



生物多样性 ›› 2012, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (1): 32-40. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2012.09142 cstr: 32101.14.SP.J.1003.2012.09142
宋普庆1, 张静2, 林龙山1,*( ), 许章程1, 朱小明3
), 许章程1, 朱小明3
收稿日期:2011-08-15
接受日期:2011-11-01
出版日期:2012-01-20
发布日期:2012-02-14
通讯作者:
林龙山
作者简介:*E-mail: linlsh2005@126.com基金资助:
Puqing Song1, Jing Zhang2, Longshan Lin1,*( ), Zhangcheng Xu1, Xiaoming Zhu3
), Zhangcheng Xu1, Xiaoming Zhu3
Received:2011-08-15
Accepted:2011-11-01
Online:2012-01-20
Published:2012-02-14
Contact:
Longshan Lin
摘要:
根据2006-2007年在台湾海峡进行的四个季度航次定点底拖网调查资料, 分析了台湾海峡游泳动物的种类组成、数量分布、优势种和多样性等特征。结果表明, 调查海域共鉴定出游泳动物373种, 其中鱼类273种, 甲壳类81种, 头足类19种; 渔获物组成以鱼类为主, 占渔获物总重量的65.6%, 其次为甲壳类和头足类, 分别占21.1%和13.3%, 所有调查站位游泳动物的年平均生物量密度指数为24.91 kg/h, 主要优势种类为带鱼(Trichiurus japonicus)、拥剑梭子蟹(Portunus haanii)、二长棘鲷(Parargyrops edita)、龙头鱼(Harpadon nehereus)、竹筴鱼(Trachurus japonicus)、火枪乌贼(Loligo beka)等。对多样性的分析显示, 台湾海峡游泳动物物种多样性指数(H′)变化范围为1.45-3.21, 平均为2.47, 其中秋季最高, 夏季最低, 且呈现南高北低的特点。与历史资料相比, 目前台湾海峡游泳动物种类数明显减少, 尤其是闽东和闽南—台湾浅滩海域表现最为突出; 优势种类个体呈现小型化和低龄化趋势, 表明台湾海峡游泳动物资源衰退明显。
宋普庆, 张静, 林龙山, 许章程, 朱小明 (2012) 台湾海峡游泳动物种类组成及其多样性. 生物多样性, 20, 32-40. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2012.09142.
Puqing Song, Jing Zhang, Longshan Lin, Zhangcheng Xu, Xiaoming Zhu (2012) Nekton species composition and biodiversity in Taiwan Strait. Biodiversity Science, 20, 32-40. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2012.09142.
| 纲 Class | 目 Order | 科 Family | 属 Genus | 种 Species |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 软骨鱼纲 Chondrichthyes | 真鲨目 Carcharhiniformes | 1 | 3 | 4 |
| 鳐形目 Rajiformes | 3 | 3 | 3 | |
| 鲼形目 Myliobatiformes | 2 | 2 | 4 | |
| 硬骨鱼纲 Osteichthyes | 鼠鱚目 Gonorhynchiformes | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 鲱形目 Clupeiformes | 2 | 8 | 13 | |
| 灯笼鱼目 Myctophiformes | 2 | 5 | 7 | |
| 鳗鲡目 Anguilliformes | 6 | 8 | 13 | |
| 鲇形目 Siluriformes | 2 | 2 | 2 | |
| 颌针鱼目 Beloniformes | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| 鳕形目 Gadiformes | 2 | 2 | 3 | |
| 月鱼目 Lampridiformes | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| 刺鱼目 Gasterosteiformes | 3 | 4 | 6 | |
| 鲻形目 Mugiliformes | 3 | 5 | 6 | |
| 鲈形目 Perciformes | 40 | 76 | 125 | |
| 鲉形目 Scorpaeniformes | 7 | 22 | 30 | |
| 鲽形目 Pleuronectiformes | 4 | 21 | 42 | |
| 鲀形目 Tetraodontiformes | 3 | 7 | 9 | |
| 鮟鱇目 Lophiiformes | 2 | 2 | 3 | |
| 甲壳纲 Crustacea | 十足目 Decapoda | 19 | 32 | 74 |
| 口足目 Stomatopoda | 1 | 1 | 7 | |
| 头足纲 Cephalopoda | 枪形目 Teuthoidea | 1 | 2 | 5 |
| 乌贼目 Sepioidea | 2 | 3 | 8 | |
| 八腕目 Octopoda | 1 | 1 | 6 |
表1 2006-2007年调查到的台湾海峡游泳动物的种类组成
Table 1 Species composition of nekton in Taiwan Strait in 2006-2007
| 纲 Class | 目 Order | 科 Family | 属 Genus | 种 Species |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 软骨鱼纲 Chondrichthyes | 真鲨目 Carcharhiniformes | 1 | 3 | 4 |
| 鳐形目 Rajiformes | 3 | 3 | 3 | |
| 鲼形目 Myliobatiformes | 2 | 2 | 4 | |
| 硬骨鱼纲 Osteichthyes | 鼠鱚目 Gonorhynchiformes | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 鲱形目 Clupeiformes | 2 | 8 | 13 | |
| 灯笼鱼目 Myctophiformes | 2 | 5 | 7 | |
| 鳗鲡目 Anguilliformes | 6 | 8 | 13 | |
| 鲇形目 Siluriformes | 2 | 2 | 2 | |
| 颌针鱼目 Beloniformes | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| 鳕形目 Gadiformes | 2 | 2 | 3 | |
| 月鱼目 Lampridiformes | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| 刺鱼目 Gasterosteiformes | 3 | 4 | 6 | |
| 鲻形目 Mugiliformes | 3 | 5 | 6 | |
| 鲈形目 Perciformes | 40 | 76 | 125 | |
| 鲉形目 Scorpaeniformes | 7 | 22 | 30 | |
| 鲽形目 Pleuronectiformes | 4 | 21 | 42 | |
| 鲀形目 Tetraodontiformes | 3 | 7 | 9 | |
| 鮟鱇目 Lophiiformes | 2 | 2 | 3 | |
| 甲壳纲 Crustacea | 十足目 Decapoda | 19 | 32 | 74 |
| 口足目 Stomatopoda | 1 | 1 | 7 | |
| 头足纲 Cephalopoda | 枪形目 Teuthoidea | 1 | 2 | 5 |
| 乌贼目 Sepioidea | 2 | 3 | 8 | |
| 八腕目 Octopoda | 1 | 1 | 6 |
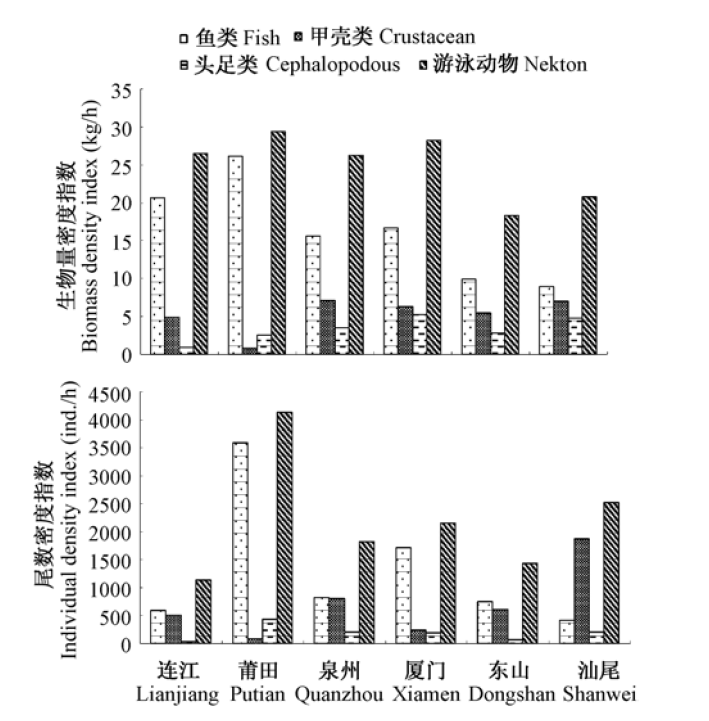
图2 台湾海峡不同断面游泳动物平均生物量密度指数和尾数密度指数
Fig. 2 The composition of the mean biomass density index and individual density index of nekton in different sections of Taiwan Strait
| 季节 Season | 优势种 Dominant species | |
|---|---|---|
| 重量比例 Weight percent | 尾数比例 Individual percent | |
| 春季 Spring | 竹筴鱼 Trachurus japonicus (20.76%) 二长棘鲷 Parargyrops edita (11.70%) 火枪乌贼 Loligo beka (9.38%) 长蛇鲻 Saurida elongata (5.48%) 龙头鱼 Harpadon nehereus (4.34%) 条尾绯鲤 Upeneus bensasi (3.63%) 大头狗母鱼 Trachinocephalus myops (3.30%) | 竹筴鱼 Trachurus japonicus (42.85%) 二长棘鲷 Parargyrops edita (24.03%) 银光梭子蟹 Portunus argentatus (4.99%) 火枪乌贼 Loligo beka (4.15%) 须赤虾 Metapenaeopsis barbata (3.00%) |
| 夏季 Summer | 带鱼 Trichiurus japonicus (19.35%) 拥剑梭子蟹 Portunus haanii (11.27%) 二长棘鲷 Parargyrops edita (6.67%) 大头狗母鱼 Trachinocephalus myops (4.53%) 金乌贼 Sepia esculenta (3.96%) 长蛇鲻 Saurida elongata (3.41%) 黄鲫 Setipinna taty (3.13%) | 鹿斑鲾 Secuter ruconius (28.59%) 麦氏犀鳕 Bregmaceros macclellandii (14.28%) 四线天竺鲷 Apogon quadrifasciatus (4.78%) 粗纹鲾 Leiognathus lineolatus (4.24%) 带鱼 Trichiurus japonicus (4.24%) 拥剑梭子蟹 Portunus haanii (3.58%) |
| 秋季 Autumn | 带鱼 Trichiurus japonicus (6.93%) 小管枪乌贼 Loligo oshimai (6.11%) 二长棘鲷 Parargyrops edita (5.82%) 龙头鱼 Harpadon nehereus (5.78%) 六指马鲅 Polydactylus sextarius (5.39%) 黄魟 Dasyatis bennetti (4.44%) 拥剑梭子蟹 Portunus haanii (4.31%) 刺鲳 Psenopsis anomala (4.07%) 棕斑腹刺鲀 Gastrophysus spadiceus (3.91%) 白姑鱼 Argyrosomus argentatus (3.35%) | 银光梭子蟹 Portunus argentatus (16.88%) 七星底灯鱼 Benthosema pterotum (10.96%) 矛形梭子蟹 Portunus hastatoides (9.05%) 小管枪乌贼 Loligo oshimai (6.31%) 带鱼 Trichiurus japonicus (6.03%) 鹰爪虾 Trachypenaeus curvirostris (5.56%) 须赤虾 Metapenaeopsis barbata (5.42%) |
| 冬季 Winter | 龙头鱼 Harpadon nehereus (7.54%) 火枪乌贼 Loligo beka (6.68%) 叫姑鱼 Johnius belengerii (6.21%) 拥剑梭子蟹 Portunus haanii (5.94%) 口虾蛄 Oratosquilla oratoria (5.74%) 带鱼 Trichiurus japonicus (4.69%) 拟目乌贼 Sepia lycidas (3.74%) 湾鱼或 Wak Sinai (3.07%) | 拥剑梭子蟹 Portunus haanii (11.93%) 火枪乌贼 Loligo beka (7.98%) 中华管鞭虾 Solenocera crassicornis (7.51%) 口虾蛄 Oratosquilla oratoria (6.39%) 须赤虾 Metapenaeopsis barbata (5.87%) 鹰爪虾 Trachypenaeus curvirostris (4.36%) 哈氏仿对虾 Parapenaeopsis hardwickii (3.86%) 叫姑鱼 Johnius belengerii (3.01%) |
表2 2006-2007年调查中台湾海峡各季节游泳动物优势种类组成(>3%)
Table 2 The composition of dominant species (>3%) in four seasons in Taiwan Strait
| 季节 Season | 优势种 Dominant species | |
|---|---|---|
| 重量比例 Weight percent | 尾数比例 Individual percent | |
| 春季 Spring | 竹筴鱼 Trachurus japonicus (20.76%) 二长棘鲷 Parargyrops edita (11.70%) 火枪乌贼 Loligo beka (9.38%) 长蛇鲻 Saurida elongata (5.48%) 龙头鱼 Harpadon nehereus (4.34%) 条尾绯鲤 Upeneus bensasi (3.63%) 大头狗母鱼 Trachinocephalus myops (3.30%) | 竹筴鱼 Trachurus japonicus (42.85%) 二长棘鲷 Parargyrops edita (24.03%) 银光梭子蟹 Portunus argentatus (4.99%) 火枪乌贼 Loligo beka (4.15%) 须赤虾 Metapenaeopsis barbata (3.00%) |
| 夏季 Summer | 带鱼 Trichiurus japonicus (19.35%) 拥剑梭子蟹 Portunus haanii (11.27%) 二长棘鲷 Parargyrops edita (6.67%) 大头狗母鱼 Trachinocephalus myops (4.53%) 金乌贼 Sepia esculenta (3.96%) 长蛇鲻 Saurida elongata (3.41%) 黄鲫 Setipinna taty (3.13%) | 鹿斑鲾 Secuter ruconius (28.59%) 麦氏犀鳕 Bregmaceros macclellandii (14.28%) 四线天竺鲷 Apogon quadrifasciatus (4.78%) 粗纹鲾 Leiognathus lineolatus (4.24%) 带鱼 Trichiurus japonicus (4.24%) 拥剑梭子蟹 Portunus haanii (3.58%) |
| 秋季 Autumn | 带鱼 Trichiurus japonicus (6.93%) 小管枪乌贼 Loligo oshimai (6.11%) 二长棘鲷 Parargyrops edita (5.82%) 龙头鱼 Harpadon nehereus (5.78%) 六指马鲅 Polydactylus sextarius (5.39%) 黄魟 Dasyatis bennetti (4.44%) 拥剑梭子蟹 Portunus haanii (4.31%) 刺鲳 Psenopsis anomala (4.07%) 棕斑腹刺鲀 Gastrophysus spadiceus (3.91%) 白姑鱼 Argyrosomus argentatus (3.35%) | 银光梭子蟹 Portunus argentatus (16.88%) 七星底灯鱼 Benthosema pterotum (10.96%) 矛形梭子蟹 Portunus hastatoides (9.05%) 小管枪乌贼 Loligo oshimai (6.31%) 带鱼 Trichiurus japonicus (6.03%) 鹰爪虾 Trachypenaeus curvirostris (5.56%) 须赤虾 Metapenaeopsis barbata (5.42%) |
| 冬季 Winter | 龙头鱼 Harpadon nehereus (7.54%) 火枪乌贼 Loligo beka (6.68%) 叫姑鱼 Johnius belengerii (6.21%) 拥剑梭子蟹 Portunus haanii (5.94%) 口虾蛄 Oratosquilla oratoria (5.74%) 带鱼 Trichiurus japonicus (4.69%) 拟目乌贼 Sepia lycidas (3.74%) 湾鱼或 Wak Sinai (3.07%) | 拥剑梭子蟹 Portunus haanii (11.93%) 火枪乌贼 Loligo beka (7.98%) 中华管鞭虾 Solenocera crassicornis (7.51%) 口虾蛄 Oratosquilla oratoria (6.39%) 须赤虾 Metapenaeopsis barbata (5.87%) 鹰爪虾 Trachypenaeus curvirostris (4.36%) 哈氏仿对虾 Parapenaeopsis hardwickii (3.86%) 叫姑鱼 Johnius belengerii (3.01%) |
| 断面 Section | 多样性指数 Shannon-Wiener diversity index (H′) | 物种丰富度指数 Margalef richness index (D) | 均匀度指数 Pielou evenness index (J′) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 平均 Average | 范围 Range | 平均 Average | 范围 Range | 平均 Average | 范围 Range | |||
| 连江 Lianjiang | 2.19±0.34 | 1.68-2.74 | 1.77±0.37 | 1.24-2.01 | 0.61±0.07 | 0.50-0.76 | ||
| 莆田 Putian | 2.16±0.45 | 1.45-2.57 | 1.59±0.50 | 0.88-2.42 | 0.63±0.14 | 0.39-0.81 | ||
| 泉州 Quanzhou | 2.66±0.31 | 1.92-2.96 | 2.46±0.72 | 1.55-3.60 | 0.68±0.07 | 0.57-0.75 | ||
| 厦门 Xiamen | 2.49±0.32 | 1.61-2.85 | 2.09±0.35 | 1.47-2.67 | 0.67±0.10 | 0.38-0.79 | ||
| 东山 Dongshan | 2.59±0.41 | 1.80-3.12 | 1.97±0.78 | 0.77-3.07 | 0.71±0.06 | 0.62-0.81 | ||
| 汕尾 Shanwei | 2.61±0.37 | 1.73-3.21 | 2.09±0.63 | 1.27-3.03 | 0.70±0.09 | 0.50-0.82 | ||
表3 台湾海峡不同断面游泳动物多样性指数
Table 3 The horizontal distribution of the biodiversity of nekton in Taiwan Strait
| 断面 Section | 多样性指数 Shannon-Wiener diversity index (H′) | 物种丰富度指数 Margalef richness index (D) | 均匀度指数 Pielou evenness index (J′) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 平均 Average | 范围 Range | 平均 Average | 范围 Range | 平均 Average | 范围 Range | |||
| 连江 Lianjiang | 2.19±0.34 | 1.68-2.74 | 1.77±0.37 | 1.24-2.01 | 0.61±0.07 | 0.50-0.76 | ||
| 莆田 Putian | 2.16±0.45 | 1.45-2.57 | 1.59±0.50 | 0.88-2.42 | 0.63±0.14 | 0.39-0.81 | ||
| 泉州 Quanzhou | 2.66±0.31 | 1.92-2.96 | 2.46±0.72 | 1.55-3.60 | 0.68±0.07 | 0.57-0.75 | ||
| 厦门 Xiamen | 2.49±0.32 | 1.61-2.85 | 2.09±0.35 | 1.47-2.67 | 0.67±0.10 | 0.38-0.79 | ||
| 东山 Dongshan | 2.59±0.41 | 1.80-3.12 | 1.97±0.78 | 0.77-3.07 | 0.71±0.06 | 0.62-0.81 | ||
| 汕尾 Shanwei | 2.61±0.37 | 1.73-3.21 | 2.09±0.63 | 1.27-3.03 | 0.70±0.09 | 0.50-0.82 | ||
| 季节 Season | 多样性指数 Shannon-Wiener diversity index (H′) | 物种丰富度指数 Margalef richness index (D) | 均匀度指数 Pielou evenness index (J′) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 平均 Average | 范围 Range | 平均 Average | 范围 Range | 平均 Average | 范围 Range | |||
| 春季 Spring | 2.34±0.38 | 1.61-2.79 | 1.61±0.39 | 1.06-2.67 | 0.69±0.11 | 0.39-0.81 | ||
| 夏季 Summer | 2.32±0.51 | 1.45-3.21 | 1.83±0.53 | 0.77-2.71 | 0.65±0.12 | 0.38-0.82 | ||
| 秋季 Autumn | 2.64±0.30 | 2.19-3.11 | 2.52±0.62 | 1.69-3.60 | 0.66±0.05 | 0.60-0.77 | ||
| 冬季 Winter | 2.58±0.31 | 1.92-2.99 | 2.11±0.56 | 1.09-3.07 | 0.69±0.08 | 0.52-0.80 | ||
表4 台湾海峡不同季节游泳动物多样性指数
Table 4 The seasonal variation of the biodiversity of nekton in Taiwan Strait
| 季节 Season | 多样性指数 Shannon-Wiener diversity index (H′) | 物种丰富度指数 Margalef richness index (D) | 均匀度指数 Pielou evenness index (J′) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 平均 Average | 范围 Range | 平均 Average | 范围 Range | 平均 Average | 范围 Range | |||
| 春季 Spring | 2.34±0.38 | 1.61-2.79 | 1.61±0.39 | 1.06-2.67 | 0.69±0.11 | 0.39-0.81 | ||
| 夏季 Summer | 2.32±0.51 | 1.45-3.21 | 1.83±0.53 | 0.77-2.71 | 0.65±0.12 | 0.38-0.82 | ||
| 秋季 Autumn | 2.64±0.30 | 2.19-3.11 | 2.52±0.62 | 1.69-3.60 | 0.66±0.05 | 0.60-0.77 | ||
| 冬季 Winter | 2.58±0.31 | 1.92-2.99 | 2.11±0.56 | 1.09-3.07 | 0.69±0.08 | 0.52-0.80 | ||
| 区域 Region | 调查时间 Investigation time | 种类 Species | 每小时渔获物重量CPUE(kg/h) | 优势种 Dominant species |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 闽东 Eastern coast of Fujian | 2006-2007 | 133 | 26.49 | 龙头鱼(Harpadon nehereus)、口虾蛄(Oratosquilla oratoria)、尖嘴魟(Dasyatis zugei)、叫姑鱼(Johnius belengerii)、黄鲫(Setipinna taty) |
| 2000-2001* | 239 | 15.81 | 棕斑腹刺鲀(Gastrophysus spadiceus)、口虾蛄(Oratosquilla oratoria)、刺鲳(Psenopsis anomala)、白姑鱼(Argyrosomus argentatus) | |
| 1989-1990* | - | 65.27 | 带鱼(Trichiurus japonicus)、短尾大眼鲷(Priacanthus macracanthus)、竹筴鱼(Trachurus japonicus) | |
| 闽中 Central coast of Fujian | 2006-2007 | 248 | 27.83 | 带鱼(Trichiurus japonicus)、刺鲳(Psenopsis anomala)、灰鲳(Pampus cinereus)、叫姑鱼(Johnius belengerii)、六指马鲅(Polydactylus sextarius)、小管枪乌贼(Loligo oshimai)、 棕斑腹刺鲀(Gastrophysus spadiceus)、锈斑蟳(Charybdis feriatus) |
| 2000-2001* | 245 | 17.34 | 带鱼(Trichiurus japonicus)、口虾蛄(Oratosquilla oratoria)、哈氏仿对虾(Parapenaeopsis hardwickii)、龙头鱼(Harpadon nehereus)、发光鲷(Acropoma japonicum) | |
| 1982* | - | 42.24 | 白姑鱼(Argyrosomus argentatus)、带鱼(Trichiurus japonicus)、丁氏鱼或(Wak tingi) | |
| 闽南- 台湾浅滩 Southern Fujian and Taiwan bank | 2006-2007 | 273 | 22.43 | 二长棘鲷(Parargyrops edita)、竹筴鱼(Trachurus japonicus)、长蛇鲻(Saurida elongata)、大头狗母鱼(Trachinocephalus myops)、绿布氏筋鱼(Bleekeria anguilliviridis)、拥剑梭子蟹(Portunus haanii) |
| 2000-2001* | 365 | 45.46 | 中国枪乌贼(Loligo chinensis)、拥剑梭子蟹(Portunus haanii)、大头狗母鱼(Trachinocephalus myops)、条尾绯鲤(Upeneus bensasi) | |
| 1977* | - | 794.79 | 乔氏台雅鱼(Daya jordani)、二长棘鲷(Parargyrops edita)、金带细鲹(Selaroides leptolepis)、长蛇鲻(Saurida elongata) |
表5 台湾海峡游泳动物种类组成和数量现状及与历史资料的对比
Table 5 The comparison of nekton resource between present and historic data
| 区域 Region | 调查时间 Investigation time | 种类 Species | 每小时渔获物重量CPUE(kg/h) | 优势种 Dominant species |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 闽东 Eastern coast of Fujian | 2006-2007 | 133 | 26.49 | 龙头鱼(Harpadon nehereus)、口虾蛄(Oratosquilla oratoria)、尖嘴魟(Dasyatis zugei)、叫姑鱼(Johnius belengerii)、黄鲫(Setipinna taty) |
| 2000-2001* | 239 | 15.81 | 棕斑腹刺鲀(Gastrophysus spadiceus)、口虾蛄(Oratosquilla oratoria)、刺鲳(Psenopsis anomala)、白姑鱼(Argyrosomus argentatus) | |
| 1989-1990* | - | 65.27 | 带鱼(Trichiurus japonicus)、短尾大眼鲷(Priacanthus macracanthus)、竹筴鱼(Trachurus japonicus) | |
| 闽中 Central coast of Fujian | 2006-2007 | 248 | 27.83 | 带鱼(Trichiurus japonicus)、刺鲳(Psenopsis anomala)、灰鲳(Pampus cinereus)、叫姑鱼(Johnius belengerii)、六指马鲅(Polydactylus sextarius)、小管枪乌贼(Loligo oshimai)、 棕斑腹刺鲀(Gastrophysus spadiceus)、锈斑蟳(Charybdis feriatus) |
| 2000-2001* | 245 | 17.34 | 带鱼(Trichiurus japonicus)、口虾蛄(Oratosquilla oratoria)、哈氏仿对虾(Parapenaeopsis hardwickii)、龙头鱼(Harpadon nehereus)、发光鲷(Acropoma japonicum) | |
| 1982* | - | 42.24 | 白姑鱼(Argyrosomus argentatus)、带鱼(Trichiurus japonicus)、丁氏鱼或(Wak tingi) | |
| 闽南- 台湾浅滩 Southern Fujian and Taiwan bank | 2006-2007 | 273 | 22.43 | 二长棘鲷(Parargyrops edita)、竹筴鱼(Trachurus japonicus)、长蛇鲻(Saurida elongata)、大头狗母鱼(Trachinocephalus myops)、绿布氏筋鱼(Bleekeria anguilliviridis)、拥剑梭子蟹(Portunus haanii) |
| 2000-2001* | 365 | 45.46 | 中国枪乌贼(Loligo chinensis)、拥剑梭子蟹(Portunus haanii)、大头狗母鱼(Trachinocephalus myops)、条尾绯鲤(Upeneus bensasi) | |
| 1977* | - | 794.79 | 乔氏台雅鱼(Daya jordani)、二长棘鲷(Parargyrops edita)、金带细鲹(Selaroides leptolepis)、长蛇鲻(Saurida elongata) |
| 种类 Species | 年份 Year | 长度范围 Range (mm) | 优势体长组 Dominant range (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 带鱼 Trichiurus japonicus | 2006-2007 | 45-460 | 200-240 |
| 1994* | 107-532 | 211-260 | |
| 1976* | 118-669 | 231-270 | |
| 二长棘鲷 Parargyrops edita | 2006-2007 | 30-180 | 90-110 |
| 1994* | 33-155 | 91-110 | |
| 1976* | 30-180 | 91-120 | |
| 白姑鱼 Argyrosomus argentatus | 2006-2007 | 45-202 | 110-130 |
| 1994* | 65-216 | 111-150 | |
| 1982* | 67-258 | 121-150 | |
| 条尾绯鲤 Upeneus bensasi | 2006-2007 | 30-130 | 80-110 |
| 1994* | 75-163 | 91-120 | |
| 1976* | 81-172 | 101-120 |
表6 几种主要经济鱼类的体长变化
Table 6 Length variation of some principle species
| 种类 Species | 年份 Year | 长度范围 Range (mm) | 优势体长组 Dominant range (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 带鱼 Trichiurus japonicus | 2006-2007 | 45-460 | 200-240 |
| 1994* | 107-532 | 211-260 | |
| 1976* | 118-669 | 231-270 | |
| 二长棘鲷 Parargyrops edita | 2006-2007 | 30-180 | 90-110 |
| 1994* | 33-155 | 91-110 | |
| 1976* | 30-180 | 91-120 | |
| 白姑鱼 Argyrosomus argentatus | 2006-2007 | 45-202 | 110-130 |
| 1994* | 65-216 | 111-150 | |
| 1982* | 67-258 | 121-150 | |
| 条尾绯鲤 Upeneus bensasi | 2006-2007 | 30-130 | 80-110 |
| 1994* | 75-163 | 91-120 | |
| 1976* | 81-172 | 101-120 |
| [1] | Connell SD, Lincoln-Smith MP (1999) Depth and the structure of assemblages of demersal fish: experimental trawling along a temperate coast. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 48,483-495. |
| [2] | Dai QS (戴泉水), Lu ZB (卢振彬), Hong MJ (洪明进), Xiao FS (肖方森), Zhu JF (朱进福) (2004) Fauna composition of nekton and fishery resources in the southern waters of Taiwan Strait. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China (中国水产科学), 11,360-366. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [3] | Dai QS (戴泉水), Lu ZB (卢振彬), Dai TY (戴天元), Xiao FS (肖方森), Lin FL (林法玲), Lin X (林晞) (2005) Species composition of nekton and resources state of Taiwan Strait and its adjacent waters. Journal of Fisheries of China (水产学报), 29,205-210. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [4] | Dai TY (戴天元) (2005) Sustainable yield of fishery resources in the Taiwan Straits and its adjacent waters. Marine Fisheries Research (海洋水产研究), 26(3),1-8. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [5] | Fei HN (费鸿年), He BQ (何宝全), Chen GM (陈国铭) (1981) Regional and seasonal changes of demersal fish diversity and dominant species in the continental shelf of northern South China Sea. Journal of Fisheries of China (水产学报), 5(1),1-20. (in Chinese) |
| [6] | Fisheries Division Office of Fujian (福建省渔业区划办公室) (1988) Fisheries Resources of Fujian Province (福建省渔业资源). Fujian Science andTechnology Press, Fuzhou. (in Chinese) |
| [7] | Gaertner JC, Chessel D, Bertrand J (1998) Stability of spatial structures of demersal assemblages: a new approach. Aquatic Living Resources, 11,75-85. |
| [8] | Huang PM (黄培民) (2006) Status analysis of the otter trawl fishery in Fujian Sea Area. Journal of Fujian Fisheries (福建水产), 2,16-18. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [9] | Jay CV (1996) Distribution of bottom-trawl fish assemblages over the continental shelf and upper slope of the U.S. west coast, 1977-1992. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, 53,1203-1225. |
| [10] | Li SF (李圣法), Cheng JH (程家骅), Li CS (李长松), Li JS (李建生) (2007) Seasonal changes on fish community diversity in the middle part of the East China Sea. Marine Fisheries (海洋渔业), 27,113-119. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [11] | Lin LS (林龙山), Zheng YJ (郑元甲), Ma CY (马春艳) (2005) Distribution of nekton stock density and its community structure in Taiwan Strait in summer and autumn. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology (应用生态学报), 16, 1948-1951. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [12] | Liu Y (刘勇), Li SF (李圣法), Cheng JH (程家骅) (2006) A study on seasonal changes of the fish communities in the East China Sea and the Huanghai Sea. Acta Oceanologica Sinica (海洋学报), 18(4),108-114. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [13] | Lu ZB (卢振彬), Dai QS (戴泉水), Zhu JF (朱进福), Yan YM (颜尤明) (1999) Change in structure of the fisheries resources and ecology of the major population in Fujian Offshore Waters. Journal of Fujian Fisheries (福建水产), 3,1-7. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [14] | Lu ZB (卢振彬), Dai QS (戴泉水) (2002) Productivity and maximum sustainable yield of fishery resources in Taiwan Strait and its adjacent waters. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China (中国水产科学), 9,28-32. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [15] | Lu ZB (卢振彬) (2005) Fish stock yield by various eco-groups in eastern Fujian fishing ground. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China (中国水产科学), 12,731-738. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [16] | Lu ZB (卢振彬), Dai QS (戴泉水), Xiao FS (肖方森), Zhu JF (朱进福) (2006) The resources production of fish and its different ecological type in Minnan-Taiwan Bank fishing grounds. Journal of Fisheries of China (水产学报), 30,359-366. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [17] | Ludwig JA, Reynolds JF (1988) Statistical Ecology. John Wiley & Sons, New York. |
| [18] | Magnussen E (2002) Demersal fish assemblages of Faroe Bank: species composition, distribution, biomass spectrum and diversity. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 238,211-225. |
| [19] | Ma KP (马克平) (1994) The measurement of community diversity. In: Principles and Methodologies of Biodiversity Studies (生物多样性研究的原理与方法) (eds Qian YQ (钱迎倩), Ma KP (马克平)). China Science and Technology Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [20] | Mueter FJ, Norcross BL (2002) Spatial and temporal patterns in the demersal fish community on the shelf and upper slope regions of the Gulf of Alaska. Fishery Bulletin, 100,559-581. |
| [21] | Nelson JS (1976) Fishes of the World. John Wiley & Sons, New York. |
| [22] | Shen GY (沈国英), Shi BZ (施并章) (2002) Marine Ecology (海洋生态学), 2nd edn. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [23] | Zhu XH (朱鑫华), Wu HZ (吴鹤洲), Xu FS (徐凤山), Ye MZ (叶懋中), Zhao ZJ (赵紫晶) (1994) Study on nekton community diversity and correlation factors in Huanghai and Bohai area. Acta Oceanologica Sinica (海洋学报), 16(3),102-112. (in Chinese) |
| [1] | 吴晓晴 张美惠 葛苏婷 李漫淑 宋坤 沈国春 达良俊 张健. 上海近自然林重建过程中木本植物物种多样性与地上生物量的时空动态——以闵行区生态岛为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24444-. |
| [2] | 王太, 宋福俊, 张永胜, 娄忠玉, 张艳萍, 杜岩岩. 河西走廊内陆河水系鱼类多样性及资源现状[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24387-. |
| [3] | 张晶晶, 黄文彬, 陈奕廷, 杨泽鹏, 柯伟业, 彭昭杰, 魏世超, 张志伟, 胡怡思, 余文华, 周文良. 广东南澎列岛海洋生态国家级自然保护区造礁石珊瑚多样性及分布特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24424-. |
| [4] | 尚华丹, 张楚晴, 王梅, 裴文娅, 李国宏, 王鸿斌. 中国杨树害虫物种多样性及其地理分布[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24370-. |
| [5] | 吴昱萱, 王平, 胡晓生, 丁一, 彭甜恬, 植秋滢, 巴德木其其格, 李文杰, 关潇, 李俊生. 呼伦贝尔草地退化现状评估与植被特征变化[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24118-. |
| [6] | 陈自宏, 张翼飞, 陈凯, 陈见影, 徐玲. 高黎贡山南段昆虫病原真菌物种多样性及影响因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(1): 24228-. |
| [7] | 谭珂, 宁瑶, 王仁芬, 王晴, 梁丹萍, 辛子兵, 温放. 中国苦苣苔科植物名录与地理分布数据集[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(1): 23275-. |
| [8] | 何泽嵘, 叶鹏, 王舒婷, 关永鑫, 闫淑君, 洪心茹. 中国城市草坪的杂草优势种组成及空间分布[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(1): 24133-. |
| [9] | 韩佳楠, 苏杨, 李霏, 刘君妍, 赵依林, 李琳, 赵建成, 梁红柱, 李敏. 河北省苔藓植物多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(9): 24096-. |
| [10] | 李东红, 郝媛媛, 甘辉林, 张航, 刘耀猛, 他富源, 胡桂馨. 祁连山北麓中段不同类型草地蝗虫种类及分布[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(9): 24119-. |
| [11] | 牛红玉, 陈璐, 赵恒月, 古丽扎尔·阿不都克力木, 张洪茂. 城市化对动物的影响: 从群落到个体[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(8): 23489-. |
| [12] | 白雪, 李正飞, 刘洋, 张君倩, 张多鹏, 罗鑫, 杨佳莉, 杜丽娜, 蒋玄空, 武瑞文, 谢志才. 西江流域大型底栖无脊椎动物物种多样性及维持机制[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(7): 23499-. |
| [13] | 许佳, 崔小娟, 张翼飞, 吴昌, 孙远东. 南岭地区鱼类多样性及其地理分布[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(7): 23482-. |
| [14] | 邝起宇, 胡亮. 广东东海岛与硇洲岛海域底栖贝类物种多样性及其地理分布[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(5): 24065-. |
| [15] | 赵勇强, 阎玺羽, 谢加琪, 侯梦婷, 陈丹梅, 臧丽鹏, 刘庆福, 隋明浈, 张广奇. 退化喀斯特森林自然恢复中不同生活史阶段木本植物物种多样性与群落构建[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(5): 23462-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn