



生物多样性 ›› 2013, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (5): 547-553. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2013.07050 cstr: 32101.14.SP.J.1003.2013.07050
收稿日期:2013-03-18
接受日期:2013-03-28
出版日期:2013-09-20
发布日期:2013-10-08
通讯作者:
申玉春
基金资助:
Sheng Ke1, Yuchun Shen2,*( ), Enyi Xie2, Zailiang Li2
), Enyi Xie2, Zailiang Li2
Received:2013-03-18
Accepted:2013-03-28
Online:2013-09-20
Published:2013-10-08
Contact:
Shen Yuchun
摘要:
为了解高密度贝类养殖模式下潮间带底栖贝类的物种组成、时空分布以及多样性特征。作者于2008-2009年分别对雷州半岛流沙湾海草床区、贝类养殖区以及非养殖区等三个海区潮间带进行底栖贝类采样。结果表明: (1)潮间带共有贝类97种, 非养殖区分布种类最多(58种), 海草床区则最少(49种), 珠带拟蟹守螺(Cerithidea cingulata)与纵带滩栖螺(Batillaria zonalis)均属三海区的优势种类; (2)非养殖区与海草床区底栖贝类生物量及丰度均以9月份最高, 5月份最低。海草床区及贝类养殖区底栖贝类的生物量与丰度均为高潮区>中潮区>低潮区。(3)Margalef丰富度指数与Shannon-Wiener多样性指数最高的海区是非养殖区, Pielou均匀度指数则以贝类养殖区的最高。从K-优势度曲线亦分析得出贝类养殖区受干扰程度最大。分析表明, 贝类养殖区与海草床区潮间带底栖贝类的群落结构不稳定且生物多样性较低, 其中较低的贝类养殖密度、适量面积的海草床覆盖率、混合型底质类型及强波浪扰动能提高底栖贝类的群落结构稳定性与生物多样性。
柯盛, 申玉春, 谢恩义, 李再亮 (2013) 雷州半岛流沙湾潮间带底栖贝类多样性. 生物多样性, 21, 547-553. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2013.07050.
Sheng Ke,Yuchun Shen,Enyi Xie,Zailiang Li (2013) Biodiversity of the benthic shellfish in the intertidal zone of the Liusha Bay, Leizhou Peninsula. Biodiversity Science, 21, 547-553. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2013.07050.
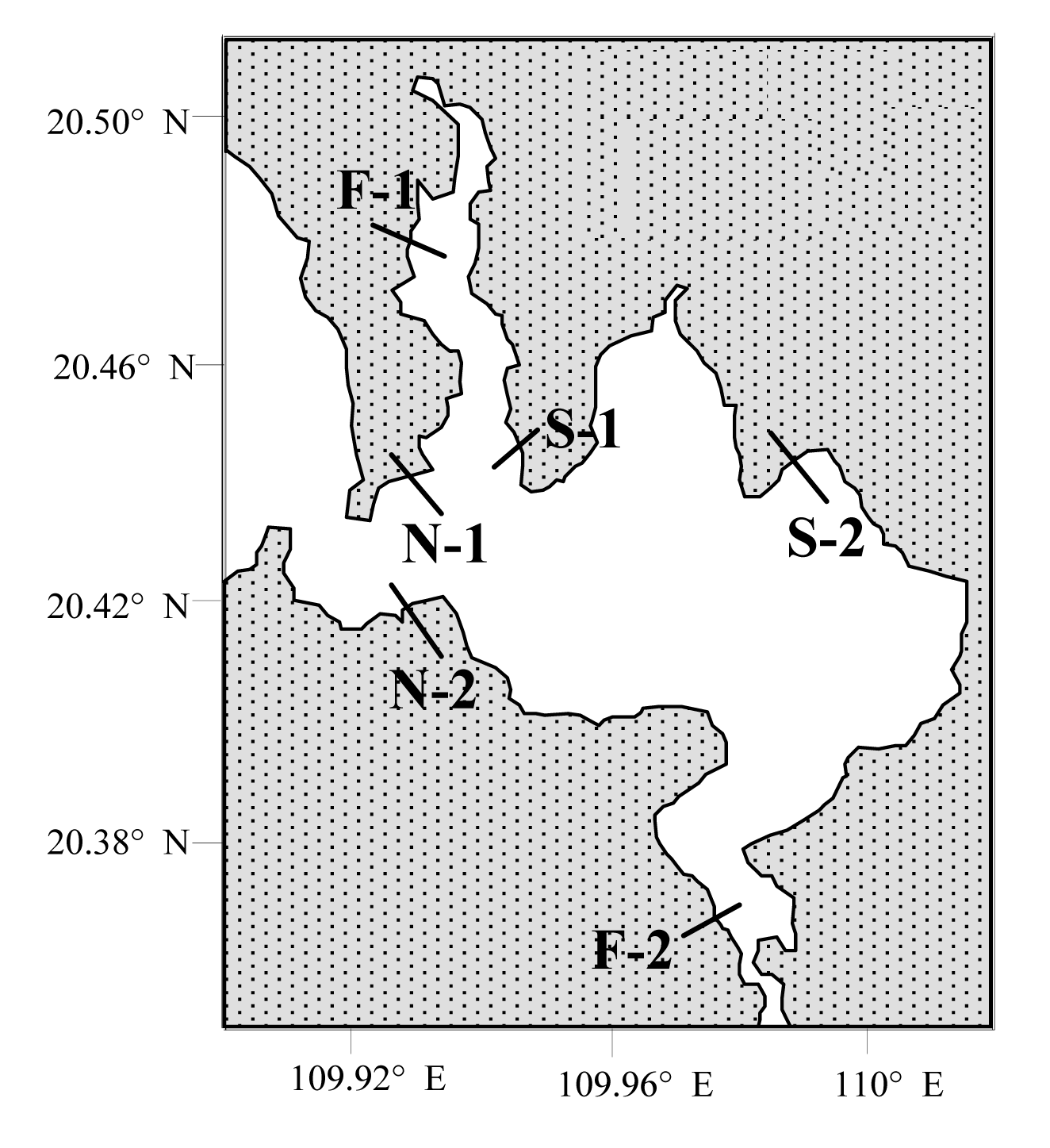
图1 流沙湾潮间带采样断面分布图。N: 非养殖区; F: 贝类养殖区; S: 大型海草床区
Fig. 1 Diagram of the sampling sections at Liusha Bay. N, Non-cultured areas; F, Cultured shellfish areas; S, Seagrass beds.
| 科 Family | 非养殖区 Non-cultured shellfish areas | 大型海草床区 Seagrass beds | 贝类养殖区 Cultured shellfish areas | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 种数 Species | 比例% Proportion% | 种数 Species | 比例% Proportion% | 种数 Species | 比例% Proportion% | |||
| 蚶科 Arcidae | 2 | 3.4 | 2 | 4.1 | 1 | 1.8 | ||
| 贻贝科 Mytilidae | 4 | 6.9 | 4 | 8.2 | 4 | 7.1 | ||
| 江珧科 Pinnidae | - | - | 1 | 2.0 | - | - | ||
| 珍珠贝科 Pteriidae | 1 | 1.7 | 1 | 2.0 | 1 | 1.8 | ||
| 不等蛤科 Anomiidae | - | - | 2 | 4.1 | 2 | 3.6 | ||
| 牡蛎科 Ostreidae | 3 | 5.2 | 1 | 2.0 | 3 | 5.4 | ||
| 扇贝科 Pectinidae | 2 | 3.4 | 1 | 2.0 | - | - | ||
| 帘蛤科 Veneracea | 12 | 20.7 | 10 | 20.4 | 17 | 30.4 | ||
| 蛤蜊科 Mactridae | 1 | 1.7 | 1 | 2.0 | 1 | 1.8 | ||
| 樱蛤科 Tellinidae | 1 | 1.7 | 1 | 2.0 | - | - | ||
| 双带蛤科 Semelisae | 1 | 1.7 | 1 | 2.0 | - | - | ||
| 紫云蛤科 Psammobiidae | - | - | - | - | 1 | 1.8 | ||
| 竹蛏科 Solenidae | - | - | 1 | 2.0 | - | - | ||
| 刀蛏科 Cultellidae | 1 | 1.7 | 0 | 0.0 | - | - | ||
| 同心蛤科 Lsocardidae | - | - | 1 | 2.0 | - | - | ||
| 棱蛤科 Trapeziidae | 1 | 1.7 | 1 | 2.0 | 1 | 1.8 | ||
| 绿螂科 Glauconomidae | 1 | 1.7 | - | - | 1 | 1.8 | ||
| 鸭嘴蛤科 Laternulidae | - | - | - | - | 1 | 1.8 | ||
| 马蹄螺科 Trochidae | 3 | 5.2 | 2 | 4.1 | 1 | 1.8 | ||
| 蝾螺科 Turbinidae | 2 | 3.4 | 2 | 4.1 | 1 | 1.8 | ||
| 蜒螺科 Neritidae | 2 | 3.4 | 3 | 6.1 | 3 | 5.4 | ||
| 宝贝科 Cypraeidae | - | - | - | - | 1 | 1.8 | ||
| 钥孔虫戚科 Fissurellidae | 1 | 1.7 | - | - | 1 | 1.8 | ||
| 滨螺科 Littorinidae | 2 | 3.4 | - | - | 2 | 3.6 | ||
| 汇螺科 Potamididae | 4 | 6.9 | 3 | 6.1 | 5 | 8.9 | ||
| 蟹守螺科 Cerithiidae | 2 | 3.4 | 1 | 2.0 | 1 | 1.8 | ||
| 风螺科 Strombidae | 1 | 1.7 | 1 | 2.0 | 0 | 0.0 | ||
| 玉螺科 Naticidae | - | - | - | - | 1 | 1.8 | ||
| 嵌线螺科 Cymatiidae | 1 | 1.7 | - | - | - | - | ||
| 牙螺科 Columbellidae | 1 | 1.7 | - | - | - | - | ||
| 盔螺科 Galeodidae | - | - | 1 | 2.0 | - | - | ||
| 骨螺科 Muricidae | 2 | 3.4 | 2 | 4.1 | 1 | 1.8 | ||
| 织纹螺科 Nassariidae | 4 | 6.9 | 2 | 4.1 | 3 | 5.4 | ||
| 笔螺科 Mitridae | 1 | 1.7 | 2 | 4.1 | 1 | 1.8 | ||
| 阿地螺科 Atyidae | 1 | 1.7 | 1 | 2.0 | 1 | 1.8 | ||
| 海兔科 Aplysiidae | 1 | 1.7 | 1 | 2.0 | 1 | 1.8 | ||
| 总计 Total | 58 | 100 | 49 | 100 | 56 | 100 | ||
表1 流沙湾三个不同海区的贝类分布
Table 1 Distribution of shellfish species in three different areas of Liusha Bay
| 科 Family | 非养殖区 Non-cultured shellfish areas | 大型海草床区 Seagrass beds | 贝类养殖区 Cultured shellfish areas | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 种数 Species | 比例% Proportion% | 种数 Species | 比例% Proportion% | 种数 Species | 比例% Proportion% | |||
| 蚶科 Arcidae | 2 | 3.4 | 2 | 4.1 | 1 | 1.8 | ||
| 贻贝科 Mytilidae | 4 | 6.9 | 4 | 8.2 | 4 | 7.1 | ||
| 江珧科 Pinnidae | - | - | 1 | 2.0 | - | - | ||
| 珍珠贝科 Pteriidae | 1 | 1.7 | 1 | 2.0 | 1 | 1.8 | ||
| 不等蛤科 Anomiidae | - | - | 2 | 4.1 | 2 | 3.6 | ||
| 牡蛎科 Ostreidae | 3 | 5.2 | 1 | 2.0 | 3 | 5.4 | ||
| 扇贝科 Pectinidae | 2 | 3.4 | 1 | 2.0 | - | - | ||
| 帘蛤科 Veneracea | 12 | 20.7 | 10 | 20.4 | 17 | 30.4 | ||
| 蛤蜊科 Mactridae | 1 | 1.7 | 1 | 2.0 | 1 | 1.8 | ||
| 樱蛤科 Tellinidae | 1 | 1.7 | 1 | 2.0 | - | - | ||
| 双带蛤科 Semelisae | 1 | 1.7 | 1 | 2.0 | - | - | ||
| 紫云蛤科 Psammobiidae | - | - | - | - | 1 | 1.8 | ||
| 竹蛏科 Solenidae | - | - | 1 | 2.0 | - | - | ||
| 刀蛏科 Cultellidae | 1 | 1.7 | 0 | 0.0 | - | - | ||
| 同心蛤科 Lsocardidae | - | - | 1 | 2.0 | - | - | ||
| 棱蛤科 Trapeziidae | 1 | 1.7 | 1 | 2.0 | 1 | 1.8 | ||
| 绿螂科 Glauconomidae | 1 | 1.7 | - | - | 1 | 1.8 | ||
| 鸭嘴蛤科 Laternulidae | - | - | - | - | 1 | 1.8 | ||
| 马蹄螺科 Trochidae | 3 | 5.2 | 2 | 4.1 | 1 | 1.8 | ||
| 蝾螺科 Turbinidae | 2 | 3.4 | 2 | 4.1 | 1 | 1.8 | ||
| 蜒螺科 Neritidae | 2 | 3.4 | 3 | 6.1 | 3 | 5.4 | ||
| 宝贝科 Cypraeidae | - | - | - | - | 1 | 1.8 | ||
| 钥孔虫戚科 Fissurellidae | 1 | 1.7 | - | - | 1 | 1.8 | ||
| 滨螺科 Littorinidae | 2 | 3.4 | - | - | 2 | 3.6 | ||
| 汇螺科 Potamididae | 4 | 6.9 | 3 | 6.1 | 5 | 8.9 | ||
| 蟹守螺科 Cerithiidae | 2 | 3.4 | 1 | 2.0 | 1 | 1.8 | ||
| 风螺科 Strombidae | 1 | 1.7 | 1 | 2.0 | 0 | 0.0 | ||
| 玉螺科 Naticidae | - | - | - | - | 1 | 1.8 | ||
| 嵌线螺科 Cymatiidae | 1 | 1.7 | - | - | - | - | ||
| 牙螺科 Columbellidae | 1 | 1.7 | - | - | - | - | ||
| 盔螺科 Galeodidae | - | - | 1 | 2.0 | - | - | ||
| 骨螺科 Muricidae | 2 | 3.4 | 2 | 4.1 | 1 | 1.8 | ||
| 织纹螺科 Nassariidae | 4 | 6.9 | 2 | 4.1 | 3 | 5.4 | ||
| 笔螺科 Mitridae | 1 | 1.7 | 2 | 4.1 | 1 | 1.8 | ||
| 阿地螺科 Atyidae | 1 | 1.7 | 1 | 2.0 | 1 | 1.8 | ||
| 海兔科 Aplysiidae | 1 | 1.7 | 1 | 2.0 | 1 | 1.8 | ||
| 总计 Total | 58 | 100 | 49 | 100 | 56 | 100 | ||
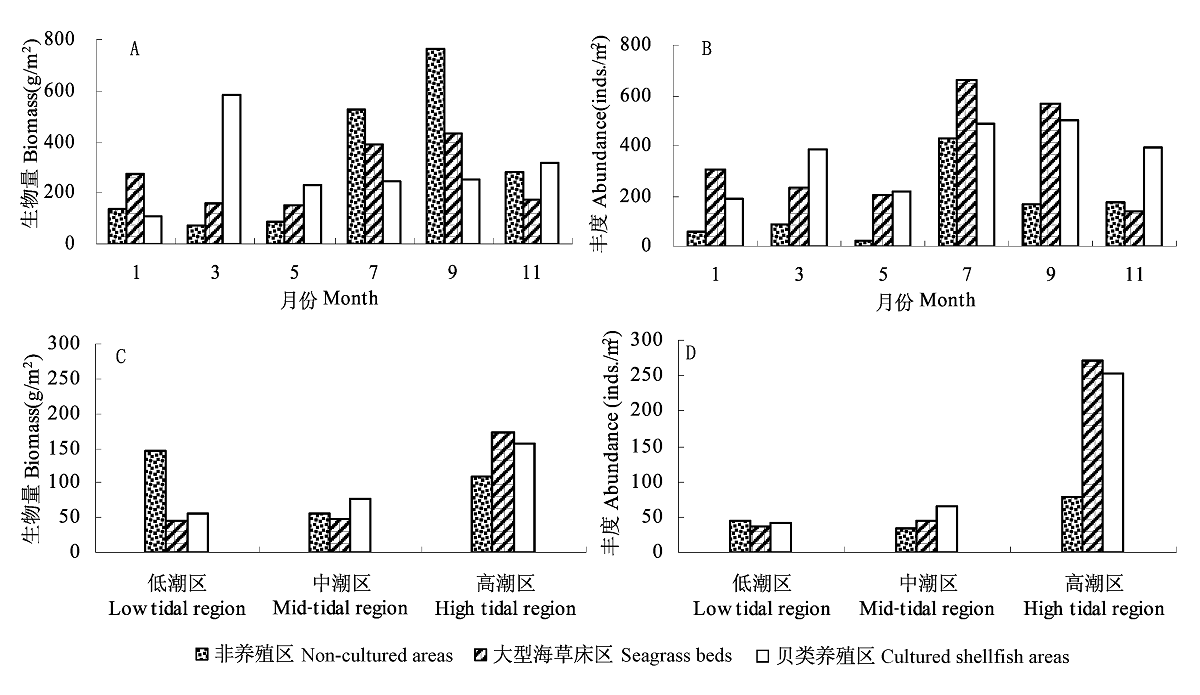
图2 流沙湾底栖贝类生物量和丰度的时间分布(A与B)与垂直分布(C与D)
Fig. 2 The temporal (A & B) and vertical (C & D) distribution of biomass and abundance of benthic shellfishes in different areas of Liusha Bay
| 海区 Area | 航次 Time | 指数 Index | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| d | J' | H' | ||
| 非养殖区 Non-cultured shellfish areas | 1月 Jan. | 0.60 | 0.81 | 1.61 |
| 3月 Mar. | 2.98 | 0.66 | 2.69 | |
| 5月 May | 1.36 | 0.90 | 2.33 | |
| 7月 July | 1.49 | 0.78 | 2.71 | |
| 9月 Sept. | 1.04 | 0.67 | 1.87 | |
| 11月 Nov. | 1.20 | 0.70 | 2.11 | |
| 平均 Average | 3.04 | 2.51 | 0.71 | |
| 大型海草床区 Seagrass beds | 1月 Jan. | 1.03 | 0.53 | 1.58 |
| 3月 Mar. | 1.72 | 0.38 | 1.50 | |
| 5月 May | 1.56 | 0.39 | 1.34 | |
| 7月 July | 1.05 | 0.50 | 1.59 | |
| 9月 Sept. | 0.94 | 0.33 | 0.98 | |
| 11月 Nov. | 0.83 | 0.20 | 1.46 | |
| 平均 Average | 1.65 | 1.89 | 0.48 | |
| 贝类养殖区 Cultured shellfish areas | 1月 Jan. | 1.04 | 0.58 | 1.84 |
| 3月 Mar. | 3.56 | 0.56 | 2.59 | |
| 5月 May | 1.52 | 0.42 | 1.49 | |
| 7月 July | 1.29 | 0.61 | 2.02 | |
| 9月 Sept. | 1.04 | 0.67 | 1.87 | |
| 11月 Nov. | 0.91 | 0.56 | 0.60 | |
| 平均 Average | 1.94 | 2.57 | 0.43 | |
表2 底栖贝类的生物多样性指数的时空变化
Table 2 The indexes of biodiversity of benthic shellfishes
| 海区 Area | 航次 Time | 指数 Index | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| d | J' | H' | ||
| 非养殖区 Non-cultured shellfish areas | 1月 Jan. | 0.60 | 0.81 | 1.61 |
| 3月 Mar. | 2.98 | 0.66 | 2.69 | |
| 5月 May | 1.36 | 0.90 | 2.33 | |
| 7月 July | 1.49 | 0.78 | 2.71 | |
| 9月 Sept. | 1.04 | 0.67 | 1.87 | |
| 11月 Nov. | 1.20 | 0.70 | 2.11 | |
| 平均 Average | 3.04 | 2.51 | 0.71 | |
| 大型海草床区 Seagrass beds | 1月 Jan. | 1.03 | 0.53 | 1.58 |
| 3月 Mar. | 1.72 | 0.38 | 1.50 | |
| 5月 May | 1.56 | 0.39 | 1.34 | |
| 7月 July | 1.05 | 0.50 | 1.59 | |
| 9月 Sept. | 0.94 | 0.33 | 0.98 | |
| 11月 Nov. | 0.83 | 0.20 | 1.46 | |
| 平均 Average | 1.65 | 1.89 | 0.48 | |
| 贝类养殖区 Cultured shellfish areas | 1月 Jan. | 1.04 | 0.58 | 1.84 |
| 3月 Mar. | 3.56 | 0.56 | 2.59 | |
| 5月 May | 1.52 | 0.42 | 1.49 | |
| 7月 July | 1.29 | 0.61 | 2.02 | |
| 9月 Sept. | 1.04 | 0.67 | 1.87 | |
| 11月 Nov. | 0.91 | 0.56 | 0.60 | |
| 平均 Average | 1.94 | 2.57 | 0.43 | |
| 1 | Cai YY (蔡英亚), Xie SH (谢绍河) (2006) Seashells of Guangdong (广东的海贝). The Press of Shantou University, Shantou. (in Chinese) |
| 2 | Chen BL (陈斌林), Fang T (方涛), Li DJ (李道季) (2007) Community structure and biodiversity characteristics of macrobenthos in the costal area of Lianyungang. Journal of East China Normal University (Natural Science) (华东师范大学学报(自然科学版)), (2), 1-10. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 3 | Duan XH (段学花), Wang ZY (王兆印), Cheng DS (程东升) (2007) Benthic macroinvertebrates communities and biodiversity in various stream substrata.Acta Ecologica Sinica(生态学报), 27, 1664-1672. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 4 | Gao AG (高爱根), Dong YT (董永庭), Wang HZ (王慧珍), Wang YH (王永泓) (2008) Preliminary study on the distribution of mollusca ecology in sublittoral area of Nanji Island.Journal of Marine Sciences(海洋学研究), 26, 49-54. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 5 | Lambshead PJD, Platt HM, Shaw KM (1983) The detection of differences among assemblages of marine benthic species based on an assessment of dominance and diversity.Journal of Natural History, 17, 859-874. |
| 6 | Li XZ (李新正) (2011) An overview of studies on marine macrobenthic biodiversity from Chinese waters: principally from the Yellow Sea.Biodiversity Science(生物多样性), 19, 676-684. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 7 | Ma Y (马勇), Deng GF (邓国藩), Cheng QT (成庆泰), Zhu HF (朱弘复) (1997) Fauna Sinica, Phylum Mollusca (中国动物志—软体动物门). Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| 8 | Margalef R (1968) Perspective in Ecological Theory. University of Chicago Press, Chicago. |
| 9 | Pielou EC (1975) Ecological Diversity, pp. 16-51. Wiley Interscience, New York. |
| 10 | Shannon CE, Warren W (1949) The Mathematical Theory of Communication. University of Illinois, Urbana. |
| 11 | Shen YC (申玉春), Li ZL (李再亮), Huang SC (黄石成), Zhu CH (朱春华), Wu ZH (吴灶和), Du XD (杜晓东) (2010) Analysis on the aquaculture structure and distribution in the Liusha Bay sea area.Chinese Fisheries Economics(中国渔业经济), 28, 105-109. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 12 | Wise SA, Zeisler R (1984) The pilot environmental specimen bank program.Environmental Science and Technology, 18, 302-307. |
| 13 | Xie EY (谢恩义), Shen YC (申玉春), Ye N (叶宁), Wu ZH (吴灶和) (2009) Benthic marine macroalgae survey in Liusha gulf.Journal of Guangdong Ocean University(广东海洋大学学报), 29(4), 29-34. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 14 | Xie JJ (谢进金), Xie JH (谢进辉), Lin JJ (林娟娟), Feng L (冯琳), Qi ZM (齐兆明) (2006) Ecological distribution of mollusca in intertidal zone of Quanzhou, Fujian.Marine Science(海洋科学), 30, 54-62. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 15 | Xu FS (徐凤山), Zhang JL (张均龙) (2011) Characteristics of bivalve diversity in typical habitats of China seas.Biodiversity Science(生物多样性), 19, 716-722. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 16 | Xu ZL (徐兆礼), Chen YQ (陈亚瞿) (1989) Aggregated intensity of dominant species of zooplankton in autumn in the East China Sea and Yellow Sea.Chinese Journal of Ecology(生态学杂志), 8(4), 13-15. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 17 | Zhang CX (张才学), Chen HY (陈慧妍), Sun XL (孙省利), Zhang YB (张瑜斌), Chen CL (陈春亮) (2012) Temporal and spatial distribution of phytoplankton in Liusha Bay. Acta Ecologica Sinica(生态学报), 32, 1527-1537. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 18 | Zhou H (周红), Zhang ZN (张志南) (2003) Rationale of the multivariate statistical software PRIMER and its application in benthic community ecology.Journal of Ocean University of Qingdao(青岛海洋大学学报), 33, 58-64. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [1] | 吴晓晴 张美惠 葛苏婷 李漫淑 宋坤 沈国春 达良俊 张健. 上海近自然林重建过程中木本植物物种多样性与地上生物量的时空动态——以闵行区生态岛为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24444-. |
| [2] | 干靓 刘巷序 鲁雪茗 岳星. 全球生物多样性热点地区大城市的保护政策与优化方向[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24529-. |
| [3] | 曾子轩 杨锐 黄越 陈路遥. 清华大学校园鸟类多样性特征与环境关联[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24373-. |
| [4] | 臧明月, 刘立, 马月, 徐徐, 胡飞龙, 卢晓强, 李佳琦, 于赐刚, 刘燕. 《昆明-蒙特利尔全球生物多样性框架》下的中国城市生物多样性保护[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24482-. |
| [5] | 祝晓雨, 王晨灏, 王忠君, 张玉钧. 城市绿地生物多样性研究进展与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 25027-. |
| [6] | 袁琳, 王思琦, 侯静轩. 大都市地区的自然留野:趋势与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24481-. |
| [7] | 胡敏, 李彬彬, Coraline Goron. 只绿是不够的: 一个生物多样性友好的城市公园管理框架[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24483-. |
| [8] | 王欣, 鲍风宇. 基于鸟类多样性提升的南滇池国家湿地公园生态修复效果分析[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24531-. |
| [9] | 明玥, 郝培尧, 谭铃千, 郑曦. 基于城市绿色高质量发展理念的中国城市生物多样性保护与提升研究[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24524-. |
| [10] | 谢淦, 宣晶, 付其迪, 魏泽, 薛凯, 雒海瑞, 高吉喜, 李敏. 草地植物多样性无人机调查的物种智能识别模型构建[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24236-. |
| [11] | 褚晓琳, 张全国. 演化速率假说的实验验证研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 25019-. |
| [12] | 宋威, 程才, 王嘉伟, 吴纪华. 土壤微生物对植物多样性–生态系统功能关系的调控作用[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24579-. |
| [13] | 卢晓强, 董姗姗, 马月, 徐徐, 邱凤, 臧明月, 万雅琼, 李孪鑫, 于赐刚, 刘燕. 前沿技术在生物多样性研究中的应用现状、挑战与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24440-. |
| [14] | 农荞伊, 曹军, 程文达, 彭艳琼. 不同方法对蜜蜂总科昆虫资源与多样性监测效果的比较[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 25057-. |
| [15] | 郭雨桐, 李素萃, 王智, 解焱, 杨雪, 周广金, 尤春赫, 朱萨宁, 高吉喜. 全国自然保护地对国家重点保护野生物种的覆盖度及其分布状况[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(3): 24423-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn