



生物多样性 ›› 2019, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (5): 491-504. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2018233 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2018233
所属专题: 生物入侵
收稿日期:2018-09-04
接受日期:2019-05-07
出版日期:2019-05-20
发布日期:2019-05-20
通讯作者:
战爱斌
基金资助:
Li Hanxi1,2,Huang Xuena1,Li Shiguo1,2,Zhan Aibin1,2,*( )
)
Received:2018-09-04
Accepted:2019-05-07
Online:2019-05-20
Published:2019-05-20
Contact:
Zhan Aibin
摘要:
外来生物入侵是继生境破坏后造成生物多样性丧失的第二大威胁因素, 已对入侵地的生态安全、经济和社会发展及人类健康等造成严重负面影响, 成为21世纪五大全球性环境问题之一。作为水产养殖、航运和水生宠物交易大国, 我国水生生态系统的生物入侵问题尤为严重。研究表明, 系统地构建并应用早期监测预警技术是防控水生生态系统生物入侵最有效的途径。和陆生生物相比, 水生生物群落的物种繁多、群落结构复杂、生物形体微小且在入侵初期群体规模极小、隐匿于水下、可用于物种鉴定的外部形态缺乏, 使得在水生生态系统中构建并应用早期监测和预警体系在技术层面更具挑战。随着高通量测序技术的快速发展, 环境DNA-宏条形码技术成为构建水生生态系统入侵生物早期监测与预警技术的首选。本文主要综述了基于环境DNA-宏条形码技术的水生生态系统入侵生物的早期监测与预警技术方法; 解析了环境DNA-宏条形码监测系统的应用现状、技术优势; 着重探讨了影响监测结果准确性的I型和II型错误及其产生原因, 并为避免两类错误提供了可行的优化/改进方案; 最后对该方法在水生入侵生物监测中的应用前景进行了展望。
李晗溪, 黄雪娜, 李世国, 战爱斌 (2019) 基于环境DNA-宏条形码技术的水生生态系统入侵生物的早期监测与预警. 生物多样性, 27, 491-504. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2018233.
Li Hanxi, Huang Xuena, Li Shiguo, Zhan Aibin (2019) Environmental DNA (eDNA)-metabarcoding-based early monitoring and warning for invasive species in aquatic ecosystems. Biodiversity Science, 27, 491-504. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2018233.
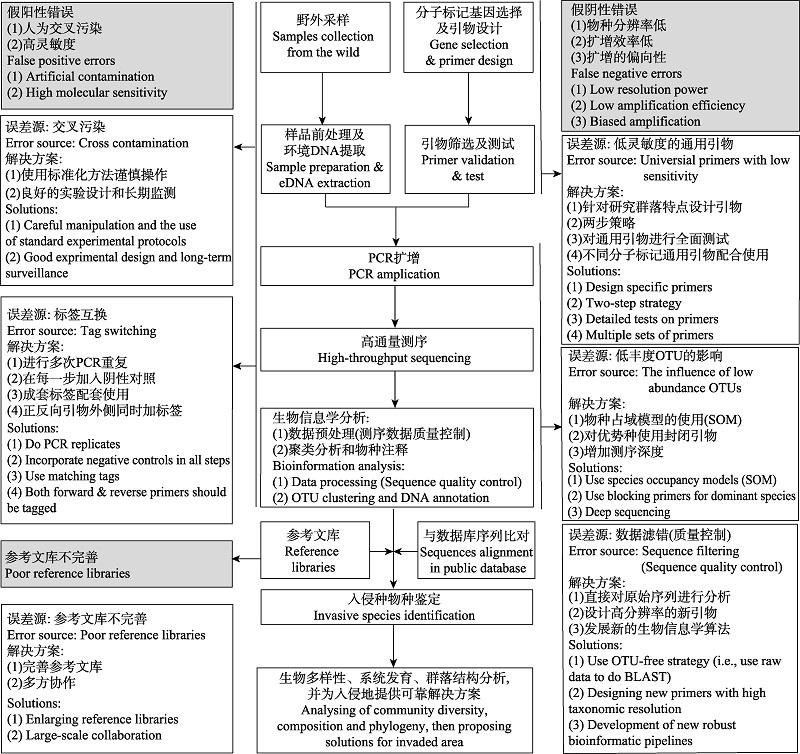
图1 基于环境DNA-宏条形码技术的水生入侵生物早期监测与预警技术现存的主要问题及可能的解决方案
Fig. 1 A summary of error sources and possible solutions for both false positive and false negative errors when using environmental DNA-metabarcoding methods for early detection and warning of aquatic invasive species
| [1] | Avó AP, Daniell TJ, Neilson R, Oliveira S, Branco J, Adão H ( 2017) DNA barcoding and morphological identification of benthic nematodes assemblages of estuarine intertidal sediments: Advances in molecular tools for biodiversity assessment. Frontiers in Marine Science, 4, 66. |
| [2] | Bellemain E, Carlsen T, Brochmann C, Coissac E, Taberlet P, Kauserud H ( 2010) ITS as an environmental DNA barcode for fungi: An in silico approach reveals potential PCR biases. BMC Microbiology, 10, 189. |
| [3] | Brannock PM, Ortmann AC, Moss AG, Halanych KM ( 2016) Metabarcoding reveals environmental factors influencing spatiotemporal variation in pelagic microeukaryotes. Molecular Ecology, 25, 3593-3604. |
| [4] | Bråte J, Logares R, Berney C, Ree DK, Klaveness D, Jakobsen KS, Tabrizi KS ( 2010) Freshwater Perkinsea and marine- freshwater colonizations revealed by Pyrosequencing and phylogeny of environmental rDNA. The ISME Journal, 4, 1144-1153. |
| [5] | Briski E, Cristescu ME, Bailey SA, MacIsaac HJ ( 2011) Use of DNA barcoding to detect invertebrate invasive species from diapausing eggs. Biological Invasions, 13, 1325-1340. |
| [6] | Boessenkool S, Epp LS, Haile J, Bellemain E ( 2012) Blocking human contaminant DNA during PCR allows amplification of rare mammal species from sedimentary ancient DNA. Molecular Ecology, 21, 1806-1815. |
| [7] | Bourlat SJ, Borja A, Gilbert J, Taylor MI, Davies N, Weisberg SB, Griffith JF, Lettieri J, Field D, Benzie J, Glpckner FO, Rodríguez-Ezpeleta N, Faith DP, Bean TP, Obst M ( 2013) Genomics in marine monitoring: New opportunities for assessing marine health status. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 74, 19-31. |
| [8] | Bucklin A, Ortman BD, Jennings RM, Nigro LM, Sweetman CJ, Copley NJ, Suttonb T, Wiebec PH ( 2010) A “Rosetta Stone” for metazoan zooplankton: DNA barcode analysis of species diversity of the Sargasso Sea (Northwest Atlantic Ocean). Deep-Sea Research Part II: Topical Studies in Oceanography, 57, 2234-2247. |
| [9] | Carlsen T, Aas AB, Lindner D, Vrålstad T, Chumacher T, Kauserud H ( 2012) Don’t make a mistake: Is tag switching an overlooked source of error in amplicon Pyrosequencing studies? Fungal Ecology, 5, 747-749. |
| [10] | Chen L, Wu L, Liu Y, Xu HG ( 2016) Application of environmental DNA metabarcoding in ecology. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 36, 4573-4582. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 陈炼, 吴琳, 刘燕, 徐海根 ( 2016) 环境DNA metabarcoding及其在生态学研究中的应用. 生态学报, 36, 4573-4582.] | |
| [11] | Chen Y, Sun C, Zhan A ( 2017) Biological invasions in aquatic ecosystems in China. Aquatic Ecosystem Health & Management, 10, 402-412. |
| [12] | Chen YY, Gao YC, Peng H, Xiong W, Li SG, Zhan AB ( 2018) Community structure of benthic macroinvertebrates and water quality assessment in the Songhua River. Journal of Biosafety, 27(2), 95-104. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 陈义永, 高养春, 彭衡, 熊薇, 李世国, 战爱斌 ( 2018) 松花江流域大型底栖动物群落结构与水质评价. 生物安全学报, 27(2), 95-104.] | |
| [13] | Cheung MK, Au CH, Chu KH ( 2010) Composition and genetic diversity of picoeukaryotes in subtropical coastal waters as revealed by 454 Pyrosequencing. The ISME Journal, 4, 1053-1059. |
| [14] | Darling JA, Mahon AR ( 2011) From molecules to management: Adopting DNA-based methods for monitoring biological invasions in aquatic environments. Environmental Research, 111, 978-988. |
| [15] | Davey ML, Kauserud H, Ohlson M ( 2014) Forestry impacts on the hidden fungal biodiversity associated with bryophytes. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 90, 313-325. |
| [16] | Deagle BE, Jarman SN, Coissac E, Pompanon F, Taberlet P ( 2014) DNA metabarcoding and the cytochrome C oxidase subunit I marker: Not a perfect match. Biology Letters, 10, 20140562. |
| [17] | Dudgeon D, Arthington AH, Gessner MO ( 2006) Freshwater biodiversity: Importance, threats, status and conservation challenges. Biological Reviews, 81, 163-182. |
| [18] | Emily AB, Frederic JJ, Zhan A, Hugh JM, Melania EC ( 2016) Detection of aquatic invaders using metabarcoding reveals a high number of non-indigenous species in Canadian ports. Diversity and Distributions, 22, 1045-1059. |
| [19] | Egan SP, Grey E, Olds B ( 2015) Rapid molecular detection of invasive species in ballast and harbor water by integrating environmental DNA and light transmission sectroscopy. Environmental Science & Technology, 49, 4113-4121. |
| [20] | Elbrecht V, Taberlet P, Dejean T, Valentini A, Usseglio- Polatera P, Beisel JN, Coissac E, Boyer F, Leese F ( 2016) Testing the potential of a ribosomal 16S marker for DNA metabarcoding of insects. PeerJ, 4, e1966. |
| [21] | Engelbrektson A, Kunin V, Wrighton K, Zvenigorodsky N, Chen F, Ochman H, Hugenholtz P ( 2010) Experimental factors affecting PCR-based estimates of microbial species richness and evenness. The ISME Journal, 4, 642-647. |
| [22] | Ficetola GF, Miaud C, Pompanon F, Taberlet P ( 2008) Species detection using environmental DNA from water samples. Biology Letters, 4, 423-425. |
| [23] | Ficetola GF, Pansu J, Bonin A, Coissac E, Giguet-Covex C, De Barba M, Gielly L, Lopes CM, Boyer F, Pompanon F, Rayé G, Taberlet P ( 2015) Replication levels, false presences and the estimation of the presence/absence from eDNA metabarcoding data. Molecular Ecology Resources, 15, 543-556. |
| [24] | Galand PE, Casamayor EO, Kirchman DL ( 2009) Unique archaeal assemblages in the Arctic Ocean unveiled by massively parallel tag sequencing. The ISME Journal, 3, 860-869. |
| [25] |
Goldberg CS, Sepulveda A, Ray A, Baumgardt J, Waits LP ( 2013) Environmental DNA as a new method for early detection of New Zealand mudsnails (Potamopyrgus antipodarum). Freshwater Science, 32, 792-800.
DOI URL |
| [26] | Hao YB, Zhang AJ, Liu JD, Gu ZM ( 2018) Application of environmental DNA technology in the study of fish resources. Biotechnology Bulletin, 34(12), 56-62. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 郝雅宾, 张爱菊, 刘金殿, 顾志敏 ( 2018) 环境DNA技术在鱼类资源研究中的应用. 生物技术通报, 34(12), 56-62.] | |
| [27] | Hajibabaei M, Shokralla S, Zhou X ( 2011) Environmental barcoding: A next-generation sequencing approach for biomonitoring applications using river benthos. PLoS ONE, 6, e17497. |
| [28] | Hambler C, Henderson PA, Speight MR ( 2011) Extinction rates, extinction-prone habitats, and indicator groups in Britain and at larger scales. Biological Conservation, 144, 713-721. |
| [29] | Holland RA, Darwall WRT, Smith KG ( 2012) Conservation priorities for freshwater biodiversity: The key biodiversity area approach refined and tested for continental Africa. Biological Conservation, 148, 167-179. |
| [30] |
Jerde CL, Mahon AR, Chadderton WL, Lodge DM ( 2011) ‘‘Sight-unseen’’ detection of rare aquatic species using environmental DNA. Conservation Letters, 4, 150-157.
DOI URL |
| [31] | Jiang W, Wang QJ, Deng J ( 2016) Protocol optimization of eDNA analysis workflow for detecting Hucho bleekeri. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 27, 2372-2378. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 姜维, 王启军, 邓捷 ( 2016) 以川陕哲罗鲑为目标物种的水样环境DNA分析流程的优化. 应用生态学报, 27, 2372-2378.] | |
| [32] | Ju RT, Li H, Shih CJ, Li B ( 2012) Progress of biological invasions research in China over the last decade. Biodiversity Science, 20, 581-611. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 鞠瑞亭, 李慧, 石正人, 李博 ( 2012) 近十年中国生物入侵研究进展. 生物多样性, 20, 581-611.] | |
| [33] | Kanagawa T ( 2003) Bias and artifacts in multitemplate polymerase chain reactions (PCR). Journal of Bioscience and Bioengieering, 96, 317-323. |
| [34] | Kauserud H, Kumar S, Brysting AK, Norden J, Carlsen T ( 2012) High consistency between replicate 454 Pyrosequencing analyses of ectomycorrhizal plant root samples. Mycorrhiza, 22, 309-315. |
| [35] | Kelly RP, Port JA, Yamahara KM, Crowder LB ( 2014) Using environmental DNA to census marine fishes in a large mesocosm. PLoS ONE, 9, e86175. |
| [36] | Keskin E, Atar HH ( 2013) DNA barcoding commercially important fish species of Turkey. Molecular Ecology Resources, 13, 788-797. |
| [37] | Kunin V, Engelbrektson A, Ochman H, Hugenholtz P ( 2010) Wrinkles in the rare biosphere: Pyrosequencing errors can lead to artificial inflation of diversity estimates. Environmental Microbiology, 12, 118-123. |
| [38] | Lang DD, Tang M, Zhou X ( 2018) Qualitative and quantitative molecular construction of plant-pollinator network: Application and prospective. Biodiversity Science, 26, 445-456. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 郎丹丹, 唐敏, 周欣 ( 2018) 传粉网络构建的定性定量分子研究: 应用与展望. 生物多样性, 26, 445-456.] | |
| [39] | Leray M, Yang JY, Meyer CP, Mills SC, Agudelo N ( 2013) A new versatile primer set targeting a short fragment of the mitochondrial COI region for metabarcoding metazoan diversity: Application for characterizing coral reef fish gut contents. Frontiers in Zoology, 10, 34. |
| [40] | Levy-Booth DJ, Campbell RG, Gulden RH, Hart MM, Powell JR ( 2007) Cycling of extracellular DNA in the soil environment. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 39, 2977-2991. |
| [41] | Li FL, Yang JH, Yang YN, Zhang XW ( 2018) Using environmental DNA metabarcoding to monitor the changes and health status of aquatic ecosystems. Environmental Monitoring in China, 34(6), 37-46. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 李飞龙, 杨江华, 杨雅楠, 张效伟 ( 2018) 环境DNA宏条形码监测水生态系统变化与健康状态. 中国环境监测, 34(6), 37-46.] | |
| [42] | Li Q, Wu JG, Kou XJ ( 2013) Applications of camera trap in wildlife population ecology. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 24, 947-955. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 李勤, 邬建国, 寇晓军 ( 2013) 相机陷阱在野生动物种群生态学中的应用. 应用生态学报, 24, 947-955.] | |
| [43] | Lin Y, Gao Z, Zhan A ( 2015) Introduction and use of non-native species for aquaculture in China: Status, risks and management solutions. Reviews Aquaculture, 7, 28-58. |
| [44] | Liu FM, Miu JL, Zheng Z, Wang YB ( 2007) Present situation, hazards and prevention and control measures of marine invasive alien species into China. Coastal Engineering, 26(4), 49-57. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 刘芳明, 缪锦来, 郑洲, 王以斌 ( 2007) 中国外来海洋生物入侵的现状、危害及其防治对策. 海岸工程, 26(4), 49-57.] | |
| [45] | Lockwood JL, Hoopes MF, Marchetti MP ( 2013) Invasion Ecology, 2nd edn. Blackwell Scientific Publications, Chichester, West Sussex. |
| [46] | MacKenzie DIM, Nichols JD, Lachman GB, Droege S, Royle JA, Langtimm CA ( 2002) Estimating site occupancy rates when detection probabilities are less than one. Ecology, 83, 2248-2255. |
| [47] | Ma HJ, Stewart K, Ma LM, Ren WW, Zhao JF ( 2016) Environmental DNA and its application in protecting aquatic ecosystem. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 35, 516-523. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 马鸿娟, Stewart K, 马利民, 任文伟, 赵建夫 ( 2016) 环境DNA及其在水生生态系统保护中的应用. 生态学杂志, 35, 516-523.] | |
| [48] | McDonald LL ( 2004) Sampling rare populations. In: Sampling Rare or Elusive Species: Concepts, Designs, and Techniques for Estimating Population Parameters (ed. Thompson WL), pp. 11-42.Island Press,New York. |
| [49] |
Odelberg SJ, Weiss RB, Hata A, White R ( 1995) Template- switching during DNA synthesis by Therms aquaticus DNA polymerase. Nucleic Acids Research, 23, 2049-2057.
DOI URL |
| [50] | Pagenkopp LKM, Fleischer RC, Carney KJ, Holzer KK, Ruiz GM ( 2016) Amplicon-based Pyrosequencing reveals high diversity of protistan parasites in ships’ ballast water: Implications for biogeography and infectious diseases. Microbiology Ecology, 71, 530-542. |
| [51] | Pietramellara G ( 2009) Extracellular DNA in soil and sediment: Fate and ecological relevance. Biology and Fertility of Soils, 45, 219-235. |
| [52] | Polz MF, Cavanaugh CM ( 1998) Bias in template-to-product ratios in multitemplate PCR. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 64, 3724-3730. |
| [53] |
Prosser JI ( 2010) Replicate or lie. Environmental Microbiology, 12, 1806-1810.
DOI URL |
| [54] | Pysek P, Richardson DM ( 2010) Invasive species, environmental change and management, and health. Annual Review of Environment and Resources, 35, 25-55. |
| [55] | Rees HC, Maddison BC, Middleditch DJ ( 2014) The detection of aquatic animal species using environmental DNA: A review of eDNA as a survey tool in ecology. Journal of Applied Ecology, 51, 1450-1459. |
| [56] | Saunders GW ( 2005) Applying DNA barcoding to red macroalgae: A preliminary appraisal holds promise for future applications. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 360, 1879-1888. |
| [57] | Schmieder R, Edwards R ( 2011) Fast identification and removal of sequence contamination from genomic and metagenomic datasets. PLoS ONE, 6, e17288. |
| [58] | Shan XJ, Li M, Wang WJ ( 2018) Application of environmental DNA technology in aquatic ecosystem. Progress in Fishery Sciences, 39(3), 23-29. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 单秀娟, 李苗, 王伟继 ( 2018) 环境DNA (eDNA)技术在水生生态系统中的应用研究进展. 渔业科学进展, 39(3), 23-29.] | |
| [59] | Shi XL, Lepère C, Scanlan DJ, Vaulot D ( 2011) Plastid 16S rRNA gene diversity among eukaryotic picophytoplankton sorted by flow cytometry from the South Pacific Ocean. PLoS ONE, 6, e18979. |
| [60] |
Sogin ML, Morrison HG, Huber JA, Welch DM, Huse SM, Neal PR, Arrieta JM, Herndl GJ ( 2006) Microbial diversity in the deep sea and the underexplored “rare biosphere”. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 103, 12115-12120.
DOI URL |
| [61] | Song JW, Small MJ, Casman EA ( 2017) Making sense of the noise: The effect of hydrology on silver carp eDNA detection in the Chicago area waterway system. Science of the Total Environment, 605, 713-720. |
| [62] | Sun C, Zhao Y, Li H, Dong Y, MacIsaac HJ, Zhan A ( 2015) Unreliable quantitation of species abundance based on high- throughput sequencing data of zooplankton communities. Aquatic Biology, 24, 9-15. |
| [63] | Suzuki MT, Giovannoni SJ ( 1996) Bias caused by template annealing in the amplification of mixtures of 16S rRNA genes by PCR. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 62, 625-630. |
| [64] |
Taberlet P, Coissac E, Hajibabaei M ( 2012) Environmental DNA. Molecular Ecology, 21, 1789-1793.
DOI URL |
| [65] | Takahara T, Minamoto T, Yamanaka H, Doi H, Kawabata Z (2012) Estimation of fish biomass using environmental DNA. PLoS ONE, 7, e35868. |
| [66] | Tang CQ, Leasi F, Obertegger U, Kieneke A, Barraclough TG, Fontaneto D ( 2012) The widely used small subunit 18S rDNA molecule greatly underestimates true diversity in biodiversity surveys of the meiofauna. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 109, 16208-16212. |
| [67] | Tang M, Yi TS, Wang X, Tan MH, Zhou X ( 2013) The application of metabarcoding technology in identification of plant species diversity. Plant Diversity and Resources, 35, 769-773. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 唐敏, 伊廷双, 王欣, 谭美华, 周欣 ( 2013) Metabarcoding技术在植物鉴定和多样性研究中的应用. 植物分类与资源学报, 35, 769-773.] | |
| [68] | Tedersoo L, Nilsson RH, Abarenkov K, Jairus T, Sadam A, Saar I ( 2010) 454 Pyrosequencing and Sanger sequencing of tropical mycorrhizal fungi provide similar results but reveal substantial methodological biases. New Phytologist, 188, 291-301. |
| [69] | Thomsen PF, Møller PR, Sigsgaard EE, Knudsen SW, Jørgensen OA, Willerslev E ( 2016) Environmental DNA from seawater samples correlate with trawl catches of Subarctic, deepwater fishes. PLoS ONE, 11, e0165252. |
| [70] |
Tréguier A, Paillisson J, Dejean T ( 2014) Environmental DNA surveillance for invertebrate species: Advantages and technical limitations to detect invasive crayfish (Procambarus clarkii) in freshwater ponds. Journal of Applied Ecology, 51, 871-879.
DOI URL |
| [71] | Valentini A, Taberlet P, Miaud C, Civade R, Herder J, Thomsen PF, Bellemain E, Besnard A, Coissac E, Boyer F, Gaboriaud C, Jean P, Poulet N, Roset N, Copp GH, Geniez P, Pont D, Argillier C, Baudoin JM, Peroux T, Crivelli AJ, Olivier A, Acqueberge M, Le Brun M, Møller PR, Willerslev E, Dejean T ( 2016) Next-generation monitoring of aquatic biodiversity using environmental DNA metabarcoding. Molecular Ecology, 25, 929-942. |
| [72] | Veach AM, Dodds WK, Jumpponen A ( 2015) Woody plant encroachment, and its removal, impact bacterial and fungal communities across stream and terrestrial habitats in a tallgrass prairie ecosystem. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 91, fiv109. |
| [73] | Wan FH, Guo JY, Zhang F ( 2009) Research on Biological Invasions in China. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 万方浩, 郭建英, 张峰 ( 2009) 中国生物入侵研究. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [74] | Wan YQ, Guo WB, Wu J, Li L, Xu HG ( 2017) Site occupancy model: Principles and research progress. Journal of Ecology and Rural Environment, 33, 673-679. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 万雅琼, 郭伟波, 吴军, 李莉, 徐海根 ( 2017) 物种占域模型的基本原理及其研究进展. 生态与农村环境学报, 33, 673-679.] | |
| [75] | Wang ZH, Chen JF, Yang YF ( 2010) Control and management of harmful algal bloom species introduced by ballast water. Marine Environmental Science, 29, 920-922. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 王朝晖, 陈菊芳, 杨宇峰 ( 2010) 船舶压舱水引起的有害赤潮藻类生态入侵及其控制管理. 海洋环境科学, 29, 920-922.] | |
| [76] | Weber AAT, Pawlowski J ( 2013) Can abundance of protists be inferred from sequence data: A case study of foraminifera. PLoS ONE, 8, e56739. |
| [77] | Wu B, Zhao Q, Liu HM, Liu ZH, Sun XJ, Sun C, Zhou LQ, Yang AG ( 2018) Comparative analysis of different DNA barcoding methods for Veneroida classification and identification. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 25, 880-890. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 吴彪, 赵庆, 刘寒苗, 刘志鸿, 孙秀俊, 孙超, 周丽青, 杨爱国 ( 2018) 不同DNA条形码基因在帘蛤目贝类分类鉴定中的比较分析. 中国水产科学, 25, 880-890.] | |
| [78] | Wu YS, Tang YK, Li JL, Liu K, Li HX, Wang Q, Yu JH, Xu P ( 2019) The application of environmental DNA in the monitoring of the Yangtze finless porpoise, Neophocaena phocaenoides asaeorientalis. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 26(1), 126-134. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 吴昀晟, 唐永凯, 李建林, 刘凯, 李红霞, 王钦, 俞菊华, 徐跑 ( 2019) 环境DNA在长江江豚监测中的应用. 中国水产科学, 26(1), 126-134.] | |
| [79] | Xiong W, Li H, Zhan A ( 2016) Early detection of invasive species in marine ecosystems using high-throughput sequencing: Technical challenges and possible solutions. Marine Biology, 163, 139. |
| [80] | Xu N, Chang JB ( 2016) Preliminary study on fish species detection in the middle and lower Yangtze River using environmental DNA. Journal of Hydroecology, 37(5), 49-55. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 徐念, 常剑波 ( 2016) 长江中下游干流环境DNA样本鱼类物种检测的初步研究. 水生态学杂志, 37(5), 49-55.] | |
| [81] | Yang JH ( 2017) Adaptive Strategies of Clonal Plants Growing in Heterogeneous Environments. PhD dissertation, Nanjing University, Nanjing. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 杨江华 ( 2017) 太湖流域浮游动物物种多样性与环境污染群落生态效应研究.博士学位论文, 南京大学, 南京.] | |
| [82] | Yoon TH, Kang HE, Kang CK, Lee SH, Ahn DH, Park H, Kim HW ( 2016) Development of a cost-effective metabarcoding strategy for analysis of the marine phytoplankton community. PeerJ, 4, e2. |
| [83] | Zaiko A, Martinez JL, Schmidtpetersen J ( 2015a) Metabarcoding approach for the ballast water surveillance — An advantageous solution or an awkward challenge? Marine Pollution Bulletin, 92, 25-34. |
| [84] | Zaiko A, Samuiloviene A, Ardura A, Garcia-Vazquez E (2015b) Metabarcoding approach for nonindigenous species surveillance in marine coastal waters. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 100, 53-59. |
| [85] | Zhan A, Hulák M, Sylvester F, Huang X, Adebayo AA, Abbott CL, Adamowicz SJ, Heath DD, Cristescu ME, Maclsaac HJ ( 2013) High sensitivity of 454 Pyrosequencing for detection of rare species in aquatic communities. Methods in Ecology and Evolution, 4, 558-565. |
| [86] | Zhan A, Bailey SA, Heath DD, Maclsaac HJ ( 2014 a) Performance comparison of genetic markers for high-throughput sequencing-based biodiversity assessment in complex communities. Molecular Ecology Resources, 14, 1049-1059. |
| [87] | Zhan A, Xiong W, He S, Maclsaac HJ ( 2014 b) Influence of artifact removal on rare species recovery in natural complex communities using high-throughput sequencing. PLoS ONE, 9, e96928. |
| [88] | Zhan A, He EA, Brown FJJ, Chain TW, Therriault CL, Abbott DD, Heath ME, Maclsaac Cristescu HJ ( 2014 c) Reproducibility of Pyrosequencing data for biodiversity assessment in complex communities. Methods in Ecology and Evolution, 5, 881-890. |
| [89] | Zhan A, Maclsaac HJ ( 2015) Rare biosphere exploration using high-throughput sequencing: Research progress and perspectives. Conservation Genetics, 16, 513-522. |
| [90] | Zhan A, Ni P, Xiong W, Chen Y, Lin Y, Huang X ( 2017) Biological invasions in aquatic ecosystems in China. Aquatic Ecosystem Health & Management, 10, 402-412. |
| [91] | Zhou J, Wu L, Deng Y, Zhi X, Jiang Y, Tu Q, Xie J, Van Nostrand JD, He Z, Yang Y ( 2011) Reproducibility and quantitation of amplicon sequencing-based detection. The ISME Journal, 5, 1303-1313. |
| [92] |
Zhou X, Li Y, Liu S, Yang Q, Su X, Zhou L, Tang M, Fu R, Li J, Huang Q ( 2013) Ultradeep sequencing enables high- fidelity recovery of biodiversity for bulk arthropod samples without PCR amplification. GigaScience, 2(1), 4.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 干靓 刘巷序 鲁雪茗 岳星. 全球生物多样性热点地区大城市的保护政策与优化方向[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24529-. |
| [2] | 曾子轩 杨锐 黄越 陈路遥. 清华大学校园鸟类多样性特征与环境关联[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24373-. |
| [3] | 臧明月, 刘立, 马月, 徐徐, 胡飞龙, 卢晓强, 李佳琦, 于赐刚, 刘燕. 《昆明-蒙特利尔全球生物多样性框架》下的中国城市生物多样性保护[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24482-. |
| [4] | 祝晓雨, 王晨灏, 王忠君, 张玉钧. 城市绿地生物多样性研究进展与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 25027-. |
| [5] | 袁琳, 王思琦, 侯静轩. 大都市地区的自然留野:趋势与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24481-. |
| [6] | 胡敏, 李彬彬, Coraline Goron. 只绿是不够的: 一个生物多样性友好的城市公园管理框架[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24483-. |
| [7] | 王欣, 鲍风宇. 基于鸟类多样性提升的南滇池国家湿地公园生态修复效果分析[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24531-. |
| [8] | 明玥, 郝培尧, 谭铃千, 郑曦. 基于城市绿色高质量发展理念的中国城市生物多样性保护与提升研究[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24524-. |
| [9] | 谢淦, 宣晶, 付其迪, 魏泽, 薛凯, 雒海瑞, 高吉喜, 李敏. 草地植物多样性无人机调查的物种智能识别模型构建[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24236-. |
| [10] | 褚晓琳, 张全国. 演化速率假说的实验验证研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 25019-. |
| [11] | 宋威, 程才, 王嘉伟, 吴纪华. 土壤微生物对植物多样性–生态系统功能关系的调控作用[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24579-. |
| [12] | 卢晓强, 董姗姗, 马月, 徐徐, 邱凤, 臧明月, 万雅琼, 李孪鑫, 于赐刚, 刘燕. 前沿技术在生物多样性研究中的应用现状、挑战与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24440-. |
| [13] | 农荞伊, 曹军, 程文达, 彭艳琼. 不同方法对蜜蜂总科昆虫资源与多样性监测效果的比较[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 25057-. |
| [14] | 郭雨桐, 李素萃, 王智, 解焱, 杨雪, 周广金, 尤春赫, 朱萨宁, 高吉喜. 全国自然保护地对国家重点保护野生物种的覆盖度及其分布状况[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(3): 24423-. |
| [15] | 赵维洋, 王伟, 马冰然. 其他有效的区域保护措施(OECMs)研究进展与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(3): 24525-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn