



生物多样性 ›› 2017, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (3): 255-264. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2016274 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2016274
黄华1, 陈智发1, 刘德团1, 和国星2, 和荣华2, 李德铢1,*( ), 许琨1,*(
), 许琨1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2016-09-22
接受日期:2017-01-23
出版日期:2017-03-20
发布日期:2017-04-07
通讯作者:
李德铢,许琨
基金资助:
Hua Huang1, Zhifa Chen1, Detuan Liu1, Guoxing He2, Ronghua He2, Dezhu Li1,*( ), Kun Xu1,*(
), Kun Xu1,*( )
)
Received:2016-09-22
Accepted:2017-01-23
Online:2017-03-20
Published:2017-04-07
Contact:
Li Dezhu,Xu Kun
摘要:
云冷杉林是玉龙雪山东坡保存最完整的森林植被, 为了更好地了解其物种组成和群落结构等基本特征, 中国科学院昆明植物研究所联合玉龙雪山省级自然保护区管护局, 按照CTFS (Center for Tropical Forest Science)的样地建设标准, 于2012-2014年在玉龙雪山省级自然保护区内建立了25 ha (500 m × 500 m)的长期监测样地。本研究以样地内所有胸径(DBH) ≥ 1 cm的木本植物(不含竹子)为研究对象, 分析了该样地的区系成分、群落组成、垂直结构及径级结构。结果表明: 样地内DBH ≥ 1 cm的木本植物(不含竹子)独立个体数为47,751, 分属26科41属62种, 以温带分布尤其是北温带成分为主要区系特征。重要值 ≥ 1的物种有18个, 贡献了90.24%的重要值。群落垂直结构可分为4层, 川滇冷杉(Abies forrestii)、丽江云杉(Picea likiangensis)和帽斗栎(Quercus guajavifolia)为主林层优势种和建群种, 径级分布为峰型或近倒“J”型, 持续更新能力较好; 吴茱萸五加(Gamblea ciliata var. evodiifolia)、篦齿槭(Acer pectinatum)和短梗稠李(Padus brachypoda)是主亚林层的优势种, 在某些片段可形成落叶阔叶林的优势群落, 径级分布出现明显断层, 未来将出现衰退。西康花楸(Sorbus prattii)、桦叶荚蒾(Viburnum betulifolium)和云南杜鹃(Rhododendron yunnanense)是次林层的优势种; 灌木层假小檗(Berberis fallax)是样地内个体数最多的物种, 占总个体数的59.51%, 其重要值最高, 占总数的22.75%, 径级分布呈“L”型。
黄华, 陈智发, 刘德团, 和国星, 和荣华, 李德铢, 许琨 (2017) 玉龙雪山寒温性云冷杉林动态监测样地的物种组成及群落结构. 生物多样性, 25, 255-264. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2016274.
Hua Huang, Zhifa Chen, Detuan Liu, Guoxing He, Ronghua He, Dezhu Li, Kun Xu (2017) Species composition and community structure of the Yulongxueshan (Jade Dragon Snow Mountains) forest dynamics plot in the cold tem- perate spruce-fir forest, Southwest China. Biodiversity Science, 25, 255-264. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2016274.
| 科 Family | 属数 No. of genus | 种数 No. of species | 多度 Abundance | 胸高断面积 Basal area (m2) | 重要值 Importance values |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 小檗科 Berberidaceae | 1 | 3 | 28,697 | 5.05 | 23.34 |
| 松科 Pinaceae | 4 | 4 | 5,837 | 612.32 | 26.02 |
| 忍冬科 Caprifoliaceae | 3 | 7 | 2,888 | 7.46 | 8.21 |
| 蔷薇科 Rosaceae | 7 | 12 | 2,014 | 47.57 | 7.67 |
| 壳斗科 Fagaceae | 1 | 1 | 1,324 | 323.03 | 12.04 |
| 槭树科 Aceraceae | 1 | 4 | 1,315 | 67.32 | 5.68 |
| 杜鹃花科 Ericaceae | 1 | 5 | 1,265 | 17.33 | 2.83 |
| 五加科 Araliaceae | 2 | 2 | 1,243 | 67.50 | 4.93 |
| 冬青科 Aquifoliaceae | 1 | 1 | 656 | 0.32 | 1.40 |
| 清风藤科 Sabiaceae | 2 | 2 | 605 | 0.77 | 1.48 |
| 绣球花科 Hydrangeaceae | 1 | 1 | 528 | 2.51 | 1.70 |
| 樟科 Lauraceae | 1 | 2 | 402 | 3.39 | 1.40 |
| 卫矛科 Celastraceae | 1 | 2 | 374 | 1.20 | 1.31 |
| 茶藨子科 Grossulariaceae | 1 | 2 | 277 | 0.16 | 0.84 |
| 唇形科 Labiatae | 1 | 1 | 130 | 0.02 | 0.35 |
| 木樨科 Oleaceae | 2 | 2 | 53 | 0.49 | 0.23 |
| 五味子科 Schisandraceae | 1 | 1 | 52 | 0.03 | 0.14 |
| 红豆杉科 Taxaceae | 1 | 1 | 40 | 0.72 | 0.19 |
| 毛茛科 Ranunculaceae | 1 | 1 | 21 | 0.00 | 0.11 |
| 山茱萸科 Cornaceae | 2 | 2 | 8 | 0.11 | 0.04 |
| 杨柳科 Salicaceae | 1 | 1 | 5 | 0.03 | 0.02 |
| 柏科 Cupressaceae | 1 | 1 | 4 | 0.01 | 0.02 |
| 芍药科 Paeoniaceae | 1 | 1 | 4 | 0.00 | 0.02 |
| 菊科 Compositae | 1 | 1 | 4 | 0.00 | 0.01 |
| 旌节花科 Stachyuraceae | 1 | 1 | 4 | 0.04 | 0.01 |
| 椴树科 Tiliaceae | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.12 | 0.01 |
| 总计 Total | 41 | 62 | 47,751 | 1,157.47 | 100 |
表1 玉龙雪山云冷杉林25 ha样地的物种组成
Table 1 Species composition of the Yulongxueshan spruce-fir forest 25 ha dynamics plot
| 科 Family | 属数 No. of genus | 种数 No. of species | 多度 Abundance | 胸高断面积 Basal area (m2) | 重要值 Importance values |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 小檗科 Berberidaceae | 1 | 3 | 28,697 | 5.05 | 23.34 |
| 松科 Pinaceae | 4 | 4 | 5,837 | 612.32 | 26.02 |
| 忍冬科 Caprifoliaceae | 3 | 7 | 2,888 | 7.46 | 8.21 |
| 蔷薇科 Rosaceae | 7 | 12 | 2,014 | 47.57 | 7.67 |
| 壳斗科 Fagaceae | 1 | 1 | 1,324 | 323.03 | 12.04 |
| 槭树科 Aceraceae | 1 | 4 | 1,315 | 67.32 | 5.68 |
| 杜鹃花科 Ericaceae | 1 | 5 | 1,265 | 17.33 | 2.83 |
| 五加科 Araliaceae | 2 | 2 | 1,243 | 67.50 | 4.93 |
| 冬青科 Aquifoliaceae | 1 | 1 | 656 | 0.32 | 1.40 |
| 清风藤科 Sabiaceae | 2 | 2 | 605 | 0.77 | 1.48 |
| 绣球花科 Hydrangeaceae | 1 | 1 | 528 | 2.51 | 1.70 |
| 樟科 Lauraceae | 1 | 2 | 402 | 3.39 | 1.40 |
| 卫矛科 Celastraceae | 1 | 2 | 374 | 1.20 | 1.31 |
| 茶藨子科 Grossulariaceae | 1 | 2 | 277 | 0.16 | 0.84 |
| 唇形科 Labiatae | 1 | 1 | 130 | 0.02 | 0.35 |
| 木樨科 Oleaceae | 2 | 2 | 53 | 0.49 | 0.23 |
| 五味子科 Schisandraceae | 1 | 1 | 52 | 0.03 | 0.14 |
| 红豆杉科 Taxaceae | 1 | 1 | 40 | 0.72 | 0.19 |
| 毛茛科 Ranunculaceae | 1 | 1 | 21 | 0.00 | 0.11 |
| 山茱萸科 Cornaceae | 2 | 2 | 8 | 0.11 | 0.04 |
| 杨柳科 Salicaceae | 1 | 1 | 5 | 0.03 | 0.02 |
| 柏科 Cupressaceae | 1 | 1 | 4 | 0.01 | 0.02 |
| 芍药科 Paeoniaceae | 1 | 1 | 4 | 0.00 | 0.02 |
| 菊科 Compositae | 1 | 1 | 4 | 0.00 | 0.01 |
| 旌节花科 Stachyuraceae | 1 | 1 | 4 | 0.04 | 0.01 |
| 椴树科 Tiliaceae | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.12 | 0.01 |
| 总计 Total | 41 | 62 | 47,751 | 1,157.47 | 100 |
| 分布区类型 Areal types | 科数 No. of family | 属数 No. of genera |
|---|---|---|
| 1 世界广布 Cosmopolitan | 6 | - |
| 2 泛热带 Pantropic | 3 | 1 |
| 3 东亚(热带、亚热带)及热带南美间断 Tropical & Subtropical East Asia & (South) Tropical America disjuncted | 2 | 2 |
| 4 旧世界热带 Old World Tropics | - | 1 |
| 5 热带亚洲至热带大洋洲 Tropical Asia to Tropical Australasia Oceania | - | - |
| 6 热带亚洲至热带非洲 Tropical Asia to Tropical Africa | 1 | - |
| 7 热带东南亚至印度-马来, 太平洋诸岛(热带亚洲) Tropical Southeast Asia + Indo-Malaya + Tropical South & Southwest Pacific Island (Tropical Asia) | 1 | 1 |
| 8 北温带 North Temperate | 11 | 22 |
| 9 东亚及北美间断 East Asia & North America disjuncted | 1 | 3 |
| 10 旧世界温带 Old World Temperate | - | 3 |
| 11 温带亚洲 Temperate Asia | - | - |
| 12 地中海、西亚至中亚 Mediterranean, West to Central Asia | - | - |
| 13 中亚 Central Asia | - | - |
| 14 东亚 East Asia | 1 | 4 |
| 15 中国特有 Endemic to China | - | 1 |
| 16 南半球热带以外间断或星散分布 Extratropical South Hemisphere disjuncted or dispersed | - | - |
| 17 热带非洲-热带美洲间断 Tropical Africa & Tropical America disjuncted | - | - |
| 18 泛南极 Holantarctic | - | - |
| 合计 Total | 26 | 41 |
表2 玉龙雪山云冷杉林25 ha样地乔木种子植物的分布区类型
Table 2 Distribution types of spermatophytes in the Yulongxueshan spruce-fir forest 25 ha dynamics plot
| 分布区类型 Areal types | 科数 No. of family | 属数 No. of genera |
|---|---|---|
| 1 世界广布 Cosmopolitan | 6 | - |
| 2 泛热带 Pantropic | 3 | 1 |
| 3 东亚(热带、亚热带)及热带南美间断 Tropical & Subtropical East Asia & (South) Tropical America disjuncted | 2 | 2 |
| 4 旧世界热带 Old World Tropics | - | 1 |
| 5 热带亚洲至热带大洋洲 Tropical Asia to Tropical Australasia Oceania | - | - |
| 6 热带亚洲至热带非洲 Tropical Asia to Tropical Africa | 1 | - |
| 7 热带东南亚至印度-马来, 太平洋诸岛(热带亚洲) Tropical Southeast Asia + Indo-Malaya + Tropical South & Southwest Pacific Island (Tropical Asia) | 1 | 1 |
| 8 北温带 North Temperate | 11 | 22 |
| 9 东亚及北美间断 East Asia & North America disjuncted | 1 | 3 |
| 10 旧世界温带 Old World Temperate | - | 3 |
| 11 温带亚洲 Temperate Asia | - | - |
| 12 地中海、西亚至中亚 Mediterranean, West to Central Asia | - | - |
| 13 中亚 Central Asia | - | - |
| 14 东亚 East Asia | 1 | 4 |
| 15 中国特有 Endemic to China | - | 1 |
| 16 南半球热带以外间断或星散分布 Extratropical South Hemisphere disjuncted or dispersed | - | - |
| 17 热带非洲-热带美洲间断 Tropical Africa & Tropical America disjuncted | - | - |
| 18 泛南极 Holantarctic | - | - |
| 合计 Total | 26 | 41 |
| 物种 Species | 多度 Abundance | 相对频度 Relative frequency | 胸高断面积 Basal area (m2) | 胸径 DBH (mean ± SE) (cm) | 重要值 Importance values |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 假小檗 Berberis fallax | 28,416 | 8.31 | 4.98 | 1.44 ± 0.00 | 22.75 |
| 川滇冷杉 Abies forrestii | 5,207 | 7.78 | 379.53 | 19.63 ± 0.32 | 17.16 |
| 帽斗栎 Quercus guajavifolia | 1,324 | 5.45 | 323.03 | 45.09 ± 0.90 | 12.04 |
| 丽江云杉 Picea likiangensis | 596 | 4.78 | 225.75 | 50.84 ± 1.94 | 8.51 |
| 吴茱萸五加 Gamblea ciliata var. evodiifolia | 1,065 | 5.84 | 66.66 | 25.74 ± 0.36 | 4.61 |
| 篦齿槭 Acer pectinatum | 958 | 5.32 | 50.16 | 23.30 ± 0.36 | 3.89 |
| 西康花楸 Sorbus prattii | 915 | 5.80 | 12.36 | 11.78 ± 0.19 | 2.93 |
| 桦叶荚蒾 Viburnum betulifolium | 1,114 | 5.91 | 1.53 | 3.78 ± 0.05 | 2.79 |
| 云南杜鹃 Rhododendron yunnanense | 1,162 | 3.47 | 16.73 | 10.95 ± 0.23 | 2.45 |
| 短梗稠李 Padus brachypoda | 328 | 2.74 | 25.92 | 28.46 ± 0.77 | 1.89 |
| 唐古特忍冬 Lonicera tangutica | 671 | 4.02 | 0.54 | 2.78 ± 0.06 | 1.82 |
| 丽江山梅花 Philadelphus calvescens | 528 | 3.77 | 2.51 | 7.08 ± 0.14 | 1.70 |
| 陷脉冬青 Ilex delavayi | 656 | 2.79 | 0.32 | 2.20 ± 0.05 | 1.40 |
| 阔叶清风藤 Sabia yunnanensis subsp. latifolia | 581 | 2.82 | 0.39 | 2.63 ± 0.05 | 1.36 |
| 高山木姜子 Litsea chunii | 372 | 2.89 | 2.85 | 8.56 ± 0.26 | 1.30 |
| 湖北花楸 Sorbus hupehensis | 309 | 2.67 | 6.43 | 14.65 ± 0.40 | 1.29 |
| 紫花卫矛 Euonymus porphyreus | 366 | 2.95 | 0.91 | 5.05 ± 0.13 | 1.27 |
| 华西忍冬 Lonicera webbiana | 265 | 2.59 | 1.38 | 6.94 ± 0.26 | 1.09 |
| 云南双盾木 Dipelta yunnanensis | 385 | 1.88 | 3.19 | 9.64 ± 0.18 | 0.99 |
| 其他 Others | 2,533 | 18.20 | 32.31 | - | 8.77 |
| 总计 Total | 47,751 | 100 | 1,157.47 | - | 100 |
表3 玉龙雪山云冷杉林25 ha样地重要值 ≥ 1的物种
Table 3 Species with the importance value ≥ 1 in the Yulongxueshan spruce-fir forest 25 ha dynamics plot
| 物种 Species | 多度 Abundance | 相对频度 Relative frequency | 胸高断面积 Basal area (m2) | 胸径 DBH (mean ± SE) (cm) | 重要值 Importance values |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 假小檗 Berberis fallax | 28,416 | 8.31 | 4.98 | 1.44 ± 0.00 | 22.75 |
| 川滇冷杉 Abies forrestii | 5,207 | 7.78 | 379.53 | 19.63 ± 0.32 | 17.16 |
| 帽斗栎 Quercus guajavifolia | 1,324 | 5.45 | 323.03 | 45.09 ± 0.90 | 12.04 |
| 丽江云杉 Picea likiangensis | 596 | 4.78 | 225.75 | 50.84 ± 1.94 | 8.51 |
| 吴茱萸五加 Gamblea ciliata var. evodiifolia | 1,065 | 5.84 | 66.66 | 25.74 ± 0.36 | 4.61 |
| 篦齿槭 Acer pectinatum | 958 | 5.32 | 50.16 | 23.30 ± 0.36 | 3.89 |
| 西康花楸 Sorbus prattii | 915 | 5.80 | 12.36 | 11.78 ± 0.19 | 2.93 |
| 桦叶荚蒾 Viburnum betulifolium | 1,114 | 5.91 | 1.53 | 3.78 ± 0.05 | 2.79 |
| 云南杜鹃 Rhododendron yunnanense | 1,162 | 3.47 | 16.73 | 10.95 ± 0.23 | 2.45 |
| 短梗稠李 Padus brachypoda | 328 | 2.74 | 25.92 | 28.46 ± 0.77 | 1.89 |
| 唐古特忍冬 Lonicera tangutica | 671 | 4.02 | 0.54 | 2.78 ± 0.06 | 1.82 |
| 丽江山梅花 Philadelphus calvescens | 528 | 3.77 | 2.51 | 7.08 ± 0.14 | 1.70 |
| 陷脉冬青 Ilex delavayi | 656 | 2.79 | 0.32 | 2.20 ± 0.05 | 1.40 |
| 阔叶清风藤 Sabia yunnanensis subsp. latifolia | 581 | 2.82 | 0.39 | 2.63 ± 0.05 | 1.36 |
| 高山木姜子 Litsea chunii | 372 | 2.89 | 2.85 | 8.56 ± 0.26 | 1.30 |
| 湖北花楸 Sorbus hupehensis | 309 | 2.67 | 6.43 | 14.65 ± 0.40 | 1.29 |
| 紫花卫矛 Euonymus porphyreus | 366 | 2.95 | 0.91 | 5.05 ± 0.13 | 1.27 |
| 华西忍冬 Lonicera webbiana | 265 | 2.59 | 1.38 | 6.94 ± 0.26 | 1.09 |
| 云南双盾木 Dipelta yunnanensis | 385 | 1.88 | 3.19 | 9.64 ± 0.18 | 0.99 |
| 其他 Others | 2,533 | 18.20 | 32.31 | - | 8.77 |
| 总计 Total | 47,751 | 100 | 1,157.47 | - | 100 |
| 物种 Species | 占总个体数的比例 Accounts for the proportion of the total number of individuals (%) |
|---|---|
| 假小檗 Berberis fallax | 59.51 |
| 川滇冷杉 Abies forrestii | 10.90 |
| 帽斗栎 Quercus guajavifolia | 2.77 |
| 云南杜鹃 Rhododendron yunnanense | 2.43 |
| 桦叶荚蒾 Viburnum betulifolium | 2.33 |
| 吴茱萸五加 Gamblea ciliata var. evodiifolia | 2.23 |
| 篦齿槭 Acer pectinatum | 2.01 |
| 其他 Others | 17.81 |
表4 玉龙雪山云冷杉林25 ha样地物种数排名前7位的树种
Table 4 Top seven tree species with the maximum number in the Yulongxueshan spruce-fir forest 25 ha dynamics plot
| 物种 Species | 占总个体数的比例 Accounts for the proportion of the total number of individuals (%) |
|---|---|
| 假小檗 Berberis fallax | 59.51 |
| 川滇冷杉 Abies forrestii | 10.90 |
| 帽斗栎 Quercus guajavifolia | 2.77 |
| 云南杜鹃 Rhododendron yunnanense | 2.43 |
| 桦叶荚蒾 Viburnum betulifolium | 2.33 |
| 吴茱萸五加 Gamblea ciliata var. evodiifolia | 2.23 |
| 篦齿槭 Acer pectinatum | 2.01 |
| 其他 Others | 17.81 |
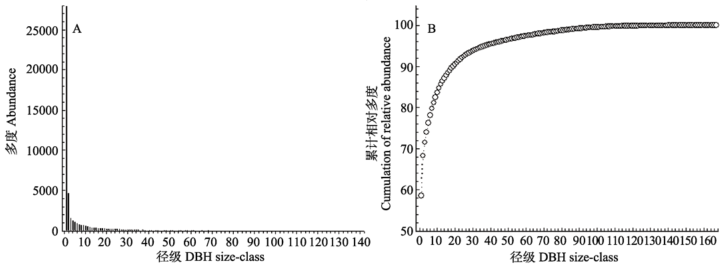
图3 玉龙雪山云冷杉林25 ha样地所有树种的径级分布图(A)和径级累计分布图(B)
Fig. 3 DBH size-class abundance (A) and cumulative distribution (B) of all tree species in the Yulongxueshan spruce-fir forest 25 ha dynamics plot
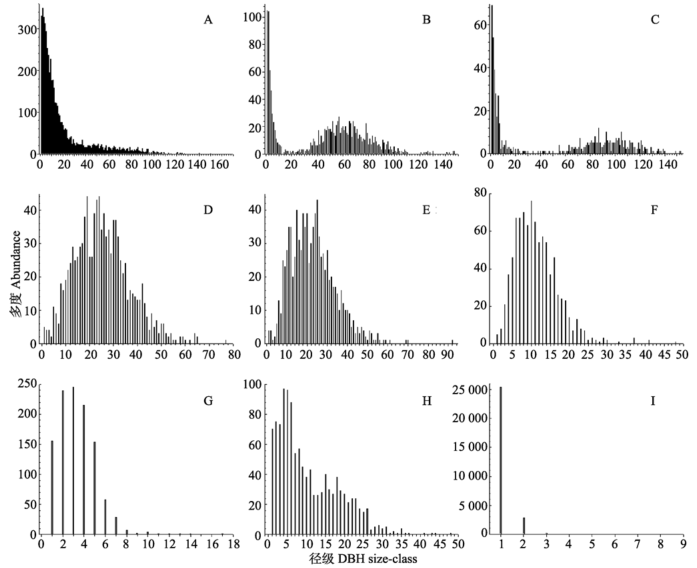
图5 9个优势物种的径级结构图。A, 川滇冷杉; B, 帽斗栎; C, 丽江云杉; D, 吴茱萸五加; E, 篦齿槭; F, 西康花楸; G, 桦叶荚蒾; H, 云南杜鹃; I, 假小檗。
Fig. 5 DBH size-class distribution of the nine dominant species. A, Abies forrestii; B, Quercus guajavifolia; C, Picea likiangensis; D, Gamblea ciliata var. evodiifolia; E, Acer pectinatum; F, Sorbus prattii; G, Viburnum betulifolium; H, Rhododendron yunnanense; I, Berberis fallax.
| 8 | Hooper DU, Chapin FS III, Ewel JJ, Hector A, Inchausti P, Lavorel S, Lawton JH, Lodge DM, Loreau M, Naeem S, Schmid B, Setala H, Symstad AJ, Vandermeer J, Wardle DA (2005) Effects of biodiversity on ecosystem functioning: a consensus of current knowledge. Ecological Monographs, 75, 3-35. |
| 9 | Hubbell SP, Foster RB (1986) Commonness and rarity in a neotropical forest: implications for tropical tree conservation. In: Conservation Biology: the Science of Scarcity and Diversity (ed. Soulé ME), pp. 205-231. Sinauer Associates, Sunderland. |
| 10 | Lan GY, Hu YH, Cao M, Zhu H, Wang H, Zhou SS, Deng XB, Cui JY, Huang JG, Liu LY, Xu HL, Song JP, He YC (2008) Establishment of Xishuangbanna tropical forest dynamic plot: species composition and spatial distribution pattern. Journal of Plant Ecology (Chinese Version), 32, 287-298.(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [兰国玉, 胡跃华, 曹敏, 朱华, 王洪, 周仕顺, 邓晓保, 崔景云, 黄建国, 刘林云, 许海龙, 宋军平, 何有才 (2008) 西双版纳热带森林动态监测样地——树种组成与空间分布格局. 植物生态学报 32, 287-298.] | |
| 11 | Li XW (1996) Floristic statistics and analyses of seed plants from China. Acta Botanica Yunnanica, 18, 363-384.(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [李锡文 (1996) 中国种子植物区系统计分析. 云南植物研究 18, 363-384.] | |
| 12 | Liu HF, Li L, Sang WG (2011) Species composition and community structure of the Donglingshan forest dynamic plot in a warm temperate deciduous broad-leaved secondary forest, China. Biodiversity Science, 19, 232-242.(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [刘海丰, 李亮, 桑卫国 (2011) 东灵山暖温带落叶阔叶次生林动态监测样地: 物种组成与群落结构. 生物多样性 19, 232-242.] | |
| 13 | Liu Q, Wu Y, Wu N (2003) Forest gap characteristic in a coniferous-Picea likiangensis forest in the Yulong Snow Mountain Natural Reserve, Yunnan Province, China. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 14, 845-848.(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [刘庆, 吴彦, 吴宁 (2003) 玉龙雪山自然保护区丽江云杉林林窗特征研究. 应用生态学报 14, 845-848.] | |
| 14 | Loreau M, Naeem S, Inchausti P, Bengtsson J, Grime JP, Hector A, Hooper DU, Huston MA, Raffaelli D, Schmid B, Tilman D, Wardle DA (2001) Biodiversity and ecosystem functioning: current knowledge and future challenge. Science, 294, 804-808. |
| 15 | Lu ZJ, Bao DC, Guo YL, Lu JM, Wang QG, He D, Zhang KH, Xu YN, Liu HB, Meng HJ, Huang HD, Wei XZ, Liao JX, Qiao XJ, Jiang MX, Gu ZR, Liao CL (2013) Community composition and structure of Badagongshan (BDGS) forest dynamic plot in a mid-tropical mountain evergreen and deciduous broad-leaved mixed forest, central China. Plant Science Journal, 31, 336-344.(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [卢志军, 鲍大川, 郭屹立, 路俊盟, 王庆刚, 何东, 张奎汉, 徐耀粘, 刘海波, 孟红杰, 黄汉东, 魏新增, 廖建雄, 乔秀娟, 江明喜, 谷志容, 廖春林 (2013) 八大公山中亚热带山地常绿落叶阔叶混交林物种组成与结构. 植物科学学报 31, 336-344.] | |
| 16 | Qu ZX, Wu YS, Jiang HQ, Tang TG (1983) Plant Ecology. Higher Education Press, Beijing.(in Chinese) |
| [曲仲湘, 吴玉树, 姜汉侨, 唐廷贵 (1983) 植物生态学. 高等教育出版社, 北京.] | |
| 17 | Sun RY, Li QF, Niu CJ, Lou AR (2002) Basic Ecology. Higher Education Press, Beijing.(in Chinese) |
| [孙儒泳, 李庆芬, 牛翠娟, 娄安如 (2002) 基础生态学. 高等教育出版社, 北京.] | |
| 18 | Tilman D, Reich PB, Knops JMH (2006) Biodiversity and ecosystem stability in a decade long grassland experiment. Nature, 441, 629-632. |
| 19 | Wang B, Huang YS, Li XK, Xiang WS, Ding T, Huang FZ, Lu SH, Han WH, Wen SJ, He LJ (2014) Species composition and spatial distribution of the 15 ha northern tropical karst seasonal rain forest dynamic plot in Nonggang of Guangxi, southern China. Biodiversity Science, 22, 141-156.(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王斌, 黄俞淞, 李先琨, 向悟生, 丁涛, 黄甫昭, 陆树华, 韩文衡, 文淑均, 何兰军 (2014) 弄岗北热带喀斯特季节性雨林15ha监测样地的树种组成与空间分布. 生物多样性 22, 141-156.] | |
| 20 | Wu ZY, Zhou ZK, Li DZ, Peng H, Sun H (2003) The areal- types of the world families of seed plant. Acta Botanica Yunanica, 25, 245-257.(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [吴征镒, 周浙昆, 李德铢, 彭华, 孙航 (2003) 世界种子植物科的分布区类型系统. 云南植物研究 25, 245-257.] | |
| 21 | Wu ZY, Zhu YC (1987) Vegetation in Yunnan. Science Press, Beijing. |
| (in Chinese) [吴征镒, 朱彦丞 (1987) 云南植被. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| 22 | Yang QS, Ma ZP, Xie YB, Zhang ZG, Wang ZH, Liu HM, Li P, Zhang N, Wang DL, Yang HB, Fang XF, Yan ER, Wang XH (2011) Community structure and species composition of an evergreen broad-leaved forest in Tiantong’s 20 ha dynamic plot, Zhejiang Province, eastern China. Biodiversity Science, 19, 215-223.(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [杨庆松, 马遵平, 谢玉彬, 张志国, 王樟华, 刘何铭, 李萍, 张娜, 王达力, 杨海波, 方晓峰, 阎恩荣, 王希华 (2011) 浙江天童20 ha常绿阔叶林动态监测样地的群落特征. 生物多样性 19, 215-223.] | |
| 23 | Ye WH, Cao HL, Huang ZL, Lian JY, Wang ZG, Li L, Wei SG, Wang ZM (2008) Community structure of a 20 ha lower subtropical evergreen broadleaved forest plot in Dinghushan, China. Journal of Plant Ecology (Chinese Version), 32, 274-286.(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [叶万辉, 曹洪麟, 黄忠良, 练琚愉, 王志高, 李林, 魏识广, 王章明 (2008) 鼎湖山南亚热带常绿阔叶林20 ha样地群落特征研究. 植物生态学报 32, 274-286.] | |
| 24 | Zhao SQ, Fang JY, Lei CG (2000) Global 200: an approach to setting large-scale biodiversity conservation priorities. Chinese Biodiversity, 8, 435-440.(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [赵淑清, 方精云, 雷光春 (2000) 全球200: 确定大尺度生物多样性优先保护的一种方法. 生物多样性 8, 435-440.] | |
| 25 | Zhu Y, Zhao GF, Zhang LW, Shen GC, Mi XC, Ren HB, Yu MJ, Chen JH, Chen SW, Fang T, Ma KP (2008) Community composition and structure of Gutianshan forest dynamics plot in a mid-subtropical evergreen broad-leaved forest, East China. Journal of Plant Ecology (Chinese Version), 32, 262-273.(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [祝燕, 赵谷风, 张俪文, 沈国春, 米湘成, 任海保, 于明坚, 陈建华, 陈声文, 方腾, 马克平 (2008) 古田山中亚热带常绿阔叶林动态监测样地——群落组成与结构. 植物生态学报 32, 262-273.] | |
| 1 | Condit R (1995) Research in large, long-term tropical forest plots. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 10, 18-22. |
| 2 | Condit R (1998) Tropical Forest Census Plots: Methods and Results from Barro Colorado Island, Panama and a Comparison with Other Plots. Springer, Berlin. |
| 3 | Feng JM, Wang XP, Li J, Fang JY (2006) Effect of area and mid-domain effect on altitudinal pattern of seed plants richness in Lijiang, Yunnan, China. Biodiversity Science, 14, 107-113.(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [冯建孟, 王襄平, 李晶, 方精云 (2006) 面积和中间膨胀效应对丽江地区种子植物物种丰富度垂直分布格局的影响. 生物多样性 14, 107-113.] | |
| 4 | Gao F, He RH, Liu DT, Liu WW, Chen ZF, Wu ZK, Huang H, Chen XL, Xu K (2013) Spatial and temporal patterns of the surface soil moisture in southern Jade Dragon Snow Mountain forest ecosystem. Journal of West China Forestry Science, 42(4), 87-90.(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [高富, 和荣华, 刘德团, 刘维暐, 陈智发, 吴之坤, 黄华, 陈小灵, 许琨 (2013) 玉龙雪山南段主要森林群落表层土壤水分的时空变化研究. 西部林业科学 42(4), 87-90.] | |
| 5 | Guo HJ, Long CL (1998) Biodiversity of Yunnan, SW China. Yunnan Science and Technology Press, Kunming.(in Chinese) |
| [郭辉军, 龙春林 (1998) 云南生物多样性. 云南科技出版社, 昆明.] | |
| 6 | Hao ZQ, Li BH, Zhang J, Wang XG, Ye J, Yao XL (2008) Broad-leaved Korean pine (Pinus koraiensis) mixed forest plot in Changbaishan (CBS) of China: community composition and structure. Journal of Plant Ecology (Chinese Version), 32, 238-250.(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [郝占庆, 李步杭, 张健, 王绪高, 叶吉, 姚晓琳 (2008) 长白山阔叶红松林样地(CBS): 群落组成与结构. 植物生态学报 32, 238-250.] | |
| 7 | He FL, Legendre P, LaFrankie JV (1997) Distribution patterns of tree species in a Malaysian tropical rain forest. Journal of Vegetation Science, 8, 105-114. |
| [1] | 干靓 刘巷序 鲁雪茗 岳星. 全球生物多样性热点地区大城市的保护政策与优化方向[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24529-. |
| [2] | 曾子轩 杨锐 黄越 陈路遥. 清华大学校园鸟类多样性特征与环境关联[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24373-. |
| [3] | 臧明月, 刘立, 马月, 徐徐, 胡飞龙, 卢晓强, 李佳琦, 于赐刚, 刘燕. 《昆明-蒙特利尔全球生物多样性框架》下的中国城市生物多样性保护[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24482-. |
| [4] | 祝晓雨, 王晨灏, 王忠君, 张玉钧. 城市绿地生物多样性研究进展与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 25027-. |
| [5] | 袁琳, 王思琦, 侯静轩. 大都市地区的自然留野:趋势与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24481-. |
| [6] | 胡敏, 李彬彬, Coraline Goron. 只绿是不够的: 一个生物多样性友好的城市公园管理框架[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24483-. |
| [7] | 王欣, 鲍风宇. 基于鸟类多样性提升的南滇池国家湿地公园生态修复效果分析[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24531-. |
| [8] | 明玥, 郝培尧, 谭铃千, 郑曦. 基于城市绿色高质量发展理念的中国城市生物多样性保护与提升研究[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24524-. |
| [9] | 谢淦, 宣晶, 付其迪, 魏泽, 薛凯, 雒海瑞, 高吉喜, 李敏. 草地植物多样性无人机调查的物种智能识别模型构建[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24236-. |
| [10] | 褚晓琳, 张全国. 演化速率假说的实验验证研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 25019-. |
| [11] | 宋威, 程才, 王嘉伟, 吴纪华. 土壤微生物对植物多样性–生态系统功能关系的调控作用[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24579-. |
| [12] | 卢晓强, 董姗姗, 马月, 徐徐, 邱凤, 臧明月, 万雅琼, 李孪鑫, 于赐刚, 刘燕. 前沿技术在生物多样性研究中的应用现状、挑战与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24440-. |
| [13] | 农荞伊, 曹军, 程文达, 彭艳琼. 不同方法对蜜蜂总科昆虫资源与多样性监测效果的比较[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 25057-. |
| [14] | 郭雨桐, 李素萃, 王智, 解焱, 杨雪, 周广金, 尤春赫, 朱萨宁, 高吉喜. 全国自然保护地对国家重点保护野生物种的覆盖度及其分布状况[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(3): 24423-. |
| [15] | 赵维洋, 王伟, 马冰然. 其他有效的区域保护措施(OECMs)研究进展与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(3): 24525-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn