



生物多样性 ›› 2017, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (12): 1267-1275. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2017284 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2017284
所属专题: 生物入侵
王家宜1, 余涵霞1, 赖玉芳1, 万方浩2, 钱万强2, 彭长连1, 李伟华1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2017-10-23
接受日期:2017-12-18
出版日期:2017-12-20
发布日期:2017-12-10
通讯作者:
李伟华
基金资助:
Jiayi Wang1, Hanxia Yu1, Yufang Lai1, Fanghao Wan2, Wanqiang Qian2, Changlian Peng1, Weihua Li1,*( )
)
Received:2017-10-23
Accepted:2017-12-18
Online:2017-12-20
Published:2017-12-10
Contact:
Li Weihua
摘要:
薇甘菊(Mikania micrantha)是华南地区危害最严重的外来入侵杂草, 对天然次生林及其他生境造成了极大危害。为了探明本地植物粉葛(Pueraria lobata var. thomsonii)对薇甘菊进行替代控制的可能性, 本实验设置了3个水分水平(土壤含水量低于10%、60-70%和120-130%)分别模拟干旱、正常水分(对照)和涝害, 比较了粉葛与薇甘菊对干旱和涝害胁迫的生理响应差异。结果表明, 在干旱胁迫条件下, 薇甘菊的总生物量显著降低, 为对照的72%。在涝害胁迫条件下, 粉葛的总生物量与对照相比上升了16%, 薇甘菊则下降了15%。在干旱条件下, 粉葛的根冠比、叶绿素含量均显著高于对照(P < 0.05), 恢复正常水分后仍维持在较高水平; 薇甘菊的根冠比则与对照无显著差异(P > 0.05), 仅叶绿素含量显著高于对照(P < 0.05), 在恢复正常水分后低于正常水平。这可能与粉葛体内积累了较多的渗透调节物质脯氨酸和可溶性糖有关。在涝害条件下, 粉葛的丙二醛(malondialdehyde, MDA)含量约为对照的2.1倍, 薇甘菊则为对照的3.0倍; 恢复正常水平后, 薇甘菊和粉葛的MDA含量仍维持在较高水平, 分别为对照组的1.72倍和1.45倍, 显示粉葛受涝害影响的膜脂过氧化水平低于薇甘菊。可见, 粉葛比薇甘菊有更强的抗干旱能力和抗涝害能力, 对水分胁迫有更强的抗逆性, 抵抗力指数也印证了这一点。这为选用粉葛对华南地区天然次生林林缘或林窗生境薇甘菊的替代控制提供了理论支持。
王家宜, 余涵霞, 赖玉芳, 万方浩, 钱万强, 彭长连, 李伟华 (2017) 入侵杂草薇甘菊与本地植物粉葛对水分胁迫的生理响应. 生物多样性, 25, 1267-1275. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2017284.
Jiayi Wang, Hanxia Yu, Yufang Lai, Fanghao Wan, Wanqiang Qian, Changlian Peng, Weihua Li (2017) Physiological response of the invasive weed Mikania micrantha and the native species Pueraria lobata var. thomsonii to water stress. Biodiversity Science, 25, 1267-1275. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2017284.
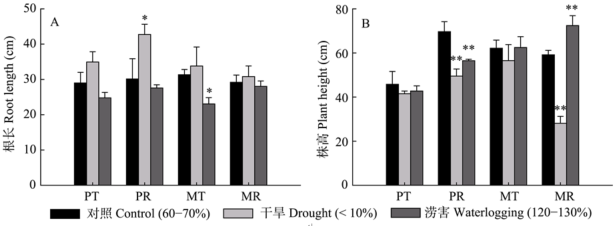
图1 水分胁迫与恢复正常水分后粉葛(P)和薇甘菊(M)根长与株高的变化(平均值 ± 标准差, n = 5)。处理(T): 对照、干旱、涝害; 恢复(R): 恢复土壤水分至60-70%。Dunnett检验, *表示同种植物处理组与对照组之间差异显著(P < 0.05), **表示同种植物处理组与对照组之间差异极显著(P < 0.01)。
Fig. 1 Changes of root length and plant height of Pueraria lobata var. thomsonii (P) and Mikania micrantha (M) after water stress and restoration to normal water content(mean ± SD, n = 5). Treatments (T), control, drought and waterlogging; Recovery (R), recovery of water content to 60-70%. Dunnett-test, * indicated significant difference between treatment and control group in the same plant (P < 0.05), ** indicated highly significant difference between treatment and control group (P < 0.01).
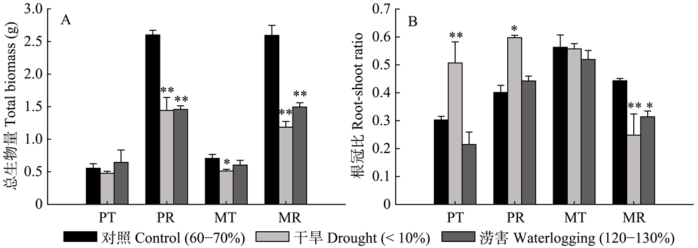
图2 水分胁迫与恢复正常水分后粉葛(P)和薇甘菊(M)总生物量与根冠比的变化(平均值 ± 标准差, n = 5)。图中字母简写和Dunnett显著性检验同图1。
Fig. 2 Changes of total biomass and root-shoot ratio of Pueraria lobata var. thomsonii (P) and Mikania micrantha (M) after water stress and restoration to normal water content(mean ± SD, n = 5). The abbreviations and Dunnett-test were same as those in Fig. 1.
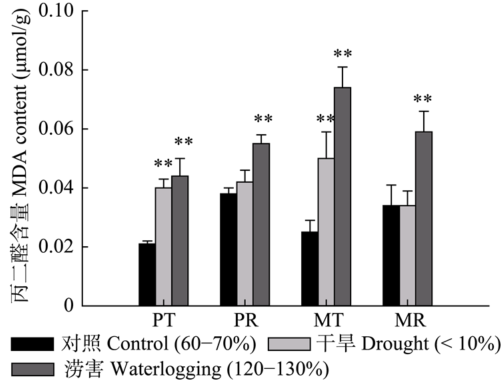
图3 水分胁迫与恢复正常水分后粉葛(P)和薇甘菊(M)的丙二醛含量(平均值 ± 标准差, n = 5)。图中字母简写和Dunnett显著性检验同图1。
Fig. 3 Contents of malondialdehyde (MDA) in Pueraria lobata var. thomsonii (P) and Mikania micrantha (M) after water stress and restoration to normal water content (mean ± SD, n = 5). The abbreviations and Dunnett-test were same as those in Fig. 1.
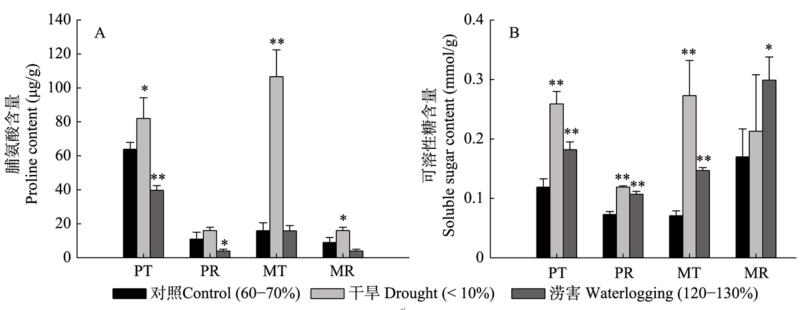
图4 水分胁迫与恢复正常水分后粉葛(P)和薇甘菊(M)的脯氨酸与可溶性糖含量比较(平均值 ± 标准差, n = 5)。图中字母简写和Dunnett显著性检验同图1。
Fig. 4 Comparison of proline and soluble sugar content between Pueraria lobata var. thomsonii (P) and Mikania micrantha (M) after water stress and restoring to normal water content(mean ± SD, n = 5). The abbreviations and Dunnett-test were same as those in Fig. 1.
| 土壤含水量 Water content (%) | 粉葛处理 P treatments | 粉葛恢复 P recovery | 薇甘菊处理 M treatments | 薇甘菊恢复 M recovery |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 对照 Control (60-70) | 1.76 ± 0.10 | 1.44 ± 0.08 | 0.94 ± 0.07 | 0.40 ± 0.05 |
| 干旱 Drought (0-10) | 3.35 ± 0.29** | 1.43 ± 0.12 | 1.91 ± 0.07** | 0.25 ± 0.03** |
| 涝害 Waterlogging (120-130) | 1.59 ± 0.35 | 1.50 ± 0.09* | 1.26 ± 0.20** | 0.26 ± 0.02** |
表1 水分胁迫条件下粉葛(P)和薇甘菊(M)叶绿素含量(mg/g)的变化(平均值 ± 标准差, n = 5)
Table 1 Changes of chlorophyll content of Pueraria lobata var. thomsonii (P) and Mikania micrantha (M) under water stress (mg/g) (mean ± SD, n = 5)
| 土壤含水量 Water content (%) | 粉葛处理 P treatments | 粉葛恢复 P recovery | 薇甘菊处理 M treatments | 薇甘菊恢复 M recovery |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 对照 Control (60-70) | 1.76 ± 0.10 | 1.44 ± 0.08 | 0.94 ± 0.07 | 0.40 ± 0.05 |
| 干旱 Drought (0-10) | 3.35 ± 0.29** | 1.43 ± 0.12 | 1.91 ± 0.07** | 0.25 ± 0.03** |
| 涝害 Waterlogging (120-130) | 1.59 ± 0.35 | 1.50 ± 0.09* | 1.26 ± 0.20** | 0.26 ± 0.02** |
| 干旱 Drought | 涝害 Waterlogging | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 粉葛 P | 薇甘菊 M | Dunnett检验 Dunnett-test | 粉葛 P | 薇甘菊 M | Dunnett检验 Dunnett-test | |
| 根长 Root length | 0.67 ± 0.15 | 0.73 ± 0.05 | ns | 0.75 ± 0.08 | 0.58 ± 0.07 | ns |
| 株高 Plant height | 0.83 ± 0.04 | 0.84 ± 0.18 | ns | 0.88 ± 0.09 | 0.88 ± 0.04 | ns |
| 生物量 Biomass | 0.76 ± 0.09 | 0.57 ± 0.05 | * | 0.72 ± 0.38 | 0.76 ± 0.17 | ns |
| 丙二醛 Malondialdehyde | 0.08 ± 0.001 | 0.02 ± 0.001 | ** | -0.02 ± 0.003 | -0.33 ± 0.06 | ** |
| 脯氨酸 Proline | 0.58 ± 0.23 | -0.69 ± 0.007 | ** | 0.44 ± 0.03 | 0.89 ± 0.03 | ** |
| 可溶性糖 Soluble sugar | -0.07 ± 0.07 | -0.45 ± 0.13 | * | 0.32 ± 0.11 | 0.001 ± 0.04 | ** |
| 叶绿素 Chlorophyll | 0.05 ± 0.01 | -0.01 ± 0.02 | ** | 0.68 ± 0.1 | 0.54 ± 0.15 | ns |
表2 水分胁迫条件下粉葛(P)和薇甘菊(M)不同指标抵抗力指数的比较(平均值 ± 标准差, n = 3)
Table 2 Comparison of resistance index in Pueraria lobata var. thomsonii (P) and Mikania micrantha (M) under water stress (mean ± SD, n = 3)
| 干旱 Drought | 涝害 Waterlogging | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 粉葛 P | 薇甘菊 M | Dunnett检验 Dunnett-test | 粉葛 P | 薇甘菊 M | Dunnett检验 Dunnett-test | |
| 根长 Root length | 0.67 ± 0.15 | 0.73 ± 0.05 | ns | 0.75 ± 0.08 | 0.58 ± 0.07 | ns |
| 株高 Plant height | 0.83 ± 0.04 | 0.84 ± 0.18 | ns | 0.88 ± 0.09 | 0.88 ± 0.04 | ns |
| 生物量 Biomass | 0.76 ± 0.09 | 0.57 ± 0.05 | * | 0.72 ± 0.38 | 0.76 ± 0.17 | ns |
| 丙二醛 Malondialdehyde | 0.08 ± 0.001 | 0.02 ± 0.001 | ** | -0.02 ± 0.003 | -0.33 ± 0.06 | ** |
| 脯氨酸 Proline | 0.58 ± 0.23 | -0.69 ± 0.007 | ** | 0.44 ± 0.03 | 0.89 ± 0.03 | ** |
| 可溶性糖 Soluble sugar | -0.07 ± 0.07 | -0.45 ± 0.13 | * | 0.32 ± 0.11 | 0.001 ± 0.04 | ** |
| 叶绿素 Chlorophyll | 0.05 ± 0.01 | -0.01 ± 0.02 | ** | 0.68 ± 0.1 | 0.54 ± 0.15 | ns |
| 干旱 Drought | 涝害 Waterlogging | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 粉葛 P | 薇甘菊 M | Dunnett检验 Dunnett-test | 粉葛 P | 薇甘菊 M | Dunnett检验 Dunnett-test | |
| 根长 Root length | -0.39 ± 0.15 | 0.31 ± 0.13 | ** | 0.25 ± 0.03 | 0.77 ± 0.19 | ** |
| 株高 Plant height | -0.65 ± 0.03 | -0.73 ± 0.27 | ns | -0.64 ± 0.26 | -0.52 ± 0.26 | ns |
| 生物量 Biomass | -0.88 ± 0.04 | -0.76 ± 0.02 | ** | -0.84 ± 0.22 | -0.84 ± 0.11 | ns |
| 丙二醛 Malondialdehyde | 0.66 ± 0.26 | 0.76 ± 0.11 | ns | 0.14 ± 0.06 | 0.34 ± 0.17 | ns |
| 脯氨酸 Proline | 0.49 ± 0.3 | 0.85 ± 0.06 | ns | 0.54 ± 0.06 | -0.62 ± 0.27 | ** |
| 可溶性糖 Soluble sugar | -0.17 ± 0.1 | 0.39 ± 0.06 | ** | -0.08 ± 0.02 | -0.26 ± 0.02 | ** |
| 叶绿素 Chlorophyll | 0.96 ± 0.04 | 0.75 ± 0.03 | ** | 0.50 ± 0.09 | 0.32 ± 0.01 | * |
表3 水分胁迫条件下粉葛(P)和薇甘菊(M)不同指标恢复力指数的比较(平均值 ± 标准差, n = 3)
Table 3 Comparison of resilience index in Pueraria lobata var. thomsonii (P) and Mikania micrantha (M) under water stress (mean ± SD, n = 3)
| 干旱 Drought | 涝害 Waterlogging | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 粉葛 P | 薇甘菊 M | Dunnett检验 Dunnett-test | 粉葛 P | 薇甘菊 M | Dunnett检验 Dunnett-test | |
| 根长 Root length | -0.39 ± 0.15 | 0.31 ± 0.13 | ** | 0.25 ± 0.03 | 0.77 ± 0.19 | ** |
| 株高 Plant height | -0.65 ± 0.03 | -0.73 ± 0.27 | ns | -0.64 ± 0.26 | -0.52 ± 0.26 | ns |
| 生物量 Biomass | -0.88 ± 0.04 | -0.76 ± 0.02 | ** | -0.84 ± 0.22 | -0.84 ± 0.11 | ns |
| 丙二醛 Malondialdehyde | 0.66 ± 0.26 | 0.76 ± 0.11 | ns | 0.14 ± 0.06 | 0.34 ± 0.17 | ns |
| 脯氨酸 Proline | 0.49 ± 0.3 | 0.85 ± 0.06 | ns | 0.54 ± 0.06 | -0.62 ± 0.27 | ** |
| 可溶性糖 Soluble sugar | -0.17 ± 0.1 | 0.39 ± 0.06 | ** | -0.08 ± 0.02 | -0.26 ± 0.02 | ** |
| 叶绿素 Chlorophyll | 0.96 ± 0.04 | 0.75 ± 0.03 | ** | 0.50 ± 0.09 | 0.32 ± 0.01 | * |
| [1] | Bao SD (2000) Soil Agricultural Chemistry Analysis, p. 24. China Agriculture Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [鲍士旦 (2000) 土壤农化分析, 24页. 中国农业出版社, 北京.] | |
| [2] | Bu YS, Miao GY, Shao HL, Wang JC (2006) Analysis of growth and development and yield of corn mulched with plastic film and straw. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 32, 1090-1093. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [卜玉山, 苗果园, 邵海林, 王建程 (2006) 对地膜和秸秆覆盖玉米生长发育与产量的分析. 作物学报, 32, 1090-1093.] | |
| [3] | Celedonio RPDS, Abeledo LG, Mantese AI, Miralles DJ (2017) Differential root and shoot biomass recovery in wheat and barley with transient waterlogging during preflowering. Plant and Soil, 417, 481-498. |
| [4] | Ding LL, Zheng JY, Fu H (2015) Progress in research of climate change in South China based on historical documents. Tropical Geography, 35, 890-894. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [丁玲玲, 郑景云, 傅辉 (2015) 基于历史文献的华南地区气候变化研究进展. 热带地理, 35, 890-894.] | |
| [5] | Du XM, Yin WX, Zhao YX, Zhang H (2001) The production and scavenging of reactive oxygen species in plants. Chinese Journal of Biotechnology, 17, 121-126. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [杜秀敏, 殷文璇, 赵彦修, 张慧 (2001) 植物中活性氧的产生及清除机制. 生物工程学报, 17, 121-126.] | |
| [6] | Fan LL, Zhang FY, Hu ZX, Wei L (2013) Spatial and temporal features of dry and wet states in South China in recent 50 years. Transactions of Atmospheric Sciences, 36, 29-36. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [范伶俐, 张福颖, 胡祯祥, 魏蕾 (2013) 近50 a华南干湿状态的时空特征. 大气科学学报, 36, 29-36.] | |
| [7] | Ghaderi N, Siosemareh A (2011) Response to drought stress of two strawberry cultivars (cv. Kurdistan and Selva). Horticulture, Environment and Biotechnology, 52, 6-12. |
| [8] | Haffani S, Mezni M, Slama I, Ksontini M, Chaïbi W (2014) Plant growth, water relations and proline content of three vetch species under water-limited conditions. Grass and Forage Science, 69, 323-333. |
| [9] | Herzog M, Striker GG, Colmer TD, Pedersen O (2016) Mechanisms of waterlogging tolerance in wheat—a review of root and shoot physiology. Plant, Cell & Environment, 39, 1068-1086. |
| [10] | Kong GH, Wu QG, Hu QM (2000) The emergence of exotic weed Mikania micrantha H. B. K. in China. Journal of Tropical and Subtropical Botany, 8, 27-28. (in Chinese) |
| [孔国辉, 吴七根, 胡启明 (2000) 外来杂草薇甘菊(Mikania micrantha H. B. K.)在我国的出现. 热带亚热带植物学报, 8, 27-28.] | |
| [11] | Li HS (2000) Principles and Techniques of Plant Physiology and Biochemistry Experiment, pp. 258-260. Higher Education Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [李合生 (2000) 植物生理生化实验原理和技术, 258-260页. 高等教育出版社, 北京.] | |
| [12] | Li L (2009) Module Test Guidance of Plant Physiology, p. 37. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [李玲 (2009) 植物生理学模块试验指导, 37页. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [13] | Li RY, Lin GQ (2012) Occurrence and control of alien pest Mikania micrantha H. B. K. Journal of Agricultural Catastrophology, 2(4), 11-13, 77. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [李瑞叶, 林干琼 (2012) 外来有害生物薇甘菊的发生与防治. 农业灾害研究, 2(4), 11-13, 77.] | |
| [14] | Orwin KH, Wardle DA (2004) New indices for quantifying the resistance and resilience of soil biota to exogenous disturbances. Soil Biology & Biochemistry, 36, 1907-1912. |
| [15] | Piemeisel RL, Carsner E (1951) Replacement control and biological control. Science, 113, 14-15. |
| [16] | Pimm SL (1984) The complexity and the stability of ecosystems. Nature, 307, 321-326. |
| [17] | Smucker AJM, Aiken RM (1992) Dynamic root responses to water deficits. Soil Science, 154, 281-289. |
| [18] | Stevens KJ, Stephenson GR, Peterson RL (1997) Morphological and anatomical responses of Lythrum salicaria L. (purple loosestrife) to an imposed water gradient. International Journal of Plant Sciences, 158, 172-183. |
| [19] | Tang ZC (1983) Response and adaptability of plants to water stress—II: response and adaptability to drought stress of plant. Plant Physiology Communications, (4), 3-9. (in Chinese) |
| [汤章城 (1983) 植物对水分胁迫的反应和适应性——II: 植物对干旱的反应和适应性. 植物生理学通讯, (4), 3-9.] | |
| [20] | Wang J (2015) Effect of waterlogging on physiological characteristics of peony. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 34, 3341-3347. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王娟 (2015) 淹水对牡丹生理特性的影响. 生态学杂志, 34, 3341-3347. ] | |
| [21] | Wang YT, Mai J, Li SS, Lars OB (2012) Invasion mechanisms of the exotic and noxious invasive plants Mikania micrantha and Ipomoea cairica in South China. Journal of South China Normal University (Natural Science Edition), 44(4), 1-5. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王宇涛, 麦菁, 李韶山, Lars OB (2012) 华南地区严重危害入侵植物薇甘菊和五爪金龙入侵机制研究. 华南师范大学学报(自然科学版), 44(4), 1-5.] | |
| [22] | Wang ZW, Mou SW, Yan LL, Han QF, Yang BP (2013) Effects of physiological and biochemical characteristics and growth under water stress in seedling of spring maize. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 33, 343-351. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王智威, 牟思维, 闫丽丽, 韩清芳, 杨宝平 (2013) 水分胁迫对春播玉米苗期生长及其生理生化特性的影响. 西北植物学报, 33, 343-351.] | |
| [23] | Wen DZ, Ye WH, Feng HL, Cai CX (2000) Comparison of basic photosynthetic characteristics between exotic invader weed Mikania micrantha and its companion species. Journal of Tropical and Subtropical Botany, 8, 139-146. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [温达志, 叶万辉, 冯惠玲, 蔡楚雄 (2000) 外来入侵杂草薇甘菊及其伴生种基本光合特性的比较. 热带亚热带植物学报, 8, 139-146.] | |
| [24] | Weng CJ (1992) A wild forage plant worth comprehensive exploitation—Pueraria lobata var. thomsonii. Feed Research, (2), 15-16. (in Chinese) |
| [翁长江 (1992) 值得综合开发利用的野生饲用植物——粉葛. 饲料研究, (2), 15-16.] | |
| [25] | Wu Q, Zhang GC, Pei B, Fang LD (2013) Physiological and biochemical responses to different soil drought stress in three tree species. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 33, 3648-3656. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [吴芹, 张光灿, 裴斌, 方立东 (2013) 3个树种对不同程度土壤干旱的生理生化响应. 生态学报, 33, 3648-3656.] | |
| [26] | Wu TH, Yang LH, Li YL (2014) The distribution and hazard of invasive species Mikania micrantha Kunth in Huizhou. Journal of Jilin Forestry Science and Technology, 43(6), 40-43. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [巫添辉, 杨丽华, 李运龙 (2014) 外来入侵种薇甘菊在惠州的分布与危害. 吉林林业科技, 43(6), 40-43.] | |
| [27] | Ye WH, Feng HL (2000) The growth and damaging effect of Mikania micrantha in different habitats. Journal of Tropical and Subtropical Botany, 8, 131-138. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [叶万辉, 冯惠玲 (2000) 不同生境和森林内薇甘菊的生存与危害状况. 热带亚热带植物学报, 8, 131-138.] | |
| [28] | Yu JP, Yu S, Liang YW, Ni XJ, Ren QJ (2014) Effect of NaCl stress on some physiological indices of Fraxinus americana seedling. Journal of Plant Resources and Environment, 23, 110-112. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [于金平, 俞珊, 梁有旺, 倪学军, 任全进 (2014) NaCl 胁迫对美国白蜡幼苗部分生理指标的影响. 植物资源与环境学报, 23, 110-112.] | |
| [29] | Zhang WY, Wang BS, Li MG, Zan QJ, Wang YJ (2002) The branching pattern and biomass of Mikania micrantha shoot modules in Acacia confusa community and Miscanthus sinensis Community. Acta Phytoecologica Sinica, 26, 346-350. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [张炜银, 王伯荪, 李鸣光, 昝启杰, 王勇军 (2002) 台湾相思林和芒草草丛中薇甘菊枝构件的分枝格局及其生物量. 植物生态学报, 26, 346-350.] | |
| [30] | Zhang ZM, Song WW, Ding H, Ci DW, Kang T, Ning TY, Dai LX (2013) The responses of leaf osmoregulation substance and protective enzyme activity of different peanut cultivars to non-sufficient irrigation. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 33, 4257-4265. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [张智猛, 宋文武, 丁红, 慈敦伟, 康涛, 宁堂原, 戴良香 (2013) 不同生育期花生渗透调节物质含量和抗氧化酶活性对土壤水分的响应. 生态学报, 33, 4257-4265.] | |
| [31] | Zhao SJ, Xu CC, Zou Q, Meng QW (1994) Improvements of method for measurement of malondialdehyde in plant tissues. Plant Physiology Communications, 30, 207-210. (in Chinese) |
| [赵世杰, 许长成, 邹琦, 孟庆伟 (1994) 植物组织中丙二醛测定方法的改进. 植物生理学通讯, 30, 207-210.] | |
| [32] | Zhao TH, Shen XY, Yang DG, Ma XF (2003) Effects on chlorophyll content and photosynthetic rate of maize leaves under water stress and rewatering. Rain Fed Crops, 23, 33-35. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [赵天宏, 沈秀瑛, 杨德光, 马秀芳 (2003) 水分胁迫及复水对玉米叶片叶绿素含量和光合作用的影响. 杂粮作物, 23, 33-35.] | |
| [33] | Zhu XQ, Zhou JM, Huang YN, Cao L, Liu CH, Peng FY (2011) Chinese Pueraria lobata resources utilization. Subtropical Agriculture Research, 7, 230-234. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [朱校奇, 周佳民, 黄艳宁, 曹亮, 刘朝晖, 彭福元 (2011) 中国葛资源及其利用. 亚热带农业研究, 7, 230-234.] |
| [1] | 张旋, 杜薇, 徐颖, 王永龙. 包头市半干旱型森林公园土壤细菌多样性与功能[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(7): 22245-. |
| [2] | 徐鹏, 荣晓莹, 刘朝红, 杜芳, 尹本丰, 陶冶, 张元明. 极端干旱对温带荒漠土壤真菌群落和生态网络的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(3): 21327-. |
| [3] | 王寅, 王健铭, 曲梦君, 李景文. 干旱内陆河流域植物群落构建过程及其关键驱动因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(2): 21419-. |
| [4] | 宋成军, 孙锋. 干旱对不同花椒种植模式下土壤微生物和线虫群落的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(10): 1348-1357. |
| [5] | 刘继亮, 李锋瑞. 干旱区绿洲扩张方式对土壤生物优势类群及功能的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2018, 26(10): 1116-1126. |
| [6] | 张明理. 中国西北干旱区和中亚植物区系地理研究[J]. 生物多样性, 2017, 25(2): 147-155. |
| [7] | 杨顺, 孙微, 刘杏忠, 向梅春. 石生真菌研究现状与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2016, 24(9): 1068-1076. |
| [8] | 杨阳, 韩杰, 刘晔, 忠永茨仁, 石松林, 斯那此里, 许玥, 应凌霄, 张婉君, 沈泽昊. 三江并流地区干旱河谷植物物种多样性海拔梯度格局比较[J]. 生物多样性, 2016, 24(4): 440-452. |
| [9] | 韩杰, 沈泽昊, 石松林, 彭培好. 雅砻江和大渡河干旱河谷植被物种多样性比较:气候、地形与空间的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2016, 24(4): 421-430. |
| [10] | 刘晔, 李鹏, 许玥, 石松林, 应凌霄, 张婉君, 彭培好, 沈泽昊. 中国西南干旱河谷植物群落的数量分类和排序分析[J]. 生物多样性, 2016, 24(4): 378-388. |
| [11] | 刘晔, 朱鑫鑫, 沈泽昊, 孙航. 中国西南干旱河谷植被的区系地理成分与空间分异[J]. 生物多样性, 2016, 24(4): 367-377. |
| [12] | 沈泽昊, 张志明, 胡金明, 韩杰, 杨济达, 应凌霄. 西南干旱河谷植物多样性资源的保护与利用[J]. 生物多样性, 2016, 24(4): 475-488. |
| [13] | 李云琴, 杜凡, 汪健, 李瑞年, 刘洋. 金沙江上游干旱河谷植被[J]. 生物多样性, 2016, 24(4): 489-494. |
| [14] | 巩合德, 杨国平, 鲁志云, 刘玉洪, 曹敏. 哀牢山常绿阔叶林乔木树种的幼苗组成及时空分布特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2011, 19(2): 151-157. |
| [15] | 尧婷婷, 孟婷婷, 倪健, 阎顺, 冯晓华, 王国宏. 新疆准噶尔荒漠植物叶片功能性状的进化和环境驱动机制初探[J]. 生物多样性, 2010, 18(2): 188-197. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2026 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn
![]()