



生物多样性 ›› 2020, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (7): 806-820. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2020114 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2020114
赵莹1,2, 申小莉1,*( ), 李晟3, 张雁云4, 彭任华5, 马克平1
), 李晟3, 张雁云4, 彭任华5, 马克平1
收稿日期:2020-08-11
接受日期:2020-08-28
出版日期:2020-07-20
发布日期:2020-09-29
通讯作者:
申小莉
作者简介:* E-mail: xlshen@ibcas.ac.cn基金资助:
Ying Zhao1,2, Xiaoli Shen1,*( ), Sheng Li3, Yanyun Zhang4, Renhua Peng5, Keping Ma1
), Sheng Li3, Yanyun Zhang4, Renhua Peng5, Keping Ma1
Received:2020-08-11
Accepted:2020-08-28
Online:2020-07-20
Published:2020-09-29
Contact:
Xiaoli Shen
摘要:
声景生态学以景观中的声音为研究对象, 探讨其在不同时空维度上的分布和变化模式, 从而揭示自然环境、野生动物和人类活动的相互作用关系。本文通过系统检索声景生态学研究的相关文献, 回顾了该学科的研究框架和研究方法, 总结了目前常用的声学指标, 重点归纳了声景生态学的研究内容, 包括声景组成和各组分间的相互作用, 声景的时空格局, 以及声景生态学在生物多样性监测中的应用。目前, 声景监测中存在的问题主要包括监测的生态系统类型和物种类群有限、声学指标效力有待提高等。建议未来着重推进建立系统性的声景监测网络和数据管理平台, 开发和完善音频数据采集、分析方法和评估指标, 并重视声景数据的采集, 将声景视作一种资源进行研究和保护。
赵莹, 申小莉, 李晟, 张雁云, 彭任华, 马克平 (2020) 声景生态学研究进展和展望. 生物多样性, 28, 806-820. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2020114.
Ying Zhao, Xiaoli Shen, Sheng Li, Yanyun Zhang, Renhua Peng, Keping Ma (2020) Progress and outlook for soundscape ecology. Biodiversity Science, 28, 806-820. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2020114.
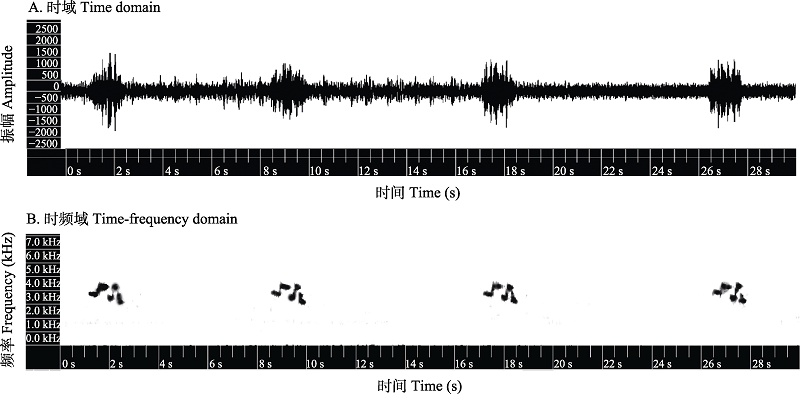
图1 在Kaleidoscope pro5软件中显示的褐顶雀鹛(Alcippe brunnea)鸣唱的波形图(A)和声谱图(B)
Fig. 1 Oscillogram (A) and spectrogram (B) of the song of Alcippe brunnea shown in Kaleidoscope pro5 (Wildlife Acoustics Inc., Maynard, MA, USA)
| 声学指标 Acoustic indices | 指标定义及其应用案例 Definition of indices and application cases | |
|---|---|---|
| α声学指标 α acoustic index | ||
| 声音复杂度指数 Acoustic complexity index (ACI) ( | 音频中声强的变异性。 | |
| 生物声学指数 Bioacoustic index (BIO) ( | 声谱图中超过分贝阈值部分的面积。该面积与动物鸣声的声强和占据的频段数有关。 | |
| 时间熵指数 Temporal entropy index (Ht) ( | 通过将音频切割为若干等时间间隔的声音片段, 计算每个时间片段内的振幅值A(t), 然后求振幅值A(t)的Shannon均匀度(Shannon evenness): $H_t=-\sum^n_{t=1} A(t)×log_2 A(t)×log_2 (n)^{-1},H_{t}\in[0,1]$ | |
| 频谱熵指数 Spectral entropy index (Hf) ( | 声信号平均频率谱S(f)的Shannon均匀度指数(Shannon evenness), 指示声信号在频率分布上的丰富和均匀程度: $H_f=-\sum^n_{f=1} S(f)×log_2 S(f)×log_2 (N)^{-1},H_{f}\in[0,1]$ | |
| 声学熵指数 Acoustic entropy index (H) ( | 时间熵指数(Ht)与频谱熵指数(Hf)的乘积, 体现声信号在时频域上的均匀度和复杂度。对于单调纯音, H趋向于0; 对于随机噪声, H趋向于1: H = Ht × Hf, H∈[0, 1]。 | |
| 声音丰富度指数 Acoustic richness index (AR) ( | 基于振幅指数(M)和时间熵指数(Ht)所得指标, 用于评估发声动物多样性与声学活动水平: M = median(A(t))×2(1-depth), 0 ≤ M ≤ 1, depth为信号数字化的深度 $AR=\frac{(rank(H_t)×rank(M))}{n^2}$, 0 ≤ AR ≤ 1, n为音频文件数量 | |
| 声音多样性指数 Acoustic diversity index (ADI) ( | 提取每一频段中超过特定声压级阈值(默认为?50 dBFS)的声信号参数, 计算Shannon指数(Shannon’s index), 指示声音多样性:$ADI=\sum^s_{i=1}p_i ln p_i$, pi是声信号在第i个频段所占比例, s是频段数量。 | |
| 声音均匀度指数 Acoustic evenness index (AEI) ( | 提取每一频段中超过特定声压级阈值(默认为?50 dBFS)的声信号参数, 计算吉尼指数(Gini index)来表示声信号强度在不同频段的不均等程度。 | |
| 标准化声景差异指数 Normalised difference soundscape index (NDSI) ( | 人类产生声音(anthropophony)与生物产生声音(biophony)声学成分间的比率, 评估人为干扰对声景的影响程度。 | |
| β声学指标 β acoustic index | ||
| 声学差异性指数 Acoustic dissimilarity index (D) ( | 时域差异性指数(temporal dissimilarity index, Dt)和频域差异性指数(spectral dissimilarity index, Df)的乘积, 评估群落间声信号在时域和频域上的差异性: $D_t=0.5×\sum^N_{t=1}|A_1(t)- A_2(t)|$, $D_f=0.5×\sum^n_{t=1}|S_1(f)- S_2(f)$, D = Dt × Df, D∈[0, 1] | |
Box 1 常见声学指标定义及其应用案例
| 声学指标 Acoustic indices | 指标定义及其应用案例 Definition of indices and application cases | |
|---|---|---|
| α声学指标 α acoustic index | ||
| 声音复杂度指数 Acoustic complexity index (ACI) ( | 音频中声强的变异性。 | |
| 生物声学指数 Bioacoustic index (BIO) ( | 声谱图中超过分贝阈值部分的面积。该面积与动物鸣声的声强和占据的频段数有关。 | |
| 时间熵指数 Temporal entropy index (Ht) ( | 通过将音频切割为若干等时间间隔的声音片段, 计算每个时间片段内的振幅值A(t), 然后求振幅值A(t)的Shannon均匀度(Shannon evenness): $H_t=-\sum^n_{t=1} A(t)×log_2 A(t)×log_2 (n)^{-1},H_{t}\in[0,1]$ | |
| 频谱熵指数 Spectral entropy index (Hf) ( | 声信号平均频率谱S(f)的Shannon均匀度指数(Shannon evenness), 指示声信号在频率分布上的丰富和均匀程度: $H_f=-\sum^n_{f=1} S(f)×log_2 S(f)×log_2 (N)^{-1},H_{f}\in[0,1]$ | |
| 声学熵指数 Acoustic entropy index (H) ( | 时间熵指数(Ht)与频谱熵指数(Hf)的乘积, 体现声信号在时频域上的均匀度和复杂度。对于单调纯音, H趋向于0; 对于随机噪声, H趋向于1: H = Ht × Hf, H∈[0, 1]。 | |
| 声音丰富度指数 Acoustic richness index (AR) ( | 基于振幅指数(M)和时间熵指数(Ht)所得指标, 用于评估发声动物多样性与声学活动水平: M = median(A(t))×2(1-depth), 0 ≤ M ≤ 1, depth为信号数字化的深度 $AR=\frac{(rank(H_t)×rank(M))}{n^2}$, 0 ≤ AR ≤ 1, n为音频文件数量 | |
| 声音多样性指数 Acoustic diversity index (ADI) ( | 提取每一频段中超过特定声压级阈值(默认为?50 dBFS)的声信号参数, 计算Shannon指数(Shannon’s index), 指示声音多样性:$ADI=\sum^s_{i=1}p_i ln p_i$, pi是声信号在第i个频段所占比例, s是频段数量。 | |
| 声音均匀度指数 Acoustic evenness index (AEI) ( | 提取每一频段中超过特定声压级阈值(默认为?50 dBFS)的声信号参数, 计算吉尼指数(Gini index)来表示声信号强度在不同频段的不均等程度。 | |
| 标准化声景差异指数 Normalised difference soundscape index (NDSI) ( | 人类产生声音(anthropophony)与生物产生声音(biophony)声学成分间的比率, 评估人为干扰对声景的影响程度。 | |
| β声学指标 β acoustic index | ||
| 声学差异性指数 Acoustic dissimilarity index (D) ( | 时域差异性指数(temporal dissimilarity index, Dt)和频域差异性指数(spectral dissimilarity index, Df)的乘积, 评估群落间声信号在时域和频域上的差异性: $D_t=0.5×\sum^N_{t=1}|A_1(t)- A_2(t)|$, $D_f=0.5×\sum^n_{t=1}|S_1(f)- S_2(f)$, D = Dt × Df, D∈[0, 1] | |
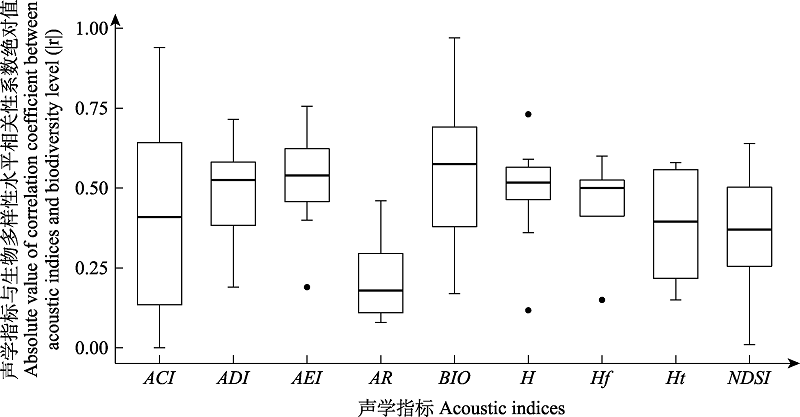
图3 声学指标与生物多样性水平相关性分析结果统计, |r|为12篇陆生环境中研究声学指标与生物多样性耦合关系的相关性系数绝对值。ACI: 声音复杂度指数; ADI: 声音多样性指数; AEI: 声音均匀度指数; AR: 声音丰富度指数; BIO: 生物声学指数; H: 声学熵指数; Hf : 频谱熵指数; Ht: 时间熵指数; NDSI: 标准化声景差异指数。
Fig. 3 Correlation between acoustic indices and biodiversity level, |r| is the absolute value of the correlation coefficient. ACI, Acoustic complexity index; ADI, Acoustic diversity index; AEI, Acoustic evenness index; AR, Acoustic richness index; BIO, Bioacoustic index; H, Acoustic entropy index; Hf, Spectral entropy index; Ht, Temporal entropy index; NDSI, Normalised difference soundscape index.
| [1] |
Aide TM, Corrada-Bravo C, Campos-Cerqueira M, Milan C, Vega G, Alvarez R (2013) Real-time bioacoustics monitoring and automated species identification. PeerJ, 1, e103.
DOI URL PMID |
| [2] |
Au WWL, Mobley J, Burgess WC, Lammers MO, Nachtigall PE (2000) Seasonal and diurnal trends of chorusing humpback whales wintering in waters off western Maui. Marine Mammal Science, 16, 530-544.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
Barber JR, Crooks KR, Fristrup KM (2010) The costs of chronic noise exposure for terrestrial organisms. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 25, 180-189.
URL PMID |
| [4] | Berg KS, Brumfield RT, Apanius V (2006) Phylogenetic and ecological determinants of the neotropical dawn chorus. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 273, 999-1005. |
| [5] | Bittencourt L, Barbosa M, Secchi E, Lailson-Brito J, Azevedo A (2016) Acoustic habitat of an oceanic archipelago in the Southwestern Atlantic. Deep-Sea Research Part I: Oceanographic Research Papers, 115, 103-111. |
| [6] | Bobryk CW, Rega-Brodsky CC, Bardhan S, Farina A, He HS, Jose S (2016) A rapid soundscape analysis to quantify conservation benefits of temperate agroforestry systems using low-cost technology. Agroforestry Systems, 90, 997-1008. |
| [7] |
Boelman NT, Asner GP, Hart PJ, Martin RE (2007) Multitrophic invasion resistance in Hawaii: Bioacoustics, field surveys, and airborne remote sensing. Ecological Applications, 17, 2137-2144.
URL PMID |
| [8] |
Borker AL, McKown MW, Ackerman JT, Eagles-Smith CA, Tershy BR, Croll DA (2014) Vocal activity as a low cost and scalable index of seabird colony size. Conservation Biology, 28, 1100-1108.
URL PMID |
| [9] |
Botteldooren D, Coensel BD, Muer TD (2006) The temporal structure of urban soundscapes. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 292, 105-123.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
Brandes TS (2008) Automated sound recording and analysis techniques for bird surveys and conservation. Bird Conservation International, 18, S163-S173.
DOI URL |
| [11] | Brewer PG, Hester K (2009) Ocean acidification and the increasing transparency of the ocean to low-frequency sound. Oceanography, 22, 86-93. |
| [12] | Brown JL, Li SH, Bhagabati N (1999) Long-term trend toward earlier breeding in an American bird: A response to global warming? Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 96, 5565-5569. |
| [13] |
Brumm H (2004) The impact of environmental noise on song amplitude in a territorial bird. Journal of Animal Ecology, 73, 434-440.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
Burivalova Z, Towsey M, Boucher T, Truskinger A, Apelis C, Roe P, Game ET (2018) Using soundscapes to detect variable degrees of human influence on tropical forests in Papua New Guinea. Conservation Biology, 32, 205-215.
DOI URL PMID |
| [15] |
Burivalova Z, Wahyudi B, Boucher TM, Ellis P, Truskinger A, Towsey M, Roe P, Marthinus D, Griscom B, Game ET (2019) Using soundscapes to investigate homogenization of tropical forest diversity in selectively logged forests. Journal of Applied Ecology, 56, 2493-2504.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
Bustamante MM, Roitman I, Aide TM, Alencar A, Anderson LO, Aragao L, Asner GP, Barlow J, Berenguer E, Chambers J, Costa MH, Fanin T, Ferreira LG, Ferreira J, Keller M, Magnusson WE, Morales-Barquero L, Morton D, Ometto JP, Palace M, Peres CA, Silverio D, Trumbore S, Vieira IC (2016) Toward an integrated monitoring framework to assess the effects of tropical forest degradation and recovery on carbon stocks and biodiversity. Global Change Biology, 22, 92-109.
DOI URL PMID |
| [17] |
Buxton RT, Brown E, Sharman L, Gabriele CM, McKenna MF (2016) Using bioacoustics to examine shifts in songbird phenology. Ecology and Evolution, 6, 4697-4710.
DOI URL PMID |
| [18] |
Buxton RT, Lendrum PE, Crooks KR, Wittemyer G (2018a) Pairing camera traps and acoustic recorders to monitor the ecological impact of human disturbance. Global Ecology and Conservation, 16, e00493.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
Buxton RT, McKenna MF, Clapp M, Meyer E, Stabenau E, Angeloni LM, Crooks K, Wittemyer G (2018b) Efficacy of extracting indices from large-scale acoustic recordings to monitor biodiversity. Conservation Biology, 32, 1174-1184.
URL PMID |
| [20] | Cai XL, Liao WM, Zhang TH, Li XM, Chen FP, Deng RG (2010) Classification and evaluation of forest soundscape types. Acta Agriculturae Universitatis Jiangxiensis, 32, 1195-1201. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 蔡学林, 廖为明, 张天海, 李小毛, 陈飞平, 邓荣根 (2010) 森林声景类型的划分与评价初探. 江西农业大学学报, 32, 1195-1201.] | |
| [21] |
Campos-Cerqueira M, Aide TM (2016) Improving distribution data of threatened species by combining acoustic monitoring and occupancy modelling. Methods in Ecology and Evolution, 7, 1340-1348.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
Chen X, Zhao J, Chen YH, Zhou W, Hughes AC (2020) Automatic standardized processing and identification of tropical bat calls using deep learning approaches. Biological Conservation, 241, 108269.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
Chesmore ED, Ohya E (2004) Automated identification of field-recorded songs of four British grasshoppers using bioacoustic signal recognition. Bulletin of Entomological Research, 94, 319-330.
DOI URL PMID |
| [24] | Cuthill IC, Macdonald WA (1990) Experimental manipulation of the dawn and dusk chorus in the blackbird Turdus merula. Behavioral Ecology and Sociobiology, 26, 209-216. |
| [25] |
Cynx J, Lewis R, Tavel B, Tse H (1998) Amplitude regulation of vocalizations in noise by a songbird, Taeniopygia guttata. Animal Behaviour, 56, 107-113.
DOI URL PMID |
| [26] | David H (2005) Handbook of Biodiversity Methods: Survey, Evaluation and Monitoring. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge. |
| [27] |
Deichmann JL, Hernandez-Serna A, Campos-Cerqueira M, Aide TM (2017) Soundscape analysis and acoustic monitoring document impacts of natural gas exploration on biodiversity in a tropical forest. Ecological Indicators, 74, 39-48.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
Depraetere M, Pavoine S, Jiguet F, Gasc A, Duvail S, Sueur J (2012) Monitoring animal diversity using acoustic indices: Implementation in a temperate woodland. Ecological Indicators, 13, 46-54.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
Desjonqueres C, Rybak F, Depraetere M, Gasc A, Le VI, Pavoine S, Sueur J (2015) First description of underwater acoustic diversity in three temperate ponds. PeerJ, 3, e1393.
DOI URL PMID |
| [30] | Dooley JM, Brown MT (2019) The quantitative relation between ambient soundscapes and landscape development intensity in North Central Florida. Landscape Ecology, 35, 113-127. |
| [31] | Drafts B (2001) Acoustic wave technology sensors. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 49, 795-802. |
| [32] | Dumyahn SL, Pijanowski BC (2011) Soundscape conservation. Landscape Ecology, 26, 1327-1344. |
| [33] | Ey E, Fischer J (2009) The “acoustic adaptation hypothesis”—A review of the evidence from birds, anurans and mammals. Bioacoustics, 19, 21-48. |
| [34] | Farina A, Gage SH (2017) Ecoacoustics: The Ecological Role of Sounds. Wiley, Hoboken. |
| [35] | Farina A, Pieretti N (2014) Sonic environment and vegetation structure: A methodological approach for a soundscape analysis of a Mediterranean maqui. Ecological Informatics, 21, 120-132. |
| [36] | Farina A, Pieretti N, Morganti N (2013) Acoustic patterns of an invasive species: The redbilled leiothrix (Leiothrix lutea Scopoli 1786) in a Mediterranean shrubland. Bioacoustics, 22, 175-194. |
| [37] | Feng AS, Schul J (2007) Sound processing in real-world environments. Hearing and Sound Communication in Amphibians, 28, 323-350. |
| [38] | Fenton MB, Bell GP (1979) Echolocation and feeding behaviour in four species of Myotis (Chiroptera). Canadian Journal of Zoology, 57, 1271-1277. |
| [39] | Ferrari MCO, McCormick MI, Meekan MG, Simpson SD, Nedelec SL, Chivers DP (2018) School is out on noisy reefs: The effect of boat noise on predator learning and survival of juvenile coral reef fishes. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 285, 20180033. |
| [40] | Ferreira L, Oliveira EG, Lopes LC, Brito MR, Baumgarten J, Rodrigues FH, Sousa-Lima R (2018) What do insects, anurans, birds, and mammals have to say about soundscape indices in a tropical savanna. Journal of Ecoacoustics, 2, 1-17. |
| [41] | Fuller S, Axel AC, Tucker D, Gage SH (2015) Connecting soundscape to landscape: Which acoustic index best describes landscape configuration? Ecological Indicators, 58, 207-215. |
| [42] | Gage SH, Axel AC (2014) Visualization of temporal change in soundscape power of a Michigan lake habitat over a 4-year period. Ecological Informatics, 21, 100-109. |
| [43] |
Garrido SA, Bertolelli L, Maria HA, Yebra AM, Munasinghe K (2020) The FrogPhone: A novel device for real-time frog call monitoring. Methods in Ecology and Evolution, 11, 222-228.
DOI URL |
| [44] | Gasc A, Gottesman BL, Francomano D, Jung J, Durham M, Mateljak J, Pijanowski BC (2018) Soundscapes reveal disturbance impacts: Biophonic response to wildfire in the Sonoran Desert Sky Islands. Landscape Ecology, 33, 1399-1415. |
| [45] |
Gasc A, Pavoine S, Lellouch L, Grandcolas P, Sueur J (2015) Acoustic indices for biodiversity assessments: Analyses of bias based on simulated bird assemblages and recommendations for field surveys. Biological Conservation, 191, 306-312.
DOI URL |
| [46] |
Gasc A, Sueur J, Jiguet F, Devictor V, Grandcolas P, Burrow C, Depraetere M, Pavoine S (2013a) Assessing biodiversity with sound: Do acoustic diversity indices reflect phylogenetic and functional diversities of bird communities? Ecological Indicators, 25, 279-287.
DOI URL |
| [47] |
Gasc A, Sueur J, Pavoine S, Pellens R, Grandcolas P (2013b) Biodiversity sampling using a global acoustic approach: Contrasting sites with microendemics in New Caledonia. PLoS ONE, 8, e65311.
DOI URL PMID |
| [48] | Gibbs JP, Breisch AR (2001) Climate warming and calling phenology of frogs near Ithaca, New York, 1900-1999. Conservation Biology, 15, 1175-1178. |
| [49] | Gilbert G, Tyler GA, Smith KW (2002) Local annual survival of booming male great Bittern Botaurus stellaris in Britain, in the period 1990-1999. Ibis, 144, 51-61. |
| [50] | Gomez WE, Isaza CV, Daza JM (2018) Identifying disturbed habitats: A new method from acoustic indices. Ecological Informatics, 45, 16-25. |
| [51] | Greenfield MD (1994) Cooperation and conflict in the evolution of signal interactions. Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics, 25, 97-126. |
| [52] | Guan S, Vignola JF, Lin TH, Chou L (2016) Soundscape Characteristics of the Eastern Taiwan Strait Indo-Pacific Humpback Dolphin Habitat. https://ieeexplore-ieee-org-443. webvpn.las.ac.cn/document/7890674. (accessed on 2020-08-27) |
| [53] | Hage SR, Jiang T, Berquist SW, Feng J, Metzner W (2013) Ambient noise induces independent shifts in call frequency and amplitude within the Lombard effect in echolocating bats. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 110, 4063-4068. |
| [54] | Halfwerk W, Slabbekoorn H (2009) A behavioural mechanism explaining noise-dependent frequency use in urban birdsong. Animal Behaviour, 78, 1301-1307. |
| [55] | Hardouin LA, Robert D, Bretagnolle V (2008) A dusk chorus effect in a nocturnal bird: Support for mate and rival assessment functions. Behavioral Ecology and Sociobiology, 62, 1909-1918. |
| [56] | Harris SA, Shears NT, Radford CA (2016) Ecoacoustic indices as proxies for biodiversity on temperate reefs. Methods in Ecology and Evolution, 7, 713-724. |
| [57] | Heywood VH, Watson RT (1995) Global Biodiversity Assessment. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, |
| [58] | Hill AP, Prince P, Piña CE, Doncaster CP, Snaddon JL, Rogers A (2018) AudioMoth: Evaluation of a smart open acoustic device for monitoring biodiversity and the environment. Methods in Ecology and Evolution, 9, 1199-1211. |
| [59] | Holles S, Simpson SD, Radford AN, Berten L, Lecchini D (2013) Boat noise disrupts orientation behaviour in a coral reef fish. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 485, 295-300. |
| [60] | Hutchinson JMC (2002) Two explanations of the dawn chorus compared: How monotonically changing light levels favour a short break from singing. Animal Behaviour, 64, 527-539. |
| [61] | Jiang JG, Shao XY, Wan HB, Qi JG, Jing CW, Cheng TY (2016) Bird diversity research using audio record files and the spectrogram segmentation method. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 36, 7713-7723. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 蒋锦刚, 邵小云, 万海波, 齐家国, 荆长伟, 程天佑 (2016) 基于语谱图特征信息分割提取的声景中鸟类生物多样性分析. 生态学报, 36, 7713-7723.] | |
| [62] |
Jiang T, Guo X, Lin A, Wu H, Sun C, Feng J, Kanwal JS (2019) Bats increase vocal amplitude and decrease vocal complexity to mitigate noise interference during social communication. Animal Cognition, 22, 199-212.
DOI URL PMID |
| [63] | Joo W, Gage SH, Kasten EP (2011) Analysis and interpretation of variability in soundscapes along an urban-rural gradient. Landscape and Urban Planning, 103, 259-276. |
| [64] | Kasten EP, Gage SH, Fox J, Joo W (2012) The remote environmental assessment laboratory’s acoustic library: An archive for studying soundscape ecology. Ecological Informatics, 12, 50-67. |
| [65] | Kirschel ANG, Cody ML, Harlow ZT, Promponas VJ, Vallejo EE, Taylor CE (2011) Territorial dynamics of Mexican ant-thrushes Formicarius moniliger revealed by individual recognition of their songs. Ibis, 153, 255-268. |
| [66] | Krause BL (1987) Bioacoustics, habitat ambience in ecological balance. Whole Earth Review, 57, 14-18. |
| [67] | Krause BL (1993) The niche hypothesis: A virtual symphony of animal sounds, the origins of musical expression and the health of habitats. The Soundscape Newsletter, 6, 6-10. |
| [68] | Krause BL, Farina A (2016) Using ecoacoustic methods to survey the impacts of climate change on biodiversity. Biological Conservation, 195, 245-254. |
| [69] | Krause BL, Gage SH, Joo W (2011) Measuring and interpreting the temporal variability in the soundscape at four places in Sequoia National Park. Landscape Ecology, 26, 1247-1256. |
| [70] |
Kuehne LM, Padgham BL, Olden JD (2013) The soundscapes of lakes across an urbanization gradient. PLoS ONE, 8, e55661.
DOI URL PMID |
| [71] |
Lecchini D, Bertucci F, Gache C, Khalife A, Besson M, Roux N, Berthe C, Singh S, Parmentier E, Nugues MM (2018) Boat noise prevents soundscape-based habitat selection by coral planulae. Scientific Reports, 8, 9283.
DOI URL PMID |
| [72] | Lengagne T, Aubin T, Lauga J, Jouventin P (1999) How do king penguins (Aptenodytes patagonicus) apply the mathematical theory of information to communicate in windy conditions? Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 266, 1623-1628. |
| [73] |
Lillis A, Bohnenstiehl D, Peters JW, Eggleston D (2016) Variation in habitat soundscape characteristics influences settlement of a reef-building coral. PeerJ, 4, e2557.
DOI URL PMID |
| [74] | Lillis A, Eggleston DB, Bohnenstiehl DR (2014) Soundscape variation from a larval perspective: The case for habitat-associated sound as a settlement cue for weakly swimming estuarine larvae. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 509, 57-70. |
| [75] | Lillis A, Mooney TA (2018) Snapping shrimp sound production patterns on Caribbean coral reefs: Relationships with celestial cycles and environmental variables. Coral Reefs, 37, 597-607. |
| [76] | Lin T, Tsao Y, Wang Y, Yen H, Lu S (2017) Computing biodiversity change via a soundscape monitoring network. 2017 Pacific Neighborhood Consortium Annual Conference and Joint Meetings (PNC), IEEE, 128-133. |
| [77] | Liu J, Kang J, Luo T, Behm H, Coppack T (2013) Spatiotemporal variability of soundscapes in a multiple functional urban area. Landscape and Urban Planning, 115, 1-9. |
| [78] | Lombard E (1911) Le signe de l’élévation de la voix. Annales des Maladies de L’Oreille et du Larynx, 37, 101-119. |
| [79] |
Lucas TCD, Moorcroft EA, Freeman R, Rowcliffe JM, Jones KE (2015) A generalised random encounter model for estimating animal density with remote sensor data. Methods in Ecology and Evolution, 6, 500-509.
DOI URL PMID |
| [80] |
Luo J, Goerlitz HR, Brumm H, Wiegrebe L (2015a) Linking the sender to the receiver: Vocal adjustments by bats to maintain signal detection in noise. Scientific Reports, 5, 18556.
DOI URL PMID |
| [81] |
Luo J, Siemers BM, Koselj K (2015b) How anthropogenic noise affects foraging. Global Change Biology, 21, 3278-3289.
DOI URL PMID |
| [82] |
Luo JH, Koselj K, Zsebok S, Siemers BM, Goerlitz HR (2014) Global warming alters sound transmission: Differential impact on the prey detection ability of echolocating bats. Journal of the Royal Society Interface, 11, 20130961.
DOI URL |
| [83] | Lü J, Guo Q, Feng HN (2012) Anomalous infrasonic waves before an small earthquake in Beijing. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 10, 3379-3385. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 吕君, 郭泉, 冯浩楠 (2012) 北京地震前的异常次声波. 地球物理学报, 10, 3379-3385.] | |
| [84] |
Ma KP (2011) Assessing progress of biodiversity conservation with monitoring approach. Biodiversity Science, 19, 125-126. (in Chinese)
DOI URL |
| [ 马克平 (2011) 监测是评估生物多样性保护进展的有效途径. 生物多样性, 19, 125-126.] | |
| [85] | MacKenzie DI, Nichols JD, Lachman GB, Droege S, Royle JA, Langtimm CA (2002) Estimating site occupancy rates when detection probabilities are less than one. Ecology, 83, 2248-2255. |
| [86] |
Martin SB, Popper AN (2016) Short- and long-term monitoring of underwater sound levels in the Hudson River (New York, USA). Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 139, 1886-1897.
DOI URL PMID |
| [87] | Mellinger DK, Stafford KM, Moore SE, Dziak RP, Matsumoto H (2007) An overview of fixed passive acoustic observation methods for cetaceans. Oceanography, 20, 36-45. |
| [88] |
Mennill DJ, Vehrencamp SL (2008) Context-dependent functions of avian duets revealed by microphone-array recordings and multispeaker playback. Current Biology, 18, 1314-1319.
DOI URL PMID |
| [89] | Morton ES (1975) Ecological sources of selection on avian sounds. The American Naturalist, 109, 17-34. |
| [90] | Murray SR (1977) The Soundscape: The Tuning of the World. Knopf, New York. |
| [91] | O’Connor P (2008) The sound of silence: Valuing acoustics in heritage conservation. Geographical Research, 46, 361-373. |
| [92] | Ospina OE, Villanueva-Rivera LJ, Corrada-Bravo CJ, Aide TM (2013) Variable response of anuran calling activity to daily precipitation and temperature: Implications for climate change. Ecosphere, 4, 1-12. |
| [93] | Parks SE, Miksis-Olds JL, Denes SL (2014) Assessing marine ecosystem acoustic diversity across ocean basins. Ecological Informatics, 21, 81-88. |
| [94] | Parmesan C (2006) Ecological and evolutionary responses to recent climate change. Annual Review of Ecology, Evolution, and Systematics, 37, 637-669. |
| [95] | Parsons MJG, Salgado-Kent CP, Marley SA, Gavrilov AN, McCauley RD (2016) Characterizing diversity and variation in fish choruses in Darwin Harbour. Ices Journal of Marine Science, 73, 2058-2074. |
| [96] |
Passchier-Vermeer W, Passchier WF (2000) Noise exposure and public health. Environmental Health Perspectives, 108, 123-131.
DOI URL PMID |
| [97] | Payne KB, Langbauer WR, Thomas EM (1986) Infrasonic calls of the Asian elephant (Elephas maximus). Behavioral Ecology and Sociobiology, 18, 297-301. |
| [98] | Payne KB, Thompson M, Kramer L (2003) Elephant calling patterns as indicators of group size and composition: The basis for an acoustic monitoring system. African Journal of Ecology, 41, 99-107. |
| [99] | Pekin BK, Jung J, Villanueva-Rivera LJ, Pijanowski BC, Ahumada JA (2012) Modeling acoustic diversity using soundscape recordings and LIDAR-derived metrics of vertical forest structure in a neotropical rainforest. Landscape Ecology, 27, 1513-1522. |
| [100] | Perez-Granados C, Bota G, Giralt D, Barrero A, Gomez-Catasus J, Rosa DBL, Traba J (2019) Vocal activity rate index: A useful method to infer terrestrial bird abundance with acoustic monitoring. Ibis, 161, 901-907. |
| [101] |
Pieretti N, Farina A, Morri D (2011) A new methodology to infer the singing activity of an avian community: The acoustic complexity index (ACI). Ecological Indicators, 11, 868-873.
DOI URL |
| [102] |
Pijanowski BC, Farina A, Gage SH, Dumyahn SL, Krause BL (2011a) What is soundscape ecology? An introduction and overview of an emerging new science. Landscape Ecology, 26, 1213-1232.
DOI URL |
| [103] |
Pijanowski BC, Villanueva-Rivera LJ, Dumyahn SL, Farina A, Krause BL, Napoletano BM, Gage SH, Pieretti N (2011b) Soundscape ecology: The science of sound in the landscape. BioScience, 61, 203-216.
DOI URL |
| [104] |
Putland RL, Constantine R, Radford CA (2017) Exploring spatial and temporal trends in the soundscape of an ecologically significant embayment. Scientific Reports, 7, 5713.
DOI URL PMID |
| [105] |
Radford CA, Jeffs AG, Tindle CT, Montgomery JC (2008) Temporal patterns in ambient noise of biological origin from a shallow water temperate reef. Oecologia, 156, 921-929.
DOI URL PMID |
| [106] | Reijnen R, Foppen R, Veenbaas G (1997) Disturbance by traffic of breeding birds: Evaluation of the effect and considerations in planning and managing road corridors. Biodiversity & Conservation, 6, 567-581. |
| [107] |
Rice AN, Soldevilla MS, Quinlan JA (2017) Nocturnal patterns in fish chorusing off the coasts of Georgia and eastern Florida. Bulletin of Marine Science, 93, 455-474.
DOI URL |
| [108] |
Rich LN, Furnas BJ, Newton DS, Brashares JS (2019) Acoustic and camera surveys inform models of current and future vertebrate distributions in a changing desert ecosystem. Diversity and Distributions, 25, 1441-1456.
DOI URL |
| [109] |
Roca IT, Proulx R (2016) Acoustic assessment of species richness and assembly rules in ensiferan communities from temperate ecosystems. Ecology, 97, 116-123.
DOI URL PMID |
| [110] |
Rodriguez A, Gasc A, Pavoine S, Grandcolas P, Gaucher P, Sueur J (2014) Temporal and spatial variability of animal sound within a neotropical forest. Ecological Informatics, 21, 133-143.
DOI URL |
| [111] | Ruppé L, Clément G, Herrel A, Ballesta L, Décamps T, Kéver L, Parmentier E (2015) Environmental constraints drive the partitioning of the soundscape in fishes. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 112, 6092-6097. |
| [112] | Russ J (1999) The Bats of Britain and Ireland: Echolocation Calls, Sound Analysis and Species Identification. Alan Books, Powys. |
| [113] |
Saito K, Nakamura K, Ueta M, Kurosawa R, Fujiwara A, Kobayashi HH, Nakayama M, Toko A, Nagahama K (2015) Utilizing the Cyberforest live sound system with social media to remotely conduct woodland bird censuses in Central Japan. Ambio, 44, 572-583.
DOI URL PMID |
| [114] | Schafer RM (1969) The New Soundscape. Berandol Music Limited, Toronto. |
| [115] | Schafer RM (1970) The Book of Noise. Price Print, Vancouver. |
| [116] | Schafer RM (1994) The Soundscape: Our Sonic Environment and the Tuning of the World. Destiny Books, Rochester. |
| [117] | Sethi SS, Ewers RM, Jones NS, Orme CDL, Picinali L (2018) Robust, real-time and autonomous monitoring of ecosystems with an open, low-cost, networked device. Methods in Ecology and Evolution, 12, 2383-2387. |
| [118] | Sierro J, Schloesing E, Pavon I, Gil D (2017) European blackbirds exposed to aircraft noise advance their chorus, modify their song and spend more time singing. Frontiers in Ecology and Evolution, 5, 1-13. |
| [119] |
Slabbekoorn H, Peet M (2003) Ecology: Birds sing at a higher pitch in urban noise. Nature, 424, 267.
DOI URL PMID |
| [120] |
Smott S, Monczak A, Miller ME, Montie EW (2018) Boat noise in an estuarine soundscape—A potential risk on the acoustic communication and reproduction of soniferous fish in the May River, South Carolina. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 133, 246-260.
DOI URL PMID |
| [121] |
Snell-Rood EC (2012) The effect of climate on acoustic signals: Does atmospheric sound absorption matter for bird song and bat echolocation? Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 131, 1650-1658.
DOI URL |
| [122] | Southworth MF (1967) The Sonic Environment of Cities. PhD dissertation, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge. |
| [123] |
Staaterman E, Paris CB, DeFerrari HA, Mann DA, Rice AN, D’Alessandro EK (2014) Celestial patterns in marine soundscapes. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 508, 17-32.
DOI URL |
| [124] |
Staples SL (1996) Human response to environmental noise: Psychological research and public policy. American Psychologist, 51, 143-150.
DOI URL PMID |
| [125] |
Stone E (2000) Separating the noise from the noise: A finding in support of the “niche hypothesis,” that birds are influenced by human-induced noise in natural habitats. Anthrozoös, 13, 225-231.
DOI URL |
| [126] |
Stowell D, Wood MD, Pamuta H, Stylianou Y, Glotin H (2019) Automatic acoustic detection of birds through deep learning: The first bird audio detection challenge. Methods in Ecology and Evolution, 10, 368-380.
DOI URL |
| [127] | Sueur J, Farina A, Gasc A, Pieretti N, Pavoine S (2014) Acoustic indices for biodiversity assessment and landscape investigation. Acta Acustica, 100, 772-781. |
| [128] |
Sueur J, Pavoine S, Hamerlynck O, Duvail S (2008) Rapid acoustic survey for biodiversity appraisal. PLoS ONE, 3, e4065.
DOI URL PMID |
| [129] |
Sugai LSM, Silva TSF, Ribeiro JJW, Llusia D (2019) Terrestrial passive acoustic monitoring: Review and perspectives. BioScience, 69, 15-25.
DOI URL |
| [130] |
Swiston KA, Mennill DJ (2009) Comparison of manual and automated methods for identifying target sounds in audio recordings of Pileated, Pale-billed, and putative Ivory-billed woodpeckers. Journal of Field Ornithology, 80, 42-50.
DOI URL |
| [131] |
Terry AMR, Peake TM, McGregor PK (2005) The role of vocal individuality in conservation. Frontiers in Zoology, 2, 10.
DOI URL PMID |
| [132] | Thompson EA (2004) The Soundscape of Modernity: Architectural Acoustics and the Culture of Listening in America. MIT Press, Cambridge. |
| [133] | Thompson ME, Schwager SJ, Payne KB (2010) Heard but not seen: An acoustic survey of the African forest elephant population at Kakum Conservation Area, Ghana. African Journal of Ecology, 48, 224-231. |
| [134] | Tobler MW, Zúñiga HA, Carrillo-Percastegui SE, Powell GVN, Lukacs P (2015) Spatiotemporal hierarchical modelling of species richness and occupancy using camera trap data. Journal of Applied Ecology, 52, 413-421. |
| [135] | Torigoe K (2003) Insights taken from three visited soundscapes in Japan. The Journal of Acoustic Ecology, 6, 9-12. |
| [136] | Towsey M, Planitz B, Nantes A, Wimmer J, Roe P (2012) A toolbox for animal call recognition. Bioacoustics, 21, 107-125. |
| [137] | Towsey M, Wimmer J, Williamson I, Roe P (2014) The use of acoustic indices to determine avian species richness in audio-recordings of the environment. Ecological Informatics, 21, 110-119. |
| [138] | Truax B (2008) Soundscape composition as global music: Electroacoustic music as soundscape. Organised Sound, 13, 103-109. |
| [139] | Tucker D, Gage SH, Williamson I, Fuller S (2014) Linking ecological condition and the soundscape in fragmented Australian forests. Landscape Ecology, 29, 745-758. |
| [140] |
Velásquez NA, Moreno-Gómez FN, Brunetti E, Penna M (2018) The acoustic adaptation hypothesis in a widely distributed South American frog: Southernmost signals propagate better. Scientific Reports, 8, 6990.
DOI URL PMID |
| [141] | Venter PJ, Hanekom JJ (2010) Automatic detection of African elephant (Loxodonta africana) infrasonic vocalisations from recordings. Biosystems Engineering, 106, 286-294. |
| [142] |
Villanueva-Rivera LJ (2014) Eleutherodactylus frogs show frequency but no temporal partitioning: Implications for the acoustic niche hypothesis. PeerJ, 2, e496.
DOI URL PMID |
| [143] | Villanueva-Rivera LJ, Pijanowski BC, Doucette J, Pekin B (2011) A primer of acoustic analysis for landscape ecologists. Landscape Ecology, 26, 1233-1246. |
| [144] | Walters CL, Freeman R, Collen A, Dietz C, Fenton MB, Jones G, Obrist MK, Puechmaille SJ, Sattler T, Siemers BM, Parsons S, Jones KE (2012) A continental-scale tool for acoustic identification of European bats. Journal of Applied Ecology, 49, 1064-1074. |
| [145] | Whytock RC, Christie J (2017) Solo: An open source, customizable and inexpensive audio recorder for bioacoustic research. Methods in Ecology and Evolution, 8, 308-312. |
| [146] |
Wimmer J, Towsey M, Roe P, Williamson I (2013) Sampling environmental acoustic recordings to determine bird species richness. Ecological Applications, 23, 1419-1428.
DOI URL PMID |
| [147] |
Xia C, Lin X, Liu W, Lloyd H, Zhang Y (2012) Acoustic identification of individuals within large avian populations: A case study of the brownish-flanked bush warbler, South-Central China. PLoS ONE, 7, e42528.
DOI URL PMID |
| [148] | Zhao Z, Xu ZY, Bellisario K, Zeng RW, Li N, Zhou WY, Pijanowski BC (2019) How well do acoustic indices measure biodiversity? Computational experiments to determine effect of sound unit shape, vocalization intensity, and frequency of vocalization occurrence on performance of acoustic indices. Ecological Indicators, 107, 105588. |
| [1] | 农荞伊, 曹军, 程文达, 彭艳琼. 不同方法对蜜蜂总科昆虫资源与多样性监测效果的比较[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 25057-. |
| [2] | 李珍珍, 杜梦甜, 朱原辛, 王大伟, 李治霖, 王天明. 基于红外相机的不可个体识别动物种群密度估算方法[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(3): 22422-. |
| [3] | 孙翊斐, 王士政, 冯佳伟, 王天明. 东北虎豹国家公园森林声景的昼夜和季节变化[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(1): 22523-. |
| [4] | 王士政, 孙翊斐, 李珍珍, 舒越, 冯佳伟, 王天明. 鸟类迁徙对图们江下游湿地声景时间格局的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(1): 22337-. |
| [5] | 张健, 孔宏智, 黄晓磊, 傅声雷, 郭良栋, 郭庆华, 雷富民, 吕植, 周玉荣, 马克平. 中国生物多样性研究的30个核心问题[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(10): 22609-. |
| [6] | 陈星, 官天培, 蒋文乐, 李丹丹, 杨孔, 李晟. 中国牛科动物分布与种群现状: 基于文献计量数据[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(5): 668-679. |
| [7] | 王天明, 冯利民, 杨海涛, 鲍蕾, 王红芳, 葛剑平. 东北虎豹生物多样性红外相机监测平台概述[J]. 生物多样性, 2020, 28(9): 1059-1066. |
| [8] | 刘炎林, 宋大昭, 刘蓓蓓, 夏凡, 陈月龙, 王一晴, 黄巧雯. 中国猫科动物红外相机监测平台介绍: 民间环保机构的数据整合[J]. 生物多样性, 2020, 28(9): 1067-1074. |
| [9] | 李晟, William J. McShea, 王大军, 申小莉, 卜红亮, 官天培, 王放, 古晓东, 张晓峰, 廖灏泓. 西南山地红外相机监测网络建设进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2020, 28(9): 1049-1058. |
| [10] | 宋瑞玲, 姚锦仙, 吴恺悦, 张晓川, 吕植, 朱争光, 殷丽洁. 海洋保护区管理与保护成效评估的方法与进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2018, 26(3): 286-294. |
| [11] | 张倩雯, 龚粤宁, 宋相金, 王新财, 杨昌腾, 束祖飞, 邹发生. 红外相机技术与其他几种森林鸟类多样性调查方法的比较[J]. 生物多样性, 2018, 26(3): 229-237. |
| [12] | 付瑞玉, 苏宏新, 张忠华, 胡刚. 中国森林生物多样性监测网络(CForBio)的研究态势与热点: 基于文献计量分析[J]. 生物多样性, 2018, 26(12): 1255-1267. |
| [13] | 沈浩, 蔡佳宁, 李萌姣, 陈青, 叶万辉, 王峥峰, 练琚愉, 宋亮. 中国森林冠层生物多样性监测[J]. 生物多样性, 2017, 25(3): 229-236. |
| [14] | 朱淑怡, 段菲, 李晟. 基于红外相机网络促进我国鸟类多样性监测: 现状、问题与前景[J]. 生物多样性, 2017, 25(10): 1114-1122. |
| [15] | 肖治术, 李欣海, 王学志, 周岐海, 权锐昌, 申小莉, 李晟. 探讨我国森林野生动物红外相机监测规范[J]. 生物多样性, 2014, 22(6): 704-711. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn