



生物多样性 ›› 2021, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (1): 10-20. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2020138 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2020138
施国杉1,2, 刘峰3, 陈典3, 邓云1,2,4( ), 林露湘1,4,*(
), 林露湘1,4,*( )(
)( )
)
收稿日期:2020-04-03
接受日期:2020-05-12
出版日期:2021-01-20
发布日期:2020-09-01
通讯作者:
林露湘
基金资助:
Guoshan Shi1,2, Feng Liu3, Dian Chen3, Yun Deng1,2,4( ), Luxiang Lin1,4,*(
), Luxiang Lin1,4,*( )(
)( )
)
Received:2020-04-03
Accepted:2020-05-12
Online:2021-01-20
Published:2020-09-01
Contact:
Luxiang Lin
摘要:
大型森林动态监测样地是研究物种共存、群落演替等生态学核心问题的重要平台。纳板河流域国家级自然保护区管理局与中国科学院西双版纳热带植物园合作, 于2016-2017年参照美国史密森热带森林科学中心的技术标准, 在纳板河流域国家级自然保护区内建立了一块热带季节雨林20 ha动态监测样地。本研究分析了该样地的树种组成特征, 并进行了群落数量分类。结果表明: 该样地中DBH ≥ 1 cm的木本植物个体共有59,498株, 分属63科197属296种; 个体数超过1,000株的常见物种有15个, 个体数小于20株的稀有物种有126个。科的区系分布型以热带成分为主, 占总科数的65.08%, 温带成分占17.46%。属的区系分布型以热带成分为主, 占总属数的88.32%, 温带成分占10.66%。该样地群落类型的形成主要受海拔和凹凸度这两个地形因子的影响, 500个20 m × 20 m的样方可以分为4个群丛, 分别为: (1)灰毛浆果楝 + 粗糠柴 - 假山萝 + 番龙眼群丛(Cipadessa baccifera + Mallotus philippensis - Harpullia cupanioides + Pometia pinnata Association); (2)长梗三宝木 + 腋球苎麻 - 顶果木 + 番龙眼群丛(Trigonostemon thyrsoideus + Boehmeria glomerulifera - Acrocarpus fraxinifolius + Pometia pinnata Association); (3)云南银柴 + 大果山香圆 - 湄公锥 + 普文楠群丛(Aporusa yunnanensis + Turpinia pomifera - Castanopsis mekongensis + Phoebe puwenensis Association); (4)歪叶榕 + 密花火筒树 - 毒药树 + 番龙眼群丛(Ficus cyrtophylla + Leea compactiflora - Sladenia celastrifolia + Pometia pinnata Association)。
施国杉, 刘峰, 陈典, 邓云, 林露湘 (2021) 云南纳板河热带季节雨林20 ha动态监测样地的树种组成与群落分类. 生物多样性, 29, 10-20. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2020138.
Guoshan Shi, Feng Liu, Dian Chen, Yun Deng, Luxiang Lin (2021) Species composition and community classification of the 20-ha tropical seasonal rainforest dynamics monitoring plot in the Naban River, Yunnan. Biodiversity Science, 29, 10-20. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2020138.
| 排序 Rank | 物种 Species | 个体数 No. of individuals | 相对多度 Relative abundance (%) | 相对胸高断面积 Relative basal area (%) | 重要值 Importance values (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 番龙眼 Pometia pinnata | 4,193 | 7.04 | 7.77 | 7.41 |
| 2 | 假山萝 Harpullia cupanioides | 3,756 | 6.31 | 1.82 | 4.07 |
| 3 | 普文楠 Phoebe puwenensis | 2,868 | 4.82 | 2.76 | 3.79 |
| 4 | 粗糠柴 Mallotus philippensis | 2,718 | 4.57 | 1.66 | 3.12 |
| 5 | 肉实树 Sarcosperma laurinum | 2,255 | 3.79 | 2.04 | 2.91 |
| 6 | 湄公锥 Castanopsis mekongensis | 588 | 0.99 | 4.33 | 2.66 |
| 7 | 西南木荷 Schima wallichii | 217 | 0.37 | 4.87 | 2.62 |
| 8 | 歪叶榕 Ficus cyrtophylla | 1,823 | 3.06 | 1.85 | 2.46 |
| 9 | 腋球苎麻 Boehmeria glomerulifera | 2,411 | 4.05 | 0.27 | 2.16 |
| 10 | 密花火筒树 Lee acompactiflora | 2,399 | 4.03 | 0.15 | 2.09 |
| 11 | 泥柯 Lithocarpus fenestratus | 1,041 | 1.75 | 2.14 | 1.94 |
| 12 | 大果山香圆 Turpinia pomifera | 1,423 | 2.39 | 1.37 | 1.88 |
| 13 | 顶果木 Acrocarpus fraxinifolius | 53 | 0.09 | 3.64 | 1.87 |
| 14 | 阔叶蒲桃 Syzygium megacarpum | 1,585 | 2.66 | 1.02 | 1.84 |
| 15 | 千果榄仁 Terminalia myriocarpa | 27 | 0.05 | 3.50 | 1.77 |
| 16 | 滇南新乌檀 Neonauclea tsaiana | 574 | 0.96 | 2.53 | 1.75 |
| 17 | 白花羊蹄甲 Bauhinia acuminata | 458 | 0.77 | 2.27 | 1.52 |
| 18 | 云南野独活 Miliusa tenuistipitata | 1,665 | 2.80 | 0.16 | 1.48 |
| 19 | 望谟崖摩 Aglaia lawii | 1,414 | 2.38 | 0.49 | 1.43 |
| 20 | 糙叶树 Aphananthe aspera | 587 | 0.99 | 1.87 | 1.43 |
| 总计 Total | 32,055 | 50.87 | 46.51 | 50.20 |
表1 云南纳板河热带雨林20 ha动态监测样地木本植物重要值前20位的物种
Table 1 Species with the top 20 importance values in the 20-ha tropical seasonal rainforest dynamics monitoring plot in the Naban River, Yunnan
| 排序 Rank | 物种 Species | 个体数 No. of individuals | 相对多度 Relative abundance (%) | 相对胸高断面积 Relative basal area (%) | 重要值 Importance values (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 番龙眼 Pometia pinnata | 4,193 | 7.04 | 7.77 | 7.41 |
| 2 | 假山萝 Harpullia cupanioides | 3,756 | 6.31 | 1.82 | 4.07 |
| 3 | 普文楠 Phoebe puwenensis | 2,868 | 4.82 | 2.76 | 3.79 |
| 4 | 粗糠柴 Mallotus philippensis | 2,718 | 4.57 | 1.66 | 3.12 |
| 5 | 肉实树 Sarcosperma laurinum | 2,255 | 3.79 | 2.04 | 2.91 |
| 6 | 湄公锥 Castanopsis mekongensis | 588 | 0.99 | 4.33 | 2.66 |
| 7 | 西南木荷 Schima wallichii | 217 | 0.37 | 4.87 | 2.62 |
| 8 | 歪叶榕 Ficus cyrtophylla | 1,823 | 3.06 | 1.85 | 2.46 |
| 9 | 腋球苎麻 Boehmeria glomerulifera | 2,411 | 4.05 | 0.27 | 2.16 |
| 10 | 密花火筒树 Lee acompactiflora | 2,399 | 4.03 | 0.15 | 2.09 |
| 11 | 泥柯 Lithocarpus fenestratus | 1,041 | 1.75 | 2.14 | 1.94 |
| 12 | 大果山香圆 Turpinia pomifera | 1,423 | 2.39 | 1.37 | 1.88 |
| 13 | 顶果木 Acrocarpus fraxinifolius | 53 | 0.09 | 3.64 | 1.87 |
| 14 | 阔叶蒲桃 Syzygium megacarpum | 1,585 | 2.66 | 1.02 | 1.84 |
| 15 | 千果榄仁 Terminalia myriocarpa | 27 | 0.05 | 3.50 | 1.77 |
| 16 | 滇南新乌檀 Neonauclea tsaiana | 574 | 0.96 | 2.53 | 1.75 |
| 17 | 白花羊蹄甲 Bauhinia acuminata | 458 | 0.77 | 2.27 | 1.52 |
| 18 | 云南野独活 Miliusa tenuistipitata | 1,665 | 2.80 | 0.16 | 1.48 |
| 19 | 望谟崖摩 Aglaia lawii | 1,414 | 2.38 | 0.49 | 1.43 |
| 20 | 糙叶树 Aphananthe aspera | 587 | 0.99 | 1.87 | 1.43 |
| 总计 Total | 32,055 | 50.87 | 46.51 | 50.20 |
| 分布区类型 Areal-types | 科数 No. of family (%) | 属数 No. of genus (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 世界分布 Widespread | 11 (17.46) | - |
| 2 泛热带 Pantropic | 31 (49.21) | 44 (22.34) |
| 3 东亚(热带、亚热带)及热带南美间断 East Asia (Tropical & Subtropical) & Tropical South America Disjuncted | 5 (7.94) | 14 (7.11) |
| 4 旧世界热带 Old World Tropic | - | 22 (11.17) |
| 5 热带亚洲至大洋洲 Tropic Asia to Tropic Australasia | 1 (1.59) | 27 (13.71) |
| 6 热带亚洲至热带非洲 Tropic Asia to Tropic Africa | 2 (3.17) | 8 (4.06) |
| 7 热带亚洲 Tropic Asia (Indo-Malesia) | 2 (3.17) | 59 (29.95) |
| 热带成分小计 Sub-total tropic elements (2-7) | 41 (65.08) | 174 (88.32) |
| 8 北温带 North Temperate | 8 (12.70) | 11 (5.58) |
| 9 东亚和南美间断 East Asia and North America Disjuncted | 2 (3.17) | 6 (3.05) |
| 10 地中海, 西亚至中亚 Mediterranea, West Asia to Central Asia | 1 (1.59) | 1 (0.51) |
| 11 东亚 East Asia | - | 3 (1.52) |
| 温带成分小计 Sub-total temperate elements (8-11) | 11 (17.46) | 21 (10.66) |
| 12 未知 Unknown | - | 2 (1.02) |
| 总计 Total | 63 (100.00) | 197 (100.00) |
表2 云南纳板河热带雨林20 ha动态监测样地木本植物科属的分布区类型统计
Table 2 Areal-types at family and genus levels of the woody flora in the 20-ha tropical seasonal rainforest dynamics monitoring plot in the Naban River, Yunnan
| 分布区类型 Areal-types | 科数 No. of family (%) | 属数 No. of genus (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 世界分布 Widespread | 11 (17.46) | - |
| 2 泛热带 Pantropic | 31 (49.21) | 44 (22.34) |
| 3 东亚(热带、亚热带)及热带南美间断 East Asia (Tropical & Subtropical) & Tropical South America Disjuncted | 5 (7.94) | 14 (7.11) |
| 4 旧世界热带 Old World Tropic | - | 22 (11.17) |
| 5 热带亚洲至大洋洲 Tropic Asia to Tropic Australasia | 1 (1.59) | 27 (13.71) |
| 6 热带亚洲至热带非洲 Tropic Asia to Tropic Africa | 2 (3.17) | 8 (4.06) |
| 7 热带亚洲 Tropic Asia (Indo-Malesia) | 2 (3.17) | 59 (29.95) |
| 热带成分小计 Sub-total tropic elements (2-7) | 41 (65.08) | 174 (88.32) |
| 8 北温带 North Temperate | 8 (12.70) | 11 (5.58) |
| 9 东亚和南美间断 East Asia and North America Disjuncted | 2 (3.17) | 6 (3.05) |
| 10 地中海, 西亚至中亚 Mediterranea, West Asia to Central Asia | 1 (1.59) | 1 (0.51) |
| 11 东亚 East Asia | - | 3 (1.52) |
| 温带成分小计 Sub-total temperate elements (8-11) | 11 (17.46) | 21 (10.66) |
| 12 未知 Unknown | - | 2 (1.02) |
| 总计 Total | 63 (100.00) | 197 (100.00) |
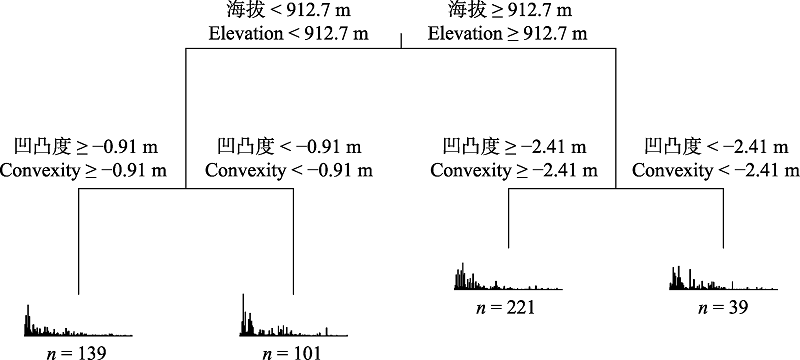
图2 云南纳板河热带季节雨林20 ha动态监测样地多元回归分析树状图(500个20 m × 20 m样方)
Fig. 2 Multivariate regression tree of the 20-ha tropical seasonal rainforest dynamics monitoring plot in the Naban River, Yunnan (500 quadrates of 20 m × 20 m)
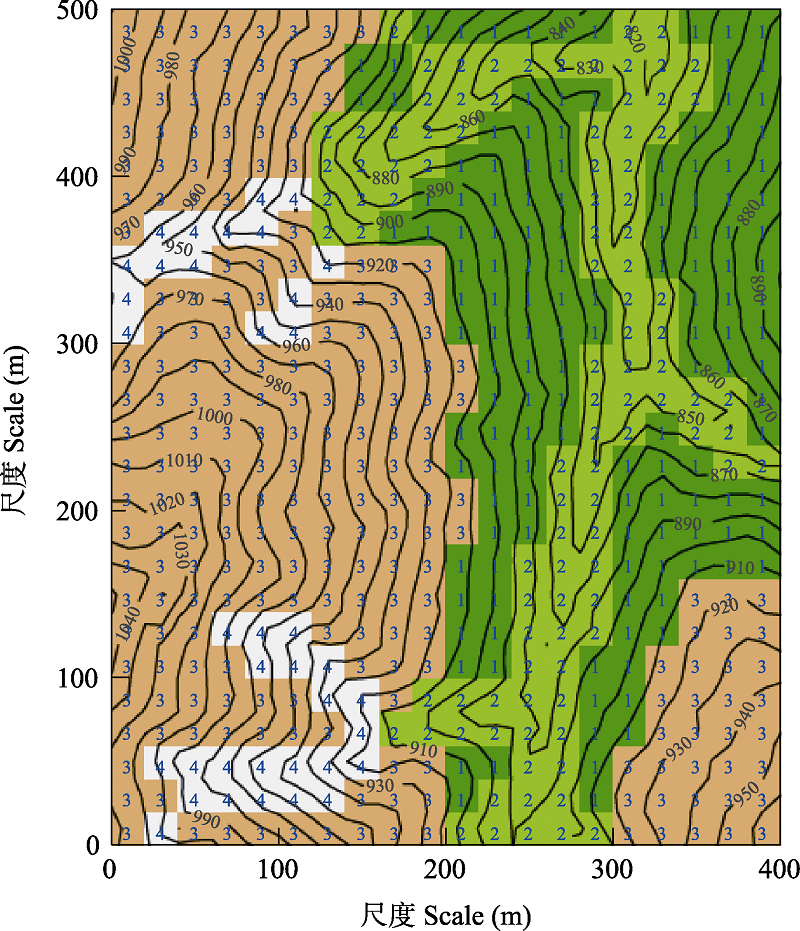
图3 云南纳板河热带季节雨林20 ha动态监测样地4个群丛的样方分布图。1-4分别表示群丛1-4。
Fig. 3 Quadrats distribution map for the four associations of the 20-ha tropical seasonal rainforest dynamics monitoring plot in the Naban River, Yunnan. 1-4, Association 1-4.
| [1] | Abrams MD, Knapp AK, Hulbert LC (1986) A ten-year record of aboveground biomass in a Kansas tallgrass prairie: Effects of fire and topographic position. American Journal of Botany, 73, 1509-1515. |
| [2] |
Bell G (2000) The distribution of abundance in neutral communities. The American Naturalist, 155, 606-617.
URL PMID |
| [3] | Bureau of Environmental Protection of Yunnan, Administration Bureau of Nabanhe National Nature Reserve (2006) Naban River Watershed National Nature Reserve of Xishuangbanna. Yunnan Science and Technology Press, Kunming. (in Chinese) |
| [ 云南省环境保护局, 西双版纳纳板河流域国家级自然保护区管理所 (2006) 西双版纳纳板河流域国家级自然保护区. 云南科技出版社, 昆明. ] | |
| [4] | Cao MC, Zhou GS, Weng ES (2005) Application and comparison of generalized models and classification and regression tree in simulating tree species distribution. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 25, 2031-2040. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 曹铭昌, 周广胜, 翁恩生 (2005) 广义模型及分类回归树在物种分布模拟中的应用与比较. 生态学报, 25, 2031-2040.] | |
| [5] | Cao M, Zou XM, Warren M, Zhu H (2006) Tropical forests of Xishuangbanna, China. Biotropica, 38, 306-309. |
| [6] | Cao M, Zhu H, Wang H, Lan GY, Hu YH, Zhou SS, Deng XB, Cui JY (2008) Xishuangbanna Tropical Seasonal Rainforest Dynamics Plot: Tree Distribution Maps, Diameter Tables and Species Documentation. Yunnan Science and Technology Press, Kunming. |
| [7] | Chu CJ, Wang YS, Liu Y, Jiang L, He FL (2017) Advances in species coexistence theory. Biodiversity Science, 25, 345-354. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 储诚进, 王酉石, 刘宇, 蒋林, 何芳良 (2017) 物种共存理论研究进展. 生物多样性, 25, 345-354.] | |
| [8] | Condit R (1998) Tropical Forest Census Plots: Methods and Results from Barro Colorado Island, Panama and Comparison with Other Plots. Springer, Berlin. |
| [9] | De’Ath G (2002) Multivariate regression trees: A new technique for modeling species-environment relationships. Ecology, 83, 1105-1117. |
| [10] | De’Ath G (2006) mvpart: Multivariate partitioning. R package version 1.2-4. http://cran.r-project.org/. (accessed on 2019- 07-15) |
| [11] | Dufrêne M, Legendre P (1997) Species assemblages and indicator species: The need for a flexible asymmetrical approach. Ecological Monographs, 67, 345-366. |
| [12] | Engelbrecht BMJ, Kursar TA, Tyree MT (2005) Drought effects on seedling survival in a tropical moist forest. Trees, 19, 312-321. |
| [13] | Fang JY, Shen ZH, Cui HT (2004) Ecological characteristics of mountains and research issues of mountain ecology. Biodiversity Science, 12, 10-19. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 方精云, 沈泽昊, 崔海亭 (2004) 试论山地的生态特征及山地生态学的研究内容. 生物多样性, 12, 10-19.] | |
| [14] | Harms KE, Condit R, Hubbell SP, Foster RB (2001) Habitat associations of trees and shrubs in a 50-ha neotropical forest plot. Journal of Ecology, 89, 947-959. |
| [15] | He JS, Chen WL (1997) A review of gradient changes in species diversity of land plant communities. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 17, 91-99. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 贺金生, 陈伟烈 (1997) 陆地植物群落物种多样性的梯度变化特征. 生态学报, 17, 91-99.] | |
| [16] | Huang FZ, Wang B, Ding T, Xiang WS, Li XK, Zhou AP (2014) Numerical classification of associations in a northern tropical karst seasonal rain forest and the relationships of these associations with environmental factors. Biodiversity Science, 22, 157-166. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 黄甫昭, 王斌, 丁涛, 向悟生, 李先琨, 周爱萍 (2014) 弄岗北热带喀斯特季节性雨林群丛数量分类及与环境的关系. 生物多样性, 22, 157-166.] | |
| [17] | Hubbell SP (2001) The Unified Neutral Theory of Biodiversity and Biogeography. Princeton University Press, Princeton, |
| [18] | Lai JS, Mi XC, Ren HB, Ma KP (2010) Numerical classification of associations in subtropical evergreen broad-leaved forest based on multivariate regression trees―A case study of 24 hm2 Gutianshan forest plot in China . Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 34, 761-769. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 赖江山, 米湘成, 任海保, 马克平 (2010) 基于多元回归树的常绿阔叶林群丛数量分类——以古田山24公顷森林样地为例. 植物生态学报, 34, 761-769.] | |
| [19] | Lan GY, Hu YH, Cao M, Zhu H, Wang H, Zhou SS, Deng XB, Cui JY, Huang JG, Liu LY, Xu HL, Song JP, He YC (2008) Establishment of Xishuangbanna tropical forest dynamics plot: Species compositions and spatial distribution patterns. Journal of Plant Ecology (Chinese Version), 32, 287-298. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 兰国玉, 胡跃华, 曹敏, 朱华, 王洪, 周仕顺, 邓晓保, 崔景云, 黄建国, 刘林云, 许海龙, 宋军平, 何有才 (2008) 西双版纳热带森林动态监测样地——树种组成与空间分布格局. 植物生态学报, 32, 287-298.] | |
| [20] | Lan GY, Zhu H, Cao M (2013) Floristic composition of tropical seasonal rain forests in Xishuangbanna. Journal of Northwest Forestry University, 28(1), 33-38. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 兰国玉, 朱华, 曹敏 (2013) 西双版纳热带季节雨林树种的区系组成成分分析. 西北林学院学报, 28(1), 33-38.] | |
| [21] | Li B (1993) General Ecology. Inner Mongolia University Press, Huhhot. (in Chinese) |
| [ 李博 (1993) 西双版纳热带季节雨林树种的区系组成成分分析. 西北林学院学报.] | |
| [22] | Li SF, Lang XD, Huang XB, Wang YH, Liu WD, Xu CH, Su JR (2020) Association classification of a 30 hm2 dynamics plot in the monsoon broad-leaved evergreen forest in Puer, Yunnan Province . Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 44, 236-247. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 李帅锋, 郎学东, 黄小波, 王艳红, 刘万德, 徐崇华, 苏建荣 (2020) 云南普洱30 hm2季风常绿阔叶林动态监测样地群丛数量分类 . 植物生态学报, 44, 236-247.] | |
| [23] | Liu F, Tao GD, Wang DS (2008) Investigation on the alien invasive plants in Nabanhe Nature Reserve and precautionary measures. Forest Inventory and Planning, 33(6), 112-114, 117. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 刘峰, 陶国达, 王东升 (2008) 纳板河自然保护区外来入侵植物状况调查及防范对策. 林业调查规划, 33(6), 112-114, 117.] | |
| [24] | Liu F, Yang SH (2015) A Comprehensive Scientific Investigation of the Naban River Watershed National Nature Reserve. Yunnan Science and Technology Press, Kunming. (in Chinese) |
| [ 刘峰, 杨树华 (2015) 纳板河流域国家级自然保护区综合科学考察报告. 云南科技出版社, 昆明.] | |
| [25] | Liu HF, Xue DY, Sang WG (2012) Effect of topographic factors on the relationship between species richness and aboveground biomass in a warm temperate forest. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 21, 1403-1407. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 刘海丰, 薛达元, 桑卫国 (2012) 地形因子对暖温带森林群落物种丰富度-地上生物量关系的影响. 生态环境学报, 21, 1403-1407.] | |
| [26] | Ma KP (2017) Forest dynamics plot is a crosscutting research platform for biodiversity science. Biodiversity Science, 25, 227-228. (in Chinese) |
| [ 马克平 (2017) 森林动态大样地是生物多样性科学综合研究平台. 生物多样性, 25, 227-228.] | |
| [27] | R Core Team (2018) R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing, Version 3.5.0. https://www.r-project.org/. (accessed on 2019-04-23) |
| [28] | Roberts DW (2006) Labdsv: Laboratory for dynamic synthetic vegephenomenology. R package version 1.2-2. http://cran.r-project.org/. (accessed on 2019-08-15) |
| [29] | Song YC (2001) Vegetation Ecology, 2nd edn. Higher Education Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 宋永昌 (2001) 植被生态学(第二版). 高等教育出版社, 北京.] | |
| [30] | Song YC (2004) Tentative classification scheme of evergreen broad-leaved forests of China. Acta Phytoecologica Sinica, 28, 435-448. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 宋永昌 (2004) 中国常绿阔叶林分类试行方案. 植物生态学报, 28, 435-448.] | |
| [31] | Song YC, Wang XH, Yan ER (2013) Evergreen Broad- leaved Forest in China: Classification, Ecology, Conservation. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 宋永昌, 王希华, 阎恩荣 (2013) 中国常绿阔叶林: 分类、生态、保育. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [32] | Song YC, Yan ER, Song K (2017) An update of the vegetation classification in China. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 41, 269-278. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 宋永昌, 阎恩荣, 宋坤 (2017) 再议中国常绿阔叶林分类试行方案. 植物生态学报, 41, 269-278.] | |
| [33] | Sun XW, Yang QS, Liu HM, Wang XH (2018) Classification of plant associations based on a 20 hm2 dynamics plot of evergreen broad-leaved forest in Mt. Tiantong, Zhejiang, China . Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 42, 550-561. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 孙小伟, 杨庆松, 刘何铭, 王希华 (2018) 基于浙江天童20 hm2常绿阔叶林动态监测样地的群丛划分 . 植物生态学报, 42, 550-561.] | |
| [34] | van der Maarel E, Franklin J (2013) Vegetation Ecology, 2nd edn. John Wiley & Sons, Chichester. |
| [35] | Valencia R, Foster RB, Villa G, Condit R, Svenning JC, Hernández C, Romoleroux K, Losos E, Magård E, Balslev H (2004) Tree species distributions and local habitat variation in the Amazon: Large forest plot in eastern Ecuador. Journal of Ecology, 92, 214-229. |
| [36] | Vayssières MP, Plant RE, Allen-Diaz BH (2000) Classification trees: An alternative non-parametric approach for predicting species distributions. Journal of Vegetation Science, 11, 679-694. |
| [37] | Wu ZY (1980) Vegetation of China Vegetation of China. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 吴征镒 (1980) 中国植被, 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [38] | Wu ZY, Lu AM, Tang YC, Chen ZD, Li DZ (2003) The Families and Genera of Angiosperms in China: A Comprehensive Analysis. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 吴征镒, 路安民, 汤彦承, 陈之端, 李德铢 (2003) 中国被子植物科属综论. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [39] | Wu ZY, Zhou ZK, Sun H, Peng H (2006) The Areal Types of Seed Plants and Their Origin and Differentiation. Yunnan Science and Technology Press, Kunming. (in Chinese) |
| [ 吴征镒, 周浙昆, 孙航, 彭华 (2006) 种子植物分布区类型及其起源和分化. 云南科技出版社, 昆明.] | |
| [40] | Wu ZY, Zhu YC (1987) Vegetation of Yunnan. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 吴征镒, 朱彦丞 (1987) 云南植被. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [41] | Xie YH (2007) The application of the classification and regression tree based on the package rpart in R-language. Statistics & Information Forum, 22(5), 67-70. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 谢益辉 (2007) 基于R软件rpart包的分类与回归树的应用. 统计与信息论坛, 22(5), 67-70.] | |
| [42] | Zhang DY (2000) Researches on Theoretical Ecology. Higher Education Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 张大勇 (2000) 理论生态学研究. 高等教育出版社, 北京.] | |
| [43] | Zhang F, Zhang JT (2000) Research progress of numerical classification and ordination of vegetation in China. Journal of Shanxi University (Natural Science Edition), 23, 278-282. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 张峰, 张金屯 (2000) 我国植被数量分类和排序研究进展. 山西大学学报(自然科学版), 23, 278-282.] | |
| [44] | Zhang WJ, Zhang QD, Wang J, Feng F, Bi RC (2015) A comparison of multivariate regression tree and two-way indicator species analysis in plant community classification. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 39, 586-592. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 张文静, 张钦弟, 王晶, 冯飞, 毕润成 (2015) 多元回归树与双向指示种分析在群落分类中的应用比较. 植物生态学报, 39, 586-592.] | |
| [45] | Zhou SR, Zhang DY (2006) Neutral theory in community ecology. Journal of Plant Ecology (Chinese Version), 30, 868-877. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 周淑荣, 张大勇 (2006) 群落生态学的中性理论. 植物生态学报, 30, 868-877.] | |
| [46] | Zhu H (1997) Ecological and biogeographical studies on the tropical rain forest of south Yunnan, SW China with a special reference to its relation with rain forests of tropical Asia. Journal of Biogeography, 24, 647-662. |
| [47] | Zhu H (2006) Forest vegetation of Xishuangbanna, South China. Forestry Studies in China, 8, 1-58. |
| [48] | Zhu H (2008) The tropical flora of southern Yunnan, China, and its biogeographical affinities. Annual Missouri Botanical Garden, 95, 661-680. |
| [49] | Zhu H (2017) Tropical flora of southern China. Biodiversity Science, 25, 204-217. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 朱华 (2017) 中国南部热带植物区系. 生物多样性, 25, 204-217.] | |
| [50] | Zhu H (2018) A sketch for classification of tropical forest vegetation in Yunnan. Guihaia, 38, 984-1004. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 朱华 (2018) 云南热带森林植被分类纲要. 广西植物, 38, 984-1004.] | |
| [51] | Zhu H, Wang H, Li BG, Zhou SS, Zhang JH (2015) Studies on the forest vegetation of Xishuangbanna. Plant Science Journal, 33, 641-726. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 朱华, 王洪, 李保贵, 周仕顺, 张建侯 (2015) 西双版纳森林植被研究. 植物科学学报, 33, 641-726.] |
| [1] | 张楚然, 李生发, 李逢昌, 唐志忠, 刘辉燕, 王丽红, 顾荣, 邓云, 张志明, 林露湘. 云南鸡足山亚热带半湿润常绿阔叶林20 ha动态监测样地木本植物生境关联与群落数量分类[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(1): 23393-. |
| [2] | 徐学红, 王巍伟, 米湘成, 陈磊, 马克平. 中国森林生物多样性监测网络(CForBio): 二十年进展与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(12): 23354-. |
| [3] | 刘丹, 郭忠玲, 崔晓阳, 范春楠. 5种东北红豆杉植物群丛及其物种多样性的比较[J]. 生物多样性, 2020, 28(3): 340-349. |
| [4] | 李霞, 朱万泽, 孙守琴, 舒树淼, 盛哲良, 张军, 刘亭, 张志才. 大渡河中游干暖河谷区生境对植物群落分布格局和多样性的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2020, 28(2): 117-127. |
| [5] | 陈惠君, 杜虎, 宋同清, 彭晚霞, 张浩, 苏樑, 曾馥平. 木论喀斯特常绿落叶阔叶混交林群丛数量分类及稳定性[J]. 生物多样性, 2019, 27(10): 1056-1068. |
| [6] | 龚雪伟, 吕光辉. 艾比湖流域杜加依林荒漠植物群落多样性及优势种生态位[J]. 生物多样性, 2017, 25(1): 34-45. |
| [7] | 黄甫昭, 王斌, 丁涛, 向悟生, 李先琨, 周爱萍. 弄岗北热带喀斯特季节性雨林群丛数量 分类及与环境的关系[J]. 生物多样性, 2014, 22(2): 157-166. |
| [8] | 汪正祥, 雷耘, Kazue Fujiwara, 刘林翰, 薛跃规. 亚热带山地亮叶水青冈林的群落分类及物种组成与更新[J]. 生物多样性, 2006, 14(1): 29-40. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn
![]()