



生物多样性 ›› 2021, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (9): 1229-1235. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2021020 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2021020
杨苗1, 张杰1, 白嘉伟1, 郭建刚2, 曲亚辉2, 李会平1,3,*( )
)
收稿日期:2021-01-14
接受日期:2021-04-12
出版日期:2021-09-20
发布日期:2021-05-28
通讯作者:
李会平
作者简介:* E-mail: 805737255@qq.com基金资助:
Miao Yang1, Jie Zhang1, Jiawei Bai1, Jiangang Guo2, Yahui Qu2, Huiping Li1,3,*( )
)
Received:2021-01-14
Accepted:2021-04-12
Online:2021-09-20
Published:2021-05-28
Contact:
Huiping Li
摘要:
大型真菌在维持生态系统稳定和为人类提供经济价值方面都具有重要作用, 本文对雾灵山国家级自然保护区中的大型真菌资源进行了详细调查, 为该保护区大型真菌资源开发和利用提供基础资料。作者于2019‒2020年采用样线法和随机踏查法对该保护区大型真菌物种资源多样性进行了初步调查和评估, 共采集大型真菌标本1,132份。结合形态学和ITS序列证据进行了鉴定, 并通过查阅相关文献资料对该保护区大型真菌物种资源价值进行了评价。结果表明: 雾灵山国家级自然保护区共有236种大型真菌, 隶属于2门6纲18目56科107属, 其中15种属于子囊菌门, 221种属于担子菌门。为方便统计, 将大于等于10个种的科定为优势科, 大于等于5个种的属定为优势属。其中优势科有红菇科、蘑菇科、多孔菌科和丝膜菌科, 每个科所包含的种数分别占总种数的8.90%、7.20%、5.93%和4.24%, 共计62种。优势属有红菇属(Russula)、蘑菇属(Agaricus)、鹅膏菌属(Amanita)、丝膜菌属(Cortinarius)、马勃属(Lycoperdon)、小皮伞属(Marasmius)等11个属, 共包含79个种, 占总种数的33.48%。对大型真菌的资源价值评价的结果显示, 保护区内共有食用菌66种、药用菌35种、有毒菌36种和食药兼用菌26种。研究结果表明, 雾灵山国家级自然保护区大型真菌资源丰富, 优势科和优势属中最为丰富的分别是红菇科和红菇属(Russula), 具有经济价值的菌达127种, 为食用菌的引种驯化、药用菌开发利用亦或有毒菌鉴别提供了丰富资源。
杨苗, 张杰, 白嘉伟, 郭建刚, 曲亚辉, 李会平 (2021) 雾灵山国家级自然保护区大型真菌物种多样性. 生物多样性, 29, 1229-1235. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2021020.
Miao Yang, Jie Zhang, Jiawei Bai, Jiangang Guo, Yahui Qu, Huiping Li (2021) Species diversity of macrofungi in the Wuling Mountain National Nature Reserve. Biodiversity Science, 29, 1229-1235. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2021020.
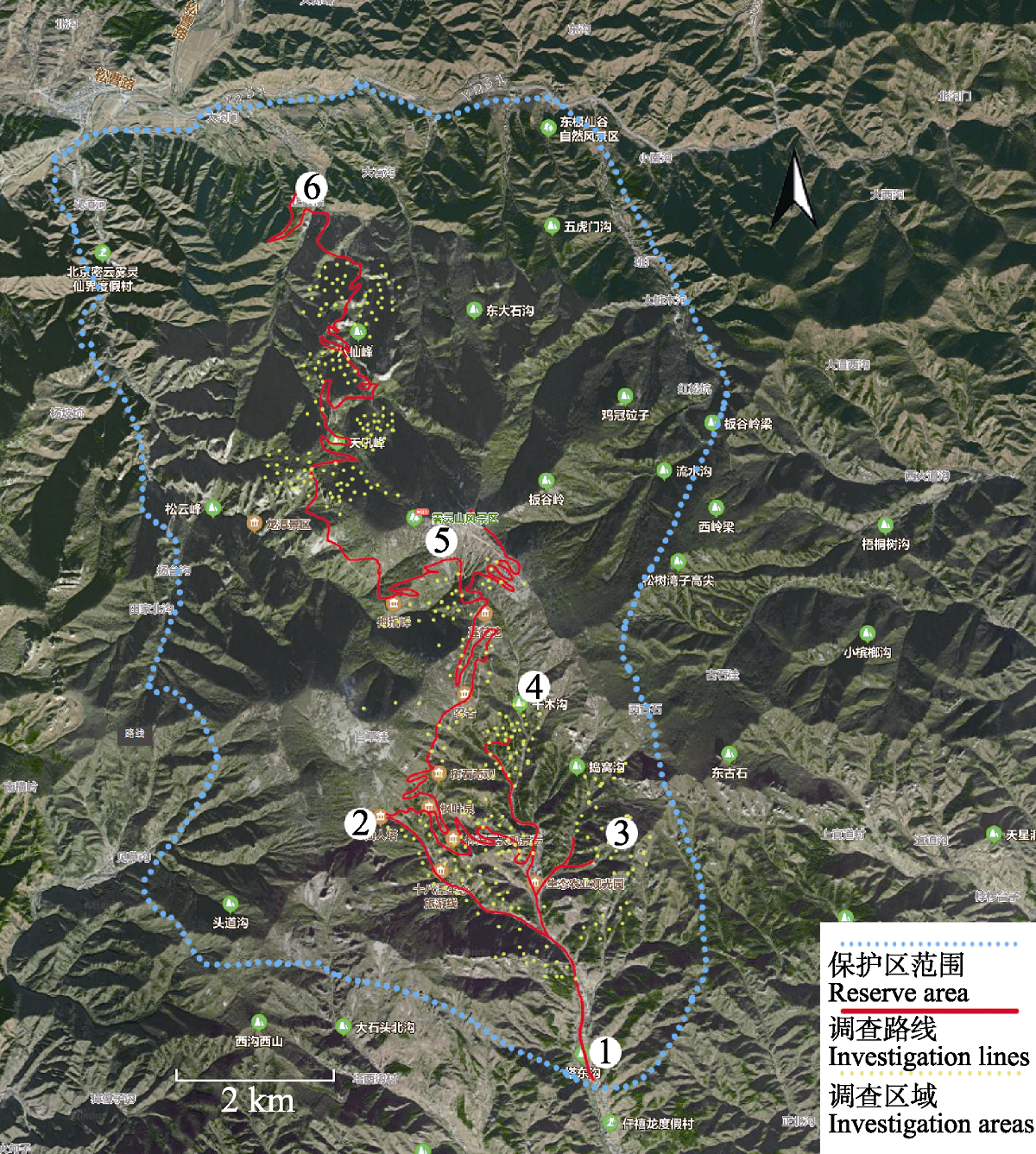
图1 雾灵山国家级自然保护区大型真菌调查线路。(1)保护区南门; (2)仙人塔; (3)娘娘洼沟; (4)五岔沟; (5)莲花池; (6)保护区北门。
Fig. 1 Investigation lines of macrofungi in the Wuling Mountain National Nature Reserve. (1) South gate of the reserve; (2) Fairy Tower; (3) Niangniangwa Valley; (4) Wucha Valley; (5) Lianhuachi; (6) North gate of the reserve.
| 科 Family | 属数 No. of genera | 种数 No. of species | 科 Family | 属数 No. of genera | 种数 No. of species |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 绿杯盘菌科 Chlorociboriaceae | 1 | 1 | 球盖菇科 Strophariaceae | 4 | 6 |
| 地锤菌科 Cudoniaceae | 1 | 1 | 口蘑科 Tricholomataceae | 2 | 4 |
| 马鞍菌科 Helvellaceae | 1 | 4 | 木耳科 Auriculariaceae | 1 | 1 |
| 羊肚菌科 Morchellaceae | 1 | 1 | 牛肝菌科 Boletaceae | 3 | 7 |
| 盘菌科 Pezizaceae | 1 | 2 | 铆钉菇科 Gomphidiaceae | 1 | 1 |
| 火丝盘菌科 Pyronemataceae | 3 | 3 | 硬皮马勃科 Sclerodermataceae | 1 | 1 |
| 肉杯菌科 Sarcoscyphaceae | 1 | 1 | 黏盖牛肝菌科 Suillaceae | 1 | 3 |
| 疣杯盘菌科 Tarzettaceae | 1 | 1 | 桩菇科 Paxillaceae | 1 | 4 |
| 炭球菌科 Hypoxylaceae | 1 | 1 | 齿菌科 Hydnaceae | 4 | 5 |
| 蘑菇科 Agaricaceae | 5 | 17 | 地星科 Geastraceae | 1 | 4 |
| 鹅膏菌科 Amanitaceae | 1 | 6 | 钉菇科 Gomphaceae | 1 | 3 |
| 碘伏革菌科 Amylocorticiaceae | 1 | 1 | 刺革菌科 Hymenochaetaceae | 2 | 3 |
| 珊瑚菌科 Clavariaceae | 1 | 1 | 藓菇科 Rickenellaceae | 1 | 1 |
| 丝膜菌科 Cortinariaceae | 1 | 10 | 革菌科 Thelephoraceae | 1 | 2 |
| 锈耳科 Crepidotaceae | 1 | 3 | 鬼笔科 Phallaceae | 2 | 2 |
| 粉褶菌科 Entolomataceae | 2 | 4 | 拟层孔菌科 Fomitopsidaceae | 1 | 1 |
| 轴腹菌科 Hydnangiaceae | 1 | 3 | 干皮菌科 Incrustoporiaceae | 1 | 1 |
| 蜡伞科 Hygrophoraceae | 2 | 4 | 耙齿菌科 Irpicaceae | 1 | 1 |
| 层腹菌科 Hymenogastraceae | 1 | 2 | 硫磺菌科 Laetiporaceae | 2 | 2 |
| 丝盖伞科 Inocybaceae | 1 | 5 | 平革菌科 Phanerochaetaceae | 1 | 1 |
| 马勃科 Lycoperdaceae | 2 | 6 | 多孔菌科 Polyporaceae | 8 | 14 |
| 小皮伞科 Marasmiaceae | 1 | 5 | 齿耳菌科 Steccherinaceae | 1 | 1 |
| 小菇科 Mycenaceae | 2 | 6 | 红菇科 Russulaceae | 2 | 21 |
| 光茸菌科 Omphalotaceae | 2 | 5 | 韧革菌科 Stereaceae | 2 | 4 |
| 膨瑚菌科 Physalacriaceae | 3 | 5 | 耳匙菌科 Auriscalpiaceae | 1 | 1 |
| 侧耳科 Pleurotaceae | 1 | 5 | 花耳科 Dacrymycetaceae | 2 | 2 |
| 光柄菇科 Pluteaceae | 1 | 7 | 银耳科 Tremellaceae | 1 | 2 |
| 小脆柄菇科 Psathyrellaceae | 3 | 6 | 未定科 Incertae sedis | 14 | 21 |
| 裂褶菌科 Schizophyllaceae | 1 | 1 | 总计 Total | 107 | 236 |
表1 雾灵山国家级自然保护区大型真菌的科、属、种数量统计
Table 1 Number of families, genera and species of macrofungi in Wuling Mountain National Nature Reserve
| 科 Family | 属数 No. of genera | 种数 No. of species | 科 Family | 属数 No. of genera | 种数 No. of species |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 绿杯盘菌科 Chlorociboriaceae | 1 | 1 | 球盖菇科 Strophariaceae | 4 | 6 |
| 地锤菌科 Cudoniaceae | 1 | 1 | 口蘑科 Tricholomataceae | 2 | 4 |
| 马鞍菌科 Helvellaceae | 1 | 4 | 木耳科 Auriculariaceae | 1 | 1 |
| 羊肚菌科 Morchellaceae | 1 | 1 | 牛肝菌科 Boletaceae | 3 | 7 |
| 盘菌科 Pezizaceae | 1 | 2 | 铆钉菇科 Gomphidiaceae | 1 | 1 |
| 火丝盘菌科 Pyronemataceae | 3 | 3 | 硬皮马勃科 Sclerodermataceae | 1 | 1 |
| 肉杯菌科 Sarcoscyphaceae | 1 | 1 | 黏盖牛肝菌科 Suillaceae | 1 | 3 |
| 疣杯盘菌科 Tarzettaceae | 1 | 1 | 桩菇科 Paxillaceae | 1 | 4 |
| 炭球菌科 Hypoxylaceae | 1 | 1 | 齿菌科 Hydnaceae | 4 | 5 |
| 蘑菇科 Agaricaceae | 5 | 17 | 地星科 Geastraceae | 1 | 4 |
| 鹅膏菌科 Amanitaceae | 1 | 6 | 钉菇科 Gomphaceae | 1 | 3 |
| 碘伏革菌科 Amylocorticiaceae | 1 | 1 | 刺革菌科 Hymenochaetaceae | 2 | 3 |
| 珊瑚菌科 Clavariaceae | 1 | 1 | 藓菇科 Rickenellaceae | 1 | 1 |
| 丝膜菌科 Cortinariaceae | 1 | 10 | 革菌科 Thelephoraceae | 1 | 2 |
| 锈耳科 Crepidotaceae | 1 | 3 | 鬼笔科 Phallaceae | 2 | 2 |
| 粉褶菌科 Entolomataceae | 2 | 4 | 拟层孔菌科 Fomitopsidaceae | 1 | 1 |
| 轴腹菌科 Hydnangiaceae | 1 | 3 | 干皮菌科 Incrustoporiaceae | 1 | 1 |
| 蜡伞科 Hygrophoraceae | 2 | 4 | 耙齿菌科 Irpicaceae | 1 | 1 |
| 层腹菌科 Hymenogastraceae | 1 | 2 | 硫磺菌科 Laetiporaceae | 2 | 2 |
| 丝盖伞科 Inocybaceae | 1 | 5 | 平革菌科 Phanerochaetaceae | 1 | 1 |
| 马勃科 Lycoperdaceae | 2 | 6 | 多孔菌科 Polyporaceae | 8 | 14 |
| 小皮伞科 Marasmiaceae | 1 | 5 | 齿耳菌科 Steccherinaceae | 1 | 1 |
| 小菇科 Mycenaceae | 2 | 6 | 红菇科 Russulaceae | 2 | 21 |
| 光茸菌科 Omphalotaceae | 2 | 5 | 韧革菌科 Stereaceae | 2 | 4 |
| 膨瑚菌科 Physalacriaceae | 3 | 5 | 耳匙菌科 Auriscalpiaceae | 1 | 1 |
| 侧耳科 Pleurotaceae | 1 | 5 | 花耳科 Dacrymycetaceae | 2 | 2 |
| 光柄菇科 Pluteaceae | 1 | 7 | 银耳科 Tremellaceae | 1 | 2 |
| 小脆柄菇科 Psathyrellaceae | 3 | 6 | 未定科 Incertae sedis | 14 | 21 |
| 裂褶菌科 Schizophyllaceae | 1 | 1 | 总计 Total | 107 | 236 |
| 属 Genus | 种数 No. species | 占总种数比例 % | 营养类型 Nutritional type |
|---|---|---|---|
| 红菇属 Russula | 12 | 5.08 | 共生 Symbiotic |
| 蘑菇属 Agaricus | 10 | 4.24 | 土生 Geophilous |
| 丝膜菌属 Cortinarius | 10 | 4.24 | 共生 Symbiotic |
| 乳菇属 Lactarius | 9 | 3.81 | 共生 Symbiotic |
| 光柄菇属 Pluteus | 7 | 2.97 | 木生 Lignicolous |
| 鹅膏菌属 Amanita | 6 | 2.54 | 共生 Symbiotic |
| 马勃属 Lycoperdon | 5 | 2.12 | 土生 Geophilous |
| 小皮伞属 Marasmius | 5 | 2.12 | 土生 Geophilous |
| 小菇属 Mycena | 5 | 2.12 | 木生、土生 Lignicolous & geophilous |
| 丝盖伞属 Inocybe | 5 | 2.12 | 土生 Geophilous |
| 侧耳属 Pleurotus | 5 | 2.12 | 木生 Lignicolous |
| 共计 Total | 79 | 33.47 |
表2 雾灵山国家级自然保护区大型真菌优势属(≥ 5种)
Table 2 Dominant genera of macrofungi in Wuling Mountain National Nature Reserve (≥ 5 species)
| 属 Genus | 种数 No. species | 占总种数比例 % | 营养类型 Nutritional type |
|---|---|---|---|
| 红菇属 Russula | 12 | 5.08 | 共生 Symbiotic |
| 蘑菇属 Agaricus | 10 | 4.24 | 土生 Geophilous |
| 丝膜菌属 Cortinarius | 10 | 4.24 | 共生 Symbiotic |
| 乳菇属 Lactarius | 9 | 3.81 | 共生 Symbiotic |
| 光柄菇属 Pluteus | 7 | 2.97 | 木生 Lignicolous |
| 鹅膏菌属 Amanita | 6 | 2.54 | 共生 Symbiotic |
| 马勃属 Lycoperdon | 5 | 2.12 | 土生 Geophilous |
| 小皮伞属 Marasmius | 5 | 2.12 | 土生 Geophilous |
| 小菇属 Mycena | 5 | 2.12 | 木生、土生 Lignicolous & geophilous |
| 丝盖伞属 Inocybe | 5 | 2.12 | 土生 Geophilous |
| 侧耳属 Pleurotus | 5 | 2.12 | 木生 Lignicolous |
| 共计 Total | 79 | 33.47 |
| [1] | Bao HY (2006) Studies on Chemical Compositions and Pharmacological Action of Some Toadstools. Inner Mongolia Education Press, Huhhot. (in Chinese) |
| [包海鹰 (2006) 毒蘑菇化学成分与药理活性的研究. 内蒙古教育出版社, 呼和浩特.] | |
| [2] | Bau T (2018) Mushroom Taxonomy. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [图力古尔 (2018) 蕈菌分类学. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [3] | Bau T, Bao HY, Li Y (2014) A revised checklist of poisonous mushrooms in China. Mycosystema, 33, 517-548. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [图力古尔, 包海鹰, 李玉 (2014) 中国毒蘑菇名录. 菌物学报, 33, 517-548.] | |
| [4] | Bau T, Li Y (2000) Fungal community diversity in Daqinggou Nature Reserve. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 20, 986-991. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [图力古尔, 李玉 (2000) 大青沟自然保护区大型真菌群落多样性研究. 生态学报, 20, 986-991.] | |
| [5] | Bau T, Li Y (2000) Study on fungal flora diversity in Daqinggou Nature Reserve. Chinese Biodiversity, 8, 73-80. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [图力古尔, 李玉 (2000) 大青沟自然保护区大型真菌区系多样性的研究. 生物多样性, 8, 73-80.] | |
| [6] |
Bau T, Wang XS, Zhang P (2019) Floristic of agarics and boletus in the Greater and Lesser Khinggan Mountains. Biodiversity Science, 27, 867-873. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[图力古尔, 王雪珊, 张鹏 (2019) 大小兴安岭地区伞菌和牛肝菌类区系. 生物多样性, 27, 867-873.]
DOI |
|
| [7] | Chen ZH, Yang ZL, Bau T, Li TH (2016) Poisonous Mushrooms:Recognition and Poisoning Treatment. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [陈作红, 杨祝良, 图力古尔, 李泰辉 (2016) 毒蘑菇识别与中毒防治. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [8] | Dai YC, Bau T (2007) Illustrations of Edible and Medicinal Fungi in Northeastern China. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [戴玉成, 图力古尔 (2007) 中国东北食药用真菌图志. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [9] | Dai YC, Yang ZL (2008) A revised checklist of medicinal fungi in China. Mycosystema, 27, 801-824. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [戴玉成, 杨祝良 (2008) 中国药用真菌名录及部分名称的修订. 菌物学报, 27, 801-824.] | |
| [10] | Dai YC, Zhou LW, Yang ZL, Wen HA, Bau T, Li TH (2010) A revised checklist of edible fungi in China. Mycosystema, 29, 1-21. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [戴玉成, 周丽伟, 杨祝良, 文华安, 图力古尔, 李泰辉 (2010) 中国食用菌名录. 菌物学报, 29, 1-21.] | |
| [11] | Li Y, Li TH, Yang ZL, Bau T, Dai YC (2015) Resources of Macrofungi in China. Central Plain Farmers Press, Zhengzhou. (in Chinese) |
| [李玉, 李泰辉, 杨祝良, 图力古尔, 戴玉成 (2015) 中国大型菌物资源图鉴. 中原农民出版社, 郑州.] | |
| [12] | Lu WL, Wei TZ, Wang XL, Li Y, Lü HM, Yang L, Yang WJ, Yao YJ (2015) Species diversity of macrofungi in Beijing, China. Mycosystema, 34, 982-995. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [卢维来, 魏铁铮, 王晓亮, 李熠, 吕红梅, 杨柳, 杨文婧, 姚一建 (2015) 北京地区大型真菌多样性分析. 菌物学报, 34, 982-995.] | |
| [13] | Mao XL (2000) Chinese Macrofungi. Henan Science and Technology Press, Zhengzhou. (in Chinese) |
| [卯晓岚 (2000) 中国大型真菌. 河南科学技术出版社, 郑州.] | |
| [14] | Mao XL (1998) Economic Fungi of China. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [卯晓岚 (1998) 中国经济真菌. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [15] | Mao XL (2006) Poisonous mushrooms and their toxins in China. Mycosystema, 25, 345-363. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [卯晓岚 (2006) 中国毒菌物种多样性及其毒素. 菌物学报, 25, 345-363.] | |
| [16] | Shao LP, Xiang CD (2017) Forest Mushrooms in China. Northeast Forestry University Press, Harbin. (in Chinese) |
| [邵力平, 项存悌 (2017) 中国森林蘑菇. 东北林业大学出版社, 哈尔滨.] | |
| [17] | Wang Q, Liu HX, Zhang JG, Lu J, Liu YX, Yang LH, Ji H, Chen WJ (2005) Investigation of wild edible and medical fungi of Wuling Mountain area. Journal of Hebei University (Natural Science Edition), 25, 523-525. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王谦, 刘会欣, 张俊刚, 卢婕, 刘玉霞, 杨立华, 冀宏, 陈文杰 (2005) 雾灵山地区野生食药用真菌资源调查. 河北大学学报(自然科学版), 25, 523-525.] | |
| [18] | Wang XS, Bau T, Bao JS, Bao H, Feng J (2020) Macrofungal diversity in Hanwula National Nature Reserve, Inner Mongolia. Mycosystema, 39, 695-706. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王雪珊, 图力古尔, 宝金山, 宝虎, 丰洁 (2020) 内蒙古罕山国家级自然保护区大型真菌多样性. 菌物学报, 39, 695-706.] | |
| [19] |
Wu F, Zhou LW, Yang ZL, Bau T, Li TH, Dai YC (2019) Resource diversity of Chinese macrofungi: Edible, medicinal and poisonous species. Fungal Diversity, 98, 1-76.
DOI URL |
| [20] | Wu JG, Zhou H, Hou CL (2020) Diversity of poisonous macrofungi in Beijing Songshan National Nature Reserve. Journal of Capital Normal University (Natural Science Edition), 41(4), 52-56. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [吴记贵, 周昊, 侯成林 (2020) 北京松山国家级自然保护区有毒大型真菌物种多样性研究. 首都师范大学学报(自然科学版), 41(4), 52-56.] | |
| [21] | Yuan MS, Sun PQ (2013) Color Atlas of Large Fungus in China. Sichuan Science and Technology Press, Chengdu. (in Chinese) |
| [袁明生, 孙佩琼 (2013) 中国大型真菌彩色图谱. 四川科学技术出版社, 成都.] | |
| [22] | Zhang JH, Yang XB, Lu SW, Bai CL, Tan HX (2014) Study on shrub-grass diversity and influence factors of different forests in Wuling Mountain of Hebei Province. Journal of Agricultural University of Hebei, 37, 27-32. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [张建华, 杨新兵, 鲁绍伟, 白翠玲, 谭海霞 (2014) 河北雾灵山不同林分灌草多样性及影响因素研究. 河北农业大学学报, 37, 27-32.] | |
| [23] | Zhao HZ, Xu YY, Fu XY, Fan L (2007) The progress of food and medical values of puff-balls. Microbiology, 34, 367-369. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [赵会珍, 胥艳艳, 付晓燕, 范黎 (2007) 马勃的食药用价值及其研究进展. 微生物学通报, 34, 367-369.] |
| [1] | 吴晓晴 张美惠 葛苏婷 李漫淑 宋坤 沈国春 达良俊 张健. 上海近自然林重建过程中木本植物物种多样性与地上生物量的时空动态——以闵行区生态岛为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24444-. |
| [2] | 王太, 宋福俊, 张永胜, 娄忠玉, 张艳萍, 杜岩岩. 河西走廊内陆河水系鱼类多样性及资源现状[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24387-. |
| [3] | 张晶晶, 黄文彬, 陈奕廷, 杨泽鹏, 柯伟业, 彭昭杰, 魏世超, 张志伟, 胡怡思, 余文华, 周文良. 广东南澎列岛海洋生态国家级自然保护区造礁石珊瑚多样性及分布特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24424-. |
| [4] | 尚华丹, 张楚晴, 王梅, 裴文娅, 李国宏, 王鸿斌. 中国杨树害虫物种多样性及其地理分布[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24370-. |
| [5] | 吴昱萱, 王平, 胡晓生, 丁一, 彭甜恬, 植秋滢, 巴德木其其格, 李文杰, 关潇, 李俊生. 呼伦贝尔草地退化现状评估与植被特征变化[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24118-. |
| [6] | 陈自宏, 张翼飞, 陈凯, 陈见影, 徐玲. 高黎贡山南段昆虫病原真菌物种多样性及影响因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(1): 24228-. |
| [7] | 谭珂, 宁瑶, 王仁芬, 王晴, 梁丹萍, 辛子兵, 温放. 中国苦苣苔科植物名录与地理分布数据集[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(1): 23275-. |
| [8] | 韩佳楠, 苏杨, 李霏, 刘君妍, 赵依林, 李琳, 赵建成, 梁红柱, 李敏. 河北省苔藓植物多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(9): 24096-. |
| [9] | 李东红, 郝媛媛, 甘辉林, 张航, 刘耀猛, 他富源, 胡桂馨. 祁连山北麓中段不同类型草地蝗虫种类及分布[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(9): 24119-. |
| [10] | 牛红玉, 陈璐, 赵恒月, 古丽扎尔·阿不都克力木, 张洪茂. 城市化对动物的影响: 从群落到个体[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(8): 23489-. |
| [11] | 王艳丽, 张英, 戚春林, 张昌达, 史佑海, 杜彦君, 丁琼. 海南热带雨林国家公园生物多样性热点与保护空缺区域识别: 基于大型真菌与植物视角[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(7): 24081-. |
| [12] | 白雪, 李正飞, 刘洋, 张君倩, 张多鹏, 罗鑫, 杨佳莉, 杜丽娜, 蒋玄空, 武瑞文, 谢志才. 西江流域大型底栖无脊椎动物物种多样性及维持机制[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(7): 23499-. |
| [13] | 许佳, 崔小娟, 张翼飞, 吴昌, 孙远东. 南岭地区鱼类多样性及其地理分布[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(7): 23482-. |
| [14] | 邝起宇, 胡亮. 广东东海岛与硇洲岛海域底栖贝类物种多样性及其地理分布[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(5): 24065-. |
| [15] | 赵勇强, 阎玺羽, 谢加琪, 侯梦婷, 陈丹梅, 臧丽鹏, 刘庆福, 隋明浈, 张广奇. 退化喀斯特森林自然恢复中不同生活史阶段木本植物物种多样性与群落构建[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(5): 23462-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn
![]()