



生物多样性 ›› 2025, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (2): 24271. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2024271 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2024271
王凤琼1,#, 张心怡1,#, 王鑫厅1,*( ), 姜超2, 侯亚丽3, 包道日娜3
), 姜超2, 侯亚丽3, 包道日娜3
收稿日期:2024-06-28
接受日期:2024-11-24
出版日期:2025-02-20
发布日期:2025-03-19
通讯作者:
*E-mail: 作者简介:#共同第一作者
基金资助:
Wang Fengqiong1,#, Zhang Xinyi1,#, Wang Xinting1,*( ), Jiang Chao2, Hou Yali3, Bao Daorina3
), Jiang Chao2, Hou Yali3, Bao Daorina3
Received:2024-06-28
Accepted:2024-11-24
Online:2025-02-20
Published:2025-03-19
Contact:
*E-mail: About author:#Co-first authors
Supported by:摘要: 植物种群空间格局是植物生态学研究的基本内容之一。由于长期过度放牧, 内蒙古典型草原退化严重, 未受放牧干扰的原生群落非常罕见。探讨原生群落的种群空间格局对于草原的利用和保护具有重要的生态学意义。羊草(Leymus chinensis)草原是典型草原区广泛分布的主要群落类型之一, 1979年中国科学院草原生态系统定位研究站在内蒙古锡林郭勒盟典型草原地带建立的围栏封育羊草样地, 是目前保存完整的羊草草原原生群落。本研究选择羊草草原的原生群落和长期过度放牧的干扰群落, 应用成对相关函数结合均质泊松模型和异质泊松模型分析了羊草种群的空间分布格局。结果表明: (1)在原生群落中, 羊草种群表现出两种分布格局, 即在小尺度范围内呈聚集分布, 而在较大尺度范围内呈随机分布; 在长期过度放牧的干扰群落中, 羊草种群呈聚集分布格局, 这种变化是由于放牧引起的生境异质性所致; (2)羊草种群格局的聚集强度, 在排除生境异质性的影响后, 在小尺度范围内长期过度放牧群落高于原生群落, 这是由放牧胁迫下物种个体间的正相互作用引起的。
王凤琼, 张心怡, 王鑫厅, 姜超, 侯亚丽, 包道日娜 (2025) 羊草草原原生群落羊草种群点格局分析. 生物多样性, 33, 24271. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2024271.
Wang Fengqiong, Zhang Xinyi, Wang Xinting, Jiang Chao, Hou Yali, Bao Daorina (2025) Point pattern analysis of Leymus chinensis population in primary L. chinensis community in the steppe ecosystem. Biodiversity Science, 33, 24271. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2024271.
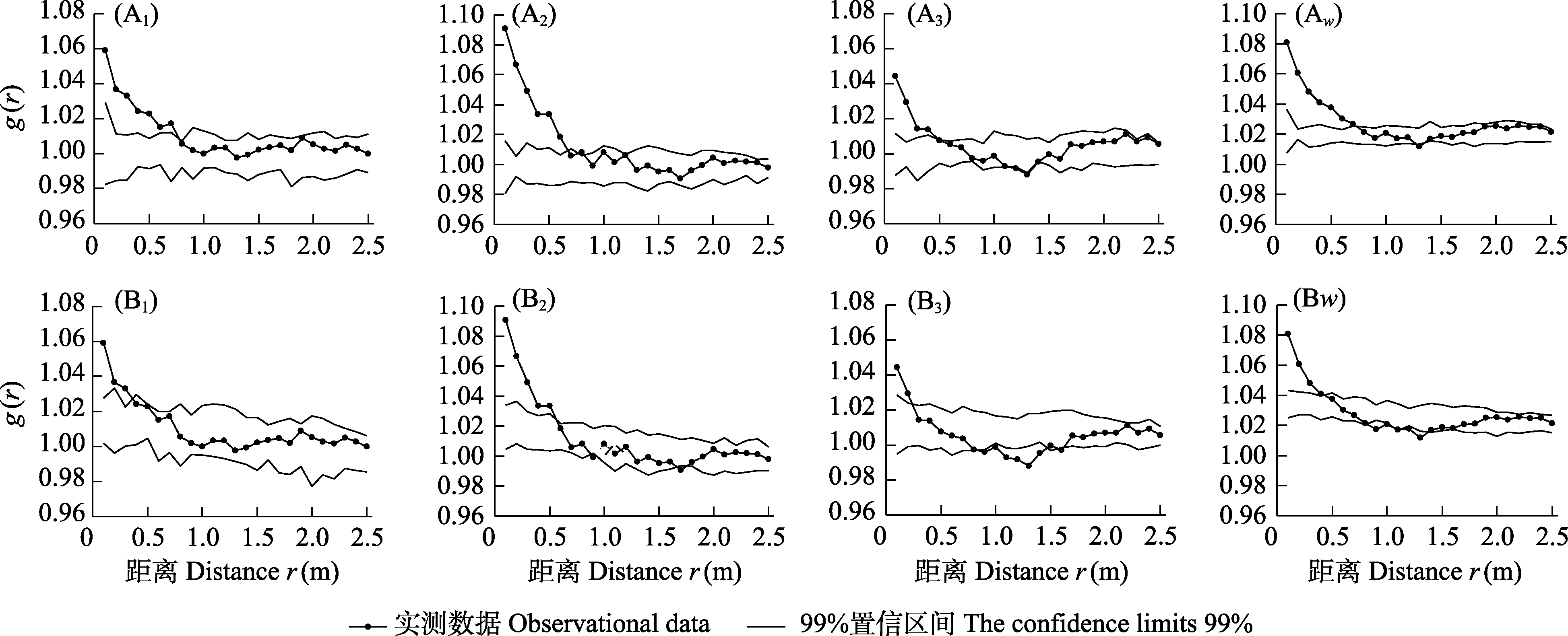
图1 羊草草原原生群落中羊草种群的点格局分析。A: 均质泊松模型; B: 异质泊松模型; 1、2和3分别指每个重复取样; w: 3个重复取样的加权平均点格局。
Fig. 1 Point pattern analysis of Leymus chinensis population in the primary L. chinensis community. A, Homogeneous Poisson process; B, Heterogeneous Poisson process; 1, 2 and 3 refer to each replicate; w, The weighted average point pattern based on three replicates.
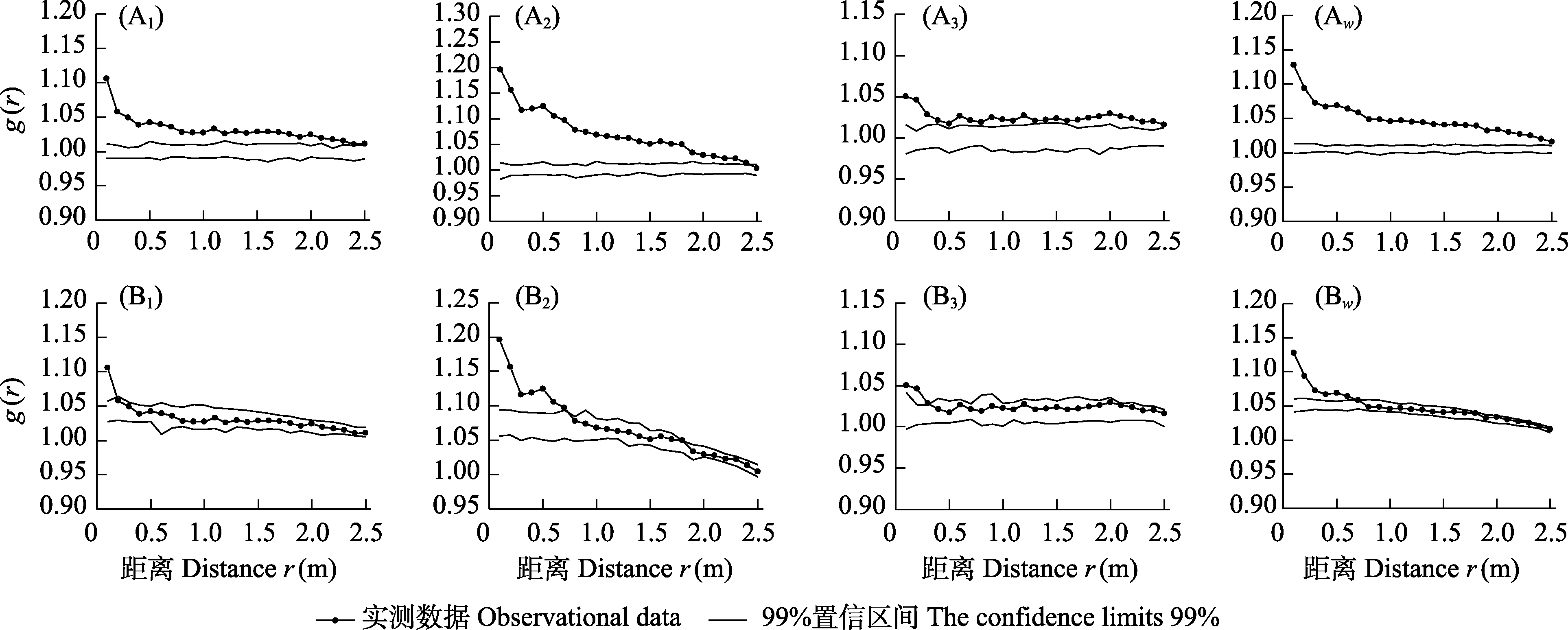
图2 羊草草原放牧群落中羊草种群的点格局分析。A: 均质泊松模型; B: 异质泊松模型; 1、2和3分别指每个重复取样; w: 3个重复取样的加权平均点格局。
Fig. 2 Point pattern analysis of Leymus chinensis population in the grazed L. chinensis community. A, Homogeneous Poisson process; B, Heterogeneous Poisson process; 1, 2 and 3 refer to each replicate; w, The weighted average point pattern based on three replicates.
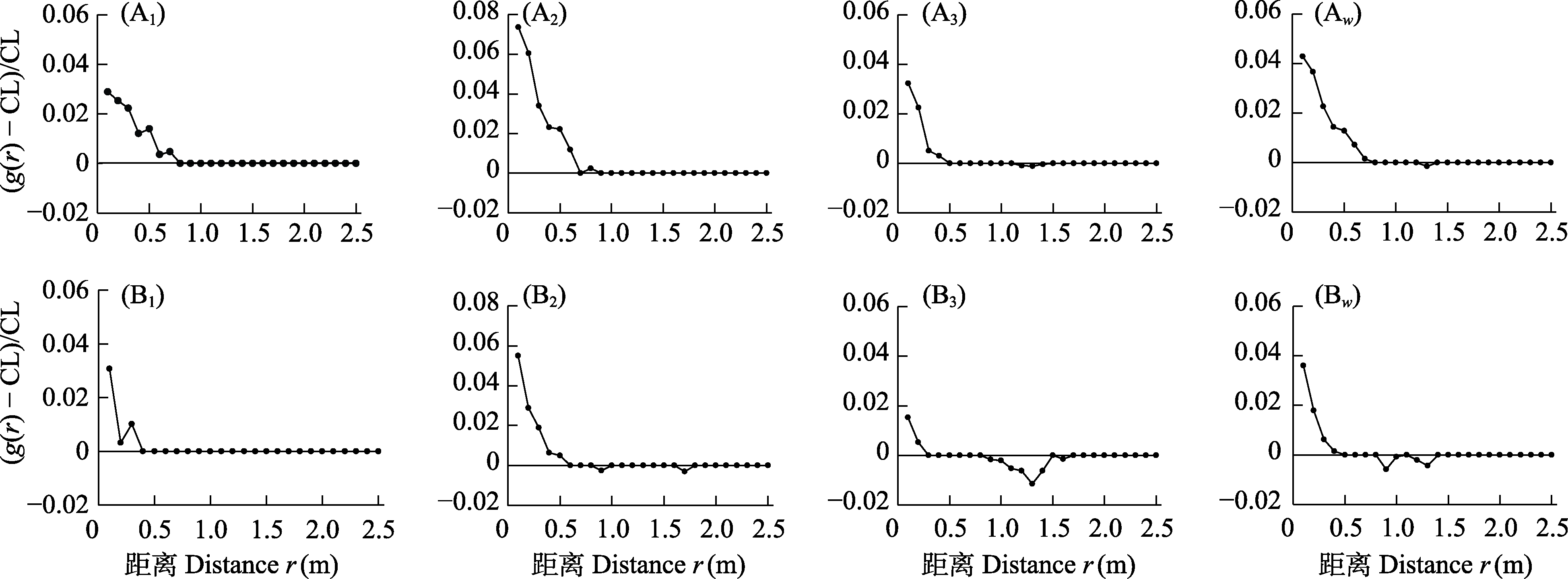
图3 羊草草原原生群落中羊草种群的聚集强度。A: 均质泊松模型; B: 异质泊松模型; 1、2和3分别指每个重复取样; w: 3个重复取样的加权平均数据。
Fig. 3 Aggregation effect of Leymus chinensis population in the primary L. chinensis community. A, Homogeneous Poisson process; B, Heterogeneous Poisson process; 1, 2 and 3 refer to each replicate; w, The weighted average data based on three replicates.
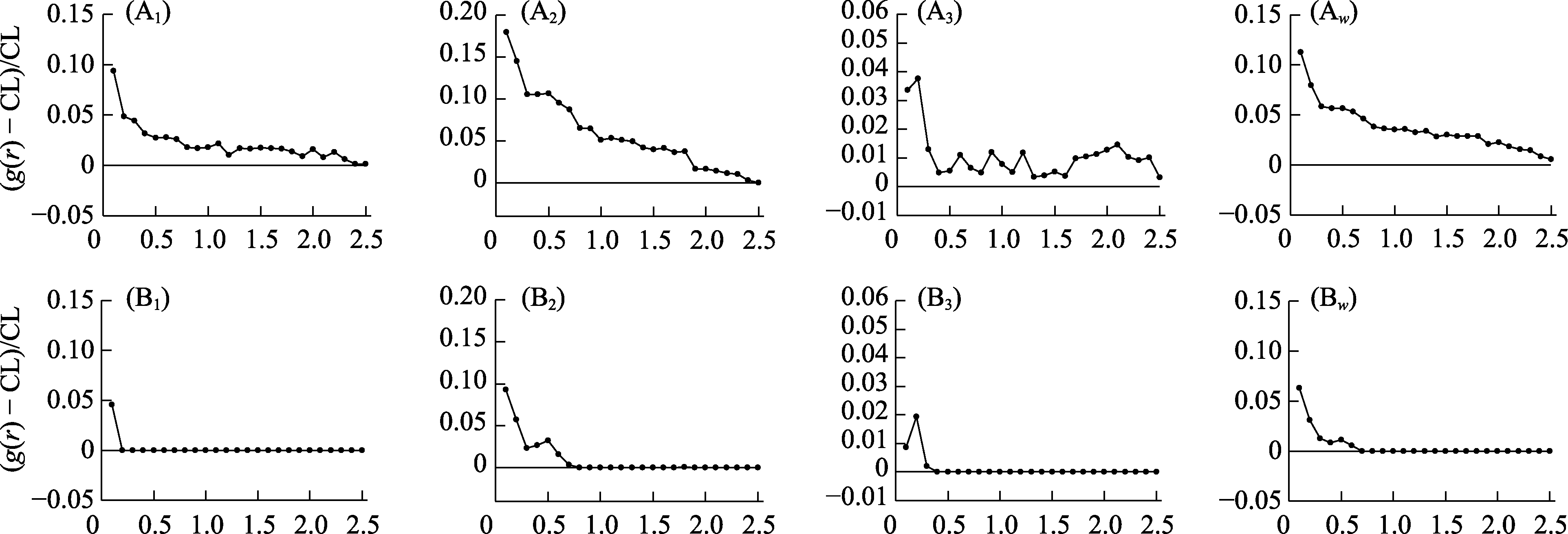
图4 羊草草原放牧群落中羊草种群的聚集强度。A: 均质泊松模型; B: 异质泊松模型; 1、2和3分别指每个重复取样; w: 3个重复取样的加权平均数据。
Fig. 4 Aggregation effect of Leymus chinensis population in the grazed L. chinensis community. A, Homogeneous Poisson process; B, Heterogeneous Poisson process; 1, 2 and 3 refer to each replicate; w, The weighted average data based on three replicates.
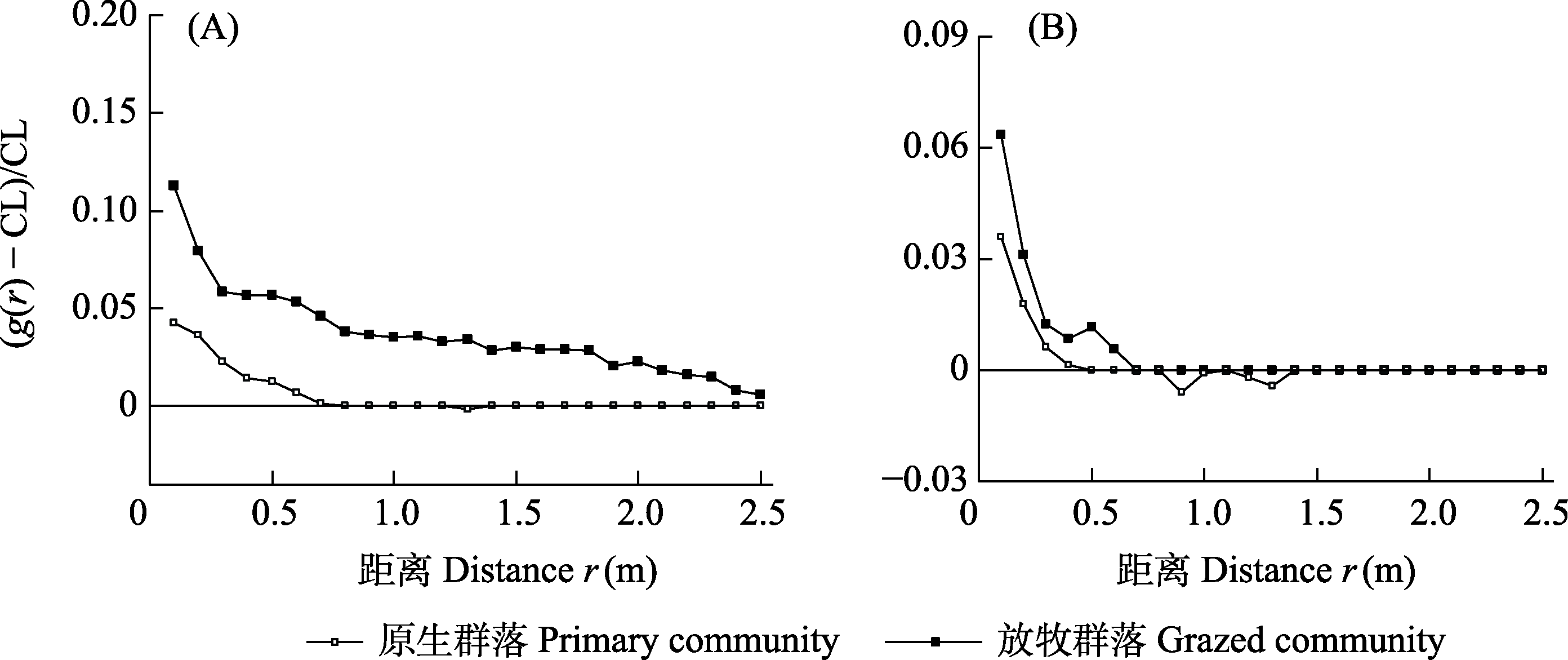
图5 原生群落与放牧群落中羊草种群聚集强度的比较。A: 均质泊松模型; B: 异质泊松模型。数据基于3个重复取样的加权平均获得。
Fig. 5 Aggregation effect of L. chinensis population in the primary vs. grazed community. A, Homogeneous Poisson process; B, Heterogeneous Poisson process. Data are expressed as (g(r) - CL)/CL by the weighted g(r) function analysis.
| [1] | Bai YF, Han XG, Wu JG, Chen ZZ, Li LH (2004) Ecosystem stability and compensatory effects in the Inner Mongolia grassland. Nature, 431, 181-184. |
| [2] | Bertness MD, Callaway RM (1994) Positive interactions in communities. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 9, 191-193. |
| [3] | Callaway RM, Walker LR (1997) Competition and facilitation: A synthetic approach to interactions in plant communities. Ecology, 78, 1958-1965. |
| [4] | Callaway RM (2007) Positive Interactions and Interdependence in Plant Communities. Springer, Dordrecht. |
| [5] | Chen M, Wang YH (1985) The observation on the biological characteristics of Aneurolepidium chinense (Leymus chinensis) under cultural conditions. Research on Grassland Ecosystem, 1, 212-223. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 陈敏, 王艳华 (1985) 栽培条件下羊草生物学特性的观察. 草原生态系统研究, 1, 212-223.] | |
| [6] | Dai JZ, Bai YT, Wei ZJ, Zhang C, Xin XP, Yan YC, Yan RR (2023) Dynamic response of functional traits to fertilization in Leymus chinensis. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 47, 943-953. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[ 代景忠, 白玉婷, 卫智军, 张楚, 辛晓平, 闫玉春, 闫瑞瑞 (2023) 羊草功能性状对施肥的动态响应. 植物生态学报, 47, 943-953.]
DOI |
|
| [7] | Diggle PJ (2013) Statistical Analysis of Spatial and Spatio-Temporal Point Patterns. CRC Press, Boca Raton. |
| [8] | Harms KE, Condit R, Hubbell SP, Foster RB (2001) Habitat associations of trees and shrubs in a 50-ha neotropical forest plot. Journal of Ecology, 89, 947-959. |
| [9] | Hao YB, Wang YF, Cui XY (2010) Drought stress reduces the carbon accumulation of the Leymus chinensis steppe in Inner Mongolia, China. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 34, 898-906. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[ 郝彦宾, 王艳芬, 崔骁勇 (2010) 干旱胁迫降低了内蒙古羊草草原的碳累积. 植物生态学报, 34, 898-906.]
DOI |
|
| [10] | Jia X, Dai XF, Shen ZX, Zhang JY, Wang GX (2011) Facilitation can maintain clustered spatial pattern of plant populations during density-dependent mortality: Insights from a zone-of-influence model. Oikos, 120, 472-480. |
| [11] | Li Y, Li HB, Jiang C, Tai Y, Liu DH, Zhang WH, Wang XT (2021) Point pattern analysis of Leymus chinensis under different grazing intensities in a temperate steppe. Journal of Inner Mongolia University (Natural Science Edition), 52, 417-424. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 李源, 李海兵, 姜超, 邰阳, 刘丹辉, 张维华, 王鑫厅 (2021) 典型草原不同放牧强度下羊草种群点格局分析. 内蒙古大学学报(自然科学版), 52, 417-424.] | |
| [12] | Li Y, Wei JP, Ma HY (2020) Variations of phenotypic characteristics in Leymus chinensis among different provenances. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 40, 1175-1183. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 李阳, 魏继平, 马红媛 (2020) 不同种源羊草表型差异性. 生态学报, 40, 1175-1183.] | |
| [13] | Li YH, Wang W, Liu ZL, Jiang S (2008) Grazing gradient versus restoration succession of Leymus chinensis (Trin.) Tzvel. grassland in Inner Mongolia. Restoration Ecology, 16, 572-583. |
| [14] | Liu ZG, Li ZQ (2004) Fine-scale spatial pattern of Artemisia frigida population under different grazing intensities. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 24, 227-234. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 刘振国, 李镇清 (2004) 不同放牧强度下冷蒿种群小尺度空间格局. 生态学报, 24, 227-234.] | |
| [15] | Luo H, Jiang C, Wang XT, Tai Y, Liu F, Li SY, Bao D, Zhao MZ (2023) Point pattern analysis of Agropyron michnoi in restorative succession of steppe ecosystem. Journal of Inner Mongolia University (Natural Science Edition), 54, 355-361. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 罗海, 姜超, 王鑫厅, 邰阳, 刘芳, 李素英, 包道日娜, 赵明智 (2023) 米氏冰草种群在恢复演替进程中的点格局分析. 内蒙古大学学报(自然科学版), 54, 355-361.] | |
| [16] | Seidler TG, Plotkin JB (2006) Seed dispersal and spatial pattern in tropical trees. PLoS Biology, 4, e344. |
| [17] |
Shen GC, Yu MJ, Hu XS, Mi XC, Ren HB, Sun IF, Ma KP (2009) Species-area relationships explained by the joint effects of dispersal limitation and habitat heterogeneity. Ecology, 90, 3033-3041.
DOI PMID |
| [18] | Sun SX, Wei ZJ, Wu XH, Jiang C, Guo LB (2016) Point pattern and spatial association of primary plant populations in the seasonal regulation of grazing intensity in desert grassland. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 36, 7570-7579. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 孙世贤, 卫智军, 吴新宏, 姜超, 郭利彪 (2016) 不同放牧强度季节调控下荒漠草原主要植物种群点格局及空间关联性. 生态学报, 36, 7570-7579.] | |
| [19] | Tilman D (1994) Competition and biodiversity in spatially structured habitats. Ecology, 75, 2-16. |
| [20] | Velázquez E, Martínez I, Getzin S, Moloney KA, Wiegand T (2016) An evaluation of the state of spatial point pattern analysis in ecology. Ecography, 39, 1042-1055. |
| [21] | Wang W, Liu ZL (1993) Study on the carlorific value dynamics of aboveground parts of Aneurolepidium chinese + Stipa grandis community and its sixteen populations. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 7, 60-76. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 王炜, 刘钟龄 (1993) 羊草草原群落及其主要植物种群地上部分热值动态的研究. 干旱区资源与环境, 7, 60-76.] | |
| [22] | Wang XT, Jiang C, Chi YY, Tai Y, Liang CZ, Li FY, Hou YL (2021) Facilitation in plants shifts along a recovery gradient induced by long-term overgrazing in a temperate steppe community. Journal of Vegetation Science, 32, e13019. |
| [23] |
Wang XT, Jiang C, Jia CZ, Tai Y, Hou YL, Zhang WH (2020) A new digital method of data collection for spatial point pattern analysis in grassland communities. Ecology and Evolution, 10, 7851-7860.
DOI PMID |
| [24] | Wang XT, Chai J, Jiang C, Tai Y, Chi YY, Zhang WH, Liu F, Li SY (2020) Population spatial pattern of Stipa grandis and its response to long-term overgrazing. Biodiversity Science, 28, 128-134. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[ 王鑫厅, 柴静, 姜超, 邰阳, 迟延艳, 张维华, 刘芳, 李素英 (2020) 典型草原大针茅种群空间格局及对长期过度放牧的响应. 生物多样性, 28, 128-134.]
DOI |
|
| [25] | Wang XT, Hou YL, Liu F, Chang Y, Wang W, Liang CZ, Miao BL (2011) Point pattern analysis of dominant populations in a degraded community in Leymus chinensis + Stipa grandis steppe in Inner Mongolia, China. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 35, 1281-1289. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[ 王鑫厅, 侯亚丽, 刘芳, 常英, 王炜, 梁存柱, 苗百岭 (2011) 羊草 + 大针茅草原退化群落优势种群空间点格局分析. 植物生态学报, 35, 1281-1289.]
DOI |
|
| [26] | Wang XT, Jiang C (2018) Spatial Point Pattern Analysis in Typical Steppe under Grazing Disturbance. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 王鑫厅, 姜超 (2018) 典型草原放牧干扰下的点格局研究. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [27] | Wang XT, Liang CZ, Wang W (2014) Balance between facilitation and competition determines spatial patterns in a plant population. Chinese Science Bulletin, 59, 1405-1415. |
| [28] | Wang XT, Zhang WH, Jiang C, Liang CZ (2017) Point pattern analysis under conditions of replicated sampling. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 41, 577-584. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[ 王鑫厅, 张维华, 姜超, 梁存柱 (2017) 重复取样条件下的点格局分析. 植物生态学报, 41, 577-584.]
DOI |
|
| [29] | Wang YF, Yong SP, Liu ZL (1985) Vegetation in Inner Mongolia. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 王义凤, 雍世鹏, 刘钟龄 (1985) 内蒙古植被. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [30] | Wang YH, He XY, Zhou GS (2002) Study on the responses of Leymus chinensis steppe to grazing in Songnen Plain. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 10, 45-49. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[ 王玉辉, 何兴元, 周广胜 (2002) 放牧强度对羊草草原的影响. 草地学报, 10, 45-49.]
DOI |
|
| [31] | Watt AS (1947) Pattern and process in the plant community. Journal of Ecology, 35, 1-22. |
| [32] | Wiegand T, Moloney KA (2014) A Handbook of Spatial Point Pattern Analysis in Ecology. Chapman and Hall/CRC Press, Boca Raton. |
| [33] | Wiegand T, Moloney KA (2004) Rings, circles, and null-models for point pattern analysis in ecology. Oikos, 104, 209-229. |
| [34] |
Xiong M, An HB, Zhao ML, Qiao JR, Zhang F, Zheng JH (2024) Effect of grazing on spatial pattern and niche characteristics of main species in desert steppe. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 32, 1177-1183. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[ 熊梅, 安海波, 赵萌莉, 乔荠瑢, 张峰, 郑佳华(2024) 放牧对荒漠草原主要植物种群空间格局与生态位的影响. 草地学报, 32, 1177-1183.]
DOI |
|
| [35] | Yang C, Hao DY, Yang ZZ (1984) Studies on spatial pattern in Aneurolepidium chinensis steppe community II. 2-dimensional net function interpolation method. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 4, 237-247. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 杨持, 郝敦元, 杨在中 (1984) 羊草草原群落水平格局研究 II. 二维网函数插值法. 生态学报, 4, 345-353.] | |
| [36] | Yang YF, Zhu TC (1989) A preliminary study on seed production of Aneurolepidium chinense population. Acta Phytoecologica et Geobotanica Sinica, 13, 73-78. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 杨允菲, 祝廷成 (1989) 羊草种群种子生产的初步研究. 植物生态学与地植物学学报, 13, 73-78.] | |
| [37] | Zhao YZ (1962) Study on yield formation factors of Leymus chinensis community in the steppe. Journal of Inner Mongolia University (Natural Science Edition), 4, 113-123. |
| [ 赵一之 (1962) 羊草草原产量形成因素的探讨. 内蒙古大学学报(自然科学版), 4, 113-123.] | |
| [38] | Zhao YZ, Zhao LQ, Cao R (2019) Flora Intramongolica. Inner Mongolia People’s Publishing House, Hohhot. (in Chinese) |
| [ 赵一之, 赵利清, 曹瑞 (2019) 内蒙古植物志. 内蒙古人民出版社, 呼和浩特.] | |
| [39] | Zhu TC, Li JD, Yang DC, Jing DW (1979) Observation on flowering rhythm of Leymus chinensis grassland in Northeast China. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 1, 42-44. (in Chinese) |
| [ 祝廷成, 李建东, 杨殿臣, 景鼎五 (1979) 东北羊草草原开花节律的观测. 中国草地学报, 1, 42-44.] |
| [1] | 弋维, 艾鷖, 吴萌, 田黎明, 泽让东科. 青藏高原高寒草甸土壤古菌群落对不同放牧强度的响应[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(1): 24339-. |
| [2] | 赵秋杰, 郭辉军, 孟广涛, 钟明川, 尹俊, 刘倬橙, 李品荣, 陈力, 陶毅, 秋生, 王红, 赵延会. 放牧对蜜蜂的影响及其生态修复建议[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(5): 23037-. |
| [3] | 王一晴, 马子驭, 王刚, 刘炎林, 宋大昭, 刘蓓蓓, 李露, 范新国, 黄巧雯, 李晟. 太行山华北豹袭击家畜的时空特点与管理建议: 以山西省和顺县为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(9): 21510-. |
| [4] | 胡远芳, 李斌强, 梁丹, 李兴权, 刘兰香, 杨家伟, 罗旭. 人为干扰对白腹锦鸡活动节律的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(8): 21484-. |
| [5] | 王雅婷, 张定海, 张志山. 古尔班通古特沙漠固定沙丘上白梭梭和梭梭的空间分布及种间关联性[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(3): 21280-. |
| [6] | 张宇, 王露雨, 向昌林, 段美春, 张志升. 不同放牧强度对赛罕乌拉草原蜘蛛多样性的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(4): 467-476. |
| [7] | 王鑫厅, 柴静, 姜超, 邰阳, 迟延艳, 张维华, 刘芳, 李素英. 典型草原大针茅种群空间格局及对长期过度放牧的响应[J]. 生物多样性, 2020, 28(2): 128-134. |
| [8] | 史晓昀,施小刚,胡强,官天培,付强,张剑,姚蒙,李晟. 四川邛崃山脉雪豹与散放牦牛潜在分布重叠与捕食风险评估[J]. 生物多样性, 2019, 27(9): 951-959. |
| [9] | 陈星, 赵联军, 胡茜茜, 罗春平, 梁春平, 蒋仕伟, 梁磊, 郑维超, 官天培. 基于地形的牲畜空间利用特征及干扰评价——以王朗国家级自然保护区为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2019, 27(6): 630-637. |
| [10] | 张中华, 周华坤, 赵新全, 姚步青, 马真, 董全民, 张振华, 王文颖, 杨元武. 青藏高原高寒草地生物多样性与生态系统功能的关系[J]. 生物多样性, 2018, 26(2): 111-129. |
| [11] | 王国宏, 王小平, 张维康, 李贺, 杜连海, 吴记贵. 北京市自然保护区植物群落对干扰胁迫的抵抗力分析[J]. 生物多样性, 2013, 21(2): 153-162. |
| [12] | 薛睿, 郑淑霞, 白永飞. 不同利用方式和载畜率对内蒙古典型草原群落初级生产力和植物补偿性生长的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2010, 18(3): 300-311. |
| [13] | 高贤明, 马克平, 陈灵芝, 李迪强. 旅游对北京东灵山亚高山草甸物种多样性影响的初步研究[J]. 生物多样性, 2002, 10(2): 189-195. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn