



Biodiv Sci ›› 2013, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (6): 738-749. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2013.12113 cstr: 32101.14.SP.J.1003.2013.12113
• Orginal Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
Jian Zhang1,*( ), Shengbin Chen2, Bin Chen3, Yanjun Du3, Xiaolei Huang4, Xubin Pan5, Qiang Zhang6
), Shengbin Chen2, Bin Chen3, Yanjun Du3, Xiaolei Huang4, Xubin Pan5, Qiang Zhang6
Received:2013-05-09
Accepted:2013-09-03
Online:2013-11-20
Published:2013-12-02
Contact:
Zhang Jian
Jian Zhang,Shengbin Chen,Bin Chen,Yanjun Du,Xiaolei Huang,Xubin Pan,Qiang Zhang. Citizen science: integrating scientific research, ecological conservation and public participation[J]. Biodiv Sci, 2013, 21(6): 738-749.
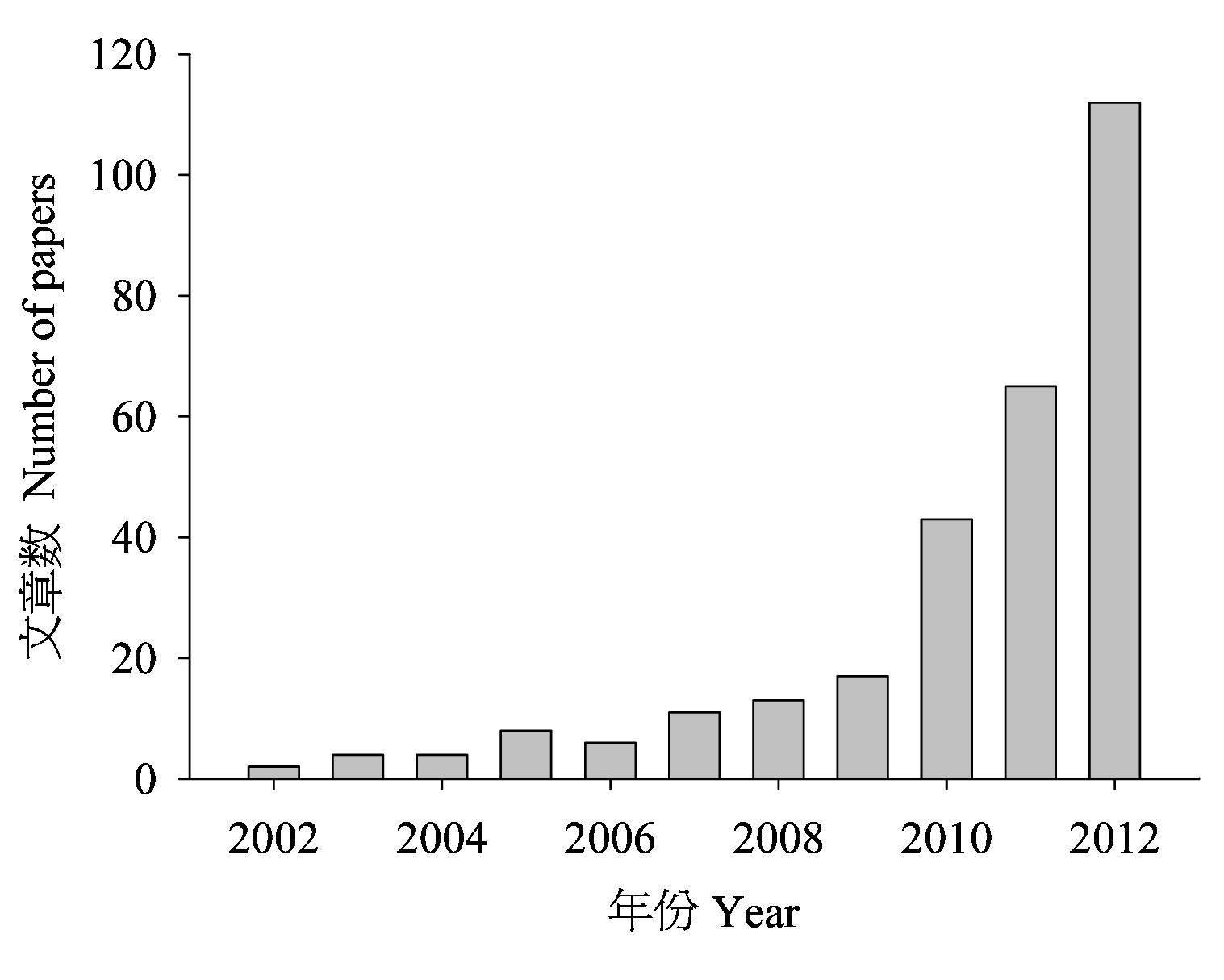
Fig. 1 The number of peer-reviewed publications with the key word “citizen science” as determined in a search of the Web of Science (accessed on April 29, 2013)
| 科学研究的步骤 Steps in scientific process | 契约型 Contractual | 辅助型 Contributory | 合作型 Collaborative | 共创型 Co-created | 学院型 Collegial |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 选择或定义研究问题 Choose or define question(s) for study | √ | √ | √ | ||
| 收集信息和资源 Gather information and resources | (√) | √ | √ | ||
| 提出假说或解释 Develop explanations (hypotheses) | √ | √ | |||
| 设计数据收集方法 Design data collection methodologies | (√) | √ | √ | ||
| 收集样品、记录数据 Collect samples and/or record data | √ | √ | √ | √ | |
| 分析样品 Analyze samples | √ | √ | √ | ||
| 分析数据 Analyze data | (√) | √ | √ | √ | |
| 解释数据、得出结论 Interpret data and draw conclusions | (√) | (√) | √ | √ | |
| 宣传研究结果或转换科研结果到实践 Disseminate conclusions/translate results into action | (√) | (√) | (√) | √ | √ |
| 讨论研究结果、提出新的问题 Discuss results and ask new questions | √ | √ | √ |
Table 1 Models for developing a citizen science project (Bonney et al., 2009a; Shirk et al., 2012)
| 科学研究的步骤 Steps in scientific process | 契约型 Contractual | 辅助型 Contributory | 合作型 Collaborative | 共创型 Co-created | 学院型 Collegial |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 选择或定义研究问题 Choose or define question(s) for study | √ | √ | √ | ||
| 收集信息和资源 Gather information and resources | (√) | √ | √ | ||
| 提出假说或解释 Develop explanations (hypotheses) | √ | √ | |||
| 设计数据收集方法 Design data collection methodologies | (√) | √ | √ | ||
| 收集样品、记录数据 Collect samples and/or record data | √ | √ | √ | √ | |
| 分析样品 Analyze samples | √ | √ | √ | ||
| 分析数据 Analyze data | (√) | √ | √ | √ | |
| 解释数据、得出结论 Interpret data and draw conclusions | (√) | (√) | √ | √ | |
| 宣传研究结果或转换科研结果到实践 Disseminate conclusions/translate results into action | (√) | (√) | (√) | √ | √ |
| 讨论研究结果、提出新的问题 Discuss results and ask new questions | √ | √ | √ |
| 网站 Websites | 提供的资源 Resources |
|---|---|
| Citizen Science Central: www.citizenscience.org | 项目开发、文献数据库、讨论组等相关的工具 Toolkit for project development, tips and tools, reference database, conference proceedings, searchable project list, discussion forum, news feed, professional network |
| SciStarter: www.scistarter.com | 项目搜索工具、项目添加工具等 Project finder and add project tools, editor’s picks, member and site blogs |
| 中国自然标本馆: www.cfh.ac.cn | 生物多样性基础数据支持, 公众科学项目数据存储、物种鉴定、编目和分类管理、团队协作等功能支持 Tools for biodiversity data collection, species identification, and group cooperation |
| CitSci.org: www.citsci.org | 制作数据输入表格的工具 Tools for creating customized data-entry forms so that volunteers can submit data |
| Data Observation Network for Earth: www.dataone.org | 数据管理、数据标准化、数据分析和可视化的工具 Tools on data management and data standards that will enable the integration of data from diverse studies and taxa, data analysis and visualization tools |
| The Public Laboratory for Open Technology and Science: www.publiclaboratory.org | 工具、方法、会议信息 Tools and methods, information on conferences |
| iSpot: http://www.ispot.org.uk | 各种动植物类群监测网络平台 Species identification and monitoring |
Table 2 A selection of projects and websites that provide cyberinfrastructure, tools, and information for project developers and participants
| 网站 Websites | 提供的资源 Resources |
|---|---|
| Citizen Science Central: www.citizenscience.org | 项目开发、文献数据库、讨论组等相关的工具 Toolkit for project development, tips and tools, reference database, conference proceedings, searchable project list, discussion forum, news feed, professional network |
| SciStarter: www.scistarter.com | 项目搜索工具、项目添加工具等 Project finder and add project tools, editor’s picks, member and site blogs |
| 中国自然标本馆: www.cfh.ac.cn | 生物多样性基础数据支持, 公众科学项目数据存储、物种鉴定、编目和分类管理、团队协作等功能支持 Tools for biodiversity data collection, species identification, and group cooperation |
| CitSci.org: www.citsci.org | 制作数据输入表格的工具 Tools for creating customized data-entry forms so that volunteers can submit data |
| Data Observation Network for Earth: www.dataone.org | 数据管理、数据标准化、数据分析和可视化的工具 Tools on data management and data standards that will enable the integration of data from diverse studies and taxa, data analysis and visualization tools |
| The Public Laboratory for Open Technology and Science: www.publiclaboratory.org | 工具、方法、会议信息 Tools and methods, information on conferences |
| iSpot: http://www.ispot.org.uk | 各种动植物类群监测网络平台 Species identification and monitoring |
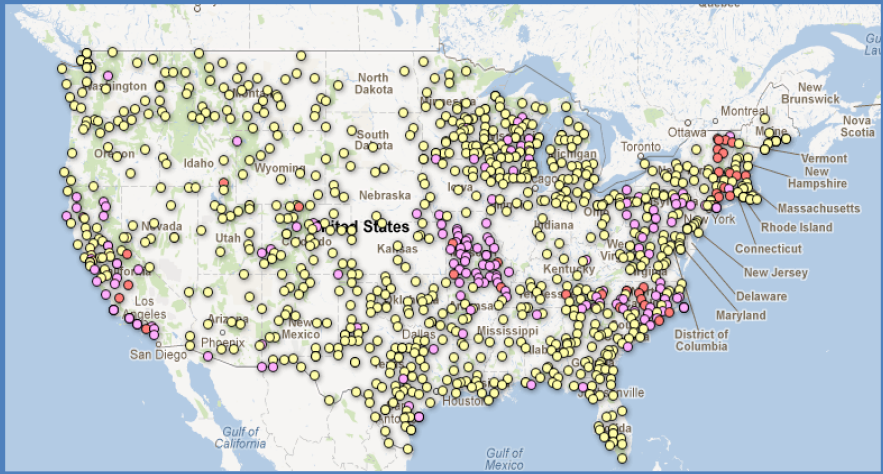
Fig. 2 The distribution of monitoring sites in 23 selected citizen science projects in USA (After Wiggins et al., 2013. Used by permission of Dr. Andrea Wiggins). Different colors of dots stand for different citizen science projects.
| 类型 Type of science | 定义 Definition | 花费 Cost | 数据质量 Data quality | 信息传播 Information dissemination |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 传统科学项目 Traditional science | 科学家执行研究活动 Scientists conduct all aspects of the research process | 高 High | 高 High | 慢 Slow |
验证式公众科学项目 Verified citizen science | 科学家和公众共同执行研究活动 Scientists and citizens conduct the research process together | 中等 Medium | 中等 Medium | 中等 Medium |
直接式公众科学项目 Direct citizen science | 完全由公众执行的研究活动 Citizens conduct all aspects of the research process | 低 Low | 低 Low | 快 Fast |
Table 3 The comparison among traditional science, verified citizen science, and direct citizen science (Gardiner et al., 2012)
| 类型 Type of science | 定义 Definition | 花费 Cost | 数据质量 Data quality | 信息传播 Information dissemination |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 传统科学项目 Traditional science | 科学家执行研究活动 Scientists conduct all aspects of the research process | 高 High | 高 High | 慢 Slow |
验证式公众科学项目 Verified citizen science | 科学家和公众共同执行研究活动 Scientists and citizens conduct the research process together | 中等 Medium | 中等 Medium | 中等 Medium |
直接式公众科学项目 Direct citizen science | 完全由公众执行的研究活动 Citizens conduct all aspects of the research process | 低 Low | 低 Low | 快 Fast |
| 费用类型 Type of costs | 费用(美元) Costs (US$) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 传统科学 Traditional science | 验证性公众科学 Verified citizen science | 直接式公众科学 Direct citizen science | |
| 实验材料费用 Traps and fence cost | 4.17 | 4.17 | 4.17 |
| 旅行费用 Travel to field site | 85.46 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| 参与者收集捕捉器的工资 Student payment for collecting trap samples | 34.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| 参与者收集数据的工资 Student payment for collecting data | 0.00 | 4.25 | 0.00 |
| 科学家帮助参与者培训的工资 Researcher investment to train students | 2.99 | 2.99 | 0.00 |
| 调查者邮寄数据给科学家的费用 Mailing cost | 0.00 | 1.61 | 0.00 |
| 举行培训班的花费 Hosting volunteer training workshops | 0.00 | 9.89 | 9.89 |
| 网站开发和维护 Website development and maintenance | 0.00 | 17.38 | 17.38 |
| 每个捕捉器的总花费 Total cost per trap | 126.62 | 40.29 | 31.44 |
Table 4 The comparison among the costs of traditional science, direct citizen science, or verified citizen science: collecting one lady beetle trap sample as an example (all currency in US$) (Gardiner et al., 2012)
| 费用类型 Type of costs | 费用(美元) Costs (US$) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 传统科学 Traditional science | 验证性公众科学 Verified citizen science | 直接式公众科学 Direct citizen science | |
| 实验材料费用 Traps and fence cost | 4.17 | 4.17 | 4.17 |
| 旅行费用 Travel to field site | 85.46 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| 参与者收集捕捉器的工资 Student payment for collecting trap samples | 34.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| 参与者收集数据的工资 Student payment for collecting data | 0.00 | 4.25 | 0.00 |
| 科学家帮助参与者培训的工资 Researcher investment to train students | 2.99 | 2.99 | 0.00 |
| 调查者邮寄数据给科学家的费用 Mailing cost | 0.00 | 1.61 | 0.00 |
| 举行培训班的花费 Hosting volunteer training workshops | 0.00 | 9.89 | 9.89 |
| 网站开发和维护 Website development and maintenance | 0.00 | 17.38 | 17.38 |
| 每个捕捉器的总花费 Total cost per trap | 126.62 | 40.29 | 31.44 |
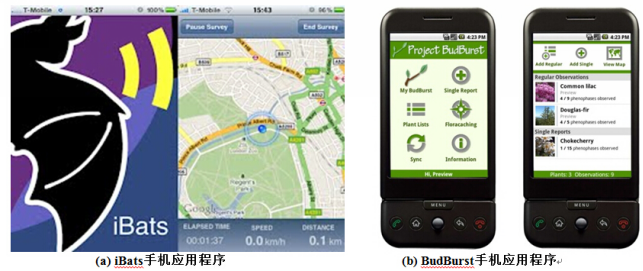
Fig. 3 The application of new techniques in citizen science projects. (a) iBats smartphone app (https://sites.google.com/site/ibatsresources), which allows a smartphone to be directly connected to the ultrasonic detector and the geo-referenced sound files can then be automatically uploaded onto the ibats website; (b) BudBurst smartphone App (http://budburst.org/gomobile.php), which uses a smartphone to monitor plants as the season changes.
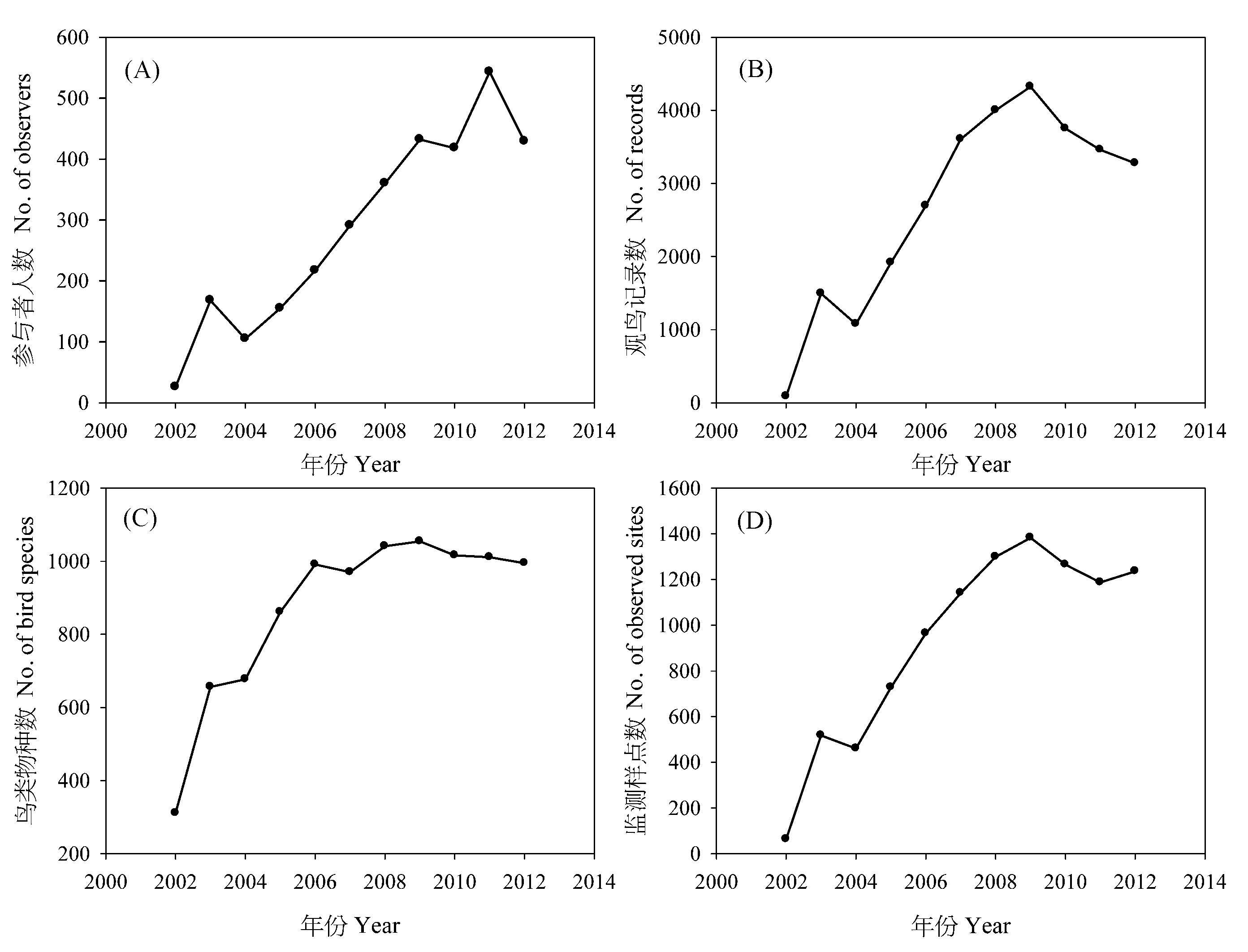
Fig. 4 Summary of China Birding Records between 2002 and 2012: the trends of recent ten years on (A) the number of observers; (B) the number of birding records; (C) the number of bird species; and (D) the number of observed sites (Data source: http://birdtalker.net/ birdtalker/report/statistics.asp).
| 1 | Benz S, Miller-Rushing A, Domroese M, Ballard H, Bonney R, DeFalco T, Newman S, Shirk J, Young A (2013) Workshop 1: Conference on Public Participation in Scientific Research 2012: an international, interdisciplinary conference.Bulletin of the Ecological Society of America, 94, 112-117. |
| 2 | Bonney R, Ballard H, Jordan R, McCallie E, Phillips T, Shirk J, Wilderman CC (2009a) Public Participation in Scientific Research: Defining the Field and Assessing Its Potential for Informal Science Education. A CAISE Inquiry Group Report. Center for Advancement of Informal Science Education (CAISE), Washington, DC. |
| 3 | Bonney R, Cooper CB, Dickinson J, Kelling S, Phillips T, Rosenberg KV, Shirk J (2009b) Citizen science: a developing tool for expanding science knowledge and scientific literacy.BioScience, 59, 977-984. |
| 4 | Brossard D, Lewenstein B, Bonney R (2005) Scientific knowledge and attitude change: the impact of a citizen science project.International Journal of Science Education, 27, 1099-1121. |
| 5 | Chen G, Kery M, Plattner M, Ma K, Gardner B (2013) Imperfect detection is the rule rather than the exception in plant distribution studies.Journal of Ecology, 101, 183-191. |
| 6 | Cox TE, Philippoff J, Baumgartner E, Smith CM (2012) Expert variability provides perspective on the strengths and weaknesses of citizen-driven intertidal monitoring program.Ecological Applications, 22, 1201-1212. |
| 7 | Crall AW, Newman GJ, Stohlgren TJ, Holfelder KA, Graham J, Waller DM (2011) Assessing citizen science data quality: an invasive species case study.Conservation Letters, 4, 433-442. |
| 8 | Delaney DG, Sperling CD, Adams CS, Leung B (2008) Marine invasive species: validation of citizen science and implications for national monitoring networks.Biological Invasion, 10, 117-128. |
| 9 | Devictor V, Whittaker RJ, Beltrame C (2010) Beyond scarcity: citizen science programmes as useful tools for conservation biogeography.Diversity and Distributions, 16, 354-362. |
| 10 | Dickinson JL, Shirk J, Bonter D, Bonney R, Crain RL, Martin J, Phillips T, Purcell K (2012) The current state of citizen science as a tool for ecological research and public engagement.Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment, 10, 291-297. |
| 11 | Dickinson JL, Zuckerberg B, Bonter DN (2010) Citizen science as an ecological research tool: challenges and benefits.Annual Review of Ecology, Evolution, and Systematics, 41, 149-172. |
| 12 | Evans C, Abrams E, Reitsma R, Roux K, Salmonsen L, Marra P (2005) The neighborhood nestwatch program: participant outcomes of a citizen-science ecological research project.Conservation Biology, 19, 589-594. |
| 13 | Fang W, Qiu YL, Huang J, Zhao B, Wei YG (2013) Didymocarpus dissectus sp. nov. (Gesneriaceae) from Fujian, eastern China.Nordic Journal of Botany, 30, 1-5. |
| 14 | Field DR, Voss PR, Kuczenski TK, Hammer RB, Radeloff VC (2003) Reaffirming social landscape analysis in landscape ecology: a conceptual framework.Society and Natural Resources, 16, 349-361. |
| 15 | Fitzpatrick MC, Preisser EL, Ellison AM, Elkinton JS (2009) Observer bias and the detection of low-density populations.Ecological Applications, 19, 1673-1679. |
| 16 | Gallo T, Waitt D (2011) Creating a successful citizen science model to detect and report invasive species.BioScience, 61, 459-465. |
| 17 | Gardiner MM, Allee LL, Brown PM, Losey JE, Roy HE, Smyth RR (2012) Lessons from lady beetles: accuracy of monitoring data from US and UK citizen-science programs.Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment, 10, 471-476. |
| 18 | Hampton SE, Strasser CA, Tewksbury JJ, Gram W K, Budden AE, Batcheller AL, Duke CS, Porter JH (2013) Big data and the future of ecology.Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment, 11, 156-162. |
| 19 | Havens K, Vitt P, Masi S (2012) Citizen science on a local scale: the Plants of Concern program.Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment, 10, 321-323. |
| 20 | Henderson S (2012) Citizen science comes of age.Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment, 10, 283. |
| 21 | Hochachka WM, Fink D (2012) Broad-scale citizen science data from checklists: prospects and challenges for macroecology.Frontiers of Biogeography, 4, 150-154. |
| 22 | Hochachka WM, Fink D, Hutchinson RA, Sheldon D, Wong WK, Kelling S (2011) Data-intensive science applied to broad-scale citizen science.Trends in Ecology and Evolution, 27, 130-137. |
| 23 | Howard E, Davis AK (2009) The fall migration flyways of monarch butterflies in eastern North America revealed by citizen scientists.Journal of Insect Conservation, 13, 279-286. |
| 24 | Hoyer MV, Wellendorf N, Frydenborg R, Bartlett D, Canfield DE Jr (2012) A comparison between professionally (Florida Department of Environmental Protection) and volunteer (Florida LAKEWATCH) collected trophic state chemistry data in Florida.Lake and Reservoir Management, 28. 277-281. |
| 25 | Jordan RC, Gray SA, Hoew DV, Brooks WR, Ehrenfeld JG (2011) Knowledge gain and behavioral change in citizen-science programs.Conservation Biology, 25, 1148-1154. |
| 26 | Kaartinen R, Hardwick B, Roslin T (2013) Using citizen scientists to measure an ecosystem service nationwide. Ecology (in press). |
| 27 | Kyba CCM, Wagner JM, Kuechly HU, Walker CE, Elvidge CD, Falchi F, Ruhtz T, Fischer J, Hölker F (2013) Citizen science provides valuable data for monitoring global night sky luminance.Scientific Reports, 3, 1835. |
| 28 | La Sorte FA, Thompson III FR (2007) Poleward shifts in winter ranges of North American birds.Ecology, 88, 1803-1812. |
| 29 | Lee T, Quinn MS, Duke D (2006) Citizen, science, highways, and wildlife: using a web-based GIS to engage citizens in collecting wildlife information.Ecology and Society, 11, 11. |
| 30 | Lepczyk CA (2005) Integrating published data and citizen science to describe bird diversity across a landscape.Journal of Applied Ecology, 42, 672-677. |
| 31 | Levrel H, Fontaine B, Henry P-Y, Jiguet F, Julliard R, Kerbirioub C, Couvet D (2010) Balancing state and volunteer investment in biodiversity monitoring for the implementation of CBD indicators: a French example.Ecological Economics, 69, 1580-1586. |
| 32 | Li XY (李雪艳), Liang L (梁璐), Gong P (宫鹏), Liu Y (刘阳), Liang FF (梁菲菲) (2012) Bird watching in China reveals bird distribution changes.Chinese Science Bulletin(科学通报), 57, 2956-2963. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 33 | Losey JE, Perlman JE, Hoebeke ER (2007) Citizen scientist rediscovers rare nine-spotted lady beetle, Coccinella novemnotata, in eastern North America.Journal of Insect Conservation, 11, 415-417. |
| 34 | Mackechnie C, Maskell L, Norton L, Roy D (2011) The role of ‘Big Society’ in monitoring the state of the natural environment.Journal of Environmental Monitoring, 13, 2687-2691. |
| 35 | Michener WK, Jones MB (2012) Ecoinformatics: supporting ecology as a data-intensive science.Trends in Ecology and Evolution, 27, 85-93. |
| 36 | Miller-Rushing A, Primack R, Bonney R (2012) The history of public participation in ecological research.Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment, 10, 285-290. |
| 37 | Nerbonne JF, Nelson KC (2004) Volunteer macroinvertebrate monitoring in the United States: resource mobilization and comparative state structures.Society and Natural Resources, 17, 817-839. |
| 38 | Newman G, Wiggins A, Crall A, Graham E, Newman S, Crowston K (2012) The future of citizen science: emerging technologies and shifting paradigms.Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment, 10, 298-304. |
| 39 | Pandya RE (2012) A framework for engaging diverse communities in citizen science in the US.Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment, 10, 314-317. |
| 40 | Parsons J, Lukyanenko R, Wiersma Y (2011) Easier citizen science is better.Nature, 471, 37. |
| 41 | Porter R (1978) Gentlemen and geology: the emergence of a scientific career, 1660-1920.The Historical Journal, 21, 809-836. |
| 42 | Roy HE, Pocock MJO, Preston CD, Roy DB, Savage J, Tweddle JC, Robinson LD (2012) Understanding Citizen Science and Environmental Monitoring. Final Report on Behalf of UK-EOF. NERC Centre for Ecology and Hydrology and Natural History Museum |
| 43 | Sauer JR, Hines JE, Fallcon JE, Pardieck KL, Ziolkowski DJ, Link WA (2012) The North American Breeding Bird Survey, Results and Analysis 1966-2011. Version 12.13.2011. USGS Patuxent Wildlife Research Center, Laurel, USA. |
| 44 | Shirk J, Ballard HL, Wilderman CC, Phillips T, Wiggins A, Jordan R, McCallie E, Minarchek M, Lewenstein BV, Krasny ME, Bonney R (2012) Public participation in scientific research: a framework for deliberate design.Ecology and Society, 17, 29. |
| 45 | Si XF (斯幸峰), Ding P (丁平) (2011) History, status of monitoring land birds in Europe and America and countermeasures of China.Biodiversity Science(生物多样性), 19, 303-310. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 46 | Silvertown J (2009) A new dawn for citizen science.Trends in Ecology and Evolution, 24, 467-471. |
| 47 | Silvertown J, Cook L, Cameron R, Dodd M, McConway K, Worthington J, Skelton P, Anton C, Bossdorf O, Baur B, Schilthuizen M, Fontaine B, Sattmann H, Bertorelle G, Correia M, Oliveira C, Pokryszko B, Ożgo M, Stalažs A, Gill E, Rammul Ü, Sólymos P, Féher Z, Juan X (2011) Citizen science reveals unexpected continental-scale evolutionary change in a model organism.PLoS ONE, 6, e18927. |
| 48 | Stafford R, Hart AG, Collins L, Kirkhope CL, Williams RL, Rees SG, LIoyd JR, Goodenough AE (2010) Eu-Social Science: the role of internet social networks in the collection of bee biodiversity data.PLoS ONE, 5, e14381. |
| 49 | Stegen JC, Freestone AL, Crist TO, Anderson MJ, Chase JM, Comita LS, Cornell HV, Davies KF, Harrison SP, Hurlbert AH, Inouye BD, Kraft NJB, Myers JA, Sanders NJ, Swenson NG, Vellend M (2013) Stochastic and deterministic drivers of spatial and temporal turnover in breeding bird communities.Global Ecology and Biogeography, 22, 202-212. |
| 50 | Tweddle JC, Robinson LD, Pocock MJO, Roy HE (2012) Guide to Citizen Science: Developing, Implementing and Evaluating Citizen Science to Study Biodiversity and the Environment in the UK. Natural History Museum and NERC Centre for Ecology & Hydrology for UK-EOF. |
| 51 | Wiggins A, Bonney R, Graham E, Henderson S, Kelling S, Littauer R, LeBuhn G, Lotts K, Michener W, Newman G, Russell E, Stevenson R, Weltzin J (2013) Data Management Guide for Public Participation in Scientific Research. DataONE, Albuquerque, USA. |
| 52 | Yu J, Wong WK, Hutchinson RA (2010) Modeling experts and novices in citizen science data for species distribution modeling. In: Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE International Conference on Data Mining (eds Webb GI, Liu B, Zhang C, Gunopulos D, Wu X), pp. 1157-1162. IEEE Computer Society, Washington, DC. |
| 53 | Zoellick B, Nelson SJ, Schauffler M (2012) Participatory science and education: bringing both views into focus.Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment, 10, 310-313. |
| [1] | Jing Gan Xiangxu Liu Xueming Lu Xing Yue. China's Large Cities in Global Biodiversity Hotspots: Conservation Policies and Optimization Directions [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 24529-. |
| [2] | Zixuan Zeng Rui Yang Yue Huang Luyao Chen. Characteristics of bird diversity and environmental relationships in Tsinghua University campus [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 24373-. |
| [3] | Mingyue Zang, Li Liu, Yue Ma, Xu Xu, Feilong Hu, Xiaoqiang Lu, Jiaqi Li, Cigang Yu, Yan Liu. China’s urban biodiversity conservation under the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 24482-. |
| [4] | Xiaoyu Zhu, Chenhao Wang, Zhongjun Wang, Yujun Zhang. Research progress and prospect of urban green space biodiversity [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 25027-. |
| [5] | Lin Yuan, Siqi Wang, Jingxuan Hou. “Leaving space for wildness” in metropolitan region: Trends and prospects [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 24481-. |
| [6] | Min Hu, Binbin Li, Coraline Goron. Green is not enough: A management framework for urban biodiversity-friendly parks [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 24483-. |
| [7] | Xin Wang, Femgyu Bao. Analysis of the ecological restoration effect of South Dianchi National Wetland Park based on the enhancement of bird diversity [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 24531-. |
| [8] | Yue Ming, Peiyao Hao, Lingqian Tan, Xi Zheng. A study on urban biodiversity conservation and enhancement in china based on the concept of green and high-quality development of cities [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 24524-. |
| [9] | Gan Xie, Jing Xuan, Qidi Fu, Ze Wei, Kai Xue, Hairui Luo, Jixi Gao, Min Li. Establishing an intelligent identification model for unmanned aerial vehicle surveys of grassland plant diversity [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 24236-. |
| [10] | Xiaolin Chu, Quanguo Zhang. A review of experimental evidence for the evolutionary speed hypothesis [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 25019-. |
| [11] | Zhiyu Liu, Xin Ji, Guohui Sui, Ding Yang, Xuankun Li. Invertebrate diversity in buffalo grass and weedy lawns at Beijing Capital International Airport [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 24456-. |
| [12] | Xiaoqiang Lu, Shanshan Dong, Yue Ma, Xu Xu, Feng Qiu, Mingyue Zang, Yaqiong Wan, Luanxin Li, Cigang Yu, Yan Liu. Current status, challenges, and prospects of frontier technologies in biodiversity conservation applications [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 24440-. |
| [13] | Qiaoyi Nong, Jun Cao, Wenda Cheng, Yanqiong Peng. Comparative study of monitoring methods for Apoidea resources and diversity [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 25057-. |
| [14] | Guo Yutong, Li Sucui, Wang Zhi, Xie Yan, Yang Xue, Zhou Guangjin, You Chunhe, Zhu Saning, Gao Jixi. Coverage and distribution of national key protected wild species in China’s nature reserves [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(3): 24423-. |
| [15] | Zhao Weiyang, Wang Wei, Ma Bingran. Advances and prospects in research on other effective area-based conservation measures (OECMs) [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(3): 24525-. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2022 Biodiversity Science
Editorial Office of Biodiversity Science, 20 Nanxincun, Xiangshan, Beijing 100093, China
Tel: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn ![]()