



生物多样性 ›› 2016, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (6): 649-657. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2015290 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2015290
所属专题: 生物多样性与生态系统功能
欧阳明, 杨清培*( ), 陈昕, 杨光耀, 施建敏, 方向民
), 陈昕, 杨光耀, 施建敏, 方向民
收稿日期:2015-10-25
接受日期:2016-04-19
出版日期:2016-06-20
发布日期:2016-06-20
通讯作者:
杨清培
基金资助:
Ming Ouyang, Qingpei Yang*( ), Xin Chen, Guangyao Yang, Jianmin Shi, Xiangmin Fang
), Xin Chen, Guangyao Yang, Jianmin Shi, Xiangmin Fang
Received:2015-10-25
Accepted:2016-04-19
Online:2016-06-20
Published:2016-06-20
Contact:
Yang Qingpei
摘要:
毛竹(Phyllostachys edulis)向邻近次生常绿阔叶林扩张现象明显, 极大地影响了常绿阔叶林的生态功能, 但关于其扩张对常绿阔叶林的群落结构与生物多样性影响的后效研究较少。本文采用时空替代法, 在江西井冈山国家级自然保护区沿毛竹扩张方向, 依次设置毛竹林、竹阔混交林和常绿阔叶林样地, 比较分析了扩张前后群落物种相似性、群落结构和多样性指数等特征。结果表明: (1)毛竹林与常绿阔叶林乔木层、灌木层和草本层的Bray-Curtis相似性指数很小, 分别为0.003、0.046和0.030。(2)毛竹林的垂直结构呈“>”型, 高度12-14 m区间的多度百分比达33.3%, 径级结构集中分布于5-10 cm区间, 达总数的90.0%; 常绿阔叶林的垂直结构为“L”型, 高度2-4 m的物种数占54.3%, 径级分布范围较广, 4个较大径级区间的平均百分比为10.3%。(3)乔木层的Shannon-Wiener指数由常绿阔叶林的2.56降至毛竹林的0.06, 降幅高达98%; 灌木层也由2.58降至2.03, 降幅21%。以上结果说明, 毛竹扩张会导致次生常绿阔叶林群落组成和结构简化、物种多样性下降, 对森林生态系统功能产生负面影响。
欧阳明, 杨清培, 陈昕, 杨光耀, 施建敏, 方向民 (2016) 毛竹扩张对次生常绿阔叶林物种组成、结构与多样性的影响. 生物多样性, 24, 649-657. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2015290.
Ming Ouyang, Qingpei Yang, Xin Chen, Guangyao Yang, Jianmin Shi, Xiangmin Fang (2016) Effects of the expansion of Phyllostachys edulis on species composition, structure and diversity of the secondary evergreen broad-leaved forests. Biodiversity Science, 24, 649-657. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2015290.
| 扩张阶段 Expansion phase | 群落类型 Community type | 毛竹立竹度 Density of bamboo stand | 其他树种立木数 Stem number of other trees | 总立木数 Total stem number |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 前期 Early stage | 常绿阔叶林 EBF | 0 | 1,867 | 1,867 |
| 中期 Middle stage | 竹阔混交林 PBMF | 3,667 | 1,017 | 4,684 |
| 后期 Later stage | 毛竹林 PEF | 6,233 | 100 | 6,333 |
| 扩张前后的变化 Δ | 6,233 | -1,767 | 4,466 |
表1 毛竹扩张对次生常绿阔叶林群落立木数的影响(株/ha)
Table 1 Effect of the expansion of Phyllostachys edulis on stem number in the secondary evergreen broad-leaved forest (ind./ha)
| 扩张阶段 Expansion phase | 群落类型 Community type | 毛竹立竹度 Density of bamboo stand | 其他树种立木数 Stem number of other trees | 总立木数 Total stem number |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 前期 Early stage | 常绿阔叶林 EBF | 0 | 1,867 | 1,867 |
| 中期 Middle stage | 竹阔混交林 PBMF | 3,667 | 1,017 | 4,684 |
| 后期 Later stage | 毛竹林 PEF | 6,233 | 100 | 6,333 |
| 扩张前后的变化 Δ | 6,233 | -1,767 | 4,466 |
| 层次 Layer | 群落 Community | 物种 Species | 重要值 Importance value |
|---|---|---|---|
| 乔木层 Tree | 毛竹林 Phyllostachys edulis forest | 毛竹 Phyllostachys edulis | 87.02 |
| 杉木 Cunninghamia lanceolata | 8.73 | ||
| 黄丹木姜子 Litsea elongata | 2.37 | ||
| 竹阔混交林 Phyllostachys edulis-broad-leaved mixed forest | 毛竹 Phyllostachys edulis | 57.28 | |
| 红楠 Machilus thunbergii | 11.51 | ||
| 杉木 Cunninghamia lanceolata | 9.98 | ||
| 青榨槭 Acer davidii | 3.83 | ||
| 常绿阔叶林 Evergreen broad-leaved forest | 红楠 Machilus thunbergii | 30.22 | |
| 杉木 Cunninghamia lanceolata | 14.06 | ||
| 赤杨叶 Alniphyllum fortunei | 8.33 | ||
| 青榨槭 Acer davidii | 7.65 | ||
| 黄丹木姜子 Litsea elongata | 4.22 | ||
| 交让木 Daphniphyllum macropodum | 3.23 | ||
| 灌木层 Shrub | 毛竹林 Phyllostachys edulis forest | 毛竹 Phyllostachys edulis | 51.24 |
| 赤杨叶 Alniphyllum fortunei | 8.98 | ||
| 青榨槭 Acer davidii | 6.43 | ||
| 香港四照花 Dendrobenthamia hongkongensis | 5.64 | ||
| 竹阔混交林 Phyllostachys edulis-broad-leaved mixed forest | 鹿角杜鹃 Rhododendron latoucheae | 15.21 | |
| 油茶 Camellia oleifera | 8.44 | ||
| 红楠 Machilus thunbergii | 7.99 | ||
| 香港四照花 Dendrobenthamia hongkongensis | 7.27 | ||
| 常绿阔叶林 Evergreen broad-leaved forest | 鹿角杜鹃 Rhododendron latoucheae | 19.86 | |
| 黄丹木姜子 Litsea elongata | 8.84 | ||
| 油茶 Camellia oleifera | 7.92 | ||
| 红楠 Machilus thunbergii | 7.42 | ||
| 草本层 Herb | 毛竹林 Phyllostachys edulis forest | 翠云草 Selaginella uncinata | 19.99 |
| 麦冬 Ophiopogon japonicus | 15.39 | ||
| 星蕨 Microsorum punctatum | 8.54 | ||
| 竹阔混交林 Phyllostachys edulis-broad-leaved mixed forest | 星蕨 Microsorum punctatum | 28.54 | |
| 翠云草 Selaginella uncinata | 8.53 | ||
| 短毛熊巴掌 Phyllagathis cavaleriei | 6.58 | ||
| 常绿阔叶林 Evergreen broad-leaved forest | 短毛熊巴掌 Phyllagathis cavaleriei | 25.83 | |
| 淡竹叶 Lophatherum gracile | 11.13 | ||
| 薹草 Carex tristachya | 10.79 |
表2 毛竹扩张对次生常绿阔叶林主要物种组成与重要值的影响
Table 2 Effects of the expansion of Phyllostachys edulis on main species composition and importance value in the secondary evergreen broad-leaved forest
| 层次 Layer | 群落 Community | 物种 Species | 重要值 Importance value |
|---|---|---|---|
| 乔木层 Tree | 毛竹林 Phyllostachys edulis forest | 毛竹 Phyllostachys edulis | 87.02 |
| 杉木 Cunninghamia lanceolata | 8.73 | ||
| 黄丹木姜子 Litsea elongata | 2.37 | ||
| 竹阔混交林 Phyllostachys edulis-broad-leaved mixed forest | 毛竹 Phyllostachys edulis | 57.28 | |
| 红楠 Machilus thunbergii | 11.51 | ||
| 杉木 Cunninghamia lanceolata | 9.98 | ||
| 青榨槭 Acer davidii | 3.83 | ||
| 常绿阔叶林 Evergreen broad-leaved forest | 红楠 Machilus thunbergii | 30.22 | |
| 杉木 Cunninghamia lanceolata | 14.06 | ||
| 赤杨叶 Alniphyllum fortunei | 8.33 | ||
| 青榨槭 Acer davidii | 7.65 | ||
| 黄丹木姜子 Litsea elongata | 4.22 | ||
| 交让木 Daphniphyllum macropodum | 3.23 | ||
| 灌木层 Shrub | 毛竹林 Phyllostachys edulis forest | 毛竹 Phyllostachys edulis | 51.24 |
| 赤杨叶 Alniphyllum fortunei | 8.98 | ||
| 青榨槭 Acer davidii | 6.43 | ||
| 香港四照花 Dendrobenthamia hongkongensis | 5.64 | ||
| 竹阔混交林 Phyllostachys edulis-broad-leaved mixed forest | 鹿角杜鹃 Rhododendron latoucheae | 15.21 | |
| 油茶 Camellia oleifera | 8.44 | ||
| 红楠 Machilus thunbergii | 7.99 | ||
| 香港四照花 Dendrobenthamia hongkongensis | 7.27 | ||
| 常绿阔叶林 Evergreen broad-leaved forest | 鹿角杜鹃 Rhododendron latoucheae | 19.86 | |
| 黄丹木姜子 Litsea elongata | 8.84 | ||
| 油茶 Camellia oleifera | 7.92 | ||
| 红楠 Machilus thunbergii | 7.42 | ||
| 草本层 Herb | 毛竹林 Phyllostachys edulis forest | 翠云草 Selaginella uncinata | 19.99 |
| 麦冬 Ophiopogon japonicus | 15.39 | ||
| 星蕨 Microsorum punctatum | 8.54 | ||
| 竹阔混交林 Phyllostachys edulis-broad-leaved mixed forest | 星蕨 Microsorum punctatum | 28.54 | |
| 翠云草 Selaginella uncinata | 8.53 | ||
| 短毛熊巴掌 Phyllagathis cavaleriei | 6.58 | ||
| 常绿阔叶林 Evergreen broad-leaved forest | 短毛熊巴掌 Phyllagathis cavaleriei | 25.83 | |
| 淡竹叶 Lophatherum gracile | 11.13 | ||
| 薹草 Carex tristachya | 10.79 |
| 层次 Layer | 群落 Community | 竹阔混交林 PBMF | 毛竹林 Phyllostachys edulis forest |
|---|---|---|---|
| 乔木层 Tree | 常绿阔叶林 Evergreen broad-leaved forest | 0.219 | 0.003 |
| 竹阔混交林 Phyllostachys edulis-broad-leaved mixed forest (PBMF) | 0.626 | ||
| 灌木层 Shrub | 常绿阔叶林 Evergreen broad-leaved forest | 0.383 | 0.046 |
| 竹阔混交林 Phyllostachys edulis-broad-leaved mixed forest | 0.202 | ||
| 草本层 Herb | 常绿阔叶林 Evergreen broad-leaved forest | 0.463 | 0.030 |
| 竹阔混交林 Phyllostachys edulis-broad-leaved mixed forest | 0.319 |
表3 3个群落乔木层、灌木层和草本层的Bray-Curtis相似性系数比较
Table 3 Comparison of Bray-Curtis similarity coefficient between three community types in tree, shrub and herb layers.
| 层次 Layer | 群落 Community | 竹阔混交林 PBMF | 毛竹林 Phyllostachys edulis forest |
|---|---|---|---|
| 乔木层 Tree | 常绿阔叶林 Evergreen broad-leaved forest | 0.219 | 0.003 |
| 竹阔混交林 Phyllostachys edulis-broad-leaved mixed forest (PBMF) | 0.626 | ||
| 灌木层 Shrub | 常绿阔叶林 Evergreen broad-leaved forest | 0.383 | 0.046 |
| 竹阔混交林 Phyllostachys edulis-broad-leaved mixed forest | 0.202 | ||
| 草本层 Herb | 常绿阔叶林 Evergreen broad-leaved forest | 0.463 | 0.030 |
| 竹阔混交林 Phyllostachys edulis-broad-leaved mixed forest | 0.319 |
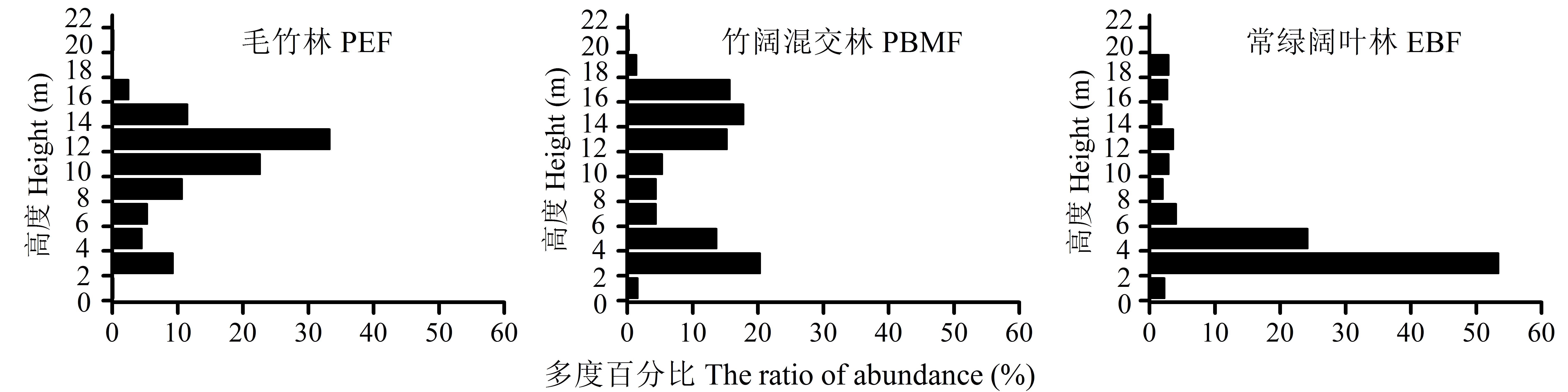
图1 毛竹扩张对次生常绿阔叶林群落垂直结构的影响。三种群落类型见表1。
Fig. 1 Effect of the expansion of Phyllostachys edulis on vertical structure in the secondary evergreen broad-leaved forest. The three community types see Table 1.
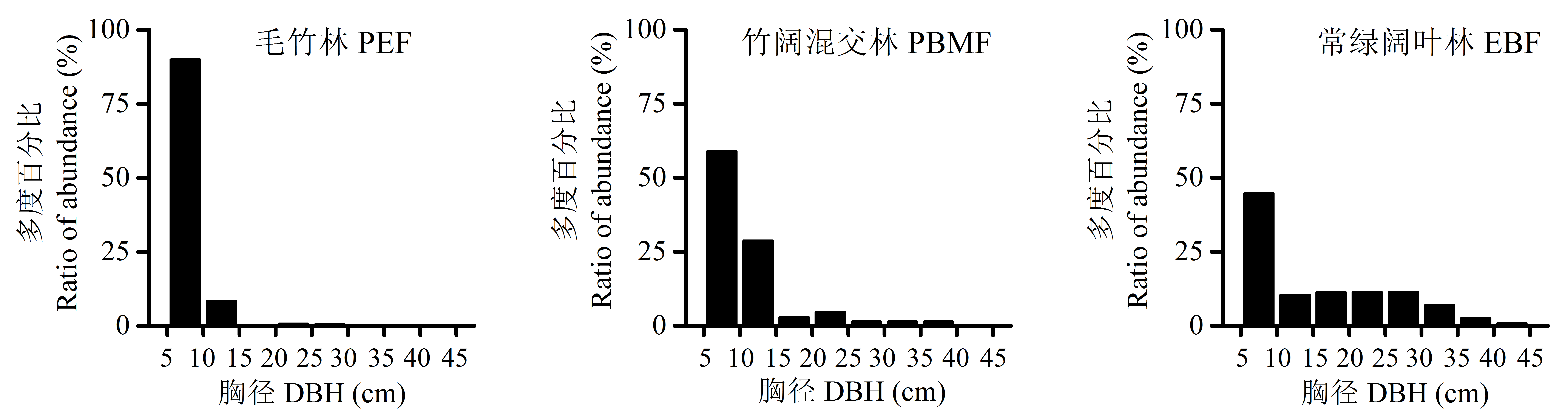
图2 毛竹扩张对次生常绿阔叶林群落径级结构的影响。三种群落类型见表1。
Fig. 2 Effect of the expansion of Phyllostachys edulis on diameter at breast height (DBH) class structure in the secondary evergreen broad-leaved forest. The three community types see Table 1.
| 群落 Community | 物种丰富度 Species richness | Margalef指数 Margalef index | Simpson指数 Simpson index | Shannon-Wiener指数 Shannon-Wiener index | Pielou均匀度 Pielou eveness | 生态优势度 Ecological dominance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PEF | 3.00 ± 1.41b | 0.38 ± 0.26b | 1.03 ± 0.00b | 0.06 ± 0.03c | 0.08 ± 0.07c | 0.97 ± 0.00a |
| PBMF | 11.50 ± 4.95ab | 2.12 ± 0.98ab | 1.62 ± 0.21b | 0.93 ± 0.25b | 0.39 ± 0.03b | 0.63 ± 0.08b |
| EBF | 20.00 ± 4.24a | 4.70 ± 1.08a | 10.72 ± 0.74a | 2.56 ± 0.12a | 0.86 ± 0.02a | 0.11 ± 0.01c |
表4 毛竹扩张对次生常绿阔叶林乔木层物种多样性的影响(平均值±标准误)
Table 4 Effect of the expansion of Phyllostachys edulis on species diversity of tree layer in the secondary evergreen broad-leaved forest (mean ± SE)
| 群落 Community | 物种丰富度 Species richness | Margalef指数 Margalef index | Simpson指数 Simpson index | Shannon-Wiener指数 Shannon-Wiener index | Pielou均匀度 Pielou eveness | 生态优势度 Ecological dominance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PEF | 3.00 ± 1.41b | 0.38 ± 0.26b | 1.03 ± 0.00b | 0.06 ± 0.03c | 0.08 ± 0.07c | 0.97 ± 0.00a |
| PBMF | 11.50 ± 4.95ab | 2.12 ± 0.98ab | 1.62 ± 0.21b | 0.93 ± 0.25b | 0.39 ± 0.03b | 0.63 ± 0.08b |
| EBF | 20.00 ± 4.24a | 4.70 ± 1.08a | 10.72 ± 0.74a | 2.56 ± 0.12a | 0.86 ± 0.02a | 0.11 ± 0.01c |
| 群落 Community | 物种丰富度 Species richness | Margalef指数 Margalef index | Simpson指数 Simpson index | Shannon-Wiener指数 Shannon-Wiener index | Pielou均匀度 Pielou eveness | 生态优势度 Ecological dominance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PEF | 15.50 ± 6.36b | 3.66 ± 1.66a | 4.65 ± 1.93c | 2.01 ± 0.47a | 0.74 ± 0.06a | 0.25 ± 0.09a |
| PBMF | 27.50 ± 4.95ab | 6.13 ± 0.66a | 17.13 ± 1.31a | 2.95 ± 0.12a | 0.89 ± 0.01a | 0.07 ± 0.01a |
| EBF | 33.50 ± 3.54a | 6.42 ± 0.16a | 11.07 ± 2.00b | 2.58 ± 0.33a | 0.74 ± 0.12a | 0.10 ± 0.02a |
表5 毛竹扩张对次生常绿阔叶林灌木层物种多样性的影响(平均值±标准误)
Table 5 Effect of the expansion of Phyllostachys edulis on species diversity of shrub layer in the secondary evergreen broad-leaved forest (mean ± SE)
| 群落 Community | 物种丰富度 Species richness | Margalef指数 Margalef index | Simpson指数 Simpson index | Shannon-Wiener指数 Shannon-Wiener index | Pielou均匀度 Pielou eveness | 生态优势度 Ecological dominance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PEF | 15.50 ± 6.36b | 3.66 ± 1.66a | 4.65 ± 1.93c | 2.01 ± 0.47a | 0.74 ± 0.06a | 0.25 ± 0.09a |
| PBMF | 27.50 ± 4.95ab | 6.13 ± 0.66a | 17.13 ± 1.31a | 2.95 ± 0.12a | 0.89 ± 0.01a | 0.07 ± 0.01a |
| EBF | 33.50 ± 3.54a | 6.42 ± 0.16a | 11.07 ± 2.00b | 2.58 ± 0.33a | 0.74 ± 0.12a | 0.10 ± 0.02a |
| 群落 Community | 物种丰富度 Species richness | Margalef指数 Margalef index | Simpson指数 Simpson index | Shannon-Wiener指数 Shannon-Wiener index | Pielou均匀度 Pielou eveness | 生态优势度 Ecological dominance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PEF | 31.00a | 6.32a | 15.00a | 2.95a | 0.86a | 0.07a |
| PBMF | 28.00a | 5.40a | 16.48a | 2.95a | 0.89a | 0.07a |
| EBF | 18.00b | 3.93b | 13.77a | 2.64a | 0.91a | 0.08a |
表6 毛竹扩张对次生常绿阔叶林草本层物种多样性的影响
Table 6 Effect of the expansion of Phyllostachys edulis on species diversity of herb layer in the secondary evergreen broad-leaved forest
| 群落 Community | 物种丰富度 Species richness | Margalef指数 Margalef index | Simpson指数 Simpson index | Shannon-Wiener指数 Shannon-Wiener index | Pielou均匀度 Pielou eveness | 生态优势度 Ecological dominance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PEF | 31.00a | 6.32a | 15.00a | 2.95a | 0.86a | 0.07a |
| PBMF | 28.00a | 5.40a | 16.48a | 2.95a | 0.89a | 0.07a |
| EBF | 18.00b | 3.93b | 13.77a | 2.64a | 0.91a | 0.08a |
| [1] | Bai SB, Zhou GM, Wang YX, Liang QQ, Chen J, Cheng YY, Shen R (2013) Plant species diversity and dynamics in forests invaded by moso bamboo (Phyllostachys edulis) in Tianmu Mountain Nature Reserve. Biodiversity Science, 21, 288-295. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [白尚斌, 周国模, 王懿祥, 梁倩倩, 陈娟, 程艳艳, 沈蕊 (2013) 天目山保护区森林群落植物多样性对毛竹入侵的响应及动态变化. 生物多样性, 21, 288-295.] | |
| [2] | Bray JR, Curtis JT (1957) An ordination of the upland forest communities of southern Wisconsin. Ecological Monographs, 27, 325-349. |
| [3] | Cardinale BJ, Duffy JE, Gonzalez A, Hooper DU, Perrings C, Venail P, Narwani A, Mace GM, Tilman D, Wardle DA (2012) Biodiversity loss and its impact on humanity. Nature, 486, 59-67. |
| [4] | Chapin III FS, Zavaleta ES, Eviner VT, Naylor RL, Vitousek PM, Reynolds HL, Hooper DU, Lavorel S, Sala OE, Hobbie SE (2000) Consequences of changing biodiversity. Nature, 405, 234-242. |
| [5] | Deng XL, Liu YC, Wu Y (2003) Interconnection among dominant plant populations of Castanopsis community in Jinggang Mountain Nature Reserve. Acta Phytoecologica Sinica, 27, 531-536. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [邓贤兰, 刘玉成, 吴杨 (2003) 井冈山自然保护区栲属群落优势种群的种间联结关系研究. 植物生态学报, 27, 531-536.] | |
| [6] | Ding LX, Wang ZL, Zhou GM, Du QZ (2006) Monitoring Phyllostachys pubescens stands expansion in National Nature Reserve of Mount Tianmu by remote sensing. Journal of Zhejiang Forestry College, 23, 297-300. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [丁丽霞, 王祖良, 周国模, 杜晴洲 (2006) 天目山国家级自然保护区毛竹林扩张遥感监测. 浙江林学院学报, 23, 297-300.] | |
| [7] | Ellison AM, Bank MS, Clinton BD, Colburn EA, Elliott K, Ford CR, Foster DR, Kloeppel BD, Knoepp JD, Lovett GM (2005) Loss of foundation species: consequences for the structure and dynamics of forested ecosystems. Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment, 3, 479-486. |
| [8] | Fukushima K, Usui N, Ogawa R, Tokuchi N (2015) Impacts of moso bamboo (Phyllostachys pubescens) invasion on dry matter and carbon and nitrogen stocks in a broad-leaved secondary forest located in Kyoto, western Japan. Plant Species Biology, 30, 81-95. |
| [9] | Geng BJ, Wang ZP (1996) Flora Peipublicae Popularis Sinicae, Vol. 9(1). Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [耿伯介, 王正平 (1996) 中国植物志(第九卷第一分册). 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [10] | Hejda M, Pyšek P, Jarošík V (2009) Impact of invasive plants on the species richness, diversity and composition of invaded communities. Journal of Ecology, 97, 393-403. |
| [11] | Hooper DU, Chapin III FS, Ewel JJ, Hector A, Inchausti P, Lavorel S, Lawton JH, Lodge DM, Loreau M, Naeem S, Schmid B, Setala H, Symstad AJ, Vandermeer J, Wardle DA (2005) Effects of biodiversity on ecosystem functioning: a consensus of current knowledge. Ecological Monographs, 75, 3-35. |
| [12] | Huang W, Pohjonen V, Johansson S, Nashanda M, Katigula MIL, Luukkanen O (2003) Species diversity, forest structure and species composition in Tanzanian tropical forests. Forest Ecology and Management, 173, 11-24. |
| [13] | Isagi Y, Torii A (1997) Range expansion and its mechanisms in a naturalized bamboo species, Phyllostachys pubescens, in Japan. Journal of Sustainable Forestry, 6, 127-141. |
| [14] | Jiang ZH (2007) Bamboo and Rattan in the World. China Forestry Publishing House, Beijing. |
| [15] | Lavorel S, Garnier E (2002) Predicting changes in community composition and ecosystem functioning from plant traits: revisiting the Holy Grail. Functional Ecology, 16, 545-556. |
| [16] | Lima RAF, Rother DC, Muler AE, Lepsch IF, Rodrigues RR (2012) Bamboo overabundance alters forest structure and dynamics in the Atlantic forest hotspot. Biological Conservation, 147, 32-39. |
| [17] | Lin QQ, Wang B, Ma YD, Wu CY, Zhao MS (2014) Effects of Phyllostachys pubescens forest expansion on biodiversity in Tianmu Mountain National Nature Reserve. Journal of Northeast Forestry University, 42(9), 43-47, 71. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [林倩倩, 王彬, 马元丹, 吴呈昱, 赵明水 (2014) 天目山国家级自然保护区毛竹林扩张对生物多样性的影响. 东北林业大学学报, 42(9), 43-47, 71.] | |
| [18] | Ma KP, Liu CR, Liu YM (1995) Measurement of biotic community diversity. II. β diversity. Chinese Biodiversity, 3, 38-43. (in Chinese) |
| [马克平, 刘灿然, 刘玉明 (1995) 生物群落多样性的测度方法.II. β多样性的测度方法. 生物多样性, 3, 38-43.] | |
| [19] | Ma KP, Liu YM (1994) Measurement of biotic community diversity. I. α diversity (Part 2). Chinese Biodiversity, 2, 231-239. (in Chinese) |
| [马克平, 刘玉明 (1994) 生物群落多样性的测度方法. I. α多样性的测度方法(下). 生物多样性, 2, 231-239.] | |
| [20] | Peet RK (1992) Plant succession—theory and prediction. In: Community Structure and Ecosystem Function (eds Glenn-Lewin DC, Peet RK, Veblen TT), pp.103-151. Chapman and Hall, London. |
| [21] | Pommerening A (2002) Approaches to quantifying forest structures. Forestry, 75, 305-324. |
| [22] | Ru WM, Zhang JT, Zhang F, Zhang GP, Liu RX (2006) Species diversity and community structure of forest communities in Lishan Mountain. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 17, 561-566. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [茹文明, 张金屯, 张峰, 张桂萍, 刘瑞祥 (2006) 历山森林群落物种多样性与群落结构研究. 应用生态学报, 17, 561-566.] | |
| [23] | Shinohara Y, Otsuki K (2015) Comparisons of soil-water content between a moso bamboo (Phyllostachys pubescens) forest and an evergreen broadleaved forest in western Japan. Plant Species Biology, 30, 96-103. |
| [24] | Song QN, Yang QP, Ouyang M, Long CL, Chen FS, Shi JM (2015) Changes in the hydrological functions of litter layer following Phyllostachys edulis expansion into evergreen broadleaved forest. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 34, 2281-2287. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [宋庆妮, 杨清培, 欧阳明, 龙春玲, 陈伏生, 施建敏 (2015) 毛竹扩张的生态后效: 凋落物水文功能评价. 生态学杂志, 34, 2281-2287.] | |
| [25] | Song YC, Wang XH, Yan ER (2013) Evergreen Broad-leaved Forest in China:Classification-Ecology-Conservation. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [宋永昌, 王希华, 阎恩荣 (2013) 中国常绿阔叶林: 分类·生态·保育. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [26] | Tilman D, Knops J, Wedin D, Reich P, Ritchie M, Siemann E (1997) The influence of functional diversity and composition on ecosystem processes. Science, 277, 1300-1302. |
| [27] | Wang YF, Yu SX (2002) A new species diversity index and its fractal analysis. Acta Phytoecologica Sinica, 26, 391-395. |
| a)(in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| 28 | [王永繁, 余世孝 (2002) 物种多样性指数及其分形分析. 植物生态学报, 26, 391-395.] |
| [28] | Wu JS, Jiang PK, Wang ZL (2008) The effects of Phyllostachys pubescens expansion on soil fertility in National Nature Reserve of Mount Tianmu. Acta Agriculturae Universitatis Jiangxiensis, 30, 689-692. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [吴家森, 姜培坤, 王祖良 (2008) 天目山国家级自然保护区毛竹扩张对林地土壤肥力的影响. 江西农业大学学报, 30, 689-692.] | |
| [29] | Wu ZY (1980) Vegetation of China. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [吴征镒 (1980)中国植被. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [30] | Yang H, Li PX, Dai HT, Liu D, Yao XS (2010) Effects of Phyllostachys pubescens expansion on plant species diversity in Jigong Mountain and discussion of control measures. Journal of Xinyang Normal University (Natural Science), 23, 553-557. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [杨怀, 李培学, 戴慧堂, 刘丹, 姚贤胜 (2010) 鸡公山毛竹扩张对植物多样性的影响及控制措施. 信阳师范学院学报(自然科学版), 23, 553-557.] | |
| [31] | Yang QP, Yang GY, Song QN, Shi JM, Ouyang M, Qi HY, Fang XM (2015) Ecological studies on bamboo expansion: process, consequence and mechanism. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 39, 110-124. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [杨清培, 杨光耀, 宋庆妮, 施建敏, 欧阳明, 祁红艳, 方向民 (2015) 竹子扩张生态学研究: 过程、后效与机制. 植物生态学报, 39, 110-124.] | |
| [32] | Zhang JP, Zhang LB, Wang FY, Liu WL, Wo X (2014) Spatial variation of soil nutrient contents in the Jinggangshan National Nature Reserve. Soils, 46, 262-268. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [张继平, 张林波, 王风玉, 刘伟玲, 沃笑 (2014) 井冈山国家级自然保护区森林土壤养分含量的空间变化. 土壤, 46, 262-268.] | |
| [33] | Zhang WH, Wang YP, Kang YX, Liu XJ (2004) Age structure and time sequence prediction of populations of an endangered plant, Larix potaninii var. chinensis. Biodiversity Science, 12, 361-369. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [张文辉, 王延平, 康永祥, 刘祥君 (2004) 濒危植物太白红杉种群年龄结构及其时间序列预测分析. 生物多样性, 12, 361-369.] | |
| [34] | Zhu Y, Zhao GF, Zhang LW, Shen GC, Mi XC, Ren HB, Yu MJ, Chen JH, Chen SW, Fang T, Ma KP (2008) Community composition and structure of Gutianshan forest dynamic plot in a mid-subtropical evergreen broad-leaved forest, East China. Journal of Plant Ecology (Chinese version), 32, 262-273. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [祝燕, 赵谷风, 张俪文, 沈国春, 米湘成, 任海保, 于明坚, 陈建华, 陈声文, 方腾, 马克平 (2008) 古田山中亚热带常绿阔叶林动态监测样地—群落组成与结构. 植物生态学报, 32, 262-273.] |
| [1] | 吴晓晴 张美惠 葛苏婷 李漫淑 宋坤 沈国春 达良俊 张健. 上海近自然林重建过程中木本植物物种多样性与地上生物量的时空动态——以闵行区生态岛为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24444-. |
| [2] | 王太, 宋福俊, 张永胜, 娄忠玉, 张艳萍, 杜岩岩. 河西走廊内陆河水系鱼类多样性及资源现状[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24387-. |
| [3] | 张晶晶, 黄文彬, 陈奕廷, 杨泽鹏, 柯伟业, 彭昭杰, 魏世超, 张志伟, 胡怡思, 余文华, 周文良. 广东南澎列岛海洋生态国家级自然保护区造礁石珊瑚多样性及分布特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24424-. |
| [4] | 贾贞妮, 张意岑, 杜彦君, 任海保. 干扰对中亚热带森林群落物种多样性演替动态的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24078-. |
| [5] | 尚华丹, 张楚晴, 王梅, 裴文娅, 李国宏, 王鸿斌. 中国杨树害虫物种多样性及其地理分布[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24370-. |
| [6] | 吴昱萱, 王平, 胡晓生, 丁一, 彭甜恬, 植秋滢, 巴德木其其格, 李文杰, 关潇, 李俊生. 呼伦贝尔草地退化现状评估与植被特征变化[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24118-. |
| [7] | 陈自宏, 张翼飞, 陈凯, 陈见影, 徐玲. 高黎贡山南段昆虫病原真菌物种多样性及影响因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(1): 24228-. |
| [8] | 谭珂, 宁瑶, 王仁芬, 王晴, 梁丹萍, 辛子兵, 温放. 中国苦苣苔科植物名录与地理分布数据集[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(1): 23275-. |
| [9] | 韩佳楠, 苏杨, 李霏, 刘君妍, 赵依林, 李琳, 赵建成, 梁红柱, 李敏. 河北省苔藓植物多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(9): 24096-. |
| [10] | 李东红, 郝媛媛, 甘辉林, 张航, 刘耀猛, 他富源, 胡桂馨. 祁连山北麓中段不同类型草地蝗虫种类及分布[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(9): 24119-. |
| [11] | 牛红玉, 陈璐, 赵恒月, 古丽扎尔·阿不都克力木, 张洪茂. 城市化对动物的影响: 从群落到个体[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(8): 23489-. |
| [12] | 金泉泉, 向颖, 王华, 习新强. 南京仙林大学城三种绿地类型中果蝇多样性及其被寄生率[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(8): 24156-. |
| [13] | 白雪, 李正飞, 刘洋, 张君倩, 张多鹏, 罗鑫, 杨佳莉, 杜丽娜, 蒋玄空, 武瑞文, 谢志才. 西江流域大型底栖无脊椎动物物种多样性及维持机制[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(7): 23499-. |
| [14] | 许佳, 崔小娟, 张翼飞, 吴昌, 孙远东. 南岭地区鱼类多样性及其地理分布[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(7): 23482-. |
| [15] | 邝起宇, 胡亮. 广东东海岛与硇洲岛海域底栖贝类物种多样性及其地理分布[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(5): 24065-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn