



生物多样性 ›› 2020, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (9): 1081-1089. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2019292 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2019292
李佳1#, 王秀磊1#, 杨明伟2, 陈大祥2, 王晓菊3, 罗平4, 刘芳1, 薛亚东1, 李广良1, 张于光1, 张宇1, 李迪强1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2019-09-17
接受日期:2020-07-20
出版日期:2020-09-20
发布日期:2020-10-22
通讯作者:
李迪强
作者简介:*E-mail: lidiq@qq.com基金资助:
Jia Li1#, Xiulei Wang1#, Mingwei Yang2, Daxiang Chen2, Xiaoju Wang3, Ping Luo4, Fang Liu1, Yadong Xue1, Guangliang Li1, Yuguang Zhang1, Yu Zhang1, Diqiang Li1,*( )
)
Received:2019-09-17
Accepted:2020-07-20
Online:2020-09-20
Published:2020-10-22
Contact:
Diqiang Li
About author:First author contact: Co-first author
摘要:
红外相机技术在野生动物调查研究中得到广泛应用, 其发展和普及为中国自然保护地生物多样性保护带来了诸多机会。为进一步推广该技术在我国自然保护地野生动物监测中的应用, 中国林业科学研究院森林生态环境与保护研究所在自然保护区生物标本资源共享子平台增设野生动物红外相机数据库专栏, 并通过门户网站“中国自然保护区生物标本资源共享平台” (
李佳, 王秀磊, 杨明伟, 陈大祥, 王晓菊, 罗平, 刘芳, 薛亚东, 李广良, 张于光, 张宇, 李迪强 (2020) 自然保护区生物标本资源共享子平台红外相机数据库建设进展. 生物多样性, 28, 1081-1089. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2019292.
Jia Li, Xiulei Wang, Mingwei Yang, Daxiang Chen, Xiaoju Wang, Ping Luo, Fang Liu, Yadong Xue, Guangliang Li, Yuguang Zhang, Yu Zhang, Diqiang Li (2020) Construction progress of camera-trapping database from the Nature Reserves Biological Specimen Resources Sharing Sub-platform. Biodiversity Science, 28, 1081-1089. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2019292.
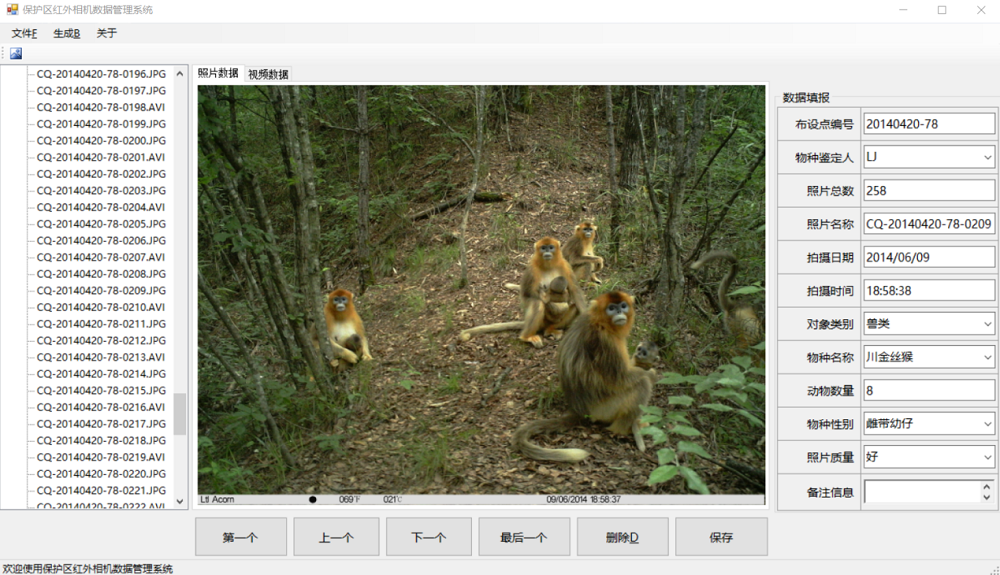
图1 自然保护区生物标本资源共享子平台红外相机数据库管理系统界面。该系统自动提取布设点编号、照片总数、照片名称、拍摄到的图像日期、时期; 人工填写物种类型、物种名称、数量、物种性别。点击保存按键, 信息自动保存至后台Access数据库。图示红外相机在陕西长青国家级自然保护区拍到的成年雌性川金丝猴照顾幼体。
Fig. 1 Interface of camera-trapping database management system in Nature Reserves Biological Specimen Resources Sharing Sub-platform. The system automatically extracts sites ID, the total no. of photographs, photograph name, the date and time of photograph. Type, name, no. and gender of species should be manually filled in. After clicking save button, the information is automatically saved in Access database. The picture shows baby golden moneys stay with adult golden monkeys in the Changqing National Nature Reserve (photo taken by camera-trap).

图2 自然保护区生物标本资源共享子平台红外相机数据库管理流程
Fig. 2 Management process of the camera-trapping database in Nature Reserves Biological Specimen Resources Sharing Sub-platform
| 名称 Name | 省区 Province | 保护地级别 Protective state | 面积 Area (km2) | 经度 Longitude | 纬度 Latitude | 起始年 Start year | 结束年 End year | 有效相机位点 Effective camera site | 独立照片 Independent photograph | 有效工作日 Effective camera-days | 发表与否 Published | 布设方式Setting way |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 祁连山 Qilianshan (QLS) | 青海 Qinghai | 国家公园 National park | 15,800 | 99.53° E | 38.24° N | 2017 | 2019 | 126 | 9,675 | 12,096 | Yes | 公里网格 Grid |
| 中铁-军功 Zhongtie- Jungong (ZT-JG) | 青海 Qinghai | 国家级 保护区 National reserve | 7,700 | 100.09° E | 35.06° N | 2015 | 2015 | 37 | 698 | 2, 984 | Yes | 样线 Line transect |
| 神农架 Shennongjia (SNJ) | 湖北 Hubei | 国家公园 National park | 152 | 110.24° E | 31.46° N | 2010 | 2016 | 278 | 6,125 | 30,877 | Not | 样线 Line transect |
| 后河 Houhe (HH) | 湖北 Hubei | 国家级 保护区 National reserve | 402 | 110.60° E | 30.09° N | 2017 | 2019 | 179 | 8,536 | 44,960 | Not | 公里网格 Grid |
| 松山 Songshan (SS) | 北京 Beijing | 国家级 保护区 National reserve | 45 | 115.81° E | 40.52° N | 2010 | 2010 | 210 | 2,203 | 6,300 | Yes | 公里网格 Grid |
| 长青 Changqing (CQ) | 陕西 Shaanxi | 国家级 保护区 National reserve | 229 | 107.63° E | 33.61° N | 2014 | 2017 | 624 | 28,861 | 93,606 | Not | 公里网格 Grid |
| 壶瓶山 Hupingshan (HPS) | 湖南 Hunan | 国家级 保护区 National reserve | 666 | 110.73° E | 30.00° N | 2012 | 2015 | 20 | 4,440 | 19,592 | Yes | 公里网格 Grid |
| 高望界 Gaowangjie (GWJ) | 湖南 Hunan | 国家级 保护区 National reserve | 42 | 110.09° E | 28.68° N | 2012 | 2013 | 50 | 2,826 | 6,406 | Yes | 植被类型 Vegetation |
| 凤阳山 Fengyangshan (FYS) | 浙江 Zhejiang | 国家级 保护区 National reserve | 153 | 119.16° E | 27.86° N | 2008 | 2016 | 58 | 8,208 | 28,256 | Yes | 公里网格 Grid |
| 尖峰岭 Jianfengling (JFL) | 海南 Hainan | 国家级 保护区 National reserve | 451 | 108.91° E | 18.74° N | 2014 | 2015 | 57 | 5,383 | 14,715 | Yes | 固定监测样地 Monitoring network |
| 铜壁关 Tongbiguan (TBG) | 云南 Yunnan | 省级 保护区 Provincial reserve | 517 | 97.61° E | 24.54° N | 2017 | 2017 | 17 | 527 | 3,059 | Yes | 样线 Line transect |
| 罗布泊 Luobupo (LBP) | 新疆 Xinjiang | 国家级 保护区 National reserve | 22,800 | 91.55° E | 40.33° N | 2010 | 2012 | 7 | 6,655 | 7,098 | Yes | 水源点 Water site |
| 敦煌西湖 Dunhuangxihu (DHXH) | 甘肃 Gansu | 国家级 保护区 National reserve | 6,600 | 93.34° E | 40.14° N | 2012 | 2013 | 4 | 257 | 2,626 | Yes | 水源点 Water site |
