



生物多样性 ›› 2019, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (9): 970-983. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2019133 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2019133
谭一波1,2,3,申文辉1,2,3,*( ),付孜4,郑威1,2,3,欧芷阳1,2,3,谭长强1,2,3,彭玉华1,2,3,庞世龙1,2,3,何琴飞1,2,3,黄小荣1,2,3,何峰1,2,3
),付孜4,郑威1,2,3,欧芷阳1,2,3,谭长强1,2,3,彭玉华1,2,3,庞世龙1,2,3,何琴飞1,2,3,黄小荣1,2,3,何峰1,2,3
收稿日期:2019-04-18
接受日期:2019-09-11
出版日期:2019-09-20
发布日期:2019-09-25
通讯作者:
申文辉
基金资助:
Yibo Tan1,2,3,Wenhui Shen1,2,3,*( ),Zi Fu4,Wei Zheng1,2,3,Zhiyang Ou1,2,3,Zhangqiang Tan1,2,3,Yuhua Peng1,2,3,Shilong Pang1,2,3,Qinfei He1,2,3,Xiaorong Huang1,2,3,Feng He1,2,3
),Zi Fu4,Wei Zheng1,2,3,Zhiyang Ou1,2,3,Zhangqiang Tan1,2,3,Yuhua Peng1,2,3,Shilong Pang1,2,3,Qinfei He1,2,3,Xiaorong Huang1,2,3,Feng He1,2,3
Received:2019-04-18
Accepted:2019-09-11
Online:2019-09-20
Published:2019-09-25
Contact:
Wenhui Shen
摘要:
探索林下植被分布格局及其影响因素, 对于天然林保护和森林生物多样性维持机制研究具有重要意义。本文以桂西南喀斯特地区不同蚬木(Excentrodendron tonkinense)天然成熟林为研究对象, 采用植物群落样方调查、单因素方差分析、Pearson相关分析和冗余分析(RDA)等方法, 研究了8个县市蚬木天然成熟林林下植被物种多样性的变异及其对土壤、地形和光照等环境因子的响应。结果表明, 林下植被中灌木层优势种主要有越南槐(Sophora tonkinensis)、鹅掌柴(Schefflera heptaphylla)、毛果翼核果(Ventilago calyculata), 以及乔木层幼苗如蚬木、广西澄广花(Orophea anceps)、岩樟(Cinnamomum saxatile)、金丝李(Garcinia paucinervis)等, 主要来自豆科、五加科、鼠李科、椴树科、番荔枝科、樟科、藤黄科和大戟科等; 草本层优势种主要有肾蕨(Nephrolepis cordifolia)、石山棕(Guihaia argyrata)、崖姜(Pseudodrynaria coronans)、柔枝莠竹(Microstegium vimineum)、水蔗草(Apluda mutica)、沿阶草(Ophiopogon bodinieri)等, 主要来自肾蕨科、棕榈科、槲蕨科、禾本科、百合科、铁角蕨科和鳞毛蕨科等。土壤pH值、土壤含水量(SWC)、土壤全钾(TK)、土壤全磷(TP)和坡度(SLO)是林下植被物种多样性的主要影响因素, 它们分别解释了林下植被物种多样性32.3%、16.1%、9.7%、8.6%和8.6%的变异。灌木丰富度、灌木多样性指数与TK、SWC、土壤pH值和TP显著负相关, 而草本丰富度、草本多样性指数则与TK显著正相关; 灌木密度、灌木盖度与土壤pH值显著正相关, 草本密度与SWC和TK显著正相关, 草本盖度与TP、TK显著正相关, 与坡度显著负相关。土壤和地形因素是影响林下植被物种多样性变异的最主要因素, 而林分冠层结构的影响较小, 土壤各因素对林下植被物种多样性的影响高于地形因素。
谭一波,申文辉,付孜,郑威,欧芷阳,谭长强,彭玉华,庞世龙,何琴飞,黄小荣,何峰 (2019) 环境因子对桂西南蚬木林下植被物种多样性变异的解释. 生物多样性, 27, 970-983. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2019133.
Yibo Tan,Wenhui Shen,Zi Fu,Wei Zheng,Zhiyang Ou,Zhangqiang Tan,Yuhua Peng,Shilong Pang,Qinfei He,Xiaorong Huang,Feng He (2019) Effect of environmental factors on understory species diversity in Southwest Guangxi Excentrodendron tonkinense forests. Biodiversity Science, 27, 970-983. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2019133.
| 样地名称 Sample plots | 纬度 Latitude | 经度 Longitude | 海拔 Altitude (m) | 坡度 Slope | 坡向指数 Transformation of aspect | 平均胸径 Mean DBH (cm) | 平均树高 Mean height (m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 大新县 Daxin County | 22°49′ N | 106°46′ E | 400 | 43° | 0.97 | 4.93 ± 0.24 | 4.72 ± 0.12 |
| 靖西市 Jingxi City | 22o53′ N | 106o26′ E | 357 | 40° | 0.10 | 4.89 ± 0.30 | 5.65 ± 0.19 |
| 龙州县 Longzhou County | 22o27′ N | 106o56′ E | 208 | 46° | 0.98 | 5.30 ± 0.36 | 5.56 ± 0.19 |
| 隆安县 Longan County | 23o4′ N | 107o24′ E | 409 | 42° | 0.39 | 4.66 ± 0.29 | 5.48 ± 0.24 |
| 那坡县 Napo County | 23°0′ N | 105°52′ E | 823 | 23° | 0.77 | 12.49 ± 1.73 | 7.35 ± 0.52 |
| 平果县 Pingguo County | 23°24′ N | 107°32′ E | 350 | 35° | 0.97 | 3.65 ± 0.10 | 3.72 ± 0.05 |
| 天等县 Tiandeng County | 23o8′ N | 107o16′ E | 418 | 40° | 0.43 | 7.48 ± 0.53 | 7.77 ± 0.25 |
| 武鸣区 Wuming District | 23o16′ N | 107o51′ E | 271 | 35° | 0.98 | 10.34 ± 0.79 | 8.38 ± 0.42 |
表1 桂西南喀斯特地区8个蚬木群落样地林分特征(平均值 ± 标准误差)
Table 1 Stand characteristics of eight Excentrodendron tonkinense community sampling plots in karst area of Southwest Guangxi (mean ± SE)
| 样地名称 Sample plots | 纬度 Latitude | 经度 Longitude | 海拔 Altitude (m) | 坡度 Slope | 坡向指数 Transformation of aspect | 平均胸径 Mean DBH (cm) | 平均树高 Mean height (m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 大新县 Daxin County | 22°49′ N | 106°46′ E | 400 | 43° | 0.97 | 4.93 ± 0.24 | 4.72 ± 0.12 |
| 靖西市 Jingxi City | 22o53′ N | 106o26′ E | 357 | 40° | 0.10 | 4.89 ± 0.30 | 5.65 ± 0.19 |
| 龙州县 Longzhou County | 22o27′ N | 106o56′ E | 208 | 46° | 0.98 | 5.30 ± 0.36 | 5.56 ± 0.19 |
| 隆安县 Longan County | 23o4′ N | 107o24′ E | 409 | 42° | 0.39 | 4.66 ± 0.29 | 5.48 ± 0.24 |
| 那坡县 Napo County | 23°0′ N | 105°52′ E | 823 | 23° | 0.77 | 12.49 ± 1.73 | 7.35 ± 0.52 |
| 平果县 Pingguo County | 23°24′ N | 107°32′ E | 350 | 35° | 0.97 | 3.65 ± 0.10 | 3.72 ± 0.05 |
| 天等县 Tiandeng County | 23o8′ N | 107o16′ E | 418 | 40° | 0.43 | 7.48 ± 0.53 | 7.77 ± 0.25 |
| 武鸣区 Wuming District | 23o16′ N | 107o51′ E | 271 | 35° | 0.98 | 10.34 ± 0.79 | 8.38 ± 0.42 |
| 大新县 Daxin County | 靖西市 Jingxi City | 龙州县 Longzhou County | 隆安县 Longan County | 那坡县 Napo County | 平果县 Pingguo County | 天等县 Tiandeng County | 武鸣区 Wuming District | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 土壤pH Soil pH | 6.66 ± 0.25e | 7.49 ± 0.11abc | 7.61 ± 0.10ab | 7.11 ± 0.08d | 7.30 ± 0.02bcd | 6.59 ± 0.02e | 7.24 ± 0.09cd | 7.76 ± 0.02a |
| 土壤有机质 Soil organic matter (g/kg) | 124.17 ± 18.07cd | 156.42 ± 21.96bc | 97.15 ± 7.06d | 144.18 ± 6.59bc | 369.20 ± 9.79a | 131.96 ± 10.62bcd | 174.81 ± 20.34b | 172.66 ± 5.77b |
| 土壤全氮 Soil total nitrogen (g/kg) | 7.64 ± 1.02b | 8.82 ± 1.08b | 5.11 ± 0.26c | 6.81 ± 0.28bc | 22.38 ± 0.40a | 7.26 ± 0.63b | 8.37 ± 0.77b | 7.75 ± 0.29b |
| 土壤全磷 Soil total phosphorus (g/kg) | 1.75 ± 0.08bc | 1.88 ± 0.12b | 0.88 ± 0.05ef | 0.62 ± 0.03f | 6.47 ± 0.36a | 1.90 ± 0.07b | 1.26 ± 0.06de | 1.37 ± 0.09cd |
| 土壤全钾 Soil total potassium (g/kg) | 1.70 ± 0.24d | 7.81 ± 0.86a | 2.29 ± 0.16cd | 3.24 ± 0.49bc | 3.34 ± 0.23bc | 3.11 ± 0.64bcd | 2.38 ± 0.25cd | 4.37 ± 0.26b |
| 土壤C : N Soil C : N | 9.42 ± 0.34c | 10.24 ± 0.24bc | 11.01 ± 0.32b | 12.27 ± 0.10a | 9.57 ± 0.11c | 10.55 ± 0.21b | 12.07 ± 0.32a | 12.94 ± 0.47a |
| 土壤N : P Soil N : P | 4.33 ± 0.44cd | 4.68 ± 0.39cd | 5.86 ± 0.68bc | 11.04 ± 0.65a | 3.48 ± 0.13d | 3.85 ± 0.48d | 6.74 ± 0.89b | 5.68 ± 0.16bc |
| 土壤含水量 Soil water content (g/g) | 0.40 ± 0.09b | 0.48 ± 0.06b | 0.35 ± 0.03b | 0.40 ± 0.02b | 1.44 ± 0.06a | 0.41 ± 0.03b | 0.44 ± 0.03b | 0.47 ± 0.04b |
| 林冠开阔度 Canopy openness (%) | 17.24 ± 0.41a | 14.20 ± 0.31b | 13.27 ± 0.88b | 13.68 ± 1.42b | 15.89 ± 1.78ab | 13.46 ± 0.23b | 12.79 ± 0.54b | 13.83 ± 0.40b |
| 叶面积指数 Leaf area index | 2.13 ± 0.02b | 2.40 ± 0.05ab | 2.50 ± 0.09a | 2.54 ± 0.08a | 2.34 ± 0.26ab | 2.40 ± 0.08ab | 2.37 ± 0.02ab | 2.31 ± 0.07ab |
| 林内直射光 Transmitted direct in forest (mol·m-2·d-1) | 4.42 ± 0.16a | 3.08 ± 0.27b | 3.20 ± 0.33b | 2.96 ± 0.24b | 3.28 ± 0.45b | 3.16 ± 0.25b | 3.47 ± 0.11b | 3.55 ± 0.32b |
| 林内散射光 Transmitted diffuse in forest (mol·m-2·d-1) | 4.03 ± 0.05a | 3.35 ± 0.15b | 3.10 ± 0.13b | 2.92 ± 0.16b | 3.45 ± 0.43b | 3.12 ± 0.15b | 3.17 ± 0.05b | 3.36 ± 0.13b |
| 林内总光照 Transmitted total in forest (mol·m-2·d-1) | 8.45 ± 0.21a | 6.43 ± 0.39b | 6.30 ± 0.39b | 5.88 ± 0.34b | 6.73 ± 0.88b | 6.28 ± 0.40b | 6.64 ± 0.09b | 6.91 ± 0.41b |
| 消光系数Extinction coefficient (k) | 0.72 ± 0.02a | 0.76 ± 0.02a | 0.74 ± 0.03a | 0.75 ± 0.01a | 0.77 ± 0.04a | 0.76 ± 0.01a | 0.75 ± 0.01a | 0.75 ± 0.01a |
表2 桂西南喀斯特地区8个蚬木群落样地环境因子汇总(平均值 ± 标准误差)。同行不同字母表示在不同样地间存在显著差异(P < 0.05)。
Table 2 Information on environment factors of eight Excentrodendron tonkinense community sampling plots in karst area of Southwest Guangxi (mean ± SE). Different letters within the same row meant significant difference among the sampling plots at 0.05 level.
| 大新县 Daxin County | 靖西市 Jingxi City | 龙州县 Longzhou County | 隆安县 Longan County | 那坡县 Napo County | 平果县 Pingguo County | 天等县 Tiandeng County | 武鸣区 Wuming District | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 土壤pH Soil pH | 6.66 ± 0.25e | 7.49 ± 0.11abc | 7.61 ± 0.10ab | 7.11 ± 0.08d | 7.30 ± 0.02bcd | 6.59 ± 0.02e | 7.24 ± 0.09cd | 7.76 ± 0.02a |
| 土壤有机质 Soil organic matter (g/kg) | 124.17 ± 18.07cd | 156.42 ± 21.96bc | 97.15 ± 7.06d | 144.18 ± 6.59bc | 369.20 ± 9.79a | 131.96 ± 10.62bcd | 174.81 ± 20.34b | 172.66 ± 5.77b |
| 土壤全氮 Soil total nitrogen (g/kg) | 7.64 ± 1.02b | 8.82 ± 1.08b | 5.11 ± 0.26c | 6.81 ± 0.28bc | 22.38 ± 0.40a | 7.26 ± 0.63b | 8.37 ± 0.77b | 7.75 ± 0.29b |
| 土壤全磷 Soil total phosphorus (g/kg) | 1.75 ± 0.08bc | 1.88 ± 0.12b | 0.88 ± 0.05ef | 0.62 ± 0.03f | 6.47 ± 0.36a | 1.90 ± 0.07b | 1.26 ± 0.06de | 1.37 ± 0.09cd |
| 土壤全钾 Soil total potassium (g/kg) | 1.70 ± 0.24d | 7.81 ± 0.86a | 2.29 ± 0.16cd | 3.24 ± 0.49bc | 3.34 ± 0.23bc | 3.11 ± 0.64bcd | 2.38 ± 0.25cd | 4.37 ± 0.26b |
| 土壤C : N Soil C : N | 9.42 ± 0.34c | 10.24 ± 0.24bc | 11.01 ± 0.32b | 12.27 ± 0.10a | 9.57 ± 0.11c | 10.55 ± 0.21b | 12.07 ± 0.32a | 12.94 ± 0.47a |
| 土壤N : P Soil N : P | 4.33 ± 0.44cd | 4.68 ± 0.39cd | 5.86 ± 0.68bc | 11.04 ± 0.65a | 3.48 ± 0.13d | 3.85 ± 0.48d | 6.74 ± 0.89b | 5.68 ± 0.16bc |
| 土壤含水量 Soil water content (g/g) | 0.40 ± 0.09b | 0.48 ± 0.06b | 0.35 ± 0.03b | 0.40 ± 0.02b | 1.44 ± 0.06a | 0.41 ± 0.03b | 0.44 ± 0.03b | 0.47 ± 0.04b |
| 林冠开阔度 Canopy openness (%) | 17.24 ± 0.41a | 14.20 ± 0.31b | 13.27 ± 0.88b | 13.68 ± 1.42b | 15.89 ± 1.78ab | 13.46 ± 0.23b | 12.79 ± 0.54b | 13.83 ± 0.40b |
| 叶面积指数 Leaf area index | 2.13 ± 0.02b | 2.40 ± 0.05ab | 2.50 ± 0.09a | 2.54 ± 0.08a | 2.34 ± 0.26ab | 2.40 ± 0.08ab | 2.37 ± 0.02ab | 2.31 ± 0.07ab |
| 林内直射光 Transmitted direct in forest (mol·m-2·d-1) | 4.42 ± 0.16a | 3.08 ± 0.27b | 3.20 ± 0.33b | 2.96 ± 0.24b | 3.28 ± 0.45b | 3.16 ± 0.25b | 3.47 ± 0.11b | 3.55 ± 0.32b |
| 林内散射光 Transmitted diffuse in forest (mol·m-2·d-1) | 4.03 ± 0.05a | 3.35 ± 0.15b | 3.10 ± 0.13b | 2.92 ± 0.16b | 3.45 ± 0.43b | 3.12 ± 0.15b | 3.17 ± 0.05b | 3.36 ± 0.13b |
| 林内总光照 Transmitted total in forest (mol·m-2·d-1) | 8.45 ± 0.21a | 6.43 ± 0.39b | 6.30 ± 0.39b | 5.88 ± 0.34b | 6.73 ± 0.88b | 6.28 ± 0.40b | 6.64 ± 0.09b | 6.91 ± 0.41b |
| 消光系数Extinction coefficient (k) | 0.72 ± 0.02a | 0.76 ± 0.02a | 0.74 ± 0.03a | 0.75 ± 0.01a | 0.77 ± 0.04a | 0.76 ± 0.01a | 0.75 ± 0.01a | 0.75 ± 0.01a |
| 样地 Plot | 物种 Species | 层次 Layer | 重要值 IV (%) | 样地 Plot | 物种 Species | 层次 Layer | 重要值 IV (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 大新县 Daxin County | 蚬木 Excentrodendron tonkinense | T | 58.84 | 那坡县 Napo County | 蚬木 Excentrodendron tonkinense | T | 33.10 |
| 广西澄广花 Orophea anceps | T | 7.29 | 苹婆 Sterculia monosperma | T | 8.90 | ||
| 岩柿 Diospyros dumetorum | T | 3.46 | 樟叶槭 Acer coriaceifolia | T | 5.59 | ||
| 榔榆 Ulmus parvifolia | T | 3.36 | 漆 Toxicodendron vernicifluum | T | 5.41 | ||
| 蚬木 Excentrodendron tonkinense | S | 13.89 | 鹅掌柴 Schefflera heptaphylla | S | 26.90 | ||
| 红背山麻杆 Alchornea trewioides | S | 12.52 | 蚬木 Excentrodendron tonkinense | S | 19.93 | ||
| 光叶紫玉盘 Uvaria boniana | S | 7.78 | 香蒲桃 Syzygium odoratum | S | 5.71 | ||
| 鱼骨木 Canthium dicoccum | S | 6.66 | 香叶树 Lindera communis | S | 4.49 | ||
| 石山棕 Guihaia argyrata | H | 27.03 | 巢蕨 Neottopteris nidus | H | 14.46 | ||
| 江南卷柏 Selaginella moellendorffii | H | 13.09 | 贯众 Cyrtomium fortunei | H | 10.34 | ||
| 槲蕨 Drynaria roosii | H | 9.37 | 肾蕨 Nephrolepis cordifolia | H | 8.77 | ||
| 铁角蕨 Asplenium trichomanes | H | 8.92 | 艾麻 Laportea cuspidata | H | 8.76 | ||
| 靖西市 Jingxi City | 蚬木 Excentrodendron tonkinense | T | 33.69 | 平果县Pingguo County | 蚬木 Excentrodendron tonkinense | T | 11.02 |
| 岩樟 Cinnamomum saxatile | T | 17.76 | 黄荆 Vitex negundo | T | 8.76 | ||
| 苹婆 Sterculia monosperma | T | 5.18 | 清香木 Pistacia weinmannifolia | T | 6.53 | ||
| 广西澄广花 Orophea anceps | T | 1.58 | 岩柿 Diospyros dumetorum | T | 5.53 | ||
| 苎麻 Boehmeria nivea | S | 48.41 | 黄荆 Vitex negundo | S | 21.05 | ||
| 岩樟 Cinnamomum saxatile | S | 18.45 | 蚬木 Excentrodendron tonkinense | S | 15.33 | ||
| 蚬木 Excentrodendron tonkinense | S | 13.92 | 薄皮酒饼簕 Atalantia henryi | S | 10.25 | ||
| 老虎刺 Pterolobium punctatum | S | 9.99 | 山石榴 Catunaregam spinosa | S | 3.68 | ||
| 肾蕨 Nephrolepis cordifolia | H | 11.10 | 柔枝莠竹 Microstegium vimineum | H | 50.02 | ||
| 蔓生莠竹 Microstegium fasciculatum | H | 10.26 | 水蔗草 Apluda mutica | H | 19.18 | ||
| 苦苣菜 Sonchus oleraceus | H | 5.91 | 假鞭叶铁线蕨 Adiantum malesianum | H | 7.75 | ||
| 艾麻 Laportea cuspidata | H | 3.78 | 硬叶兰 Cymbidium bicolor | H | 4.87 | ||
| 龙州县Longzhou County | 蚬木 Excentrodendron tonkinense | T | 25.22 | 天等县Tiandeng County | 蚬木 Excentrodendron tonkinense | T | 43.08 |
| 广西澄广花 Orophea anceps | T | 11.38 | 金丝李 Garcinia paucinervis | T | 10.74 | ||
| 金丝李 Garcinia pauc | T | 11.28 | 异叶榕 Ficus heteromorpha | T | 4.48 | ||
| 假肥牛树 Cleistanthus petelotii | T | 4.23 | 广西澄广花 Orophea anceps | T | 4.24 | ||
| 广西澄广花 Orophea anceps | S | 21.26 | 毛果翼核果 Ventilago calyculata | S | 17.39 | ||
| 九里香 Murraya exotica | S | 10.89 | 异叶榕 Ficus heteromorpha | S | 7.48 | ||
| 金丝李 Garcinia paucinervis | S | 7.29 | 海红豆 Adenanthera pavonina | S | 7.25 | ||
| 牛筋藤 Malaisia scandens | S | 6.95 | 金丝李 Garcinia paucinervis | S | 4.73 | ||
| 崖姜 Pseudodrynaria coronans | H | 9.10 | 肾蕨 Nephrolepis cordifolia | H | 20.28 | ||
| 鞭叶蕨 Cyrtomidictyum lepidocaulon | H | 5.56 | 狭叶沿阶草 Ophiopogon stenophyllus | H | 9.57 | ||
| 竹叶草 Oplismenus compositus | H | 5.31 | 槲蕨 Drynaria roosii | H | 8.98 | ||
| 鞭叶铁线蕨 Adiantum caudatum | H | 4.37 | 石韦 Pyrrosia lingua | H | 8.64 | ||
| 隆安县Longan County | 蚬木 Excentrodendron tonkinense | T | 46.81 | 武鸣区Wuming District | 蚬木 Excentrodendron tonkinense | T | 69.88 |
| 九里香 Murraya exotica | T | 5.98 | 苹婆 Sterculia monosperma | T | 8.42 | ||
| 肥牛树 Cephalomappa sinensis | T | 4.65 | 菜豆树 Radermachera sinica | T | 5.07 | ||
| 青檀 Pteroceltis tatarinowii | T | 4.58 | 黄荆 Vitex negundo | T | 3.29 | ||
| 越南槐 Sophora tonkinensis | S | 23.65 | 越南槐 Sophora tonkinensis | S | 34.65 | ||
| 九里香 Murraya exotica | S | 10.05 | 红背山麻杆 Alchornea trewioides | S | 18.87 | ||
| 肥牛树 Cephalomappa sinensis | S | 5.55 | 潺槁木姜子 Litsea glutinosa | S | 5.45 | ||
| 红鳞蒲桃 Syzygium hancei | S | 4.05 | 黄荆 Vitex negundo | S | 3.47 | ||
| 沿阶草 Ophiopogon bodinieri | H | 47.05 | 肾蕨 Nephrolepis cordifolia | H | 48.21 | ||
| 褐果薹草 Carex brunnea | H | 14.07 | 艾麻 Laportea cuspidata | H | 6.70 | ||
| 肾蕨 Nephrolepis cordifolia | H | 6.57 | 鞭叶铁线蕨 Adiantum caudatum | H | 5.46 | ||
| 广西前胡 Peucedanum guangxiense | H | 4.35 | 硬叶兰 Cymbidium bicolor | H | 1.99 |
表3 桂西南喀斯特地区8个蚬木群落样地优势物种组成及其重要值。T: 乔木层; S: 灌木层; H: 草本层。
Table 3 Composition and importance value (IV) of dominant species in eight Excentrodendron tonkinense community sampling plots in karst area of Southwest Guangxi. T, Tree layer; S, Shrub layer; H, Herb layer.
| 样地 Plot | 物种 Species | 层次 Layer | 重要值 IV (%) | 样地 Plot | 物种 Species | 层次 Layer | 重要值 IV (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 大新县 Daxin County | 蚬木 Excentrodendron tonkinense | T | 58.84 | 那坡县 Napo County | 蚬木 Excentrodendron tonkinense | T | 33.10 |
| 广西澄广花 Orophea anceps | T | 7.29 | 苹婆 Sterculia monosperma | T | 8.90 | ||
| 岩柿 Diospyros dumetorum | T | 3.46 | 樟叶槭 Acer coriaceifolia | T | 5.59 | ||
| 榔榆 Ulmus parvifolia | T | 3.36 | 漆 Toxicodendron vernicifluum | T | 5.41 | ||
| 蚬木 Excentrodendron tonkinense | S | 13.89 | 鹅掌柴 Schefflera heptaphylla | S | 26.90 | ||
| 红背山麻杆 Alchornea trewioides | S | 12.52 | 蚬木 Excentrodendron tonkinense | S | 19.93 | ||
| 光叶紫玉盘 Uvaria boniana | S | 7.78 | 香蒲桃 Syzygium odoratum | S | 5.71 | ||
| 鱼骨木 Canthium dicoccum | S | 6.66 | 香叶树 Lindera communis | S | 4.49 | ||
| 石山棕 Guihaia argyrata | H | 27.03 | 巢蕨 Neottopteris nidus | H | 14.46 | ||
| 江南卷柏 Selaginella moellendorffii | H | 13.09 | 贯众 Cyrtomium fortunei | H | 10.34 | ||
| 槲蕨 Drynaria roosii | H | 9.37 | 肾蕨 Nephrolepis cordifolia | H | 8.77 | ||
| 铁角蕨 Asplenium trichomanes | H | 8.92 | 艾麻 Laportea cuspidata | H | 8.76 | ||
| 靖西市 Jingxi City | 蚬木 Excentrodendron tonkinense | T | 33.69 | 平果县Pingguo County | 蚬木 Excentrodendron tonkinense | T | 11.02 |
| 岩樟 Cinnamomum saxatile | T | 17.76 | 黄荆 Vitex negundo | T | 8.76 | ||
| 苹婆 Sterculia monosperma | T | 5.18 | 清香木 Pistacia weinmannifolia | T | 6.53 | ||
| 广西澄广花 Orophea anceps | T | 1.58 | 岩柿 Diospyros dumetorum | T | 5.53 | ||
| 苎麻 Boehmeria nivea | S | 48.41 | 黄荆 Vitex negundo | S | 21.05 | ||
| 岩樟 Cinnamomum saxatile | S | 18.45 | 蚬木 Excentrodendron tonkinense | S | 15.33 | ||
| 蚬木 Excentrodendron tonkinense | S | 13.92 | 薄皮酒饼簕 Atalantia henryi | S | 10.25 | ||
| 老虎刺 Pterolobium punctatum | S | 9.99 | 山石榴 Catunaregam spinosa | S | 3.68 | ||
| 肾蕨 Nephrolepis cordifolia | H | 11.10 | 柔枝莠竹 Microstegium vimineum | H | 50.02 | ||
| 蔓生莠竹 Microstegium fasciculatum | H | 10.26 | 水蔗草 Apluda mutica | H | 19.18 | ||
| 苦苣菜 Sonchus oleraceus | H | 5.91 | 假鞭叶铁线蕨 Adiantum malesianum | H | 7.75 | ||
| 艾麻 Laportea cuspidata | H | 3.78 | 硬叶兰 Cymbidium bicolor | H | 4.87 | ||
| 龙州县Longzhou County | 蚬木 Excentrodendron tonkinense | T | 25.22 | 天等县Tiandeng County | 蚬木 Excentrodendron tonkinense | T | 43.08 |
| 广西澄广花 Orophea anceps | T | 11.38 | 金丝李 Garcinia paucinervis | T | 10.74 | ||
| 金丝李 Garcinia pauc | T | 11.28 | 异叶榕 Ficus heteromorpha | T | 4.48 | ||
| 假肥牛树 Cleistanthus petelotii | T | 4.23 | 广西澄广花 Orophea anceps | T | 4.24 | ||
| 广西澄广花 Orophea anceps | S | 21.26 | 毛果翼核果 Ventilago calyculata | S | 17.39 | ||
| 九里香 Murraya exotica | S | 10.89 | 异叶榕 Ficus heteromorpha | S | 7.48 | ||
| 金丝李 Garcinia paucinervis | S | 7.29 | 海红豆 Adenanthera pavonina | S | 7.25 | ||
| 牛筋藤 Malaisia scandens | S | 6.95 | 金丝李 Garcinia paucinervis | S | 4.73 | ||
| 崖姜 Pseudodrynaria coronans | H | 9.10 | 肾蕨 Nephrolepis cordifolia | H | 20.28 | ||
| 鞭叶蕨 Cyrtomidictyum lepidocaulon | H | 5.56 | 狭叶沿阶草 Ophiopogon stenophyllus | H | 9.57 | ||
| 竹叶草 Oplismenus compositus | H | 5.31 | 槲蕨 Drynaria roosii | H | 8.98 | ||
| 鞭叶铁线蕨 Adiantum caudatum | H | 4.37 | 石韦 Pyrrosia lingua | H | 8.64 | ||
| 隆安县Longan County | 蚬木 Excentrodendron tonkinense | T | 46.81 | 武鸣区Wuming District | 蚬木 Excentrodendron tonkinense | T | 69.88 |
| 九里香 Murraya exotica | T | 5.98 | 苹婆 Sterculia monosperma | T | 8.42 | ||
| 肥牛树 Cephalomappa sinensis | T | 4.65 | 菜豆树 Radermachera sinica | T | 5.07 | ||
| 青檀 Pteroceltis tatarinowii | T | 4.58 | 黄荆 Vitex negundo | T | 3.29 | ||
| 越南槐 Sophora tonkinensis | S | 23.65 | 越南槐 Sophora tonkinensis | S | 34.65 | ||
| 九里香 Murraya exotica | S | 10.05 | 红背山麻杆 Alchornea trewioides | S | 18.87 | ||
| 肥牛树 Cephalomappa sinensis | S | 5.55 | 潺槁木姜子 Litsea glutinosa | S | 5.45 | ||
| 红鳞蒲桃 Syzygium hancei | S | 4.05 | 黄荆 Vitex negundo | S | 3.47 | ||
| 沿阶草 Ophiopogon bodinieri | H | 47.05 | 肾蕨 Nephrolepis cordifolia | H | 48.21 | ||
| 褐果薹草 Carex brunnea | H | 14.07 | 艾麻 Laportea cuspidata | H | 6.70 | ||
| 肾蕨 Nephrolepis cordifolia | H | 6.57 | 鞭叶铁线蕨 Adiantum caudatum | H | 5.46 | ||
| 广西前胡 Peucedanum guangxiense | H | 4.35 | 硬叶兰 Cymbidium bicolor | H | 1.99 |
| 林下植被物种多样性 Understory species diversity | 平方和 Sum of squares | 均方 Mean squares | F |
|---|---|---|---|
| 灌木丰富度 Shrub richness (S_shrub) | 502.625 | 71.804 | 4.97** |
| 灌木多样性 Shrub diversity (SW_shrub) | 10.455 | 1.494 | 6.08** |
| 灌木密度 Shrub density (D_shrub) | 3,728,711.958 | 532,673.137 | 11.19** |
| 灌木盖度 Shrub coverage (C_shrub) | 2,969.312 | 424.187 | 4.93** |
| 草本丰富度 Herb richness (S_herb) | 256.000 | 36.571 | 3.46* |
| 草本多样性 Herb diversity (SW_herb) | 7.880 | 1.126 | 2.46 |
| 草本密度 Herb density (D_herb) | 167,753,218.958 | 23,964,745.565 | 10.51** |
| 草本盖度 Herb coverage (C_herb) | 11,636.273 | 1,662.325 | 20.44** |
表4 桂西南喀斯特地区8个蚬木群落样地林下植被物种多样性方差分析。* P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01。
Table 4 Variance analysis of understory species diversity in eight Excentrodendron tonkinense community sampling plots in karst area of Southwest Guangxi. * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01.
| 林下植被物种多样性 Understory species diversity | 平方和 Sum of squares | 均方 Mean squares | F |
|---|---|---|---|
| 灌木丰富度 Shrub richness (S_shrub) | 502.625 | 71.804 | 4.97** |
| 灌木多样性 Shrub diversity (SW_shrub) | 10.455 | 1.494 | 6.08** |
| 灌木密度 Shrub density (D_shrub) | 3,728,711.958 | 532,673.137 | 11.19** |
| 灌木盖度 Shrub coverage (C_shrub) | 2,969.312 | 424.187 | 4.93** |
| 草本丰富度 Herb richness (S_herb) | 256.000 | 36.571 | 3.46* |
| 草本多样性 Herb diversity (SW_herb) | 7.880 | 1.126 | 2.46 |
| 草本密度 Herb density (D_herb) | 167,753,218.958 | 23,964,745.565 | 10.51** |
| 草本盖度 Herb coverage (C_herb) | 11,636.273 | 1,662.325 | 20.44** |
| 灌木多样性 Shrub diversity | 灌木密度 Shrub density | 灌木盖度 Shrub coverage | 草本丰富度 Herb richness | 草本多样性 Herb diversity | 草本密度 Herb density | 草本盖度 Herb coverage | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 灌木丰富度 Shrub richness | 0.867** | 0.063 | 0.297 | -0.327 | -0.268 | -0.619** | -0.706** |
| 灌木多样性 Shrub diversity | 0.103 | 0.293 | -0.25 | -0.049 | -0.576** | -0.660** | |
| 灌木密度 Shrub density | 0.738** | -0.314 | -0.111 | -0.076 | -0.205 | ||
| 灌木盖度 Shrub coverage | -0.350 | -0.171 | 0.05 | -0.169 | |||
| 草本丰富度 Herb richness | 0.783** | 0.431* | 0.634** | ||||
| 草本多样性 Herb diversity | 0.275 | 0.430* | |||||
| 草本密度 Herb density | 0.861** |
表5 桂西南喀斯特地区8个蚬木群落样地林下植被物种多样性指标间的相关系数。* P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01。
Table 5 Correlation coefficients of understory species diversity in eight Excentrodendron tonkinense community sampling plots in karst area of Southwest Guangxi. * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01.
| 灌木多样性 Shrub diversity | 灌木密度 Shrub density | 灌木盖度 Shrub coverage | 草本丰富度 Herb richness | 草本多样性 Herb diversity | 草本密度 Herb density | 草本盖度 Herb coverage | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 灌木丰富度 Shrub richness | 0.867** | 0.063 | 0.297 | -0.327 | -0.268 | -0.619** | -0.706** |
| 灌木多样性 Shrub diversity | 0.103 | 0.293 | -0.25 | -0.049 | -0.576** | -0.660** | |
| 灌木密度 Shrub density | 0.738** | -0.314 | -0.111 | -0.076 | -0.205 | ||
| 灌木盖度 Shrub coverage | -0.350 | -0.171 | 0.05 | -0.169 | |||
| 草本丰富度 Herb richness | 0.783** | 0.431* | 0.634** | ||||
| 草本多样性 Herb diversity | 0.275 | 0.430* | |||||
| 草本密度 Herb density | 0.861** |
| 排序概要 Summary of ordination | 第1轴 Axis 1 | 第2轴 Axis 2 | 第3轴 Axis 3 | 第4轴 Axis 4 | 总方差 Total variance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 特征值 Eigenvalues | 0.611 | 0.254 | 0.035 | 0.017 | 1 |
| 林下植被物种多样性-环境因子相关 Understory species diversity-environmental factors correlations | 0.980 | 0.969 | 0.886 | 0.892 | |
| 解释的林下植被物种多样性组成变异的累积百分比 Cumulative percentage variance of understory species diversity data (%) | 61.1 | 86.5 | 90.0 | 91.7 | |
| 林下植被物种多样性-环境因子关系方差的累积百分比 Cumulative percentage variance of understory species diversity-environmental factors relation (%) | 65.3 | 92.5 | 96.2 | 98.1 | |
| 特征值总和 Sum of eigenvalues | 1 | ||||
| 典型特征值总和 Sum of canonical eigenvalues | 0.935 | ||||
| 第一典范轴的显著性测验 Significant test of the first canonical axis | F = 10.975, P = 0.002 | ||||
| 所有典范轴的显著性测验 Significant test of all canonical axes | F = 6.248, P= 0.002 | ||||
表6 林下植被物种多样性与环境因子的冗余分析(RDA)排序
Table 6 Summary of redundancy analysis (RDA) ordination of understory species diversity and environmental factors
| 排序概要 Summary of ordination | 第1轴 Axis 1 | 第2轴 Axis 2 | 第3轴 Axis 3 | 第4轴 Axis 4 | 总方差 Total variance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 特征值 Eigenvalues | 0.611 | 0.254 | 0.035 | 0.017 | 1 |
| 林下植被物种多样性-环境因子相关 Understory species diversity-environmental factors correlations | 0.980 | 0.969 | 0.886 | 0.892 | |
| 解释的林下植被物种多样性组成变异的累积百分比 Cumulative percentage variance of understory species diversity data (%) | 61.1 | 86.5 | 90.0 | 91.7 | |
| 林下植被物种多样性-环境因子关系方差的累积百分比 Cumulative percentage variance of understory species diversity-environmental factors relation (%) | 65.3 | 92.5 | 96.2 | 98.1 | |
| 特征值总和 Sum of eigenvalues | 1 | ||||
| 典型特征值总和 Sum of canonical eigenvalues | 0.935 | ||||
| 第一典范轴的显著性测验 Significant test of the first canonical axis | F = 10.975, P = 0.002 | ||||
| 所有典范轴的显著性测验 Significant test of all canonical axes | F = 6.248, P= 0.002 | ||||
| 环境因子 Environmental factors | 解释率 Contribution (%) | F |
|---|---|---|
| 土壤pH Soil pH | 32.3 | 9.4** |
| 土壤含水量 Soil water content (SWC) | 16.1 | 6.0** |
| 土壤全钾 Soil total potassium (TK) | 9.7 | 4.7** |
| 土壤全磷 Soil total phosphorus (TP) | 8.6 | 4.9** |
| 坡度 Slope (SLO) | 8.6 | 3.4* |
| 海拔 Elevation (ELE) | 3.6 | 2.2 |
| 土壤有机质 Soil organic matter (SOM) | 3.6 | 2.2 |
| 林内散射光 Transmitted diffuse in forest (Trans Dif) | 3.1 | 1.9 |
| 林冠开阔度 Canopy openness (CO) | 2.5 | 1.5 |
| 坡向 Slope aspect (SLOA) | 2.4 | 1.4 |
| 林内总光照 Transmitted total in forest (Trans Tot) | 2.3 | 1.3 |
| 土壤全氮 Soil total nitrogen (TN) | 2 | 1.2 |
| 林内直射光 Transmitted direct in forest (Trans Dir) | 1.6 | 0.9 |
| 坡位 Slope position | 1.5 | 0.8 |
| 叶面积指数 Leaf area index (LAI) | 1 | 0.5 |
| 消光系数 Extinction coefficient (k) | 0.6 | 0.3 |
表7 冗余分析(RDA)中环境因子对林下植被物种多样性的解释率。* P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01。
Table 7 Contribution of significant environmental factors affecting understory species diversity in redundancy analysis (RDA). * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01.
| 环境因子 Environmental factors | 解释率 Contribution (%) | F |
|---|---|---|
| 土壤pH Soil pH | 32.3 | 9.4** |
| 土壤含水量 Soil water content (SWC) | 16.1 | 6.0** |
| 土壤全钾 Soil total potassium (TK) | 9.7 | 4.7** |
| 土壤全磷 Soil total phosphorus (TP) | 8.6 | 4.9** |
| 坡度 Slope (SLO) | 8.6 | 3.4* |
| 海拔 Elevation (ELE) | 3.6 | 2.2 |
| 土壤有机质 Soil organic matter (SOM) | 3.6 | 2.2 |
| 林内散射光 Transmitted diffuse in forest (Trans Dif) | 3.1 | 1.9 |
| 林冠开阔度 Canopy openness (CO) | 2.5 | 1.5 |
| 坡向 Slope aspect (SLOA) | 2.4 | 1.4 |
| 林内总光照 Transmitted total in forest (Trans Tot) | 2.3 | 1.3 |
| 土壤全氮 Soil total nitrogen (TN) | 2 | 1.2 |
| 林内直射光 Transmitted direct in forest (Trans Dir) | 1.6 | 0.9 |
| 坡位 Slope position | 1.5 | 0.8 |
| 叶面积指数 Leaf area index (LAI) | 1 | 0.5 |
| 消光系数 Extinction coefficient (k) | 0.6 | 0.3 |
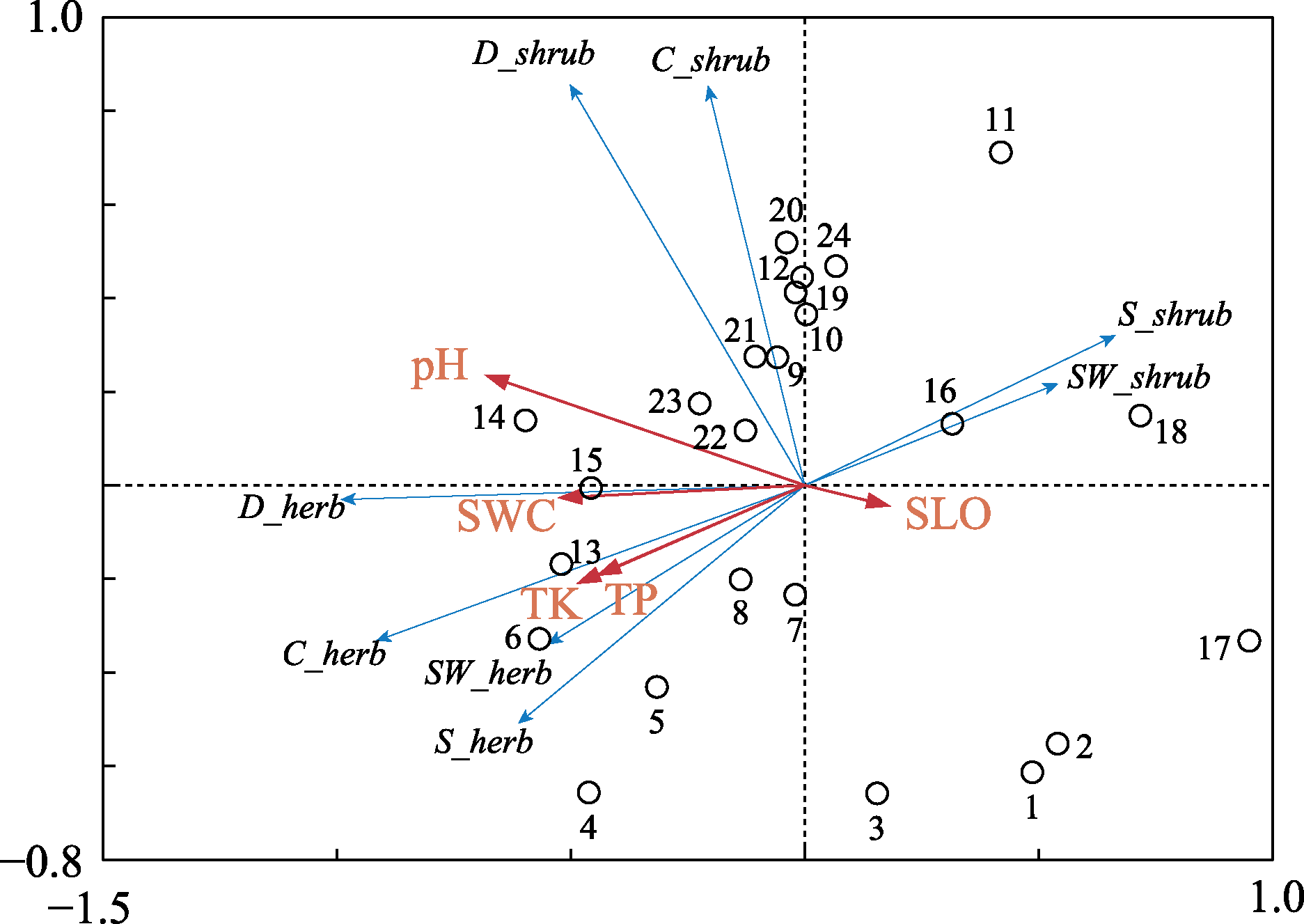
图1 林下植被物种多样性和环境因子的RDA排序图。图中阿拉伯数字代表24个样地; 红色箭头线段表示环境因子(仅显示具有显著影响的因子, P < 0.05), 蓝色箭头表示林下植物多样性因子。pH、SWC、SLO、TK、TP、SW_shrub、D_shrub、C_shrub、S_herb、SW_herb、D_herb和C_herb含义见表4和表7。
Fig. 1 RDA ordination diagram of understory species diversity and environmental factors. The arabic numerals in the figure represent 24 sample plots. The red arrow lines represent environmental factors (the factors with significant effects are display only, P < 0.05). The blue arrows lines represent diversity factors of understory plants. pH, SWC, SLO, TK, TP, SW_shrub, D_shrub, C_shrub, S_herb, SW_herb, D_herb and C_herb are the same as in Table 4 and Table 7.
| 林下植被物种多样性 Understory species diversity | 逐步回归方程 Stepwise regression equation | 调整后决定系数 Adjusted R square (R2adj) | P |
|---|---|---|---|
| 灌木丰富度 Shrub richness (S_shrub) | S_shrub = 57.560 - 1.184TK - 6.416SWC - 5.410pH | 0.599 | 0.015 |
| 灌木多样性 Shrub diversity (SW_shrub) | SW_shrub = 3.938 - 0.290TK - 0.173TP | 0.661 | 0.004 |
| 灌木密度 Shrub density (D_shrub) | D_shrub = - 2888.420 + 482.654pH | 0.189 | 0.019 |
| 灌木盖度 Shrub coverage (C_shrub) | C_shrub = 5.855 + 0.023D_shrub | 0.524 | < 0.001 |
| 草本丰富度 Herb richness (S_herb) | S_herb = 4.752 + 1.156TK | 0.239 | 0.009 |
| 草本多样性 Herb diversity (SW_herb) | SW_herb = 0.849 + 0.148S_herb | 0.595 | < 0.001 |
| 草本密度 Herb density (D_herb) | D_herb = - 3061.719 + 6073.551SWC + 579.980TK | 0.663 | 0.005 |
| 草本盖度 Herb coverage (C_herb) | C_herb = - 90.729 + 7.579TK + 12.862TP - 1.653SLO | 0.725 | 0.007 |
表8 林下植被物种多样性与环境因子的逐步回归分析。SWC、SLO、TK和TP含义见表7。
Table 8 Stepwise regression analysis of understory species diversity and environmental factors. SWC, SLO, TK and TP are the same as in Table 7.
| 林下植被物种多样性 Understory species diversity | 逐步回归方程 Stepwise regression equation | 调整后决定系数 Adjusted R square (R2adj) | P |
|---|---|---|---|
| 灌木丰富度 Shrub richness (S_shrub) | S_shrub = 57.560 - 1.184TK - 6.416SWC - 5.410pH | 0.599 | 0.015 |
| 灌木多样性 Shrub diversity (SW_shrub) | SW_shrub = 3.938 - 0.290TK - 0.173TP | 0.661 | 0.004 |
| 灌木密度 Shrub density (D_shrub) | D_shrub = - 2888.420 + 482.654pH | 0.189 | 0.019 |
| 灌木盖度 Shrub coverage (C_shrub) | C_shrub = 5.855 + 0.023D_shrub | 0.524 | < 0.001 |
| 草本丰富度 Herb richness (S_herb) | S_herb = 4.752 + 1.156TK | 0.239 | 0.009 |
| 草本多样性 Herb diversity (SW_herb) | SW_herb = 0.849 + 0.148S_herb | 0.595 | < 0.001 |
| 草本密度 Herb density (D_herb) | D_herb = - 3061.719 + 6073.551SWC + 579.980TK | 0.663 | 0.005 |
| 草本盖度 Herb coverage (C_herb) | C_herb = - 90.729 + 7.579TK + 12.862TP - 1.653SLO | 0.725 | 0.007 |
| 1 | Bai KD, Mo L, Liu M, Zhang DN, He CX, Wan XC, Jiang DB ( 2015) Nutrient resorption patterns of evergreen and deciduous tree species at different altitudes on Mao’er Mountain, Guangxi. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 35, 5776-5787. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 白坤栋, 莫凌, 刘铭, 张德楠, 何成新, 万贤崇, 蒋得斌 ( 2015) 广西猫儿山不同海拔常绿和落叶树种的营养再吸收模式. 生态学报, 35, 5776-5787.] | |
| 2 | Bao SD ( 2000) Soil Agro-Chemistrical Analysis. China Agriculture Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 鲍士旦 ( 2000) 土壤农化分析. 中国农业出版社, 北京.] | |
| 3 | Cao JH, Jiang ZC, Yang DS, Pei JG, Yang H, Luo WQ ( 2008) Grading of soil erosion intensity in Southwest karst area of China. Science of Soil and Water Conservation, 6(6), 1-7, 20. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 曹建华, 蒋忠诚, 杨德生, 裴建国, 杨慧, 罗为群 ( 2008) 我国西南岩溶区土壤侵蚀强度分级标准研究. 中国水土保持科学, 6(6), 1-7, 20.] | |
| 4 | Chen SS, Huang XQ ( 2018) Plant functional traits and the factors influencing them in the islands of eastern China. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 38, 7699-7707. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 陈思思, 黄秀清 ( 2018) 中国东部海岛植物功能性状及其影响因子. 生态学报, 38, 7699-7707.] | |
| 5 | Chen ZG, Fan DY, Zhang WF, Xie ZQ ( 2005) Effects of gap and understory environments on the regeneration of Quercus aliena var. acuteserrata and Fagus engleriana. Acta Phytoecologica Sinica, 29, 354-360. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 陈志刚, 樊大勇, 张旺锋, 谢宗强 ( 2005) 林隙与林下环境对锐齿槲栎和米心水青冈种群更新的影响. 植物生态学报, 29, 354-360.] | |
| 6 | Duan BB, Zhao CZ, Xu T, Zheng HL, Feng W, Han L ( 2016) Correlation analysis between vein density and stomatal traits of Robinia pseudoacacia in different aspects of Beishan Mountain in Lanzhou. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 40, 1289-1297. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 段贝贝, 赵成章, 徐婷, 郑慧玲, 冯威, 韩玲 ( 2016) 兰州北山不同坡向刺槐叶脉密度与气孔性状的关联性分析. 植物生态学报, 40, 1289-1297.] | |
| 7 | Du H, Peng WX, Song TQ, Wang KL, Zeng FP, Lu SY, Shi WW, Tang C, Tan QJ ( 2013) Plant community characteristics and its coupling relationships with soil in depressions between karst hills, North Guangxi, China. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 37, 197-208. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 杜虎, 彭晚霞, 宋同清, 王克林, 曾馥平, 鹿士杨, 时伟伟, 唐成, 谭秋锦 ( 2013) 桂北喀斯特峰丛洼地植物群落特征及其与土壤的耦合关系. 植物生态学报, 37, 197-208.] | |
| 8 | Engler R, Randin CF, Vittoz P, Czáka T, Beniston M, Zimmermann NE, Guisan A ( 2009) Predicting future distributions of mountain plants under climate change: Does dispersal capacity matter? Ecography, 32, 34-45. |
| 9 | Fang JY, Wang XP, Shen ZH, Tang ZY, He JS, Yu D, Jiang Y, Wang ZH, Zheng CY, Zhu JL, Guo ZD ( 2009) Methods and protocols for plant community inventory. Biodiversity Science, 17, 533-548. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 方精云, 王襄平, 沈泽昊, 唐志尧, 贺金生, 于丹, 江源, 王志恒, 郑成洋, 朱江玲, 郭兆迪 ( 2009) 植物群落清查的主要内容、方法和技术规范. 生物多样性, 17, 533-548.] | |
| 10 | Fu SL, Lin YB, Rao XQ, Liu SP ( 2011) The Dataset of Observation and Research on Chinese Ecosystem: Forest Ecosystem of Heshan Station, Guangdong Province (1998-2008). China Agriculture Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 傅声雷, 林永标, 饶兴权, 刘素萍 ( 2011) 中国生态系统定位观测与研究数据集: 森林生态系统卷(广东鹤山站1998-2008). 中国农业出版社, 北京.] | |
| 11 | Gracia M, Montané F, Piqué J, Retana J ( 2007) Overstory structure and topographic gradients determining diversity and abundance of understory shrub species in temperate forests in central Pyrenees (NE Spain). Forest Ecology and Management, 242, 391-397. |
| 12 | Guo YL, Li DX, Wang B, Bai KD, Xiang WS, Li XK ( 2017) C, N and P stoichiometric characteristics of soil and litter fall for six common tree species in a northern tropical karst seasonal rainforest in Nonggang, Guangxi, southern China. Biodiversity Science, 25, 1085-1094. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 郭屹立, 李冬兴, 王斌, 白坤栋, 向悟生, 李先琨 ( 2017) 北热带喀斯特季节性雨林土壤和6个常见树种凋落物的C、N、P化学计量学特征. 生物多样性, 25, 1085-1094.] | |
| 13 | Hájek M, Hájková P, Kočí M, Jiroušek M, Mikulášková E, Kintrová K ( 2013) Do we need soil moisture measurements in the vegetation-environment studies in wetlands? Journal of Vegetation Science, 24, 127-137. |
| 14 | Hall SJ, Matson PA ( 1999) Nitrogen oxide emissions after nitrogen additions in tropical forests. Nature, 400, 152-155. |
| 15 | Hao WF, Du F, Chen XY, Liang ZS ( 2012) Composition and diversity analysis of natural-community plants in the Loess Hilly Region. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 20, 609-615. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 郝文芳, 杜峰, 陈小燕, 梁宗锁 ( 2012) 黄土丘陵区天然群落的植物组成、植物多样性及其与环境因子的关系. 草地学报, 20, 609-615.] | |
| 16 | He CX, Huang YQ, Li XK, Wang XY, Wang Q ( 2007) The ecophysiological traits of three karst rockey desert restoration species. Guihaia, 27, 53-61. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 何成新, 黄玉清, 李先琨, 王晓英, 汪青 ( 2007) 岩溶石漠化地区几种生态恢复植物的生理生态学特征. 广西植物, 27, 53-61.) | |
| 17 | Huang FZ, Ding T, Li XK, Guo YL, Wang B, Xiang WS, Wen SJ, Li DX, He YL ( 2016) Species diversity for various associations along an altitudinal gradient in the karst seasonal rainforest in Nonggang. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 36, 4509-4517. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 黄甫昭, 丁涛, 李先琨, 郭屹立, 王斌, 向悟生, 文淑均, 李冬兴, 何运林 ( 2016) 弄岗喀斯特季节性雨林不同群丛物种多样性随海拔的变化. 生态学报, 36, 4509-4517.] | |
| 18 | Jiang ZC, Li XK, Hu BQ ( 2011) Rocky Desertification and Its Comprehensive Management in Karst Mountain Areas of Guangxi. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 蒋忠诚, 李先琨, 胡宝清 ( 2011) 广西岩溶山区石漠化及其综合治理研究. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| 19 | Liao JJ, Huang B, Sun WX, Zou Z, Su JP, Ding F, Huang Y ( 2007) Spatio-temporal variation of soil available phosphorus and its influencing factors—A case study of Rugao County, Jiangsu Province. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 44, 620-628. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 廖菁菁, 黄标, 孙维侠, 邹忠, 苏建平, 丁峰, 黄耀 ( 2007) 农田土壤有效磷的时空变异及其影响因素分析——以江苏省如皋市为例. 土壤学报, 44, 620-628.] | |
| 20 | Li XK, Jiang ZC, Huang YQ, Xiang WS, Lü SH, Ye D, Su ZM ( 2008) Dynamics of dominant population and its influence on karstifikation in Southwest Guangxi, China. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 29, 253-259. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 李先琨, 蒋忠诚, 黄玉清, 向悟生, 吕仕洪, 叶铎, 苏宗明 ( 2008) 桂西南岩溶山地优势植物种群动态及其对岩溶作用的影响. 地球学报, 29, 253-259.] | |
| 21 | Lin F, Comita LS, Wang XG, Bai XJ, Yuan ZQ, Xing DL, Hao ZQ ( 2014) The contribution of understory light availability and biotic neighborhood to seedling survival in secondary versus old-growth temperate forest. Plant Ecology, 215, 795-807. |
| 22 | Liu HM, Ma ZP, Yang QS, Fang XF, Lin QK, Zong Y, Aqing A, Wang XH ( 2017) Relationships between established seedling survival and growth in evergreen broad-leaved forest in Tiantong. Biodiversity Science, 25, 11-22. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 刘何铭, 马遵平, 杨庆松, 方晓峰, 林庆凯, 宗意, 阿尔达克·阿庆, 王希华 ( 2017) 天童常绿阔叶林定居幼苗存活和生长的关联. 生物多样性, 25, 11-22.] | |
| 23 | Liu Z, Li Q, Chen DD, Zhai WT, Zhao L, Xu SX, Zhao XQ ( 2015) Patterns of plant species diversity along an altitudinal gradient and its effect on above-ground biomass in alpine meadows in Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Biodiversity Science, 23, 451-462. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 刘哲, 李奇, 陈懂懂, 翟文婷, 赵亮, 徐世晓, 赵新全 ( 2015) 青藏高原高寒草甸物种多样性的海拔梯度分布格局及对地上生物量的影响. 生物多样性, 23, 451-462.] | |
| 24 | Lü YZ, Li BG ( 2006) Soil Science. China Agriculture Press, Beijing. ( in Chinese) |
| [ 吕贻忠, 李保国 ( 2006) 土壤学. 中国农业出版社, 北京.] | |
| 25 | Lu XL, Ding SY, You L, Zhang HY ( 2013) Effects of forest canopy structure on understory vegetation characteristics of Funiu Mountain Nature Reserve. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 33, 4715-4723. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 卢训令, 丁圣彦, 游莉, 张恒月 ( 2013) 伏牛山自然保护区森林冠层结构对林下植被特征的影响. 生态学报, 33, 4715-4723.] | |
| 26 | Ma KP, Liu YM ( 1994) Measurement of biotic community diversity. I. α diversity (Part 2). Chinese Biodiversity, 2, 231-239. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 马克平, 刘玉明 ( 1994) 生物群落多样性的测度方法. I. α多样性的测度方法(下). 生物多样性, 2, 231-239.] | |
| 27 | Ma M, Zhou X, Du G ( 2012) Changes in soil seed bank composition after wetland drying up and soil salinization on the Tibetan Plateau. Ecological Engineering, 44, 18-26. |
| 28 | Ma MJ, Baskin CC, Yu KL, Ma Z, Du GZ ( 2017) Wetland drying indirectly influences plant community and seed bank diversity through soil pH. Ecological Indicators, 80, 186-195. |
| 29 | Matson P, Lohse KA, Hall SJ ( 2002) The globalization of nitrogen deposition: Consequences for terrestrial ecosystems. Ambio, 31, 113-119. |
| 30 | Ning ZY, Li YL, Yang HL, Zhang ZQ, Zhang JP ( 2019) Stoichiometry and effects of carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus in soil of desertified grasslands on community productivity and species diversity. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 39, 3537-3546. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 宁志英, 李玉霖, 杨红玲, 张子谦, 张建鹏 ( 2019) 沙化草地土壤碳氮磷化学计量特征及其对植被生产力和多样性的影响. 生态学报, 39, 3537-3546.] | |
| 31 | Nie YP, Chen HS, Wang KL ( 2011) Seasonal variation of water sources for plants growing on continuous rock outcrops in limestone area of Southwest China. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 35, 1029-1037. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 聂云鹏, 陈洪松, 王克林 ( 2011) 石灰岩地区连片出露石丛生境植物水分来源的季节性差异. 植物生态学报, 35, 1029-1037.] | |
| 32 | Ou YD, Su ZY ( 2012) Dynamics of canopy structure and understory light in montane evergreen broadleaved forest following a natural disturbance in North Guangdong. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 32, 5637-5645. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 区余端, 苏志尧 ( 2012) 粤北山地常绿阔叶林自然干扰后冠层结构与林下光照动态. 生态学报, 32, 5637-5645.] | |
| 33 | Ou ZY, Su ZY, Peng YH, He QF, Huang XR ( 2013a) Natural regeneration of young Excentrodendron hsienmu in karst mountainous region in Southwest Guangxi, China. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 24, 2440-2446. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 欧芷阳, 苏志尧, 彭玉华, 何琴飞, 黄小荣 ( 2013a) 桂西南喀斯特山地蚬木幼龄植株的天然更新. 应用生态学报, 24, 2440-2446.] | |
| 34 | Ou ZY, Zhu JY, Cao YY, He QF, Huang XR, Peng YH, Pang SL ( 2013 b) Coupling relationships between woody plants in Excentrodendron hsienmu community and related edaphic and topographic factors. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 32, 3182-3189. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 欧芷阳, 朱积余, 曹艳云, 何琴飞, 黄小荣, 彭玉华, 庞世龙 ( 2013 b) 蚬木生存群落木本植物与土壤和地形因子的耦合关系. 生态学杂志, 32, 3182-3189.] | |
| 35 | Ou ZY, Zhu JY, Peng YH, He QF, Pang SL ( 2014) Relationship between plant diversity and environmental factors of Excentrodendron hsienmu community in karst mountains in Pingguo County, Guangxi. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 34, 204-211. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 欧芷阳, 朱积余, 彭玉华, 何琴飞, 庞世龙 ( 2014) 广西平果县喀斯特山地蚬木生存群落物种多样性与环境的关系. 植物研究, 34, 204-211.] | |
| 36 | Pan YF, Li JF, Huang CY, Liu RH, Jiang Y, Lu ZR, Liang SC ( 2019) Relationship between plant diversity of shrubs and soil environmental factors along with slope aspects in karst hills of Guilin, Southwest China. Guihaia, 39, 1115-1125. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 盘远方, 李娇凤, 黄昶吟, 刘润红, 姜勇, 陆志任, 梁士楚 ( 2019) 桂林岩溶石山不同坡向灌丛植物多样性与土壤环境因子的关系. 广西植物, 39, 1115-1125.] | |
| 37 | Peng WX ( 2009) Study on Patterns of Forest Vegetation and Its Maintenance Mechanism in Karst Peak-Cluster-Depression Region. PhD dissertation, Hunan Agricultural University, Changsha. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 彭晚霞 ( 2009) 喀斯特峰丛洼地森林植被分布格局及其维持机制研究. 博士学位论文, 湖南农业大学, 长沙.] | |
| 38 | Peng Y, Qing FT, Mi K, Xue DY ( 2015) Study progress on spatial scale effects and coupling relationships of different levels in biodiversity. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 35, 577-583. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 彭羽, 卿凤婷, 米凯, 薛达元 ( 2015) 生物多样性不同层次尺度效应及其耦合关系研究进展. 生态学报, 35, 577-583.] | |
| 39 | Potts MD, Ashton PS, Plotkin JB, Kaufmann LS ( 2002) Habitat patterns in tropical rainforests: A comparison of 105 plots in Northwest Borneo. Ecology, 83, 2782-2797. |
| 40 | Qiu Y, Zhang JT ( 2000) The ordination axes clustering based on detrended canonical correspondence analysis ordination and its application to the analysis of the ecological gradients of plant communities. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 20, 199-206. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 邱扬, 张金屯 ( 2000) DCCA排序轴分类及其在关帝山八水沟植物群落生态梯度分析中的应用. 生态学报, 20, 199-206.] | |
| 41 | Shen WH, Ou ZY, Pang SL, He QF, Liang Y ( 2017) Relationship between the spatial distributions of dominant arbor species and environmental factors of Excentrodendron hsienmu community in Southwest Guangxi, China. Guihaia, 37, 694-701. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 申文辉, 欧芷阳, 庞世龙, 何琴飞, 梁艳 ( 2017) 桂西南蚬木群落优势树种分布与环境因子的关系. 广西植物, 37, 694-701.] | |
| 42 | Shen WH, Tan ZQ, He QF, Peng YH, Zheng W, He F ( 2016) Species composition and diversity characteristics of Excentrodendron hsienmu-dominated communities in southwestern Guangxi, China. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 35, 1204-1211. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 申文辉, 谭长强, 何琴飞, 彭玉华, 郑威, 何峰 ( 2016) 桂西南蚬木优势群落物种组成及多样性特征. 生态学杂志, 35, 1204-1211.] | |
| 43 | Siefert A, Ravenscroft C, Althoff D, Alvarez-Yépiz JC, Carter BE, Glennon KL, Heberling JM, Jo IS, Pontes A, Sauer A, Willis A, Fridley JD ( 2012) Scale dependence of vegetation- environment relationships: A meta-analysis of multivariate data. Journal of Vegetation Science, 23, 942-951. |
| 44 | Sohlberg E, Bliss LC ( 1984) Microscale pattern of vascular plant distribution in two high arctic plant communities. Canadian Journal of Botany, 62, 2033-2042. |
| 45 | Steidinger B ( 2015) Qualitative differences in tree species distributions along soil chemical gradients give clues to the mechanisms of specialization: Why boron may be the most important soil nutrient at Barro Colorado Island. New Phytologist, 206, 895-899. |
| 46 | Tan HW, Zhou LQ, Xie RL, Huang MF ( 2006) Study on the potassium characteristic of rendzina soil in the sub-tropical karst of Guangxi. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 14, 58-60. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 谭宏伟, 周柳强, 谢如林, 黄美福 ( 2006) 广西亚热带岩溶地区石灰性土壤钾素特征研究. 中国生态农业学报, 14, 58-60.] | |
| 47 | Tan YB, He QF, Zheng W, Peng YH, Hou YR, He F, Shen WH ( 2016) Effects of canopy structure on understory vegetation in shelterbelt forests along the middle and upper reaches of Pearl River. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 35, 3148-3156. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 谭一波, 何琴飞, 郑威, 彭玉华, 侯远瑞, 何峰, 申文辉 ( 2016) 珠江流域中上游防护林冠层结构对林下植被的影响. 生态学杂志, 35, 3148-3156.] | |
| 48 | Tian HQ, Chen GS, Zhang C, Melillo JM, Hall CAS ( 2010) Pattern and variation of C : N : P ratios in China’s soils: A synthesis of observational data. Biogeochemistry, 98, 139-151. |
| 49 | Wang SL ( 2012) The Dataset of Observation and Research on Chinese Ecosystem:Forest Ecosystem of Huitong Station, Hunan Province (1960-2006). China Agriculture Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 汪思龙 ( 2012) 中国生态系统定位观测与研究数据集:森林生态系统卷(湖南会同站1960-2006). 中国农业出版社, 北京.] | |
| 50 | Wang XH ( 2010) The Dataset of Observation and Research on Chinese Ecosystem:Forest Ecosystem of Tiantong Station, Zhejiang Province (1983-2009). China Agriculture Press,Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 王希华 ( 2010) 中国生态系统定位观测与研究数据集:森林生态系统卷(浙江天童站1983-2009). 中国农业出版社,北京.] | |
| 51 | Weaver SE, Hamill AS ( 1985) Effects of soil pH on competitive ability and leaf nutrient content of corn (Zea mays L.) and three weed species. Weed Science, 33, 447-451. |
| 52 | Wen L, Song TQ, Du H, Wang KL, Peng WX, Zeng FP, Zeng ZX, He TG ( 2015) The succession characteristics and its driving mechanism of plant community in karst region, Southwest China. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 35, 5822-5833. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 文丽, 宋同清, 杜虎, 王克林, 彭晚霞, 曾馥平, 曾昭霞, 何铁光 ( 2015) 中国西南喀斯特植物群落演替特征及驱动机制. 生态学报, 35, 5822-5833.] | |
| 53 | Wright SJ, Yavitt JB, Wurzburger N, Turner BL, Tanner EV, Sayer EJ, Santiago LS, Kaspari M, Hedin LO, Harms KE, Garcia MN, Corre MD ( 2011) Potassium, phosphorus, or nitrogen limit root allocation, tree growth, or litter production in a lowland tropical forest. Ecology, 92, 1616-1625. |
| 54 | Xiang WS, Nong CG, Wang B, Liu SY, Ding T, He LJ, Li XK, Huang FZ ( 2013) Growth models of Excentrodendron hsienmu population in a karst seasonal rain forest. Guihaia, 33, 285-290. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 向悟生, 农重刚, 王斌, 刘晟源, 丁涛, 何兰军, 李先琨, 黄甫昭 ( 2013) 喀斯特季节性雨林蚬木种群的增长模型. 广西植物, 33, 285-290.] | |
| 55 | Xie YB, Ma ZP, Yang QS, Fang XF, Zhang ZG, Yan ER, Wang XH ( 2012) Coexistence mechanisms of evergreen and deciduous trees based on topographic factors in Tiantong region, Zhejiang Province, eastern China. Biodiversity Science, 20, 159-167. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 谢玉彬, 马遵平, 杨庆松, 方晓峰, 张志国, 阎恩荣, 王希华 ( 2012) 基于地形因子的天童地区常绿树种和落叶树种共存机制研究. 生物多样性, 20, 159-167.] | |
| 56 | Xu YJ, Lin DM, Shi M, Xie YJ, Wang YZ, Guan ZH, Xiang JY ( 2017) Spatial heterogeneity and its causes in evergreen broad-leaved forests in the Ailao Mountains, Yunnan Province. Biodiversity Science, 25, 23-33. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 徐远杰, 林敦梅, 石明, 谢妍洁, 王逸之, 管振华, 向建英 ( 2017) 云南哀牢山常绿阔叶林的空间分异及其影响因素. 生物多样性, 25, 23-33.] | |
| 57 | You YM, Wu XP, Ming AG, Liu T, Chen YK, Zhu HG, Wen YG, Liao SS, Huang XM ( 2018) Changes of plant functional group in understory and environmental interpretation in the transformation of typical coniferous plantation to native broadleaved species plantation in south subtropical China. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 37, 3194-3201. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 尤业明, 吴溪玭, 明安刚, 刘通, 陈永康, 朱宏光, 温远光, 廖树寿, 黄雪蔓 ( 2018) 南亚热带典型针叶林改造成乡土阔叶林后林下植物功能群的变化及其环境解释. 生态学杂志, 37, 3194-3201.] | |
| 58 | Yu M, Zhou ZY, Kang FF, Ouyang S, Mi XC, Sun JX ( 2013) Gradient analysis and environmental interpretation of understory herb-layer communities in Xiaoshegou of Lingkong Mountain, Shanxi, China. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 37, 373-383. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 余敏, 周志勇, 康峰峰, 欧阳帅, 米湘成, 孙建新 ( 2013) 山西灵空山小蛇沟林下草本层植物群落梯度分析及环境解释. 植物生态学报, 37, 373-383.] | |
| 59 | Yuan TX, Zhang HP, Ou ZY, Tan YB ( 2014) Effects of topography on the diversity and distribution pattern of ground plants in karst montane forests in Southwest Guangxi, China. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 25, 2803-2810. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 袁铁象, 张合平, 欧芷阳, 谭一波 ( 2014) 地形对桂西南喀斯特山地森林地表植物多样性及分布格局的影响. 应用生态学报, 25, 2803-2810.] | |
| 60 | Zhang ZH, Hu G, Ni J ( 2013) Effects of topographical and edaphic factors on the distribution of plant communities in two subtropical karst forests, Southwestern China. Journal of Mountain Science, 10, 95-104. |
| [1] | 刘咏华, 童光蓉, 余航远, 王宁宁, 任海保, 陈磊, 马克平, 米湘成. 钱江源-百山祖国家公园候选区钱江源园区冠层三维结构及光谱特征对人为干扰的响应[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24174-. |
| [2] | 杜晴晴, 任思远, Nicole Tsz Shun Yuan, 祝燕. 北京东灵山暖温带落叶阔叶林幼树及成树生产力的影响因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(12): 24284-. |
| [3] | 陈明苗, 张楚然, 邓云, 李生发, 李逢昌, 唐志忠, 魏兆喆, 张彩彩, 林露湘. 地形因子对亚热带半湿润常绿阔叶林木本植物萌生特征的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(12): 24282-. |
| [4] | 冯嘉谊, 练琚愉, 冯瑜莙, 张东旭, 曹洪麟, 叶万辉. 鼎湖山南亚热带常绿阔叶林群落垂直分层对群落结构及功能的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(12): 24306-. |
| [5] | 王爱霞, 马婧婧, 龚会蝶, 范国安, 王茂, 赵红梅, 程军回. 北疆一年生早春短命植物物种丰富度分布格局及其影响因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(6): 735-745. |
| [6] | 朱杰, 吴安驰, 邹顺, 熊鑫, 刘世忠, 褚国伟, 张倩媚, 刘菊秀, 唐旭利, 闫俊华, 张德强, 周国逸. 南亚热带常绿阔叶林树木多样性与生物量和生产力的关联及其影响因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(11): 1435-1446. |
| [7] | 王亚, 王玮倩, 王钦克, 李晓霞, 刘延, 黄乔乔. 土壤养分对菊科一年生入侵种和本地种繁殖性状的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(1): 1-9. |
| [8] | 张媚, 林马水, 曹秀秀, 赵树民, 蒋达青, 王冰璇, 汪石莹, 樊炎迪, 郭明, 林海萍. 不同经营模式山核桃林地土壤pH值、养分与细菌多样性的差异[J]. 生物多样性, 2018, 26(6): 611-619. |
| [9] | 倪娟平, 程赛赛, 高梅香, 卢廷玉, 金光泽. 丰林典型阔叶红松林地表鞘翅目成虫空间异质性及其与环境因子的空间关联性[J]. 生物多样性, 2018, 26(1): 14-26. |
| [10] | 闫静, 张晓亚, 陈雪, 王月, 张风娟, 万方浩. 三叶鬼针草与不同本地植物竞争对土壤 微生物和土壤养分的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2016, 24(12): 1381-1389. |
| [11] | 郭屹立, 王斌, 向悟生, 丁涛, 陆树华, 黄甫昭, 文淑均, 李冬兴, 何运林, 李先琨. 喀斯特季节性雨林木本植物胸高断面积分布格局及其对地形因子的响应[J]. 生物多样性, 2016, 24(1): 30-39. |
| [12] | 黄甫昭, 王斌, 丁涛, 向悟生, 李先琨, 周爱萍. 弄岗北热带喀斯特季节性雨林群丛数量 分类及与环境的关系[J]. 生物多样性, 2014, 22(2): 157-166. |
| [13] | 卢品, 金毅, 陈建华, 李铭红, 于明坚. 地理距离和地形差异对两个大型森林动态样地β多样性的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2013, 21(5): 554-563. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2026 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn
![]()