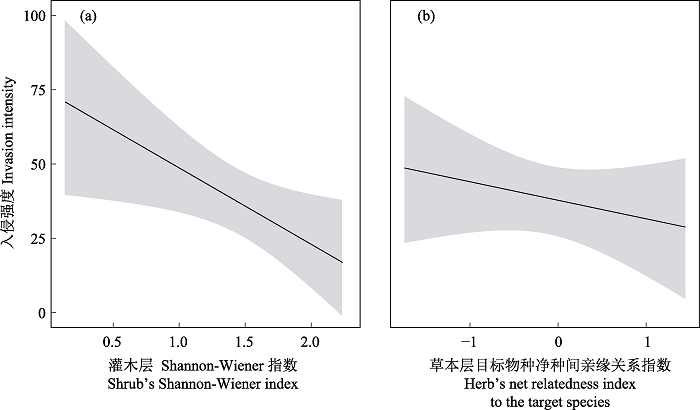
图2 灌木层Shannon-Wiener指数(a)、草本层目标物种净种间亲缘关系指数(b)对紫茎泽兰入侵影响的预测曲线
Fig. 2 Prediction curves of the effects of Shannon-Wiener index of shrub layer (a) and the net relatedness index of herb layer to the target species (b) on the invasion of Ageratina adenophora
| [1] |
Alpert P, Bone E, Holzapfel C (2000) Invasiveness, invasibility and the role of environmental stress in the spread of non-native plants. Perspectives in Plant Ecology, Evolution and Systematics, 3, 52-66.
DOI URL |
| [2] | Auld BA (1970) Eupatorium weed species in Australia. Pest Articles & News Summaries, 16, 82-86. |
| [3] | Bates D, Mächler M, Bolker B, Walker S (2015) Fitting linear mixed-effects models using lme4. Journal of Statistical Software, 67, 1-48. |
| [4] |
Blossey B, Notzold R (1995) Evolution of increased competitive ability in invasive nonindigenous plants: A hypothesis. Journal of Ecology, 83, 887-889.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
Cadotte MW, Campbell SE, Li SP, Sodhi DS, Mandrak NE (2018) Preadaptation and naturalization of nonnative species: Darwin’s two fundamental insights into species invasion. Annual Review of Plant Biology, 69, 661-684.
DOI PMID |
| [6] | Cai NH, Li GQ, Zhu CF, Huang YX, Li JN, Zhao WD (2007) A comparison study on the community structure between artificial and natural forests of Pinus yunnanensis. Journal of Northwest Forestry University, 22(2), 1-4, 163. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 蔡年辉, 李根前, 朱存福, 黄永祥, 李俊楠, 赵文东 (2007) 云南松人工林与天然林群落结构的比较研究. 西北林学院学报, 22(2), 1-4, 163.] | |
| [7] |
Crawley MJ, Brown SL, Heard MS, Edwards GR (1999) Invasion-resistance in experimental grassland communities: Species richness or species identity? Ecology Letters, 2, 140-148.
DOI URL |
| [8] | Darwin C (1859) On the Origin of Species. John Murray, London. |
| [9] | Dobson AJ (1990) An Introduction to Generalized Linear Models. Chapman and Hall, London. |
| [10] | El-Barougy R, MacIvor JS, Arnillas CA, Nada RM, Khedr AHA, Cadotte MW (2020) Richness, phylogenetic diversity, and abundance all have positive effects on invader performance in an arid ecosystem. Ecosphere, 11, e03045. |
| [11] | Elton CS (1958) The Ecology of Invasions by Animals and Plants. University of Chicago Press, Chicago. |
| [12] |
Fang JY, Wang XP, Shen ZH, Tang ZY, He JS, Yu D, Jiang Y, Wang ZH, Zheng CY, Zhu JL, Guo ZD (2009) Methods and protocols for plant community inventory. Biodiversity Science, 17, 533-548. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
| [ 方精云, 王襄平, 沈泽昊, 唐志尧, 贺金生, 于丹, 江源, 王志恒, 郑成洋, 朱江玲, 郭兆迪 (2009) 植物群落清查的主要内容、方法和技术规范. 生物多样性, 17, 533-548.] | |
| [13] | Fox J, Weisberg S (2019) An R Companion to Applied Regression, 3rd edn. Thousand Oaks CA, Sage. https://socialsciences.mcmaster.ca/jfox/Books/Companion/. (accessed 2020-12-25) |
| [14] | Gui FR (2006) Genetic Diversity and Population Structure Ageratina adenophora Spreng. (Asteraceae) in China. PhD dissertation, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Beijing. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 桂富荣 (2006) 紫茎泽兰的遗传多样性及其种群结构分析. 博士学位论文, 中国农业科学院, 北京.] | |
| [15] |
Halpern SL, Underwood N (2006) Approaches for testing herbivore effects on plant population dynamics. Journal of Applied Ecology, 43, 922-929.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
Hierro JL, Maron JL, Callaway RM (2005) A biogeographical approach to plant invasions: The importance of studying exotics in their introduced and native range. Journal of Ecology, 93, 5-15.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
Horvitz N, Wang R, Zhu M, Wan FH, Nathan R (2014) A simple modeling approach to elucidate the main transport processes and predict invasive spread: River-mediated invasion of Ageratina adenophora in China. Water Resources Research, 50, 9738-9747.
DOI URL |
| [18] | Hou TP (2000) Study on the Active Substances and Preparations of Poisonous Grassland Plant Eupatorium adenophorum. PhD dissertation, Gansu Agricultural University, Lanzhou. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 侯太平 (2000) 草地有毒植物紫茎泽兰灭蚜活性物质及制剂研究. 博士学位论文, 甘肃农业大学, 兰州.] | |
| [19] |
Kembel SW, Cowan PD, Helmus MR, Cornwell WK, Morlon H, Ackerly DD, Blomberg SP, Webb CO (2010) Picante: R tools for integrating phylogenies and ecology. Bioinformatics, 26, 1463-1464.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
Levine JM, D’Antonio CM (1999) Elton revisited: A review of evidence linking diversity and invasibility. Oikos, 87, 15-26.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
Li SP, Cadotte MW, Meiners SJ, Hua ZS, Shu HY, Li JT, Shu WS (2015) The effects of phylogenetic relatedness on invasion success and impact: Deconstructing Darwin’s naturalisation conundrum. Ecology Letters, 18, 1285-1292.
DOI URL |
| [22] | Liendo D, Biurrun I, Campos JA, García-Mijangos I, Pearman PB (2021) Effects of disturbance and alien plants on the phylogenetic structure of riverine communities. Journal of Vegetation Science, 32, e12933. |
| [23] | Liu JL, Ai W, Chen WH, Niu YD (2019) Restoration of Pinus yunnanensis forest after fire and flora analysis of substitute tree species in Daxi Mountain. Journal of Agricultural Catastrophology, 9, 43-44. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 刘经伦, 艾薇, 陈文华, 牛源东 (2019) 大西山云南松林火灾后的恢复情况及替代树种区系分析. 农业灾害研究, 9, 43-44.] | |
| [24] | Liu LH, Xie SC, Zhang JH (1985) Studies on the distribution, harmfulness and control of Eupatorium adenophorum Spreng. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 5, 1-6. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 刘伦辉, 谢寿昌, 张建华 (1985) 紫茎泽兰在我国的分布、危害与防除途径的探讨. 生态学报, 5, 1-6.] | |
| [25] | Lu ZJ (2005) Plant Community Resistance to the Invasion of Croftonweed (Eupatorium adenophorum) in Southwest China. PhD dissertation, Institute of Botany, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 卢志军 (2005) 中国西南地区植物群落的可入侵性与紫茎泽兰的入侵. 博士学位论文, 中国科学院植物研究所, 北京.] | |
| [26] |
Lu ZJ, Ma KP (2005) Scale dependent relationships between native plant diversity and the invasion of croftonweed (Eupatorium adenophorum) in southwest China. Weed Science, 53, 600-604.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
Metz MR, Sousa WP, Valencia R (2010) Widespread density-dependent seedling mortality promotes species coexistence in a highly diverse Amazonian rain forest. Ecology, 91, 3675-3685.
DOI URL |
| [28] | Miller JT, Hui C, Thornhill AH, Gallien L, Le Roux JJ, Richardson DM (2016) Is invasion success of Australian trees mediated by their native biogeography, phylogenetic history, or both? AoB PLANTS, 9, plw080. |
| [29] |
Minteer CR, Smith MC, Madeira P, Goosem C, Zonneveld R, Makinson J, Wheeler GS, Purcell M (2020) Is biological control for earleaf acacia (Acacia auriculiformis) feasible in the United States? Biocontrol Science and Technology, 30, 1275-1299.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
O’Sullivan BM (1979) Crofton weed (Eupatorium adenophorum) toxicity in horses. Australian Veterinary Journal, 55, 19-21.
DOI URL |
| [31] | Oksanen J, Guillaume FB, Michael F, Roeland K, Pierre L, Dan M, Minchin PR, O’Hara RB, Gavin LS, Peter S, Henry HS, Szoecs E, Wagner H (2019) Vegan: Community Ecology Package. R package version 2.5-6. https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=vegan/. (accessed 2020-12-25) |
| [32] |
Pimm SL (1984) The complexity and stability of ecosystems. Nature, 307, 321-326.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
Pokorny ML, Sheley RL, Zabinski CA, Engel RE, Svejcar TJ, Borkowski JJ (2005) Plant functional group diversity as a mechanism for invasion resistance. Restoration Ecology, 13, 448-459.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
Poudel AS, Jha PK, Shrestha BB, Muniappan R (2019) Biology and management of the invasive weed Ageratina adenophora (Asteraceae): Current state of knowledge and future research needs. Weed Research, 59, 79-92.
DOI |
| [35] | Qiang S (1998) The history and status of the study on crofton weed (Eupatorium adenophorum Spreng.) A worst worldwide weed. Journal of Wuhan Botanical Research, 16, 366-372. (in Chinese) |
| [ 强胜 (1998) 世界性恶性杂草——紫茎泽兰研究的历史及现状. 武汉植物学研究, 16, 366-372.] | |
| [36] |
Shea K, Chesson P (2002) Community ecology theory as a framework for biological invasions. Trends in Ecology and Evolution, 17, 170-176.
DOI URL |
| [37] |
Stachowicz JJ, Whitlatch RB, Osman RW (1999) Species diversity and invasion resistance in a marine ecosystem. Science, 286, 1577-1579.
PMID |
| [38] | Strauss SY, Webb CO, Salamin N (2006) Exotic taxa less related to native species are more invasive. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 103, 5841-5845. |
| [39] | Swenson NG (2014) Functional and Phylogenetic Ecology in R, pp. 85-108. Springer, New York. |
| [40] |
Symstad AJ (2000) A test of the effects of functional group richness and composition on grassland invasibility. Ecology, 81, 99-109.
DOI URL |
| [41] |
Thuiller W, Richardson DM, Rouget M, Procheş S, Wilson JRU (2006) Interactions between environment, species traits, and human uses describe patterns of plant invasions. Ecology, 87, 1755-1769.
DOI URL |
| [42] | Wan FH, Guo JY, Wang DH (2002) Alien invasive species in China: Their damages and management strategies. Biodiversity Science, 10, 119-125. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 万方浩, 郭建英, 王德辉 (2002) 中国外来入侵生物的危害与管理对策. 生物多样性, 10, 119-125.] | |
| [43] |
Wan FH, Liu WX, Guo JY, Qiang S, Li BP, Wang JJ, Yang GQ, Niu HB, Gui FR, Huang WK, Jiang ZL, Wang WQ (2010) Invasive mechanism and control strategy of Ageratina adenophora (Sprengel). Science China: Life Sciences, 53, 1291-1298.
DOI URL |
| [44] | Wang JY, Yang YQ, Chen WH, Yang LH (2015) Study on AIS-Ageratina adenophora population of Pinus yunnanensis pure forest from Longyang region, Baoshan, Yunnan. Journal of Baoshan University, 34(5), 1-3, 10. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 汪建云, 杨玉琴, 陈文华, 杨丽华 (2015) 保山市隆阳区云南松纯林入侵物种紫茎泽兰种群的研究. 保山学院学报, 34(5), 1-3, 10.] | |
| [45] |
Warton DI, Hui FKC (2011) The arcsine is asinine: The analysis of proportions in ecology. Ecology, 92, 3-10
PMID |
| [46] |
Webb CO, Ackerly DD, McPeek MA, Donoghue MJ (2002) Phylogenies and community ecology. Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics, 33, 475-505.
DOI URL |
| [47] | Wickham H (2016) Ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis. Springer-Verlag, New York. |
| [48] | Wu H, Zhang C, Dai WK (2020) Interactive effects of climate warming and species diversity on the invasiveness of the alien weed Alternanthera philoxeroides. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 29, 38-48. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 吴昊, 张辰, 代文魁 (2020) 气候变暖和物种多样性交互效应对空心莲子草入侵的影响. 草业学报, 29, 38-48.] | |
| [49] | Yu XJ (2005) Studies on Biological Invasion by Eupatorium adenpohorum. PhD dissertation, Wuhan University, Wuhan. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 于兴军 (2005) 紫茎泽兰入侵生态学研究. 博士学位论文, 武汉大学, 武汉.] | |
| [50] | Zhang LP, Xue Y, Guo X, Wang MT (2020) Climatic ecological suitability and potential distribution for Boletus edulis in mountainous areas of Western Sichuan Plateau, China. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 31, 3823-3832. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 张利平, 薛燕, 郭翔, 王明田 (2020) 川西高原山地美味牛肝菌气候生态适宜性及潜在分布. 应用生态学报, 31, 3823-3832.] | |
| [51] | Zhang WX, Wang H, Fan XL, Dun XJ, Fang Y, Liang Y (2020) Impacts of black locust forest on understory plant species diversity and phylogenetic diversity in Shandong Province. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 39, 2868-2877. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 张文馨, 王蕙, 范小莉, 囤兴建, 房用, 梁玉 (2020) 山东刺槐林对林下植物物种多样性及谱系多样性的影响. 生态学杂志, 39, 2868-2877.] | |
| [52] | Zhang XY, Xu ZC, Song WW, Li Z, Zhao XG, Hu XB (2010) Biodiversity of invaded area of Eupatorium adenophorum. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 19, 1525-1531. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 张修玉, 许振成, 宋巍巍, 黎忠, 赵晓光, 胡习邦 (2010) 紫茎泽兰(Eupatorium adenophorum)入侵地的生物多样性. 生态环境学报, 19, 1525-1531.] | |
| [53] | Zhang Z, Xu L, Zhu XM (2010) Effect on species diversity of plant communities caused by invasion of Alternanthera philoxeroides in different habitats. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 19, 10-15. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 张震, 徐丽, 朱晓敏 (2010) 喜旱莲子草对不同生境植物群落多样性的影响. 草业学报, 19, 10-15.] | |
| [54] | Zhang ZJ, Liu YJ, Brunel C, van Kleunen M (2020) Evidence for Elton’s diversity-invasibility hypothesis from belowground. Ecology, 101, e03187. |
| [55] | Zhou S, Xie YL (1999) The investigation report on the poisonous and injurious plant—Eupatorium adenophorum Spreng. in Sichuan Province. Sichuan Grassland, (2), 39-42. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 周俗, 谢永良 (1999) 四川省毒害植物——紫茎泽兰调查报告. 四川草原, (2), 39-42.] | |
| [56] |
Zhu L, Sun OJ, Sang WG, Li ZY, Ma KP (2007) Predicting the spatial distribution of an invasive plant species (Eupatorium adenophorum) in China. Landscape Ecology, 22, 1143-1154.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 吴晓晴 张美惠 葛苏婷 李漫淑 宋坤 沈国春 达良俊 张健. 上海近自然林重建过程中木本植物物种多样性与地上生物量的时空动态——以闵行区生态岛为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24444-. |
| [2] | 王太, 宋福俊, 张永胜, 娄忠玉, 张艳萍, 杜岩岩. 河西走廊内陆河水系鱼类多样性及资源现状[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24387-. |
| [3] | 张浩斌, 肖路, 刘艳杰. 夜间灯光对外来入侵植物和本地植物群落多样性和生长的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24553-. |
| [4] | 张晶晶, 黄文彬, 陈奕廷, 杨泽鹏, 柯伟业, 彭昭杰, 魏世超, 张志伟, 胡怡思, 余文华, 周文良. 广东南澎列岛海洋生态国家级自然保护区造礁石珊瑚多样性及分布特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24424-. |
| [5] | 尚华丹, 张楚晴, 王梅, 裴文娅, 李国宏, 王鸿斌. 中国杨树害虫物种多样性及其地理分布[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24370-. |
| [6] | 吴昱萱, 王平, 胡晓生, 丁一, 彭甜恬, 植秋滢, 巴德木其其格, 李文杰, 关潇, 李俊生. 呼伦贝尔草地退化现状评估与植被特征变化[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24118-. |
| [7] | 陈自宏, 张翼飞, 陈凯, 陈见影, 徐玲. 高黎贡山南段昆虫病原真菌物种多样性及影响因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(1): 24228-. |
| [8] | 谭珂, 宁瑶, 王仁芬, 王晴, 梁丹萍, 辛子兵, 温放. 中国苦苣苔科植物名录与地理分布数据集[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(1): 23275-. |
| [9] | 韩佳楠, 苏杨, 李霏, 刘君妍, 赵依林, 李琳, 赵建成, 梁红柱, 李敏. 河北省苔藓植物多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(9): 24096-. |
| [10] | 李东红, 郝媛媛, 甘辉林, 张航, 刘耀猛, 他富源, 胡桂馨. 祁连山北麓中段不同类型草地蝗虫种类及分布[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(9): 24119-. |
| [11] | 牛红玉, 陈璐, 赵恒月, 古丽扎尔·阿不都克力木, 张洪茂. 城市化对动物的影响: 从群落到个体[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(8): 23489-. |
| [12] | 白雪, 李正飞, 刘洋, 张君倩, 张多鹏, 罗鑫, 杨佳莉, 杜丽娜, 蒋玄空, 武瑞文, 谢志才. 西江流域大型底栖无脊椎动物物种多样性及维持机制[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(7): 23499-. |
| [13] | 许佳, 崔小娟, 张翼飞, 吴昌, 孙远东. 南岭地区鱼类多样性及其地理分布[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(7): 23482-. |
| [14] | 邝起宇, 胡亮. 广东东海岛与硇洲岛海域底栖贝类物种多样性及其地理分布[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(5): 24065-. |
| [15] | 赵勇强, 阎玺羽, 谢加琪, 侯梦婷, 陈丹梅, 臧丽鹏, 刘庆福, 隋明浈, 张广奇. 退化喀斯特森林自然恢复中不同生活史阶段木本植物物种多样性与群落构建[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(5): 23462-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn
![]()