表1 自然保护区生物标本资源子平台红外相机监测区域基本信息表(截至2019年6月)
Table 1 Basic information of camera-trapping monitoring area in Nature Reserves Biological Specimen Resources Sharing Sub-platform (Before June 2019)
| 名称 Name | 省区 Province | 保护地级别 Protective state | 面积 Area (km2) | 经度 Longitude | 纬度 Latitude | 起始年 Start year | 结束年 End year | 有效相机位点 Effective camera site | 独立照片 Independent photograph | 有效工作日 Effective camera-days | 发表与否 Published | 布设方式Setting way |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 祁连山 Qilianshan (QLS) | 青海 Qinghai | 国家公园 National park | 15,800 | 99.53° E | 38.24° N | 2017 | 2019 | 126 | 9,675 | 12,096 | Yes | 公里网格 Grid |
| 中铁-军功 Zhongtie- Jungong (ZT-JG) | 青海 Qinghai | 国家级 保护区 National reserve | 7,700 | 100.09° E | 35.06° N | 2015 | 2015 | 37 | 698 | 2, 984 | Yes | 样线 Line transect |
| 神农架 Shennongjia (SNJ) | 湖北 Hubei | 国家公园 National park | 152 | 110.24° E | 31.46° N | 2010 | 2016 | 278 | 6,125 | 30,877 | Not | 样线 Line transect |
| 后河 Houhe (HH) | 湖北 Hubei | 国家级 保护区 National reserve | 402 | 110.60° E | 30.09° N | 2017 | 2019 | 179 | 8,536 | 44,960 | Not | 公里网格 Grid |
| 松山 Songshan (SS) | 北京 Beijing | 国家级 保护区 National reserve | 45 | 115.81° E | 40.52° N | 2010 | 2010 | 210 | 2,203 | 6,300 | Yes | 公里网格 Grid |
| 长青 Changqing (CQ) | 陕西 Shaanxi | 国家级 保护区 National reserve | 229 | 107.63° E | 33.61° N | 2014 | 2017 | 624 | 28,861 | 93,606 | Not | 公里网格 Grid |
| 壶瓶山 Hupingshan (HPS) | 湖南 Hunan | 国家级 保护区 National reserve | 666 | 110.73° E | 30.00° N | 2012 | 2015 | 20 | 4,440 | 19,592 | Yes | 公里网格 Grid |
| 高望界 Gaowangjie (GWJ) | 湖南 Hunan | 国家级 保护区 National reserve | 42 | 110.09° E | 28.68° N | 2012 | 2013 | 50 | 2,826 | 6,406 | Yes | 植被类型 Vegetation |
| 凤阳山 Fengyangshan (FYS) | 浙江 Zhejiang | 国家级 保护区 National reserve | 153 | 119.16° E | 27.86° N | 2008 | 2016 | 58 | 8,208 | 28,256 | Yes | 公里网格 Grid |
| 尖峰岭 Jianfengling (JFL) | 海南 Hainan | 国家级 保护区 National reserve | 451 | 108.91° E | 18.74° N | 2014 | 2015 | 57 | 5,383 | 14,715 | Yes | 固定监测样地 Monitoring network |
| 铜壁关 Tongbiguan (TBG) | 云南 Yunnan | 省级 保护区 Provincial reserve | 517 | 97.61° E | 24.54° N | 2017 | 2017 | 17 | 527 | 3,059 | Yes | 样线 Line transect |
| 罗布泊 Luobupo (LBP) | 新疆 Xinjiang | 国家级 保护区 National reserve | 22,800 | 91.55° E | 40.33° N | 2010 | 2012 | 7 | 6,655 | 7,098 | Yes | 水源点 Water site |
| 敦煌西湖 Dunhuangxihu (DHXH) | 甘肃 Gansu | 国家级 保护区 National reserve | 6,600 | 93.34° E | 40.14° N | 2012 | 2013 | 4 | 257 | 2,626 | Yes | 水源点 Water site |
| [1] | Jiang ZG, Jiang JP, Wang YZ, Zhang E, Zhang YY, Li LL, Xie F, Cai B, Cao L, Zheng GM, Dong L, Zhang ZW, Ding P, Luo ZH, Ding CQ, Ma ZJ, Tang SH, Cao WX, Li CW, Hu HJ, Ma Y, Wu Y, Wang YX, Zhou KY, Liu SY, Chen YY, Li JT, Feng ZJ, Wang Y, Wang B, Li C, Song XL, Cai L, Zang CX, Zeng Y, Meng ZB, Fang HX, Ping XG (2016) Red List of China’s Vertebrates. Biodiversity Science, 24, 500-551.(in Chinese and in English) |
| [ 蒋志刚, 江建平, 王跃招, 张鹗, 张雁云, 李立立, 谢锋, 蔡波, 曹亮, 郑光美, 董路, 张正旺, 丁平, 罗振华, 丁长青, 马志军, 汤宋华, 曹文宣, 李春旺, 胡慧建, 马勇, 吴毅, 王应祥, 周开亚, 刘少英, 陈跃英, 李家堂, 冯祚建, 王燕, 王斌, 李成, 宋雪琳, 蔡蕾, 曾岩, 孟智斌, 方红霞, 平晓鸽 (2016) 中国脊椎动物红色名录. 生物多样性, 24, 500-551.] | |
| [2] | Jiang ZG, Liu SY, Wu Y, Jiang XL, Zhou KY (2017) China’s mammal diversity (2nd edition). Biodiversity Science, 25, 886-895.(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 蒋志刚, 刘少英, 吴毅, 蒋学龙, 周开亚 (2017) 中国哺乳动物多样性(第2版). 生物多样性, 28, 886-895.] | |
| [3] | Li GL, Li DQ, Xue YD, Wang XL, Yang JY, Yu HL (2014) Distribution of wildlife surveyed with infra-red cameras in the Shennongjia National Nature Reserve. Science Silvae Sinicae, 50, 97-104.(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 李广良, 李迪强, 薛亚东, 王秀磊, 杨敬元, 余辉亮 (2014) 利用红外相机研究神农架自然保护区野生动物分布规律. 林业科学, 50, 97-104.] | |
| [4] | Li J, Cong J, Liu X, Zhou YY, Wang XL, Li GL, Li DQ (2015) Effect of tourist roads on mammal activity in Shennongjia National Nature Reserve based on the trap technique of infrared cameras. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 34, 2195-2200.(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 李佳, 丛静, 刘晓, 周芸芸, 王秀磊, 李广良, 李迪强 (2015) 基于红外相机技术调查神农架旅游公路对兽类活动的影响. 生态学杂志, 34, 2195-2200.] | |
| [5] |
Li J, Li DQ, Xue YD, Wu B, He XJ, Liu F (2018) Identifying potential refugia and corridors under climate change: A case study of endangered Sichuan golden monkey (Rhinopithecus roxellana) in Qinling Mountains, China. American Journal of Primatology, 80, e22929.
URL PMID |
| [6] | Li J, Liu F, Li DQ, Xu HQ, Jiang J (2017) Daily activity rhythm of Temminick’s Tragopan (Tragopan temminckii) based on infrared camera monitoring. Science Sivae Sinicae, 53, 170-176.(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 李佳, 刘芳, 李迪强, 徐海青, 蒋军 (2017) 基于红外相机监测分析的红腹角雉日活动节律. 林业科学, 53, 170-176.] | |
| [7] |
Li J, Liu F, Xue YD, Zhang Y, Li DQ (2017) Assessing vulnerability of giant panda to climate change in the Qinling Mountain of China. Ecology and Evolution, 7, 4003-4015.
DOI URL PMID |
| [8] | Li J, Liu F, Ye LX, Ye LX, Liu SL, Peng H, Li DQ (2018) Camera-trapping survey of diversity of mammals and birds in Fengyang Mountain of Zhejinag Province, China. Acta Theriologica Sinica, 38, 95-103.(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 李佳, 刘芳, 叶立新, 刘胜龙, 彭辉, 李迪强 (2018) 利用红外相机调查浙江凤阳山兽类和鸟类多样性. 兽类学报, 38, 95-103.] | |
| [9] | Li J, Liu F, Zhang Y, Li GL, Li DQ (2016a) Using camera traps to survey mammals in Zhongtie-Jungong area of Sanjiangyuan National Nature Reserve, Qinghai Province. Biodiversity Science, 24, 709-713.(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 李佳, 刘芳, 张宇, 李广良, 李迪强 (2016a) 利用红外相机调查青海三江源国家级自然保护区中铁-军功分区兽类资源. 生物多样性, 24, 709-713.] | |
| [10] |
Li J, Xue YD, Zhang Y, Dong W, Shan GY, Sun RQ, Hacker C, Wu B, Li DQ (2020) Spatial and temporal activity patterns of Golden takin (Budorcas taxicolor bedfordi) recorded by camera trapping. PeerJ, 8, e10353.
DOI URL PMID |
| [11] | Li J, Ye LX, Li DQ, Liu F, Liu SL, Peng H (2016b) Barred Cuckoo Dove (Maropygia unchall) found in Longquan, Zhejiang Province, China. Chinese Journal of Zoology, 51, 948.(in Chinese) |
| [ 李佳, 叶立新, 李迪强, 刘芳, 刘胜龙, 彭辉 (2016b) 浙江龙泉发现斑尾鹃鸠. 动物学杂志, 51, 948.] | |
| [12] | Li S, Wang DJ, Xiao ZS, Li XH, Wang TM, Feng LM, Wang Y (2014) Camera-trapping in wildlife research and conservation in China: Review and outlook. Biodiversity Science, 22, 685-695.(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 李晟, 王大军, 肖治术, 李欣海, 王天明, 冯利民, 王云 (2014) 红外相机技术在我国野生动物研究与保护中的应用与前景. 生物多样性, 22, 685-695.] | |
| [13] | Liu F, Li DQ, Wu JG (2012) Using infra-red cameras to survey wildlife in Beijing Songshan National Nature Reserve. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 32, 730-739.(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 刘芳, 李迪强, 吴记贵 (2012) 利用红外相机调查北京松山国家自然保护区的野生动物物种. 生态学报, 32, 730-739.] | |
| [14] | Liu F, Su XJ, Li DQ, Wang BZ, Zhang ZL (2014) Using camera trap to investigate animal diversity in Hunan Gaowangjie National Nature Reserve. Biodiversity Science, 22, 779-784.(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 刘芳, 宿秀江, 李迪强, 王本忠, 张自亮 (2014) 利用红外相机调查湖南高望界国家级自然保护区鸟兽多样性. 生物多样性, 22, 779-784.] | |
| [15] | MacKinnon J, Phillipps K, He FQ (2000) A Field Guide to the Birds of China, Hunan Education Press, Changsha.(in Chinese) |
| [ 约翰·马敬能, 卡伦·菲利普斯, 何芬奇 (2000) 中国鸟类野外手册. 湖南教育出版社, 长沙.] | |
| [16] |
Michalski F, Peres CA (2007) Disturbance-mediated mammal persistence and abundance-area relationships in Amazonian forest fragments. Conservation Biology, 21, 1626-1640.
DOI URL PMID |
| [17] | O’Connell AF, Nichols JD, Karanth KU (2011) Camera Traps in Animal Ecology: Methods and Analyses. Springer, New York. |
| [18] | Smith AT, Xie Y (2009) A Guide to the Mammals of China, Hunan Education Press, Changsha.(in Chinese) |
| [ Smith AT, 解焱 (2009) 中国兽类野外手册. 湖南教育出版社, 长沙.] | |
| [19] | Xiao ZS (2016) Wildlife resource inventory using camera-trapping in natural reserves in China. Acta Theriologica Sinica, 36, 270-271.(in Chinese) |
| [ 肖治术 (2016) 红外相机技术促进我国自然保护区野生动物资源编目调查. 兽类学报, 36, 270-271.] | |
| [20] | Xue YD, Li DQ, Xiao WF, Liu F, Zhang YG, Wang XL, Jia H (2015a) Activity patterns of wild Bactrian camels (Camelus bactrianus) in the northern piedmont of the Altun Mountains, China. Animal Biology, 65, 209-217. |
| [21] | Xue YD, Li DQ, Xiao WF, Zhang YG, Feng B, Jia H (2015b) Records of the dhole (Cuon alpinus) in an arid region of the Altun Mountains in western China. European Journal of Wildlife Research, 61, 903-907. |
| [22] | Xue YD, Li J, Sagen GL, Zhang Y, Dai YC, Li DQ (2018) Activity patterns and resource partitioning: Seven species at watering sites in the Altun Mountains, China. Journal of Arid Land, 10, 959-967. |
| [23] | Yasuda M (2004) Monitoring diversity and abundance of mammals with camera traps: A case study on Mount Tsukuba, central Japan. Mammal Study, 29, 37-46. |
| [24] | Zheng GM (2017) A Checklist on the Classification and Distribution of the Birds of China, 3rd edn, Science Press, Beijing.(in Chinese) |
| [ 郑光美 (2017) 中国鸟类分类与分布名录(第三版), 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [25] | Zhang LB, Cui SP, Huang YJ, Chen DQ, Qiao HJ, Li CW, Jiang ZG (2014) Infrared camera traps in wildlife research and monitoring in China: Issues and insights. Biodiversity Science, 22, 696-703.(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 张履冰, 崔绍朋, 黄元骏, 陈代强, 乔慧捷, 李春旺, 蒋志刚 (2014) 红外相机技术在我国野生动物监测中的应用: 问题与限制. 生物多样性, 22, 696-703.] |
| [1] | 郭雨桐, 李素萃, 王智, 解焱, 杨雪, 周广金, 尤春赫, 朱萨宁, 高吉喜. 全国自然保护地对国家重点保护野生物种的覆盖度及其分布状况[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(3): 24423-. |
| [2] | 王大伟, 程帅, 冯佳伟, 王天明. 东北地区张广才岭2015-2020年野生动物红外相机监测数据集[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24384-. |
| [3] | 韩佳楠, 苏杨, 李霏, 刘君妍, 赵依林, 李琳, 赵建成, 梁红柱, 李敏. 河北省苔藓植物多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(9): 24096-. |
| [4] | 靳川, 张子嘉, 底凯, 张卫荣, 乔栋, 程思源, 胡中民. 海南热带雨林植物光合荧光气体交换和叶功能性状数据集[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(9): 24139-. |
| [5] | 张雨琦, 文君, 张引, 李晟之. 大熊猫国家公园全民公益性评价研究: 基于利益相关者感知视角[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(9): 24240-. |
| [6] | 卢佳玉, 石小亿, 多立安, 王天明, 李治霖. 基于红外相机技术的天津城市地栖哺乳动物昼夜活动节律评价[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(8): 23369-. |
| [7] | 鲁彬悦, 李坤, 王晨溪, 李晟. 基于传感器标记的野生动物追踪技术在中国的应用现状与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(5): 23497-. |
| [8] | 鄢德奎. 中国生物多样性保护政策的共同要素、不足和优化建议[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(5): 23293-. |
| [9] | 何凯莹, 徐心慧, 张承云, 郝泽周, 肖治术, 郭莹莹. 生物声学数据档案的管理标准及管理技术进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(10): 24266-. |
| [10] | 陈慧妹, 李文军, 邱娟, 马占仓, 李波, 杨宗宗, 闻志彬, 孟岩, 曹秋梅, 邱东, 刘丹辉, 金光照. 新疆野生维管植物名录[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(9): 23124-. |
| [11] | 崔国发. 关于自然保护地整合优化工作中几个关键问题的讨论与建议[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(9): 22447-. |
| [12] | 楼晨阳, 任海保, 陈小南, 米湘成, 童冉, 朱念福, 陈磊, 吴统贵, 申小莉. 钱江源国家公园森林群落的物种多样性、结构多样性及其对黑麂出现概率的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(6): 22518-. |
| [13] | 赵坤明, 陈圣宾, 杨锡福. 基于红外相机技术调查四川都江堰破碎化森林鸟兽多样性及优势种活动节律[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(6): 22529-. |
| [14] | 林木青, 张应明, 欧阳芳, 束祖飞, 朱朝东, 肖治术. 广东车八岭国家级自然保护区独栖性胡蜂多样性空间分布特征及其对环境因子的响应[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(2): 22310-. |
| [15] | 邓雪琴, 刘统, 刘天时, 徐恺, 姚松, 黄小群, 肖治术. 河南内乡宝天曼国家级自然保护区豹猫及其潜在猎物之间日活动节律的季节性[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(9): 22263-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2026 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn
![]()