



生物多样性 ›› 2020, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (7): 876-888. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2019259 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2019259
所属专题: 罗霄山脉生物多样性专题
胡宜峰1, 王晓云1, 邓学建2, 吴华3, 黄正澜懿1, 岳阳1, 黎舫1, 张秋萍1, 郭伟健1, 李锋1, 陈柏承1, 徐忠鲜1, 周全1, 余文华1,*( ), 吴毅1,*(
), 吴毅1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2020-06-03
接受日期:2020-09-11
出版日期:2020-07-20
发布日期:2020-09-29
通讯作者:
余文华,吴毅
作者简介:wuyizhouq@263.net基金资助:
Yifeng Hu1, Xiaoyun Wang1, Xuejian Deng2, Hua Wu3, Zhenglanyi Huang1, Yang Yue1, Fang Li1, Qiuping Zhang1, Weijian Guo1, Feng Li1, Bocheng Chen1, Zhongxian Xu1, Quan Zhou1, Wenhua Yu1,*( ), Yi Wu1,*(
), Yi Wu1,*( )
)
Received:2020-06-03
Accepted:2020-09-11
Online:2020-07-20
Published:2020-09-29
Contact:
Wenhua Yu,Yi Wu
摘要:
罗霄山脉位于中国大陆东南部, 是一条南北走向的大型山脉, 面积约6.76万km2。该山脉位于欧亚大陆东部季风区, 生物多样性丰富, 是亚洲东部第三纪冰期动物重要的避难所。为了解罗霄山脉翼手目物种多样性状况, 本研究组于2013-2018年, 使用雾网、手网和竖琴网等工具开展了针对性调查与标本采集, 同时运用形态分类学和分子系统发生学方法鉴定物种。根据调查结果并结合文献记载: 罗霄山脉地区现有翼手目物种4科14属40种, 其中罗霄山脉翼手目新记录种25种, 省级翼手目分布新记录种9种。同时, 本研究基于5年的调查采集位点, 使用生物多样 性与气候变化虚拟实验室(the Biodiversity & Climate Change Virtual Laboratory)在线生境预测平台, 对罗霄山脉翼手目物种当前的适生区, 以及3种不同量温室气体排放情景下(representative concentration pathway, RCP 2.6 / 6.0 / 8.5) 2050年的适生区进行预测, 其中随机森林算法(random forest)的模型解释力较优, 其预测结果显示: 影响该区域翼手目分布的主要环境因子为降水季节性和年平均温度; 山脉中部及南部为翼手目的高适生区, 面积约为罗霄山脉的30%; 与当前适生区相比, RCP 2.6情景下2050年该类群适生区有所扩增, RCP 6.0和RCP 8.5情景下均会导致翼手目适生区急剧缩减, 且分布区将迁移至高海拔区域以响应气候变化。而本项目的开展不仅初步掌握了罗霄山脉翼手目物种多样性本底状况, 也为开展后续的翼手目研究和保护管理提供了参考。
胡宜峰, 王晓云, 邓学建, 吴华, 黄正澜懿, 岳阳, 黎舫, 张秋萍, 郭伟健, 李锋, 陈柏承, 徐忠鲜, 周全, 余文华, 吴毅 (2020) 罗霄山脉翼手目物种多样性及适生区预测. 生物多样性, 28, 876-888. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2019259.
Yifeng Hu, Xiaoyun Wang, Xuejian Deng, Hua Wu, Zhenglanyi Huang, Yang Yue, Fang Li, Qiuping Zhang, Weijian Guo, Feng Li, Bocheng Chen, Zhongxian Xu, Quan Zhou, Wenhua Yu, Yi Wu (2020) Species diversity and suitable habitat prediction of Chiroptera in the Luoxiao Mountains. Biodiversity Science, 28, 876-888. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2019259.
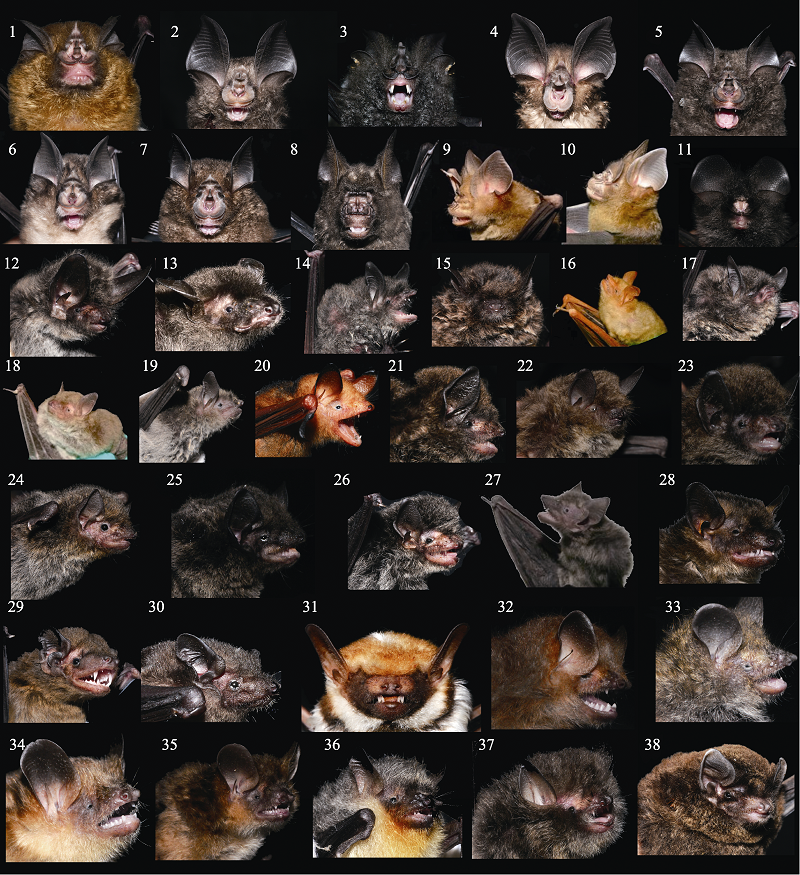

图2 罗霄山脉翼手目物种外形图。1: 中菊头蝠; 2: 华南菊头蝠; 3: 大菊头蝠; 4: 大耳菊头蝠; 5: 皮氏菊头蝠; 6: 小菊头蝠; 7: 中华菊头蝠; 8: 大蹄蝠; 9: 中蹄蝠; 10: 普氏蹄蝠; 11: 无尾蹄蝠; 12: 西南鼠耳蝠; 13: 中华鼠耳蝠; 14: 长指鼠耳蝠; 15: 大卫鼠耳蝠; 16: 金黄鼠耳蝠; 17: 华南水鼠耳蝠; 18: 东亚水鼠耳蝠; 19: 大足鼠耳蝠; 20: 渡濑氏鼠耳蝠; 21: 鼠耳蝠1; 22: 鼠耳蝠2; 23: 鼠耳蝠3; 24: 东亚伏翼; 25: 伏翼1; 26: 伏翼2; 27: 灰伏翼; 28: 大棕蝠; 29: 中华山蝠; 30: 褐扁颅蝠; 31: 斑蝠; 32: 毛翼管鼻蝠; 33: 艾氏管鼻蝠; 34: 哈氏管鼻蝠; 35: 中管鼻蝠; 36: 水甫管鼻蝠; 37: 暗褐彩蝠; 38: 亚洲长翼蝠。
Fig. 2 Bats sampled from the Luoxiao Mountains. 1, Rhinolophus affinis; 2, Rhinolophus huananus; 3, Rhinolophus luctus; 4, Rhinolophus macrotis; 5, Rhinolophus pearsoni; 6, Rhinolophus pusillus; 7, Rhinolophus sinicus; 8, Hipposideros armiger; 9, Hipposideros larvatus; 10, Hipposideros pratti; 11, Coelops frithii; 12, Myotis altarium; 13, Myotis chinensis; 14, Myotis longipes; 15, Myotis davidii; 16, Myotis formosus; 17, Myotis laniger; 18, Myotis petax; 19, Myotis pilosus; 20, Myotis rufoniger; 21, Myotis sp.1; 22, Myotis sp.2; 23, Myotis sp.3; 24, Pipistrellus abramus; 25, Pipistrellus sp.1; 26, Pipistrellus sp.2; 27, Hypsugo pulveratus; 28, Eptesicus serotinus; 29, Nyctalus plancyi; 30, Tylonycteris robustula; 31, Scotomanes ornatus; 32, Harpiocephalus harpia; 33, Murina eleryi; 34, Murina harrisoni; 35, Murina huttoni; 36, Murina shuipuensis; 37, Kerivoula furva; 38, Miniopterus fuliginosus.
| 物种 | 分布型 | 濒危等级 | 栖息环境 | 分布区域 | 资料来源 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Species | Distribution | Endangered category | Habitat | Location | Sources |
| 菊头蝠科 Rhinolophidae | |||||
| 1.中菊头蝠 Rhinolophus affinis | W | LC | 洞穴 Cave | c, d | 标本 Specimen |
| 2.华南菊头蝠 Rhinolophus huananus* | - | NT | 洞穴 Cave | c, d | 标本 Specimen |
| 3.大菊头蝠 Rhinolophus luctus | W | NT | 洞穴 Cave | a, b, c, d | 标本 Specimen |
| 4.大耳菊头蝠 Rhinolophus macrotis | W | LC | 洞穴 Cave | c, d | 标本 Specimen |
| 5.皮氏菊头蝠 Rhinolophus pearsoni | W | LC | 洞穴 Cave | c, d | 标本 Specimen |
| 6.小菊头蝠 Rhinolophus pusillus | S | LC | 洞穴 Cave | a, c, d | 标本 Specimen |
| 7.中华菊头蝠 Rhinolophus sinicus | W | LC | 洞穴 Cave | a, b, c, d | 标本 Specimen |
| 蹄蝠科 Hipposideridae | |||||
| 8.大蹄蝠 Hipposideros armiger | W | LC | 洞穴 Cave | d | 标本 Specimen |
| 9.中蹄蝠 Hipposideros larvatus# | W | LC | 洞穴 Cave | c | 标本 Specimen; |
| 10.普氏蹄蝠 Hipposideros pratti* | W | NT | 洞穴 Cave | c | 标本 Specimen |
| 11.无尾蹄蝠 Coelops frithii | W | VU | 洞穴 Cave | d | 标本 Specimen; |
| 蝙蝠科 Vespertilionidae | |||||
| 12.西南鼠耳蝠 Myotis altarium | S | NT | 洞穴 Cave | c, d | 标本 Specimen |
| 13.中华鼠耳蝠 Myotis chinensis | U | NT | 洞穴 Cave | a | 标本 Specimen |
| 14.长指鼠耳蝠 Myotis longipes*# | O | LC | 洞穴 Cave | c, d | 标本 Specimen; |
| 15.大卫鼠耳蝠 Myotis davidii*# | E | LC | 洞穴 Cave | a, b, c, d | 标本 Specimen; |
| 16.长尾鼠耳蝠 Myotis frater | O | DD | 洞穴 Cave | c, d | |
| 17.金黄鼠耳蝠 Myotis formosus* | S | VU | 森林 Forest | c | 标本 Specimen |
| 18.华南水鼠耳蝠 Myotis laniger* | O | LC | 森林 Forest | c, d | 标本 Specimen |
| 19.东亚水鼠耳蝠 Myotis petax*# | O | DD | 洞穴 Cave | c | 标本 Specimen; |
| 20.大足鼠耳蝠 Myotis pilosus* | U | NT | 洞穴 Cave | c | 标本 Specimen |
| 21.渡濑氏鼠耳蝠 Myotis rufoniger* | S | VU | 洞穴 Cave | d | 标本 Specimen |
| 22.鼠耳蝠1 Myotis sp.1* | - | - | 森林 Forest | d | 标本 Specimen |
| 23.鼠耳蝠2 Myotis sp.2* | - | - | 森林 Forest | d | 标本 Specimen |
| 24.鼠耳蝠3 Myotis sp.3* | - | - | 森林 Forest | d | 标本 Specimen |
| 25.东亚伏翼 Pipistrellus abramus | E | LC | 房屋 House | a, d | 标本 Specimen |
| 26.爪哇伏翼 Pipistrellus javanicus | S | NT | 森林 Forest | d | |
| 27.伏翼1 Pipistrellus sp.1* | - | - | 森林 Forest | c, d | 标本 Specimen |
| 28.伏翼2 Pipistrellus sp.2* | - | - | 森林 Forest | d | 标本 Specimen |
| 29.灰伏翼 Hypsugo pulveratus* | S | NT | 森林 Forest | c | 标本 Specimen |
| 30.大棕蝠 Eptesicus serotinus* | U | LC | 森林 Forest | a | 标本 Specimen |
| 31.中华山蝠 Nyctalus plancyi* | S | LC | 房屋 House | d | 标本 Specimen |
| 32.褐扁颅蝠 Tylonycteris robustula*# | W | NT | 森林 Forest | c, d | 标本 Specimen; |
| 33.斑蝠 Scotomanes ornatus* | S | LC | 森林 Forest | a | 标本 Specimen |
| 34.毛翼管鼻蝠 Harpiocephalus harpia*# | W | NT | 森林 Forest | a, c, d | 标本 Specimen; |
| 35.艾氏管鼻蝠 Murina eleryi* | W | NT | 森林 Forest | c, d | 标本 Specimen |
| 36.哈氏管鼻蝠 Murina harrisoni* | W | DD | 森林 Forest | d | 标本 Specimen |
| 37.中管鼻蝠 Murina huttoni*# | W | LC | 森林 Forest | a, b, c, d | 标本 Specimen; |
| 38.水甫管鼻蝠 Murina shuipuensis*# | - | DD | 森林 Forest | d | 标本 Specimen; |
| 39.暗褐彩蝠 Kerivoula furva*# | W | DD | 森林 Forest | c, d | 标本 Specimen; |
| 长翼蝠科 Miniopteridae | |||||
| 40.亚洲长翼蝠 Miniopterus fuliginosus | O | NT | 山洞 Cave | a, c, d | 标本 Specimen |
表1 罗霄山脉翼手目物种多样性
Table 1 List of Chiroptera diversity in the Luoxiao Mountains
| 物种 | 分布型 | 濒危等级 | 栖息环境 | 分布区域 | 资料来源 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Species | Distribution | Endangered category | Habitat | Location | Sources |
| 菊头蝠科 Rhinolophidae | |||||
| 1.中菊头蝠 Rhinolophus affinis | W | LC | 洞穴 Cave | c, d | 标本 Specimen |
| 2.华南菊头蝠 Rhinolophus huananus* | - | NT | 洞穴 Cave | c, d | 标本 Specimen |
| 3.大菊头蝠 Rhinolophus luctus | W | NT | 洞穴 Cave | a, b, c, d | 标本 Specimen |
| 4.大耳菊头蝠 Rhinolophus macrotis | W | LC | 洞穴 Cave | c, d | 标本 Specimen |
| 5.皮氏菊头蝠 Rhinolophus pearsoni | W | LC | 洞穴 Cave | c, d | 标本 Specimen |
| 6.小菊头蝠 Rhinolophus pusillus | S | LC | 洞穴 Cave | a, c, d | 标本 Specimen |
| 7.中华菊头蝠 Rhinolophus sinicus | W | LC | 洞穴 Cave | a, b, c, d | 标本 Specimen |
| 蹄蝠科 Hipposideridae | |||||
| 8.大蹄蝠 Hipposideros armiger | W | LC | 洞穴 Cave | d | 标本 Specimen |
| 9.中蹄蝠 Hipposideros larvatus# | W | LC | 洞穴 Cave | c | 标本 Specimen; |
| 10.普氏蹄蝠 Hipposideros pratti* | W | NT | 洞穴 Cave | c | 标本 Specimen |
| 11.无尾蹄蝠 Coelops frithii | W | VU | 洞穴 Cave | d | 标本 Specimen; |
| 蝙蝠科 Vespertilionidae | |||||
| 12.西南鼠耳蝠 Myotis altarium | S | NT | 洞穴 Cave | c, d | 标本 Specimen |
| 13.中华鼠耳蝠 Myotis chinensis | U | NT | 洞穴 Cave | a | 标本 Specimen |
| 14.长指鼠耳蝠 Myotis longipes*# | O | LC | 洞穴 Cave | c, d | 标本 Specimen; |
| 15.大卫鼠耳蝠 Myotis davidii*# | E | LC | 洞穴 Cave | a, b, c, d | 标本 Specimen; |
| 16.长尾鼠耳蝠 Myotis frater | O | DD | 洞穴 Cave | c, d | |
| 17.金黄鼠耳蝠 Myotis formosus* | S | VU | 森林 Forest | c | 标本 Specimen |
| 18.华南水鼠耳蝠 Myotis laniger* | O | LC | 森林 Forest | c, d | 标本 Specimen |
| 19.东亚水鼠耳蝠 Myotis petax*# | O | DD | 洞穴 Cave | c | 标本 Specimen; |
| 20.大足鼠耳蝠 Myotis pilosus* | U | NT | 洞穴 Cave | c | 标本 Specimen |
| 21.渡濑氏鼠耳蝠 Myotis rufoniger* | S | VU | 洞穴 Cave | d | 标本 Specimen |
| 22.鼠耳蝠1 Myotis sp.1* | - | - | 森林 Forest | d | 标本 Specimen |
| 23.鼠耳蝠2 Myotis sp.2* | - | - | 森林 Forest | d | 标本 Specimen |
| 24.鼠耳蝠3 Myotis sp.3* | - | - | 森林 Forest | d | 标本 Specimen |
| 25.东亚伏翼 Pipistrellus abramus | E | LC | 房屋 House | a, d | 标本 Specimen |
| 26.爪哇伏翼 Pipistrellus javanicus | S | NT | 森林 Forest | d | |
| 27.伏翼1 Pipistrellus sp.1* | - | - | 森林 Forest | c, d | 标本 Specimen |
| 28.伏翼2 Pipistrellus sp.2* | - | - | 森林 Forest | d | 标本 Specimen |
| 29.灰伏翼 Hypsugo pulveratus* | S | NT | 森林 Forest | c | 标本 Specimen |
| 30.大棕蝠 Eptesicus serotinus* | U | LC | 森林 Forest | a | 标本 Specimen |
| 31.中华山蝠 Nyctalus plancyi* | S | LC | 房屋 House | d | 标本 Specimen |
| 32.褐扁颅蝠 Tylonycteris robustula*# | W | NT | 森林 Forest | c, d | 标本 Specimen; |
| 33.斑蝠 Scotomanes ornatus* | S | LC | 森林 Forest | a | 标本 Specimen |
| 34.毛翼管鼻蝠 Harpiocephalus harpia*# | W | NT | 森林 Forest | a, c, d | 标本 Specimen; |
| 35.艾氏管鼻蝠 Murina eleryi* | W | NT | 森林 Forest | c, d | 标本 Specimen |
| 36.哈氏管鼻蝠 Murina harrisoni* | W | DD | 森林 Forest | d | 标本 Specimen |
| 37.中管鼻蝠 Murina huttoni*# | W | LC | 森林 Forest | a, b, c, d | 标本 Specimen; |
| 38.水甫管鼻蝠 Murina shuipuensis*# | - | DD | 森林 Forest | d | 标本 Specimen; |
| 39.暗褐彩蝠 Kerivoula furva*# | W | DD | 森林 Forest | c, d | 标本 Specimen; |
| 长翼蝠科 Miniopteridae | |||||
| 40.亚洲长翼蝠 Miniopterus fuliginosus | O | NT | 山洞 Cave | a, c, d | 标本 Specimen |
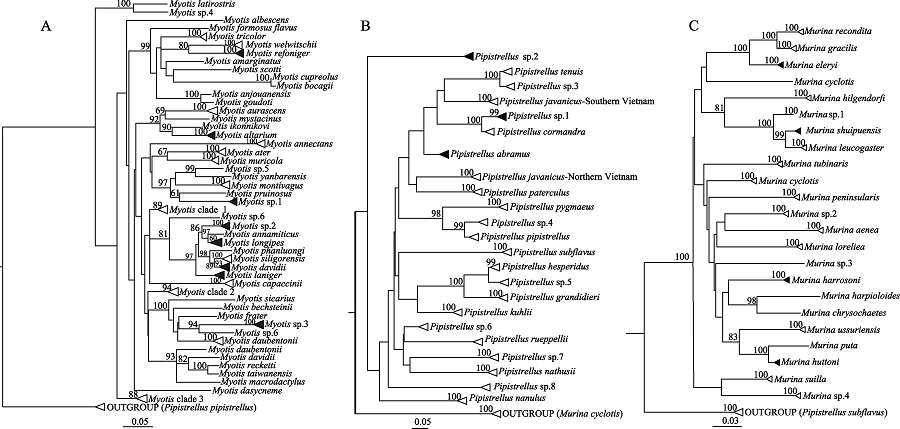
图3 罗霄山脉鼠耳蝠、伏翼和管鼻蝠三属系统发生树。A: 基于线粒体Cyt b基因构建的鼠耳蝠属最大似然树; B: 基于线粒体COI基因构建的伏翼属最大似然树; C: 基于线粒体COI基因构建的管鼻蝠属最大似然树。
Fig. 3 Phylogenetic tree of three genera Myotis, Pipistrellus and Murina in the Luoxiao Mountains. A, Maximum likelihood tree of Myotis based on Cyt b gene; B, Maximum likelihood tree of Pipistrellus based on COI gene; C, Maximum likelihood tree of Murina based on COI gene.
| 框架模型 Profile models | 机器学习模型 Machine learning models | 统计回归模型 Statistical models | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bioclim | ANN | CT | MaxEnt | RF | FDA | GLM | |
| 真阳性率 True positive rate | 0.999 | 0.998 | 0.833 | 0.944 | 0.999 | 0.972 | 0.917 |
| 真实技巧统计法 True skill statistic | 0.889 | 0.998 | 0.750 | 0.896 | 0.999 | 0.917 | 0.917 |
| 准确度 Accuracy | 0.944 | 0.998 | 0.875 | 0.951 | 0.999 | 0.958 | 0.958 |
| 受试者特征曲线下面积 Area under the receiving operator curve | 0.970 | 0.998 | 0.880 | 0.970 | 0.999 | 0.980 | 0.980 |
表2 不同适生区预测模型之间的预测效果对比
Table 2 Habitat distribution prediction analysis from different models
| 框架模型 Profile models | 机器学习模型 Machine learning models | 统计回归模型 Statistical models | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bioclim | ANN | CT | MaxEnt | RF | FDA | GLM | |
| 真阳性率 True positive rate | 0.999 | 0.998 | 0.833 | 0.944 | 0.999 | 0.972 | 0.917 |
| 真实技巧统计法 True skill statistic | 0.889 | 0.998 | 0.750 | 0.896 | 0.999 | 0.917 | 0.917 |
| 准确度 Accuracy | 0.944 | 0.998 | 0.875 | 0.951 | 0.999 | 0.958 | 0.958 |
| 受试者特征曲线下面积 Area under the receiving operator curve | 0.970 | 0.998 | 0.880 | 0.970 | 0.999 | 0.980 | 0.980 |
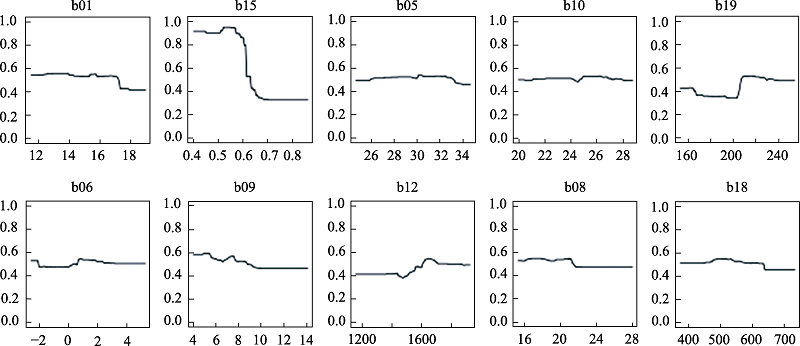
图5 随机森林算法的响应曲线。b01: 年平均温度; b15: 降水季节性; b05: 最热月最高温; b10: 最热季度平均温度; b19: 最冷季度降水量; b06: 最冷月最低温; b09: 最干季度平均温度; b12: 年平均降水量; b08: 最湿季度平均温度; b18: 最热季度降水量。
Fig. 5 Response curves for random forest. b01, Annual mean temperature; b15, Precipitation seasonality; b05, Max temperature of warmest month; b10, Mean temperature of warmest quarter; b19, Precipitation of coldest quarter; b06, Min temperature of coldest month; b09, Mean temperature of driest quarter; b12, Annual precipitation; b08, Mean temperature of wettest quarter; b18, Precipitation of warmest quarter.
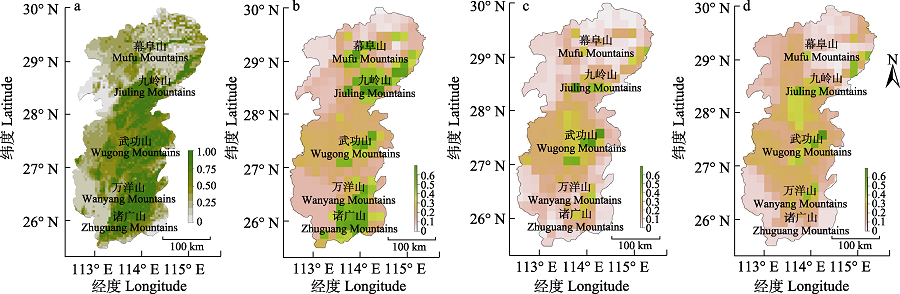
图6 罗霄山脉翼手目分布生境预测。a: 当前环境下; b: 2050年RCP 2.6情景下; c: 2050年RCP 6.0情景下; d: 2050年RCP 8.6情景下。
Fig. 6 Suitable habitat distribution predictions of Chiroptera in the Luoxiao Mountains. a, Present; b, RCP 2.6-2050; c, RCP 6.0-2050; d, RCP 8.5-2050.
| [1] |
Adams RA (2010) Bat reproduction declines when conditions mimic climate change projections for western North America. Ecology, 91, 2437-2445.
DOI URL PMID |
| [2] | Adams RA (2017) Dark side of climate change: Species- specific responses and indications of disruption in spring altitudinal migration in Myotis bats. Journal of Zoology, 304, 1-7. |
| [3] | Adams RA, Hayes MA (2018) Assemblage-level analysis of sex-ratios in Coloradan bats in relation to climate variables: A model for future exceptions. Global Ecology and Conservation, 14, e00379. |
| [4] | Arthur L, Lemaire M, Dufrene L, Viol IL, Julien JF, Kerbiriou C (2014) Understanding bat-habitat associations and the effects of monitoring on long-term roost success using a volunteer dataset. Acta Chiropterologica, 16, 397-411. |
| [5] | Bates PJJ, Harrison DL (1997) Bats of the Indian Subcontinent. Harrison Zoological Museum Publication, Sevenoaks. |
| [6] | Boyles JG, Cryan PM, McCracken GF, Kunz TH (2011) Economic importance of bats in agriculture. Science, 332, 41-42. |
| [7] | Bronrier GN, Maloney SK, Buffenstein R (1999) Survival tactics within thermally-challenging roosts: Heat tolerance and cold sensitivity in the Angolan free-tailed bat, Mops condylurus. South African Journal of Zoology, 34, 1-10. |
| [8] |
Calisher CH, Childs JE, Field HE, Holmes KV, Schountz T (2006) Bats: Important reservoir hosts of emerging viruses. Clinical Microbiology Reviews, 19, 531-545.
DOI URL PMID |
| [9] | Cameron EZ (2004) Facultative adjustment of mammalian sex ratios in support of the Trivers-Willard hypothesis: Evidence for a mechanism. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 271, 1723-1728. |
| [10] | Chen BC, Yu WH, Wu Y, Li F, Xu ZX, Zhang QP, Harada M, Motokawa M, Peng HY (2015) New record and sexual dimorphism of Harpiocephalus harpia in Guangxi and Jiangxi, China. Sichuan Journal of Zoology, 34, 211-215, 222. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 陈柏承, 余文华, 吴毅, 李锋, 徐忠鲜, 张秋萍, 原田正史, 本川雅治, 彭红元 (2015) 毛翼管鼻蝠在广西和江西分布新纪录及其性二型现象. 四川动物, 34, 211-215, 222.] | |
| [11] | Cheng HC, Fang YP, Chou CH (2015) A Photographic Guide to the Bats of Taiwan, 2nd edn. Endemic Species Research Institute, Taizhong. (in Chinese) |
| [ 郑锡奇, 方引平, 周政翰 (2015) 台湾蝙蝠图鉴(第2版). “行政院农业委员会”特有生物研究保育中心, 台中.] | |
| [12] | Dang FH, Yu WH, Wang XY, Guo WJ, Zhuang ZS, Mei TY, Zhang QP, Li F, Li YC (2016) Taxonomic clarification of Myotis rufoniger from China. Sichuan Journal of Zoology, 36, 7-13. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 党飞红, 余文华, 王晓云, 郭伟健, 庄卓生, 梅廷媛, 张秋萍, 李锋, 李玉春 (2016) 中国渡濑氏鼠耳蝠种名订正. 四川动物, 36, 7-13.] | |
| [13] |
Daszak P (2010) Bats, in black and white. Science, 329, 634-635.
DOI URL PMID |
| [14] | Ding TM, Wang ZY (1989) Scotomanes ornatus found in Jinggangshan Nature Reserve. Jiangxi Forestry Science and Technology, (1), 32. (in Chinese) |
| [ 丁铁明, 王作义 (1989) 井冈山自然保护区发现斑蝠. 江西林业科技, (1), 32.] | |
| [15] |
Drummond MJ, McCarthy JJ, Sinha M, Spratt HM, Volpi E, Esser KA, Rasmussen BB (2011) Aging and microRNA expression in human skeletal muscle: A microarray and bioinformatics analysis. Physiological Genomics, 43, 595-603.
DOI URL PMID |
| [16] |
Edgar RC (2004) MUSCLE: Multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucleic Acids Research, 32, 1792-1797.
DOI URL PMID |
| [17] | Feng L, Wu QQ, Shi SC, Ren RJ, Liu YM, Yu ZH, Deng XJ (2017) Morphostructure and phylogenesis of Horsfield’s leaf-nosed bat (Hipposideros larvatus) from Hunan Province. Life Science Research, 21, 515-518. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 冯磊, 吴倩倩, 石胜超, 任锐君, 刘宜敏, 余子寒, 邓学建 (2017) 湖南发现的中蹄蝠形态结构及系统发育研究. 生命科学研究, 21, 515-518.] | |
| [18] | Feng L, Wu QQ, Yu ZH, Liu Z, Deng XJ, Liu Y (2019) Eastern Daubenton’s myotis (Myotis petax) discovered in Hengdong County, Hunan Province. Chinese Journal of Zoology, 54, 22-29. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 冯磊, 吴倩倩, 余子寒, 刘钊, 邓学建, 柳勇 (2019) 湖南衡东发现东亚水鼠耳蝠. 动物学杂志, 54, 22-29.] | |
| [19] | Fenton MB, Simmons NB (2014) Bats: A World of Science and Mystery. University of Chicago Press, Chicago. |
| [20] |
Foster GL, Royer DL, Lunt DJ (2017) Future climate forcing potentially without precedent in the last 420 million years. Nature Communications, 8, 14845.
DOI URL PMID |
| [21] | Gong HL, Zhuang WY, Liao WB (2016) Comprehensive scientific investigation on biodiversity in Luoxiao Mountains. China Science and Technology Achievements, 17(22), 9-10. (in Chinese) |
| [ 宫辉力, 庄文颖, 廖文波 (2016) 罗霄山脉地区生物多样性综合科学考察. 科技计划成果, 17(22), 9-10.] | |
| [22] | Griffiths GM, Chambers LE, Haylock MR, Manton MJ, Nicholls N, Baek HJ, Choi Y, Dellamarta PM, Gosai A, Iga N, Lata R, Laurent V, Mairtrepierre L, Nakamigawa H, Ouprasitwong N, Solofa D, Tahani L, Thuy DT, Tibig L, Trewin B, Vediapan K, Zhai P (2005) Change in mean temperature as a predictor of extreme temperature change in the Asia-Pacific region. International Journal of Climatology, 25, 1301-1330. |
| [23] | Guo XC, Lu GJ, Sun KP, Huang GS, Feng J (2010) Characteristics of echolocation call and morphology of five sympatric bats species. Journal of Jiangxi Normal University (Natural Science), 34, 84-88. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 郭新春, 卢冠军, 孙克萍, 黄赣生, 冯江 (2010) 5种共栖蝙蝠的形态和回声定位声波特征. 江西师范大学学报(自然科学版), 34, 84-88.] | |
| [24] | Hallgren W, Beaumont L, Bowness A, Chambers L, Graham E, Holewa H, Laffan S, Mackey B, Nix H, Price J, Vanderwal J, Warren R, Weis G (2015) The Biodiversity and Climate Change Virtual Laboratory: Where ecology meets big data. Environmental Modeling & Software, 76, 182-186. |
| [25] | Hu T, Sun Y, Zhang XB (2017) Temperature and precipitation projection at 1.5 and 2℃ increase in global mean temperature. Chinese Science Bulletin, 62, 3098-3111. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 胡婷, 孙颖, 张学斌 (2017) 全球1.5和2℃温升时的气温和降水变化预估. 科学通报, 62, 3098-3111.] | |
| [26] | Hu YF, Yu WH, Yue Y, Huang ZLY, Li YC, Wu Y (2019) Species diversity and potential distribution of Chiroptera on Hainan Island, China. Biodiversity Science, 27, 400-408. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 胡宜峰, 余文华, 岳阳, 黄正澜懿, 李玉春, 吴毅 (2019) 海南岛翼手目物种多样性现状与分布预测. 生物多样性, 27, 400-408.] | |
| [27] | Huang ZLY, Hu YF, Wu H, Cao Y, Liu BQ, Zhou JJ, Wu Y, Yu WH (2018) New distribution record of Murina huttoni in Hubei and Zhejiang provinces. Journal of West China Forestry Science, 47(6), 73-77. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 黄正澜懿, 胡宜峰, 吴华, 曹阳, 刘宝权, 周佳俊, 吴毅, 余文华 (2018) 中管鼻蝠在湖北和浙江的分布新纪录. 西部林业科学, 47(6), 73-77.] | |
| [28] | Ji WH, Chen FG (1990) The relationship between the species density of Chiroptera and environmental factor. Acta Theriologica Sinica, 10, 23-30. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 纪维红, 陈服官 (1990) 翼手目物种密度分布与环境因素的关系. 兽类学报, 10, 23-30.] | |
| [29] | Jiang TL, Feng J, Sun KP, Zhao YJ, Zhang ZZ (2007) A new record of the Chiroptera in Jiangxi Province—Myotis formosus. Acta Theriologica Sinica, 27, 203-205. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 江廷磊, 冯江, 孙克萍, 赵云蛟, 张桢珍 (2007) 江西省翼手目新纪录——绯鼠耳蝠. 兽类学报, 27, 203-205.] | |
| [30] | Jiang ZG, Jiang JP, Wang YZ, Zhang E, Zhang YY, Li LL, Xie F, Cai B, Cao L, Zheng GM, Dong L, Zhang ZW, Ding P, Luo ZH, Ding CQ, Ma ZJ, Tang SH, Cao WX, Li CW, Hu HJ, Ma Y, Wu Y, Wang YX, Zhou KY, Liu SY, Chen YY, Li JT, Feng ZJ, Wang Y, Wang B, Li C, Song XL, Cai L, Zang CX, Zeng Y, Meng ZB, Fang HX, Ping XG (2016) Red List of China’s Vertebrates. Biodiversity Science, 24, 500-551. (in Chinese and in English) |
| [ 蒋志刚, 江建平, 王跃招, 张鹗, 张雁云, 李立立, 谢锋, 蔡波, 曹亮, 郑光美, 董路, 张正旺, 丁平, 罗振华, 丁长青, 马志军, 汤宋华, 曹文宣, 李春旺, 胡慧建, 马勇, 吴毅, 王应祥, 周开亚, 刘少英, 陈跃英, 李家堂, 冯祚建, 王燕, 王斌, 李成, 宋雪琳, 蔡蕾, 臧春鑫, 曾岩, 孟智斌, 方红霞, 平晓鸽 (2016) 中国脊椎动物红色名录. 生物多样性, 24, 500-551.] | |
| [31] | Kunz TH, Torrez EBD, Bauer D, Lobova T, Fleming TH (2011) Ecosystem services provided by bats. Annals of the New York Academy of Science, 1223, 1-38. |
| [32] | Law BS (1996) The ecology of bats in south-east Australian forests and potential impacts of forestry practices: A review. Pacific Conservation Biology, 2, 363-374. |
| [33] | Li DQ, Song YL (2000) Review on hot spot and GAP analysis. Chinese Biodiversity, 8, 208-214. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 李迪强, 宋延龄 (2000) 热点地区与GAP分析研究进展. 生物多样性, 8, 208-214.] | |
| [34] | Li F, Yu WH, Wu Y, Chen BC, Zhang QP, Xu ZX, Wang YY, Chen CQ, Harada M (2015) Kerivoula titania discovered in Jiangxi Province, China. Chinese Journal of Zoology, 50, 1-8. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 李锋, 余文华, 吴毅, 陈柏承, 张秋萍, 徐忠鲜, 王英永, 陈春泉, 原田正史 (2015) 江西省发现泰坦尼亚彩蝠. 动物学杂志, 50, 1-8.] | |
| [35] | Li YC, Meng YH, Zhang LC, Ye Q (2005) Analysis of environmental factors on geographical distribution of Chinese Chiroptera. Acta Zoologica Sinica, 51, 413-422. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 李玉春, 蒙以航, 张利存, 叶青 (2005) 中国翼手目地理分布的环境因子影响分析. 动物学报, 51, 413-422.] | |
| [36] | Liao WB, Wang L, Wang YY, Liu WQ, Jia FL, Shen HX, Fan Q, Li QH, Yang SL (2018) Study on Biodiversity of the Taoyuandong National Nature Reserve in Hunan Province. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 廖文波, 王蕾, 王英永, 刘蔚秋, 贾凤龙, 沈红星, 凡强, 李秦辉, 杨树林 (2018) 湖南桃源洞国家级自然保护区生物多样性综合科学考察. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [37] | Liao WB, Wang YY, Li Z, Peng SL, Chen CQ, Fan Q, Jia FL, Wang L, Liu WQ, Yin GS, Shi XG, Zhang DD (2014) Integrated Study on Biodiversity of Mount Jinggangshan Regions in China. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 廖文波, 王英永, 李贞, 彭少麟, 陈春泉, 凡强, 贾凤龙, 王蕾, 刘蔚秋, 尹国胜, 石祥刚, 张丹丹 (2014) 中国井冈山地区生物多样性综合科学考察. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [38] | Liu SY, Wu Y (2019) Handbook of the Mammals of China. The Straits Publishing & Distributing Group, Fuzhou. (in Chinese) |
| [ 刘少英, 吴毅 (2019) 中国兽类图鉴. 海峡书局出版社, 福州.] | |
| [39] | Maine JJ, Boyles JG (2015) Bats initiate vital agroecological interactions in corn. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 112, 12438-12443. |
| [40] |
Moss RH, Edmonds JA, Hibbard KA, Manning MR, Rose SK, Vuuren DP, Carter TR, Emori S, Kainuma M, Kram T, Meehl GA, Mitchell JFB, Nakicenovic N, Riahi K, Smith SJ, Stouffer RJ, Thomson AM, Weyant JP, Wilbanks TJ (2010) The next generation of scenarios for climate change research and assessment. Nature, 463, 747-756.
DOI URL PMID |
| [41] | Olival KJ, Hosseini PR, Zambrana-Torrelio C, Ross N, Bogich TL, Daszak P (2017) Host and viral traits predict zoonotic spillover from mammals. Nature, 546, 646-650. |
| [42] |
Posada D, Crandall KA (1998) Modeltest: Testing the model of DNA substitution. Bioinformatics, 14, 817-818.
DOI URL PMID |
| [43] | Rebelo H, Tarroso P, Jones G (2010) Predicted impact of climate change on European bats in relation to their biogeographic patterns. Global Change Biology, 16, 561-576. |
| [44] | Ren RJ, Shi SC, Wu QQ, Deng XJ, Chen YZ (2017) David’s myotis (Myotis davidii) found in Hengdong County, Hunan Province, China. Chinese Journal of Zoology, 53, 870-876. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 任锐君, 石胜超, 吴倩倩, 邓学建, 陈意中 (2017) 湖南省衡东县发现大卫鼠耳蝠. 动物学杂志, 53, 870-876.] | |
| [45] | Rusticucci M (2012) Observed and simulated variability of extreme temperature events over South America. Atmospheric Research, 106, 1-17. |
| [46] | Simmons NB (2005) Order Chiroptera. pp. 312-529. The Johns Hopkins University Press, Baltimore, |
| [47] | Solomon SD, Qin D, Manning M, Chen Z, Marquis M, Avery KB, Tignor M, Miller HL (2007) Climate Change 2007: The Physical Science Basis: Working Group I Contribution to the Fourth Assessment Report of the IPCC. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, |
| [48] |
Stamatakis A (2014) RAxML version 8: A tool for phylogenetic analysis and post-analysis of large phylogenies. Bioinformatics, 30, 1312-1313.
DOI URL PMID |
| [49] | Voigt CC, Kingston T (2016) Bats in the Anthropocene: Conservation of Bats in a Changing World. Springer International Publishing, Cham, |
| [50] | Walsh AL, Morton PA (2009) Methods to promote bats conservation, outreach, and education through science and research-based activities. In: Ecological and Behavioral Methods for the Study of Bats, 2nd edn. (eds Kunz TH, Parsons S), pp. 868-885. The Johns Hopkins University Press, Baltimore. |
| [51] | Wang XY, Zhang QP, Guo WJ, Li F, Chen BC, Xu ZX, Wang YY, Wu Y, Yu WH (2016) Discovery of Murina shuipuensis outside of its type locality—New record from Guangdong and Jiangxi provinces, China. Acta Theriologica Sinica, 36, 118-122. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 王晓云, 张秋萍, 郭伟健, 李锋, 陈柏承, 徐忠鲜, 王英永, 吴毅, 余文华 (2016) 水甫管鼻蝠在模式产地外的发现——广东和江西省新纪录. 兽类学报, 36, 118-122.] | |
| [52] | Wang YX (2003) A Complete Checklist of Mammal Species and Subspecies in China: A Taxonomic and Geographic Reference. China Forestry Publishing House, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 王应祥 (2003) 中国哺乳动物物种与亚种分类名录与分布大全. 中国林业出版社, 北京.] | |
| [53] | Wang YY, Chen CQ, Zhao J, Wu Y, Lü ZT, Yang JH, Yu WH, Lin JS, Liu ZY, Wang J, Du Q, Zhang Z, Song YZ, Wang ZR, He GQ (2017) Colored Atlas of Terrestrial Vertebrates of the Jinggangshan Region in China. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 王英永, 陈春泉, 赵健, 吴毅, 吕植桐, 杨剑焕, 余文华, 林剑声, 刘祖尧, 王健, 杜卿, 张忠, 宋玉赞, 汪志如, 何桂强 (2017) 中国井冈山地区陆生脊椎动物彩色图谱. 科学出版社. 北京.] | |
| [54] | Wanger TC, Darras K, Bumrungsri S, Tscharntke T, Klein AM (2014) Bat pest control contributes to food security in Thailand. Biological Conservation, 171, 220-223. |
| [55] | Webb PI, Speakman JR, Racey PA (1995) How hot is a hibernaculum? A review of the temperatures at which bats hibernate. Canadian Journal of Zoology, 74, 761-765. |
| [56] | Wei SG, Li L, Xu R, Huang ZL, Cao HL (2015) Spatial pattern and interspecific relationship of dominant species in plant community in Jinggang Mountain. Journal of Tropical and Subtropical Botany, 23, 74-80. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 魏识广, 李林, 许睿, 黄忠良, 曹洪麟 (2015) 井冈山植物群落优势种空间分布格局与种间关联. 热带亚热带植物学报, 23, 74-80.] | |
| [57] |
Williamsguillén K, Prefecto I, Vandermeer J (2008) Bats limit insects in a neotropical agroforestry system. Science, 320, 70.
DOI URL PMID |
| [58] |
Wong S, Lau S, Woo P, Yuen KY (2010) Bats as a continuing source of emerging infections in humans. Reviews in Medical Virology, 17, 67-91.
DOI URL PMID |
| [59] | Xu ZX, Yu WH, Wu Y, Wang YY, Chen CQ, Zhao J, Zhang Z, Li YC (2013) A new record bat of Coelops frithii in Jiangxi Province, China. Sichuan Journal of Zoology, 32, 263-266, 268. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 徐忠鲜, 余文华, 吴毅, 王英永, 陈春泉, 赵健, 张忠, 李玉春 (2013) 江西省翼手目一新纪录——无尾蹄蝠. 四川动物, 32, 263-266, 268.] | |
| [60] | Yang QS, Xia L, Feng ZJ, Ma Y, Quan GQ, Wu Y (2007) A guide to the measurement of mammal skull Ⅴ. Insectivora and Chiroptera. Chinese Journal of Zoology, 42(2), 56-62. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 杨奇森, 夏霖, 冯祚建, 马勇, 全国强, 吴毅 (2007) 兽类头骨测量标准Ⅴ: 食虫目、翼手目. 动物学杂志, 42(2), 56-62.] | |
| [61] | Yu WH, Hu YF, Guo WJ, Li F, Wang XY, Li YC, Wu Y (2017) New discovery of Harpiocephalus harpia in Hunan Province and its potential distribution area in China. Journal of Guangzhou University (Natural Science Edition), 16(3), 15-20. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 余文华, 胡宜峰, 郭伟健, 黎舫, 王晓云, 李玉春, 吴毅 (2017) 毛翼管鼻蝠在湖南的新发现及中国适生分布区预测. 广州大学学报(自然科学版), 16(3), 15-20.] | |
| [62] | Yu ZH, Wu QQ, Shi SC, Ren RJ, Liu YM, Feng L, Deng XJ (2018) The Kashmir cave myotis (Myotis longipes) was found in Hengdong County, Hunan Province, China. Chinese Journal of Zoology, 53, 701-708. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 余子寒, 吴倩倩, 石胜超, 任锐君, 刘宜敏, 冯磊, 邓学建 (2018) 湖南衡东县发现长指鼠耳蝠. 动物学杂志, 53, 701-708.] | |
| [63] | Yue Y, Hu YF, Lei BY, Wu Y, Wu H, Liu BQ, Yu WH (2019) Sexual dimorphism in Harpiocephalus harpia and its new records from Hubei and Zhejiang, China. Acta Theriologica Sinica, 39, 142-154. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 岳阳, 胡宜峰, 雷博宇, 吴毅, 吴华, 刘宝权, 余文华 (2019) 毛翼管鼻蝠性二型特征及其在湖北和浙江的分布新纪录. 兽类学报, 39, 142-154.] | |
| [64] | Zhang PL, Huang TF, Zhang YX, Liu ZX (2019) The checklist, distribution and conservation of Chiroptera in Wulingshan Region, China. International Journal of Ecology, 8(2), 57-64. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 张佩玲, 黄太福, 张佑祥, 刘志霄 (2019) 武陵山区翼手目物种名录、分布及保护. 世界生态学, 8(2), 57-64.] | |
| [65] | Zhang QP, Yu WH, Wu Y, Xu ZX, Li F, Chen BC, Harada M, Motokawa M, Wang YY, Li YC (2014) A new record of Tylonycteris robustula in Jiangxi Province, China and its karyotype. Sichuan Journal of Zoology, 33, 746-749, 757. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 张秋萍, 余文华, 吴毅, 徐忠鲜, 李锋, 陈柏承, 原田正史, 本川雅治, 王英永, 李玉春 (2014) 江西省蝙蝠新纪录——褐扁颅蝠及其核型报道. 四川动物, 33, 746-749, 757.] | |
| [66] | Zhang RZ (1999) Zoogeography of China. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 张荣祖 (1999) 中国动物地理. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [67] | Zhao WY (2017) The Floristic Phytogeography of Spermatophyte Flora in Luoxiao Range. PhD dissertation, Sun Yat-Sen University, Guangzhou. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 赵万义 (2017) 罗霄山脉种子植物区系地理学研究. 博士学位论文, 中山大学, 广州.] |
| [1] | 吴晓晴 张美惠 葛苏婷 李漫淑 宋坤 沈国春 达良俊 张健. 上海近自然林重建过程中木本植物物种多样性与地上生物量的时空动态——以闵行区生态岛为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24444-. |
| [2] | 王太, 宋福俊, 张永胜, 娄忠玉, 张艳萍, 杜岩岩. 河西走廊内陆河水系鱼类多样性及资源现状[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24387-. |
| [3] | 廖雅晴, 黄泽锋, 王晓云, 张礼标, 吴毅, 余文华. 广东省翼手目物种名录更新及分子条形码数据库[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24584-. |
| [4] | 张晶晶, 黄文彬, 陈奕廷, 杨泽鹏, 柯伟业, 彭昭杰, 魏世超, 张志伟, 胡怡思, 余文华, 周文良. 广东南澎列岛海洋生态国家级自然保护区造礁石珊瑚多样性及分布特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24424-. |
| [5] | 尚华丹, 张楚晴, 王梅, 裴文娅, 李国宏, 王鸿斌. 中国杨树害虫物种多样性及其地理分布[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24370-. |
| [6] | 吴昱萱, 王平, 胡晓生, 丁一, 彭甜恬, 植秋滢, 巴德木其其格, 李文杰, 关潇, 李俊生. 呼伦贝尔草地退化现状评估与植被特征变化[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24118-. |
| [7] | 陈自宏, 张翼飞, 陈凯, 陈见影, 徐玲. 高黎贡山南段昆虫病原真菌物种多样性及影响因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(1): 24228-. |
| [8] | 谭珂, 宁瑶, 王仁芬, 王晴, 梁丹萍, 辛子兵, 温放. 中国苦苣苔科植物名录与地理分布数据集[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(1): 23275-. |
| [9] | 韩佳楠, 苏杨, 李霏, 刘君妍, 赵依林, 李琳, 赵建成, 梁红柱, 李敏. 河北省苔藓植物多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(9): 24096-. |
| [10] | 李东红, 郝媛媛, 甘辉林, 张航, 刘耀猛, 他富源, 胡桂馨. 祁连山北麓中段不同类型草地蝗虫种类及分布[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(9): 24119-. |
| [11] | 牛红玉, 陈璐, 赵恒月, 古丽扎尔·阿不都克力木, 张洪茂. 城市化对动物的影响: 从群落到个体[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(8): 23489-. |
| [12] | 白雪, 李正飞, 刘洋, 张君倩, 张多鹏, 罗鑫, 杨佳莉, 杜丽娜, 蒋玄空, 武瑞文, 谢志才. 西江流域大型底栖无脊椎动物物种多样性及维持机制[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(7): 23499-. |
| [13] | 许佳, 崔小娟, 张翼飞, 吴昌, 孙远东. 南岭地区鱼类多样性及其地理分布[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(7): 23482-. |
| [14] | 邝起宇, 胡亮. 广东东海岛与硇洲岛海域底栖贝类物种多样性及其地理分布[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(5): 24065-. |
| [15] | 赵勇强, 阎玺羽, 谢加琪, 侯梦婷, 陈丹梅, 臧丽鹏, 刘庆福, 隋明浈, 张广奇. 退化喀斯特森林自然恢复中不同生活史阶段木本植物物种多样性与群落构建[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(5): 23462-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2026 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn
![]()