



生物多样性 ›› 2023, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (7): 22633. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2022633 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2022633
热依拉穆·麦麦提吐尔逊1, 艾沙江·阿不都沙拉木1,2,*( )
)
收稿日期:2022-11-10
接受日期:2023-07-10
出版日期:2023-07-20
发布日期:2023-07-22
通讯作者:
*E-mail: 作者简介:*E-mail: aysajanxj@sina.com基金资助:
Reyilamu Maimaitituerxun1, Aysajan Abdusalam1,2,*( )
)
Received:2022-11-10
Accepted:2023-07-10
Online:2023-07-20
Published:2023-07-22
Contact:
*E-mail: 摘要:
植物‒传粉者相互关系中植物形成多种多样的视觉(花色)和嗅觉(花气味)信号来影响传粉者的访花过程, 促进传粉成功。石榴(Punica granatum)花瓣红色而雄蕊黄色, 这种花内不同结构的颜色差异对于石榴吸引传粉者可能有不同的作用。本文比较了石榴花各部位发出的视觉信号(颜色、大小)和嗅觉信号(气味及含量)、花蜜体积、不同处理下的昆虫访花频率及坐果率, 以探讨石榴花各部位颜色在传粉过程中的作用。结果发现: 新疆喀什地区石榴主要传粉者为意大利蜜蜂(Apis mellifera)和食蚜蝇(Syrphidae sp.), 雄蕊黄色及其分泌挥发性化合物种类和相对含量是吸引传粉者昆虫的主要因素。去除花瓣处理组与其他3种处理组(对照、去雄蕊、去雄蕊去花瓣)比较, 意大利蜜蜂的访花频率(P < 0.05)及停留时间(P < 0.05)均显著提高, 石榴坐果率(82.33% ± 4.45%)也显著提高。上述结果表明, 石榴黄颜色的雄蕊可能是吸引传粉者的主要结构, 而红色的花瓣对其传粉成功可能有负面影响; 植物花内不同结构颜色差异可能有助于在变化的环境下吸引不同的传粉者, 促进繁殖成功。
热依拉穆·麦麦提吐尔逊, 艾沙江·阿不都沙拉木 (2023) 石榴花瓣和雄蕊对其传粉过程与繁殖成功的影响. 生物多样性, 31, 22633. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2022633.
Reyilamu Maimaitituerxun, Aysajan Abdusalam (2023) Exploring the influence of petal and stamen color on pollinator and reproductive success in Punica granatum. Biodiversity Science, 31, 22633. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2022633.
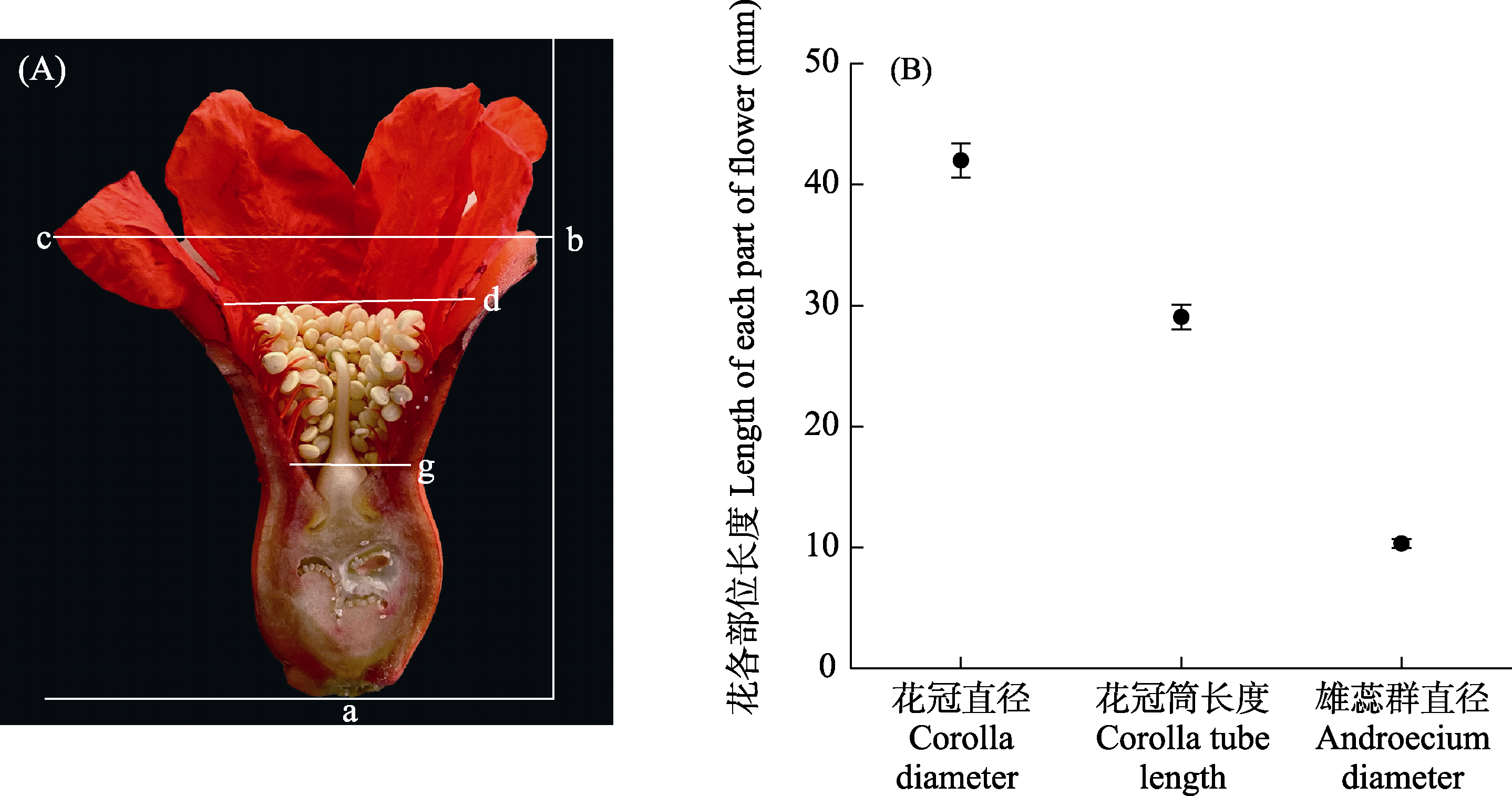
图1 石榴两性花各部位特征测量(A)和花冠筒长度、花冠直径和雄蕊群直径的相对大小(B) (平均值 ± 标准误)。A图中, a?d: 花冠筒长度; b?c: 花冠直径; d?g: 雄蕊群直径。
Fig. 1 Measurements of floral traits (A) and relative size of corolla diameter and tube length and androecium diameter of hermaphrodic flowers of Punica granatum (mean ± SE). In the figure A: a?d, Corolla tube length; b?c, Corolla diameter; d?g, Androecium diameter.
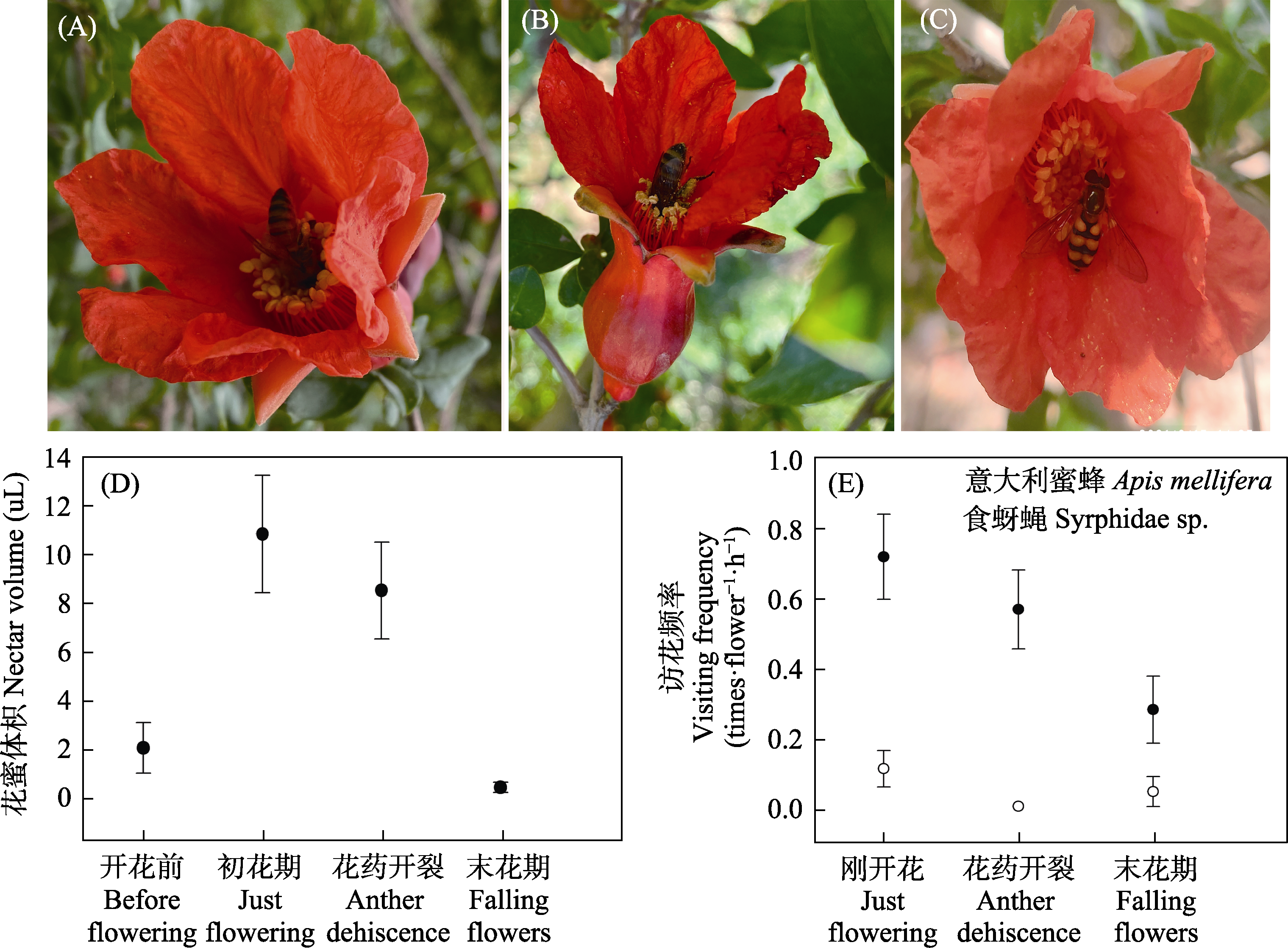
图2 石榴两性花的主要访花昆虫(A?C)、花寿命不同阶段的花蜜量(D)及传粉者访花频率(E)的变化(平均值 ± 标准误)。A?B: 意大利蜜蜂; C: 食蚜蝇。
Fig. 2 Main visiting insects (A?C), change of nectar volume (D) and visiting frequency of main pollinators (E) at the different flowering phases of hermaphrodite flowers of Punica granatum (mean ± SE). A?B, Apis mellifera; C, Syrphidae sp.
| 挥发性化合物 Volatile compounds | 相对含量 Relative content (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 花瓣 Petal | 花萼 Calyx | 雄蕊 Stamen | 雌蕊 Pistil | |
| 醇酮类 Alocohol ketone | 14.41 ± 7.04 | 10.42 ± 7.51 | 25.00 ± 13.73 | 50.00 ± 10.00 |
| 芳香类 Aromatic | 5.31 ± 1.67 | 11.59 ± 6.48 | 7.00 ± 3.04 | 12.74 ± 7.19 |
| 萜类 Terpenoid | 50.00 ± 8.14 | 20.00 ± 7.43 | 9.09 ± 2.64 | 16.67 ± 7.42 |
| 烷烃类 Alkane | 3.85 ± 0.84 | 8.70 ± 2.75 | 2.67 ± 0.75 | 10.00 ± 2.39 |
| 酯类 Ester | 11.21 ± 4.53 | 4.79 ± 2.02 | 0.75 ± 0.25 | 2.66 ± 0.81 |
| 醚胺类 Ether amine | ? | 50.00 ± 16.67 | 33.33 ± 22.05 | 50.00 ± 7.82 |
| Wald χ2 | 148.966 | 35.751 | 36.038 | 66.359 |
| P | ≤ 0.001 | ≤ 0.001 | ≤ 0.001 | ≤ 0.001 |
表1 石榴两性花花各部位气味化合物的相对组成成分分析(平均值 ± 标准误)
Table 1 Components of volatile compounds in each part of hermaphrodite flowers of Punica granatum (mean ± SE)
| 挥发性化合物 Volatile compounds | 相对含量 Relative content (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 花瓣 Petal | 花萼 Calyx | 雄蕊 Stamen | 雌蕊 Pistil | |
| 醇酮类 Alocohol ketone | 14.41 ± 7.04 | 10.42 ± 7.51 | 25.00 ± 13.73 | 50.00 ± 10.00 |
| 芳香类 Aromatic | 5.31 ± 1.67 | 11.59 ± 6.48 | 7.00 ± 3.04 | 12.74 ± 7.19 |
| 萜类 Terpenoid | 50.00 ± 8.14 | 20.00 ± 7.43 | 9.09 ± 2.64 | 16.67 ± 7.42 |
| 烷烃类 Alkane | 3.85 ± 0.84 | 8.70 ± 2.75 | 2.67 ± 0.75 | 10.00 ± 2.39 |
| 酯类 Ester | 11.21 ± 4.53 | 4.79 ± 2.02 | 0.75 ± 0.25 | 2.66 ± 0.81 |
| 醚胺类 Ether amine | ? | 50.00 ± 16.67 | 33.33 ± 22.05 | 50.00 ± 7.82 |
| Wald χ2 | 148.966 | 35.751 | 36.038 | 66.359 |
| P | ≤ 0.001 | ≤ 0.001 | ≤ 0.001 | ≤ 0.001 |
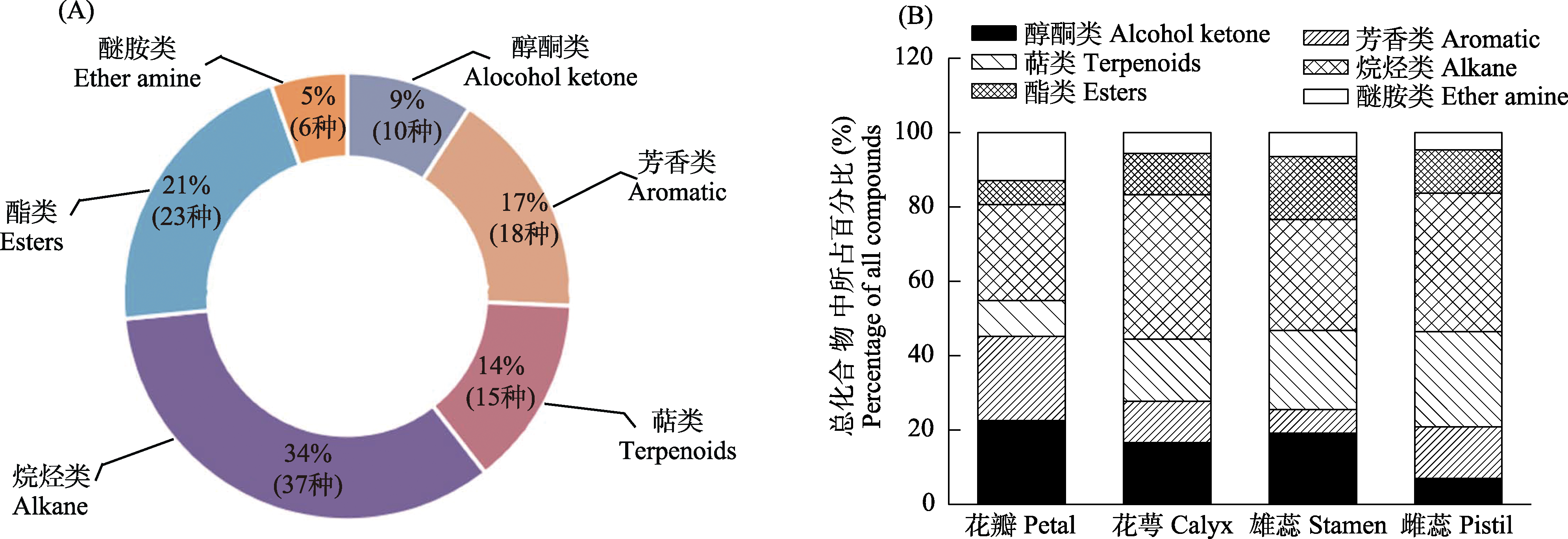
图3 石榴两性花化合物种类(A)及花各部位花气味组成比较(B)
Fig. 3 Comparison of volatile compounds (A) and floral odor composition in each part (B) of hermaphrodite flowers of Punica granatum
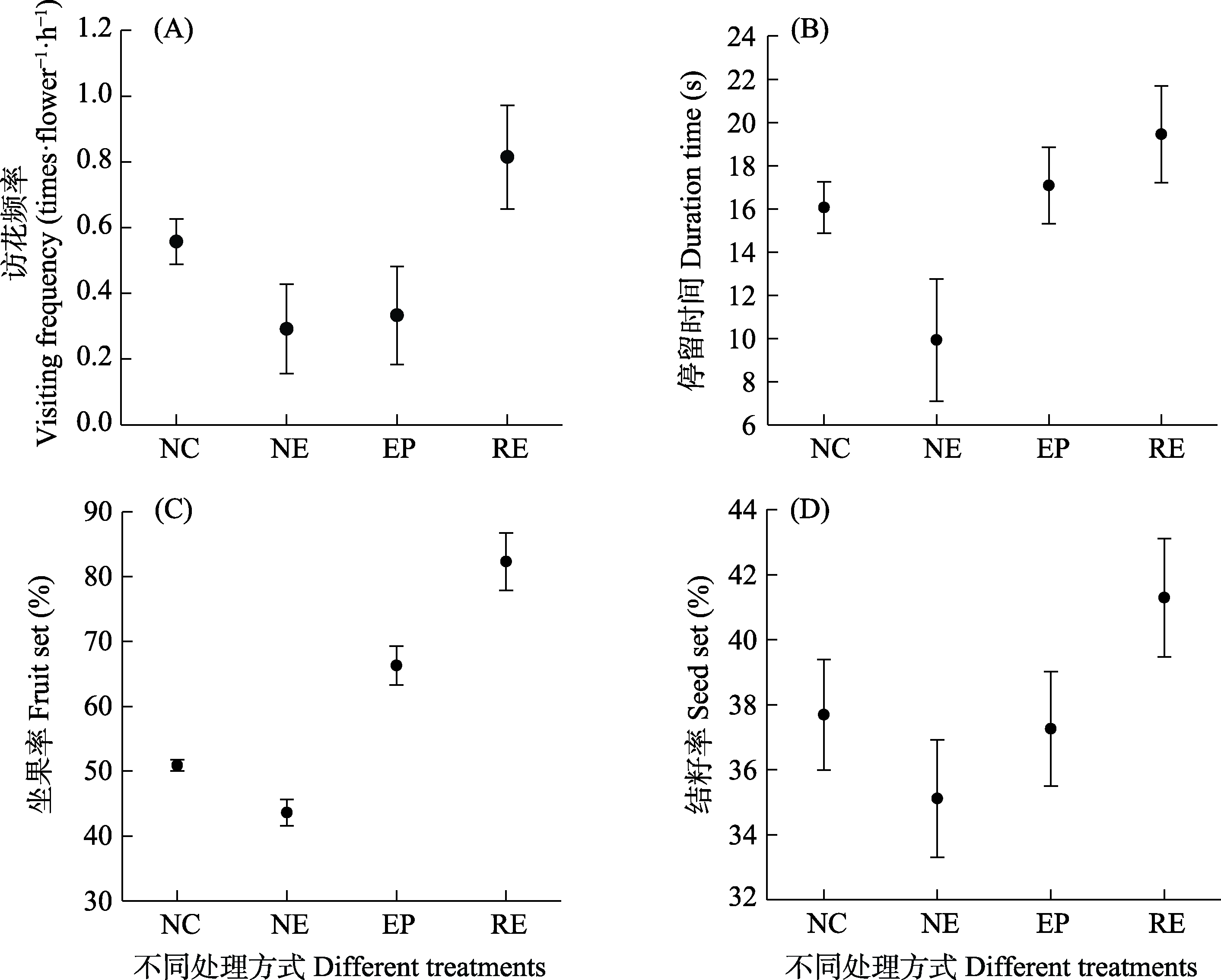
图4 石榴两性花的不同处理对意大利蜜蜂访花频率(A)、停留时间(B)以及坐果率(C)和结籽率(D) (平均值 ± 标准误)的影响。NC: 自然对照; NE: 去除雄蕊; EP: 去除花瓣和雄蕊; RE: 去除花瓣。
Fig. 4 Effects of different treatments on visiting frequency (A) and duration time (B) of Apis mellifera, fruit set (C) and seed set (D) of hermaphrodite flowers of Punica granatum (mean ± SE). NC: Natural treatment flower; NE: Flowers with stamen removal; EP: Flowers with stamen-petal removal; RE: Flowers with the removal of petals.
| [1] |
Ao CW, Lü S, Wu XJ, Zhao ZH, Liu MJ (2018) Analysis of aroma components from jujube flowers and honey. Food Science, 39, 182-189. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[敖常伟, 吕姗, 吴香菊, 赵智慧, 刘孟军 (2018) 枣花及枣花蜜香气成分分析. 食品科学, 39, 182-189.]
DOI |
|
| [2] | Ashworth L, Aguilar R, Martén-Rodríguez S, Lopezaraiza- Mikel M, Avila-Sakar G, Rosas-Guerrero V, Quesada M (2015) Pollination syndromes:A global pattern of conver- gent evolution driven by the most effective pollinator. In: Evolutionary Biology: Biodiversification from Genotype to Phenotype (ed. Pontarotti P), pp.203-224. Springer, Cham. |
| [3] |
Briscoe AD, Chittka L (2001) The evolution of color vision in insects. Annual Review of Entomology, 46, 471-510.
PMID |
| [4] |
Byers KJRP (2021) “As if they discovered it by the scent”: Improving our understanding of the chemical ecology, evolution, and genetics of floral scent and its role in pollination. American Journal of Botany, 108, 729-731.
DOI URL |
| [5] | Cao SY, Hou LF (2013) Fruit Trees in China:Pomegranate. China Forestry Publishing House, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [曹尚银, 侯乐峰 (2013) 中国果树志: 石榴卷. 中国林业出版社, 北京.] | |
| [6] | Chang SM, Rausher MD (1999) The role of inbreeding depression in maintaining the mixed mating system of the common morning glory, Ipomoea purpurea. Evolution, 53, 1366-1376. |
| [7] | Dafni A, Kevan PG, Husband BC (2005) Practical Pollination Biology. Enviroquest, Cambridge, Ontario. |
| [8] |
Lunau K, Batalha MA, Brings S, de Brito VLG, Morellato LPC (2019) How flower colour signals allure bees and hummingbirds: A community-level test of the bee avoidance hypothesis. New Phytologist, 222, 1112-1122.
DOI PMID |
| [9] |
Fenster CB, Armbruster WS, Wilson P, Dudash MR, Thomson JD (2004) Pollination syndromes and floral specialization. Annual Review of Ecology, Evolution, and Systematics, 35, 375-403.
DOI URL |
| [10] | Gigord LDB, MacNair MR, Smithson A (2001) Negative frequency dependent selection maintains a dramatic flower color polymorphism in the rewardless orchid Dactylorhiza sambucina (L.) Soò. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 98, 6253-6255. |
| [11] | Holland D, Hatib K, Bar-Ya'Akov I (2009) Pomegranate: botany, horticulture, breeding. In: Horticultural Reviews, Vol. 35 (ed. Janick J), pp.127-191. Hoboken, NJ. |
| [12] | Huang SQ, Guo YH (2000) Research progress of pollination biology. Chinese Science Bulletin, 45, 225-237. (in Chinese) |
| [黄双全, 郭友好 (2000) 传粉生物学的研究进展. 科学通报, 45, 225-237.] | |
| [13] |
Ida TY, Kudo G (2010) Modification of bumblebee behavior by floral color change and implications for pollen transfer in Weigela middendorffiana. Evolutionary Ecology, 24, 671-684.
DOI URL |
| [14] | Li JJ (2012) Analysis the content of each component in mixed gas with area normalization method. Metrology & Measure- ment Technique, 39, 86-88. (in Chinese) |
| [李健隽 (2012) 面积归一化法分析混合气体中各组分含量. 计量与测试技术, 39, 86-88.] | |
| [15] | Liu C, Fang XJ, Li JJ (2022) Research progress of pomegranate germplasm resources in China. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 50(12), 34-36, 40. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [刘春, 方锡佳, 李锦锦 (2022) 中国石榴种质资源研究进展. 安徽农业科学, 50(12), 34-36, 40.] | |
| [16] | Liu SY, Lin YL, Wang LY, Xia JX, Yang MX, Fang JG, Wang C, Shangguan LF (2022) Identification of ATG gene family of Punica granatum and analysis on their expression pattern under abiotic stress. Journal of Plant Resources and Environment, 31(5), 37-49. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [刘司瑜, 林艺灵, 王令宇, 夏家欣, 杨毓贤, 房经贵, 王晨, 上官凌飞 (2022) 石榴ATG基因家族鉴定及其在非生物胁迫下的表达模式分析. 植物资源与环境学报, 31(5), 37-49.] | |
| [17] |
Lunau K, Konzmann S, Winter L, Kamphausen V, Ren ZX (2017) Pollen and stamen mimicry: The alpine flora as a case study. Arthropod-Plant Interactions, 11, 427-447.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
Lunau K, Papiorek S, Eltz T, Sazima M (2011) Avoidance of achromatic colours by bees provides a private niche for hummingbirds. The Journal of Experimental Biology, 214, 1607-1612.
DOI PMID |
| [19] |
Maphetu N, Unuofin JO, Masuku NP, Olisah C, Lebelo SL (2022) Medicinal uses, pharmacological activities, phytochemistry, and the molecular mechanisms of Punica granatum L. (pomegranate) plant extracts: A review. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy, 153, 113256.
DOI URL |
| [20] | Mars M (2000) Pomegranate plant material: Genetic resources and breeding, a review. Options Méditerranéennes, Série A, Séminaires Méditerranéens, 42, 55-62. |
| [21] |
Martínez-Nicolás JJ, Galindo A, Griñán I, Rodríguez P, Cruz ZN, Martínez-Font R, Carbonell-Barrachina AA, Nouri H, Melgarejo P (2019) Irrigation water saving during pomegranate flowering and fruit set period do not affect wonderful and Mollar de Elche cultivars yield and fruit composition. Agricultural Water Management, 226, 105781.
DOI URL |
| [22] | Menzel R, Backhaus W (1991) Colour vision in insects. Vision and Visual Dysfunction, 6, 262-293. |
| [23] | Raine NE, Chittka L (2007) The adaptive significance of sensory bias in a foraging context: Floral colour preferences in the bumblebee Bombus terrestris. PLoS ONE, 2, e556. |
| [24] |
Raven PH (1972) Why are bird-visited flowers predominantly red? Evolution, 26, 674.
DOI PMID |
| [25] |
Sinha S, Thakur DS, Kundu M, Ahmad F (2020) Genetic analysis of exotic germplasms of pomegranate (Punica granatum L.). Bangladesh Journal of Botany, 49, 105-112.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
Sletvold N, Grindeland JM, Ågren J (2010) Pollinator-mediated selection on floral display, spur length and flowering phenology in the deceptive orchid Dactylorhiza lapponica. New Phytologist, 188, 385-392.
DOI PMID |
| [27] |
Spigler RB, Kalisz S (2013) Phenotypic plasticity in mating-system traits in the annual Collinsia verna. Botany, 91, 597-604.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
Tang LL, Huang SQ (2007) Evidence for reductions in floral attractants with increased selfing rates in two heterandrous species. New Phytologist, 175, 588-595.
DOI URL |
| [29] | Tang XX, Huang SQ (2012) Research progress on diversity and variation in flower color. Plant Diversity and Resources. 34, 239-247. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [汤晓辛, 黄双全 (2012) 花色多样性与变异的研究进展. 植物分类与资源学报, 34, 239-247.] | |
| [30] |
van der Kooi CJ, Dyer AG, Kevan PG, Lunau K (2019) Functional significance of the optical properties of flowers for visual signaling. Annals of Botany, 123, 263-276.
DOI URL |
| [31] | Volschenk T (2020) Water use and irrigation management of pomegranate trees: A review. Agricultural Water Manage- ment, 241, 106375. |
| [32] | Vorobyev M, Osorio D (1998) Receptor noise as a determinant of colour thresholds. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London B: Biological Sciences, 265, 351-358. |
| [33] | Wang S, Zhang XH, Zhao YJ, Li BB, Zhao XQ, Shen Y, Dong JM, Yuan ZH (2022) Cloning and functional analysis of PgMYB111related to anthocyanin synthesis in pomegranate. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 49, 1883-1894. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[王沙, 张心慧, 赵玉洁, 李变变, 招雪晴, 沈雨, 董建梅, 苑兆和 (2022) 石榴花青苷合成相关基因PgMYB111的克隆与功能分析. 园艺学报, 49, 1883-1894.]
DOI |
|
| [34] |
Wang XY, Quan QM, Wang B, Li YX, Huang SQ (2018) Discovery of androecium color polymorphism in Epimedium pubescens with habitat preference of anther/pollen color in the genus. Journal of Plant Ecology, 11, 533-541.
DOI URL |
| [35] |
Weiss MR (1995) Floral color change: A widespread functional convergence. American Journal of Botany, 82, 167-185.
DOI URL |
| [36] | Wester P, Lunau K (2017) Plant-pollinator communication. Advances in Botanical Research, 82, 225-257. |
| [37] |
Xiang WQ, Ren MX (2019) Adaptive significance of yellow flowered Bombax ceiba (Malvaceae). Biodiversity Science, 27, 373-379. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[向文倩, 任明迅 (2019) 木棉黄花个体的适应意义. 生物多样性, 27, 373-379.]
DOI |
|
| [38] |
Yisimayili Z, Chao Z (2022) A review on phytochemicals, metabolic profiles and pharmacokinetics studies of the different parts (juice, seeds, peel, flowers, leaves and bark) of pomegranate (Punica granatum L.). Food Chemistry, 395, 133600.
DOI URL |
| [39] |
Zhang AQ, He S, Zhai YX, Huang SQ (2015) Does persistence of showy calyces in Limonium leptolobum enhance pollina- tor attraction? Journal of Plant Ecology, 8, 182-186.
DOI URL |
| [40] | Zhang R, Dai HF, Shen DR, He C, Yuan SY, Wen YJ (2021) The diversity of pollinator bee species in Mengzi pome- granate orchard. Anhui Agricultural Bulletin, 27(9), 30-32. (in Chinese) |
| [张睿, 代宏福, 沈登荣, 何超, 袁盛勇, 文易进(2021) 蒙自石榴园传粉蜜蜂种类多样性的调查研究. 安徽农学通报, 27(9), 30-32.] |
| [1] | 王顺雨, 李杨, 吕晓琴, 李欣, 范权秀, 王晓月. 熊蜂盗蜜的花色偏好及对长距忍冬繁殖适合度的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24554-. |
| [2] | 王晓月,朱鑫鑫,杨娟,刘云静,汤晓辛. 梅花个体内花柱长度的变异及其对繁殖成功的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2019, 27(2): 159-167. |
| [3] | 黄至欢, 陆奇丰, 陈颖卓. 地锦苗在石灰岩土壤和红壤生境中的繁殖成功的比较[J]. 生物多样性, 2017, 25(9): 972-980. |
| [4] | 蒋裕良, 白坤栋, 郭屹立, 王斌, 李冬兴, 李先琨, 刘志尚. 北热带喀斯特森林木本植物花性状及其生境分异[J]. 生物多样性, 2016, 24(2): 148-156. |
| [5] | 张婵, 查绍琴, 杨永平, 段元文. 蓝翠雀花退化雄蕊上的黄色髯毛对其繁殖成功的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2012, 20(3): 348-353. |
| [6] | 宋莉英, 孙兰兰, 舒展, 李伟华, 彭长连. 夏季高光下入侵植物三裂叶蟛蜞菊叶片变红的生理功能[J]. 生物多样性, 2009, 17(2): 188-194. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2026 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn
![]()