



生物多样性 ›› 2022, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (3): 21426. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2021426 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2021426
所属专题: 传粉生物学; 昆虫多样性与生态功能
收稿日期:2021-10-25
接受日期:2022-01-25
出版日期:2022-03-20
发布日期:2022-03-10
通讯作者:
杨春锋
作者简介:*E-mail: cfyang@wbgcas.cn基金资助:
Dexin Liu1,2,3, Qingfeng Wang3, Chunfeng Yang3,*( )
)
Received:2021-10-25
Accepted:2022-01-25
Online:2022-03-20
Published:2022-03-10
Contact:
Chunfeng Yang
摘要:
天南星科植物具有特殊的佛焰苞花序及多样化的传粉策略, 是研究被子植物花的分化与动植物之间进化生态学联系的理想材料。本文简述了天南星科不同类型的花序结构及其传粉适应意义, 总结了天南星科传粉策略的基本类型与演化历史。天南星科的苞片结构主要包括原始型、外展平面型、直立宽佛焰苞型和直立狭佛焰苞4种类型, 呈现出从简单的片状与外展平面状结构向复杂的立体包裹状的佛焰苞结构演化的趋势。肉穗花序可分为两性花花序、单性花雌雄同序和单性花雌雄异序3种类型, 演化路线为两性花花序→单性花雌雄同序→单性花雌雄异序。天南星科的传粉者主要有鞘翅目、双翅目、膜翅目昆虫, 表现出5种主要传粉策略: 食物报酬型互利传粉、气味吸引型欺骗性传粉、交配场所型互利传粉、产卵场所型互利传粉和致死陷阱型欺骗性传粉。天南星科植物通过花序的形状、颜色、产热以及花部挥发物来吸引传粉者, 其中最主要的挥发物有二甲基硫化物、甲基吲哚化合物、萜类和苯类化合物, 模拟食物或产卵场所信号吸引鞘翅目甲虫和双翅目昆虫为其传粉。天南星科植物的佛焰苞被认为是促进该科物种分化的一个重要结构, 但该性状的演化历史及其与传粉系统分化之间的内在联系尚不明确。利用现代分子生物学技术以及模型模拟等手段, 结合生理生态学方法深入探究传粉事件与天南星科植物的花多样性以及物种分化之间的联系, 有望提升关于植物-传粉者互作与植物的花多样性分化之间关系的认识, 并丰富对被子植物多样性演化相关研究的理解。
刘德鑫, 王青锋, 杨春锋 (2022) 天南星科植物的花多样性与传粉策略. 生物多样性, 30, 21426. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2021426.
Dexin Liu, Qingfeng Wang, Chunfeng Yang (2022) Flower diversity and pollination strategy in Araceae. Biodiversity Science, 30, 21426. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2021426.
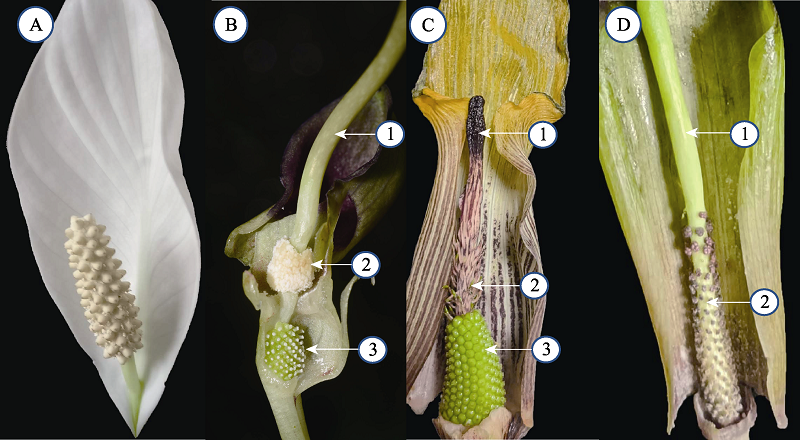
图1 天南星科肉穗花序类型。(A)两性花花序(白鹤芋); (B)单性花雌雄同花序(滴水珠: ①附属器; ②雄花序; ③雌花序); (C)单性花雌花序(邑田南星: ①附属器; ②丝状退化不育花; ③雌花序); (D)单性花雄花序(邑田南星: ①附属器; ②雄花序)。
Fig. 1 Inflorescence types of Araceae. (A) Bisexual inflorescence (Spathiphyllum kochii); (B) Monoecious inflorescence (Pinellia cordata: ① Appendix; ② Staminate inflorescence; ③ Pistillate inflorescence); (C) Unisexual pistillate inflorescence (Arisaema muratae: ① Appendix; ② Elongated sterile flowers; ③ Pistillate inflorescence); (D) Unisexual staminate inflorescence (Arisaema muratae: ① Appendix; ② Staminate inflorescence).
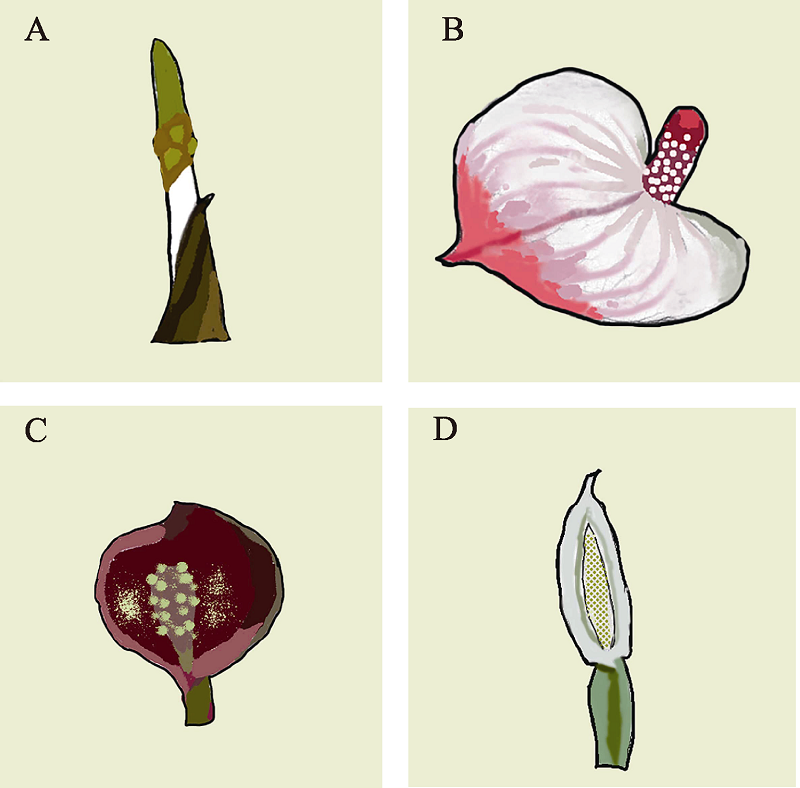
图2 天南星科佛焰苞类型。A: 原始型佛焰苞(类型I, 水金杖); B: 外展平面型(类型II, 花烛); C: 直立宽佛焰苞(类型III, 臭菘); D: 直立狭佛焰苞(类型IV, 野芋)。
Fig. 2 Spathe types of Araceae. A, Unmodified spathe (I) (Orontium aquaticum); B, Expanded planar spathe (II) (Anthurium andraeanum); C, Erect broad spathe (III) (Symplocarpus renifolius); D, Erect narrow spathe (IV) (Colocasia antiquorum).
| 传粉策略类型 Types of pollination strategies | 花序类型 Inflorescence type | 主要传粉者 Pollinators | 代表种 Species | 主要花部挥发物 Flower volatiles | 参考文献 References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 食物报酬型互利 传粉 Food-rewards mutualistic pollination | AⅠ | 膜翅目和鞘翅目 Hymenoptera and Coleoptera | 水金杖 Orontium aquaticum | - | Jiménez et al, |
| AⅡ | 膜翅目蜜蜂科 Hymenoptera: Apidae | Anthurium acutifolium | 脂肪烃、吲哚和萜类化合物 Aliphatic hydrocarbons, indoles and terpenes | Etl et al, | |
| AⅢ | 鞘翅目露尾甲科 Coleoptera: Nitidulidae | Monstera lentii | - | Prieto & Cascante -Marín, | |
| 气味吸引型欺骗性 传粉 Odor-attracting deceptive pollination | BⅣ | 鞘翅目金龟总科 Coleoptera: Scarabaeoidea | Amorphophallus johnsonii | 二甲基硫化物 Dimethyl sulfide | Beath, |
| BⅣ | 鞘翅目隐翅虫科 Coleoptera: Staphylinidae | Typhonium brownie | 粪臭素、吲哚和对甲酚 Skatole, indole and p-cresol | Sayers et al, | |
| BⅣ | 双翅目毛蠓科 Diptera: Psychodidae | Arum italicum, A. creticum | 苯甲醇、丁香酚和甲基吲哚 Benzyl alcohol, eugenol and methyl indole | Albre et al, | |
| 交配场所互利型 传粉 Mating sites mutualistic pollination | BⅣ | 鞘翅目金龟总科 Coleoptera: Scarabaeidae | Philodendron solimoesense | - | Gibernau & Barabé, |
| BⅣ | 鞘翅目鳃金龟科 Coleoptera: Melolonthidae | Xanthosoma undipe | 萜类和苯类化合物 Terpenoids and benzenes | Milet-Pinheiro et al, | |
| 产卵场所型互利 传粉 Oviposition-attracting mutualistic pollination | BⅣ | 圆头犀金龟族 Cyclocephala and Erioscelis | Dieffenbachia longispatha | - | Young, |
| BⅣ | 果蝇亚科芋果蝇属 Drosophilinae: Colocasiomyia | Colocasia xenalocasiae | - | Bröderbauer et al, | |
| BⅢ | 果蝇亚科芋果蝇属 Drosophilinae: Colocasiomyia | Schismatoglottis pantiensis | 3-甲基-3-丁烯酸甲酯 Methyl 3-methyl-3-butenate | Hoe et al, | |
| BⅢ | 双翅目果蝇科 Diptera: Drosophilidae | 泉七 Steudnera colocasiifolia | - | Takenaka et al, | |
| BⅣ | 果蝇亚科芋果蝇属 Drosophilinae: Colocasiomyia | 海芋 Alocasia odora | - | Miyake & Yafuso, | |
| 致死陷阱型欺骗性 传粉 Lethal trap deceptive pollination | CⅣ | 双翅目菌蚊科 Diptera: Mycetophilidae | 三叶天南星 Arisaema triphyllum | 短链脂肪醛和醇 Aliphatic aldehyde and alcohol | Barriault et al, |
表1 天南星科植物传粉策略与花序类型、传粉者类群、代表种及主要花部挥发物
Table 1 Pollination strategies, inflorescence types, pollinators, representative species and major flower volatiles of Araceae
| 传粉策略类型 Types of pollination strategies | 花序类型 Inflorescence type | 主要传粉者 Pollinators | 代表种 Species | 主要花部挥发物 Flower volatiles | 参考文献 References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 食物报酬型互利 传粉 Food-rewards mutualistic pollination | AⅠ | 膜翅目和鞘翅目 Hymenoptera and Coleoptera | 水金杖 Orontium aquaticum | - | Jiménez et al, |
| AⅡ | 膜翅目蜜蜂科 Hymenoptera: Apidae | Anthurium acutifolium | 脂肪烃、吲哚和萜类化合物 Aliphatic hydrocarbons, indoles and terpenes | Etl et al, | |
| AⅢ | 鞘翅目露尾甲科 Coleoptera: Nitidulidae | Monstera lentii | - | Prieto & Cascante -Marín, | |
| 气味吸引型欺骗性 传粉 Odor-attracting deceptive pollination | BⅣ | 鞘翅目金龟总科 Coleoptera: Scarabaeoidea | Amorphophallus johnsonii | 二甲基硫化物 Dimethyl sulfide | Beath, |
| BⅣ | 鞘翅目隐翅虫科 Coleoptera: Staphylinidae | Typhonium brownie | 粪臭素、吲哚和对甲酚 Skatole, indole and p-cresol | Sayers et al, | |
| BⅣ | 双翅目毛蠓科 Diptera: Psychodidae | Arum italicum, A. creticum | 苯甲醇、丁香酚和甲基吲哚 Benzyl alcohol, eugenol and methyl indole | Albre et al, | |
| 交配场所互利型 传粉 Mating sites mutualistic pollination | BⅣ | 鞘翅目金龟总科 Coleoptera: Scarabaeidae | Philodendron solimoesense | - | Gibernau & Barabé, |
| BⅣ | 鞘翅目鳃金龟科 Coleoptera: Melolonthidae | Xanthosoma undipe | 萜类和苯类化合物 Terpenoids and benzenes | Milet-Pinheiro et al, | |
| 产卵场所型互利 传粉 Oviposition-attracting mutualistic pollination | BⅣ | 圆头犀金龟族 Cyclocephala and Erioscelis | Dieffenbachia longispatha | - | Young, |
| BⅣ | 果蝇亚科芋果蝇属 Drosophilinae: Colocasiomyia | Colocasia xenalocasiae | - | Bröderbauer et al, | |
| BⅢ | 果蝇亚科芋果蝇属 Drosophilinae: Colocasiomyia | Schismatoglottis pantiensis | 3-甲基-3-丁烯酸甲酯 Methyl 3-methyl-3-butenate | Hoe et al, | |
| BⅢ | 双翅目果蝇科 Diptera: Drosophilidae | 泉七 Steudnera colocasiifolia | - | Takenaka et al, | |
| BⅣ | 果蝇亚科芋果蝇属 Drosophilinae: Colocasiomyia | 海芋 Alocasia odora | - | Miyake & Yafuso, | |
| 致死陷阱型欺骗性 传粉 Lethal trap deceptive pollination | CⅣ | 双翅目菌蚊科 Diptera: Mycetophilidae | 三叶天南星 Arisaema triphyllum | 短链脂肪醛和醇 Aliphatic aldehyde and alcohol | Barriault et al, |
| [1] |
Albre J, Quilichini A, Gibernau M (2003) Pollination ecology of Arum italicum (Araceae). Botanical Journal of the Linnean Society, 141, 205-214.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
Barriault I, Barabé D, Cloutier L, Gibernau M (2010) Pollination ecology and reproductive success in Jack-in- the-pulpit (Arisaema triphyllum) in Québec (Canada). Plant Biology, 12, 161-171.
DOI PMID |
| [3] |
Barriault I, Barabé D, Cloutier L, Pellerin S, Gibernau M (2021) Pollination ecology of Symplocarpus foetidus (Araceae) in a seasonally flooded bog in Québec, Canada. Botany Letters, 168, 373-383.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
Beath DDN (1996) Pollination of Amorphophallus johnsonii (Araceae) by carrion beetles (Phaeochrous amplus) in a Ghanaian rain forest. Journal of Tropical Ecology, 12, 409-418.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
Bleiweiss R, Sornoza MF, Freire E, Croat TB (2019) Birdvisitation to a high Andean Anthurium (Araceae) in Eastern Ecuador. Flora, 255, 80-85.
DOI |
| [6] | Boyce PC, Croat TB (2018) The Überlist of Araceae, totals for published and estimated number of species in aroid genera. http://www.aroid.org/genera/20201008Uberlist.pdf . (access- ed on 2021-10-20) |
| [7] |
Bröderbauer D, Diaz A, Weber A (2012) Reconstructing the origin and elaboration of insect-trapping inflorescences in the Araceae. American Journal of Botany, 99, 1666-1679.
DOI PMID |
| [8] |
Bröderbauer D, Ulrich S, Weber A (2014) Adaptations for insect-trapping in brood-site pollinated Colocasia (Araceae). Plant Biology, 16, 659-668.
DOI PMID |
| [9] |
Bröderbauer D, Weber A, Diaz A (2013) The design of trapping devices in pollination traps of the genus Arum (Araceae) is related to insect type. Botanical Journal of the Linnean Society, 172, 385-397.
PMID |
| [10] |
Chartier M, Gibernau M, Renner SS (2014) The evolution of pollinator-plant interaction types in the Araceae. Evolution, 68, 1533-1543.
DOI PMID |
| [11] |
Chouteau M, Gibernau M, Barabé D (2008) Relationships between floral characters, pollination mechanisms, life forms, and habitats in Araceae. Botanical Journal of the Linnean Society, 156, 29-42.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
Coté GG, Gibernau M (2012) Distribution of calcium oxalate crystals in floral organs of Araceae in relation to pollination strategy. American Journal of Botany, 99, 1231-1242.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
Croat TB (2019) Araceae, a family with great potential. Annals of the Missouri Botanical Garden, 104, 3-9.
DOI URL |
| [14] | Croat TB, Ortiz OO (2020) Distribution of Araceae and the diversity of life forms. Acta Societatis Botanicorum Poloniae, 89, 8939. |
| [15] |
Cusimano N, Bogner J, Mayo SJ, Boyce PC, Wong SY, Hesse M, Hetterscheid WLA, Keating RC, French JC (2011) Relationships within the Araceae: Comparison of morphological patterns with molecular phylogenies. American Journal of Botany, 98, 654-668.
DOI PMID |
| [16] |
Dafni A, Lehrer M, Kevan PG (1997) Spatial flower parameters and insect spatial vision. Biological Reviews, 72, 239-282.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
Diaz A, Kite GC (2006) Why be a rewarding trap? The evolution of floral rewards in Arum (Araceae), a genus characterized by saprophilous pollination systems. Biological Journal of the Linnean Society, 88, 257-268.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
Dobson HEM, Arroyo J, Bergström G, Groth I (1997) Interspecific variation in floral fragrances within the genus Narcissus (Amaryllidaceae). Biochemical Systematics and Ecology, 25, 685-706.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
Etl F, Franschitz A, Aguiar AJC, Schoenenberger J, Doetterl S (2017) A perfume-collecting male oil bee? Evidences of a novel pollination system involving Anthurium acutifolium (Araceae) and Paratetrapedia chocoensis (Apidae, Tapinotaspidini). Flora, 232, 7-15.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
Fenster CB, Armbruster WS, Wilson P, Dudash MR, Thomson JD (2004) Pollination syndromes and floral specialization. Annual Review of Ecology, Evolution, and Systematics, 35, 375-403.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
Gaskett AC (2011) Orchid pollination by sexual deception: Pollinator perspectives. Biological Reviews, 86, 33-75.
DOI URL |
| [22] | Gibernau M (2016) Pollinators and visitors of aroid inflorescences III: Phylogenetic & Chemical insights. Aroideana, 39, 4-22. |
| [23] |
Gibernau M, Barabé D (2002) Pollination ecology of Philodendron squamiferum (Araceae). Canadian Journal of Botany, 80, 316-320.
DOI URL |
| [24] | Gibernau M, Chartier M, Barabé D (2010) Recent advances towards an evolutionary comprehension of Araceae pollination. In: Diversity, Phylogeny, and Evolution in the Monocotyledons (eds Ole S, Gitten P, Anders B, Jarrold DI), pp. 101-114. Aarhus University Press, Aarhus. |
| [25] | Gottsberger G, Amaral A (1984) Pollination strategies in Brazilian Philodendron species. Berichte der Deutschen Botanischen Gesellschaft, 97, 391-410. |
| [26] | Grant V (1994) Modes and origins of mechanical and ethological isolation in angiosperms. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 91, 3-10. |
| [27] |
Grayum MH (1990) Evolution and phylogeny of the Araceae. Annals of the Missouri Botanical Garden, 77, 628-697.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
Hoe YC, Gibernau M, Wong SY (2018) Diversity of pollination ecology in the Schismatoglottis calyptrata complex clade (Araceae). Plant Biology, 20, 563-578.
DOI PMID |
| [29] | Hu GW (2008) Reproductive Studies on Arisaema yunnanense Buchet and A. erubescens (Wall.) Schott. PhD dissertation, Kunming Institute of Botany, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Kunming. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 胡光万 (2008) 山珠南星和一把伞南星的繁殖生物学研究. 中国科学院昆明植物研究所, 昆明.] | |
| [30] | Hu H, Dai JK, Wang L, Li B, Sun C (2020) Chemical constituents and pharmacological effects of Arisaematis Rhizoma. Chemistry of Life, 40, 2216-2225. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 胡浩, 戴佳锟, 王璐, 李勃, 孙超 (2020) 中药天南星的化学成分及其药理作用. 生命的化学, 40, 2216-2225.] | |
| [31] | Huang WL (2014) The classification on tribus genus and geographic distribution of world Araceae. Guizhou Science, 32, 1-9. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 黄威廉 (2014) 天南星科植物族属分类及地理分布. 贵州科学, 32, 1-9.] | |
| [32] |
Jiménez PD, Hentrich H, Aguilar-Rodríguez PA, Krömer T, Chartier M, Gibernau M (2019) A review on the pollination of aroids with bisexual flowers. Annals of the Missouri Botanical Garden, 104, 83-104.
DOI URL |
| [33] | Johnson SD, Hobbhahn N, Bytebier B (2013) Ancestral deceit and labile evolution of nectar production in the African orchid genus Disa. Biology Letters, 9, 20130500. |
| [34] |
Johnson SD, Sivechurran J, Doarsamy S, Shuttleworth A (2020) Dung mimicry: The function of volatile emissions and corolla patterning in fly-pollinated Wurmbea flowers. New Phytologist, 228, 1662-1673.
DOI PMID |
| [35] |
Kaiser R (2006) Flowers and fungi use scents to mimic each other. Science, 311, 806-807.
PMID |
| [36] |
Kalinová B, Podskalska H, Růžička J, Hoskovec M (2009) Irresistible bouquet of death-How are burying beetles (Coleoptera: Silphidae: Nicrophorus) attracted by carcasses. Naturwissenschaften, 96, 889-899.
DOI PMID |
| [37] |
Kite GC, Hetterscheid WLA (2017) Phylogenetic trends in the evolution of inflorescence odours in Amorphophallus. Phytochemistry, 142, 126-142.
DOI URL |
| [38] |
Knudsen JT, Eriksson R, Gershenzon J, Ståhl B (2006) Diversity and distribution of floral scent. The Botanical Review, 72, 1-120.
DOI URL |
| [39] |
Kumano-Nomura Y, Yamaoka R (2009) Beetle visitations, and associations with quantitative variation of attractants in floral odors of Homalomena propinqua (Araceae). Journal of Plant Research, 122, 183-192.
DOI PMID |
| [40] | Lahondère C, Vinauger C, Okubo RP, Wolff GH, Chan JK, Akbari OS, Riffell JA (2020) The olfactory basis of orchid pollination by mosquitoes. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 117, 708-716. |
| [41] |
Lau JYY, Guo X, Pang CC, Tang CC, Thomas DC, Saunders RMK (2017) Time-dependent trapping of pollinators driven by the alignment of floral phenology with insect circadian rhythms. Frontiers in Plant Science, 8, 1119.
DOI URL |
| [42] | Li H (1996) The ecological phytogeography and origin of the family Araceae. Acta Botanica Yunnanica, 18, 14-42. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 李恒 (1996) 从生态地理探索天南星科的起源. 云南植物研究, 18, 14-42.] | |
| [43] | Liang A, Sima YK, Zhang X, Xu T (2019) The geographical distribution of the endemic species of Araceae in China. Chinese Wild Plant Resources, 38, 77-85. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 梁翱, 司马永康, 张翔, 徐涛 (2019) 中国天南星科特有种地理分布研究. 中国野生植物资源, 38, 77-85.] | |
| [44] | Liu JM, Cao Z, You Y, Zhong RH, Deng Z (2018) Recent progress in Caladium breeding and genetic research. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 45, 1791-1801. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 刘金梅, Cao Zhe, 尤毅, 钟荣辉, Deng Zhanao (2018) 花叶芋育种研究进展. 园艺学报, 45, 1791-1801.] | |
| [45] |
Marotz-Clausen G, Jürschik S, Fuchs R, Schäffler I, Sulzer P, Gibernau M, Dötterl S (2018) Incomplete synchrony of inflorescence scent and temperature patterns in Arum maculatum L. (Araceae). Phytochemistry, 154, 77-84.
DOI PMID |
| [46] |
Matsumoto TK, Hirobe M, Sueyoshi M, Miyazaki Y (2021) Selective pollination by fungus gnats potentially functions as an alternative reproductive isolation among five Arisaema species. Annals of Botany, 127, 633-644.
DOI PMID |
| [47] |
Matsumoto TK, Miyazaki Y, Sueyoshi M, Senda Y, Yamada K, Hirobe M (2019) Pre-pollination barriers between two sympatric Arisaema species in northern Shikoku Island, Japan. American Journal of Botany, 106, 1612-1621.
DOI PMID |
| [48] |
Milet-Pinheiro P, Gonçalves EG, Navarro DMAF, Nuñez- Avellaneda LA, Maia ACD (2017) Floral scent chemistry and pollination in the Neotropical aroid genus Xanthosoma (Araceae). Flora, 231, 1-10.
DOI URL |
| [49] |
Miller RE, Grant NM, Giles L, Ribas-Carbo M, Berry JA, Watling JR, Robinson SA (2011) In the heat of the night- alternative pathway respiration drives thermogenesis in Philodendron bipinnatifidum. New Phytologist, 189, 1013-1026.
DOI URL |
| [50] |
Miyake T, Yafuso M (2003) Floral scents affect reproductive success in fly-pollinated Alocasia odora (Araceae). American Journal of Botany, 90, 370-376.
DOI URL |
| [51] |
Nauheimer L, Metzler D, Renner SS (2012) Global history of the ancient monocot family Araceae inferred with models accounting for past continental positions and previous ranges based on fossils. New Phytologist, 195, 938-950.
DOI PMID |
| [52] |
Oelschlägel B, Gorb S, Wanke S, Neinhuis C (2009) Structure and biomechanics of trapping flower trichomes and their role in the pollination biology of Aristolochia plants (Aristolochiaceae). New Phytologist, 184, 988-1002.
DOI PMID |
| [53] |
Oelschlägel B, Nuss M, von Tschirnhaus M, Paetzold C, Neinhuis C, Doetterl S, Wanke S (2015) The betrayed thief-The extraordinary strategy of Aristolochia rotunda to deceive its pollinators. New Phytologist, 206, 342-351.
DOI PMID |
| [54] |
Peakall R, Ebert D, Poldy J, Barrow RA, Francke W, Bower CC, Schiestl FP (2010) Pollinator specificity, floral odour chemistry and the phylogeny of Australian sexually deceptive Chiloglottis orchids: Implications for pollinator- driven speciation. New Phytologist, 188, 437-450.
DOI PMID |
| [55] |
Prieto D, Cascante-Marín A (2017) Pollination by nitidulid beetles in the hemi-epiphytic aroid Monstera lentii (Araceae: Monsteroideae). Flora, 231, 57-64.
DOI URL |
| [56] |
Qin LY, Hu YH, Wang JP, Wang XL, Zhao R, Shan HY, Li KP, Xu P, Wu HY, Yan XQ, Liu LM, Yi X, Wanke S, Bowers JE, Leebens-Mack JH, DePamphilis CW, Soltis PS, Soltis DE, Kong HZ, Jiao YN (2021) Insights into angiosperm evolution, floral development and chemical biosynthesis from the Aristolochia fimbriata genome. Nature Plants, 7, 1239-1253.
DOI URL |
| [57] |
Raguso RA (2004) Flowers as sensory billboards: Progress towards an integrated understanding of floral advertisement. Current Opinion in Plant Biology, 7, 434-440.
DOI URL |
| [58] |
Ren ZX, Wang H, Luo YB (2012) Deceptive pollination of orchids. Biodiversity Science, 20, 270-279. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[ 任宗昕, 王红, 罗毅波 (2012) 兰科植物欺骗性传粉. 生物多样性, 20, 270-279.]
DOI |
|
| [59] |
Rupp T, Oelschlagel B, Rabitsch K, Mahfoud H, Wenke T, Disney RHL, Neinhuis C, Wanke S, Dotterl S (2021) Flowers of deceptive Aristolochia microstoma are pollinated by phorid plies and emit volatiles known from invertebrate carrion. Frontiers in Ecology and Evolution, 9, 658441.
DOI URL |
| [60] |
Sannier J, Baker WJ, Anstett MC, Nadot S (2009) A comparative analysis of pollinator type and pollen ornamentation in the Araceae and the Arecaceae, two unrelated families of the monocots. BMC Research Notes, 2, 145.
DOI PMID |
| [61] |
Sayers TDJ, Steinbauer MJ, Farnier K, Miller RE (2020) Dung mimicry in Typhonium (Araceae): Explaining floral trait and pollinator divergence in a widespread species complex and a rare sister species. Botanical Journal of the Linnean Society, 193, 375-401.
DOI URL |
| [62] |
Schiestl FP (2015) Ecology and evolution of floral volatile- mediated information transfer in plants. New Phytologist, 206, 571-577.
DOI PMID |
| [63] |
Schiestl FP (2017) Innate receiver bias: Its role in the ecology and evolution of plant-animal interactions. Annual Review of Ecology, Evolution, and Systematics, 48, 585-603.
DOI URL |
| [64] |
Schiestl FP, Dötterl S (2012) The evolution of floral scent and olfactory preferences in pollinators: Coevolution or pre- existing bias? Evolution, 66, 2042-2055.
DOI PMID |
| [65] | Sun HX, Ye YP, Xue XJ (2002) Phylogenetic analysis of sections in the genus Arisaema. Journal of Biomathematics, 17, 369-373. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 孙红祥, 叶益萍, 薛祥骥 (2002) 天南星属的系统发育分析. 生物数学学报, 17, 369-373.] | |
| [66] |
Takenaka K, Yin JT, Wen SY, Toda Masanori J( 2006) Pollination mutualism between a new species of the genus Colocasiomyia de Meijere (Diptera: Drosophilidae) and Steudnera colocasiifolia (Araceae) in Yunnan, China. Entomological Science, 9, 79-91.
DOI URL |
| [67] | Tang R, Huang BG, Sun WB, Chen G (2020) Pollination biology of Amorphophallus albus (Araceae), an endemic plant in the dry-hot valley of Jinsha River. Plant Science Journal, 38, 458-466. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 唐荣, 黄保国, 孙卫邦, 陈高 (2020) 金沙江干热河谷特有植物白魔芋的传粉生物学研究. 植物科学学报, 38, 458-466.] | |
| [68] |
Tong ZY, Huang SQ (2019) The development, misuse and evidence of the concept coevolution. Scientia Sinica Vitae, 49, 421-435. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
| [ 童泽宇, 黄双全 (2019) 协同演化概念的发展、使用误区与研究证据. 中国科学: 生命科学, 49, 421-435.] | |
| [69] |
Urru I, Stensmyr MC, Hansson BS (2011) Pollination by brood-site deception. Phytochemistry, 72, 1655-1666.
DOI URL |
| [70] |
Urru I, Stökl J, Linz J, Krügel T, Stensmyr MC, Hansson BS (2010) Pollination strategies in Cretan Arum lilies. Biological Journal of the Linnean Society, 101, 991-1001.
DOI URL |
| [71] |
Vogel S (2000) A survey of the function of the lethal kettle traps of Arisasma (Araceae), with records of pollinating fungus gnats from Nepal. Botanical Journal of the Linnean Society, 133, 61-100.
DOI URL |
| [72] |
Wang GD, Vega-Rodríguez J, Diabate A, Liu JN, Cui CL, Nignan C, Dong L, Li F, Ouedrago CO, Bandaogo AM Sawadogo PS, Maiga H, Silva TLAE, Pascini TV, Wang SB, Jacobs-Lorena M (2021) Clock genes and environmental cues coordinate Anopheles pheromone synthesis, swarming, and mating. Science, 371, 411-415.
DOI URL |
| [73] | Willmer P (2011) Pollination and Floral Ecology. Princeton University Press, Princeton. |
| [74] |
Wright GA, Schiestl FP (2009) The evolution of floral scent: The influence of olfactory learning by insect pollinators on the honest signalling of floral rewards. Functional Ecology, 23, 841-851.
DOI URL |
| [75] | Yi TS, Li H, Li DZ (2002) The course of change and development of the classification systems of the Araceae. Journal of Wuhan Botanical Research, 20, 48-61. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 伊廷双, 李恒, 李德铢 (2002) 天南星科分类系统的沿革. 武汉植物学研究, 20, 48-61.] | |
| [76] |
Young HJ (1986) Beetle pollination of Dieffenbachia longispatha (Araceae). American Journal of Botany, 73, 931-944.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 王顺雨, 李杨, 吕晓琴, 李欣, 范权秀, 王晓月. 熊蜂盗蜜的花色偏好及对长距忍冬繁殖适合度的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24554-. |
| [2] | 张婵, 赵苏雅, 张欣然, 王依凡, 王林林. 外来传粉者对本地植物‒传粉者相互作用的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24443-. |
| [3] | 丁翔, 余元钧, 宋希强, 罗毅波. 具有泛化访花者的海芋特化传粉系统[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(6): 24069-. |
| [4] | 巴苏艳, 赵春艳, 刘媛, 方强. 通过虫体花粉识别构建植物‒传粉者网络: 人工模型与AI模型高度一致[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(6): 24088-. |
| [5] | 谢华, 杨培, 李宗波. 鸡嗉子榕传粉榕小蜂表皮碳氢化合物的性二型及季节变化[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(6): 24001-. |
| [6] | 舒为杰, 何花, 曾罗, 谷志容, 谭敦炎, 杨晓琛. 雌雄异株物种一把伞南星雌雄株空间分布及性别二态性[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(6): 24084-. |
| [7] | 热依拉穆·麦麦提吐尔逊, 艾沙江·阿不都沙拉木. 石榴花瓣和雄蕊对其传粉过程与繁殖成功的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(7): 22633-. |
| [8] | 赵秋杰, 郭辉军, 孟广涛, 钟明川, 尹俊, 刘倬橙, 李品荣, 陈力, 陶毅, 秋生, 王红, 赵延会. 放牧对蜜蜂的影响及其生态修复建议[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(5): 23037-. |
| [9] | 黄曼娟, 汪雪敏, 苗白鸽, 彭艳琼. 栉颚榕小蜂在雌花期榕果内产卵及主动传粉行为的多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(5): 23060-. |
| [10] | 罗韶凡, 蒋凯, 黄卫昌. 植物花距表型趋同进化和发育机制多样化的研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(11): 23249-. |
| [11] | 谢正华, 王有琼, 曹军, 王健敏, 安建东. 传粉昆虫下降背景下的授粉生态弹性: 内涵、机制和展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(7): 980-994. |
| [12] | 胡德美, 姚仁秀, 陈燕, 游贤松, 王顺雨, 汤晓辛, 王晓月. 青篱柴通过促进亲和花粉生长而提高传粉精确性[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(7): 887-896. |
| [13] | 施雨含, 任宗昕, 王维嘉, 徐鑫, 刘杰, 赵延会, 王红. 中国-喜马拉雅三种黄耆属植物与其传粉熊蜂的空间分布预测[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(6): 759-769. |
| [14] | 施雨含, 任宗昕, 赵延会, 王红. 气候变化对植物-传粉昆虫的分布区和物候及其互作关系的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(4): 495-506. |
| [15] | 李慢如, 张玲. 桑寄生植物繁殖物候研究概述[J]. 生物多样性, 2020, 28(7): 833-841. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn