



生物多样性 ›› 2017, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (8): 807-815. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2016360 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2016360
所属专题: 物种形成与系统进化
收稿日期:2016-12-21
接受日期:2017-07-01
出版日期:2017-08-20
发布日期:2017-08-31
通讯作者:
任明迅
作者简介:具体评估过程包括信息汇总(各个渠道的标本信息、野外调查信息及文献资料)、逐条比对IUCN红色名录等级与标准、确定等级、填写评估说明。在具体评估过程中, 针对不同类群设计信息调查表, 通过电话和邮件向多位同行征询物种的居群信息。
基金资助:
Shaojun Ling, Qianwan Meng, Liang Tang, Mingxun Ren*( )
)
Received:2016-12-21
Accepted:2017-07-01
Online:2017-08-20
Published:2017-08-31
Contact:
Ren Mingxun
摘要:
岛屿是开展生物区系与生物地理学研究的天然实验室。海南岛是中国唯一的热带大陆性岛屿, 地处中国-喜马拉雅植物亚区和马来西亚亚区交界地带, 物种来源与迁移历史十分复杂。本文首先分析了海南岛苦苣苔科物种多样性与地理分布格局, 然后利用核基因ITS1/2和叶绿体基因trnL-F序列建立海南岛苦苣苔科植物的系统发育树, 揭示其物种迁移历史与特有类群的形成时间。海南岛苦苣苔科野生类群虽然仅有14属24种, 但包括了扁蒴苣苔属(Cathayanthe)和盾叶苣苔属(Metapetrocosme) 2个特有属、8个特有种(含1变种)。面积归一化处理后, 海南岛该科的特有种比例仅次于广西, 远高于云南和邻国越南。物种组成相似度分析结果显示, 海南岛与广东省的共有物种最多, 这可能是第三纪末期(~3 Ma)几度海进海退过程中, 海南岛通过雷州半岛与广东多次连接的结果。海南岛苦苣苔科植物在海拔400-1,000 m和1,400 m以上形成2个集中分布区, 特有种则集中分布在高海拔区域, 表明海南岛中南部连绵的高山是苦苣苔科特有种形成与维持的一个重要原因。海南岛有着亚洲苦苣苔科的多个基部类群, 且都与东南亚共享; 海南岛-中国大陆分布的类群则处于系统树的较新分支, 表明海南岛苦苣苔科植物早期是从东南亚迁入。海南岛两个特有属的形成时间约在12 Ma, 特有种也都在15-5 Ma才分化出来, 这可能与印度板块撞击亚欧板块导致的东亚季风气候(约28 Ma)和此时海南岛远距大陆约100 km造成的隔离作用有关。
凌少军, 孟千万, 唐亮, 任明迅 (2017) 海南岛苦苣苔科植物的地理分布格局与系统发育关系. 生物多样性, 25, 807-815. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2016360.
Shaojun Ling, Qianwan Meng, Liang Tang, Mingxun Ren (2017) Gesneriaceae on Hainan Island: distribution patterns and phylogenetic relationships. Biodiversity Science, 25, 807-815. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2016360.
| 地区 Region | 面积 Area (×104 km2) | 海拔高差 Elevation range (m) | 物种数 No. of species | 特有种数 No. of endemic species | 物种密度 Species density | 特有指数 Endemic index | 与海南岛相似性的Jaccard指数 Jaccard index of similarity between the region and Hainan Island |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 海南岛 Hainan Island | 3.54 | 1,867 | 24 | 8 | 18.985 | 0.396 | — |
| 云南 Yunnan | 39.10 | 6,664 | 236 | 106 | 64.373 | 0.222 | 0.040 |
| 广西 Guangxi | 23.67 | 2,141 | 211 | 120 | 66.683 | 0.417 | 0.044 |
| 贵州 Guizhou | 17.62 | 2,793 | 97 | 28 | 33.809 | 0.141 | 0.052 |
| 广东 Guangdong | 17.98 | 1,882 | 60 | 20 | 20.767 | 0.173 | 0.167 |
| 越南 Vietnam | 32.90 | 3,143 | 60 | 21 | 17.175 | 0.154 | 0.050 |
表1 海南岛与邻近地区苦苣苔科物种多样性比较
Table 1 Comparison of species diversity of Gesneriaceae between Hainan Island with its nearby regions
| 地区 Region | 面积 Area (×104 km2) | 海拔高差 Elevation range (m) | 物种数 No. of species | 特有种数 No. of endemic species | 物种密度 Species density | 特有指数 Endemic index | 与海南岛相似性的Jaccard指数 Jaccard index of similarity between the region and Hainan Island |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 海南岛 Hainan Island | 3.54 | 1,867 | 24 | 8 | 18.985 | 0.396 | — |
| 云南 Yunnan | 39.10 | 6,664 | 236 | 106 | 64.373 | 0.222 | 0.040 |
| 广西 Guangxi | 23.67 | 2,141 | 211 | 120 | 66.683 | 0.417 | 0.044 |
| 贵州 Guizhou | 17.62 | 2,793 | 97 | 28 | 33.809 | 0.141 | 0.052 |
| 广东 Guangdong | 17.98 | 1,882 | 60 | 20 | 20.767 | 0.173 | 0.167 |
| 越南 Vietnam | 32.90 | 3,143 | 60 | 21 | 17.175 | 0.154 | 0.050 |
| DNA片段 DNA fragment | 引物序列 Sequence | 片段大小 Fragment size | 参考文献 Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| 核基因片段 ITS1/2 | ITS1: TCCGTAGGTGAACCTGCGG | 851 bp | White et al, 1990 |
| ITS2: GCTGCGTTCTTCATCGATGC | |||
| 叶绿体基因片段 trnL-F | trnL: CGAAATCGGTAGACGCTAGG | 859 bp | Wang et al, 2010 |
| trnF: ATTTGAACTGGTGACACGAG |
表2 确定苦苣苔科植物系统关系的DNA片段及其引物
Table 2 DNA fragments and the primers used for phylogenetic studies of Gesneriaceae species
| DNA片段 DNA fragment | 引物序列 Sequence | 片段大小 Fragment size | 参考文献 Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| 核基因片段 ITS1/2 | ITS1: TCCGTAGGTGAACCTGCGG | 851 bp | White et al, 1990 |
| ITS2: GCTGCGTTCTTCATCGATGC | |||
| 叶绿体基因片段 trnL-F | trnL: CGAAATCGGTAGACGCTAGG | 859 bp | Wang et al, 2010 |
| trnF: ATTTGAACTGGTGACACGAG |
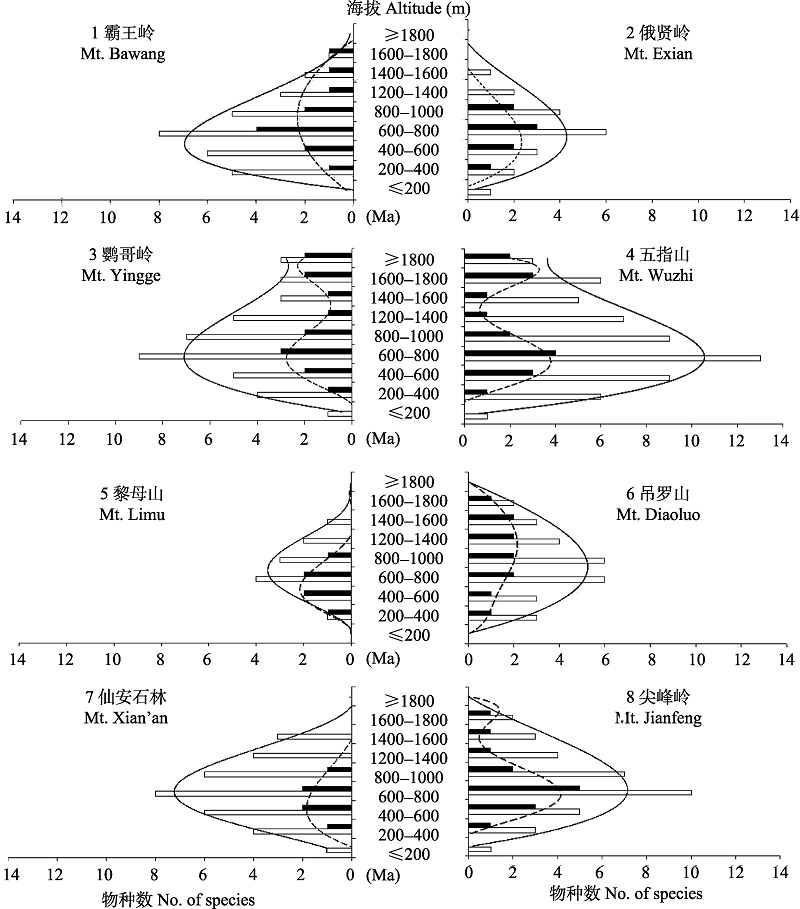
图2 海南岛苦苣苔科物种多样性的垂直分布。□所有物种; ■ 特有种。
Fig. 2 Altitudinal distribution of species diversity of Gesneriaceae on Hainan Island. □ All species, ■ Hainan-endemic species.
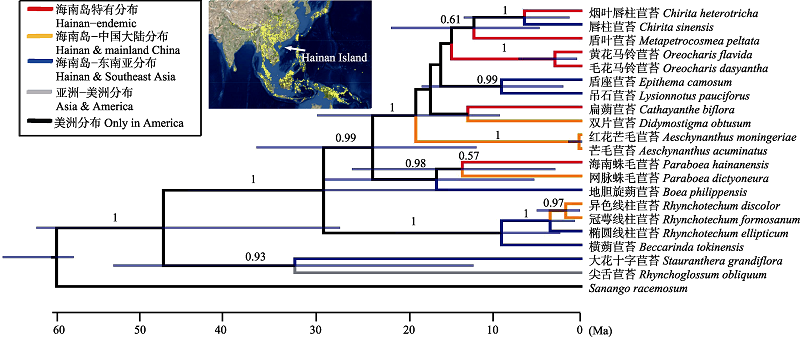
图3 根据ITS和trnL-F序列建立的海南岛苦苣苔科物种系统发育树。上方的地图显示了苦苣苔亚科在亚洲的地理分布, 示海南岛位于分布区中心。分支上的数值表示支持率。
Fig. 3 Phylogenetic tree of Hainan Gesneriaceae based on ITS and trnL-F. The insert map shows the geographical distribution of Asian Gesneriaceae. Note that Hainan Island locates at the center of the distribution range. The values above branches represent Bayesian posterior probabilities.
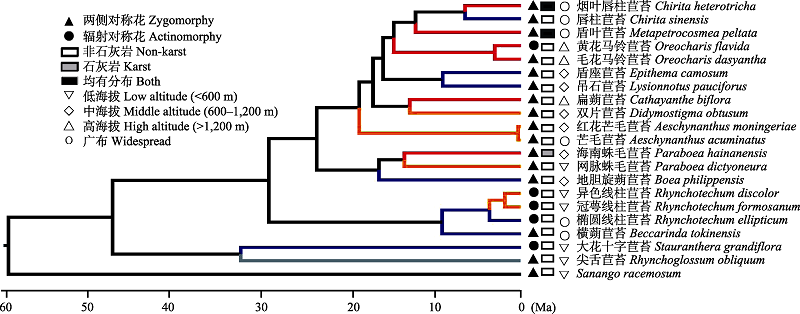
图4 海南岛苦苣苔科植物花对称性、分布生境与海拔的转变。分支颜色含义同图3。
Fig. 4 Transitions of floral symmetry, habitat type and distribution altitude of Gesneriaceae on Hainan Isand. See Fig. 3 for the indication of branch color.
| [9] | Jaccard P (1912) The distribution of the flora in the alpine zone. New Phytologist, 11(2), 37-50. |
| [10] | Jiang YX (1988) A background analysis of the flora and the characteristics of tropical vegetation in Hainan Island. Natural Sciences of Journal of Hainan University, 6(3), 1-8. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [蒋有绪 (1988) 海南岛植物区系与热带植被性质的背景分析. 海南大学学报(自然科学版), 6(3), 1-8.] | |
| [11] | Knowles LL (2001) Genealogical portraits of speciation in montane grasshoppers (genus Malanoplus) from the sky island of the Rocky Mountains. Proceeding of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 268, 319-324. |
| [12] | Kumar S, Nei M, Dudley J, Tamura K (2008) MEGA: a biologist-centric software for evolutionary analysis of DNA and protein sequences. Briefings in Bioinformatics, 9, 299-306. |
| [13] | Li R, Sun H (2017) Phylofloristics: a case study from Yunnan, China. Biodiversity Science, 25, 195-203. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [李嵘, 孙航 (2017) 植物系统发育区系地理学研究: 以云南植物区系为例. 生物多样性, 25, 195-203.] | |
| [14] | Li ZY (1996) The geographical distribution of the subfamily Cyrtanroideae Endl. Emend. Burtt (Gesneriaceae). Acta Phytotaxonmica Sinica, 34, 341-360. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [李振宇 (1996) 苦苣苔亚科的地理分布. 植物分类学报, 34, 341-360.] | |
| [15] | Li ZY, Wang YZ (2005) Plants of Gesneriaceae in China. Henan Science and Technology Publishing House, Zhengzhou. (in Chinese) |
| [李振宇, 王印政 (2005) 中国苦苣苔科植物. 河南科学技术出版社, 郑州.] | |
| [16] | Liang GH (2013) Eight evidences on Hainan Island separating from China’s Beibuwan Gulf with rotation. Acta Geologica Sinica, 87, 73-76. |
| [17] | Ling SJ, Meng QW, Tang L, Ren MX (2017) Pollination syndromes of Chinese Gesneriaceae: a comparative study between Hainan Island and neighboring regions. Botanical Review, 83, 59-74. |
| [18] | Losos JB, Ricklefs RE (2010) The Theory of Island Biogeography Revisited. Princeton University Press, New Jersey. |
| [19] | MacArthur RH, Wilson EO(1967) The Theory of Island Biogeography. Princeton University Press, New Jersey. |
| [20] | Martén-Rodríguez SA, Quesada M, Castro AA, Lopezaraiza-Mikel M, Fenster CB (2015) A comparison of reproductive strategies between island and mainland Caribbean Gesneriaceae. Journal of Ecology, 103, 1190-1204. |
| [21] | Myers N, Mittermeier RA, Mittermeier CG, Da FG, Kent J (2000) Biodiversity hotspots for conservation priorities. Nature, 403, 853-858. |
| [22] | Möller M, Forrest A, Wei YG, Weber A (2010) A molecular phylogenetic assessment of the advanced Asiatic and Malesian didymocarpoid Gesneriaceae with focus on non-monophyletic and monotypic genera. Plant Systematics and Evolution, 292, 223-248. |
| [23] | Möller M, Wei YG, Wen F, Clark JL, Weber A (2016) You win some you lose some: updated generic delineations and classification of Gesneriaceae—implications for the family in China. Guihaia, 36, 44-60. |
| [24] | Perret M, Chautems A, Araujo AOD, Salamin N (2013) Temporal and spatial origin of Gesneriaceae in the New World inferred from plastid DNA sequences. Botanical Journal of the Linnean Society, 171, 61-79. |
| [25] | Pham HH (1991) An Illustrated Flora in Vietnam. Mekong Printing, Can Tho City. |
| [26] | Posada D, Crandall KA (1998) MODELTEST: testing the model of DNA substitution. Bioinformatics, 14, 817-818. |
| [27] | Robin VV, Vishnudas CK, Gupta P, Ramakrishnan U (2015) Deep and wide valleys drive nested phylogeographic patterns across a montane bird community. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 282, 20150861. |
| [28] | Su ZY, Zhang HD (1994) The relationship between Guangxi’s flora and each of the adjacent floras. Journal of South China Agricultural University, 15(2), 38-43. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [苏志尧, 张宏达 (1994) 广西植物区系与邻近地区植物区系的关系. 华南农业大学学报, 15(2), 38-43.] | |
| [29] | Tang ZY, Wang ZH, Zheng CY, Fang JY (2006) Biodiversity in China’s mountains. Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment, 4, 347-352. |
| [30] | Vaidya G, Lohman DJ, Meier R (2011) SequenceMatrix: concatenation software for the fast assembly of multi-gene datasets with character set and codon information. Cladistics, 27, 171-180. |
| [31] | Wang FG, Qin XS, Chen HF, Zhang RJ, Liu DM, Xing FW (2006) Endemic plants in limestone region on Hainan Island. Journal of Tropical and Subtropical Botany, 14, 45-54. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王发国, 秦新生, 陈红锋, 张荣京, 刘东明, 邢福武 (2006) 海南岛石灰岩特有植物的初步研究. 热带亚热带植物学报, 14, 45-54.] | |
| [32] | Wang HS (2000) The nature of China’s flora and the relationships between its different elements. Acta Botanica Yunnanica, 22, 119-126. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王荷生 (2000) 中国植物区系的性质和各成分间的关系. 云南植物研究, 22, 119-126.] | |
| [1] | Barrett SCH, Emerson B, Mallet J (1996) The reproductive biology and genetics of island plants. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 351, 725-733. |
| [2] | Bramwell D, Caujapé-Castells J (2011) The Biology of Island Floras. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge. |
| [33] | Wang YZ, Liang RH, Wang BH, Li JM, Qiu ZY, Weber A (2010) Origin and phylogenetic relationships of the Old World Gesneriaceae with actinomorphic flowers inferred from ITS and trnL-trnF sequences. Taxon, 59, 1044-1052. |
| [34] | Wei YG, Zhong SH, Wen HQ (2004) Studies of the flora and ecology Gesneriaceae in Guangxi Province. Acta Botanica Yunnanica, 26, 173-182. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [3] | Chen SB, Ouyang ZY, Xu WH, Xiao Y (2010) A review of beta diversity studies. Biodiversity Science, 18, 323-335. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [陈圣宾, 欧阳志云, 徐卫华, 肖燚 (2010) Beta多样性研究进展. 生物多样性, 18, 323-335.] | |
| [34] | [韦毅刚, 钟树华, 文和群 (2004) 广西苦苣苔科植物区系和生态特点研究. 云南植物研究, 26, 173-182.] |
| [35] | Wei YG (2010) Gesneriaceae of South China. Guangxi Science and Technology Publishing House, Nanning. (in Chinese) |
| [4] | Ding L, Tang WX, Luo WH, Pan B, Wei YG, Huang SX (2010) Floristic characteristics of endemic plants to Guangxi. Guihaia, 30, 202-208. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [丁莉, 唐文秀, 骆文华, 盘波, 韦毅刚, 黄仕训 (2010) 广西特有植物区系特征研究. 广西植物, 30, 202-208.] | |
| [35] | [韦毅刚 (2010) 华南苦苣苔科植物. 广西科学技术出版社, 南宁.] |
| [36] | White TJ, Bruns T, Lee S, Taylor J (1990) Amplification and direct sequencing of fungal ribosomal RNA genes for phylogenetics. In: PCR Protocols: A Guide to Methods and Applications (eds Innis MA, Gelfand DH, Sninsky JJ, White TJ), pp. 315-322. Academic Press, New York. |
| [5] | Doley JJ, Doley JL (1987) A rapid DNA isolation procedure for small quantities of fresh leaf tissue. Phytochemical Bulletin, 19, 11-15. |
| [6] | Drummond AJ, Rambaut A (2007) BEAST: Bayesian evolutionary analysis by sampling trees. BMC Evolutionary Biology, 7, 214. |
| [37] | Wu ZY, Sun H, Zhou ZK, Li DZ, Peng H (2011) Floristics of Seed Plants from China. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [吴征镒, 孙航, 周浙昆, 李德铢, 彭华 (2011) 中国种子植物区系地理. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [38] | Xing FW (1995) Endemic plants of Hainan Island. Journal of Tropical and Subtropical Botany, 3, 1-12. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [邢福武 (1995) 海南岛特有植物的研究. 热带亚热带植物学报, 3, 1-12.] | |
| [39] | Xing FW (2012) Inventory of Plant Species Diversity of Hainan. Huazhong University of Science and Technology Press, Wuhan. (in Chinese) |
| [7] | Francisco-Ortega J, Wang ZS, Wang FG, Xing FW, Liu H, Xiu H, Xu WX, Luo YB, Song XQ, Gale S, Boufford DE, Maunder M, An SQ (2010) Seed plant endemism on Hainan Island: a framework for conservation action. Botanical Review, 76, 346-376. |
| [8] | Gong YB, Huang SQ (2009) Floral symmetry: pollinator-mediated stabilizing selection on flower size in bilateral species. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 276, 4013-4020. |
| [39] | [邢福武 (2012) 海南植物物种多样性编目. 华中科技大学出版社, 武汉.] |
| [40] | Yang XB (2013) Flora of Hainan. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [杨小波 (2013) 海南植物名录. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [41] | Zhang CC, Liu LF (1983) The angiospermous flora of Hainan. Journal of Sun Yat-Sen University, (3), 67-73. |
| (in Chinese with English abstract) [张超常, 刘兰芳 (1983) 海南岛被子植物区系. 中山大学学报, (3), 67-73.] | |
| [42] | Zhang HD (1962) Characteristics of Guangdong flora. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Sunyatseni, (1), 3-36. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [张宏达 (1962) 广东植物区系的特点. 中山大学学报(自然科学版), (1) , 3-36.] | |
| [43] | Zhang HD (2001) The diversity of the Hainan Flora. Ecological Science, 20, 1-10. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [张宏达 (2001) 海南植物区系的多样性. 生态科学, 20, 1-10.] | |
| [44] | Zhu H (2016) Biogeographical evidences help revealing the origin of Hainan Island. PLoS ONE, 11, e0151941. |
| [1] | 吴晓晴 张美惠 葛苏婷 李漫淑 宋坤 沈国春 达良俊 张健. 上海近自然林重建过程中木本植物物种多样性与地上生物量的时空动态——以闵行区生态岛为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24444-. |
| [2] | 王太, 宋福俊, 张永胜, 娄忠玉, 张艳萍, 杜岩岩. 河西走廊内陆河水系鱼类多样性及资源现状[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24387-. |
| [3] | 张晶晶, 黄文彬, 陈奕廷, 杨泽鹏, 柯伟业, 彭昭杰, 魏世超, 张志伟, 胡怡思, 余文华, 周文良. 广东南澎列岛海洋生态国家级自然保护区造礁石珊瑚多样性及分布特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24424-. |
| [4] | 尚华丹, 张楚晴, 王梅, 裴文娅, 李国宏, 王鸿斌. 中国杨树害虫物种多样性及其地理分布[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24370-. |
| [5] | 吴昱萱, 王平, 胡晓生, 丁一, 彭甜恬, 植秋滢, 巴德木其其格, 李文杰, 关潇, 李俊生. 呼伦贝尔草地退化现状评估与植被特征变化[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24118-. |
| [6] | 洪德元. 分类学中的方法论小叙[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24541-. |
| [7] | 陈自宏, 张翼飞, 陈凯, 陈见影, 徐玲. 高黎贡山南段昆虫病原真菌物种多样性及影响因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(1): 24228-. |
| [8] | 谭珂, 宁瑶, 王仁芬, 王晴, 梁丹萍, 辛子兵, 温放. 中国苦苣苔科植物名录与地理分布数据集[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(1): 23275-. |
| [9] | 韩佳楠, 苏杨, 李霏, 刘君妍, 赵依林, 李琳, 赵建成, 梁红柱, 李敏. 河北省苔藓植物多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(9): 24096-. |
| [10] | 李东红, 郝媛媛, 甘辉林, 张航, 刘耀猛, 他富源, 胡桂馨. 祁连山北麓中段不同类型草地蝗虫种类及分布[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(9): 24119-. |
| [11] | 牛红玉, 陈璐, 赵恒月, 古丽扎尔·阿不都克力木, 张洪茂. 城市化对动物的影响: 从群落到个体[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(8): 23489-. |
| [12] | 白雪, 李正飞, 刘洋, 张君倩, 张多鹏, 罗鑫, 杨佳莉, 杜丽娜, 蒋玄空, 武瑞文, 谢志才. 西江流域大型底栖无脊椎动物物种多样性及维持机制[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(7): 23499-. |
| [13] | 许佳, 崔小娟, 张翼飞, 吴昌, 孙远东. 南岭地区鱼类多样性及其地理分布[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(7): 23482-. |
| [14] | 邝起宇, 胡亮. 广东东海岛与硇洲岛海域底栖贝类物种多样性及其地理分布[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(5): 24065-. |
| [15] | 赵勇强, 阎玺羽, 谢加琪, 侯梦婷, 陈丹梅, 臧丽鹏, 刘庆福, 隋明浈, 张广奇. 退化喀斯特森林自然恢复中不同生活史阶段木本植物物种多样性与群落构建[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(5): 23462-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn
![]()