



生物多样性 ›› 2019, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (6): 630-637. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2019122 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2019122
陈星1,赵联军2,胡茜茜1,罗春平2,梁春平2,蒋仕伟2,梁磊1,郑维超3,*( ),官天培1,*(
),官天培1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2019-04-09
接受日期:2019-06-14
出版日期:2019-06-20
发布日期:2019-06-20
通讯作者:
郑维超,官天培
基金资助:
Chen Xing1,Zhao Lianjun2,Hu Xixi1,Luo Chunping2,Liang Chunping2,Jiang Shiwei2,Liang Lei1,Zheng Weichao3,*( ),Guan Tianpei1,*(
),Guan Tianpei1,*( )
)
Received:2019-04-09
Accepted:2019-06-14
Online:2019-06-20
Published:2019-06-20
Contact:
Zheng Weichao,Guan Tianpei
摘要:
地形是栖息地的基本要素, 从地形评价动物的空间利用特征能够掌握动物的分布规律并进行预测。为掌握保护区内牲畜的空间利用特征, 并评价它们对主要保护动物的潜在影响, 我们于2018年5-11月调查了王朗国家级自然保护区内牛和马的分布, 并结合红外相机监测结果及历史监测数据进行了分析和评价。结果表明: (1)虽然两种牲畜均偏好低海拔、低坡度、光照良好(半阳坡、阳坡)、距水源近的栖息地, 但它们在地形利用上存在显著差异; (2)牲畜活动最频繁的三条沟分别是竹根岔右一支沟、竹根岔正沟和大窝凼洋洞沟, 且呈现不同的干扰特征; (3)基于监测数据, 羚牛(Budorcas taxicolor tibetana)可能是保护区内最易受牛马活动威胁的保护动物。红外相机监测结果显示, 羚牛沿海拔分布现状可能是回避牲畜密集区域的结果。基于本研究, 我们建议: (1)保护区重点关注竹根岔(右一支沟、正沟、白沙沟)、大窝凼(洋洞沟、外侧坡)两个核心区的牲畜活动情况, 并尽快针对放牧采取措施。例如, 持续监测重点干扰区域牲畜的种群数量和空间分布趋势。(2)严格限制牲畜继续向高海拔栖息地入侵。(3)管控放牧投盐等干扰的发生频率。(4)加强执法力度, 防止牲畜对保护区带来的干扰持续和扩大, 威胁物种安全。
陈星, 赵联军, 胡茜茜, 罗春平, 梁春平, 蒋仕伟, 梁磊, 郑维超, 官天培 (2019) 基于地形的牲畜空间利用特征及干扰评价——以王朗国家级自然保护区为例. 生物多样性, 27, 630-637. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2019122.
Chen Xing, Zhao Lianjun, Hu Xixi, Luo Chunping, Liang Chunping, Jiang Shiwei, Liang Lei, Zheng Weichao, Guan Tianpei (2019) Impact of livestock terrain utilization patterns on wildlife: A case study of Wanglang National Nature Reserve. Biodiversity Science, 27, 630-637. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2019122.
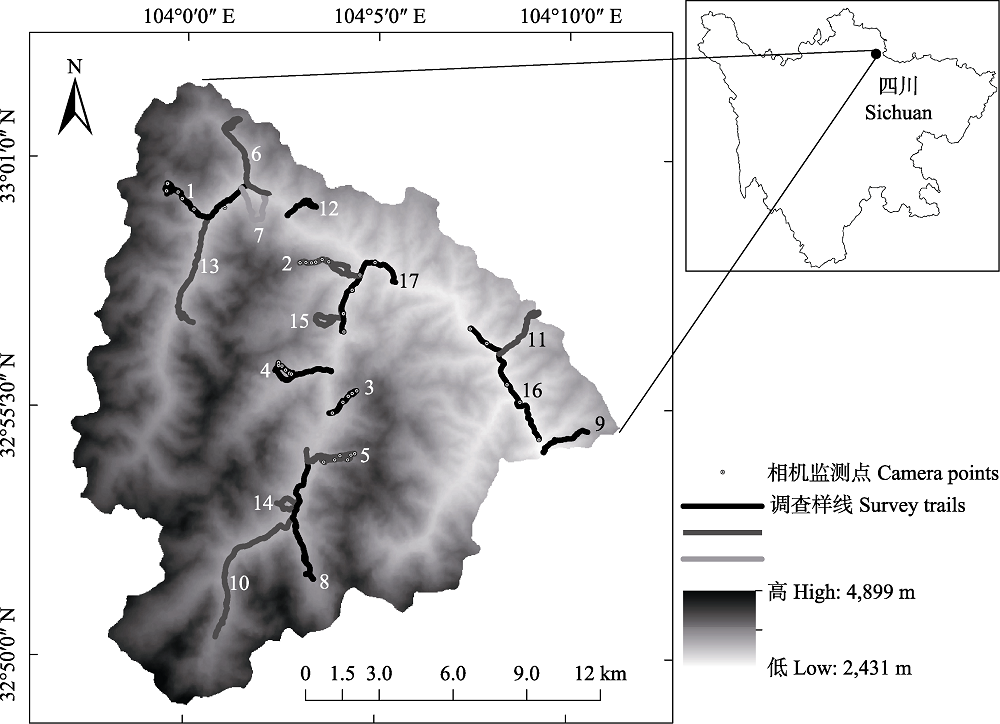
图1 王朗保护区野外调查样线及相机分布。1: 大窝凼右一支沟; 2: 竹根岔右一支沟; 3: 铁板房沟; 4: 竹根岔右二支沟; 5: 大草坪左; 6: 大窝凼洋洞沟; 7: 大窝凼外侧坡; 8: 白沙沟; 9: 豹子沟与解放沟之间的山脊; 10: 竹根岔正沟; 11: 七棵树沟; 12: 天然苗圃沟; 13: 二道坪; 14: 竹根岔老停车场对坡; 15: 竹根岔南沟; 16: 补充样线1; 17: 补充样线2。
Fig. 1 The location of camera and linear transects in Wanglang National Nature Reserve. 1, Youyizhigou of Dawodang; 2, Youyizhigou of Zhugencha; 3, Tiebanfanggou; 4, Youerzhigou of Zhugencha; 5, The left of Dacaoping; 6, Yangdonggou of Dawodang; 7, Waicepo of Dawodang; 8, Baishagou; 9, The ridge between Baozigou and Jiefanggou; 10, Zhenggou of Zhugencha; 11, Qikeshugou; 12, Tianranmiaopugou; 13, Erdaoping; 14, Laotingchechangduipo of Zhugencha; 15, Nangou of Zhugencha; 16, The first supplementary survey trail; 17, The second supplementary survey trail.
| 地形因子 Terrain factor | 牛 Cattle | 马 Horse | 可选择性 Availability |
|---|---|---|---|
| 海拔 Elevation (m) | 2,987.33 ± 7.04 | 3,092.97 ± 6.42 | 3,496.97 ± 3.44 |
| 坡度 Slope (°) | 16.28 ± 0.36 | 16.28 ± 0.28 | 30.57 ± 0.09 |
| 地形起伏度 Terrain roughness index | 28.08 ± 0.56 | 28.23 ± 0.49 | 47.51 ± 0.16 |
| 距水源距离 Distance to water (m) | 187.12 ± 7.21 | 153.48 ± 5.52 | 465.2 ± 2.25 |
| 太阳辐射值 Solar radiation value (WH/m2) | 985,160.94 ± 3,125.05 | 978,059.35 ± 2,252.7 | 947,815.03 ± 880.76 |
| 阴坡 Shady slope (%) | 5.52 | 7.11 | 11.58 |
| 阳坡 Sunny slope (%) | 18.14 | 12.24 | 10.31 |
| 半阴坡 Semi-shady slope (%) | 26.71 | 36.62 | 39.67 |
| 半阳坡 Semi-sunny slope (%) | 49.64 | 44.03 | 38.44 |
表1 牛和马的地形选择偏好
Table 1 Terrain preference of cattle and horse
| 地形因子 Terrain factor | 牛 Cattle | 马 Horse | 可选择性 Availability |
|---|---|---|---|
| 海拔 Elevation (m) | 2,987.33 ± 7.04 | 3,092.97 ± 6.42 | 3,496.97 ± 3.44 |
| 坡度 Slope (°) | 16.28 ± 0.36 | 16.28 ± 0.28 | 30.57 ± 0.09 |
| 地形起伏度 Terrain roughness index | 28.08 ± 0.56 | 28.23 ± 0.49 | 47.51 ± 0.16 |
| 距水源距离 Distance to water (m) | 187.12 ± 7.21 | 153.48 ± 5.52 | 465.2 ± 2.25 |
| 太阳辐射值 Solar radiation value (WH/m2) | 985,160.94 ± 3,125.05 | 978,059.35 ± 2,252.7 | 947,815.03 ± 880.76 |
| 阴坡 Shady slope (%) | 5.52 | 7.11 | 11.58 |
| 阳坡 Sunny slope (%) | 18.14 | 12.24 | 10.31 |
| 半阴坡 Semi-shady slope (%) | 26.71 | 36.62 | 39.67 |
| 半阳坡 Semi-sunny slope (%) | 49.64 | 44.03 | 38.44 |
| 地形因子 Terrain factor | 牛-马 Cattle-horse | 牛-背景值 Cattle-background | 马-背景值 Horse-background |
|---|---|---|---|
| 海拔 Elevation | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| 坡度 Slope | 0.663 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| 地形起伏度 Terrain roughness index | 1.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| 距水源距离 Distance to water | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| 太阳辐射值 Solar radiation value | 0.005 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
表2 牲畜地形选择特征检验
Table 2 Test of terrain utilization of livestock
| 地形因子 Terrain factor | 牛-马 Cattle-horse | 牛-背景值 Cattle-background | 马-背景值 Horse-background |
|---|---|---|---|
| 海拔 Elevation | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| 坡度 Slope | 0.663 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| 地形起伏度 Terrain roughness index | 1.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| 距水源距离 Distance to water | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| 太阳辐射值 Solar radiation value | 0.005 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
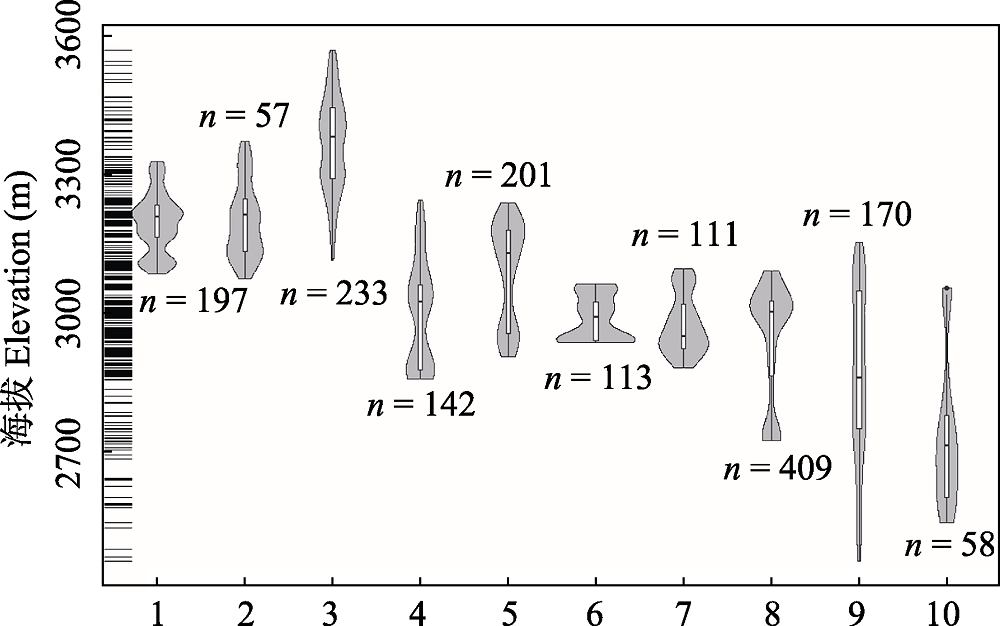
图2 王朗保护区主要沟系牲畜干扰沿海拔分布格局。1: 白沙沟; 2: 竹根岔老停车场对坡; 3: 竹根岔正沟; 4: 大窝凼外侧坡; 5: 大窝凼洋洞沟; 6: 大窝凼右一支沟; 7: 二道坪; 8: 竹根岔右一支沟; 9: 豹子沟与解放沟之间的山脊; 10: 七棵树沟。
Fig. 2 Distribution patterns of free range livestock in different valleys of Wanglang National Nature Reserve along altitudinal gradients. 1, Baishagou; 2, Laotingchechangduipo of Zhugencha; 3, Zhenggou of Zhugencha; 4, Waicepo of Dawodang; 5, Yangdonggou of Dawodang; 6, Youyizhigou of Dawodang; 7, Erdaoping; 8, Youyizhigou of Zhugencha; 9, The ridge between Baozigou and Jiefanggou; 10, Qikeshugou.
| 物种 Species | 牛 Cattle | 马 Horse |
|---|---|---|
| 大熊猫 Ailuropoda melanoleuca | 0.001 | 0.000 |
| 中华斑羚 Naemorhedus griseus | 0.091 | 0.000 |
| 中华鬣羚 Capricornis milneedwardsii | 0.661 | 0.001 |
| 羚牛 Budorcas taxicolor tibetana | 0.314 | 1.000 |
表3 牲畜与野生动物分布海拔差异检验
Table 3 Test of difference on altitudinal distribution between livestock and sympatric wildlife
| 物种 Species | 牛 Cattle | 马 Horse |
|---|---|---|
| 大熊猫 Ailuropoda melanoleuca | 0.001 | 0.000 |
| 中华斑羚 Naemorhedus griseus | 0.091 | 0.000 |
| 中华鬣羚 Capricornis milneedwardsii | 0.661 | 0.001 |
| 羚牛 Budorcas taxicolor tibetana | 0.314 | 1.000 |
| [1] |
Arlettaz R, Nusslé S, Baltic M, Vogel P, Palme R, Jenni- Eiermann S, Patthey P, Genoud M ( 2015) Disturbance of wildlife by outdoor winter recreation: Allostatic stress response and altered activity-energy budgets. Ecological Applications, 25, 1197-1212.
DOI URL |
| [2] | Atickem A, Loe LE ( 2014) Livestock-wildlife conflicts in the Ethiopian highlands: Assessing the dietary and spatial overlap between mountain nyala and cattle. African Journal of Ecology, 52, 343-351. |
| [3] |
Carmel Y, Kadmon R ( 1999) Effects of grazing and topography on long-term vegetation changes in a Mediterranean ecosystem in Israel. Plant Ecology, 145, 243-254.
DOI URL |
| [4] | Cheng CL, Li JQ ( 2006) Economic status and development strategy in local communities surrounding Wanglang Nature Reserve. Journal of Beijing Forestry University (Social Sciences), 5(1), 69-72. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 程春龙, 李俊清 ( 2006) 王朗自然保护区周边社区经济现状和发展对策研究. 北京林业大学学报(社会科学版), 5(1), 69-72.] | |
| [5] |
Craigie ID, Baillie JEM, Balmford A, Carbone C, Collen B, Green RE, Hutton JM ( 2010) Large mammal population declines in Africa’s protected areas. Biological Conservation, 143, 2221-2228.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
Guan TP, Ge BM, Mcshea WJ, Li S, Song YL, Stewart CM ( 2013) Seasonal migration by a large forest ungulate: A study on takin (Budorcas taxicolor) in Sichuan Province, China. European Journal of Wildlife Research, 59, 81-91.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
Guan TP, Wang F, Li S, Mcshea WJ ( 2015) Nature reserve requirements for landscape-dependent ungulates: The case of endangered takin (Budorcas taxicolor) in southwestern China. Biological Conservation, 182, 63-71.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
Hüseyin KF, Seefeldt SS, Sahin B ( 2007) The effects of long-term grazing exclosures on range plants in the Central Anatolian Region of Turkey. Environmental Management, 39, 326-337.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
Khadka KK, James DA ( 2016) Habitat selection by endangered Himalayan musk deer (Moschus chrysogaster) and impacts of livestock grazing in Nepal Himalaya: Implications for conservation. Journal for Nature Conservation, 31, 38-42.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
Kittur S, Sathyakumar S, Rawat GS ( 2010) Assessment of spatial and habitat use overlap between Himalayan tahr and livestock in Kedarnath Wildlife Sanctuary, India. European Journal of Wildlife Research, 56, 195-204.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
Li BB, Pimm SL, Li S, Zhao LJ, Luo CP ( 2017) Free-ranging livestock threaten the long-term survival of giant pandas. Biological Conservation, 216, 18-25.
DOI URL |
| [12] | Li JS, Song YL, Wang XZ, Zeng ZG ( 2003) Spatial pattern of small mammals community diversity in different grazing pressure in montane desert-steppe. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 25, 51-58. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 李俊生, 宋延龄, 王学志, 曾治高 ( 2003) 放牧压力条件下荒漠草原小型哺乳动物群落多样性的空间格局. 生态学报, 25, 51-58.] | |
| [13] | Ma XD, Zhang SJ, Su ZY, Ou YD, Liu G ( 2010) Community structure in relation to microtopography in a montane evergreen broadleaved forest in Chebaling National Nature Reserve. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 30, 5151-5160. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 马旭东, 张苏峻, 苏志尧, 区余端, 刘刚 ( 2010) 车八岭山地常绿阔叶林群落结构特征与微地形条件的关系. 生态学报, 30, 5151-5160.] | |
| [14] |
Madhusudan MD ( 2004) Recovery of wild large herbivores following livestock decline in a tropical Indian wildlife reserve. Journal of Applied Ecology, 41, 858-869.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
Maxwell SL, Fuller RA, Brooks TM, Watson JEM ( 2016) Biodiversity: The ravages of guns, nets and bulldozers. Nature, 536, 143-145.
DOI |
| [16] |
Mishra C, Wieren SEV, Ketner P, Heitkönig IMA, Prins HHT ( 2004) Competition between domestic livestock and wild bharal Pseudois nayaur in the Indian Trans-Himalaya. Journal of Applied Ecology, 41, 344-354.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
Qi D, Zhang SN, Zhang ZJ, Hu YB, Yang XY, Wang HJ, Wei FW ( 2012) Measures of giant panda habitat selection across multiple spatial scales for species conservation. The Journal of Wildlife Management, 76, 1092-1100.
DOI URL |
| [18] | Ran JH, Liu SY, Wang HJ, Sun ZY, Zeng ZY, Liu SC ( 2003) Habitat selection by giant pandas and grazing livestock in the Xiaoxiangling Mountains of Sichuan Province. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 23, 2253-2259. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 冉江洪, 刘少英, 王鸿加, 孙治宇, 曾宗永, 刘世昌 ( 2003) 小相岭大熊猫与放牧家畜的生境选择. 生态学报, 23, 2253-2259.] | |
| [19] | Shen ZH, Jin YX, Zhang XS ( 2000) Gradient analysis of the influence of mountain topography on vegetation pattern. Acta Phytoecologica Sinica, 24, 430-435. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 沈泽昊, 金义兴, 张新时 ( 2000) 地形对亚热带山地景观尺度植被格局影响的梯度分析. 植物生态学报, 24, 430-435.] | |
| [20] | Shi D, Yang W, Jiang SW, Yuan ZW, Lei XH ( 2009) Preliminary research on insects biodiversity in Wanglang National Nature Reserve. Sichuan Journal of Zoology, 28, 691-695. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 师丹, 杨伟, 蒋仕伟, 袁志伟, 雷喜红 ( 2009) 四川王朗国家级自然保护区昆虫生物多样性初步研究. 四川动物, 28, 691-695.] | |
| [21] | Sichuan Forestry Department ( 2015) The Pandas of Sichuan— The 4th Survey Report on Giant Panda in Sichuan Province. Sichuan Science and Technology Press, Chengdu. (in Chinese) |
| [ 四川省林业厅( 2015) 四川的大熊猫——四川省第四次大熊猫调查报告. 四川科技出版社, 成都.] | |
| [22] |
Takala T, Tahvanainen T, Kouki J ( 2014) Grazing promotes bryophyte species richness in semi-natural grasslands. Annales Botanici Fennici, 51, 148-160.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
Wang F, McShea WJ, Wang DJ, Li S ( 2015) Shared resources between giant panda and sympatric wild and domestic mammals. Biological Conservation, 186, 319-325.
DOI URL |
| [24] | Wang X, Hou J, Zhang JD, Bai WK, Huang JY, Zhou SQ, Ouyang ZY ( 2018) Divergent behavioral responses of sympatric species to grazing disturbance. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 38, 129-137. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 王晓, 侯金, 张晋东, 白文科, 黄金燕, 周世强, 欧阳志云 ( 2018) 同域分布的珍稀野生动物对放牧的行为响应策略. 生态学报, 38, 129-137.] | |
| [25] |
Watson JE, Dudley N, Segan DB, Hockings M ( 2014) The performance and potential of protected areas. Nature, 515, 67-73.
DOI |
| [26] |
Webb EL, Stanfield BJ, Jensen ML ( 1999) Effects of topography on rainforest tree community structure and diversity in American Samoa, and implications for frugivore and nectarivore populations. Journal of Biogeography, 26, 887-897.
DOI URL |
| [27] | Wei FW, Zhang ZJ, Hu JC ( 2011) Research advances and perspectives on the ecology of wild giant pandas. Acta Theriologica Sinica, 31, 412-421. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 魏辅文, 张泽钧, 胡锦矗 ( 2011) 野生大熊猫生态学研究进展与前瞻. 兽类学报, 31, 412-421.] | |
| [28] | Wei LY, Wei QZ, Mo ZP, Tong DW ( 2016) Effects of different disturbances on species diversity and productivity of the shrub-grass vegetation on the degraded land in Northwest Guangxi, China. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 23, 288-293. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 韦兰英, 韦启忠, 莫祝平, 童德文 ( 2016) 不同干扰方式对桂西北灌草植被物种多样性和生产力的影响. 水土保持研究, 23, 288-293.] | |
| [29] | Wu Y, Zhang WX, Zhang LQ, Wu J ( 2012) Analysis of correlation between terrain and forest spatial distribution based on DEM. Journal of Northeast Forestry University, 40(11), 96-98. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 吴英, 张万幸, 张丽琼, 伍静 ( 2012) 基于DEM的地形与植被分布关联分析. 东北林业大学学报, 40(11), 96-98.] | |
| [30] | Yu GQ, Kang ZJ, Liu MS, Chen ZF, Deng ZC ( 2018) Preliminary survey using infrared camera reveals fauna and avifauna diversity at Hupingshan National Nature Reserve, Hunan, China. Acta Theriologica Sinica, 38, 104-112. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 于桂清, 康祖杰, 刘美斯, 陈振法, 邓忠次 ( 2018) 利用红外相机对湖南壶瓶山国家级自然保护区兽类和鸟类多样性的初步调查. 兽类学报, 38, 104-112.] | |
| [31] | Zhang RZ ( 2011) Zoogeography of China. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 张荣祖 ( 2011) 中国动物地理. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [32] | Zhao BB, Niu KC, Du GZ ( 2009) The effect of grazing on above-ground biomass allocation of 27 plant species in an alpine meadow plant community in Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 29, 1596-1606. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 赵彬彬, 牛克昌, 杜国祯 ( 2009) 放牧对青藏高原东缘高寒草甸群落27种植物地上生物量分配的影响. 生态学报, 29, 1596-1606.] | |
| [33] | Zhao P, Qu JJ, Xu XY, Tang JN, Han QJ, Xie SB, Wang T, Lai JH ( 2019) Study on the characteristics of sandy alpine grasslands and its relationship between plant distribution and microtopography in the source regions of Yangtze River. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 39, 1030-1040. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 赵鹏, 屈建军, 徐先英, 唐进年, 韩庆杰, 谢胜波, 王涛, 赖俊华 ( 2019) 长江源区沙化高寒草地植被群落特征及其与地形因子的关系. 生态学报, 39, 1030-1040.] |
| [1] | 康燕 干靓 俞霖琳 何晨静 张理卿 吴婧彬. 基于自然解决方案的城市小微栖息地营造与网络构建模式:以上海市长宁区生境花园为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24528-. |
| [2] | 刘咏华, 童光蓉, 余航远, 王宁宁, 任海保, 陈磊, 马克平, 米湘成. 钱江源-百山祖国家公园候选区钱江源园区冠层三维结构及光谱特征对人为干扰的响应[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24174-. |
| [3] | 张明燡, 王晓梅, 郑言鑫, 吴楠, 李东浩, 樊恩源, 李娜, 单秀娟, 于涛, 赵春暖, 李波, 徐帅, 吴玉萍, 任利群. 黄河口典型牡蛎礁分布区资源状况和栖息地功能[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24208-. |
| [4] | 苏红巧, 余得光, 牟昆仑. 国家公园与国土空间规划和用途管制制度衔接路径探讨[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(3): 24570-. |
| [5] | 田志奇, 苏杨. 环境相关国际公约的中国履约模式和在《生物多样性公约》中的应用: 从完成《昆蒙框架》目标和发挥国家公园作用的角度[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(3): 24593-. |
| [6] | 王凤琼, 张心怡, 王鑫厅, 姜超, 侯亚丽, 包道日娜. 羊草草原原生群落羊草种群点格局分析[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24271-. |
| [7] | 弋维, 艾鷖, 吴萌, 田黎明, 泽让东科. 青藏高原高寒草甸土壤古菌群落对不同放牧强度的响应[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(1): 24339-. |
| [8] | 陈自宏, 张翼飞, 陈凯, 陈见影, 徐玲. 高黎贡山南段昆虫病原真菌物种多样性及影响因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(1): 24228-. |
| [9] | 魏诗雨, 宋天骄, 罗佳宜, 张燕, 赵子萱, 茹靖雯, 易华, 林雁冰. 秦岭火地塘针叶林土壤细菌群落的海拔分布格局[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(9): 24180-. |
| [10] | 李蓉姣, 董江海, 郑文芳, 刘入源, 赵立娟, 高瑞贺. 关帝山不同海拔杨桦混交林土壤动物多样性特征及其影响因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(9): 24070-. |
| [11] | 张雨琦, 文君, 张引, 李晟之. 大熊猫国家公园全民公益性评价研究: 基于利益相关者感知视角[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(9): 24240-. |
| [12] | 王秦韵, 张玉泉, 刘浩, 李明, 刘菲, 赵宁, 陈鹏, 齐敦武, 阙品甲. 成都大熊猫繁育研究基地鸟类多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(8): 24066-. |
| [13] | 李佳琪, 冯一迪, 王蕾, 潘盆艳, 刘潇如, 李雪阳, 王怡涵, 王放. 上海城市环境中貉的食性分析及家域范围内的栖息地选择[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(8): 24131-. |
| [14] | 张明军, 王合升, 颜文博, 符运南, 王琦, 曾治高. 海南大田国家级自然保护区小灵猫的活动节律与栖息地选择[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(6): 23420-. |
| [15] | 张瑶, 孙君瑶, 李伟. 雅鲁藏布江流域不同海拔梯度下消落区植被NDVI的时空变化趋势及驱动因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(5): 23432-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn