



生物多样性 ›› 2022, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (10): 22445. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2022445 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2022445
收稿日期:2022-08-03
接受日期:2022-10-27
出版日期:2022-10-20
发布日期:2022-11-01
通讯作者:
解焱
作者简介:* E-mail: xieyan@ioz.ac.cnReceived:2022-08-03
Accepted:2022-10-27
Online:2022-10-20
Published:2022-11-01
Contact:
Yan Xie
摘要:
IUCN受威胁物种红色名录已经成为世界上最全面的关于全球动物、真菌和植物物种灭绝风险状况的信息来源, 是生物多样性健康的关键指标, 是促进生物多样性保护和决策的有力工具。本文全面介绍IUCN受威胁物种红色名录(简称IUCN红色名录)的发展以及应用状况, 积极推动其在中国的物种评估和广泛应用。总结了IUCN红色名录从依赖于评估专家的主观意志决定物种濒危等级的濒危物种红皮书(Red Data Book)到IUCN受威胁物种等级和标准(3.1版)的客观量化和所有门类使用统一标准的过程。该等级体系可囊括全球所有物种, 其中“受威胁”的3个等级——极危(CR)、濒危(EN)或易危(VU)需使用5个标准进行量化评估, 对评估规范有非常严格的要求。该等级和标准体系不仅适用于全球层面, 同样也适用于地区层面物种评估, 只是在具体物种种群如果和周边其他地区(国家)存在种群交流情况时, 评估结果要进行调整。迄今为止, 全球层面使用该等级体系和标准评估了14万多种(其中在中国有分布的物种10,846种), 100多个国家和地方制定了地区/国家层面的红色名录, 中国红色名录评估了5.5万多种。IUCN红色名录已广泛应用于评估生物多样性变化速度; 为保护规划提供决策信息; 支持履行国际公约、修订国家/地区重点保护物种名录和自然保护地管理等; 指导资源有效合理分配和宣传教育等。广泛应用过程中, 讨论主要集中在获取数据的方法改进上; 另外, 一方面有专家认为标准存在缺陷需要完善, 另一方面有呼吁维持标准的长期相对稳定, 以便进行跨时间、跨区域、跨物种门类的比较。本文提出来了中国红色名录的持续机制和应用建议, 包括建立中国红色名录委员会、建立中国红色名录专业网站、发展评估专家队伍、建立中国红色名录评估更新机制, 以及加强国际协作、促进全球和中国红色名录的应用和发展。
解焱 (2022) IUCN受威胁物种红色名录进展及应用. 生物多样性, 30, 22445. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2022445.
Yan Xie (2022) Progress and application of IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Biodiversity Science, 30, 22445. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2022445.
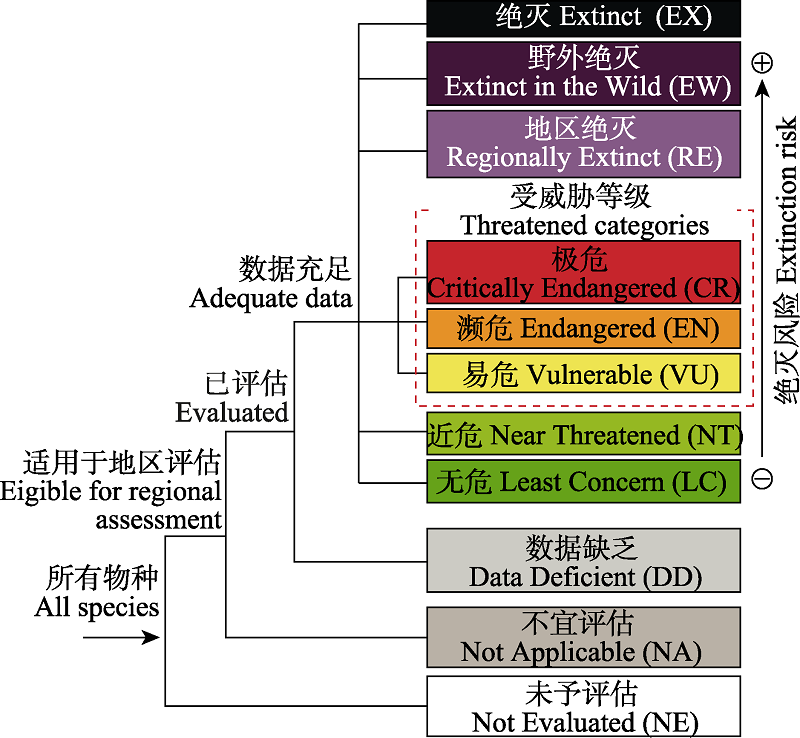
图1 适用于地区应用的IUCN红色名录受威胁等级体系 (汪松和解焱, 2004; IUCN, 2012a)
Fig. 1 IUCN category system of threatened species for regional application (Wang & Xie, 2004; IUCN, 2012a)
| 物种大类 Large group | 物种门类 Taxon | 评估数量 Number assessed | 受威胁比例 Proportion of threatened species (%) | 参考文献 Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 脊椎动物(不含海洋鱼类) Vertebrates (excluding marine fishes) | 淡水鱼类 Freshwater fish | 1,591 | 22.5 | 2021 |
| 两栖类 Amphibian | 全部475种 475 (all species) | 37.05 | 2021 | |
| 爬行类 Reptilia | 全部475种 475 (all) | 30.53 | 2021 | |
| 鸟类 Aves | 全部1,445种 1,445 (all) | 9.97 | 2021 | |
| 哺乳类 Mammalia | 全部700种 700 (all) | 25.86 | 2021 | |
| 合计 Total | 4,686 | |||
| 海洋鱼类 Marine fishes | 盲鳗纲 Myxini | 全部9种 9 (all) | 100 | 2004 |
| 软骨鱼纲、硬骨鱼纲 Chondrichthyes and Osteichthyes | 部分受威胁程度较高的物种, 合计539种 Partial species highly threatened, totaling 539 | 84 | ||
| 无脊椎动物 Invertebrate | 淡水水母目 Limnomedusae | 全部9种 9 (all) | 55.6 | |
| 造礁石珊瑚 Scleractinia | 全部260种 260 (all) | 100 | ||
| 蝶类 Butterflies | 全部1,224种 1,224 (all) | 12.8 | ||
| 肠鳃动物门 Enteropneusta | 全部6种 6 (all) | 50 | ||
| 腹足纲、双壳纲、十足目、剑尾目、蛛形纲、昆虫纲、海参纲 Gastropoda, Bivalvia, Decapoda, Xiphosura, Arachnida, Insecta and Holothuroidea | 部分934种 934 (partial) | - | ||
| 合计 Total | 2,435 | 34.74 | ||
| 高等植物(全部) Higher plant (all) | 被子植物 Angiospermae | 30,068 | 11.18 | 2017b |
| 裸子植物 Gymnospermae | 274种及种下分类单元 274 species and lower taxa | 50.7 | 2021 | |
| 石松类和蕨类植物 Lycophytes and Pteridophyta | 2,244 | 8.11 | 2017 | |
| 苔藓植物 Bryophyte | 3,221 | 5.77 | 2017 | |
| 合计 Total | 35,784 | 10.84 | 2017b | |
| 大型真菌Macrofungi | 大型担子菌 Macro-basidiomycetes | 6,268 | 0.72 | 2020 |
| 地衣类 Lichens | 2,145 | 1.31 | 2020 | |
| 非地衣型大型子囊菌 Non-lichenized macro-ascomycetes | 870 | 2.76 | 2020 | |
| 合计 Total | 9,302 | 1.04 | 2020 |
表1 中国红色名录的评估现状
Table 1 Assessment Status of the Red List of China
| 物种大类 Large group | 物种门类 Taxon | 评估数量 Number assessed | 受威胁比例 Proportion of threatened species (%) | 参考文献 Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 脊椎动物(不含海洋鱼类) Vertebrates (excluding marine fishes) | 淡水鱼类 Freshwater fish | 1,591 | 22.5 | 2021 |
| 两栖类 Amphibian | 全部475种 475 (all species) | 37.05 | 2021 | |
| 爬行类 Reptilia | 全部475种 475 (all) | 30.53 | 2021 | |
| 鸟类 Aves | 全部1,445种 1,445 (all) | 9.97 | 2021 | |
| 哺乳类 Mammalia | 全部700种 700 (all) | 25.86 | 2021 | |
| 合计 Total | 4,686 | |||
| 海洋鱼类 Marine fishes | 盲鳗纲 Myxini | 全部9种 9 (all) | 100 | 2004 |
| 软骨鱼纲、硬骨鱼纲 Chondrichthyes and Osteichthyes | 部分受威胁程度较高的物种, 合计539种 Partial species highly threatened, totaling 539 | 84 | ||
| 无脊椎动物 Invertebrate | 淡水水母目 Limnomedusae | 全部9种 9 (all) | 55.6 | |
| 造礁石珊瑚 Scleractinia | 全部260种 260 (all) | 100 | ||
| 蝶类 Butterflies | 全部1,224种 1,224 (all) | 12.8 | ||
| 肠鳃动物门 Enteropneusta | 全部6种 6 (all) | 50 | ||
| 腹足纲、双壳纲、十足目、剑尾目、蛛形纲、昆虫纲、海参纲 Gastropoda, Bivalvia, Decapoda, Xiphosura, Arachnida, Insecta and Holothuroidea | 部分934种 934 (partial) | - | ||
| 合计 Total | 2,435 | 34.74 | ||
| 高等植物(全部) Higher plant (all) | 被子植物 Angiospermae | 30,068 | 11.18 | 2017b |
| 裸子植物 Gymnospermae | 274种及种下分类单元 274 species and lower taxa | 50.7 | 2021 | |
| 石松类和蕨类植物 Lycophytes and Pteridophyta | 2,244 | 8.11 | 2017 | |
| 苔藓植物 Bryophyte | 3,221 | 5.77 | 2017 | |
| 合计 Total | 35,784 | 10.84 | 2017b | |
| 大型真菌Macrofungi | 大型担子菌 Macro-basidiomycetes | 6,268 | 0.72 | 2020 |
| 地衣类 Lichens | 2,145 | 1.31 | 2020 | |
| 非地衣型大型子囊菌 Non-lichenized macro-ascomycetes | 870 | 2.76 | 2020 | |
| 合计 Total | 9,302 | 1.04 | 2020 |
| [1] |
Akçakaya HR, Hochkirch A, Bried JT, Simaika JP, de Knijf G, Henriques S (2021) Calculating population reductions of invertebrate species for IUCN Red List assessments. Journal of Insect Conservation, 25, 377-382.
DOI URL |
| [2] | Alliance for Zero Extinction (2022) About the Alliance. https://zeroextinction.org/. (accessed on 2022-07-02) |
| [3] | Baillie J, Groombridge B (1996) 1996 IUCN Red List of Threatened Animals. IUCN, Gland, Switzerland. |
| [4] |
Bird JP, Martin R, Akçakaya HR, Gilroy J, Burfield IJ, Garnett ST, Symes A, Taylor J, Şekercioğlu ÇH, Butchart SHM (2020) Generation lengths of the world’s birds and their implications for extinction risk. Conservation Biology, 34, 1252-1261.
DOI URL |
| [5] | Böhm M, Dewhurst-Richman NI, Seddon M, Ledger SEH, Albrecht C, Allen D, Bogan AE, Cordeiro J, Cummings KS, Cuttelod A, Darrigran G, Darwall W, Fehér Z, Gibson C, Graf DL, Köhler F, Lopes-Lima M, Pastorino G, Perez KE, Smith K, Damme D, Vinarski MV, Proschwitz T, Rintelen T, Aldridge DC, Aravind NA, Budha PB, Clavijo C, Tu D, Gargominy O, Ghamizi M, Haase M, Hilton-Taylor C, Johnson PD, Kebapçı Ü, Lajtner J, Lange CN, Lepitzki DAW, Martínez-Ortí A, Moorkens EA, Neubert E, Pollock CM, Prié V, Radea C, Ramirez R, Ramos MA, Santos SB, Slapnik R, Son MO, Stensgaard AS, Collen B (2021) The conservation status of the world’s freshwater molluscs. Hydrobiologia, 848, 3231-3254. |
| [6] | Bolam FC, Mair L, Angelico M, Brooks TM, Burgman M, Hermes C, Hoffmann M, Martin RW, McGowan PJK, Rodrigues ASL, Rondinini C, Westrip JRS, Wheatley H, Bedolla-Guzmán Y, Calzada J, Child MF, Cranswick PA, Dickman CR, Fessl B, Fisher DO, Garnett ST, Groombridge JJ, Johnson CN, Kennerley RJ, King SRB, Lamoreux JF, Lees AC, Lens L, Mahood SP, Mallon DP, Meijaard E, Méndez-Sánchez F, Percequillo AR, Regan TJ, Renjifo LM, Rivers MC, Roach NS, Roxburgh L, Safford RJ, Salaman P, Squires T, Vázquez-Domínguez E, Visconti P, Woinarski JCZ, Young RP, Butchart SHM (2021) How many bird and mammal extinctions has recent conservation action prevented? Conservation Letters, 14, e12762. |
| [7] |
Borgelt J, Dorber M, Høiberg MA, Verones F (2022) More than half of data deficient species predicted to be threatened by extinction. Communications Biology, 5, 679.
DOI PMID |
| [8] |
Brooks TM, Butchart SHM, Cox NA, Heath M, Hilton-Taylor C, Hoffmann M, Kingston N, Rodríguez JP, Stuart SN, Smart J (2015) Harnessing biodiversity and conservation knowledge products to track the Aichi Targets and Sustainable Development Goals. Biodiversity, 16, 157-174.
DOI URL |
| [9] | Brooks TM, Pimm SL, Akçakaya HR, Buchanan GM, Butchart SHM, Foden W, Hilton-Taylor C, Hoffmann M, Jenkins CN, Joppa L, Li BV, Menon V, Ocampo-Peñuela N, Rondinini C (2019) Measuring terrestrial area of habitat (AOH) and its utility for the IUCN red list. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 34, 977-986. |
| [10] |
Butchart SHM, Akçakaya HR, Chanson J, Baillie JEM, Collen B, Quader S, Turner WR, Amin R, Stuart SN, Hilton-Taylor C (2007) Improvements to the Red List index. PLoS ONE, 2, e140.
DOI PMID |
| [11] |
Butchart SHM, Stattersfield AJ, Bennun LA, Shutes SM, Akçakaya HR, Baillie JEM, Stuart SN, Hilton-Taylor C, Mace GM (2004) Measuring global trends in the status of biodiversity: Red list indices for birds. PLoS Biology, 2, e383.
DOI PMID |
| [12] |
Butchart SHM, Walpole M, Collen B, van Strien A, Scharlemann JPW, Almond REA, Baillie JEM, Bomhard B, Brown C, Bruno J, Carpenter KE, Carr GM, Chanson J, Chenery AM, Csirke J, Davidson NC, Dentener F, Foster M, Galli A, Galloway JN, Genovesi P, Gregory RD, Hockings M, Kapos V, Lamarque JF, Leverington F, Loh J, McGeoch MA, McRae L, Minasyan A, Morcillo MH, Oldfield TEE, Pauly D, Quader S, Revenga C, Sauer JR, Skolnik B, Spear D, Stanwell-Smith D, Stuart SN, Symes A, Tierney M, Tyrrell TD, Vié JC, Watson R (2010) Global biodiversity: Indicators of recent declines. Science, 328, 1164-1168.
DOI PMID |
| [13] |
Cai B, Li JT, Chen YY, Wang YZ (2016) Exploring the status and causes of China’s threatened reptiles through the red list assessment. Biodiversity Science, 24, 578-587. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[蔡波, 李家堂, 陈跃英, 王跃招 (2016) 通过红色名录评估探讨中国爬行动物受威胁现状及原因. 生物多样性, 24, 578-587.]
DOI |
|
| [14] |
Cardoso P, Borges PAV, Triantis KA, Ferrández MA, Martín JL (2012) The underrepresentation and misrepresentation of invertebrates in the IUCN Red List. Biological Conservation, 149, 147-148.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
Commock T, Campbell KCSE, Meikle J, Francisco-Ortega J, Jestrow B (2015) Conservation and taxonomic updates for the Jamaican endemic genus Dendrocousinsia (Euphorbiaceae). Brittonia, 67, 87-95.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
Cui P, Xu HG, Wu J, Ding H, Cao MC, Lu XQ, Yong F, Chen B (2014) Assessing the red list index for vertebrate species in China. Biodiversity Science, 22, 589-595. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[崔鹏, 徐海根, 吴军, 丁晖, 曹铭昌, 卢晓强, 雍凡, 陈冰 (2014) 中国脊椎动物红色名录指数评估. 生物多样性, 22, 589-595.]
DOI |
|
| [17] |
Dong SY, Zuo ZY, Yan YH, Xiang JY (2017) Red list assessment of lycophytes and ferns in China. Biodiversity Science, 25, 765-773. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[董仕勇, 左政裕, 严岳鸿, 向建英 (2017) 中国石松类和蕨类植物的红色名录评估. 生物多样性, 25, 765-773.]
DOI |
|
| [18] |
Ficetola GF, Rondinini C, Bonardi A, Baisero D,Padoa- Schioppa E (2015) Habitat availability for amphibians and extinction threat: A global analysis. Diversity and Distributions, 21, 302-311.
DOI URL |
| [19] | Fitter R, Fitter M (1987) The Road to Extinction. IUCN, Gland, Switzerland. |
| [20] |
Fox R, Harrower CA, Bell JR, Shortall CR, Middlebrook I, Wilson RJ (2019) Insect population trends and the IUCN Red List process. Journal of Insect Conservation, 23, 269-278.
DOI |
| [21] | Fu LK (1991) China Plant Red Data Book (Vol. 1). Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [傅立国 (1991) 《中国植物红皮书》(第一卷). 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [22] |
Gärdenfors U, Hilton-Taylor C, Mace GM, Rodríguez JP (2001) The application of IUCN Red List criteria at regional levels. Conservation Biology, 15, 1206-1212.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
González-del-Pliego P, Freckleton RP, Edwards DP, Koo MS, Scheffers BR, Pyron RA, Jetz W (2019) Phylogenetic and trait-based prediction of extinction risk for data-deficient amphibians. Current Biology, 29, 1557-1563.
DOI URL |
| [24] | Harfoot MBJ, Johnston A, Balmford A, Burgess ND, Butchart SHM, Dias MP, Hazin C, Hilton-Taylor C, Hoffmann M, Isaac NJB, Iversen LL, Outhwaite CL, Visconti P, Geldmann J (2021) Using the IUCN Red List to map threats to terrestrial vertebrates at global scale. Nature Ecology & Evolution, 5, 1510-1519. |
| [25] | Harvis E, Campbell L, Braun A, Shao WS (2020) Science, scale and the frontier of governing mobile marine species. International Social Science Journal (Chinese Edition), 37, 77-96, 6, 7, 11. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [哈维斯∙伊丽莎白, 丽莎·坎贝尔, 艾米∙布劳恩 (2020) 科学、尺度与治理移动性海洋物种的边疆. 国际社会科学杂志(中文版), 37(1), 77-96, 6, 7, 11.] | |
| [26] |
He Q, Jia Y (2017) Assessing the threat status of China’s bryophytes. Biodiversity Science, 25, 774-780. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[何强, 贾渝 (2017) 中国苔藓植物濒危等级的评估原则和评估结果. 生物多样性, 25, 774-780.]
DOI |
|
| [27] | IPBES (2019) Global assessment report on biodiversity and ecosystem services of the Intergovernmental Science-Policy Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services. IPBES Secretariat, Bonn, Germany. |
| [28] | IUCN (1994) IUCN Red List Categories. IUCN Species Survival Commission. IUCN, Gland, Switzerland and Cambridge, UK. |
| [29] | IUCN (2001) IUCN Red List Categories and Criteria: Version 3.1. IUCN Species Survival Commission. IUCN, Gland, Switzerland and Cambridge, UK. |
| [30] | IUCN (2003) Guidelines for Application of IUCN Criteria at Regional Levels, Version 3.0. IUCN, Gland, Switzerland and Cambridge, UK. |
| [31] | IUCN (2012a) Guidelines for Application of IUCN Red List Criteria at Regional and National Levels, Version 4.0. IUCN, Gland, Switzerland and Cambridge, UK. |
| [32] | IUCN (2012b) IUCN Red List Categories and Criteria, Version 3.1, 2nd edn. IUCN, Gland, Switzerland and Cambridge, UK. |
| [33] | IUCN (2022a) The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species, Version. https://www.iucnredlist.org. (accessed on 2022-07-22) |
| [34] | IUCN (2022b) IUCN Red List 2017-2020 Report. https://nc.iucnredlist.org/redlist/resources/files/1630480997-IUCN_RED_LIST_QUADRENNIAL_REPORT_2017-2020.pdf. (accessed on 2022-07-22) |
| [35] | IUCN Standards and Petitions Committee (2022) Guidelines for Using the IUCN Red List Categories and Criteria. Version 15. https://www.iucnredlist.org/documents/RedListGuidelines.pdf. (accessed on 2022-07-22) |
| [36] | Jiang JP, Xie F, Li C, Wang B (2021) China’s Red List of Biodiversity·Vertebrates (Vol. IV): Amphibians (I and II). Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese and English) |
| [江建平, 谢锋, 李成, 王斌 (2021) 中国生物多样性红色名录·脊椎动物(第四卷): 两栖动物(上下册). 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [37] | Jiang ZG (2021) China’s Red List of Biodiversity·Vertebrates (Vol. I): Mammals (I, II and III). Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese and English) |
| [蒋志刚 (2021) 中国生物多样性红色名录·脊椎动物(第一卷): 哺乳动物(上中下册). 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [38] |
Jiang ZG, Jiang JP, Wang YZ, Zhang E, Zhang YY, Cai B (2020) Significance of country red lists of endangered species for biodiversity conservation. Biodiversity Science, 28, 558-565. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[蒋志刚, 江建平, 王跃招, 张鹗, 张雁云, 蔡波 (2020) 国家濒危物种红色名录的生物多样性保护意义. 生物多样性, 28, 558-565.]
DOI |
|
| [39] |
Jiang ZG, Luo ZH (2012) Assessing species endangerment status: Progress in research and an example from China. Biodiversity Science, 20, 612-622. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[蒋志刚, 罗振华 (2012) 物种受威胁状况评估: 研究进展与中国的案例. 生物多样性, 20, 612-622.]
DOI |
|
| [40] |
Jiang ZG, Ma KP (2017) The state’s will, scientific decision and citizen participation: In memory of the first provincial species red list in China. Biodiversity Science, 25, 794-795. (in Chinese)
DOI URL |
|
[蒋志刚, 马克平 (2017) 中国生物多样性保护的国家意志、科学决策和公众参与: 第一份省域物种红色名录研究. 生物多样性, 25, 794-795.]
DOI |
|
| [41] |
Juslén A, Pykälä J, Kuusela S, Kaila L, Kullberg J, Mattila J, Muona J, Saari S, Cardoso P (2016) Application of the Red List Index as an indicator of habitat change. Biodiversity and Conservation, 25, 569-585.
DOI URL |
| [42] | Le PQ, Chen YY (1998) China Endangered Animal Red Data Book·Fishes. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [乐佩琦, 陈宜瑜 (1998) 中国濒危动物红皮书·鱼类. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [43] | Li BV, Hughes AC, Jenkins CN, Ocampo-Peñuela N, Pimm SL (2016) Remotely sensed data informs red list evaluations and conservation priorities in Southeast Asia. PLoS ONE, 11, e0160566. |
| [44] |
Li BV, Pimm SL (2016) China’s endemic vertebrates sheltering under the protective umbrella of the giant panda. Conservation Biology, 30, 329-339.
DOI URL |
| [45] | Li JS, Jin YC, Wang W, Zhao ZP, Wu XP (2016) Priority Areas of Terrestrial Biodiversity Conservation in China. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [李俊生, 靳勇超, 王伟, 赵志平, 吴晓莆 (2016) 中国陆域生物多样性保护优先区域. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [46] |
Li Y, Liu DM, Wang K, Wu HJ, Cai L, Cai L, Li JS, Yao YJ (2020a) Red list assessment of macrofungi in China: Challenges and measures. Biodiversity Science, 28, 66-73. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[李熠, 刘冬梅, 王科, 吴海军, 蔡蕾, 蔡磊, 李俊生, 姚一建 (2020) 中国大型真菌红色名录评估中存在的问题及今后的对策. 生物多样性, 28, 66-73.]
DOI |
|
| [47] |
Li Y, Tang ZY, Yan YJ, Wang K, Cai L, He JS, Gu S, Yao YJ (2020b) Incorporating species distribution model into the red list assessment and conservation of macrofungi: A case study with Ophiocordyceps sinensis. Biodiversity Science, 28, 99-106. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[李熠, 唐志尧, 闫昱晶, 王科, 蔡磊, 贺金生, 古松, 姚一建 (2020) 物种分布模型在大型真菌红色名录评估及保护中的应用: 以冬虫夏草为例. 生物多样性, 28, 99-106.]
DOI |
|
| [48] | Liu J, Que PJ, Zhang ZW (2019) Species diversity and suggestions for adjustment of the national protection level of waterbirds in China. Wetland Science, 17, 123-136. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [刘金, 阙品甲, 张正旺 (2019) 中国水鸟的物种多样性及其国家重点保护等级调整的建议. 湿地科学, 17, 123-136.] | |
| [49] | Liu JJ, Slik F, Zheng SL, Lindenmayer DB (2022) Undescribed species have higher extinction risk than known species. Conservation Letters, 15, e12876. |
| [50] | Luther D, Cooper WJ, Wong J, Walker M, Farinelli S, Visseren-Hamakers I, Burfield IJ, Simkins A, Bunting G, Brooks TM, Dicks K, Scott J, Westrip JRS, Lamoreux J, Parr M, de Silva N, Foster M, Upgren A, Butchart SHM Butchart SHM (2021) Conservation actions benefit the most threatened species: A 13-year assessment of Alliance for Zero Extinction species. Conservation Science and Practice, 3, e510. |
| [51] | Mace GM, Collar N, Cooke J, Gaston K, Ginsberg J, Leader-Williams N, Maunder M, Milner-Gulland EJ (1992) The development of new criteria for listing species on the IUCN Red List. Species, 19, 16-22. |
| [52] |
Mace GM, Lande R (1991) Assessing extinction threats: Toward a reevaluation of IUCN threatened species categories. Conservation Biology, 5, 148-157.
DOI URL |
| [53] | MacKinnon J (2022) Field Guide to the Birds of China. The Commercial Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [约翰·马敬能 (2022) 中国鸟类野外手册. 商务印书馆, 北京.] | |
| [54] | McCay SD, Lacher Jr TE (2021) National level use of International Union for Conservation of Nature knowledge products in American National Biodiversity Strategies and Action Plans and National Reports to the Convention on Biological Diversity. Conservation Science and Practice, 3, e350. |
| [55] | Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People’s Republic of China (2010) Biodiversity Conservation Strategy and Action Plan of China (2011-2030) (in Chinese) |
| [中华人民共和国环境保护部 (2010) 中国生物多样性保护战略和行动计划(2011-2030) https://www.mee.gov.cn/gkml/hbb/bwj/201009/t20100921_194841.htm. (accessed on 2022-07-22) | |
| [56] | Ocampo-Peñuela N, Jenkins CN, Vijay V, Li BV, Pimm SL (2016) Incorporating explicit geospatial data shows more species at risk of extinction than the current Red List. Science Advances, 2, e1601367. |
| [57] | Oldfield S, Lusty C, MacKinven A (1998) The World List of Threatened Trees. World Conservation Press, Cambridge. |
| [58] |
Pacoureau N, Rigby CL, Kyne PM, Sherley RB, Winker H, Carlson JK, Fordham SV, Barreto R, Fernando D, Francis MP, Jabado RW, Herman KB, Liu KM, Marshall AD, Pollom RA, Romanov EV, Simpfendorfer CA, Yin JS, Kindsvater HK, Dulvy NK (2021) Half a century of global decline in oceanic sharks and rays. Nature, 589, 567-571.
DOI URL |
| [59] | Pimm SL, Jenkins CN, Li BV (2018) How to protect half of Earth to ensure it protects sufficient biodiversity. Science Advances, 4, eaat2616. |
| [60] | Putri MRA, Astri S, Joni H (2019) Seahorse Resources (Hippocampus spp.) in the Waters of Bintan Island, Lampung Bay and Tanakeke Island. Oseanologi dan Limnologi di Indonesia, 4 (1), 27-40. |
| [61] |
Qin HN, Yang Y, Dong SY, He Q, Jia Y, Zhao LN, Yu SX, Liu HY, Liu B, Yan YH, Xiang JY, Xia NH, Peng H, Li ZY, Zhang ZX, He XJ, Yin LK, Lin YL, Liu QR, Hou YT, Liu Y, Liu QX, Cao W, Li JQ, Chen SL, Jin XH, Gao TG, Chen WL, Ma HY, Geng YY, Jin XF, Chang CY, Jiang H, Cai L, Zang CX, Wu JY, Ye JF, Lai YJ, Liu B, Lin QW, Xue NX (2017a) Threatened Species List of China’s higher plants. Biodiversity Science, 25, 696-744. (in Chinese and in English)
DOI URL |
| [覃海宁, 杨永, 董仕勇, 何强, 贾渝, 赵莉娜, 于胜祥, 刘慧圆, 刘博, 严岳鸿, 向建英, 夏念和, 彭华, 李振宇, 张志翔, 何兴金, 尹林克, 林余霖, 刘全儒, 侯元同, 刘演, 刘启新, 曹伟, 李建强, 陈世龙, 金效华, 高天刚, 陈文俐, 马海英, 耿玉英, 金孝锋, 常朝阳, 蒋宏, 蔡蕾, 臧春鑫, 武建勇, 叶建飞, 赖阳均, 刘冰, 林秦文, 薛纳新 (2017a) 中国高等植物受威胁物种名录. 生物多样性, 25, 696-744.] | |
| [62] |
Qin HN, Zhao LN, Yu SX, Liu HY, Liu B, Xia NH, Peng H, Li ZY, Zhang ZX, He XJ, Yin LK, Lin YL, Liu QR, Hou YT, Liu Y, Liu QX, Cao W, Li JQ, Chen SL, Jin XH, Gao TG, Chen WL, Ma HY, Geng YY, Jin XF, Chang CY, Jiang H, Cai L, Zang CX, Wu JY, Ye JF, Lai YJ, Liu B, Lin QW, Xue NX (2017b) Evaluating the endangerment status of China’s angiosperms through the red list assessment. Biodiversity Science, 25, 745-757. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
| [覃海宁, 赵莉娜, 于胜祥, 刘慧圆, 刘博, 夏念和, 彭华, 李振宇, 张志翔, 何兴金, 尹林克, 林余霖, 刘全儒, 侯元同, 刘演, 刘启新, 曹伟, 李建强, 陈世龙, 金效华, 高天刚, 陈文俐, 马海英, 耿玉英, 金孝锋, 常朝阳, 蒋宏, 蔡蕾, 臧春鑫, 武建勇, 叶建飞, 赖阳均, 刘冰, 林秦文, 薛纳新 (2017b) 中国被子植物濒危等级的评估. 生物多样性, 25, 745-757.] | |
| [63] |
Regan EC, Santini L, Ingwall-King L, Hoffmann M, Rondinini C, Symes A, Taylor J, Butchart SHM (2015) Global trends in the status of bird and mammal pollinators. Conservation Letters, 8, 397-403.
DOI URL |
| [64] |
Saiz JCM, Lozano FD, Gómez MM, Baudet ÁB (2015) Application of the Red List Index for conservation assessment of Spanish vascular plants. Conservation Biology, 29, 910-919.
DOI PMID |
| [65] | Smith A, Xie Y (2013) Mammals of China. Princeton University Press, Princeton and Oxford. |
| [66] |
Tolley KA, Weeber J, Maritz B, Verburgt L, Bates MF, Conradie W, Hofmeyr MD, Turner AA, da Silva JM, Alexander GJ (2019) No safe haven: Protection levels show imperilled South African reptiles not sufficiently safe-guarded despite low average extinction risk. Biological Conservation, 233, 61-72.
DOI URL |
| [67] |
Trull N, Böhm M, Carr J (2018) Patterns and biases of climate change threats in the IUCN Red List. Conservation Biology, 32, 135-147.
DOI PMID |
| [68] |
Walls RHL, Dulvy NK (2020) Eliminating the dark matter of data deficiency by predicting the conservation status of Northeast Atlantic and Mediterranean Sea sharks and rays. Biological Conservation, 246, 108459.
DOI URL |
| [69] |
Wang K, Wang YH, Zhao MJ, Kirk PM, Yao YJ (2019) Missing names from the Fungal Name Repositories found in the literature related to Chinese fungi. Phytotaxa, 411, 1-22.
DOI |
| [70] | Wang S (1998) China Endangered Animal Red Data Book·Mammals. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [汪松 (1998) 中国濒危动物红皮书·兽类. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [71] | Wang S, Xie Y (2004) China Species Red List (Vol. I):Red List. Higher Education Press. Beijing. (in Chinese and in English) |
| [汪松, 解焱 (2004) 中国物种红色名录(第一卷): 红色名录. 高教出版社, 北京.] | |
| [72] | Wang S, Xie Y (2005) China Species Red List (Vol. III): Invertebrates. Higher Education Press. Beijing. (in Chinese and in English) |
| [汪松, 解焱 (2005) 中国物种红色名录(第三卷): 无脊椎动物. 高等教育出版社, 北京.] | |
| [73] | Wang S, Xie Y (2009a) China Species Red List (Vol. II):Fishes and Amphibians. Higher Education Press. Beijing. (in Chinese and English) |
| [汪松, 解焱 (2009) 中国物种红色名录(第二卷上): 鱼类和两栖类. 高等教育出版社, 北京.] | |
| [74] | Wang S, Xie Y (2009b) China Species Red List (Vol. II): Reptiles, Birds and Mammals. Higher Education Press, Beijing. (in Chinese and in English) |
| [汪松, 解焱 (2009) 中国物种红色名录(第二卷下): 爬行类, 鸟类和兽类, pp. 1-84. 高等教育出版社, 北京. ] | |
| [75] |
Wang WT, Yang TT, Jin L, Jiang JM (2021) Vulnerability of two Rhodiola species under climate change in the future. Biodiversity Science, 29, 1620-1628. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[王文婷, 杨婷婷, 金磊, 蒋家民 (2021) 未来气候变化下两种红景天植物的脆弱性. 生物多样性, 29, 1620-1628.]
DOI |
|
| [76] | Wang YZ (2021) China’s Red List of Biodiversity·Vertebrates (Vol. III):Reptiles. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese and in English) |
| [王跃招 (2021) 中国生物多样性红色名录·脊椎动物(第三卷): 爬行动物. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [77] |
Wei TZ, Wang K, Yu XD, Li Y, Wu HJ, Wu HM, Wang YH, Wei XD, Li BB, Jiang L, Yao YJ (2020) Assessment of the threatened status of macro-basidiomycetes in China. Biodiversity Science, 28, 41-53. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[魏铁铮, 王科, 于晓丹, 李熠, 吴海军, 吴红梅, 王永会, 卫晓丹, 李斌斌, 蒋岚, 姚一建 (2020) 中国大型担子菌受威胁现状评估. 生物多样性, 28, 41-53.]
DOI |
|
| [78] |
Wei XL, Deng H, Wei JC (2020) Threatened categories assessment of lichens in China. Biodiversity Science, 28, 54-65. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[魏鑫丽, 邓红, 魏江春 (2020) 中国地衣的濒危等级评估. 生物多样性, 28, 54-65.]
DOI |
|
| [79] |
Wen F, Fu LF, Xin ZB, Xiong C, Wei YG (2022) Endangered status and biodiversity conservation of China’s Gesneriaceae. Guangxi Plants, doi: 10.11931/guihaia.gxzw202203034. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[温放, 符龙飞, 辛子兵, 熊驰, 韦毅刚 (2022) 中国苦苣苔科植物濒危现状与多样性保护. 广西植物, doi: 10.11931/guihaia.gxzw202203034.]
DOI |
|
| [80] |
Wu RD, Zhang S, Yu DW, Zhao P, Li XH, Wang LZ, Yu Q, Ma J, Chen A, Long YC (2011) Effectiveness of China’s nature reserves in representing ecological diversity. Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment, 9, 383-389.
DOI URL |
| [81] | Xie Y, Wang S (1995) International new criteria for endangered species Categories. Chinese Biodiversity, 3, 234-239. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [解焱, 汪松 (1995) 国际濒危物种等级新标准. 生物多样性, 3, 234-239.] | |
| [82] | Xie Y, Zhang S, Wang W (2009) Biodiversity Atlas of China. Hunan Education Press, Changsha. (in Chinese) |
| [解焱, 张爽, 王伟 (2009) 中国生物多样性地理图集. 湖南教育出版社, 长沙.] | |
| [83] |
Yang Y (2021) An updated red list assessment of gymnosperms from China (Version 2021). Biodiversity Science, 29, 1599-1606. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[杨永 (2021) 中国裸子植物红色名录评估(2021版). 生物多样性, 29, 1599-1606.]
DOI |
|
| [84] |
Yao YJ (2020) Red list assessment of macrofungi in China. Biodiversity Science, 28, 1-3. (in Chinese)
DOI |
|
[姚一建 (2020) 中国大型真菌红色名录评估. 生物多样性, 28, 1-3.]
DOI |
|
| [85] |
Yao YJ, Wei JC, Zhuang WY, Cai L, Liu DM, Li JS, Wei TZ, Li Y, Wang K, Wu HJ (2020) Development of red list assessment of macrofungi in China. Biodiversity Science, 28, 4-10. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[姚一建, 魏江春, 庄文颖, 蔡蕾, 刘冬梅, 李俊生, 魏铁铮, 李熠, 王科, 吴海军 (2020) 中国大型真菌红色名录评估研究进展. 生物多样性, 28, 4-10.]
DOI |
|
| [86] |
Young RP, Hudson MA, Terry AMR, Jones CG, Lewis RE, Tatayah V, Zuël N, Butchart SHM (2014) Accounting for conservation: Using the IUCN Red List Index to evaluate the impact of a conservation organization. Biological Conservation, 180, 84-96.
DOI URL |
| [87] |
Zang CX, Cai L, Li JQ, Wu XP, Li XG, Li JS (2016) Preparation of the China Biodiversity Red List and its significance for biodiversity conservation within China. Biodiversity Science, 24, 610-614. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[臧春鑫, 蔡蕾, 李佳琦, 吴晓莆, 李晓光, 李俊生 (2016) 《中国生物多样性红色名录》的制定及其对生物多样性保护的意义. 生物多样性, 24, 610-614.]
DOI |
|
| [88] | Zhang E, Cao WX (2021) China’s Red List of Biodiversity·Vertebrates (Vol. V): Freshwater Fishes. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [张鹗, 曹文宣 (2021) 中国生物多样性红色名录·脊椎动物(第五卷): 淡水鱼类. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [89] | Zhang YY, Zheng GM (2021) China’ Red List of Biodiversity·Vertebrates (Vol. II): Birds. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese and in English) |
| [张雁云, 郑光美 (2021) 中国生物多样性红色名录·脊椎动物(第二卷): 鸟类. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [90] | Zhao EM (1998) China Endangered Animal Red Data Book·Amphibians and Reptiles. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [赵尔宓 (1998) 中国濒危动物红皮书·两栖和爬行类. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [91] | Zhao Y, Zhang YY, Zhao YH (2021) Assessment of endangerment category on Chinese cavefish: A case study of two national protected fish species. Carsologica Sinica, 40, 1032-1037. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [赵阳, 张媛媛, 赵亚辉 (2021) 中国洞穴鱼类濒危等级评估——以两种国家重点保护鱼类为例. 中国岩溶, 40, 1032-1037.] | |
| [92] | Zheng GM, Wang QS (1998) China Endangered Animal Red Data Book·Birds. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [郑光美, 王岐山 (1998) 中国濒危动物红皮书·鸟类. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [93] | Zhou DQ, Gao J, Qian ZD, Zhang HN, Xu WG, Jiang MK (2016) Evaluation of in situ conservation of vertebrates in China. Journal of Ecology and Rural Environment, 32, 7-12. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [周大庆, 高军, 钱者东, 张昊楠, 徐网谷, 蒋明康 (2016) 中国脊椎动物就地保护状况评估. 生态与农村环境学报, 32, 7-12.] | |
| [94] |
Zhuang WY, Li Y, Zheng HD, Zeng ZQ, Wang XC (2020) Threat status of non-lichenized macro-ascomycetes in China and its threatening factors. Biodiversity Science, 28, 26-40. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[庄文颖, 李熠, 郑焕娣, 曾昭清, 王新存 (2020) 中国非地衣型大型子囊菌受威胁现状评估及致危因素. 生物多样性, 28, 26-40.]
DOI |
| [1] | 彭莳嘉, 罗源, 蔡宏宇, 张晓玲, 王志恒. 全球变化情景下的中国木本植物受威胁物种名录[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(5): 21459-. |
| [2] | 张光富, 熊天石, 孙婷, 李恺頔, 邵丽鸳. 江苏珍稀濒危植物的多样性、分布及保护[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(2): 21335-. |
| [3] | 郝希阳, 贺姹, 楚克林, 申志新, 赵强, 高伟, 潘达, 孙红英. 海南岛淡水蟹类分布格局与多样性保护[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(5): 605-616. |
| [4] | 魏鑫丽,邓红,魏江春. 中国地衣的濒危等级评估[J]. 生物多样性, 2020, 28(1): 54-65. |
| [5] | 王科,刘冬梅,蔡蕾,吴海军,李熠,魏铁铮,王永会,吴红梅,卫晓丹,李斌斌,李俊生,姚一建. 中国大型真菌红色名录评估方法和程序[J]. 生物多样性, 2020, 28(1): 11-19. |
| [6] | 单章建,赵莉娜,杨宇昌,谢丹,覃海宁. 中国植物受威胁等级评估系统概述[J]. 生物多样性, 2019, 27(12): 1352-1363. |
| [7] | 董仕勇, 左政裕, 严岳鸿, 向建英. 中国石松类和蕨类植物的红色名录评估[J]. 生物多样性, 2017, 25(7): 765-773. |
| [8] | 何强, 贾渝. 中国苔藓植物濒危等级的评估原则和评估结果[J]. 生物多样性, 2017, 25(7): 774-780. |
| [9] | 覃海宁, 赵莉娜, 于胜祥, 刘慧圆, 刘博, 夏念和, 彭华, 李振宇, 张志翔, 何兴金, 尹林克, 林余霖, 刘全儒, 侯元同, 刘演, 刘启新, 曹伟, 李建强, 陈世龙, 金效华, 高天刚, 陈文俐, 马海英, 耿玉英, 金孝锋, 常朝阳, 蒋宏, 蔡蕾, 臧春鑫, 武建勇, 叶建飞, 赖阳均, 刘冰, 林秦文, 薛纳新. 中国被子植物濒危等级的评估[J]. 生物多样性, 2017, 25(7): 745-757. |
| [10] | 张殷波, 苑虎, 喻梅. 国家重点保护野生植物受威胁等级的评估[J]. 生物多样性, 2011, 19(1): 57-62. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn
![]()
