



生物多样性 ›› 2018, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (12): 1308-1317. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2018131 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2018131
所属专题: 青藏高原生物多样性与生态安全
陈自宏1, 杨晓娜1, 孙宁静1, 徐玲1,*( ), 郑元2, 杨宇明3
), 郑元2, 杨宇明3
收稿日期:2018-05-03
接受日期:2018-07-04
出版日期:2018-12-20
发布日期:2019-02-11
通讯作者:
徐玲
作者简介:# 共同第一作者
基金资助:
Zihong Chen1, Xiaona Yang1, Ningjing Sun1, Ling Xu1,*( ), Yuan Zheng2, Yuming Yang3
), Yuan Zheng2, Yuming Yang3
Received:2018-05-03
Accepted:2018-07-04
Online:2018-12-20
Published:2019-02-11
Contact:
Xu Ling
About author:# 同等贡献作者 Contributed equally to this work
摘要:
云南高黎贡山具有多样化的生态系统和生物资源。为探清该地区绿僵菌属(Metarhizium)真菌的物种多样性及其不同海拔的垂直分布特征, 沿海拔梯度(600-3,800 m)在7种典型植被类型(I: 干热河谷; II: 季风常绿阔叶林; III: 暖性针叶林; IV: 中山暖性常绿阔叶林; V: 山地苔藓矮林; VI: 寒温性灌丛或草甸; VII: 流石滩稀疏植被)中调查绿僵菌资源。从生境土壤中分离菌株, 通过多基因(nrSSU、nrLSU、EF-1α、RPB1和RPB2)系统发育分析进行物种鉴定。结果表明, 高黎贡山绿僵菌物种资源丰富, 获得的161株菌株分属于12个物种(Metarhizium rileyi, M. viridulum, M. lepidiotae, M. brunneum, M. pingshaense, M. anisopliae, M. robertsii, M. guizhouense, M. indigoticum, M. pemphigi, M. campsosterni和Metacordyceps neogunnii), 其中M. indigoticum为中国新记录种, M. anisopliae complex中的物种(8种)较集中; 同时还采集到了绿僵菌的近缘属Nigelia属物种N. martiale。高黎贡山绿僵菌广泛分布于除类型VII (海拔3,600-3,800 m)外的6种植被类型(海拔600-3,400 m)中。中低海拔植被类型(I-IV)中菌株数量较多(≥23株)、物种多样性较高(4-9种), 而高海拔植被类型(V-VI)中菌株数量较少(2-8株)、物种较单一(1-2种)。中海拔的常绿阔叶林中绿僵菌资源最丰富, 其中季风常绿阔叶林(植被类型II)中的菌株数量(52株, 占总数的32.3%)和物种数(9种)最多; 中山湿性常绿阔叶林(植被类型IV)为其次(47株, 占总数的29.2%; 7种)。高黎贡山绿僵菌优势种现象明显, M. brunneum为最优势物种, 其菌株数占总数的46.6%, 在生境条件差异很大的6种植被类型(I-VI)中都存在, 说明该物种生态适应能力最强。
陈自宏, 杨晓娜, 孙宁静, 徐玲, 郑元, 杨宇明 (2018) 中国西南高黎贡山绿僵菌物种多样性及其垂直分布特征. 生物多样性, 26, 1308-1317. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2018131.
Zihong Chen, Xiaona Yang, Ningjing Sun, Ling Xu, Yuan Zheng, Yuming Yang (2018) Species diversity and vertical distribution characteristics of Metarhizium in Gaoligong Mountains, southwestern China. Biodiversity Science, 26, 1308-1317. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2018131.

图1 高黎贡山绿僵菌不同物种的菌落及其他真菌材料。(A) M. brunneum的菌落; (B) M. lepidiotae的菌落; (C) M. indigoticum的菌落; (D) M. campsosterni的菌落; (E) M. robertsii的菌落; (F) M. guizhouense的菌落; (G) M. anisopliae的菌落; (H) M. pingshaense的菌落; (I) M. viridulum的菌落; (J) M. pemphigi的菌落; (K) M. rileyi的菌落; (L) Mc. neogunnii的菌落; (M)绿僵菌的诱导分离; (N) M. viridulum的子座; (O) M. rileyi感染鳞翅目幼虫形成的孢子; (P) M. pemphigi感染叶甲形成的孢子; (Q) N. martiale的子实体。A-O和Q的比例尺 = 1 cm; P的比例尺= 0.5 cm。
Fig. 1 Colonies of Metarhizium species and other fungal materials in Gaoligong Mountains. (A) Colony of M. brunneum; (B) Colony of M. lepidiotae; (C) Colony of M. indigoticum; (D) Colony of M. campsosterni; (E) Colony of M. robertsii; (F) Colony of M. guizhouense; (G) Colony of M. anisopliae; (H) Colony of M. pingshaense; (I) Colony of M. viridulum; (J) Colony of M. pemphigi; (K) Colony of M. rileyi; (L) Colony of Mc. neogunnii; (M) The induction and isolation of Metarhizium; (N) Stroma of M. viridulum; (O) Spores of M. rileyi on the infected Lepidoptera larva; (P) Spores of M. pemphigi on the infected beetle larva; (Q) Fruit body of N. martiale. Bar of A-O and Q = 1 cm; Bar of P = 0.5 cm.
| 物种 Species | 菌株数 strain number | 菌株百分比 % | 植被类型 Vegetation type | 海拔跨度 Altitude span (m) | 温度 Temperature (℃) | 湿度 Humidity (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Metarhizium brunneum | 75 | 46.6 | I-VI | 600-3,400 | 13-34 | 32-80 |
| M. pemphigi | 25 | 15.5 | I, II, IV | 800-2,119 | 20-32 | 39-70 |
| M. pingshaense | 11 | 6.8 | I, IV, V | 1,925-3,135 | 15-34 | 58-74 |
| M. guizhouense | 13 | 8.1 | II, IV | 1,540-2,280 | 18-30 | 57-74 |
| M. rileyi | 10 | 6.2 | II, IV | 1,780-2,495 | 17-27 | 49-54 |
| M. robertsii | 5 | 3.1 | I, IV | 723-1,981 | 22-32 | 52-63 |
| M. indigoticum | 4 | 2.5 | II, III | 1,512-1,981 | 22-30 | 58-59 |
| M. anisopliae | 4 | 2.5 | II, III | 1,370-1,900 | 25-30 | 60-76 |
| Metacordyceps neogunnii | 7 | 4.4 | II | 1,438 | 25 | 65 |
| M. campsosterni | 5 | 3.1 | IV | 2,022 | 22 | 58 |
| M. viridulum | 1 | 0.6 | II | 1,540 | 30 | 57 |
| M. lepidiotae | 1 | 0.6 | III | 1,765 | 25 | 58 |
| Nigelia martiale | - | - | II | 1,568 | 30 | 60 |
| 合计 Total | 161 | 100 | 6 | 600-3,400 | 13-34 | 32-80 |
表1 高黎贡山绿僵菌属不同物种的菌株数量及生境条件。I: 干热河谷; II: 季风常绿阔叶林; III: 暖性针叶林; IV: 中山暖性常绿阔叶林; V: 山地苔藓矮林; VI: 寒温性灌丛或草甸; VII: 流石滩稀疏植被。
Table 1 Strain numbers and habitat conditions of Metarhizium species in Gaoligong Mountains. I, Dry-hot valley; II, Monsoon evergreen broad-leaved forest; III, Warm coniferous forest; IV, Mid-montane humid evergreen broad-leaved forest; V, Mountain moss dwarf forest; VI, Cold shrubs of meadow; VII, Rocky beach sparsely vegetation.
| 物种 Species | 菌株数 strain number | 菌株百分比 % | 植被类型 Vegetation type | 海拔跨度 Altitude span (m) | 温度 Temperature (℃) | 湿度 Humidity (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Metarhizium brunneum | 75 | 46.6 | I-VI | 600-3,400 | 13-34 | 32-80 |
| M. pemphigi | 25 | 15.5 | I, II, IV | 800-2,119 | 20-32 | 39-70 |
| M. pingshaense | 11 | 6.8 | I, IV, V | 1,925-3,135 | 15-34 | 58-74 |
| M. guizhouense | 13 | 8.1 | II, IV | 1,540-2,280 | 18-30 | 57-74 |
| M. rileyi | 10 | 6.2 | II, IV | 1,780-2,495 | 17-27 | 49-54 |
| M. robertsii | 5 | 3.1 | I, IV | 723-1,981 | 22-32 | 52-63 |
| M. indigoticum | 4 | 2.5 | II, III | 1,512-1,981 | 22-30 | 58-59 |
| M. anisopliae | 4 | 2.5 | II, III | 1,370-1,900 | 25-30 | 60-76 |
| Metacordyceps neogunnii | 7 | 4.4 | II | 1,438 | 25 | 65 |
| M. campsosterni | 5 | 3.1 | IV | 2,022 | 22 | 58 |
| M. viridulum | 1 | 0.6 | II | 1,540 | 30 | 57 |
| M. lepidiotae | 1 | 0.6 | III | 1,765 | 25 | 58 |
| Nigelia martiale | - | - | II | 1,568 | 30 | 60 |
| 合计 Total | 161 | 100 | 6 | 600-3,400 | 13-34 | 32-80 |
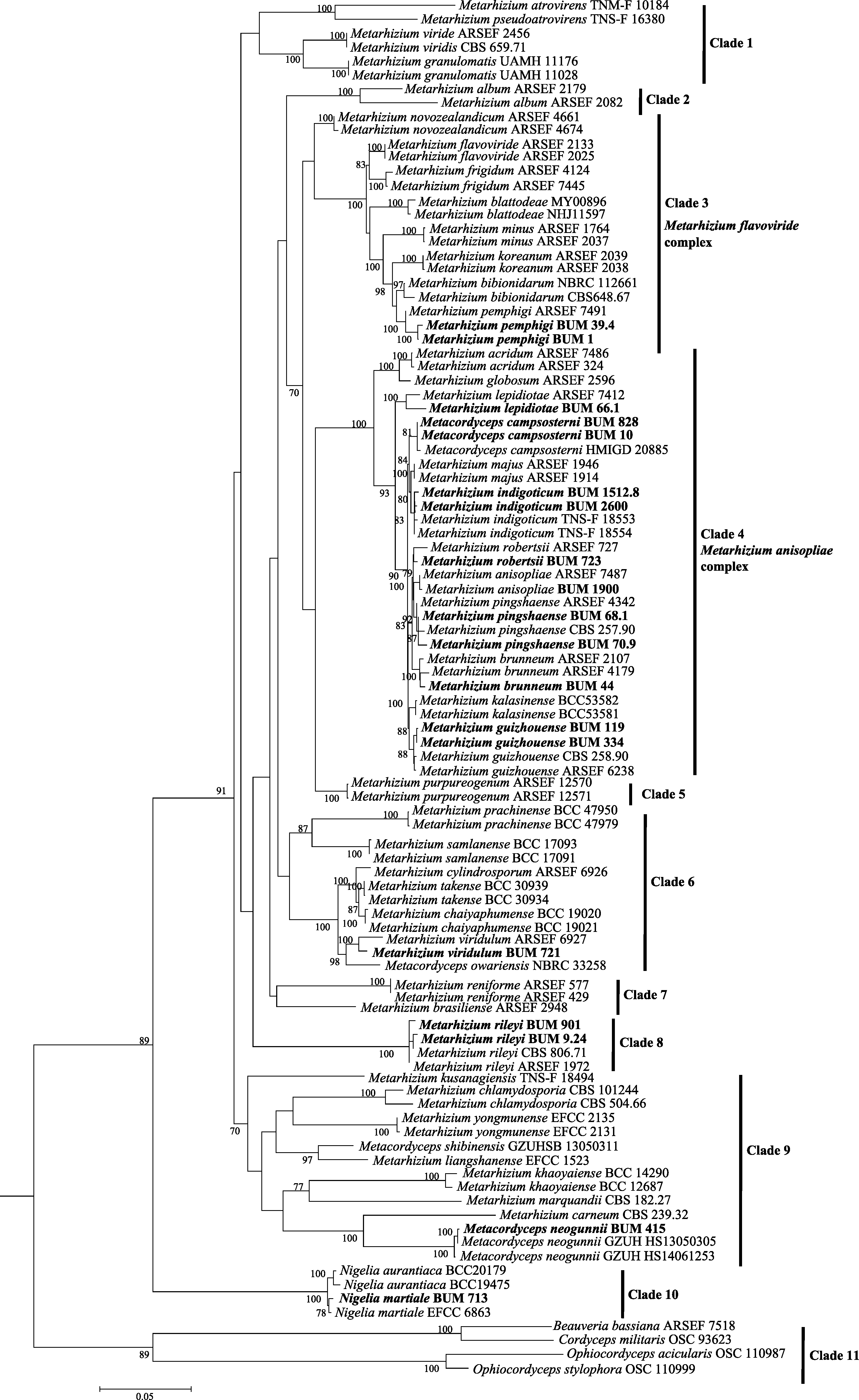
图2 基于5个基因(nrSSU、nrLSU、EF-1α、RPB1和RPB2)核苷酸序列分析获得的绿僵菌属系统发育树。采自高黎贡山的材料被标为黑体字。
Fig. 2 Phylogenetic tree of Metarhizium based on nucleotide sequences of five loci (nrSSU, nrLSU, EF-1α, RPB1and RPB2) dataset. Those from Gaoligong Mountains are marked in bold.
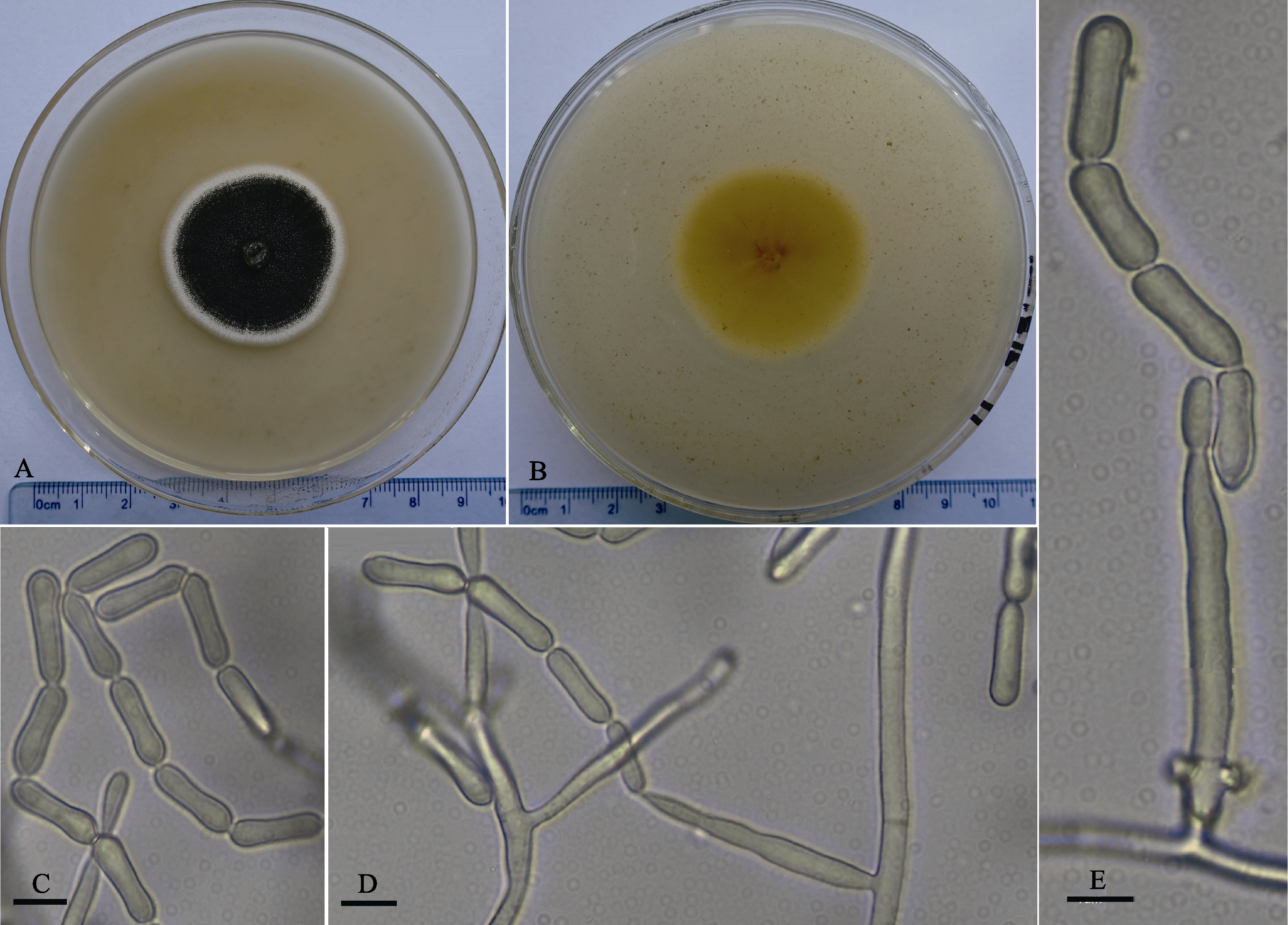
图3 中国新记录种Metarhizium indigoticum (菌株BUM 1512.8)的形态特征。(A)菌落正面; (B)菌落背面; (C)分生孢子链; (D, E)产孢结构。C-E的比例尺 = 5 µm.
Fig. 3 Morphology of the new record species in China, Metarhizium indigoticum (strain BUM 1512.8). (A) Obverse of the colony on PPDA; (B) Reverse of the colony on PPDA; (C) Conidia chains; (D, E) Conidiogenous structures. Bar of C-E = 5 µm.
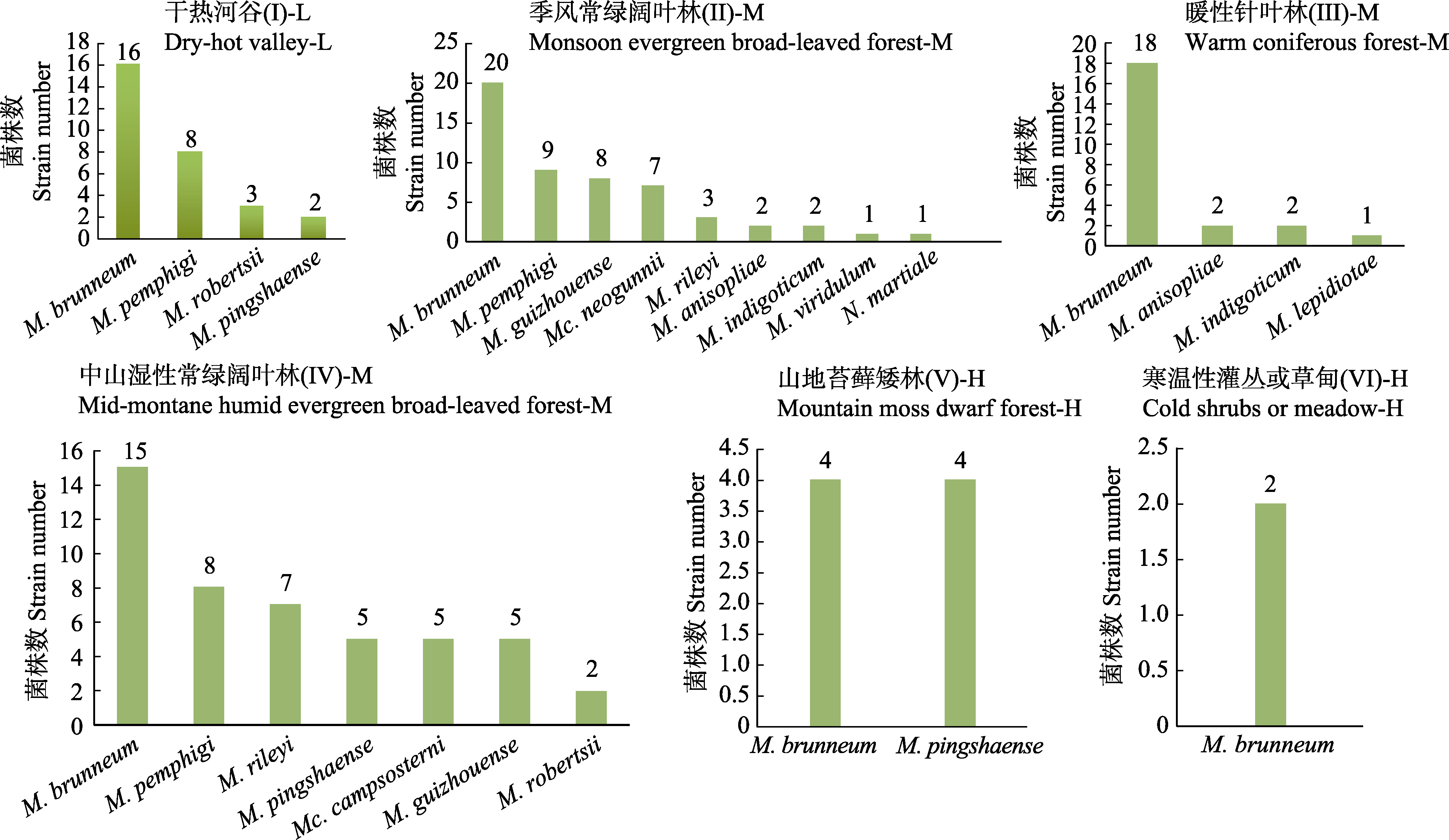
图4 高黎贡山不同植被类型中绿僵菌的物种及菌株数量。L: 低海拔; M: 中海拔; H: 高海拔。
Fig. 4 Species and strain numbers of Metarhizium in different vegetation types of Gaoligong Mountains. L, Low elevation; M, Middle elevation; H, High elevation.
| 1 | Bischoff JF, Rehner SA, Humber RA (2006) Metarhizium frigidum sp. nov.: A cryptic species of M. anisopliae and a member of the M. flavoviride complex. Mycologia, 98, 737-745. |
| 2 | Bischoff JF, Rehner SA, Humber RA (2009) A multilocus phylogeny of the Metarhizium anisopliae lineage. Mycologia, 101, 512-530. |
| 3 | Chen MJ (2008) Study on Biodiversity of Entomogenous Fungi in Different Forest Ecosystems. PhD dissertation, Anhui Agricultural University, Hefei>. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [陈名君 (2008) 不同森林生态系虫生真菌生物多样性研究. 博士学位论文, 安徽农业大学, 合肥.] | |
| 4 | Chen ZH, Dai YD, Yu H, Yang K, Yang ZL, Yuan F, Zeng WB (2013) Systematic analyses of Ophiocordyceps lanpingensis sp. nov., a new species of Ophiocordyceps in China. Microbiological Research, 168, 525-532. |
| 5 | Chu HL, Chen WH, Wen TC, Liang ZQ, Zheng FC, Liang JD, Han YF (2016) Delimitation of a novel member of genus Metarhizium (Clavicipitaceae) by phylogenetic and network analysis. Phytotaxa, 288, 51-60. |
| 6 | Driver F, Milner RJ, Trueman WH (2000) A taxonomic revision of Metarhizium based on a phylogenetic analysis of rDNA sequence data. Mycological Research, 104, 134-150. |
| 7 | Guo HL, Ye BL, Qiu YY, Chen QT, Fu CS (1986) Three new species of Metarhizium. Mycosystema, 5, 177-184. (in Chinese) |
| [郭好礼, 叶柏龄, 邱莹玉, 陈庆涛, 付仓生 (1986) 绿僵菌属的三个新种. 菌物学报, 5, 177-184.] | |
| 8 | He R, Yang W, Li YY, Chai Y, Fang B (2004) Study on soil character of two forest types in southern part of Gaoligong Mountains. Journal of West China Forestry Science, 33(3), 46-52. (in Chinese) |
| [何蓉, 杨卫, 李玉媛, 柴勇, 方波 (2004) 高黎贡山南段2种森林类型的土壤特性研究. 西部林业科学, 33(3), 46-52.] | |
| 9 | Huang B, Li SG, Li CR, Fan MZ, Li ZZ (2004) Studies on the taxonomic status of Metarhizium cylindrospora and Nomuraea viridula. Mycosystema, 23, 33-37. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [黄勃, 李世贵, 李春如, 樊美珍, 李增智 (2004) 柱孢绿僵菌和绿色野村菌分类地位的研究. 菌物学报, 23, 33-37.] | |
| 10 | Huang GQ, Zhang ZS, Liu YH (2017) Review of the comb-tailed spider genus Hahnia C. L. Koch 1841 (Hahniidae) from Gaoligong Mountains in Yunnan, China. Zootaxa, 4344, 444-464. |
| 11 | Kavanaugh DH, Hieke F, Liang HB, Dong DZ (2014) Inventory of the carabid beetle fauna of the Gaoligong Mountains, western Yunnan Province, China: Species of the tribe Zabrini (Coleoptera, Carabidae). Zookeys, 407, 55-119. |
| 12 | Kepler RM, Humber RA, Bischoff JF, Rehner SA (2014) Clarification of generic and species boundaries for Metarhizium and related fungi through multigene phylogenetics. Mycologia, 106, 811-829. |
| 13 | Kepler RM, Sung GH, Ban S, Nakagiri A, Chen MJ, Huang B, Li Z, Spatafora JW (2012) New teleomorph combinations in the entomopathogenic genus Metacordyceps. Mycologia, 104, 182-197. |
| 14 | Keyser CA, Licht HHDF, Steinwender BM, Meyling NV (2015) Diversity within the entomopathogenic fungal species Metarhizium flavoviride associated with agricultural crops in Denmark. BMC Microbiology, 15, 249. |
| 15 | Li CR, Huang B, Fan MZ, Lin YG, Li ZZ (2010) Metacordyceps guniujiangensis and its Metarhizium anamorph: A new pathogen on cicada nymphs. Mycotaxon, 111, 221-231. |
| 16 | Li R, Dao ZL, Li H (2011) Seed plant species diversity and conservation in the northern Gaoligong Mountains in western Yunnan, China. Mountain Research and Development, 31, 160-165. |
| 17 | Liang ZQ (2007) Flora Fungorum Sinicorum, Vol. 32: Cordyceps. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [梁宗琦 (2007) 中国真菌志(第32卷): 虫草属. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| 18 | Liang ZQ, Liu AY, Liu JL (1991) A new species of the genus Cordyceps and its Metarhizium anamorph.Mycosystema, 10, 257-262. (in Chinese) |
| [梁宗琦, 刘爱英, 刘杰麟 (1991) 虫草一新种及其绿僵菌无性型. 菌物学报, 10, 257-262.] | |
| 19 | Liu ZY, Liang ZQ, Whalley AJS, Yao YJ, Liu AY (2001) Cordyceps brittlebankisoides, a new pathogen of grubs and its anamorph, Metarhizium anisopliae var. majus. Journal of Invertebrate Pathology, 78, 178-182. |
| 20 | Luangsa-ard JJ, Mongkolsamrit S, Thanakitpipattana D, Khonsanit A, Tasanathai K, Noisripoom W, Humber RA (2017) Clavicipitaceous entomopathogens: New species in Metarhizium and a new genus Nigelia. Mycological Progress, 16, 369-391. |
| 21 | Nishi O, Shimizu S, Sato H (2017) Metarhizium bibionidarum and M. purpureogenum: New species from Japan. Mycological Progress, 16, 987-998. |
| 22 | Sharma SK, Gautam N (2015) Metacordyceps dhauladharensis sp. nov., a new entomopathogenic fungus from India. Turkish Journal of Botany, 39, 520-526. |
| 23 | Spatafora JW, Sung G-H, Sung JM, Hywel-Jones NL, White JF Jr (2007) Phylogenetic evidence for an animal pathogen origin of ergot and the grass endophytes. Molecular Ecology, 16, 1701-1711. |
| 24 | Su WP, Du F, Yang YM, Wang J (2014) The flora on mid-mountain humid evergreen broadleaf forest of the southern part of Mt. Gaoligongshan. Journal of Yunnan Agricultural University, 29, 792-798. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [苏文苹, 杜凡, 杨宇明, 王娟 (2014) 高黎贡山南段中山湿性常绿阔叶林植物区系研究. 云南农业大学学报, 29, 792-798.] | |
| 25 | Sung GH, Hywel-Jones NL, Sung JM, Luangsa-ard JJ, Shrestha B, Spatafora JW (2007) Phylogenetic classification of Cordyceps and the clavicipitaceous fungi. Studies in Mycology, 57(1), 5-59. |
| 26 | Tulloch M (1976) The genus Metarhizium. Transactions of the British Mycological Society, 66, 407-411. |
| 27 | Wang M, Yin YP, Wang ZK (2014) Multilocus phylogenetic analysis of the taxonomic status of 10 strains of Metarhizium. Plant Protection, 40(5), 14-21. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王萌, 殷幼平, 王中康 (2014) 10株绿僵菌菌株分类地位的多基因系统进化分析. 植物保护, 40(5), 14-21.] | |
| 28 | Wen TC, Xiao YP, Han YF, Huang SK, Zha LS, Hyde KD, Kang JC (2017) Multigene phylogeny and morphology reveal that the Chinese medicinal mushroom ‘Cordyceps gunnii’ is Metacordyceps neogunnii sp. nov. Phytotaxa, 302, 27-39. |
| 29 | Wen TC, Zha LS, Xiao YP, Wang Q, Kang JC, Hyde KD (2015) Metacordyceps shibinensis sp. nov. from larvae of Lepidoptera in Guizhou Province, southwest China. Phytotaxa, 226, 51-62. |
| 30 | Xu CD, Feng JM, Wang XP, Yang X (2008) Vertical distribution patterns of plant species diversity in northern Mt. Gaoligong, Yunnan Province. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 27, 323-327. (in Chinese) |
| [徐成东, 冯建孟, 王襄平, 杨雪 (2008) 云南高黎贡山北段植物物种多样性的垂直分布格局. 生态学杂志, 27, 323-327.] | |
| 31 | Zhang WM, Hu B, Zhong H, Chen YQ, Tao MH, Qu LH (2005) Study on the anamorph of Cordyceps campsosterna. In: Proceedings of the First Symposium on Development of China’s Medicinal Fungi Industry (ed. Mycological Society of China), pp. 81-82. Nantong, Jiangsu. (in Chinese) |
| [章卫民, 胡泊, 钟韩, 陈月琴, 陶美华, 屈良鹄 (2005) 丽叩甲虫草(Cordyceps campsosterna)无性型的研究. 见: 首届药用真菌产业发展暨学术研讨会论文集(中国菌物学会), pp. 81-82. 江苏南通.] | |
| 32 | Zhou H (2008) Studies on the Diversity of Soil Microorganisms in Gaoligongshan National Nature Reserve, Yunnan. PhD dissertation, Hunan Agricultural University, Changsha. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [周慧 (2008) 云南高黎贡山国家自然保护区土壤微生物多样性研究. 博士学位论文, 湖南农业大学, 长沙.] |
| [1] | 吴晓晴 张美惠 葛苏婷 李漫淑 宋坤 沈国春 达良俊 张健. 上海近自然林重建过程中木本植物物种多样性与地上生物量的时空动态——以闵行区生态岛为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24444-. |
| [2] | 王太, 宋福俊, 张永胜, 娄忠玉, 张艳萍, 杜岩岩. 河西走廊内陆河水系鱼类多样性及资源现状[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24387-. |
| [3] | 张晶晶, 黄文彬, 陈奕廷, 杨泽鹏, 柯伟业, 彭昭杰, 魏世超, 张志伟, 胡怡思, 余文华, 周文良. 广东南澎列岛海洋生态国家级自然保护区造礁石珊瑚多样性及分布特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24424-. |
| [4] | 尚华丹, 张楚晴, 王梅, 裴文娅, 李国宏, 王鸿斌. 中国杨树害虫物种多样性及其地理分布[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24370-. |
| [5] | 吴昱萱, 王平, 胡晓生, 丁一, 彭甜恬, 植秋滢, 巴德木其其格, 李文杰, 关潇, 李俊生. 呼伦贝尔草地退化现状评估与植被特征变化[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24118-. |
| [6] | 陈自宏, 张翼飞, 陈凯, 陈见影, 徐玲. 高黎贡山南段昆虫病原真菌物种多样性及影响因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(1): 24228-. |
| [7] | 谭珂, 宁瑶, 王仁芬, 王晴, 梁丹萍, 辛子兵, 温放. 中国苦苣苔科植物名录与地理分布数据集[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(1): 23275-. |
| [8] | 韩佳楠, 苏杨, 李霏, 刘君妍, 赵依林, 李琳, 赵建成, 梁红柱, 李敏. 河北省苔藓植物多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(9): 24096-. |
| [9] | 李东红, 郝媛媛, 甘辉林, 张航, 刘耀猛, 他富源, 胡桂馨. 祁连山北麓中段不同类型草地蝗虫种类及分布[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(9): 24119-. |
| [10] | 牛红玉, 陈璐, 赵恒月, 古丽扎尔·阿不都克力木, 张洪茂. 城市化对动物的影响: 从群落到个体[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(8): 23489-. |
| [11] | 白雪, 李正飞, 刘洋, 张君倩, 张多鹏, 罗鑫, 杨佳莉, 杜丽娜, 蒋玄空, 武瑞文, 谢志才. 西江流域大型底栖无脊椎动物物种多样性及维持机制[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(7): 23499-. |
| [12] | 许佳, 崔小娟, 张翼飞, 吴昌, 孙远东. 南岭地区鱼类多样性及其地理分布[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(7): 23482-. |
| [13] | 邝起宇, 胡亮. 广东东海岛与硇洲岛海域底栖贝类物种多样性及其地理分布[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(5): 24065-. |
| [14] | 赵勇强, 阎玺羽, 谢加琪, 侯梦婷, 陈丹梅, 臧丽鹏, 刘庆福, 隋明浈, 张广奇. 退化喀斯特森林自然恢复中不同生活史阶段木本植物物种多样性与群落构建[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(5): 23462-. |
| [15] | 徐伟强, 苏强. 分形模型与一般性物种多度分布关系的检验解析:以贝类和昆虫群落为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(4): 23410-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2026 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn
![]()