



生物多样性 ›› 2018, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (10): 1116-1126. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2018130 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2018130
所属专题: 土壤生物与土壤健康; 昆虫多样性与生态功能
收稿日期:2018-04-28
接受日期:2018-06-20
出版日期:2018-10-20
发布日期:2019-01-06
通讯作者:
李锋瑞
作者简介:# 共同第一作者
基金资助:
Jiliang Liu1,2, Fengrui Li1,2,*( )
)
Received:2018-04-28
Accepted:2018-06-20
Online:2018-10-20
Published:2019-01-06
Contact:
Li Fengrui
About author:# Co-first authors
摘要:
内陆干旱区人口数量急剧增加驱动了绿洲快速扩张, 扩张方式主要包括: 灌木地、林地和农地扩张, 尚缺乏绿洲扩张方式对土壤生物多样性和生态系统服务功能影响的研究。本文以河西走廊黑河中游张掖绿洲为研究区域, 选择绿洲边缘天然草地及其转变的人工梭梭(Haloxylon ammodendron)灌木地(无灌溉)、人工杨树(Populus gansuensis)林地(灌溉)、玉米(Zea mays)地(灌溉 + 施肥)为研究对象, 测定了4种生境土壤食物网中9种优势功能类群的密度以及反映土壤生态系统功能特征的有机碳储量、氮储量、磷储量与土壤过氧化氢酶、蔗糖酶、脲酶、碱性磷酸酶活性。主要结果如下: (1)灌木地扩张显著降低了甲螨、植食性昆虫密度, 增加了跳虫、捕食性螨密度和真菌的OTUs, 对其余类群无显著影响; 林地扩张增加了捕食性节肢动物、植食性昆虫、捕食性螨、跳虫、甲螨的密度及细菌和真菌OTUs, 对其余类群无显著影响; 农地扩张增加了蚓类、捕食性节肢动物、捕食性螨、跳虫、甲螨的密度及细菌和真菌的OTUs, 对其余类群无显著影响。(2)林地和灌木地扩张显著提高了土壤有机碳储量和氮储量, 而农地扩张显著提高了土壤有机碳储量、氮储量和磷储量。(3) 3种扩张方式显著提高了土壤过氧化氢酶、蔗糖酶、脲酶、碱性磷酸酶活性, 玉米地和杨树林地土壤酶活性的增幅高于灌木地。人工绿洲扩张方式显著和有差异地改变了土壤食物网结构及其生态功能水平, 该结果对建立基于土地利用结构优化调控的人工绿洲生物多样性保护管理新方法具有重要意义, 并为人工绿洲生态系统功能稳定性评价研究提供了基础资料。
刘继亮, 李锋瑞 (2018) 干旱区绿洲扩张方式对土壤生物优势类群及功能的影响. 生物多样性, 26, 1116-1126. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2018130.
Jiliang Liu, Fengrui Li (2018) Effects of oasis expansion regimes on ecosystem function and dominant functional groups of soil biota in arid regions. Biodiversity Science, 26, 1116-1126. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2018130.
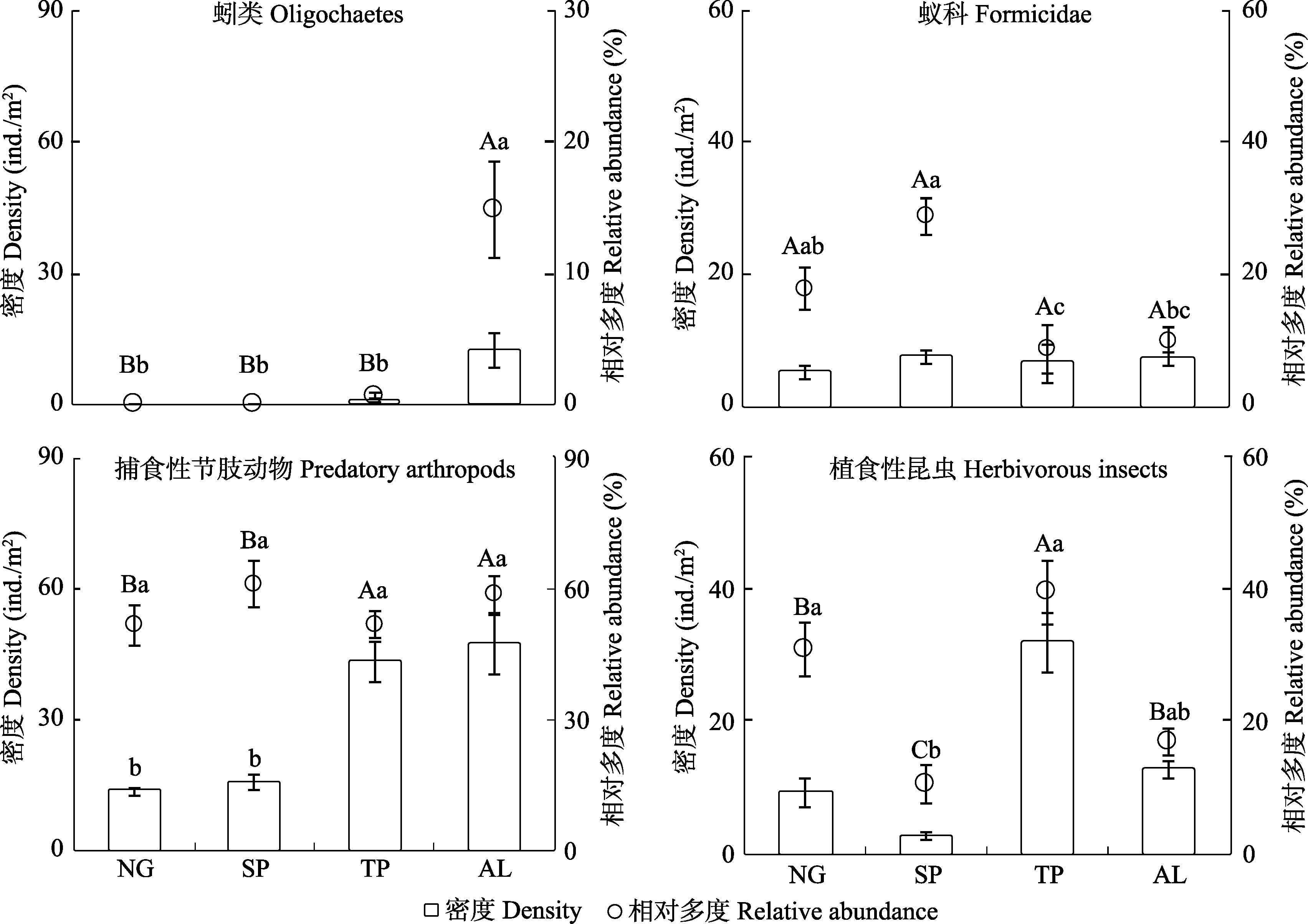
图1 绿洲边缘天然草地(NG)转变为人工梭梭灌木地(SP)、人工杨树林地(TP)、玉米地(AL)对大型土壤动物优势类群(蚓类、蚁科、捕食性节肢动物和植食性昆虫)密度和相对多度的影响。图中不同大写字母表示不同生境类型间土壤动物密度存在显著差异(P < 0.05), 不同小写字母表示不同生境类型间土壤动物相对多度存在显著差异(P < 0.05)。
Fig. 1 The effects of converting natural grasslands (NG) to shrub plantations (SP), tree plantations (TP) and arable lands (AL) on the density and relative abundance of oligochaetes, Formicidae, predatory arthropods and herbivorous insects. Means (± SE) with different capital letters indicate significant difference in the density of different groups between habitats (P < 0.05), means (± SE) with different lower-case letters indicate significant difference in the relative abundance of different groups between habitats (P < 0.05).
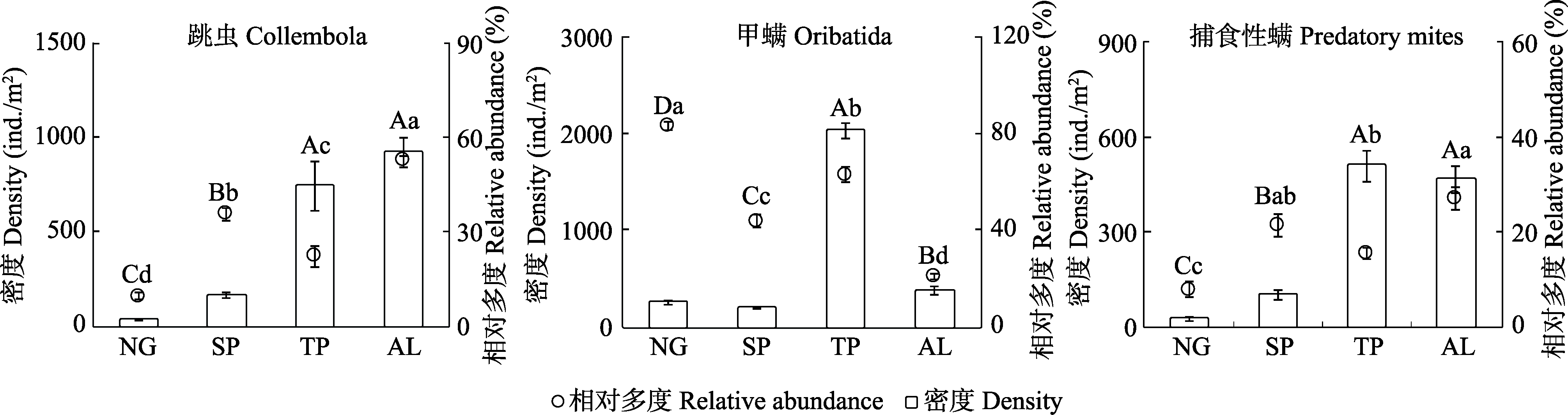
图2 绿洲边缘天然草地(NG)转变为人工梭梭灌木地(SP)、人工杨树林地(TP)、玉米地(AL)对中小型土壤动物优势类群(跳虫、甲螨和捕食性螨)密度和相对多度的影响。图中大写字母不同表示不同生境类型间土壤动物密度存在显著差异(P < 0.05), 小写字母不同表示不同生境类型间土壤动物相对多度存在显著差异(P < 0.05)。
Fig. 2 The effects of converting natural grasslands (NG) to shrub plantations (SP), tree plantations (TP) and arable lands (AL) on the density and relative abundance of Collembola, Oribatida and predatory mites. Means (± SE) with different capital letters indicate significant difference in the density of different groups between habitats (P < 0.05), means (± SE) with different lower-case letters indicate significant difference in the relative abundance of different groups between habitats (P < 0.05).
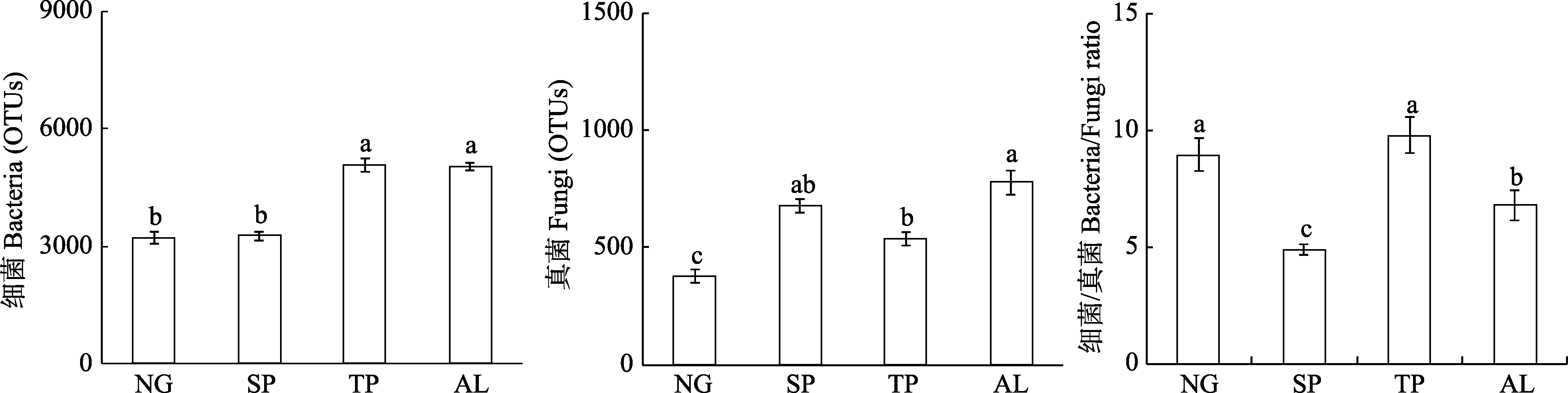
图3 绿洲边缘天然草地(NG)转变为人工梭梭灌木地(SP)、人工杨树林地(TP)、玉米地(AL)对土壤细菌和真菌及细菌/真菌比例的影响。图中字母不同表示不同生境类型间存在显著的差异(P < 0.05)。
Fig. 3 The effects of converting natural grasslands (NG) to shrub plantations (SP), tree plantations (TP), and arable lands (AL) on the OTUs of bacteria and fungi as well as the ratio of bacteria and fungi. Means (± SE) with different letters indicate significant differences between habitats (P < 0.05).
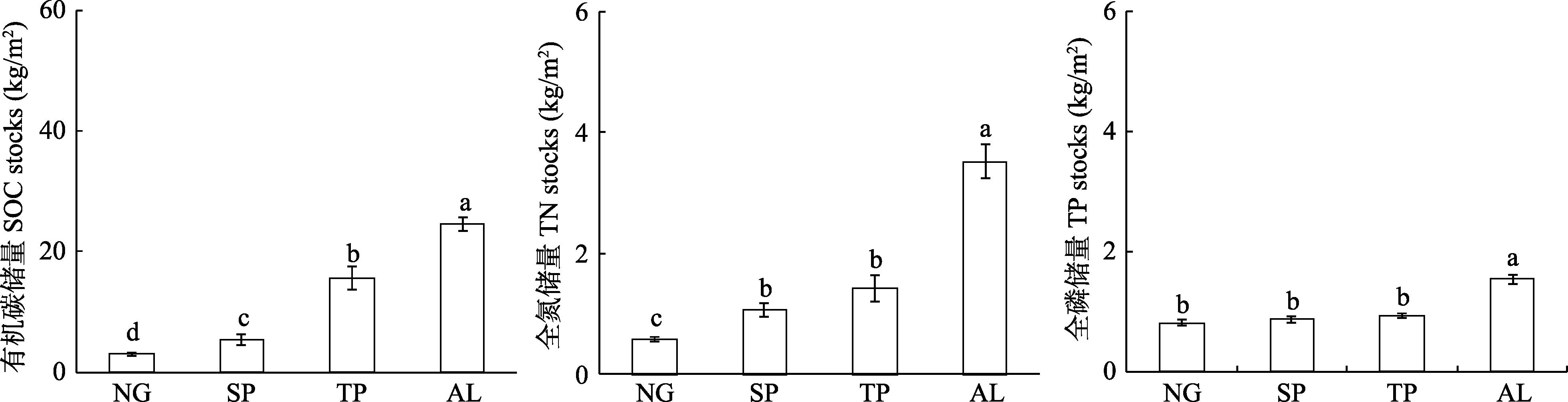
图4 绿洲边缘天然草地(NG)转变为人工梭梭灌木地(SP)、人工杨树林地(TP)、玉米地(AL)对土壤有机碳储量、全氮储量、全磷储量的影响。图中字母不同表示不同生境类型间存在显著的差异(P < 0.05)。
Fig. 4 The effects of converting natural grasslands (NG) to shrub plantations (SP), tree plantations (TP) and arable lands (AL) on the soil organic carbon (SOC), total nitrogen (TN) and total phosphorus (TP) stocks. Means (± SE) with different letters indicate significant differences between habitats (P < 0.05).
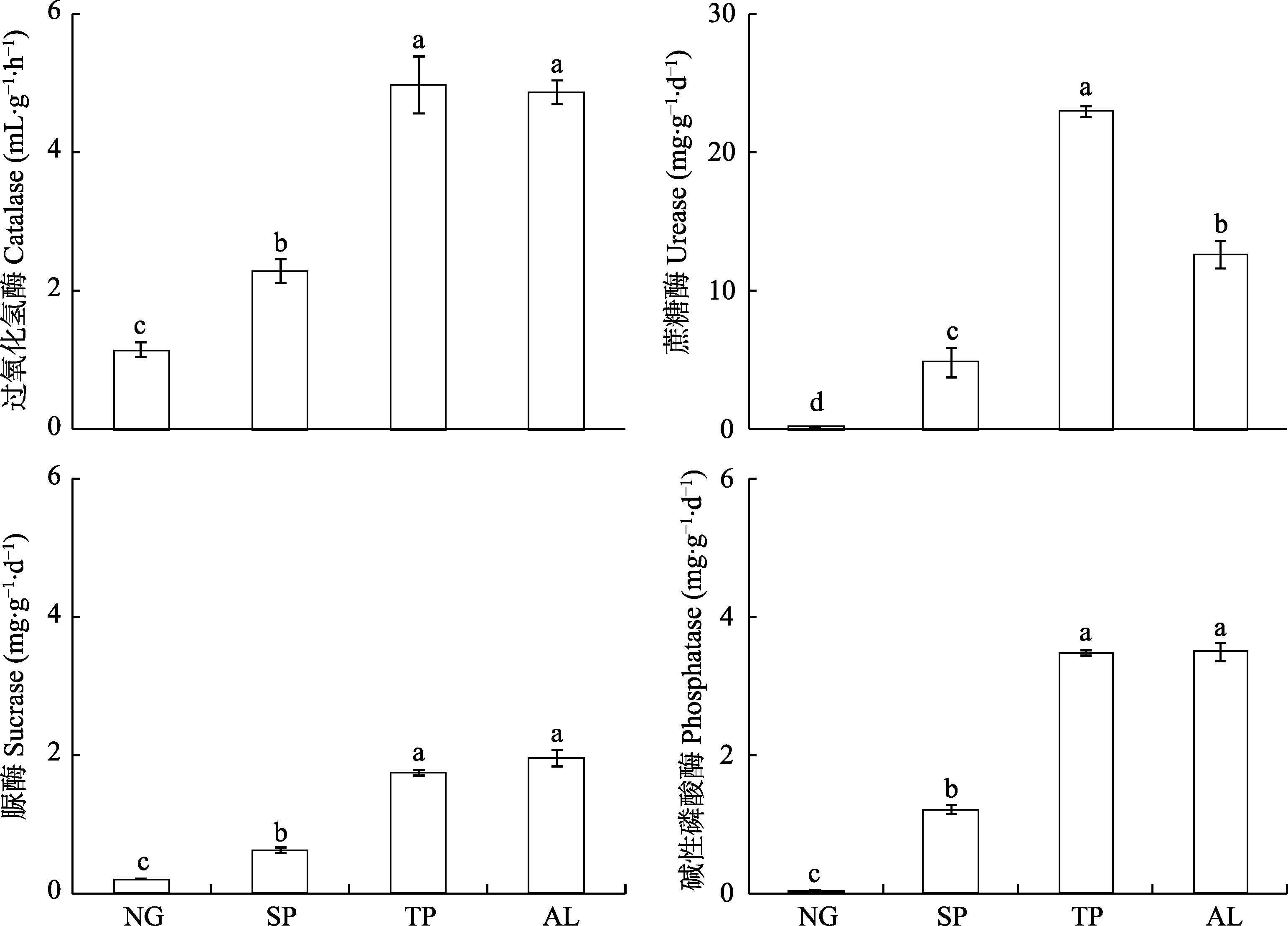
图5 绿洲边缘天然草地(NG)转变为人工梭梭灌木地(SP)、人工杨树林地(TP)、玉米地(AL)对土壤过氧化氢酶、蔗糖酶、脲酶、碱性磷酸酶活性的影响。图中字母不同表示不同生境类型间存在显著差异(P < 0.05)。
Fig. 5 The effects of converting natural grasslands (NG) to shrub plantations (SP), tree plantations (TP) and arable lands (AL) on the activities of soil catalase, urease, sucrase and phosphatase. Means (± SE) with different letters indicate significant difference between habitats (P < 0.05).
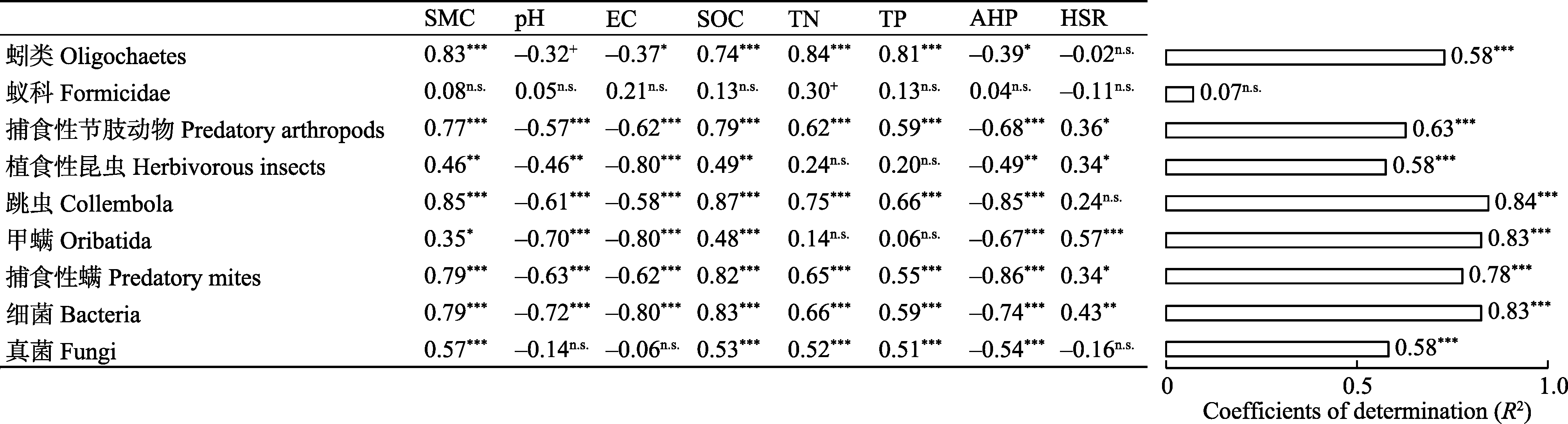
图6 9个土壤优势功能类群数量对环境因子变化的响应。左面表格为9个土壤生物类群和8个环境因子的Pearson相关系数, 右图为8个环境因子对9个土壤生物类群影响的多元回归系数。SMC: 土壤含水量; EC: 电导率; SOC: 有机碳; TN: 全氮; TP: 全磷; AHP: 草本地上生物量; HSR: 草本物种丰富度。
Fig. 6 The responses of nine dominant soil organism groups to changes in environmental factors. Pearson’s correlations between the diversity of nine dominant soil organism groups and eight environmental variables such as soil moisture content (SMC), soil pH, soil electrical conductivity (EC), soil organic carbon (SOC), total nitrogen (TN), total phosphorus (TP), aboveground herbaceous biomass (AHP), and herbaceous species richness (HSR). The overall effect of the eight selected environmental variables on variation in nine dominant soil organism groups was determined by multiple regression analyses. *** P < 0.001, ** P < 0.01, * P < 0.05, + P < 0.1, n.s. P > 0.1.
| [41] | Rusek J (1998) Biodiversity of Collembola and their functional role in the ecosystem. Biodiversity and Conservations, 7, 1207-1219. |
| [42] | Shi LL, Fu SL (2014) Review of soil biodiversity research: History, current status and future challenges. Chinese Science Bulletin, 59, 493-509. (in Chinese) |
| [时雷雷, 傅声雷 (2014) 土壤生物多样性研究: 历史、现状与挑战. 科学通报, 59, 493-509.] | |
| [43] | Siepel H, Maaskamp F (1994) Mites of different feeding guilds affect decomposition of organic matter. Soil Biology & Biochemistry, 26, 1389-1394. |
| [44] | Song DX, Zhu MS, Chen J (1999) The Spiders of China. Hebei Science & Technology Publishing House, Shijiazhuang. |
| [45] | Tripathi BM, Moroenyane I, Sherman C, Lee YK, Adams JM, Steinberger Y (2017) Trends in taxonomic and functional composition of soil microbiome along a precipitation gradient in Israel. Microbial Ecology, 74, 168-176. |
| [46] | Wagg C, Bender SF, Widmer F, van der Heijden MGA (2014) Soil biodiversity and soil community composition determine ecosystem multifunctionality. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 111, 5266-5270. |
| [47] | Whitford WG, Parker LW (1989) Contributions of soil fauna to decomposition and mineralization processes in semiarid and arid ecosystems. Arid Land Research and Management, 3, 199-215. |
| [1] | Abliz O, Nurmammat G, Tursuna A, Hajim M, Wu SL (2013) Community diversity and its seasonal dynamics of soil fauna in Fukang oasis of Xinjiang, Northwest China. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 32, 1412-1420. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [吾玛尔·阿布力孜, 古丽布斯坦·努尔买买提, 阿布都肉苏力·吐孙, 木开热木·阿吉木, 吴松林 (2013) 新疆阜康绿洲不同生境土壤动物群落多样性及其季节动态. 生态学杂志, 32, 1412-1420.] | |
| [48] | Xie YW, Wang GS (2014) Reconstruction of historic spatial pattern for water resources utilization in the Heihe River basin. Geographical Research, 33, 1977-1991. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [颉耀文, 汪桂生 (2014) 黑河流域历史时期水资源利用空间格局重建. 地理研究, 33, 1977-1991.] | |
| [2] | Bardgett RD, van der Putten WH (2014) Belowground biodiversity and ecosystem functioning. Nature, 515, 505-511. |
| [3] | Brockett BFT, Prescott CE, Grayston SJ (2010) Soil moisture is the major factor influencing microbial community structure and enzyme activities across seven biogeoclimatic zones in western Canada. Soil Biology & Biochemistry, 44, 9-20. |
| [4] | Cai WZ, Pang XF, Hua BZ, Liang GW, Song DL (2011) General Entomology, 2nd edn. China Agricultural University Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [彩万志, 庞雄飞, 花保祯, 梁广文, 宋敦伦 (2011) 普通昆虫学(第2版). 中国农业大学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [49] | Yin WY (1998) Pictorial Keys to Soil Animals of China. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [尹文英 (1998) 中国土壤动物检索图鉴. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [5] | Chen FH, Huang W, Jin LY, Chen JH, Wang JS (2011) Spatiotemporal precipitation variations in the arid Central Asia in the context of global warming. Science China Earth Sciences, 54, 1812-1821. |
| [6] | Chen YN, Chen ZS (2013) Analysis of oasis evolution and suitable development scale for arid regions: A case study of the Tarim River Basin. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 21, 134-140. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [陈亚宁, 陈忠升 (2013) 干旱区绿洲演变与适宜发展规模研究: 以塔里木河流域为例. 中国生态农业学报, 21, 134-140.] | |
| [7] | Cheng GD, Li X, Zhao WZ, Xu ZM, Feng Q, Xiao SC, Xiao HL (2014) Integrated study of the water-ecosystem-economy in the Heihe River Basin. National Science Review, 1, 413-428. |
| [8] | Darby BJ, Neher DA, Housman DC, Belnap J (2011) Few apparent short-term effects of elevated soil temperature and increased frequency of summer precipitation on the abundance and taxonomic diversity of desert soil micro- and meso-fauna. Soil Biology & Biochemistry, 43, 1474-1481. |
| [9] | De Groot GA, Jagers op Akkerhuis GAJM, Dimmers WJ, Charrier X, Faber JH (2016) Biomass and diversity of soil mite functional groups respond to intensification of land management, potentially affecting soil ecosystem services. Frontiers in Environmental Science, 4, 15. https://doi.org/10.3389/fenvs.2016.00015. |
| [50] | Zhang WX, Chen DM, Zhao CC (2007) Functions of earthworm in ecosystem. Biodiversity Science, 15, 142-153. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [张卫信, 陈迪马, 赵灿灿 (2007) 蚯蚓在生态系统中的作用. 生物多样性, 15, 142-153.] | |
| [10] | De Vries FT, Thébault E, Liiri M, Birkhofer K, Tsiafouli MA, Bjørnlund L, Jørgensen HB, Brady MV, Christensen S, de Ruiter PC, d’Hertefeldt T, Frouz J, Hedlund K, Hemerik L, Hol WHG, Hotes S, Mortimer SR, Setälä H, Sgardelis SP, Uteseny K, van der Putten WH, Wolters V, Bardgett RD (2013) Soil food web properties explain ecosystem services across European land use systems. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 110, 14296-14301. |
| [11] | Delgado-Baquerizo M, Eldridge DJ, Ochoa V, Gozalo B, Singh BK, Maestre FT (2017) Soil microbial communities drive the resistance of ecosystem multifunctionality to global change in drylands across the globe. Ecology Letters, 20, 1295-1305. |
| [51] | Zhao WZ, Yang R, Liu B, Yang QY, Li F (2016) Oasification of northwestern China: A review. Journal of Desert Research, 36, 1-5. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [赵文智, 杨荣, 刘冰, 杨淇越, 李芳 (2016) 中国绿洲化及其研究进展. 中国沙漠, 36, 1-5.] | |
| [12] | Delgado-Baquerizo M, Maestre FT, Reich PB, Jeffries TC, Gaitan JJ, Encinar D, Berdugo M, Campbell CD, Singh BK (2016) Microbial diversity drives multifunctionality in terrestrial ecosystems. Nature Communications, 7, 10541. doi.org/10.1038/ncomms10541. |
| [13] | Filser J, Fromm H, Nagel RF, Winter K (1995) Effects of previous intensive agricultural management on microorganisms and the biodiversity of soil fauna. Plant and Soil, 170, 123-129. |
| [14] | Gong J, Qian DW, Zhang LL, Xie YC, Gao YJ (2016) Spatiotemporal change of oasis/desert land and its landscape response in Linze County in recent 35 years. Arid Zone Research, 33, 805-813. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [巩杰, 钱大文, 张玲玲, 谢余初, 高彦净 (2016) 近35 a 临泽县绿洲-荒漠土地变化及其景观响应. 干旱区研究, 33, 805-813.] | |
| [52] | Zheng LY, Gui H (1999) Classification of Insects in China. Nanjing Normal University Publishing House, Nanjing. (in Chinese) |
| [郑乐怡, 归鸿 (1999) 昆虫分类. 南京师范大学出版社, 南京.] | |
| [15] | Guan PT, Zhang XK, Yu J, Cheng YY, Li Q, Andriuzzi WS, Liang WJ (2018) Soil microbial food web channels associated with biological soil crusts in desertification restoration: The carbon flow from microbes to nematodes. Soil Biology & Biochemistry, 116, 82-90. |
| [16] | Guan SY (1986)Soil Enzyme and Its Research Methods. Agriculture Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [关松荫 (1986) 土壤酶及其研究法. 农业出版社, 北京.] | |
| [17] | Han DL (1999) The process of research on oasis in China. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 19, 313-319. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [韩德林 (1999) 中国绿洲研究之进展. 地理科学, 19, 313-319.] | |
| [18] | Hu R, Wang XP, Zhang YF, Shi W, Jin YX, Chen N (2016) Insight into the influence of sand-stabilizing shrubs on soil enzyme activity in a temperate desert. Catena, 137, 526-535. |
| [19] | Institute of Soil Science, Chinese Academy of Sciences(1978) Analytical Methods of Soil Physical and Chemical Properties. Shanghai Science and Technology Press, Shanghai. (in Chinese) |
| [中国科学院南京土壤研究所(1978) 土壤理化分析. 上海科学技术出版社, 上海.] | |
| [20] | Jangid K, Williams MA, Franzluebbers AJ, Sanderlin JS, Reeves JH, Jenkins MB, Endale DM, Coleman DC, Whitman WB (2008) Relative impacts of land-use, management intensity and fertilization upon soil microbial community structure in agricultural systems. Soil Biology & Biochemistry, 40, 2843-2853. |
| [21] | Jia BQ, Ci LJ (2003)The Ecological Research of Oasis Landscape. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [贾保全, 慈龙骏 (2003) 绿洲景观生态研究. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [22] | Jia HR, Geng LL, Li YH, Wang Q, Diao QY, Zhou T, Dai PL (2016) The effects of Bt Cry1Ie toxin on bacterial diversity in the midgut of Apis mellifera ligustica (Hymenoptera: Apidae). Scientific Reports, 6, 24664. doi:10.1038/srep24664. |
| [23] | Koellner T, Geyer R (2013) Global land use impact assessment on biodiversity and ecosystem services in LCA. International Journal of Life Cycle Assessment, 18, 1185-1187. |
| [24] | Li CH, Tang LS, Jia ZJ, Li Y (2015) Profile changes in the soil microbial community when desert becomes oasis. PLoS ONE, 10, e0139626. doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0139626. |
| [25] | Li FR, Feng Q, Liu JL, Sun TS, Ren W, Guan ZH (2013) Effects of the conversion of native vegetation to farmlands on soil microarthropod biodiversity and ecosystem functioning in a desert oasis. Ecosystems, 16, 1364-1377. |
| [26] | Li FR, Liu JL, Hua W, Niu RX, Liu QJ, Liu CA (2011) Trophic group responses of ground arthropods to land-cover change and management disturbance. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 31, 4169-4181. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [李锋瑞, 刘继亮, 化伟, 牛瑞雪, 刘七军, 刘长安 (2011) 地面节肢动物营养类群对土地覆被变化和管理扰动的响应. 生态学报, 31, 4169-4181.] | |
| [27] | Li FR, Liu JL, Sun TS, Jin BW, Chen LJ (2014) Converting natural vegetation to farmland alters functional structure of ground-dwelling beetles and spiders in a desert oasis. Journal of Insect Conservation, 18, 57-67. |
| [28] | Li T, Su J, Xu ZQ, Li XL, Han GD, Zhang JP (2017) The distribution and dynamic of Curculionidae on Haloxylon ammodendron in Gurbantünggüt Desert. Journal of Shihezi University (Natural Science), 35, 201-206. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [李婷, 苏杰, 许照强, 李兴龙, 韩国栋, 张建萍 (2017) 古尔班通古特沙漠梭梭林象甲科昆虫分布及其动态研究. 石河子大学学报(自然科学版), 35, 201-206.] | |
| [29] | Lin XG (2010)Principles and Methods of Soil Microbiology Research. Higher Education Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [林先贵 (2010) 土壤微生物原理与方法. 高等教育出版社, 北京.] | |
| [30] | Liu JL, Li FR, Liu LL, Yang K (2017) Responses of different Collembola and mite taxa to experimental rain pulses in an arid ecosystem. Catena, 155, 53-61. |
| [31] | Liu JL, Li FR, Liu QJ, Niu RX (2010) Composition and diversity of surface-active soil fauna communities in arid desert ecosystems of the Heihe Basin. Journal of Desert Research, 30, 342-349. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [刘继亮, 李锋瑞, 刘七军, 牛瑞雪 (2010) 黑河流域干旱荒漠土壤动物群落组成与多样性的季节变异. 中国沙漠, 30, 342-349.] | |
| [32] | Liu RT, Zhao HL, Zhao XY (2012) Effects of different afforestation types on soil faunal diversity in Horqin Sand Land. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 23, 1104-1110. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [刘任涛, 赵哈林, 赵学勇 (2012) 科尔沁沙地不同造林类型对土壤动物多样性的影响. 应用生态学报, 23, 1104-1110.] | |
| [33] | Liu YH, Yu ZR, Gu WB, Axmacher JC (2006) Diversity of carabids (Coleoptera, Carabidae) in the desalinized agricultural landscape of Quzhou County, China. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 113, 45-50. |
| [34] | Newbold T, Hudson LN, Hill SLL, Contu S, Lysenko I, Senior RA, Börger L, Bennett DJ, Choimes A, Collen B, Day J, Palma AD, Díaz S, Echeverria-Londoño S, Edgar MJ, Feldman A, Garon M, Harrison MLK, Alhusseini T, Ingram DJ, Itescu Y, Kattge J, Kemp V, Kirkpatrick L, Kleyer M, Correia DLP, Martin CD, Meiri S, Novosolov M, Pan Y, Phillips HRP, Purves DW, Robinson A, Simpson J, Tuck SL, Weiher E, White HJ, Ewers RM, Mace GM, Scharlemann JPW, Purvis A (2015) Global effects of land use on local terrestrial biodiversity. Nature, 520, 45-50. |
| [35] | Nielsen UN, Ayres E, Wall DH, Bardgett RD (2011) Soil biodiversity and carbon cycling: A review and synthesis of studies examining diversity-function relationships. European Journal of Soil Science, 62, 105-116. |
| [36] | Nielsen UN, Ball BA (2015) Impacts of altered precipitation regimes on soil communities and biogeochemistry in arid and semi-arid ecosystems. Global Change Biology, 21, 1407-1421. |
| [37] | Nielsen UN, Osler GHR, Campbell CD, Burslem DFRP, van der Wal R (2010) The influence of vegetation type, soil properties and precipitation on the composition of soil mite and microbial communities at the landscape scale. Journal of Biogeography, 37, 1317-1328. |
| [38] | Owojori OJ, Reinecke AJ, Voua-Otomo P, Reinecke SA (2009) Comparative study of the effects of salinity on life-cycle parameters of four soil-dwelling species (Folsomia candida, Enchytraeus doerjesi, Eisenia fetida and Aporrectodea caliginosa). Pedobiologia, 52, 351-360. |
| [39] | Pan XL, Ma YJ, Gao W, Qi JG, Shi QD, Lu HY (2004) The eco-environmental evolution in arid area of West China. Journal of Desert Research, 24, 663-673. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [潘晓玲, 马映军, 高炜, 齐家国, 师庆东, 陆海燕 (2004) 中国西部干旱区生态环境演变过程. 中国沙漠, 24, 663-673.] | |
| [53] | Zhou ZY, Li FR, Chen SK, Zhang HR, Li G (2011) Dynamics of vegetation and soil carbon and nitrogen accumulation over 26 years under controlled grazing in a desert shrubland. Plant and Soil, 341, 257-268. |
| [40] | Paz-Kagan T, Caras T, Herrmann I, Shachak M, Karnieli A (2017) Multiscale mapping of species diversity under changed land use using imaging spectroscopy. Ecological Applications, 27, 1466-1484. |
| [1] | 吴乐婕, 刘泽康, 田星, 张群, 李博, 吴纪华. 海三棱藨草基因型多样性对种群营养生长和繁殖策略的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(4): 23478-. |
| [2] | 王文婷, 王蓉, 牛翠平, 白杨, 杨效东. 西双版纳农林复合橡胶林土壤多营养级生物网络结构[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(6): 22626-. |
| [3] | 张琼悦, 邓卓迪, 胡学斌, 丁志锋, 肖荣波, 修晨, 吴政浩, 汪光, 韩东晖, 张语克, 梁健超, 胡慧建. 粤港澳大湾区城市化进程对区域内鸟类分布及栖息地连通性的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(3): 22161-. |
| [4] | 朱柏菁, 薛敬荣, 夏蓉, 靳苗苗, 吴攸, 田善义, 陈小云, 刘满强, 胡锋. 不同土壤线虫功能团对水稻生长及地上部植食者的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2019, 27(4): 409-418. |
| [5] | 孙孝平,李双,余建平,方彦君,张银龙,曹铭昌. 基于土地利用变化情景的生态系统服务价值评估: 以钱江源国家公园体制试点区为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2019, 27(1): 51-63. |
| [6] | 蒋林惠, 罗琌, 肖正高, 李大明, 陈小云, 刘满强, 胡锋. 长期施肥对水稻生长和抗虫性的影响: 解析土壤生物的贡献[J]. 生物多样性, 2016, 24(8): 907-915. |
| [7] | 徐德琳, 邹长新, 徐梦佳, 游广永, 吴丹. 基于生态保护红线的生态安全格局构建[J]. 生物多样性, 2015, 23(6): 740-746. |
| [8] | 颜绍馗, Anand Narain Singh, 邱红兵, 张伟东, 汪思龙, 崔洋. DG指数在定量多样性时的缺陷及其内涵解析[J]. 生物多样性, 2009, 17(5): 524-530. |
| [9] | 王邵军, 阮宏华. 土壤生物对地上生物的反馈作用及其机制[J]. 生物多样性, 2008, 16(4): 407-416. |
| [10] | 傅声雷. 土壤生物多样性的研究概况与发展趋势[J]. 生物多样性, 2007, 15(2): 109-115. |
| [11] | 陈慧丽, 李玉娟, 李博, 陈家宽, 吴纪华. 外来植物入侵对土壤生物多样性和生态系统过程的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2005, 13(6): 555-565. |
| [12] | 韩兴国, 王智平. 土壤生物多样性与微量气体(CO2、CH4、N2O)代谢[J]. 生物多样性, 2003, 11(4): 322-332. |
| [13] | 王洪兴, 陈欣, 唐建军, 志水胜好. 释放后的转抗病虫基因作物对土壤生物群落的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2002, 10(2): 232-237. |
| [14] | 叶属峰, 陆健健. 无脊椎动物金属硫蛋白(MTs)多样性及其生态服务功能[J]. 生物多样性, 2000, 08(3): 317-324. |
| [15] | 章家恩. 土壤生物多样性的研究内容及持续利用展望[J]. 生物多样性, 1999, 07(2): 140-144. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn