



生物多样性 ›› 2021, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (10): 1403-1410. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2021114 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2021114
所属专题: 数据论文
收稿日期:2021-03-26
接受日期:2021-06-01
出版日期:2021-10-20
发布日期:2021-10-20
通讯作者:
胡亮
作者简介:* E-mail: huliang_hy@163.com基金资助:Received:2021-03-26
Accepted:2021-06-01
Online:2021-10-20
Published:2021-10-20
Contact:
Liang Hu
摘要:
海洋底栖贝类是海洋底栖无脊椎动物的重要代表。福建平潭岛地处台湾海峡西岸北部, 是中国大陆距台湾岛最近之处, 其海域内的底栖贝类区系对了解台湾海峡及其附近海域的生态环境和底栖生物地理格局具有重要意义。本文基于对2015-2018年间中山大学国土资源与环境系在平潭岛海域采集的3,346号底栖贝类标本的鉴定, 结合已发表文献整理出了平潭岛海域底栖贝类名录, 并梳理了各物种在中国近海的地理分布类型。结果显示, 本研究所采标本分属58科122属161种, 其中47种为平潭岛海域新记录。结合历史文献记录, 平潭岛海域共有底栖贝类98科244属395种。其中93.7%的种类在南海亦有分布, 82.0%的种类在东海有分布, 31.1%的种类在黄渤海有分布, 42.3%的种类在台湾岛东部海域有分布。南海-东海分布型种类占区系总种数的49.9%; 其次为南海-黄渤海分布型(27.6%)和南海-台湾海峡分布型(16.2%)。分布限于台湾海峡及其以北的种类仅占总种数的6.3%。研究结果表明, 平潭岛海域底栖贝类区系具典型的亚热带性质, 暖水性种类和广温性种类占主要优势, 与南海北部和东海大陆沿岸地区的关系密切, 与台湾岛周边海域的联系相对较弱。
胡亮 (2021) 福建平潭岛海域底栖贝类物种多样性及其地理分布. 生物多样性, 29, 1403-1410. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2021114.
Liang Hu (2021) Species diversity and geographical distribution of marine, benthic, shell-bearing mollusks on the coast and adjacent area of Pingtan Island, Fujian Province. Biodiversity Science, 29, 1403-1410. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2021114.
| 类群 Taxa | 多板纲 Polyplacophora | 掘足纲 Scaphopoda | 腹足纲 Gastropoda | 双壳纲 Bivalvia | 总计 Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 科 Family | 3 (3.1) | 3 (3.1) | 51 (52) | 41 (41.8) | 98 |
| 属 Genus | 4 (1.6) | 3 (1.2) | 114 (46.7) | 123 (50.4) | 244 |
| 种 Species | 4 (1.0) | 5 (1.3) | 185 (46.8) | 201 (50.9) | 395 |
表1 福建平潭岛海域底栖贝类多样性(括号内数值为该类群占科/属/种总数的百分比)
Table 1 Marine benthic shells diversity in the coast and adjacent area of Pingtan Island, Fujian Province. Numbers in parentheses represent proportions of each component in the total numbers of families, genera or species (%).
| 类群 Taxa | 多板纲 Polyplacophora | 掘足纲 Scaphopoda | 腹足纲 Gastropoda | 双壳纲 Bivalvia | 总计 Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 科 Family | 3 (3.1) | 3 (3.1) | 51 (52) | 41 (41.8) | 98 |
| 属 Genus | 4 (1.6) | 3 (1.2) | 114 (46.7) | 123 (50.4) | 244 |
| 种 Species | 4 (1.0) | 5 (1.3) | 185 (46.8) | 201 (50.9) | 395 |
| 科 Family | 属 Genera | 种 Species | 科 Family | 属 Genera | 种 Species |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 多板纲 Polyplacophora | (4) | (4) | 50. 鹑螺科 Tonnidae | 1 | 5 |
| 1. 毛肤石鳖科 Acanthochitonidae | 1 | 1 | 51. 马蹄螺科 Trochidae | 6 | 13 |
| 2. 石鳖科 Chitonidae | 2 | 2 | 52. 蝾螺科 Turbinidae | 3 | 5 |
| 3. 锉石鳖科 Ischnochitonidae | 1 | 1 | 53. 塔螺科 Turridae | 8 | 10 |
| 掘足纲 Scaphopoda | (3) | (5) | 54. 锥螺科 Turritellidae | 1 | 3 |
| 4. 角贝科 Dentaliidae | 1 | 3 | 55. 蛇螺科 Vermetidae | 3 | 3 |
| 5. 纤细象牙贝科 Gadilinidae | 1 | 1 | 56. 涡螺科 Volutidae | 2 | 2 |
| 6. 光滑象牙贝科 Laevidentaliidae | 1 | 1 | 57. 衣笠螺科 Xenophoridae | 2 | 2 |
| 腹足纲 Gastropoda | (114) | (185) | 双壳纲 Bivalvia | (123) | (201) |
| 7. 笠贝科 Acmaeidae | 3 | 5 | 58. 水鸭蛤科 Anatinellidae | 1 | 1 |
| 8. 轮螺科 Architectonicidae | 1 | 2 | 59. 不等蛤科 Anomiidae | 2 | 2 |
| 9. 拟沼螺科 Assimineidae | 1 | 1 | 60. 蚶科 Arcidae | 8 | 16 |
| 10. 滩栖螺科 Batillariidae | 1 | 3 | 61. 鸟蛤科 Cardiidae | 4 | 7 |
| 11. 蛾螺科 Buccinidae | 2 | 3 | 62. 心蛤科 Carditidae | 1 | 2 |
| 12. 蛙螺科 Bursidae | 1 | 2 | 63. 猿头蛤科 Chamidae | 2 | 3 |
| 13. 丽口螺科 Calliostomatidae | 2 | 2 | 64. 篮蛤科 Corbulidae | 2 | 3 |
| 14. 帆螺科 Calyptraeidae | 2 | 2 | 65. 帽蚶科 Cucullaeidae | 1 | 1 |
| 15. 衲螺科 Cancellariidae | 2 | 2 | 66. 斧蛤科 Donacidae | 1 | 3 |
| 16. 冠螺科 Cassidae | 2 | 3 | 67. 开腹蛤科 Gastrochaenidae | 1 | 1 |
| 17. 蟹守螺科 Cerithiidae | 1 | 1 | 68. 绿螂科 Glauconomidae | 1 | 1 |
| 18. 唇齿螺科 Chilodontaidae | 1 | 1 | 69. 蚶蜊科 Glycymerididae | 1 | 1 |
| 19. 核螺科 Columbellidae | 1 | 3 | 70. 曲蛎科 Gryphaeidae | 1 | 1 |
| 20. 盒螺科 Cylichnidae | 1 | 1 | 71. 钳蛤科 Isognomonidae | 1 | 1 |
| 21. 嵌线螺科 Cymatiidae | 3 | 3 | 72. 拉沙蛤科 Lasaeidae | 1 | 1 |
| 22. 宝贝科 Cypraeidae | 3 | 4 | 73. 鸭嘴蛤科 Laternulidae | 1 | 2 |
| 23. 梯螺科 Epitoniidae | 3 | 4 | 74. 锉蛤科 Limidae | 1 | 1 |
| 24. 光螺科 Eulimidae | 2 | 2 | 75. 满月蛤科 Lucinidae | 1 | 1 |
| 25. 细带螺科 Fasciolariidae | 1 | 2 | 76. 蛤蜊科 Mactridae | 5 | 13 |
| 26. 琵琶螺科 Ficidae | 1 | 2 | 77. 中带蛤科 Mesodesmatidae | 1 | 1 |
| 27. 钥孔?科 Fissurellidae | 2 | 3 | 78. 贻贝科 Mytilidae | 10 | 17 |
| 28. 鲍科 Haliotidae | 1 | 1 | 79. 细纹蚶科 Noetiidae | 3 | 3 |
| 29. 阿地螺科 Haminoeidae | 1 | 1 | 80. 牡蛎科 Ostreidae | 6 | 9 |
| 30. 竖琴螺科 Harpidae | 1 | 1 | 81. 扇贝科 Pectinidae | 7 | 10 |
| 31. 滨螺科 Littorinidae | 4 | 4 | 82. 刀蛏科 Pharidae | 3 | 5 |
| 32. 盔螺科 Melongenidae | 2 | 3 | 83. 海笋科 Pholadidae | 4 | 6 |
| 33. 笔螺科 Mitridae | 2 | 2 | 84. 江珧科 Pinnidae | 2 | 3 |
| 34. 骨螺科 Muricidae | 8 | 16 | 85. 海月蛤科 Placunidae | 1 | 1 |
| 35. 花帽贝科 Nacellidae | 1 | 3 | 86. 襞蛤科 Plicatulidae | 1 | 1 |
| 36. 织纹螺科 Nassariidae | 1 | 13 | 87. 紫云蛤科 Psammobiidae | 3 | 7 |
| 37. 玉螺科 Naticidae | 10 | 16 | 88. 珍珠贝科 Pteriidae | 2 | 5 |
| 38. 蜒螺科 Neritidae | 1 | 4 | 89. 双带蛤科 Semelidae | 2 | 3 |
| 39. 榧螺科 Olividae | 3 | 4 | 90. 截蛏科 Solecurtidae | 2 | 2 |
| 40. 梭螺科 Ovulidae | 1 | 2 | 91. 竹蛏科 Solenidae | 1 | 6 |
| 41. 帽贝科 Patellidae | 1 | 1 | 92. 海菊蛤科 Spondylidae | 1 | 2 |
| 42. 皮山螺科 Pisaniidae | 3 | 3 | 93. 樱蛤科 Tellinidae | 14 | 16 |
| 43. 汇螺科 Potamididae | 2 | 3 | 94. 船蛆科 Teredinidae | 1 | 1 |
| 44. 西美螺科 Pseudomelatomidae | 1 | 1 | 95. 色雷西蛤科 Thraciidae | 1 | 1 |
| 45. 小塔螺科 Pyramidellidae | 1 | 2 | 96. 棱蛤科 Trapezidae | 1 | 2 |
| 46. 菊花螺科 Siphonariidae | 1 | 3 | 97. 蹄蛤科 Ungulinidae | 1 | 1 |
| 47. 小阳螺科 Solariellidae | 2 | 2 | 98. 帘蛤科 Veneridae | 20 | 38 |
| 48. 凤螺科 Strombidae | 1 | 1 | 总计 Total | 244 | 395 |
| 49. 笋螺科 Terebridae | 4 | 5 |
表2 福建平潭岛海域底栖贝类的分类学组成(括号内数值为该纲下的属/种总数)
Table 2 Taxonomic composition of marine benthic shells in the coast and adjacent area of Pingtan Island, Fujian Province. Numbers in parentheses represent the total numbers of genera or species in classes.
| 科 Family | 属 Genera | 种 Species | 科 Family | 属 Genera | 种 Species |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 多板纲 Polyplacophora | (4) | (4) | 50. 鹑螺科 Tonnidae | 1 | 5 |
| 1. 毛肤石鳖科 Acanthochitonidae | 1 | 1 | 51. 马蹄螺科 Trochidae | 6 | 13 |
| 2. 石鳖科 Chitonidae | 2 | 2 | 52. 蝾螺科 Turbinidae | 3 | 5 |
| 3. 锉石鳖科 Ischnochitonidae | 1 | 1 | 53. 塔螺科 Turridae | 8 | 10 |
| 掘足纲 Scaphopoda | (3) | (5) | 54. 锥螺科 Turritellidae | 1 | 3 |
| 4. 角贝科 Dentaliidae | 1 | 3 | 55. 蛇螺科 Vermetidae | 3 | 3 |
| 5. 纤细象牙贝科 Gadilinidae | 1 | 1 | 56. 涡螺科 Volutidae | 2 | 2 |
| 6. 光滑象牙贝科 Laevidentaliidae | 1 | 1 | 57. 衣笠螺科 Xenophoridae | 2 | 2 |
| 腹足纲 Gastropoda | (114) | (185) | 双壳纲 Bivalvia | (123) | (201) |
| 7. 笠贝科 Acmaeidae | 3 | 5 | 58. 水鸭蛤科 Anatinellidae | 1 | 1 |
| 8. 轮螺科 Architectonicidae | 1 | 2 | 59. 不等蛤科 Anomiidae | 2 | 2 |
| 9. 拟沼螺科 Assimineidae | 1 | 1 | 60. 蚶科 Arcidae | 8 | 16 |
| 10. 滩栖螺科 Batillariidae | 1 | 3 | 61. 鸟蛤科 Cardiidae | 4 | 7 |
| 11. 蛾螺科 Buccinidae | 2 | 3 | 62. 心蛤科 Carditidae | 1 | 2 |
| 12. 蛙螺科 Bursidae | 1 | 2 | 63. 猿头蛤科 Chamidae | 2 | 3 |
| 13. 丽口螺科 Calliostomatidae | 2 | 2 | 64. 篮蛤科 Corbulidae | 2 | 3 |
| 14. 帆螺科 Calyptraeidae | 2 | 2 | 65. 帽蚶科 Cucullaeidae | 1 | 1 |
| 15. 衲螺科 Cancellariidae | 2 | 2 | 66. 斧蛤科 Donacidae | 1 | 3 |
| 16. 冠螺科 Cassidae | 2 | 3 | 67. 开腹蛤科 Gastrochaenidae | 1 | 1 |
| 17. 蟹守螺科 Cerithiidae | 1 | 1 | 68. 绿螂科 Glauconomidae | 1 | 1 |
| 18. 唇齿螺科 Chilodontaidae | 1 | 1 | 69. 蚶蜊科 Glycymerididae | 1 | 1 |
| 19. 核螺科 Columbellidae | 1 | 3 | 70. 曲蛎科 Gryphaeidae | 1 | 1 |
| 20. 盒螺科 Cylichnidae | 1 | 1 | 71. 钳蛤科 Isognomonidae | 1 | 1 |
| 21. 嵌线螺科 Cymatiidae | 3 | 3 | 72. 拉沙蛤科 Lasaeidae | 1 | 1 |
| 22. 宝贝科 Cypraeidae | 3 | 4 | 73. 鸭嘴蛤科 Laternulidae | 1 | 2 |
| 23. 梯螺科 Epitoniidae | 3 | 4 | 74. 锉蛤科 Limidae | 1 | 1 |
| 24. 光螺科 Eulimidae | 2 | 2 | 75. 满月蛤科 Lucinidae | 1 | 1 |
| 25. 细带螺科 Fasciolariidae | 1 | 2 | 76. 蛤蜊科 Mactridae | 5 | 13 |
| 26. 琵琶螺科 Ficidae | 1 | 2 | 77. 中带蛤科 Mesodesmatidae | 1 | 1 |
| 27. 钥孔?科 Fissurellidae | 2 | 3 | 78. 贻贝科 Mytilidae | 10 | 17 |
| 28. 鲍科 Haliotidae | 1 | 1 | 79. 细纹蚶科 Noetiidae | 3 | 3 |
| 29. 阿地螺科 Haminoeidae | 1 | 1 | 80. 牡蛎科 Ostreidae | 6 | 9 |
| 30. 竖琴螺科 Harpidae | 1 | 1 | 81. 扇贝科 Pectinidae | 7 | 10 |
| 31. 滨螺科 Littorinidae | 4 | 4 | 82. 刀蛏科 Pharidae | 3 | 5 |
| 32. 盔螺科 Melongenidae | 2 | 3 | 83. 海笋科 Pholadidae | 4 | 6 |
| 33. 笔螺科 Mitridae | 2 | 2 | 84. 江珧科 Pinnidae | 2 | 3 |
| 34. 骨螺科 Muricidae | 8 | 16 | 85. 海月蛤科 Placunidae | 1 | 1 |
| 35. 花帽贝科 Nacellidae | 1 | 3 | 86. 襞蛤科 Plicatulidae | 1 | 1 |
| 36. 织纹螺科 Nassariidae | 1 | 13 | 87. 紫云蛤科 Psammobiidae | 3 | 7 |
| 37. 玉螺科 Naticidae | 10 | 16 | 88. 珍珠贝科 Pteriidae | 2 | 5 |
| 38. 蜒螺科 Neritidae | 1 | 4 | 89. 双带蛤科 Semelidae | 2 | 3 |
| 39. 榧螺科 Olividae | 3 | 4 | 90. 截蛏科 Solecurtidae | 2 | 2 |
| 40. 梭螺科 Ovulidae | 1 | 2 | 91. 竹蛏科 Solenidae | 1 | 6 |
| 41. 帽贝科 Patellidae | 1 | 1 | 92. 海菊蛤科 Spondylidae | 1 | 2 |
| 42. 皮山螺科 Pisaniidae | 3 | 3 | 93. 樱蛤科 Tellinidae | 14 | 16 |
| 43. 汇螺科 Potamididae | 2 | 3 | 94. 船蛆科 Teredinidae | 1 | 1 |
| 44. 西美螺科 Pseudomelatomidae | 1 | 1 | 95. 色雷西蛤科 Thraciidae | 1 | 1 |
| 45. 小塔螺科 Pyramidellidae | 1 | 2 | 96. 棱蛤科 Trapezidae | 1 | 2 |
| 46. 菊花螺科 Siphonariidae | 1 | 3 | 97. 蹄蛤科 Ungulinidae | 1 | 1 |
| 47. 小阳螺科 Solariellidae | 2 | 2 | 98. 帘蛤科 Veneridae | 20 | 38 |
| 48. 凤螺科 Strombidae | 1 | 1 | 总计 Total | 244 | 395 |
| 49. 笋螺科 Terebridae | 4 | 5 |
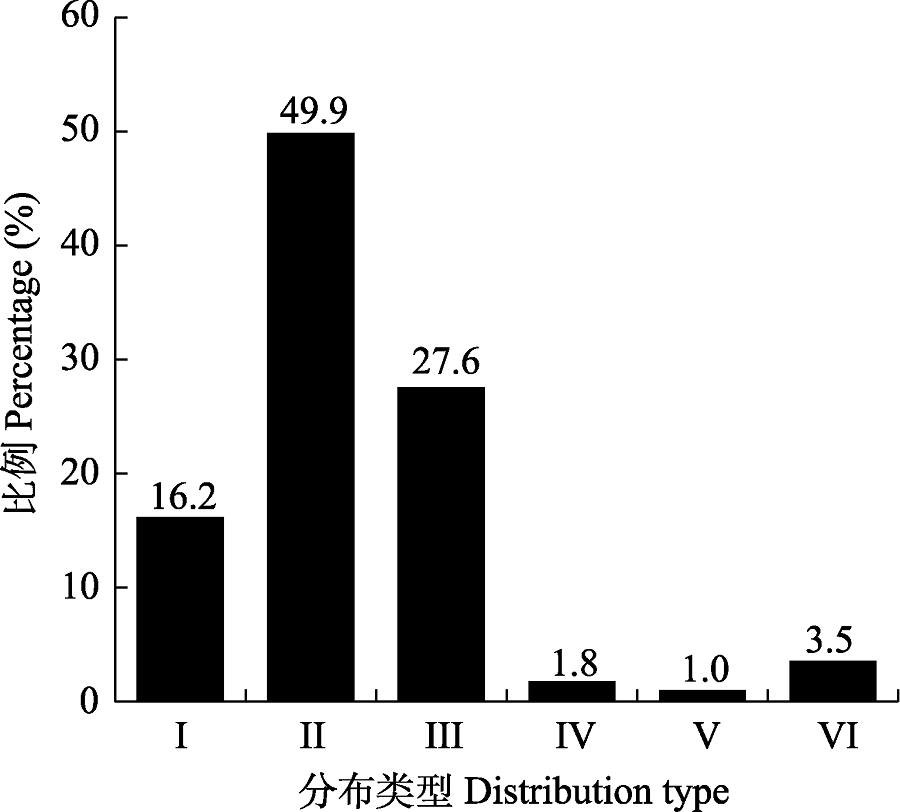
图1 平潭岛海域底栖贝类的地理分布类型。I: 南海-台湾海峡分布; II: 南海-东海分布; III: 南海-黄渤海分布; IV: 台湾海峡分布; V: 台湾海峡-东海分布; VI: 台湾海峡-黄渤海分布。
Fig. 1 Geographical distribution types of marine benthic shell species recorded from Pingtan Island and its adjacent waters. I, South China Sea-Taiwan Strait; II, South China Sea-East China Sea; III, South China Sea-Yellow and Bohai seas; IV, Taiwan Strait; V, Taiwan Strait-East China Sea; VI, Taiwan Strait-Yellow and Bohai seas.
| 类群 Taxa | 南澳及南澎列岛 Nan'ao & Nanpeng Islands | 厦门湾 Xiamen Bay | 洞头及南麂列岛 Dongtou & Nanji Islands | 澎湖列岛 Penghu Islands | 台湾岛东北部 Northeastern Taiwan |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 多板纲 Polyplacophora | 4 (1.5) | 4 (1.8) | 4 (1.7) | 2 (1.3) | 4 (3.4) |
| 掘足纲 Scaphopoda | 2 (0.7) | 3 (1.3) | 2 (0.8) | 0 | 0 |
| 腹足纲 Gastropoda | 121 (45.3) | 106 (46.5) | 123 (50.8) | 90 (58.1) | 77 (65.8) |
| 双壳纲 Bivalvia | 140 (52.4) | 115 (50.4) | 113 (46.7) | 63 (40.6) | 36 (30.8) |
| 合计 Total | 267 | 228 | 242 | 155 | 117 |
表3 福建平潭岛海域与相邻地点的海洋底栖贝类共有种组成(括号内数值为该类群占共有种总数的百分比)
Table 3 Composition of marine benthic shells shared by Pingtan Island, Fujian Province and adjacent sites. Numbers in parentheses represent proportions of each component in the total numbers of shared species (%).
| 类群 Taxa | 南澳及南澎列岛 Nan'ao & Nanpeng Islands | 厦门湾 Xiamen Bay | 洞头及南麂列岛 Dongtou & Nanji Islands | 澎湖列岛 Penghu Islands | 台湾岛东北部 Northeastern Taiwan |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 多板纲 Polyplacophora | 4 (1.5) | 4 (1.8) | 4 (1.7) | 2 (1.3) | 4 (3.4) |
| 掘足纲 Scaphopoda | 2 (0.7) | 3 (1.3) | 2 (0.8) | 0 | 0 |
| 腹足纲 Gastropoda | 121 (45.3) | 106 (46.5) | 123 (50.8) | 90 (58.1) | 77 (65.8) |
| 双壳纲 Bivalvia | 140 (52.4) | 115 (50.4) | 113 (46.7) | 63 (40.6) | 36 (30.8) |
| 合计 Total | 267 | 228 | 242 | 155 | 117 |
| [1] | Bernard FR, Cai YY, Morton B (1993) Catalogue of the Living Marine Bivalve Molluscs of China. Hong Kong University Press, Hong Kong. |
| [2] | Cai YY (1960) A preliminary investigation on the marine molluscan fauna of Pingtan Island, Fujian. Journal of Jimei Fisheries, 1(2), 1-8. (in Chinese) |
| [蔡英亚 (1960) 福建平潭岛海产软体动物的初步调查. 集水学报, 1(2), 1-8.] | |
| [3] | Cai YY (1966) A preliminary investigation on the Cladocera shells in the coast of Fujian. Chinese Journal of Zoology, 8(2), 76-80. (in Chinese) |
| [蔡英亚 (1966) 福建沿海瓣鳃纲贝类的初步调查. 动物学杂志, 8(2), 76-80.] | |
| [4] | Chen CS (1992) Preliminary investigation on benthic ecology in intertidal zone of Haitan Island. Journal of Oceanography in Taiwan Strait, 11, 294-300. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [陈昌生 (1992) 海坛岛潮间带底栖生态的初步调查. 台湾海峡, 11, 294-300.] | |
| [5] | Chen ZY (2012) Study on the Taxonomy of Pyramidellidae of China Seas. PhD dissertation, Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Qingdao, Shandong. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [陈志云 (2012) 中国海小塔螺科Pyramidellidae系统分类学研究. 博士学位论文, 中国科学院海洋研究所, 山东青岛.] | |
| [6] |
Crame JA (2000) Evolution of taxonomic diversity gradients in the marine realm: Evidence from the composition of recent bivalve faunas. Paleobiology, 26, 188-214.
DOI URL |
| [7] | Dong ZZ (2002) Fauna Sinica, Invertebrata, Vol. 29. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [董正之 (2002) 中国动物志·无脊椎动物, 第二十九卷. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [8] | Editorial Committee of China's Bays (1994) China's Bays, Vol. 7. Bays of Northern Fujian. China Ocean Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [中国海湾志编纂委员会 (1994) 中国海湾志, 第7分册 (福建省北部海湾). 海洋出版社, 北京.] | |
| [9] | Editorial Committee of Physical Geography of China (1979) Physical Geography of China:Marine Geography. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [中国自然地理编辑委员会 (1979) 中国自然地理:海洋地理. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [10] | Editorial Committee of Pingtan Local Records (2000) Pingtan Local Records. China Local Records Publishing House, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [平潭县地方志编纂委员会(2000) 平潭县志. 方志出版社, 北京.] | |
| [11] | He LJ, Ren HM, Xu SS, Zhang J (2021) Phylogeographic pattern of marine fauna in the Indo-West Pacific. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 52, 468-486. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [何利军, 任慧敏, 许莎莎, 张经 (2021) 印度洋-西太平洋海洋动物谱系地理演化格局. 海洋与湖沼, 52, 468-486.] | |
| [12] | Higo S, Callomon P, Goto Y (1999) Catalogue and Bibliography of the Marine Shell-Bearing Mollusca of Japan. Elle Scientific Publications, Osaka. |
| [13] | Hu CH, Tao HJ (1995) Shells of Taiwan Illustrated in Color. Museum of Natural Science, Taizhong. (in Chinese) |
| [胡忠恒, 陶锡珍 (1995) 台湾现生贝类彩色图鉴. 自然科学博物馆, 台中.] | |
| [14] | Huang YQ, Li RG, Jiang JX (2009) Biodiversity and distribution of mollusc around the waters of islands, Fujian Province. Marine Sciences, 33(10), 77-83. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [黄雅琴, 李荣冠, 江锦祥 (2009) 福建海岛水域软体动物多样性与分布. 海洋科学, 33(10), 77-83.] | |
| [15] | Huang ZG (2006) Diversity of Species in Xiamen Bay, China. China Ocean Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [黄宗国 (2006) 厦门湾物种多样性. 海洋出版社, 北京.] | |
| [16] | Huang ZG, Lin M (2012) The Living Species in China's Seas, Vol. 1. China Ocean Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [黄宗国, 林茂 (2012) 中国海洋物种多样性(上册). 海洋出版社, 北京.] | |
| [17] | Lai KY, Ouyang SC (1996) Molluscan fauna of the Penghu Islands (Pescadores). Annual Taiwan Museum, 39, 315-385. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [赖景阳, 欧阳盛芝 (1996) 澎湖群岛的贝类调查报告. 台湾省立博物馆年刊, 39, 315-385.] | |
| [18] | Li BQ (2007) Taxonomic and Faunal Study of Turridae (Gastropoda: Neogastropoda) of the China Seas. PhD dissertation, Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Qingdao, Shandong. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [李宝泉 (2007) 中国海塔螺科系统分类学和动物地理学研究. 博士学位论文, 中国科学院海洋研究所, 山东青岛.] | |
| [19] | Li FL, Lin MY (2016) Fauna Sinica, Invertebrata, Vol. 55. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [李凤兰, 林民玉 (2016) 中国动物志·无脊椎动物, 第五十五卷. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [20] | Li RG (2010) Macrobenthos in Fujian Coastal Zone and Western Taiwan Strait. China Ocean Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [李荣冠 (2010) 福建海岸带与台湾海峡西部海域大型底栖生物. 海洋出版社, 北京.] | |
| [21] | Li RG, Wang JJ, Huang YQ, Lin JH, Lin RS (2017) Intertidal Macrobenthos in Coastal Wetlands, Fujian Province. China Ocean Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [李荣冠, 王建军, 黄雅琴, 林俊辉, 林如山 (2017) 福建滨海湿地潮间带大型底栖生物. 海洋出版社, 北京.] | |
| [22] |
Liu JY (2013) Status of marine biodiversity of the China Seas. PLoS ONE, 8, e50719.
DOI URL |
| [23] | Lü XM, Fang SH, Zhang YP, Wu PR (2008) Community structure and secondary production of macrobenthos in the intertidal zone of Haitan Strait, Fujian Province. Acta Zoologica Sinica, 54, 428-435. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [吕小梅, 方少华, 张跃平, 吴萍茹 (2008) 福建海坛海峡潮间带大型底栖动物群落结构及次级生产力. 动物学报, 54, 428-435.] | |
| [24] | Tchang S, Hwang HM (1964) On the Chinese species of Solenidae. Acta Zoologica Sinica, 16, 193-209. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [张玺, 黄修明 (1964) 中国海竹蛏科的研究. 动物学报, 16, 193-209.] | |
| [25] | Tchang S, Tsi CY (1962) Economic Fauna of China:Marine Molluscs. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [张玺, 齐钟彦(1962) 中国经济动物志:海产软体动物. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [26] | Tchang S, Tsi CY, Zhang FS, Ma ST (1963) A preliminary study of the demarcation of marine molluscan faunal regions of China and its adjacent waters. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 5, 124-138. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [张玺, 齐钟彦, 张福绥, 马绣同 (1963) 中国海软体动物区系区划的初步研究. 海洋与湖沼, 5, 124-138.] | |
| [27] | Wang FP, Huang YM (1993) Studies on the Prosobranchia fauna of Fujian coast. Journal of Fujian Normal University (Natural Science), 9(4), 85-95. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王方平, 黄一鸣 (1993) 福建沿海前鳃类区系的研究. 福建师范大学学报(自然科学版), 9(4), 85-95.] | |
| [28] | Wang FP, Huang YM (1994) Studies on the bivalvia fauna from the Fujian coast. Journal of Fujian Normal University (Natural Science), 10(3), 81-91. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王方平, 黄一鸣 (1994) 福建沿海双壳类区系的研究. 福建师范大学学报(自然科学版), 10(3), 81-91.] | |
| [29] | Wang Y, Liu RY, Su JL (2013) Ocean Geography of China. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [王颖, 刘瑞玉, 苏纪兰 (2013) 中国海洋地理. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [30] | Wang ZR (1997) Fauna Sinica, Mollusca, Bivalvia, Mytiloida. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [王祯瑞 (1997) 中国动物志·软体动物门·双壳纲·贻贝目. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [31] | Wu WL, Jian SJ (2008) The Mollusks of Taoyuan, Hsinchu, and Miaoli Area, Taiwan. Taiwan Forestry Bureau, Taipei. (in Chinese) |
| [巫文隆, [简士杰 (2008) 桃竹苗地区贝类研究图志. 台湾“农业委员会林务局”, 台北.] | |
| [32] | Xu FS (1997) Bivalve Molluscs of China Sea. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [徐凤山 (1997) 中国海双壳类软体动物. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [33] | Xu FS (2012) Fauna Sinica, Invertebrata, Vol. 48. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [徐凤山(2012) 中国动物志·无脊椎动物, 第四十八卷. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [34] | Xu FS, Zhang JL (2018) Fauna Sinica, Invertebrata, Vol. 57. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [徐凤山, 张均龙 (2018) 中国动物志·无脊椎动物, 第五十七卷. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [35] | Yang W, Cai YY, Kuang XM (2017) Color Atlas of Molluscs of the South China Sea. China Agriculture Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [杨文, 蔡英亚, 邝雪梅 (2017) 中国南海经济贝类原色图鉴. 中国农业出版社, 北京.] | |
| [36] | Zhang SP (2007) On nine new record species of Ergalataxinae (Gastropoda, Muricidae) from China coast. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 38, 542-548. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [张素萍 (2007) 中国近海爱尔螺亚科九新记录(腹足纲: 骨螺科). 海洋与湖沼, 38, 542-548.] | |
| [37] | Zhang SP (2008) Atlas of Marine Molluscs of China. China Ocean Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [张素萍 (2008) 中国海洋贝类图鉴. 海洋出版社, 北京.] | |
| [38] | Zhang SP (2016) Fauna Sinica, Invertebrata, Vol. 56. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [张素萍 (2016) 中国动物志·无脊椎动物, 第五十六卷. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [39] | Zhang SP, Ma XT (2004) Fauna Sinica, Invertebrata, Vol. 34. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [张素萍, 马绣同 (2004) 中国动物志·无脊椎动物, 第三十四卷. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [40] | Zhang SP, Zhang JL, Chen ZY, Xu FS (2016) Mollusks of the Yellow Sea and Bohai Sea. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [张素萍, 张均龙, 陈志云, 徐凤山 (2016) 黄渤海软体动物图志. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [41] | Zhang SQ (2015) Study on the Taxonomy and Zoogeography of the Buccinidae of China Seas. PhD dissertation, Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Qingdao, Shandong. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [张树乾 (2015) 中国海蛾螺科Buccinidae系统分类学与动物地理学研究. 博士学位论文, 中国科学院海洋研究所, 山东青岛.] | |
| [42] | Zheng XD, Qu XC, Zeng XQ, Li Q (2013) Atlas of Aquatic Molluscs in China. Qingdao Publishing House, Qingdao. (in Chinese) |
| 郑小东, 曲学存, 曾晓起, 李琪 (2013) 中国水生贝类图鉴. 青岛出版社, 青岛.] | |
| [43] | Zhong YP, Yang RQ (1996) The new record of Prosobranchia along the Coast of Fujian. Journal of Xiamen Fisheries College, 18(1), 50-54. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [钟幼平, 杨瑞琼 (1996) 福建沿海前鳃类软体动物种类新记录. 厦门水产学院学报, 18(1), 50-54.] | |
| [44] | Zhuang QQ (2001) Fauna Sinica, Mollusca, Bivalvia, Veneridae. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [庄启谦 (2001) 中国动物志·软体动物门·双壳纲·帘蛤科. 科学出版社, 北京.] |
| [1] | 吴晓晴 张美惠 葛苏婷 李漫淑 宋坤 沈国春 达良俊 张健. 上海近自然林重建过程中木本植物物种多样性与地上生物量的时空动态——以闵行区生态岛为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24444-. |
| [2] | 王太, 宋福俊, 张永胜, 娄忠玉, 张艳萍, 杜岩岩. 河西走廊内陆河水系鱼类多样性及资源现状[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24387-. |
| [3] | 张晶晶, 黄文彬, 陈奕廷, 杨泽鹏, 柯伟业, 彭昭杰, 魏世超, 张志伟, 胡怡思, 余文华, 周文良. 广东南澎列岛海洋生态国家级自然保护区造礁石珊瑚多样性及分布特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24424-. |
| [4] | 尚华丹, 张楚晴, 王梅, 裴文娅, 李国宏, 王鸿斌. 中国杨树害虫物种多样性及其地理分布[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24370-. |
| [5] | 吴昱萱, 王平, 胡晓生, 丁一, 彭甜恬, 植秋滢, 巴德木其其格, 李文杰, 关潇, 李俊生. 呼伦贝尔草地退化现状评估与植被特征变化[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24118-. |
| [6] | 陈自宏, 张翼飞, 陈凯, 陈见影, 徐玲. 高黎贡山南段昆虫病原真菌物种多样性及影响因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(1): 24228-. |
| [7] | 谭珂, 宁瑶, 王仁芬, 王晴, 梁丹萍, 辛子兵, 温放. 中国苦苣苔科植物名录与地理分布数据集[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(1): 23275-. |
| [8] | 韩佳楠, 苏杨, 李霏, 刘君妍, 赵依林, 李琳, 赵建成, 梁红柱, 李敏. 河北省苔藓植物多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(9): 24096-. |
| [9] | 李东红, 郝媛媛, 甘辉林, 张航, 刘耀猛, 他富源, 胡桂馨. 祁连山北麓中段不同类型草地蝗虫种类及分布[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(9): 24119-. |
| [10] | 牛红玉, 陈璐, 赵恒月, 古丽扎尔·阿不都克力木, 张洪茂. 城市化对动物的影响: 从群落到个体[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(8): 23489-. |
| [11] | 白雪, 李正飞, 刘洋, 张君倩, 张多鹏, 罗鑫, 杨佳莉, 杜丽娜, 蒋玄空, 武瑞文, 谢志才. 西江流域大型底栖无脊椎动物物种多样性及维持机制[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(7): 23499-. |
| [12] | 许佳, 崔小娟, 张翼飞, 吴昌, 孙远东. 南岭地区鱼类多样性及其地理分布[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(7): 23482-. |
| [13] | 邝起宇, 胡亮. 广东东海岛与硇洲岛海域底栖贝类物种多样性及其地理分布[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(5): 24065-. |
| [14] | 赵勇强, 阎玺羽, 谢加琪, 侯梦婷, 陈丹梅, 臧丽鹏, 刘庆福, 隋明浈, 张广奇. 退化喀斯特森林自然恢复中不同生活史阶段木本植物物种多样性与群落构建[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(5): 23462-. |
| [15] | 徐伟强, 苏强. 分形模型与一般性物种多度分布关系的检验解析:以贝类和昆虫群落为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(4): 23410-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn
