



生物多样性 ›› 2015, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (2): 210-216. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2014205 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2014205
收稿日期:2014-09-25
接受日期:2015-01-28
出版日期:2015-03-20
发布日期:2015-04-09
通讯作者:
徐宾铎
基金资助:
Xiling Luo, Yiping Ren, Lei Xing, Binduo Xu*( )
)
Received:2014-09-25
Accepted:2015-01-28
Online:2015-03-20
Published:2015-04-09
Contact:
Xu Binduo
摘要:
本研究根据2011年3月、5月、7月、9月和12月在海州湾海域进行的渔业资源底拖网调查数据, 采用Margalef种类丰富度指数(D)、Shannon-Wiener多样性指数(H′)和Pielou均匀度指数(J′)等分析了该海域蟹类群落种类组成及其多样性的时空变化。结果表明, 本次调查共捕获蟹类34种, 隶属于18科27属, 其中玉蟹科种数最多, 有3属4种。从适温属性来看, 主要以暖水种(16种)和暖温种(15种)为主, 冷温种3种。蟹类群落各多样性指数的月际间变化较大, 其中物种丰富度指数(D)3月最高, 12月最低; 多样性指数(H′)和均匀度指数(J′)均在7月最高, 12月最低。多样性指数的空间分布呈现一定的月变化: 在3月、5月、7月均表现为北高南低; 9月为中部低, 南、北部海域较高; 12月均呈南高北低的趋势。蟹类单位网次渔获尾数空间分布格局呈现明显的月变化; 平均单位网次渔获尾数呈现一定的月变化, 总体上表现为3月、5月、12月高于7月和9月。Pearson相关分析结果表明, 在5月, 多样性指数(H′)和均匀度指数(J′)与底层水温呈显著负相关, 与底层盐度呈极显著正相关, 多样性指数还与水深呈显著正相关; 12月均匀度指数与底层水温和水深均呈极显著负相关, 与底层盐度呈显著负相关; 在3月、7月和9月, 各多样性指数与底层水温、底层盐度及水深均无显著相关性。海州湾蟹类种类组成及多样性的时空变化主要与海州湾地处温带海域、水温等海洋环境因子的季节变化以及优势种的数量分布有关。
罗西玲, 任一平, 邢磊, 徐宾铎 (2015) 海州湾蟹类群落种类组成及其多样性. 生物多样性, 23, 210-216. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2014205.
Xiling Luo, Yiping Ren, Lei Xing, Binduo Xu (2015) Species composition and diversity of crab assemblage in Haizhou Bay. Biodiversity Science, 23, 210-216. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2014205.
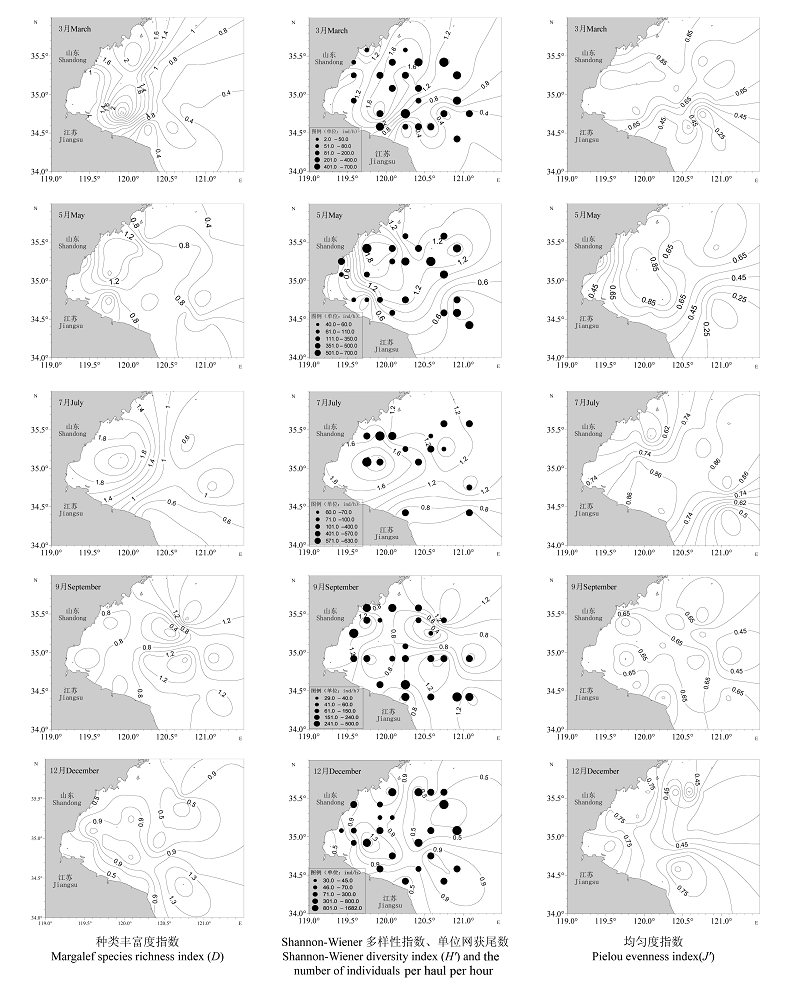
图3 海州湾海域蟹类群落各多样性指数及单位网次渔获尾数的空间分布
Fig. 3 Spatial distributions of ecological diversity indices of crab assemblage and the number of individuals per haul per hour in Haizhou Bay
| 月份 Month | 种类丰富度指数 Margalef species richness index (D) | 多样性指数 Shannon-Wiener diversity index (H′) | 均匀度指数 Pielou evenness index (J′) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3月 March (n = 24) | |||
| 底层水温 Bottom water temperature | -0.269 | -0.353 | -0.399 |
| 底层盐度 Bottom water salinity | -0.282 | -0.137 | -0.114 |
| 水深 Water depth | -0.047 | 0.293 | 0.107 |
| 5月 May (n = 24) | |||
| 底层水温 Bottom water temperature | -0.160 | -0.493* | -0.418* |
| 底层盐度 Bottom water salinity | 0.294 | 0.677** | 0.548** |
| 水深 Water depth | 0.180 | 0.488* | 0.287 |
| 7月 July (n = 14) | |||
| 底层水温 Bottom water temperature | -0.001 | -0.066 | -0.047 |
| 底层盐度 Bottom water salinity | 0.145 | 0.003 | -0.402 |
| 水深 Water depth | -0.209 | 0.031 | 0.071 |
| 9月 September (n = 14) | |||
| 底层水温 Bottom water temperature | -0.108 | -0.006 | -0.240 |
| 底层盐度 Bottom water salinity | 0.208 | 0.191 | 0.417 |
| 水深 Water depth | 0.303 | 0.025 | 0.021 |
| 12月 December (n = 24) | |||
| 底层水温 Bottom water temperature | -0.036 | -0.149 | -0.531** |
| 底层盐度 Bottom water salinity | 0.074 | -0.159 | -0.423* |
| 水深 Water depth | -0.236 | -0.312 | -0.605** |
表1 海州湾蟹类多样性指数与环境因子的Pearson相关性分析
Table 1 Pearson correlation between diversity indices of crab assemblage and environmental factors in Haizhou Bay
| 月份 Month | 种类丰富度指数 Margalef species richness index (D) | 多样性指数 Shannon-Wiener diversity index (H′) | 均匀度指数 Pielou evenness index (J′) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3月 March (n = 24) | |||
| 底层水温 Bottom water temperature | -0.269 | -0.353 | -0.399 |
| 底层盐度 Bottom water salinity | -0.282 | -0.137 | -0.114 |
| 水深 Water depth | -0.047 | 0.293 | 0.107 |
| 5月 May (n = 24) | |||
| 底层水温 Bottom water temperature | -0.160 | -0.493* | -0.418* |
| 底层盐度 Bottom water salinity | 0.294 | 0.677** | 0.548** |
| 水深 Water depth | 0.180 | 0.488* | 0.287 |
| 7月 July (n = 14) | |||
| 底层水温 Bottom water temperature | -0.001 | -0.066 | -0.047 |
| 底层盐度 Bottom water salinity | 0.145 | 0.003 | -0.402 |
| 水深 Water depth | -0.209 | 0.031 | 0.071 |
| 9月 September (n = 14) | |||
| 底层水温 Bottom water temperature | -0.108 | -0.006 | -0.240 |
| 底层盐度 Bottom water salinity | 0.208 | 0.191 | 0.417 |
| 水深 Water depth | 0.303 | 0.025 | 0.021 |
| 12月 December (n = 24) | |||
| 底层水温 Bottom water temperature | -0.036 | -0.149 | -0.531** |
| 底层盐度 Bottom water salinity | 0.074 | -0.159 | -0.423* |
| 水深 Water depth | -0.236 | -0.312 | -0.605** |
| 科 Family | 3月 March | 5月 May | 7月 July | 9月 Sept. | 12月 Dec. | 适温类型 Temperature adaptive type | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 瓷蟹科 Porcellanidae | |||||||
| 细足蟹属 Raphidopus | |||||||
| 绒毛细足蟹 Raphidopus ciliatus | + | + | + | WW | |||
| 豆瓷蟹属 Pisidia | |||||||
| 锯额豆瓷蟹 Pisidia serratifrons | + | WW | |||||
| 大眼蟹科 Macrophthalmidae | |||||||
| 三强蟹属 Tritodynamia | |||||||
| 霍氏三强蟹 Tritodynamia horvathi | + | T | |||||
| 兰氏三强蟹 Tritodynamia rathbunae | + | + | + | T | |||
| 豆蟹科 Pinnotheridae | |||||||
| 豆蟹属 Pinnotheres | |||||||
| 中华豆蟹 Pinnotheres sinensis | + | + | T | ||||
| 圆豆蟹 Pinnotheres cyclinus | + | T | |||||
| 海阳豆蟹 Pinnotheres haiyangensis | + | T | |||||
| 短眼蟹科 Xenophthalmidae | |||||||
| 短眼蟹属 Xenophthalmus | |||||||
| 豆形短眼蟹 Xenophthalmus pinnotheroides | + | WW | |||||
| 弓蟹科 Varunidae | |||||||
| 近方蟹属 Hemigrapsus | |||||||
| 中华近方蟹 Hemigrapsus sinensis | + | T | |||||
| 肉球近方蟹 Hemigrapsus sanguineus | + | WW | |||||
| 倒颚蟹属 Asthenognathus | |||||||
| 异足倒颚蟹 Asthenognathus inaequipes | + | T | |||||
| 关公蟹科 Dorippidae | |||||||
| 拟关公蟹属 Paradorippe | |||||||
| 端正拟关公蟹 Paradorippe polita | + | + | WW | ||||
| 颗粒拟关公蟹 Paradorippe granulata | + | + | CT | ||||
| 拟平家蟹属 Heikeopsis | |||||||
| 日本拟平家蟹 Heikeopsis japonicus | + | + | + | + | + | WW | |
| 黄道蟹科 Cancridae | |||||||
| 黄道蟹属 Cancer | |||||||
| 隆背黄道蟹 Cancer gibbosulus | + | + | + | + | + | CT | |
| 静蟹科 Galenidae | |||||||
| 精武蟹属 Parapanipe | |||||||
| 贪精武蟹 Parapanipe euagora | + | WW | |||||
| 宽背蟹科 Euryplacidae | |||||||
| 强蟹属 Eucrate | |||||||
| 隆线强蟹 Eucrate crenata | + | + | + | + | + | WW | |
| 菱蟹科 Parthenopidae | |||||||
| 菱蟹属 Parthenope | |||||||
| 强壮菱蟹 Parthenope validus | + | + | + | + | + | WW | |
| 毛刺蟹科 Pilumnidae | |||||||
| 毛刺蟹属 Pilumnus | |||||||
| 小型毛刺蟹 Pilumnus spinulus | + | + | + | + | T | ||
| 异毛蟹属 Heteropilumnus | |||||||
| 披发异毛蟹 Heteropilumnus ciliatus | + | + | T | ||||
| 拟盲蟹属 Typhlocarcinops | |||||||
| 沟纹拟盲蟹 Typhlocarcinops canaliculata | + | WW | |||||
| 绵蟹科 Dromiidae | |||||||
| 板蟹属 Petalomera | |||||||
| 沈板蟹 Petalomera sheni | + | + | + | + | + | T | |
| 扇蟹科 Xanthidae | |||||||
| 大权蟹属 Macromedaeus | |||||||
| 特异大权蟹 Macromedaeus distinguendus | + | + | + | WW | |||
| 梭子蟹科 Portunidae | |||||||
| 梭子蟹属 Portunus | |||||||
| 三疣梭子蟹 Portunus trituberculatus | + | + | + | + | + | WW | |
| 蟳属 Charybdis | |||||||
| 日本蟳 Charybdis japonica | + | + | + | + | + | WW | |
| 双斑蟳 Charybdis bimaculata | + | + | + | + | + | T | |
| 突眼蟹科 Oregoniidae | |||||||
| 突眼蟹属 Oregonia | |||||||
| 枯瘦突眼蟹 Oregonia gracilis | + | + | + | + | + | T | |
| 卧蜘蛛蟹科 Epialtidae | |||||||
| 矶蟹属 Pugettia | |||||||
| 四齿矶蟹 Pugettia quadridens | + | + | + | + | + | CT | |
| 玉蟹科 Leucosiidae | |||||||
| 五角蟹属 Nursia | |||||||
| 斜方五角蟹 Nursia rhomboidalis | + | + | + | T | |||
| 栗壳蟹属 Arcania | |||||||
| 球形栗壳蟹 Arcania globata | + | + | + | + | + | WW | |
| 圆十一刺栗壳蟹 Arcania novemspinosa | + | + | + | + | T | ||
| 拳蟹属 Philyra | |||||||
| 杂粒拳蟹 Philyra heterograna | + | T | |||||
| 长脚蟹科 Goneplacidae | |||||||
| 隆背蟹属 Carcinoplax | |||||||
| 泥脚隆背蟹 Carcinoplax vestita | + | + | + | + | + | WW | |
| 盲蟹属 Typhlocarcinus | |||||||
| 裸盲蟹 Typhlocarcinus nudus | + | WW | |||||
| 总种数 Total number of species | 34 | ||||||
附表1 海州湾海域捕获蟹类名录
Table S1 List of crab species caught in Haizhou Bay
| 科 Family | 3月 March | 5月 May | 7月 July | 9月 Sept. | 12月 Dec. | 适温类型 Temperature adaptive type | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 瓷蟹科 Porcellanidae | |||||||
| 细足蟹属 Raphidopus | |||||||
| 绒毛细足蟹 Raphidopus ciliatus | + | + | + | WW | |||
| 豆瓷蟹属 Pisidia | |||||||
| 锯额豆瓷蟹 Pisidia serratifrons | + | WW | |||||
| 大眼蟹科 Macrophthalmidae | |||||||
| 三强蟹属 Tritodynamia | |||||||
| 霍氏三强蟹 Tritodynamia horvathi | + | T | |||||
| 兰氏三强蟹 Tritodynamia rathbunae | + | + | + | T | |||
| 豆蟹科 Pinnotheridae | |||||||
| 豆蟹属 Pinnotheres | |||||||
| 中华豆蟹 Pinnotheres sinensis | + | + | T | ||||
| 圆豆蟹 Pinnotheres cyclinus | + | T | |||||
| 海阳豆蟹 Pinnotheres haiyangensis | + | T | |||||
| 短眼蟹科 Xenophthalmidae | |||||||
| 短眼蟹属 Xenophthalmus | |||||||
| 豆形短眼蟹 Xenophthalmus pinnotheroides | + | WW | |||||
| 弓蟹科 Varunidae | |||||||
| 近方蟹属 Hemigrapsus | |||||||
| 中华近方蟹 Hemigrapsus sinensis | + | T | |||||
| 肉球近方蟹 Hemigrapsus sanguineus | + | WW | |||||
| 倒颚蟹属 Asthenognathus | |||||||
| 异足倒颚蟹 Asthenognathus inaequipes | + | T | |||||
| 关公蟹科 Dorippidae | |||||||
| 拟关公蟹属 Paradorippe | |||||||
| 端正拟关公蟹 Paradorippe polita | + | + | WW | ||||
| 颗粒拟关公蟹 Paradorippe granulata | + | + | CT | ||||
| 拟平家蟹属 Heikeopsis | |||||||
| 日本拟平家蟹 Heikeopsis japonicus | + | + | + | + | + | WW | |
| 黄道蟹科 Cancridae | |||||||
| 黄道蟹属 Cancer | |||||||
| 隆背黄道蟹 Cancer gibbosulus | + | + | + | + | + | CT | |
| 静蟹科 Galenidae | |||||||
| 精武蟹属 Parapanipe | |||||||
| 贪精武蟹 Parapanipe euagora | + | WW | |||||
| 宽背蟹科 Euryplacidae | |||||||
| 强蟹属 Eucrate | |||||||
| 隆线强蟹 Eucrate crenata | + | + | + | + | + | WW | |
| 菱蟹科 Parthenopidae | |||||||
| 菱蟹属 Parthenope | |||||||
| 强壮菱蟹 Parthenope validus | + | + | + | + | + | WW | |
| 毛刺蟹科 Pilumnidae | |||||||
| 毛刺蟹属 Pilumnus | |||||||
| 小型毛刺蟹 Pilumnus spinulus | + | + | + | + | T | ||
| 异毛蟹属 Heteropilumnus | |||||||
| 披发异毛蟹 Heteropilumnus ciliatus | + | + | T | ||||
| 拟盲蟹属 Typhlocarcinops | |||||||
| 沟纹拟盲蟹 Typhlocarcinops canaliculata | + | WW | |||||
| 绵蟹科 Dromiidae | |||||||
| 板蟹属 Petalomera | |||||||
| 沈板蟹 Petalomera sheni | + | + | + | + | + | T | |
| 扇蟹科 Xanthidae | |||||||
| 大权蟹属 Macromedaeus | |||||||
| 特异大权蟹 Macromedaeus distinguendus | + | + | + | WW | |||
| 梭子蟹科 Portunidae | |||||||
| 梭子蟹属 Portunus | |||||||
| 三疣梭子蟹 Portunus trituberculatus | + | + | + | + | + | WW | |
| 蟳属 Charybdis | |||||||
| 日本蟳 Charybdis japonica | + | + | + | + | + | WW | |
| 双斑蟳 Charybdis bimaculata | + | + | + | + | + | T | |
| 突眼蟹科 Oregoniidae | |||||||
| 突眼蟹属 Oregonia | |||||||
| 枯瘦突眼蟹 Oregonia gracilis | + | + | + | + | + | T | |
| 卧蜘蛛蟹科 Epialtidae | |||||||
| 矶蟹属 Pugettia | |||||||
| 四齿矶蟹 Pugettia quadridens | + | + | + | + | + | CT | |
| 玉蟹科 Leucosiidae | |||||||
| 五角蟹属 Nursia | |||||||
| 斜方五角蟹 Nursia rhomboidalis | + | + | + | T | |||
| 栗壳蟹属 Arcania | |||||||
| 球形栗壳蟹 Arcania globata | + | + | + | + | + | WW | |
| 圆十一刺栗壳蟹 Arcania novemspinosa | + | + | + | + | T | ||
| 拳蟹属 Philyra | |||||||
| 杂粒拳蟹 Philyra heterograna | + | T | |||||
| 长脚蟹科 Goneplacidae | |||||||
| 隆背蟹属 Carcinoplax | |||||||
| 泥脚隆背蟹 Carcinoplax vestita | + | + | + | + | + | WW | |
| 盲蟹属 Typhlocarcinus | |||||||
| 裸盲蟹 Typhlocarcinus nudus | + | WW | |||||
| 总种数 Total number of species | 34 | ||||||
| 1 | Cai M (蔡萌), Xu ZL (徐兆礼), He XC (何新春) (2009) Quantitative distribution and dominant species variation of crab in the winter and summer of Sanmen Bay, Zhejiang Province. Marine Fisheries(海洋渔业), 31, 34-40. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 2 | Chen XQ (陈小庆), Yu CG (俞存根), Yu CD (虞聪达), Ning P (宁平), Zhang FJ (章飞军), Zheng J (郑基) (2009) Structural characteristics of crab communities in offshore waters of mid-southern East China Sea.Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology(应用生态学报), 20, 2527-2534. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 3 | Chu YT (朱元鼎), Wu HL (伍汉霖) (1965) A preliminary study of the zoogeography of the gobioid fishes of China. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica(海洋与湖沼), 7, 122-140. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 4 | Dai AY (戴爱云), Yang SL (杨思谅), Song YZ (宋玉枝), Chen GX (陈国孝) (1986) Crabs of the China Seas (中国海洋蟹类). China Ocean Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| 5 | Du RQ (杜荣骞) (2009) Biostatistics, 3rd edn. (生物统计学). Higher Education Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| 6 | Jin S (金施), Xu ZL (徐兆礼), Chen JJ (陈佳杰), Wang CH (王翠华) (2013) Distribution characteristics of crabs near Lianyungang in Haizhou Bay.Transactions of Oceanology and Limnology(海洋湖沼通报), (1), 45-52. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 7 | Liu JT (刘吉堂), Xu GX (徐国想) (2008) Characteristic factors and the formation of red tide in Haizhou Bay.Reservoir Fisheries(水利渔业), 28(2), 77-79. (in Chinese) |
| 8 | Liu RY (刘瑞玉) (2008) Checklist of Marine Biota of China Seas (中国海洋生物名录). Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| 9 | Margalef R (1958) Information theory in ecology.Yearbook of the International Society for the Systems Sciences, 3, 36-71. |
| 10 | Pang ZW (逄志伟), Xu BD (徐宾铎), Ji YP (纪毓鹏), Ren YP (任一平) (2014) Monthly changes and related affecting factors in community structure and diversity of the crab assemblages in central Jiaozhou Bay, China.Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology(应用生态学报), 25, 591-598. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 11 | Pielou EC (1975) Ecological Diversity. Wiley, New York. |
| 12 | Shannon EC, Weaver W (1949) The Mathematical Theory of Communication. Urbana University of Illinois Press, Illinois. |
| 13 | Shen JR (沈嘉瑞), Liu RY (刘瑞玉) (1963) Preliminary studies on the characteristics of the crab fauna of China Seas. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica(海洋与湖沼), 5, 139-153. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 14 | Si Z, Li SY, Huang LZ, Chen YL (2010) Visualization programming for batch processing of contour maps based on VB and Surfer software.Advances in Engineering Software, 41, 962-965. |
| 15 | Wang WH (王文海), Xia DX (夏东兴), Gao XC (高兴辰), Zheng PY (郑培迎), Li XT (李秀亭) (1993) Bays in China (Volume Four): The Bay of Southern Shandong Peninsula and Jiangsu Province (中国海湾志·第四分册·山东半岛南部和江苏省海湾). China Ocean Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| 16 | Xu ZL (徐兆礼) (2009) Relationship of crab density distribution with environment in the Oujiang Estuary during summer and autumn.Journal of Fisheries of China(水产学报), 33, 237-244. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 17 | Xue LJ (薛利建), Lu ZH (卢占晖) (2011) Community structure and species diversity of crab in middle East China Sea.South China Fisheries Science(南方水产科学), 7(6), 66-71. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 18 | Ye SZ (叶孙忠), Zhang ZL (张壮丽), Ye QT (叶泉土) (2006) Species composition and characteristics of crab distribution in south East China Sea.Journal of Oceanography in Taiwan Strait(台湾海峡), 25, 381-387. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 19 | Yu CG (俞存根), Song HT (宋海棠), Yao GZ (姚光展) (2003) Geographical distribution and faunal analysis of crab resources in the East China Sea. Journal of Zhejiang Ocean University (Natural Science) (浙江海洋学院学报(自然科学版)), 22, 108-113. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 20 | Yu CG (俞存根), Song HT (宋海棠), Yao GZ (姚光展) (2005) Crab community structure in the East China Sea. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica(海洋与湖沼), 36, 213-220. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 21 | Zhang HL (张洪亮), Zhang L (张龙), Chen F (陈峰), Zhou YD (周永东) (2013) Analysis of crab community characteristics in south Zhejiang coastal areas during spring.Journal of Fishery Sciences of China(中国水产科学), 20, 1050-1056. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 22 | Zhang SY (章守宇), Zhang HJ (张焕君), Jiao JP (焦俊鹏), Li YS (李曰嵩), Zhu KW (朱孔文) (2006) Change of ecological environment of artificial reef waters in Haizhou Bay. Journal of Fisheries of China(水产学报), 30, 475-480. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 23 | Zheng XZ (郑献之), Yu CG (俞存根), Chen XQ (陈小庆), Zheng J (郑基), Ning P (宁平), Jiang XQ (江新琴) (2012) Species composition and spatio-temporal distribution of crabs in Zhoushan fishing ground and its adjacent areas. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica(海洋与湖沼), 43, 147-153. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 24 | Zhu KW (朱孔文), Sun MC (孙满昌), Zhang S (张硕) (2011) Marine Ranching in Haizhou Bay: Construction of Artificial Reef (海州湾海洋牧场: 人工鱼礁建设). China Agriculture Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| 25 | Zhu XH (朱鑫华), Wu HZ (吴鹤洲), Xu FS (徐凤山), Ye MZ (叶懋中), Zhao ZJ (赵紫晶) (1994) Study on diversity and related factors of nekton community in the coastal waters of Yellow Sea and Bohai Sea.Acta Oceanologica Sinica(海洋学报), 16(3), 102-112. (in Chinese) |
| [1] | 干靓 刘巷序 鲁雪茗 岳星. 全球生物多样性热点地区大城市的保护政策与优化方向[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24529-. |
| [2] | 曾子轩 杨锐 黄越 陈路遥. 清华大学校园鸟类多样性特征与环境关联[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24373-. |
| [3] | 臧明月, 刘立, 马月, 徐徐, 胡飞龙, 卢晓强, 李佳琦, 于赐刚, 刘燕. 《昆明-蒙特利尔全球生物多样性框架》下的中国城市生物多样性保护[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24482-. |
| [4] | 祝晓雨, 王晨灏, 王忠君, 张玉钧. 城市绿地生物多样性研究进展与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 25027-. |
| [5] | 袁琳, 王思琦, 侯静轩. 大都市地区的自然留野:趋势与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24481-. |
| [6] | 胡敏, 李彬彬, Coraline Goron. 只绿是不够的: 一个生物多样性友好的城市公园管理框架[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24483-. |
| [7] | 王欣, 鲍风宇. 基于鸟类多样性提升的南滇池国家湿地公园生态修复效果分析[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24531-. |
| [8] | 明玥, 郝培尧, 谭铃千, 郑曦. 基于城市绿色高质量发展理念的中国城市生物多样性保护与提升研究[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24524-. |
| [9] | 谢淦, 宣晶, 付其迪, 魏泽, 薛凯, 雒海瑞, 高吉喜, 李敏. 草地植物多样性无人机调查的物种智能识别模型构建[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24236-. |
| [10] | 褚晓琳, 张全国. 演化速率假说的实验验证研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 25019-. |
| [11] | 宋威, 程才, 王嘉伟, 吴纪华. 土壤微生物对植物多样性–生态系统功能关系的调控作用[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24579-. |
| [12] | 卢晓强, 董姗姗, 马月, 徐徐, 邱凤, 臧明月, 万雅琼, 李孪鑫, 于赐刚, 刘燕. 前沿技术在生物多样性研究中的应用现状、挑战与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24440-. |
| [13] | 农荞伊, 曹军, 程文达, 彭艳琼. 不同方法对蜜蜂总科昆虫资源与多样性监测效果的比较[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 25057-. |
| [14] | 郭雨桐, 李素萃, 王智, 解焱, 杨雪, 周广金, 尤春赫, 朱萨宁, 高吉喜. 全国自然保护地对国家重点保护野生物种的覆盖度及其分布状况[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(3): 24423-. |
| [15] | 赵维洋, 王伟, 马冰然. 其他有效的区域保护措施(OECMs)研究进展与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(3): 24525-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn