



生物多样性 ›› 2022, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (2): 21235. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2021235 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2021235
张语克1,2,*( ), 张琼悦2,3, 张跃2,4, 肖维阳2,4, 杜杰2,4, 谢超2, 赵上娟2, 余水英2,5, 翟宗玉2,5, 郭沂2,5, 杨为亚2, 王定瑶2,4, 格让久2,4, 杨金秀2,4, 李英2,4, 王燕2,4, 孙鸿鸥2,4, 郭西南2, 周亮1
), 张琼悦2,3, 张跃2,4, 肖维阳2,4, 杜杰2,4, 谢超2, 赵上娟2, 余水英2,5, 翟宗玉2,5, 郭沂2,5, 杨为亚2, 王定瑶2,4, 格让久2,4, 杨金秀2,4, 李英2,4, 王燕2,4, 孙鸿鸥2,4, 郭西南2, 周亮1
收稿日期:2021-06-10
接受日期:2021-10-17
出版日期:2022-02-20
发布日期:2022-02-28
通讯作者:
张语克
作者简介:*E-mail: zhyuke@gmail.com
Yuke Zhang1,2,*( ), Qiongyue Zhang2,3, Yue Zhang2,4, Weiyang Xiao2,4, Jie Du2,4, Chao Xie2, Shangjuan Zhao2, Shuiying Yu2,5, Zongyu Zhai2,5, Yi Guo2,5, Weiya Yang2, Dingyao Wang2,4, Jinxiu Yang2,4, Ying Li2,4, Yan Wang2,4, Hongou Sun2,4, Xinan Guo2, Liang Zhou1
), Qiongyue Zhang2,3, Yue Zhang2,4, Weiyang Xiao2,4, Jie Du2,4, Chao Xie2, Shangjuan Zhao2, Shuiying Yu2,5, Zongyu Zhai2,5, Yi Guo2,5, Weiya Yang2, Dingyao Wang2,4, Jinxiu Yang2,4, Ying Li2,4, Yan Wang2,4, Hongou Sun2,4, Xinan Guo2, Liang Zhou1
Received:2021-06-10
Accepted:2021-10-17
Online:2022-02-20
Published:2022-02-28
Contact:
Yuke Zhang
About author:*E-mail: zhyuke@gmail.com摘要:
环境解说是自然保护地实现自然保护与环境教育目标的重要手段。目前我国自然保护地对解说资源的时空分布研究不足, 且缺乏相应的实地调查方法, 限制了解说系统的发展, 难以满足公众对自然认知的需要, 达不到环境教育的目的。开展解说资源的调查与研究, 有助于更好地展示保护地的资源独特性和重要性。本文以九寨沟国家级自然保护区芦苇海解说步道为例, 总结了解说资源的6个选择标准, 并对区域的解说资源进行调查和监测, 以期为我国自然保护地体系的环境解说资源调查和解说系统构建提供方法借鉴。芦苇海解说步道共筛选得到195种解说资源, 包括植物与菌类100种、动物62种、生态系统类型5种、地质与水文7种、天象与气候2种、文化资源19种。空间上, 植物与菌类、动物和生态系统类解说资源主要分布于内侧步道, 而文化类解说资源在外侧栈道分布更多; 时间上, 夏秋季解说资源数量最多, 冬春季较少, 且动植物与菌类解说资源的数量具有明显的季节性。基于解说资源的属性、意义和分布特点, 采用主旨式解说(thematic interpretation)方法设计了8条解说主旨, 为解说内容的组织提供参考。
张语克, 张琼悦, 张跃, 肖维阳, 杜杰, 谢超, 赵上娟, 余水英, 翟宗玉, 郭沂, 杨为亚, 王定瑶, 格让久, 杨金秀, 李英, 王燕, 孙鸿鸥, 郭西南, 周亮 (2022) 自然保护地环境解说资源研究: 以九寨沟芦苇海解说步道为例. 生物多样性, 30, 21235. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2021235.
Yuke Zhang, Qiongyue Zhang, Yue Zhang, Weiyang Xiao, Jie Du, Chao Xie, Shangjuan Zhao, Shuiying Yu, Zongyu Zhai, Yi Guo, Weiya Yang, Dingyao Wang, Jinxiu Yang, Ying Li, Yan Wang, Hongou Sun, Xinan Guo, Liang Zhou (2022) Environmental interpretation resources for protected areas: Using the Reed Lake interpretation trail in the Jiuzhaigou as a case study. Biodiversity Science, 30, 21235. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2021235.
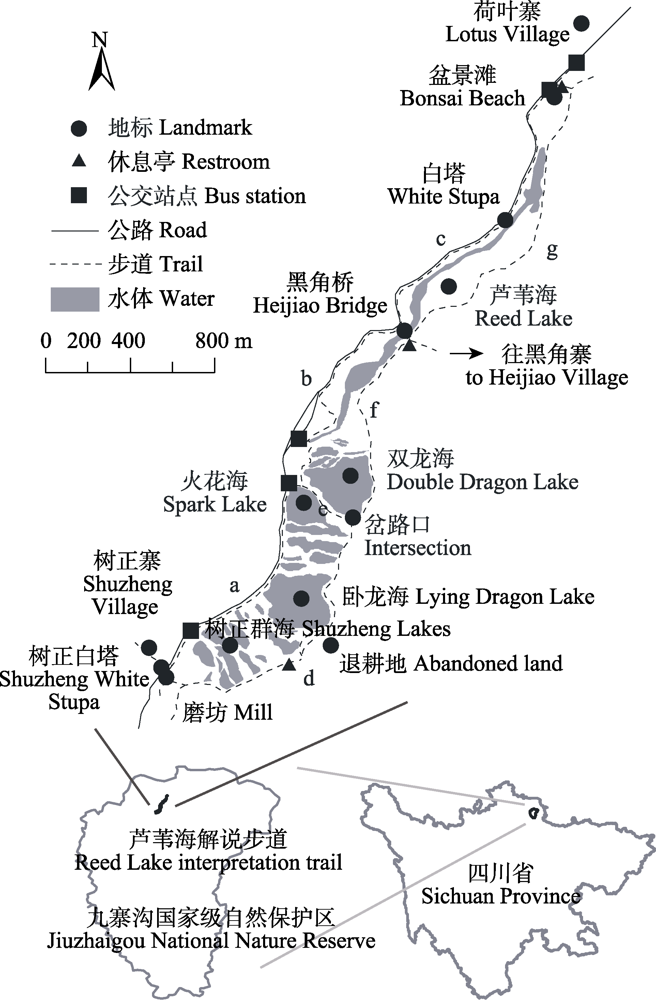
图1 九寨沟国家级自然保护区芦苇海解说步道。a-g代表不同步道段: a: 树正磨坊-火花海公交站; b: 火花海公交站-黑角桥; c: 黑角桥-白塔-荷叶寨公交站; d: 树正磨坊-岔路口; e: 火花海公交站-岔路口; f: 岔路口-黑角桥; g: 黑角桥-荷叶寨公交站东线。
Fig. 1 Reed Lake interpretation trail in the Jiuzhaigou National Nature Reserve. a-g indicate different sections of the trail: a, Shuzheng Mill-Spark Lake bus station; b, Spark Lake Bus Station-Heijiao Bridge; c, Heijiao Bridge-White Stupa- Lotus Village bus station; d, Shuzheng Mill-Intersection; e, Spark Lake bus station-Intersection; f, Intersection-Heijiao Bridge; g, East line of Heijiao Bridge-Lotus Village bus station.
| 标准 Criteria | 内容 Content |
|---|---|
| 独特性 Uniqueness | 自然、文化、科学、娱乐和启发灵感等方面的独特性。该资源相对周围的景观在色、形、味、年龄、稀有程度或其他方面的特征有较强烈的差异, 容易引起受众的特别兴趣。例如某一植物在花、叶、茎、根、生态功能等方面有显著而有趣的特点, 或独特的种间关系、行为适应等。 It is unique in nature, culture, science, entertainment and inspiration. Compared with the surrounding landscape, the resource has strong differences in color, shape, taste, age, rarity or other aspects, which is easy to arouse audiences’ interest. For example, a plant has significant and interesting characteristics in flowers, leaves, stems, roots, ecological functions, or unique interspecific relationships, behavioral adaptation, etc. |
| 代表性 Representativeness | 具有该地方代表性。如森林群落中的优势种; 植物种的分布范围越窄, 地方代表性越强。 It is representative of local area. For example, the dominant species in a forest community; the narrower the distribution range of a plant species, the more its local representativeness. |
| 重要性 Importance | 具有重要功能。如旗舰种、关键种、关键的地质过程、文化图腾等。 It has important functions, including the flagship species, key species, key geological process, cultural totem and so on. |
| 价值性 Value | 能够服务于解说主题, 建立受众与资源意义的连接。例如, 用来解说生物多样性的大中型野生动物(体重 > 1 kg)的活动痕迹(如脚印、粪便、食迹等)或红外相机监测数据; 用来解说环境问题的人为干扰、生态灾难等。 It can serve the interpretation theme and establish connections between audiences and the meaning of resources. For example, the traces (e.g., footprints, feces, food traces, etc.) or camera trapping data of large- and medium-sized animals (weight > 1 kg) used to explain biodiversity; human disturbances and ecological disasters that used to explain environmental problems. |
| 相关性 Relevance | 与人们日常生产生活有较高的密切程度, 易引发受众的兴趣, 通过解说也能使人较为直观地了解它们。 It is closely related to peopleʼs daily life and production, and it is easy to arouse audiences’ interest, therefore, people can have intuitive understanding through interpretation. |
| 方便性 Convenience | 位于对公众开放且可以安全到达的地方; 在区内有一定的数量分布, 且至少在一个季节内有较高的遇见率, 容易观赏到。如步道两旁的常见树种。 It has a certain number of distributions in areas open to the public and safely accessible; and has a high rate of encounters in at least one season, so it is easy to be found, e.g., the common tree species on both sides of the trail. |
表1 九寨沟国家级自然保护区芦苇海解说步道解说资源选择标准(参考Larsen, 2003; Yan, 2005; Chen et al, 2020)
Table 1 Selection criteria for interpretation resources of Reed Lake interpretation trail in the Jiuzhaigou National Nature Reserve (cited from Larsen, 2003; Yan, 2005; Chen et al, 2020)
| 标准 Criteria | 内容 Content |
|---|---|
| 独特性 Uniqueness | 自然、文化、科学、娱乐和启发灵感等方面的独特性。该资源相对周围的景观在色、形、味、年龄、稀有程度或其他方面的特征有较强烈的差异, 容易引起受众的特别兴趣。例如某一植物在花、叶、茎、根、生态功能等方面有显著而有趣的特点, 或独特的种间关系、行为适应等。 It is unique in nature, culture, science, entertainment and inspiration. Compared with the surrounding landscape, the resource has strong differences in color, shape, taste, age, rarity or other aspects, which is easy to arouse audiences’ interest. For example, a plant has significant and interesting characteristics in flowers, leaves, stems, roots, ecological functions, or unique interspecific relationships, behavioral adaptation, etc. |
| 代表性 Representativeness | 具有该地方代表性。如森林群落中的优势种; 植物种的分布范围越窄, 地方代表性越强。 It is representative of local area. For example, the dominant species in a forest community; the narrower the distribution range of a plant species, the more its local representativeness. |
| 重要性 Importance | 具有重要功能。如旗舰种、关键种、关键的地质过程、文化图腾等。 It has important functions, including the flagship species, key species, key geological process, cultural totem and so on. |
| 价值性 Value | 能够服务于解说主题, 建立受众与资源意义的连接。例如, 用来解说生物多样性的大中型野生动物(体重 > 1 kg)的活动痕迹(如脚印、粪便、食迹等)或红外相机监测数据; 用来解说环境问题的人为干扰、生态灾难等。 It can serve the interpretation theme and establish connections between audiences and the meaning of resources. For example, the traces (e.g., footprints, feces, food traces, etc.) or camera trapping data of large- and medium-sized animals (weight > 1 kg) used to explain biodiversity; human disturbances and ecological disasters that used to explain environmental problems. |
| 相关性 Relevance | 与人们日常生产生活有较高的密切程度, 易引发受众的兴趣, 通过解说也能使人较为直观地了解它们。 It is closely related to peopleʼs daily life and production, and it is easy to arouse audiences’ interest, therefore, people can have intuitive understanding through interpretation. |
| 方便性 Convenience | 位于对公众开放且可以安全到达的地方; 在区内有一定的数量分布, 且至少在一个季节内有较高的遇见率, 容易观赏到。如步道两旁的常见树种。 It has a certain number of distributions in areas open to the public and safely accessible; and has a high rate of encounters in at least one season, so it is easy to be found, e.g., the common tree species on both sides of the trail. |
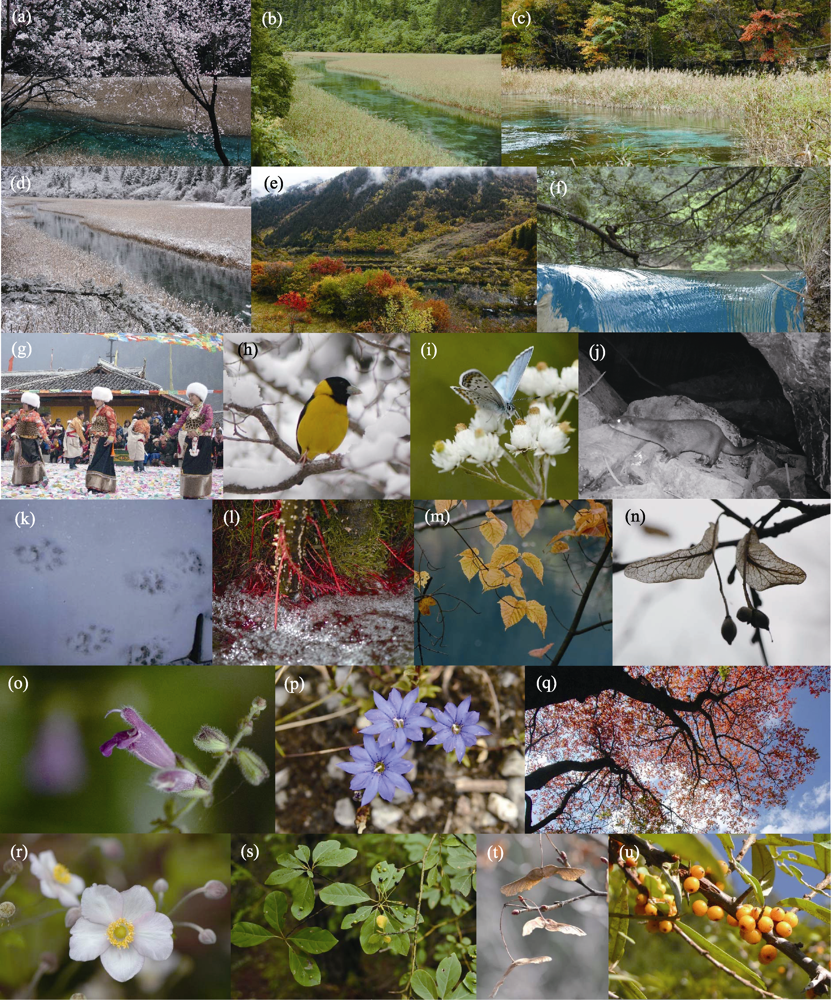

图3 九寨沟国家级自然保护区芦苇海解说步道的解说资源。a-d: 天象与气候, 分别为春夏秋冬的芦苇海景观; e: 生态系统组合, 可见湖泊、退耕地、阔叶林及针叶林; f: 地质与水文, 钙华堤埂的缺口提供了对水流的视觉和听觉体验; g: 文化, 荷叶寨春节民俗活动; h-k: 动物, 分别为雪后枝头的黄颈拟蜡嘴雀(Mycerobas affinis)、多眼灰蝶(Polyommatus eros)在吸食香青(Anaphalis sinica)花蜜、红外影像中的欧亚水獭(Lutra lutra)及步道积雪上的兽类足迹; l-u: 植物与菌类, 分别为“树在水中生”的秘诀——气生根、彩林植物青榨槭(Acer davidii)的秋叶、可用于游戏的华椴(Tilia chinensis)翅果, 具有杠杆状雄蕊结构与传粉者形成密切关系的鼠尾草(Salvia spp.)、高山植物蓝白龙胆(Gentiana leucomelaena)、彩林植物盐肤木(Rhus spp.)、当地居民曾利用的大火草(Anemone tomentosa)、提供嗅觉体验的高山木姜子(Litsea chunii)、槭树科的翅果和具有独特味觉体验的沙棘(Hippophe rhamnoides)。
Fig. 3 Interpretation resources of Reed Lake interpretation trail in the Jiuzhaigou National Nature Reserve. a-d, Astronomical phenomena and climate, indicate aspects of Reed Lake in spring, summer, autumn and winter, respectively. e, Ecosystem composition, including lakes, abandoned land, broad-leaved forests and coniferous forests. f, Geology and hydrology, the gap of travertine dyke provides visual and auditory experiences of water flow. g, Culture, Spring Festival folk activities in Lotus Village. h-k, Animals, they are collared grosbeak (Mycerobas affinis) on the branches after snow, multi-eyed grey butterfly (Polyommatus eros) sucking the nectar of Anaphalis sinica, an infrared image of Eurasian otter (Lutra Lutra) and animal footprints on the snow on the trail. l-u, Plants and fungi, they are aerial rooting-the secret of “trees grow in water”; autumn leaves of Acer davidii, one of color-forest plants; samara of Tilia chinensis, which can be used for games; Salvia spp., which has lever-like stamen structure and forms a close relationship with pollinators; Gentiana leucomelaena, an alpine plant; Rhus spp., one of color-forest plants; Anemone tomentosa, once used by local residents; Litsea chunii, providing olfactory experiences; samara of Aceraceae and Hippophe rhamnoides with unique taste experiences.
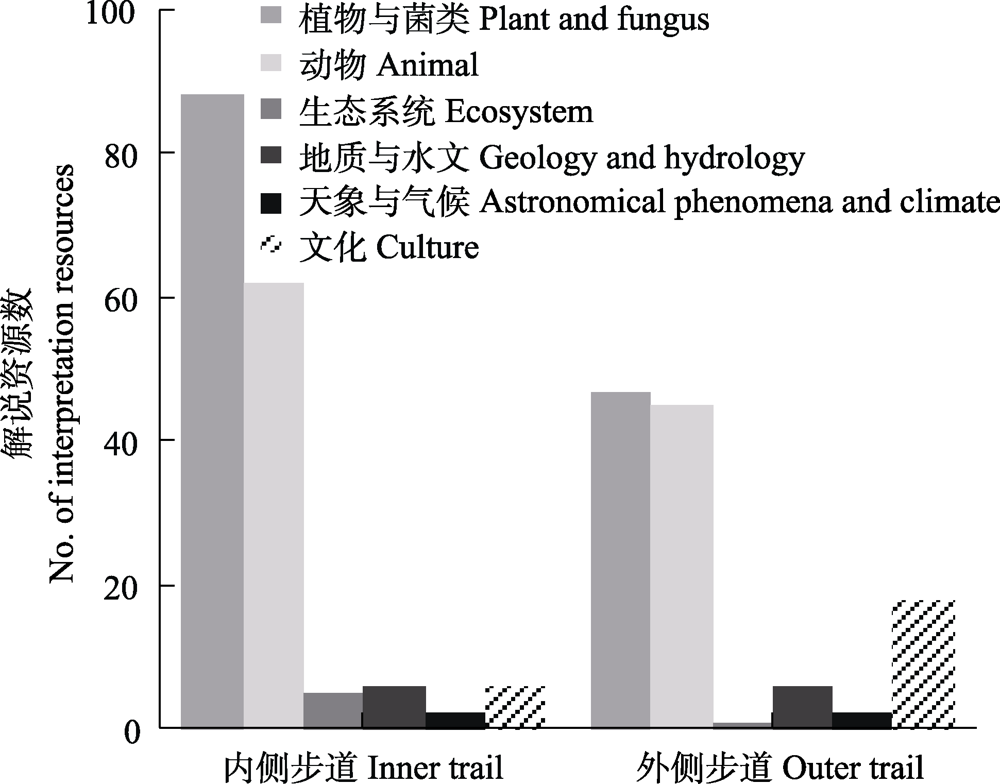
图4 九寨沟国家级自然保护区芦苇海解说步道解说资源分布
Fig. 4 Distribution of interpretation resources in Reed Lake interpretation trail in the Jiuzhaigou National Nature Reserve
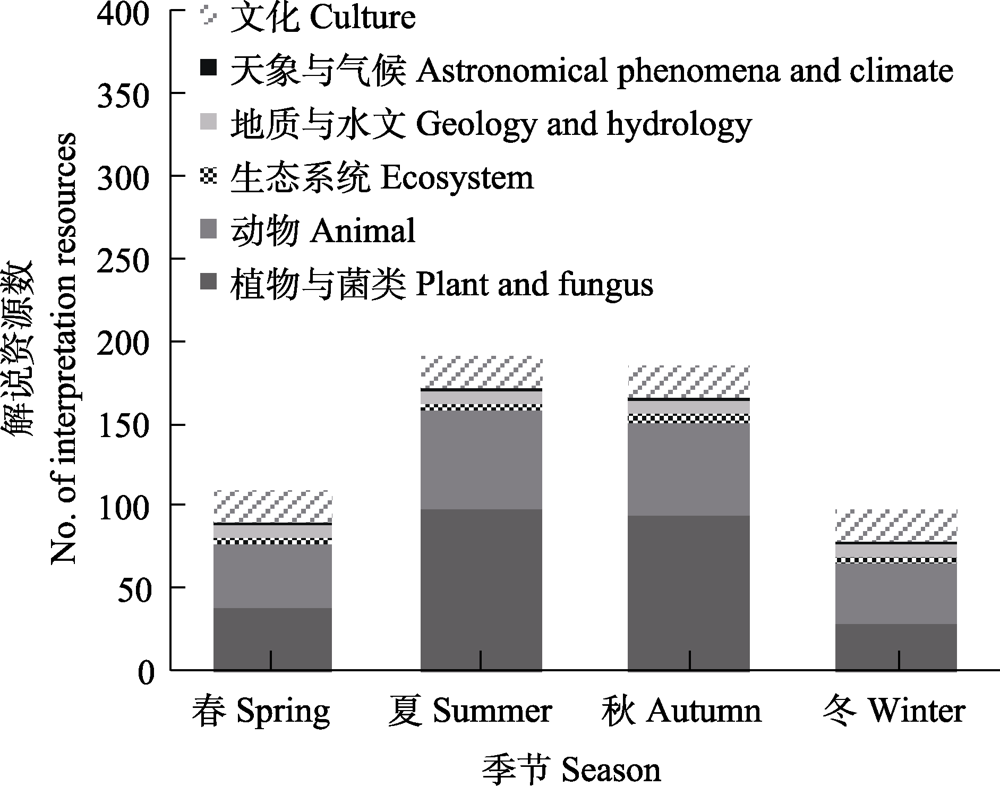
图5 九寨沟国家级自然保护区芦苇海解说步道解说资源季节变化
Fig. 5 Seasonal dynamics of interpretation resources in Reed Lake interpretation trail in the Jiuzhaigou National Nature Reserve
| 主旨 Themes | 解说资源 Interpretation resources | 解说要点 Key points of interpretation | 主要分布区 Main distribution | 季节性 Seasonality | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 春Sp. | 夏Su. | 秋Au. | 冬Wi. | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 1. 保护区为我们体验和认识荒野之美提供了绝佳的机会。 The nature reserve provides us with an excellent opportunity to get close to nature. | 鼠尾草 Salvia spp. | 视觉(花), 触觉 Vision (flower) and touch | 灌草丛 Shrub grassland | + | + | ||||||||||||||||||
| 高山木姜子 Litsea chunii | 视觉(花), 嗅觉 Vision (flower) and smell | + | + | + | |||||||||||||||||||
| 华椴 Tilia chinensis | 视觉(叶形、翅果、彩林植物), 自然创作, 种子传播 Vision (leaf shape, samara, color-forest plants), natural handicrafts and seed transmission | + | + | + | + | ||||||||||||||||||
| 沙棘 Hippophe rhamnoides | 味觉, 鸟类食物, 地方文化 Taste, bird food and local culture | + | + | + | |||||||||||||||||||
| 盐肤木 Rhus spp. | 视觉(彩林植物), 味觉, 红叶的形成 Vision (color-forest plants), taste and red leaf formation | + | + | + | + | ||||||||||||||||||
| 白顶溪鸲 Chaimarrornis leucocephalus | 观鸟, 听觉 Bird watching and hearing | 溪流边石头上 On the rocks by the stream | + | + | + | + | |||||||||||||||||
| 2. “适者生存”的背后, 是无穷的智慧和顽强的生命力。 “Survival of the fittest” needs infinite wisdom and tenacious vitality. | 针叶林 Coniferous forest | 植被类型与气候 Vegetation types and climate | 步道两侧山坡 Slopes on both sides of the trail | + | + | + | + | ||||||||||||||||
| 高山柳 Salix cupularis | 视觉(气生根, “水在林间流, 树在水中生”) Vision (aerial rooting, “water flows in the forest and trees grow in the water”) | + | + | + | + | ||||||||||||||||||
| 桑寄生 Taxillus sutchuenensis | 寄生, 种子传播(借助鸟) Parasitism and seed transmission (with the help of birds) | 林冠层 Canopy | + | + | + | + | |||||||||||||||||
| 铁杉 Tsuga chinensis | 视觉(果、树抱石、二代木), 自然创作 Vision (fruit, rocks wrapped by tree roots and new plants sprout from a fallen tree) and natural handicrafts | + | + | + | + | ||||||||||||||||||
| 四声杜鹃 Cuculus micropterus | 观鸟, 听觉, 物候 Bird watching, hearing and phenology | 林冠层 Canopy | + | + | |||||||||||||||||||
| 3. 大熊猫是原始森林的保护伞。 The giant panda is the umbrella of the primary forest. | 大熊猫 Ailuropoda melanoleuca | 旗舰种, 竹子开花与生态廊道 Flagship species, bamboo flowering and ecological corridor | 黑角山(步道以外) Heijiao Mountaion (outside the trail) | + | + | + | + | ||||||||||||||||
| 欧亚水獭 Lutra lutra | 水体顶级捕食者, 生态系统健康指示种, 行为, 近危, 地方文化 Top predator in waters, ecosystem health indicator, behaviors, near threatened and local culture | + | + | + | + | ||||||||||||||||||
| 4. 自然保护区肩负着守护地球家园的使命。 Nature reserves shoulder the mission of protecting our planet. | 野猪 Sus scrofa | 痕迹识别, 监测数据, 行为 Trace identification, monitoring data and behaviors | + | + | + | + | |||||||||||||||||
| 红豆杉 Taxus chinensis | 视觉(假种皮), 植物大熊猫, 药用价值 Vision (aril), giant panda in vegetable kingdom and medicinal value | + | + | + | + | ||||||||||||||||||
| 华西箭竹 Fargesia nitida | 大熊猫栖息地, 竹子开花与生态廊道 Giant panda habitat, bamboo flowering and ecological corridor | + | + | + | + | ||||||||||||||||||
| 5. 多样化的地貌、极富特色的水体和钙华体, 带你走入童话世界。 Diversified landforms, distinctive water bodies and travertine present a fairy tale world for you. | 青榨槭 Acer davidii | 视觉(叶形、翅果、彩林植物), 自然创作, 种子传播 Vision (leaf shape, samara, color-forest plants), natural handicrafts and seed transmission | 步道全线 On the whole trail | + | + | + | + | ||||||||||||||||
| 湿地 Wetland | 湿地生态系统结构与功能 Structure and function of wetland ecosystem | 步道全线 On the whole trail | + | + | + | + | |||||||||||||||||
| 喀斯特地貌 Karst | 喀斯特地貌的形成, 世界遗产独特性 The formation of karst and the uniqueness of world heritage | 步道全线 On the whole trail | + | + | + | + | |||||||||||||||||
| 火花海 Spark Lake | 地震与九寨沟景观成因, 震后修复, 自然创造力与人为修饰 Earthquake and the genesis of Jiuzhaigou landscape, post-earthquake restoration, natural creativity and artificial modification | 火花海 Spark Lake | + | + | + | + | |||||||||||||||||
| 水流 Water flow | 水声, 水循环, 水的理化性质, 实验演示 Sound of water, water cycle, physical and chemical properties of water, and experimental demonstration | + | + | + | + | ||||||||||||||||||
| 主旨 Themes | 解说资源 Interpretation resources | 解说要点 Key points of interpretation | 主要分布区 Main distribution | 季节性 Seasonality | |||||||||||||||||||
| 春Sp. | 夏Su. | 秋Au. | 冬Wi. | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 6. 九寨沟生动展示了自然在塑造和再塑造地球表面的角色作用。 Jiuzhaigou vividly demonstrates the role of nature in shaping and reshaping the earth’s surface. | 火花海 Spark Lake | 地震与九寨沟景观成因, 震后修复, 自然创造力与人为修饰 Earthquake and the genesis of Jiuzhaigou landscape, post-earthquake restoration, natural creativity and artificial modification | 火花海 Spark Lake | + | + | + | + | ||||||||||||||||
| 崩塌与滑坡 Collapse and landslide | 崩塌、滑坡与九寨沟景观成因, 植被保护 Collapse, landslide and genesis of Jiuzhaigou landscape, and vegetation protection | + | + | + | + | ||||||||||||||||||
| 芦苇海 Reed Lake | 泥石流与芦苇海的形成, 群落演替与沼泽化作用 Debris flow and the formation of Reed Lake, community succession and swamping | 芦苇海 Reed Lake | + | + | + | + | |||||||||||||||||
| 芦苇 Phragmites australis | 鸟类栖息地, 湿地生态系统, 群落演替, 地方文化 Bird habitat, wetland ecosystem, community succession and local culture | 芦苇海 Reed Lake | + | + | + | + | |||||||||||||||||
| 青杄 Picea wilsonii | 视觉(果、树抱石) Vision (fruit and rocks wrapped by tree roots) | + | + | + | + | ||||||||||||||||||
| 7. 九寨沟独特的民俗文化和宗教信仰, 蕴含着人与自然和谐相处的智 慧。 Jiuzhaigou’s unique folk culture and religious beliefs contain the wisdom of living in harmony with nature. | 山神 Mountain deity | 文化中的自然保护思想(敬畏自然, 对破坏环境、杀生的禁忌) The thought of conservation in culture (nature-awing, taboo against destroying the environment and killing animals) | 树正寨、荷叶寨、黑角桥草地 Shuzheng Village, Lotus Village and grassland near Heijiao Bridge | + | + | + | + | ||||||||||||||||
| 建筑与起居 Architecture and living | 气候影响生活方式, 木匠, 对光能的利用Climate affects lifestyle, carpenters and utilization of solar energy | 树正寨、荷叶寨 Shuzheng Village, Lotus Village | + | + | + | + | |||||||||||||||||
| 磨坊 Mill | 地方农业与文化关系, 利用自然力 The relationship between local agriculture and culture, and utilization of natural forces | 树正磨坊 Shuzheng Mill | + | + | + | + | |||||||||||||||||
| 牛蒡 Arctium lappa | 视觉(花), 嗅觉, 地方文化 Vision (flower), smell and local culture | 灌草丛 Shrub grassland | + | + | + | + | |||||||||||||||||
| 夏嫫锅庄 Xiamo national dance | 农耕文化与民族艺术的融合, 民族文化的生态知识 The integration of farming culture and national art, and the ecological knowledge in national culture | 树正寨、荷叶寨 Shuzheng Village and Lotus Village | + | + | + | + | |||||||||||||||||
| 8. 九寨沟的发展史是人类寻求与自然和谐的典型案例。 The development history of Jiuzhaigou is a typical case of human seeking harmony with nature. | 历史 History | 发现、开发、保护历史, 当前的管理与挑战 Discovery, development and protection history, and current management and challenges | 步道全线 On the whole trail | + | + | + | + | ||||||||||||||||
| 青稞 Highland barley | 地方农业与文化关系 Relationship between local agriculture and culture | 树正寨、荷叶寨 Shuzheng Village and Lotus Village | + | + | + | + | |||||||||||||||||
| 退耕地 Abandoned land | 半农半牧、“二牛抬杠”, 气候影响生产、生活方式, 生态工程 Semi-agriculture and semi-husbandry, double-ox-drawn plough, climate affects production and life style, and ecological engineering | + | + | + | + | ||||||||||||||||||
| 落叶阔叶林 Deciduous broad-leaved forest | 群落季相(彩林), 九寨沟采伐与保护历史 Community seasonality (color-forest), Jiuzhaigou cutting and protection history | + | + | + | + | ||||||||||||||||||
| 泥石流拦坝 Debris flow dam | 泥石流与九寨沟景观成因, 植被保护 Debris flow and the genesis of Jiuzhaigou landscape, and vegetation protection | 树正寨、荷叶寨 Shuzheng Village and Lotus Village | + | + | + | + | |||||||||||||||||
表2 九寨沟国家级自然保护区芦苇海解说步道解说主旨及对应解说资源举例
Table 2 Interpretation themes and examples of corresponding resources for Reed Lake interpretation trail in the Jiuzhaigou National Nature Reserve
| 主旨 Themes | 解说资源 Interpretation resources | 解说要点 Key points of interpretation | 主要分布区 Main distribution | 季节性 Seasonality | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 春Sp. | 夏Su. | 秋Au. | 冬Wi. | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 1. 保护区为我们体验和认识荒野之美提供了绝佳的机会。 The nature reserve provides us with an excellent opportunity to get close to nature. | 鼠尾草 Salvia spp. | 视觉(花), 触觉 Vision (flower) and touch | 灌草丛 Shrub grassland | + | + | ||||||||||||||||||
| 高山木姜子 Litsea chunii | 视觉(花), 嗅觉 Vision (flower) and smell | + | + | + | |||||||||||||||||||
| 华椴 Tilia chinensis | 视觉(叶形、翅果、彩林植物), 自然创作, 种子传播 Vision (leaf shape, samara, color-forest plants), natural handicrafts and seed transmission | + | + | + | + | ||||||||||||||||||
| 沙棘 Hippophe rhamnoides | 味觉, 鸟类食物, 地方文化 Taste, bird food and local culture | + | + | + | |||||||||||||||||||
| 盐肤木 Rhus spp. | 视觉(彩林植物), 味觉, 红叶的形成 Vision (color-forest plants), taste and red leaf formation | + | + | + | + | ||||||||||||||||||
| 白顶溪鸲 Chaimarrornis leucocephalus | 观鸟, 听觉 Bird watching and hearing | 溪流边石头上 On the rocks by the stream | + | + | + | + | |||||||||||||||||
| 2. “适者生存”的背后, 是无穷的智慧和顽强的生命力。 “Survival of the fittest” needs infinite wisdom and tenacious vitality. | 针叶林 Coniferous forest | 植被类型与气候 Vegetation types and climate | 步道两侧山坡 Slopes on both sides of the trail | + | + | + | + | ||||||||||||||||
| 高山柳 Salix cupularis | 视觉(气生根, “水在林间流, 树在水中生”) Vision (aerial rooting, “water flows in the forest and trees grow in the water”) | + | + | + | + | ||||||||||||||||||
| 桑寄生 Taxillus sutchuenensis | 寄生, 种子传播(借助鸟) Parasitism and seed transmission (with the help of birds) | 林冠层 Canopy | + | + | + | + | |||||||||||||||||
| 铁杉 Tsuga chinensis | 视觉(果、树抱石、二代木), 自然创作 Vision (fruit, rocks wrapped by tree roots and new plants sprout from a fallen tree) and natural handicrafts | + | + | + | + | ||||||||||||||||||
| 四声杜鹃 Cuculus micropterus | 观鸟, 听觉, 物候 Bird watching, hearing and phenology | 林冠层 Canopy | + | + | |||||||||||||||||||
| 3. 大熊猫是原始森林的保护伞。 The giant panda is the umbrella of the primary forest. | 大熊猫 Ailuropoda melanoleuca | 旗舰种, 竹子开花与生态廊道 Flagship species, bamboo flowering and ecological corridor | 黑角山(步道以外) Heijiao Mountaion (outside the trail) | + | + | + | + | ||||||||||||||||
| 欧亚水獭 Lutra lutra | 水体顶级捕食者, 生态系统健康指示种, 行为, 近危, 地方文化 Top predator in waters, ecosystem health indicator, behaviors, near threatened and local culture | + | + | + | + | ||||||||||||||||||
| 4. 自然保护区肩负着守护地球家园的使命。 Nature reserves shoulder the mission of protecting our planet. | 野猪 Sus scrofa | 痕迹识别, 监测数据, 行为 Trace identification, monitoring data and behaviors | + | + | + | + | |||||||||||||||||
| 红豆杉 Taxus chinensis | 视觉(假种皮), 植物大熊猫, 药用价值 Vision (aril), giant panda in vegetable kingdom and medicinal value | + | + | + | + | ||||||||||||||||||
| 华西箭竹 Fargesia nitida | 大熊猫栖息地, 竹子开花与生态廊道 Giant panda habitat, bamboo flowering and ecological corridor | + | + | + | + | ||||||||||||||||||
| 5. 多样化的地貌、极富特色的水体和钙华体, 带你走入童话世界。 Diversified landforms, distinctive water bodies and travertine present a fairy tale world for you. | 青榨槭 Acer davidii | 视觉(叶形、翅果、彩林植物), 自然创作, 种子传播 Vision (leaf shape, samara, color-forest plants), natural handicrafts and seed transmission | 步道全线 On the whole trail | + | + | + | + | ||||||||||||||||
| 湿地 Wetland | 湿地生态系统结构与功能 Structure and function of wetland ecosystem | 步道全线 On the whole trail | + | + | + | + | |||||||||||||||||
| 喀斯特地貌 Karst | 喀斯特地貌的形成, 世界遗产独特性 The formation of karst and the uniqueness of world heritage | 步道全线 On the whole trail | + | + | + | + | |||||||||||||||||
| 火花海 Spark Lake | 地震与九寨沟景观成因, 震后修复, 自然创造力与人为修饰 Earthquake and the genesis of Jiuzhaigou landscape, post-earthquake restoration, natural creativity and artificial modification | 火花海 Spark Lake | + | + | + | + | |||||||||||||||||
| 水流 Water flow | 水声, 水循环, 水的理化性质, 实验演示 Sound of water, water cycle, physical and chemical properties of water, and experimental demonstration | + | + | + | + | ||||||||||||||||||
| 主旨 Themes | 解说资源 Interpretation resources | 解说要点 Key points of interpretation | 主要分布区 Main distribution | 季节性 Seasonality | |||||||||||||||||||
| 春Sp. | 夏Su. | 秋Au. | 冬Wi. | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 6. 九寨沟生动展示了自然在塑造和再塑造地球表面的角色作用。 Jiuzhaigou vividly demonstrates the role of nature in shaping and reshaping the earth’s surface. | 火花海 Spark Lake | 地震与九寨沟景观成因, 震后修复, 自然创造力与人为修饰 Earthquake and the genesis of Jiuzhaigou landscape, post-earthquake restoration, natural creativity and artificial modification | 火花海 Spark Lake | + | + | + | + | ||||||||||||||||
| 崩塌与滑坡 Collapse and landslide | 崩塌、滑坡与九寨沟景观成因, 植被保护 Collapse, landslide and genesis of Jiuzhaigou landscape, and vegetation protection | + | + | + | + | ||||||||||||||||||
| 芦苇海 Reed Lake | 泥石流与芦苇海的形成, 群落演替与沼泽化作用 Debris flow and the formation of Reed Lake, community succession and swamping | 芦苇海 Reed Lake | + | + | + | + | |||||||||||||||||
| 芦苇 Phragmites australis | 鸟类栖息地, 湿地生态系统, 群落演替, 地方文化 Bird habitat, wetland ecosystem, community succession and local culture | 芦苇海 Reed Lake | + | + | + | + | |||||||||||||||||
| 青杄 Picea wilsonii | 视觉(果、树抱石) Vision (fruit and rocks wrapped by tree roots) | + | + | + | + | ||||||||||||||||||
| 7. 九寨沟独特的民俗文化和宗教信仰, 蕴含着人与自然和谐相处的智 慧。 Jiuzhaigou’s unique folk culture and religious beliefs contain the wisdom of living in harmony with nature. | 山神 Mountain deity | 文化中的自然保护思想(敬畏自然, 对破坏环境、杀生的禁忌) The thought of conservation in culture (nature-awing, taboo against destroying the environment and killing animals) | 树正寨、荷叶寨、黑角桥草地 Shuzheng Village, Lotus Village and grassland near Heijiao Bridge | + | + | + | + | ||||||||||||||||
| 建筑与起居 Architecture and living | 气候影响生活方式, 木匠, 对光能的利用Climate affects lifestyle, carpenters and utilization of solar energy | 树正寨、荷叶寨 Shuzheng Village, Lotus Village | + | + | + | + | |||||||||||||||||
| 磨坊 Mill | 地方农业与文化关系, 利用自然力 The relationship between local agriculture and culture, and utilization of natural forces | 树正磨坊 Shuzheng Mill | + | + | + | + | |||||||||||||||||
| 牛蒡 Arctium lappa | 视觉(花), 嗅觉, 地方文化 Vision (flower), smell and local culture | 灌草丛 Shrub grassland | + | + | + | + | |||||||||||||||||
| 夏嫫锅庄 Xiamo national dance | 农耕文化与民族艺术的融合, 民族文化的生态知识 The integration of farming culture and national art, and the ecological knowledge in national culture | 树正寨、荷叶寨 Shuzheng Village and Lotus Village | + | + | + | + | |||||||||||||||||
| 8. 九寨沟的发展史是人类寻求与自然和谐的典型案例。 The development history of Jiuzhaigou is a typical case of human seeking harmony with nature. | 历史 History | 发现、开发、保护历史, 当前的管理与挑战 Discovery, development and protection history, and current management and challenges | 步道全线 On the whole trail | + | + | + | + | ||||||||||||||||
| 青稞 Highland barley | 地方农业与文化关系 Relationship between local agriculture and culture | 树正寨、荷叶寨 Shuzheng Village and Lotus Village | + | + | + | + | |||||||||||||||||
| 退耕地 Abandoned land | 半农半牧、“二牛抬杠”, 气候影响生产、生活方式, 生态工程 Semi-agriculture and semi-husbandry, double-ox-drawn plough, climate affects production and life style, and ecological engineering | + | + | + | + | ||||||||||||||||||
| 落叶阔叶林 Deciduous broad-leaved forest | 群落季相(彩林), 九寨沟采伐与保护历史 Community seasonality (color-forest), Jiuzhaigou cutting and protection history | + | + | + | + | ||||||||||||||||||
| 泥石流拦坝 Debris flow dam | 泥石流与九寨沟景观成因, 植被保护 Debris flow and the genesis of Jiuzhaigou landscape, and vegetation protection | 树正寨、荷叶寨 Shuzheng Village and Lotus Village | + | + | + | + | |||||||||||||||||
| [1] |
Amin VL, Yok MCK (2015) Thematic interpretation approach in environmental adult education. Procedia: Social and Behavioral Sciences, 167, 261-266.
DOI URL |
| [2] | Cai J (2019) Park as learning place: Interpretation and environmental educational development of national parks. Landscape Architecture, 26(6), 91-96. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 蔡君 (2019) 公园作为学习场所--国家公园解说和环境教育发展探讨. 风景园林, 26(6), 91-96.] | |
| [3] | Chen N, Wu WY, Tang HM (2018) Review of the development history of natural education in China. World Environment, (5), 72-73. (in Chinese) |
| [ 陈南, 吴婉滢, 汤红梅 (2018) 中国自然教育发展历程之追索. 世界环境, (5), 72-73.] | |
| [4] | Chen RQ, Li M, Wei D (2020) The optimal design of environmental interpretation board in forest park from the perspective of nature education. Flowers, (8), 294-295. (in Chinese) |
| [ 陈日强, 黎明, 魏丹 (2020) 自然教育视角下森林公园环境解说牌的优化设计. 花卉, (8), 294-295.] | |
| [5] | Cheng YH, Long TT, Li WJ, Liu GY, Yang PY (2020) Suggestions on natural education strategy of the Wolong National Nature Reserve based on SWOT analysis. Forestry Education in China, 38(5), 13-17. (in Chinese) |
| [ 程跃红, 龙婷婷, 李文静, 刘桂英, 杨攀艳 (2020) 基于SWOT分析的四川卧龙国家级自然保护区自然教育策略建议. 中国林业教育, 38(5), 13-17.] | |
| [6] | Di H, Sun XX, Che ZX (2020) Planning of natural education route and interpretation system in Gansu area of the Qilian Mountain National Park. Forest Science and Technology, (1), 85-87. (in Chinese) |
| [ 邸华, 孙小霞, 车宗玺 (2020) 祁连山国家公园甘肃片区自然教育线路及解说系统的规划. 林业科技通讯, (1), 85-87.] | |
| [7] | Gao CX, Liu JM, Zhang SY, Zhu H (2021) Research progress of the natural preserve utilization in China from the perspective of ecotourism. Journal of Chinese Ecotourism, 11, 127-140. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 高彩霞, 刘家明, 张书颖, 朱鹤 (2021) 生态旅游理念下国内自然保护地利用模式研究进展. 中国生态旅游, 11, 127-140.] | |
| [8] |
General Office of the CPC Central Committee (2017) Overall Plan for Establishing National Park System. Biodiversity Science, 25, 1033-1036. (in Chinese)
DOI URL |
| [中办发 (2017) 建立国家公园体制总体方案. 生物多样性, 25, 1033-1036.] | |
| [9] |
Geng DH, Innes J, Wu WL, Wang GY (2021) Impacts of COVID-19 pandemic on urban park visitation: A global analysis. Journal of Forestry Research, 32, 553-567.
DOI URL |
| [10] | Gross M, Zimmerman R, Buchholz J (translated by Zhao JL, Zhang L)(2018) Signs, Trails, and Wayside Exhibits: Connecting People and Places, 3rd edn. China Environment Publishing Group, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 赵金凌, 张岚,(译)(2018) 指示牌、自然小径和路边展板设计指南: 人类与环境的连接点(第三版). 中国环境出版集团,北京.] | |
| [11] | Guo HJ, Ye W, Zhao MY, Wang XM (2015) The comparative study of interpretive panels system in northwest Yunnan protected areas. Journal of Central South University of Forestry & Technology (Social Sciences), 9(2), 69-73, 93. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 郭海健, 叶文, 赵敏燕, 王西敏 (2015) 滇西北保护地解说牌示系统比较研究. 中南林业科技大学学报(社会科学版), 9(2), 69-73, 93.] | |
| [12] | Guo QX (2015) Diary of nature observation in Jiuzhaigou. Jiuzhaigou, (2), 38-39. (in Chinese) |
| [ 郭倩僖 (2015) 九寨沟自然观察日记. 九寨沟, (2), 38-39.] | |
| [13] | Ham SH (1992) Environmental Interpretation:A Practical Guide for People with Big Ideas and Small Budgets. North American Press, Colorado. |
| [14] | Hu JC, Reid DG, Dong S, Wang W, Huang Y (1990) The behaviour and carrying capacity of the giant panda during the bamboo dying-off period. Journal Sichuan Teach College, 11(2), 103-113. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 胡锦矗, Reid DG, 董赛, 王威, 黄炎 (1990) 竹子开花后大熊猫的觅食行为与容纳量. 四川师范学院学报, 11(2), 103-113.] | |
| [15] | Jiang L, Zhang ZQ, Yao MY, Jiao Z, Yu B, Zhang CF (2021) Current situation and suggestions of natural education based on nature protected areas. Journal of Jilin Forestry Science and Technology, 50(3), 39-42. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 姜力, 张占庆, 姚明远, 焦铮, 于波, 张超凡 (2021) 基于自然保护地开展自然教育的现状及建议. 吉林林业科技, 50(3), 39-42.] | |
| [16] | Lan SR (2015) Environmental interpretation system: The golden key to unlock the ecological and cultural code of forest park. China Green Times. (in Chinese) |
| [ 兰思仁(2015) 环境解说系统: 解开森林公园生态文化密码的金钥匙. 中国绿色时报.] http://www.greentimes.com/green/econo/slly/lycs/content/2015-08/25/content_313661.htm/. (accessed on 2021-06-07) | |
| [17] | Larsen DL (2003) Meaningful Interpretation: How to Connect Hearts and Minds to Places, Objects, and Other Resources. Eastern National, Washington, DC. |
| [18] | Li GQ, Tian GZ (2021) Research on the types and development of research travel bases in China. Journal of Teaching and Management, (9), 40-42. (in Chinese) |
| [ 李贵清, 田广增 (2021) 我国研学旅行基地的类型与发展研究. 教学与管理, (9), 40-42.] | |
| [19] | Li H, Chen XE, Guo F (2010) The research of interpretation object and content of ecotourism in nature protected area. Journal of Capital Normal University (Natural Science Edition), 31(2), 41-46, 53. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 李宏, 陈享尔, 郭飞 (2010) 自然保护区生态旅游解说对象与内容探讨. 首都师范大学学报(自然科学版), 31(2), 41-46, 53.] | |
| [20] | Li H, Wu DL, Wu FY, Zhang XF (2013) Research on interpretation objects of seed plants based-on stratified sampling-A case study of Wulingshan Natural Reserve. Journal of Capital Normal University (Natural Science Edition), 34(1), 47-53. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 李宏, 吴东亮, 吴飞影, 张雪飞 (2013) 基于分层抽样的种子植物解说对象探讨--以雾灵山自然保护区为例. 首都师范大学学报(自然科学版), 34(1), 47-53.] | |
| [21] | Li ZP, Wei DY, He YQ, Wang M (2013) Study on the progress in interpretation system research and practice of natural heritage site and its enlightenment. Geography and Geo-Information Science, 29(2), 105-111, 124. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 李振鹏, 蔚东英, 何亚琼, 王民 (2013) 国内外自然遗产地解说系统研究与实践综述及启示. 地理与地理信息科学, 29(2), 105-111, 124.] | |
| [22] | Liu SY, Zhang XP, Zeng ZY (2007) Biodiversity of the Jiuzhaigou National Nature Reserve. Sichuan Publishing Group, Sichuan Science and Technology Press, Chengdu. (in Chinese and in English) |
| 刘少英, 章小平, 曾宗永 (2007) 九寨沟自然保护区的生物多样性. 四川科学技术出版社, 成都. ] | |
| [23] |
Littlefair C, Buckley R (2008) Interpretation reduces ecological impacts of visitors to world heritage site. Ambio, 37, 321-324.
DOI URL |
| [24] | Luo F, Zhong YD, Wu ZH, Zhang XL (2008) Tourism interpretive demand of visitors in world natural heritage site-Take Wulingyuan as an example. Tourism Tribune, 23(8), 69-73. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 罗芬, 钟永德, 吴忠宏, 张西林 (2008) 世界自然遗产地游客旅游解说需求之研究--以湖南武陵源风景名胜区为例. 旅游学刊, 23(8), 69-73.] | |
| [25] | Ma ML, Wang XQ, Wu M, Liu GY, He H, Wang XM, Chen J (2019) Environmental educational outcomes of night hike in a botanical garden explored by the means-end theory. Studies on Science Popularization, 14(6), 47-57, 114. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 马明乐, 王雪琦, 吴蒙, 刘光裕, 贺赫, 王西敏, 陈进 (2019) 用“方法-目的链”理论探究植物园夜游环境教育效果. 科普研究, 14(6), 47-57, 114.] | |
| [26] | Mao YY (2013) Environmental education in modern landscape architecture in the West. Journal of Central South University of Forestry & Technology (Social Sciences), 7(5), 135-138. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 毛祎月 (2013) 论西方现代风景园林中的环境教育. 中南林业科技大学学报 (社会科学版), 7(5), 135-138.] | |
| [27] | Meng MH, Yu YW, Gu XY, Li TY, Zhang ZP (2005) Case study of composing commentary system for tourist attractions. Journal of Zhejiang Forestry College, 22, 572-576. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 孟明浩, 俞益武, 顾晓艳, 李天佑, 章志攀 (2005) 旅游景区环境解说系统设计方法及个案探讨. 浙江林学院学报, 22, 572-576.] | |
| [28] | Ouyang ZY, Du A, Xu WH (2020) Research on China’s protected area system classification. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 40, 7207-7215. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 欧阳志云, 杜傲, 徐卫华 (2020) 中国自然保护地体系分类研究. 生态学报, 40, 7207-7215.] | |
| [29] | Ouyang ZY, Wang XK, Miao H (1999) A primary study on Chinese terrestrial ecosystem services and their ecological-economic values. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 19, 607-613. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 欧阳志云, 王效科, 苗鸿 (1999) 中国陆地生态系统服务功能及其生态经济价值的初步研究. 生态学报, 19, 607-613.] | |
| [30] | Pan H, Yu T, Xiao TT, Qin XH (2015) Mining of animal culture in forest park and studying of its supporting interpretation system. Journal of Fujian Forestry Science and Technology, 42, 183-187. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 潘辉, 俞婷, 肖婷婷, 秦秀虹 (2015) 森林公园动物文化挖掘及其配套解说系统研究. 福建林业科技, 42, 183-187.] | |
| [31] | Pan WS, Lü Z, Zhu XJ, Wang DJ, Wang H, Long Y, Fu DL, Zhou X (2001) A Chance for Lasting Survival. Peking University Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 潘文石, 吕植, 朱小健, 王大军, 王昊, 龙玉, 付达莉, 周欣 (2001) 继续生存的机会. 北京大学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [32] | Ren JH, Zhang Y, Chu T, Xiao WY (2020) A preliminary study on summer and autumn activities of otters in Jiuzhaigou wetland reserve based on infrared trigger camera. Wetland Science & Management, 16(2), 57-60. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 任锦海, 张跃, 出塔, 肖维阳 (2020) 基于红外相机技术对九寨沟湿地保护区水獭夏秋季活动的初步研究. 湿地科学与管理, 16(2), 57-60.] | |
| [33] | Schaller GB, Hu JC, Pan WS, Zhu J (1985) The Giant Pandas of Wolong. University of Chicago Press, Chicago and London. |
| [34] | Shen H, Li N (2021) The connotation interpretation and value realization of ecological products. Reform, (9), 145-155. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 沈辉, 李宁 (2021) 生态产品的内涵阐释及其价值实现. 改革, (9), 145-155.] | |
| [35] | Sichuan Forestry Department (2015) The Pandas of Sichuan:The 4th Survey Report on Giant Panda in Sichuan Province. Sichuan Science and Technology Press, Chengdu. (in Chinese) |
| [四川省林业厅 (2015) 四川的大熊猫:四川省第四次大熊猫调查报告. 四川科学技术出版社, 成都.] | |
| [36] | Skanavis C, Giannoulis C (2009) A training model for environmental educators and interpreters employed in Greek protected areas and ecotourism settings. International Journal of Sustainable Development & World Ecology, 16, 164-176. |
| [37] | State Council of the People’s Republic of China (1994) Regulations of the People’s Republic of China on Nature Reserves. Gazette of the State Council of the People’s Republic of China, (24), 15-22. (in Chinese) |
| [中华人民共和国国务院 (1994) 中华人民共和国自然保护区条例. 中华人民共和国国务院公报, (24), 15-22.] | |
| [38] | Sun HL, Wu XH (2021) Research on the design of forest park nature interpretation system based on audience behavior characteristics. China Forestry Economics, (2), 6-9. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 孙慧玲, 吴晓华 (2021) 基于受众行为特征的森林公园自然解说系统设计研究. 中国林业经济, (2), 6-9.] | |
| [39] | Sun YN, Wu SH (2020) The elements of environmental education in nature reserves. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Sunyatseni, 60(5), 126-135. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 孙雅妮, 武曙红 (2021) 自然保护地环境教育的组成要素. 中山大学学报(自然科学版), 60(5), 126-135.] | |
| [40] | Tilden F (1977) Interpreting Our Heritage, 3rd edn. University of North Carolina Press, North Carolina. |
| [41] | Wang J, Zhong LS, Chen T (2015) Progress of tourism interpretation at home and abroad. Human Geography, 30(1), 33-39. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 王婧, 钟林生, 陈田 (2015) 国内外旅游解说研究进展. 人文地理, 30 (1), 33-39.] | |
| [42] | Wang M, Wei DY (2007) Significance of environmental interpretation system to geoparks. Geopark Yuntai International Forum-Collection of Essays on Interpretation and Sustainable Development.Jiaozuo. (in Chinese) |
| [ 王民, 蔚东英 (2007) 环境解说系统对地质公园的意义. 地质公园云台国际论坛--解说与可持续发展论文集. 焦作.] | |
| [43] | Wang M, Zhang Y, Hua X, Wang YM (2010) Investigation on the background of environmental interpretation in four types of interpretation sites. Environmental Education, (8), 39-43. (in Chinese) |
| [ 王民, 张英, 花溪, 王元楣 (2010) 四种类型解说地环境解说背景调查研究. 环境教育, (8), 39-43.] | |
| [44] |
Wang YQ, Qi XY, Gao YF (2019) Human-wildlife conflict: A challenge to symbiotic human-nature relationship. Science, 71(5), 1-4, 69. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
| [ 王一晴, 戚新悦, 高煜芳 (2019) 人与野生动物冲突: 人与自然共生的挑战. 科学, 71(5), 1-4, 69.] | |
| [45] | Wei DY (2019) Interpretation Manual of Sanjiangyuan National Park. China Science and Technology Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 蔚东英 (2019) 三江源国家公园解说手册. 中国科学技术出版社, 北京.] | |
| [46] | Wen SW, Wu ZW (2009) Effects of ecological educational on recreational impacts. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 29, 768-775. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 文首文, 吴章文 (2009) 生态教育对游憩冲击的影响. 生态学报, 29, 768-775.] | |
| [47] | Wu BH, Gao XP, Deng B (2003) Progress in environmental interpretation: A literature review. Progress in Geography, 22, 326-334. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 吴必虎, 高向平, 邓冰 (2003) 国内外环境解说研究综述. 地理科学进展, 22, 326-334.] | |
| [48] | Wu BH, Jin H, Zhang L (1999) Planning and management of tourism interpretation system. Tourism Tribune, (1), 44-46. (in Chinese) |
| [ 吴必虎, 金华, 张丽 (1999) 旅游解说系统的规划和管理. 旅游学刊, (1), 44-46.] | |
| [49] | Wu E, Cheng J (2011) On the present situation of China natural park environmental interpretation and education. Chinese Landscape Architecture, 27(2), 17-20. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 乌恩, 成甲 (2011) 中国自然公园环境解说与环境教育现状刍议. 中国园林, 27(2), 17-20.] | |
| [50] | Wu GS (2010) Natural history education: Returning to nature and reshaping human nature. Green Leaves, (7), 73-78. (in Chinese) |
| [ 吴国盛 (2010) 博物学教育: 回归自然、重塑人性. 绿叶, (7), 73-78.] | |
| [51] | Wu Y, Liu ZW, Lu YF, Ma JZ (2020) The United States National Park planning and management of environmental education and its inspiration to China. Chinese Landscape Architecture, 36(1), 102-107. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 吴妍, 刘紫微, 陆怡帆, 马建章 (2020) 美国国家公园环境教育规划与管理现状研究及其对中国的启示. 中国园林, 36(1), 102-107.] | |
| [52] | Xiao LY, Lu Z, Li XY, Zhao X, Li BV (2021) Why do we need a wildlife consumption ban in China? Current Biology, 31, R168-R172. |
| [53] | Xiao WY, Jiang LJ, Ge FQ, Zhu ZF (2015) Characteristic of Typha latifolia growth and harvest influence on its growth. Wetland Science, 13, 197-201. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 肖维阳, 江丽君, 葛凤琼, 朱忠福 (2015) 九寨沟宽叶香蒲的生长特征及收割对其生长影响. 湿地科学, 13, 197-201.] | |
| [54] | Xie M (2014) Stories of Jiuzhaigou ecological summer camp. Jiuzhaigou, (3), 33-40. (in Chinese) |
| [ 谢敏 (2014) 缘起, 缘定--九寨沟生态游学夏令营分享. 九寨沟, (3), 33-40.] | |
| [55] |
Xu HG, Cui QM, Ballantyne R, Packer J (2013) Effective environmental interpretation at Chinese natural attractions: The need for an aesthetic approach. Journal of Sustainable Tourism, 21, 117-133.
DOI URL |
| [56] | Xu Y (2019) Research on the construction of interpretation system of natural heritage sites. Technology and Economic Guide, 27(29), 93-94. (in Chinese) |
| [ 许颖 (2019) 自然遗产地解说系统构建研究. 科技经济导刊, 27(29), 93-94.] | |
| [57] | Xu ZF (1996) Popular science education in botanical gardens and its development. Chinese Biodiversity, 4, 52-53. (in Chinese) |
| [ 许再富 (1996) 植物园的科普教育及其发展. 生物多样性, 4, 52-53.] | |
| [58] | Yan SJ, Cao H (2018) Natural education function of city park and its realization. Chinese Landscape Architecture, 34(5), 48-51. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 闫淑君, 曹辉 (2018) 城市公园的自然教育功能及其实现途径. 中国园林, 34(5), 48-51.] | |
| [59] | Yan YJ (2005) Plant selection of interpretation system design in forest park. Hunan Forestry Science and Technology, 32(3), 76-77. (in Chinese) |
| [ 颜玉娟 (2005) 森林公园解说系统设计的植物选择. 湖南林业科技, 32(3), 76-77.] | |
| [60] |
Yang C (2015) Using an ‘interpretative model’ for contextual design of Heritage Landscape Databases: The case of St Helena Island National Park in Queensland, Australia. Geographical Research, 53, 321-335.
DOI URL |
| [61] | Yang R, Zhao ZC, Zhuang YB (2019) Study on Ecological Experience and Environmental Education Planning of Sanjiangyuan National Park. China Construction Industry Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 杨锐, 赵智聪, 庄优波 (2019) 三江源国家公园生态体验与环境教育规划研究. 中国建筑工业出版社, 北京.] | |
| [62] | Yang WH, Wang Z (2021) Ecological interpretation of “Two Mountains” theory-Also on the strategic plan of ecological civilization construction at the Fifth Plenary Session of the 19th CPC Central Committee. Tribune of Study, (3), 41-48. (in Chinese) |
| [ 杨文华, 王竹 (2021) “两山”理论的生态诠释--兼论党的十九届五中全会生态文明建设战略部署. 学习论坛, (3), 41-48.] | |
| [63] | Yang WY, Zhang YK (2014) Star of Jiuzhaigou. Jiuzhaigou, (3), 45-46. (in Chinese) |
| [ 杨为亚, 张语克 (2014) 九寨之星. 九寨沟, (3), 45-46.] | |
| [64] | Yong Y (2020) Converting to Nature with the Xinghai:An Environmental Interpretation of the Source Area of the Yellow River in Sanjiangyuan National Park. Commercial Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 雍怡 (2020) 心随星海皈自然: 三江源国家公园黄河源区环境解说. 商务印书馆, 北京.] | |
| [65] | Yue W, Xu FC (2020) Nature experience education: Practical exploration of ecological civilization education. Journal of Guangxi Normal University (Philosophy and Social Sciences Edition), 56(2), 115-123. (in Chinese) |
| [ 岳伟, 徐凤雏 (2020) 自然体验教育的价值意蕴与实践逻辑. 广西师范大学学报(哲学社会科学版), 56(2), 115-123. ] | |
| [66] |
Zeppel H, Muloin S (2008) Aboriginal interpretation in Australian wildlife tourism. Journal of Ecotourism, 7, 116-136.
DOI URL |
| [67] | Zhan C, Peng HX (2021) Deliberations on establishing a nature reserve system with national parks as the main body. Journal of Green Science and Technology, 23(11), 192-196. (in Chinese) |
| [ 詹成, 彭红霞 (2021) 关于建立以国家公园为主体的自然保护地体系的思考. 绿色科技, 23(11), 192-196.] | |
| [68] | Zhang HN, Qin WH, Zhou DQ, Fan LN, Li ZL, Jiang MK (2016) Status quo of ecological tourism in nature reserves in China. Journal of Ecology and Rural Environment, 32, 24-29. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 张昊楠, 秦卫华, 周大庆, 范鲁宁, 李中林, 蒋明康 (2016) 中国自然保护区生态旅游活动现状. 生态与农村环境学报, 32, 24-29.] | |
| [69] | Zhang JP, Zhu L (2012) Environmental Interpretation System Construction and Empirical Research in Nature Reserve. China Tourism Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 张建萍, 朱亮 (2012) 自然保护区环境解说系统的构建与实证研究. 中国旅游出版社, 北京.] | |
| [70] | Zhang QF (2012) Wild animals enter the city under dispute. Guangdong Science and Technology News, 9th June, 004. (in Chinese) |
| [ 张奇锋 (2012) 野生动物争议中进城. 广东科技报, 6月9日, 004.] | |
| [71] |
Zhang Y, Lei KM, Zhang YK, Xiao CL, Yang YH, Sun HO, Li SJ (2012) Effects of vegetation, elevation and human disturbance on the distribution of large- and medium-sized wildlife: A case study in Jiuzhaigou Nature Reserve. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 32, 4228-4235. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
| [ 张跃, 雷开明, 张语克, 肖长林, 杨玉花, 孙鸿鸥, 李淑君 (2012) 植被、海拔、人为干扰对大中型野生动物分布的影响--以九寨沟自然保护区为例. 生态学报, 32, 4228-4235.] | |
| [72] | Zhang Y, Yang R (2020) The analysis of the current situation and reform proposals of community-based co-management in China’s nature reserves. Chinese Landscape Architecture, 36(8), 31-35. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 张引, 杨锐 (2020) 中国自然保护区社区共管现状分析和改革建议. 中国园林, 36(8), 31-35.] | |
| [73] | Zhao M (2012) On the study of construction of environment interpretation system of national forest parks based on the mode of SMRE. Journal of Central South University of Forestry & Technology (Social Sciences), 6(3), 12-15, 31. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 赵明 (2012) 基于SMRM的国家森林公园环境解说系统构建研究. 中南林业科技大学学报(社会科学版), 6(3), 12-15, 31.] | |
| [74] | Zhao MY, Dong SC, Guo HJ, Gao N, Li Y, Tang TT, Su TW (2019a) Effects of environmental interpretation service of national park on guiding public’s behavior. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 33(7), 202-208. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 赵敏燕, 董锁成, 郭海健, 高宁, 李宇, 唐甜甜, 苏腾伟 (2019a) 国家公园环境解说服务对引导公众行为的影响. 干旱区资源与环境, 33(7), 202-208.] | |
| [75] | Zhao MY, Dong SC, Yu H, Li Y (2019b) Environmental Interpretation System for Forest Parks of China. China Forestry Publishing House, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 赵敏燕, 董锁成, 俞晖, 李宇 (2019b) 中国森林公园环境解说系统研究. 中国林业出版社, 北京.] | |
| [76] | Zhao MY, Ye W, Dong SC, Li Y, Guo HJ (2016) Research progress of differences in ecotourism interpretation between China and Western countries and localization of interpretation. Progress in Geography, 35, 691-701. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[ 赵敏燕, 叶文, 董锁成, 李宇, 郭海健 (2016) 中西生态旅游解说系统差异化研究进展及本土化路径. 地理科学进展, 35, 691-701.]
DOI |
|
| [77] | Zheng Y, Xu XF (2019) Clarification and comparison of the concept of nature education. Education Modernization, 6(50), 65-67. (in Chinese) |
| [ 郑芸, 徐小飞 (2019) 自然教育的概念厘清及比较. 教育现代化, 6(50), 65-67.] | |
| [78] |
Zhong LS, Buckley RC, Wardle C, Wang LG (2015) Environmental and visitor management in a thousand protected areas in China. Biological Conservation, 181, 219-225.
DOI URL |
| [79] | Zhou R (2013) Nature is the Best School:Practice of Environmental Education in Taiwan. Shanghai Science and Technology Press, Shanghai. (in Chinese) |
| [ 周儒 (2013) 自然是最好的学校:台湾自然教育实践. 上海科学技术出版社, 上海.] | |
| [80] | Zhu L, Zhang JP (2012) Construction of evaluation system for environmental interpretation system of nature reserve-Taking Beijing Hanshiqiao Wetland Nature Reserve as a case study. Social Scientist, (4), 81-84. (in Chinese) |
| [ 朱亮, 张建萍 (2012) 自然保护区环境解说系统评估体系的构建--以北京汉石桥湿地自然保护区为例. 社会科学家, (4), 81-84.] | |
| [81] | Zhu X (2011) Literature review on environment interpretation and visitor education in China. Tourism Science, 25(2), 85-94. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 朱璇 (2011) 关于国内环境解说和游客教育的研究综述. 旅游科学, 25(2), 85-94.] | |
| [82] | Zhu X, Zhu HS (2011) The reconstruction of China’s natural heritage interpretation system: Focusing on the education function. Areal Research and Development, 30(3), 134-139. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 朱璇, 朱海森 (2011) 国内自然遗产地的解说系统重构--注重启智教育功能开发. 地域研究与开发, 30(3), 134-139.] |
| [1] | 郭雨桐, 李素萃, 王智, 解焱, 杨雪, 周广金, 尤春赫, 朱萨宁, 高吉喜. 全国自然保护地对国家重点保护野生物种的覆盖度及其分布状况[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(3): 24423-. |
| [2] | 张雨琦, 文君, 张引, 李晟之. 大熊猫国家公园全民公益性评价研究: 基于利益相关者感知视角[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(9): 24240-. |
| [3] | 姜熠辉, 刘岳, 曾旭, 林喆滢, 王楠, 彭吉豪, 曹玲, 曾聪. 东海六个国家级海洋保护区鱼类多样性和连通性[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(6): 24128-. |
| [4] | 田瑜, 李俊生. 《昆明-蒙特利尔全球生物多样性框架》“3030”目标的内涵及实现路径分析[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(6): 24086-. |
| [5] | 鄢德奎. 中国生物多样性保护政策的共同要素、不足和优化建议[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(5): 23293-. |
| [6] | 崔国发. 关于自然保护地整合优化工作中几个关键问题的讨论与建议[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(9): 22447-. |
| [7] | 林木青, 张应明, 欧阳芳, 束祖飞, 朱朝东, 肖治术. 广东车八岭国家级自然保护区独栖性胡蜂多样性空间分布特征及其对环境因子的响应[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(2): 22310-. |
| [8] | 马子驭, 何再新, 王一晴, 宋大昭, 夏凡, 崔士明, 苏红信, 邓建林, 李平, 李晟. 中国云豹种群分布现状与关键栖息地信息更新[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(9): 22349-. |
| [9] | 张敏, 田春坡, 车先丽, 赵岩岩, 陈什旺, 周霞, 邹发生. 广东省鸟类新记录及其与自然和社会经济因素的关联性[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(5): 21396-. |
| [10] | 吴必虎, 谢冶凤, 李奕, 丛丽. 生态保护红线战略视域下自然保护地如何划界和分区管控?[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(4): 21372-. |
| [11] | 张书杰, 庄优波. 管控视角下生态空间与生态保护红线关系研究[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(4): 21441-. |
| [12] | 朱华, 杜凡. 设立云南金沙江干热河谷萨王纳植被自然保护地的建议[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(3): 21519-. |
| [13] | 胡官正, 曾维华, 马冰然. 保护地区域经济建设与生态保护协同发展路线图: 以三江源地区为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(2): 21225-. |
| [14] | 肖治术, 肖文宏, 王天明, 李晟, 连新明, 宋大昭, 邓雪琴, 周岐海. 中国野生动物红外相机监测与研究: 现状及未来[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(10): 22451-. |
| [15] | 曲方圆, 李淑芸, 赵林林, 杨松颖, 万铭扬, 蔡吕彤, 张朝晖. 黄海生态区保护空缺分析[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(3): 385-393. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn