



生物多样性 ›› 2014, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (3): 320-328. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2014.13137 cstr: 32101.14.SP.J.1003.2014.13137
所属专题: 海洋生物多样性
收稿日期:2013-06-08
接受日期:2014-04-24
出版日期:2014-05-20
发布日期:2014-06-04
通讯作者:
林茂
基金资助:
Rouxin Sun, Yanguo Wang, Guangshan Lian, Mao Lin*( )
)
Received:2013-06-08
Accepted:2014-04-24
Online:2014-05-20
Published:2014-06-04
Contact:
Lin Mao
摘要:
为了解昌江沿岸海域生态系统的现状, 探讨海域环境因素对浮游动物的生存环境造成的影响。本文根据2008年11月至2009年7月在海南西部昌江沿岸水域21个测站、4个季度月调查所获的浮游桡足类样品数据, 对该海域浮游桡足类群落结构、分布、季节变化及影响因素进行了分析。本调查共鉴定出桡足类44种, 隶属4目17科24属, 其中秋季25种, 冬季23种, 春季22种, 夏季23种。本次调查共发现优势种6种, 分别是微刺哲水蚤(Canthocalanus pauper)、亚强次真哲水蚤(Subeucalanus subcrassus)、锥形宽水蚤(Temora turbinata)、刺尾纺锤水蚤(Acartia spinicauda)、椭形长足水蚤(Calanopia elliptica)和精致真刺水蚤(Euchaeta concinna), 优势种以近岸暖水种居多。浮游桡足类丰度季节变化明显: 冬季最高, 达409 ind./m3; 秋季次之, 为144 ind./m3, 春季为55 ind./m3, 夏季最低仅为17 ind./m3。其丰度的平面分布显示: 秋、冬季节分别在海区中部和南部形成明显密集区, 春、夏季节则大致呈现由外海向近岸逐渐递减的趋势。浮游桡足类的多样性指数(H')表现为夏季>春季>秋季>冬季, 春、夏季的均匀度指数(J')明显高于秋、冬季。本调查反映出该海区的桡足类群落具有热带—亚热带区系特征, 种类组成季节更替明显, 桡足类种群受海域水温和硅藻的影响明显, 受盐度影响不明显。
孙柔鑫, 王彦国, 连光山, 林茂 (2014) 海南岛西北沿岸海域浮游桡足类的分布及群落特征. 生物多样性, 22, 320-328. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2014.13137.
Rouxin Sun, Yanguo Wang, Guangshan Lian, Mao Lin (2014) Distribution and community characteristics of planktonic copepods in the northwest coastal waters off Hainan Island. Biodiversity Science, 22, 320-328. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2014.13137.
| 春/夏 Spring /Summer | 夏/秋 Summer/Autumn | 秋/冬 Autumn/Winter | 冬/春 Winter/Spring | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 种数 Species richness | 22/23 | 23/25 | 25/23 | 23/22 |
| 共有种数 Number of common species | 12 | 14 | 14 | 12 |
| 季节更替率 Seasonal change rate | 63.6% | 58.8% | 58.8% | 63.6% |
表1 2008-2009年海南昌江近岸浮游桡足类季节更替率
Table 1 Seasonal change rate of planktonic copepods in Changjiang coastal waters off Hainan Island between 2008 and 2009
| 春/夏 Spring /Summer | 夏/秋 Summer/Autumn | 秋/冬 Autumn/Winter | 冬/春 Winter/Spring | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 种数 Species richness | 22/23 | 23/25 | 25/23 | 23/22 |
| 共有种数 Number of common species | 12 | 14 | 14 | 12 |
| 季节更替率 Seasonal change rate | 63.6% | 58.8% | 58.8% | 63.6% |
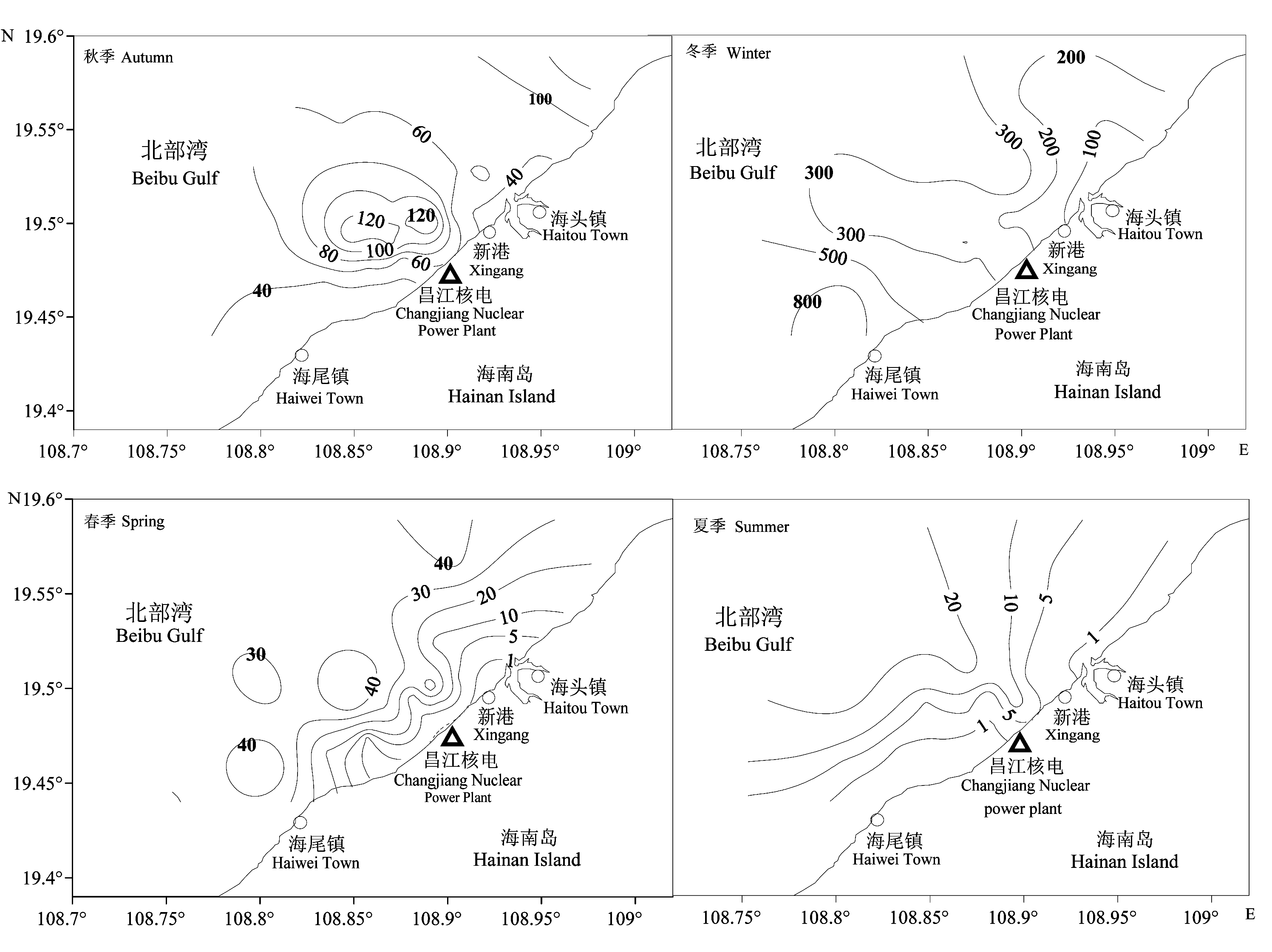
图2 2008-2009年海南昌江近岸亚强次真哲水蚤平面分布(ind./m3)
Fig. 2 Horizontal distribution of Subeucalanus subcrassus in Changjiang coastal waters off Hainan Island between 2008 and 2009 (ind./m3)
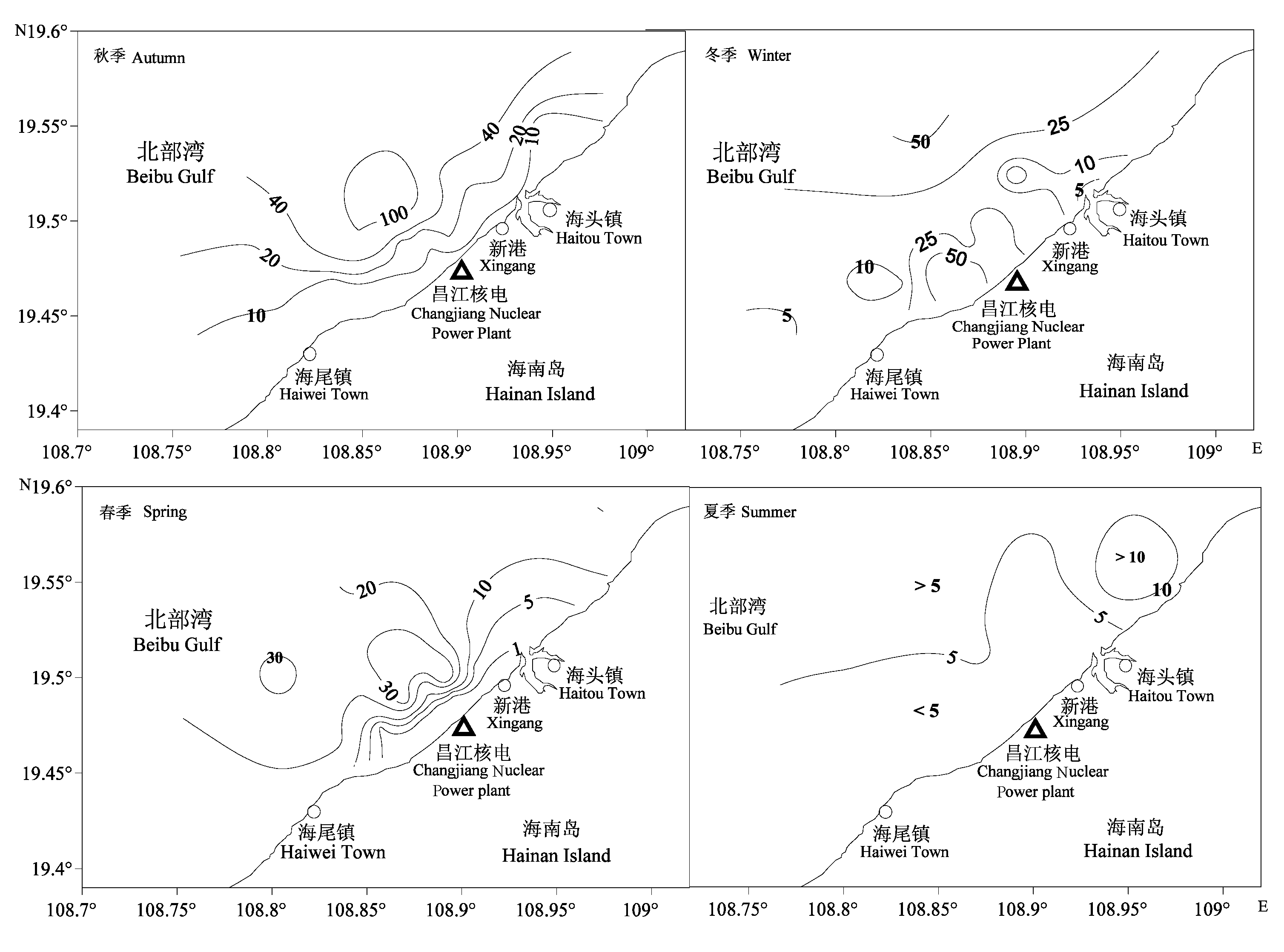
图3 2008-2009年海南昌江近岸微刺哲水蚤平面分布(ind./m3)
Fig. 3 Horizontal distribution of Canthocalanus pauper in Changjiang coastal waters off Hainan Island between 2008 and 2009 (ind./m3)
| 季节 Season | 优势种类 Dominant species | 出现频度 Frequency | 平均丰度 Average abundance (ind./m3) | 丰度变化范围 Abundance range (ind./m3) | 优势度 Dominancy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 秋季 (11月) | 微刺哲水蚤 Canthocalanus pauper | 1.00 | 34 | 3-155 | 0.11 |
| Autumn (Nov.) | 亚强次真哲水蚤 Subeucalanus subcrassus | 1.00 | 72 | 21-147 | 0.24 |
| 冬季 (1月) | 刺尾纺锤水蚤 Acartia spinicauda | 0.86 | 16 | 2-36 | 0.02 |
| Winter (Jan.) | 微刺哲水蚤 Canthocalanus pauper | 0.90 | 28 | 7-86 | 0.05 |
| 亚强次真哲水蚤 Subeucalanus subcrassus | 1.00 | 297 | 6-994 | 0.59 | |
| 锥形宽水蚤 Temora turbinata | 0.95 | 51 | 3-158 | 0.09 | |
| 春季 (4月) | 微刺哲水蚤 Canthocalanus pauper | 0.95 | 17 | 1-45 | 0.23 |
| Spring (Apr.) | 亚强次真哲水蚤 Subeucalanus subcrassus | 0.95 | 22 | 1-51 | 0.31 |
| 精致真刺水蚤 Euchaeta concinna | 0.38 | 12 | 1-34 | 0.03 | |
| 夏季 (7月) | 微刺哲水蚤 Canthocalanus pauper | 0.86 | 4 | 1-14 | 0.05 |
| Summer (July) | 椭形长足水蚤 Calanopia elliptica | 0.95 | 5 | 1-24 | 0.08 |
| 亚强次真哲水蚤 Subeucalanus subcrassus | 0.95 | 7 | 1-28 | 0.13 |
表2 2008-2009年海南昌江近岸浮游桡足类主要优势种的季节变化
Table 2 Seasonal variation of dominant species of planktonic copepods in Changjiang coastal waters off Hainan Island between 2008 and 2009
| 季节 Season | 优势种类 Dominant species | 出现频度 Frequency | 平均丰度 Average abundance (ind./m3) | 丰度变化范围 Abundance range (ind./m3) | 优势度 Dominancy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 秋季 (11月) | 微刺哲水蚤 Canthocalanus pauper | 1.00 | 34 | 3-155 | 0.11 |
| Autumn (Nov.) | 亚强次真哲水蚤 Subeucalanus subcrassus | 1.00 | 72 | 21-147 | 0.24 |
| 冬季 (1月) | 刺尾纺锤水蚤 Acartia spinicauda | 0.86 | 16 | 2-36 | 0.02 |
| Winter (Jan.) | 微刺哲水蚤 Canthocalanus pauper | 0.90 | 28 | 7-86 | 0.05 |
| 亚强次真哲水蚤 Subeucalanus subcrassus | 1.00 | 297 | 6-994 | 0.59 | |
| 锥形宽水蚤 Temora turbinata | 0.95 | 51 | 3-158 | 0.09 | |
| 春季 (4月) | 微刺哲水蚤 Canthocalanus pauper | 0.95 | 17 | 1-45 | 0.23 |
| Spring (Apr.) | 亚强次真哲水蚤 Subeucalanus subcrassus | 0.95 | 22 | 1-51 | 0.31 |
| 精致真刺水蚤 Euchaeta concinna | 0.38 | 12 | 1-34 | 0.03 | |
| 夏季 (7月) | 微刺哲水蚤 Canthocalanus pauper | 0.86 | 4 | 1-14 | 0.05 |
| Summer (July) | 椭形长足水蚤 Calanopia elliptica | 0.95 | 5 | 1-24 | 0.08 |
| 亚强次真哲水蚤 Subeucalanus subcrassus | 0.95 | 7 | 1-28 | 0.13 |
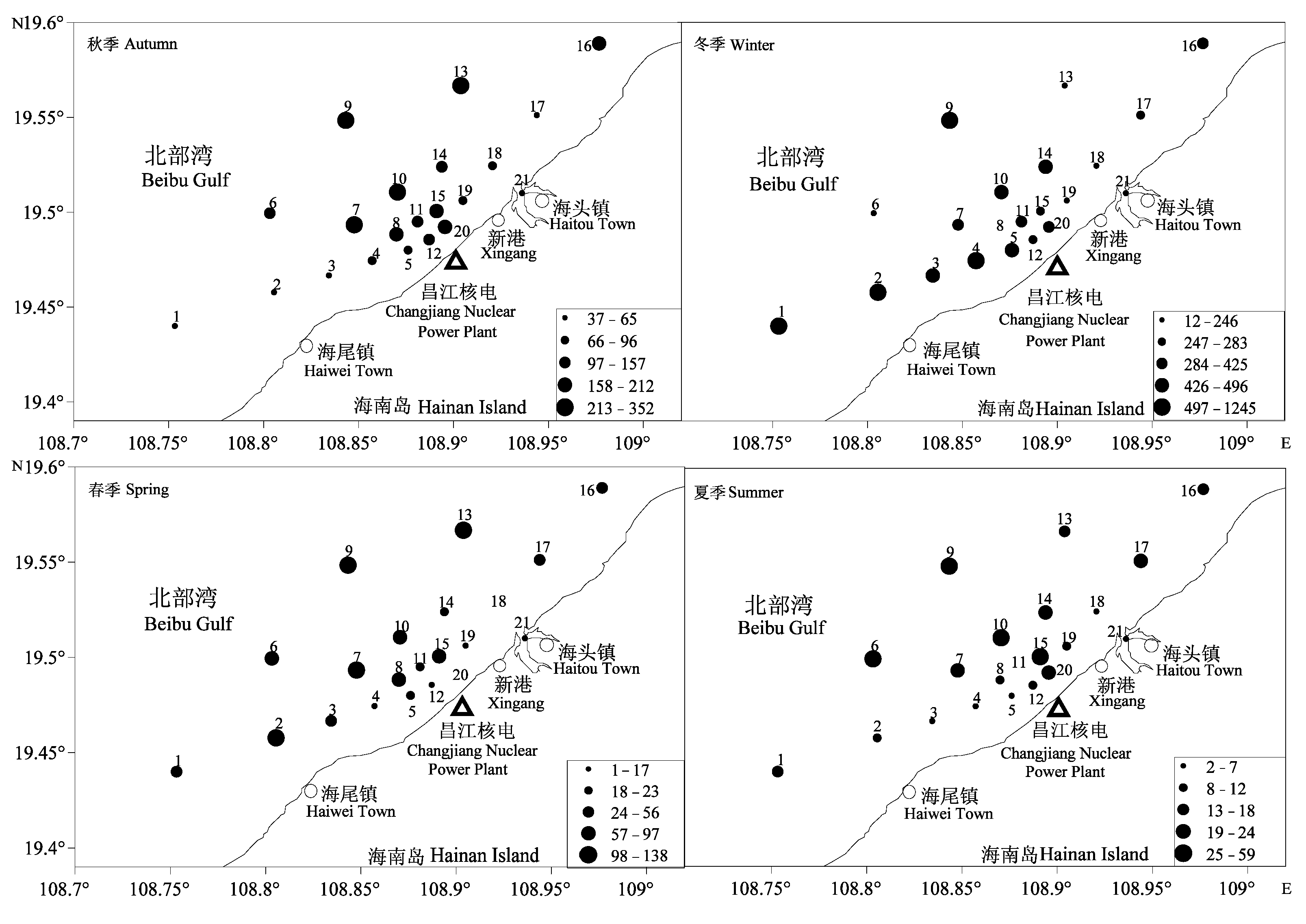
图4 2008-2009年海南昌江近岸桡足类丰度(ind./m3)的平面分布
Fig. 4 Horizontal distribution of planktonic copepods abundance (ind./m3) in Changjiang coastal waters off Hainan Island between 2008 and 2009
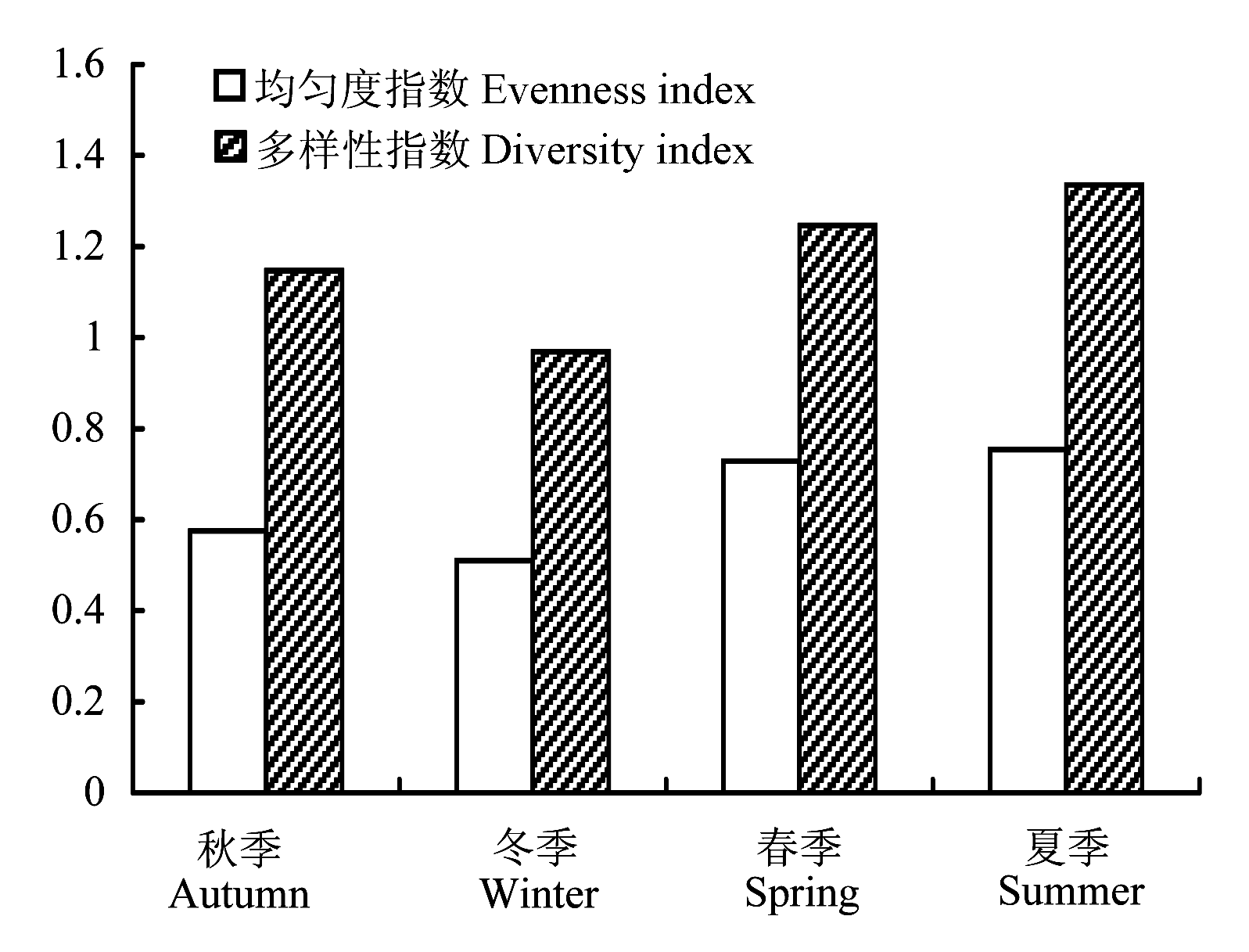
图5 2008-2009年海南昌江近岸浮游桡足类群落多样性指数(H′)和均匀度(J′)的季节变化
Fig. 5 Seasonal variations of planktonic copepods species diversity index and evenness index in Changjiang coastal waters off Hainan Island between 2008 and 2009
| 环境因子 Environmental variable | 秋季 Autumn | 冬季 Winter | 春季 Spring | 夏季 Summer | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | H′ | N | H′ | N | H′ | N | H′ | ||||
| 水温 Temperature | -0.26 | -0.02 | 0.39 | -0.06 | -0.04 | -0.30 | -0.06 | -0.43 | |||
| 盐度 Salinity | 0.25 | -0.06 | 0.38 | -0.25 | 0.28 | 0.69** | 0.12 | 0.41 | |||
表3 2008-2009年海南昌江近岸桡足类丰度(N)和多样性指数(H′)与温度和盐度的相关性分析
Table 3 Regression analysis between abundance and diversity index of copepods and temperature and salinity in Changjiang coastal waters off Hainan Island between 2008 and 2009
| 环境因子 Environmental variable | 秋季 Autumn | 冬季 Winter | 春季 Spring | 夏季 Summer | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | H′ | N | H′ | N | H′ | N | H′ | ||||
| 水温 Temperature | -0.26 | -0.02 | 0.39 | -0.06 | -0.04 | -0.30 | -0.06 | -0.43 | |||
| 盐度 Salinity | 0.25 | -0.06 | 0.38 | -0.25 | 0.28 | 0.69** | 0.12 | 0.41 | |||
| 时间 Time | 海域 Sea area | 种类数 Species richness | 资料来源 Data source | 优势种(优势度) Dominant species (Dominancy) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1998-1999年夏 The summer of 1998 and 1999 | 北部湾 Beibu Gulf | 84 | 廖秀丽等, 2011 | 叉胸刺水蚤 Centropages furcatus (0.181) 微刺哲水蚤 Canthocalanus pauper (0.069) 异尾宽水蚤 Temora discaudata (0.038) 亚强次真哲水蚤 Subeucalanus subcrassus (0.029) 奥氏胸刺水蚤 Centropages orsinii (0.028) 椭形长足水蚤 Calanopia elliptica (0.022) 小唇角水蚤 Labidocera minuta (0.019) 长角隆哲水蚤 Acrocalanus longicornis (0.018) |
| 1998-1999年冬 The winter of 1998 and 1999 | 北部湾 Beibu Gulf | 67 | 廖秀丽等, 2011 | 微刺哲水蚤 Canthocalanus pauper (0.154) 亚强次真哲水蚤 Subeucalanus subcrassus (0.059) 异尾宽水蚤 Temora discaudata (0.029) 长角隆哲水蚤 Acrocalanus longicornis (0.024) 驼背隆哲水蚤 Acrocalanus gibber (0.020) 羽长腹剑水蚤 Oithona plumifera (0.019) |
| 2006年夏 The summer of 2006 | 北部湾 Beibu Gulf | 113 | 郭东晖等, 2008 | 亚强次真哲水蚤 Subeucalanus subcrassus (0.21) 异尾宽水蚤 Temora discaudata (0.09) 椭形长足水蚤 Calanopia elliptica (0.05) 伯氏平头水蚤 Candacia bradyi (0.04) 普通波水蚤 Undinula vulgaris (0.03) |
| 2006年冬 The winter of 2006 | 北部湾 Beibu Gulf | 84 | 郭东晖等, 2008 | 亚强次真哲水蚤 Subeucalanus subcrassus (0.43) 精致真刺水蚤 Euchaeta concinna (0.32) 微刺哲水蚤 Canthocalanus pauper (0.04) 伯氏平头水蚤 Candacia bradyi (0.02) |
| 2008-2009年夏 The summer of 2008 and 2009 | 海南昌江沿岸 Changjiang coastal waters of Hainan Island | 26 | 本研究 This study | 亚强次真哲水蚤 Subeucalanus subcrassus (0.13) 椭形长足水蚤 Calanopia elliptica (0.08) 微刺哲水蚤 Canthocalanus pauper (0.05) |
| 2008-2009年冬 The winter of 2008 and 2009 | 海南昌江沿岸 Changjiang coastal waters of Hainan Island | 27 | 本研究 This study | 亚强次真哲水蚤 Subeucalanus subcrassus (0.59) 锥形宽水蚤 Temora turbinata (0.09) 微刺哲水蚤 Canthocalanus pauper (0.05) 刺尾纺锤水蚤 Acartia spinicauda (0.02) |
表4 2008-2009年海南西部近岸浮游桡足类优势种与历史资料比较
Table 4 Comparison of dominant species of planktonic copepods between the Changjiang coastal waters off Hainan Island and the historical data
| 时间 Time | 海域 Sea area | 种类数 Species richness | 资料来源 Data source | 优势种(优势度) Dominant species (Dominancy) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1998-1999年夏 The summer of 1998 and 1999 | 北部湾 Beibu Gulf | 84 | 廖秀丽等, 2011 | 叉胸刺水蚤 Centropages furcatus (0.181) 微刺哲水蚤 Canthocalanus pauper (0.069) 异尾宽水蚤 Temora discaudata (0.038) 亚强次真哲水蚤 Subeucalanus subcrassus (0.029) 奥氏胸刺水蚤 Centropages orsinii (0.028) 椭形长足水蚤 Calanopia elliptica (0.022) 小唇角水蚤 Labidocera minuta (0.019) 长角隆哲水蚤 Acrocalanus longicornis (0.018) |
| 1998-1999年冬 The winter of 1998 and 1999 | 北部湾 Beibu Gulf | 67 | 廖秀丽等, 2011 | 微刺哲水蚤 Canthocalanus pauper (0.154) 亚强次真哲水蚤 Subeucalanus subcrassus (0.059) 异尾宽水蚤 Temora discaudata (0.029) 长角隆哲水蚤 Acrocalanus longicornis (0.024) 驼背隆哲水蚤 Acrocalanus gibber (0.020) 羽长腹剑水蚤 Oithona plumifera (0.019) |
| 2006年夏 The summer of 2006 | 北部湾 Beibu Gulf | 113 | 郭东晖等, 2008 | 亚强次真哲水蚤 Subeucalanus subcrassus (0.21) 异尾宽水蚤 Temora discaudata (0.09) 椭形长足水蚤 Calanopia elliptica (0.05) 伯氏平头水蚤 Candacia bradyi (0.04) 普通波水蚤 Undinula vulgaris (0.03) |
| 2006年冬 The winter of 2006 | 北部湾 Beibu Gulf | 84 | 郭东晖等, 2008 | 亚强次真哲水蚤 Subeucalanus subcrassus (0.43) 精致真刺水蚤 Euchaeta concinna (0.32) 微刺哲水蚤 Canthocalanus pauper (0.04) 伯氏平头水蚤 Candacia bradyi (0.02) |
| 2008-2009年夏 The summer of 2008 and 2009 | 海南昌江沿岸 Changjiang coastal waters of Hainan Island | 26 | 本研究 This study | 亚强次真哲水蚤 Subeucalanus subcrassus (0.13) 椭形长足水蚤 Calanopia elliptica (0.08) 微刺哲水蚤 Canthocalanus pauper (0.05) |
| 2008-2009年冬 The winter of 2008 and 2009 | 海南昌江沿岸 Changjiang coastal waters of Hainan Island | 27 | 本研究 This study | 亚强次真哲水蚤 Subeucalanus subcrassus (0.59) 锥形宽水蚤 Temora turbinata (0.09) 微刺哲水蚤 Canthocalanus pauper (0.05) 刺尾纺锤水蚤 Acartia spinicauda (0.02) |
| 物种 Taxa | 秋季 Autumn | 冬季 Winter | 春季 Spring | 夏季 Summer |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 哲水蚤科 Calanidae 微刺哲水蚤 Canthocalanus pauper | + | + | + | + |
| 普通波水蚤 Undinula vulgaris | + | + | + | + |
| 真哲水蚤科 Eucalanidae 强次真哲水蚤 Eucalanus crassua | + | + | ||
| 亚强次真哲水蚤 Subeucalanus subcrassus | + | + | + | + |
| 拟哲水蚤科 Paracalanidae 驼背隆哲水蚤 Acrocalanus gibber | + | + | ||
| 微驼隆哲水蚤 A. gracilis | + | |||
| 厦门矮隆哲水蚤 Bestiola amoyensis | + | |||
| 小拟哲水蚤 Paracalanus parvus | + | + | ||
| 宽水蚤科 Temoridae 锥形宽水蚤 Temora turbinata | + | + | + | + |
| 异尾宽水蚤 T. discaudata | + | + | + | |
| 柱形宽水蚤 T. stylifera | + | + | ||
| 胸刺水蚤科 Centropagidae 瘦尾胸刺水蚤 Centropages tenuiremis | + | + | + | + |
| 叉胸刺水蚤 C. furcatus | + | |||
| 背针胸刺水蚤 C. dorsispinatus | + | |||
| 奥氏胸刺水蚤 C. orsinii | + | |||
| 真刺水蚤科 Euchaetidae 精致真刺水蚤 Euchaeta concinna | + | + | + | + |
| 光水蚤科 Lucicutiidae 黄角光水蚤 Lucicutia flavicornis 卵形光水蚤 L. ovalis | + | + + | + | |
| 厚壳水蚤科 Scolecithricidae 绿齿厚壳水蚤 Scolecithrix nicobarica | + | + | + | |
| 平头水蚤科 Candaciidae 伯氏平头水蚤 Candacia bradyi | + | + | ||
| 平头水蚤一种 Candacia. sp. | + | |||
| 角水蚤科 Pontellidae 汤氏长足水蚤 Calanopia thompsoni | + | + | ||
| 椭形长足水蚤 C. elliptica | + | + | + | |
| 双刺唇角水蚤 Labidocera bipinnata | + | + | + | + |
| 小唇角水蚤 L. minuta | + | + | + | + |
| 真刺唇角水蚤 L. euchaeta | + | |||
| 科氏唇角水蚤 L. kroyeri | + | |||
| 扩指简角水蚤 Pontellopsis inflatodigitata | + | + | ||
| 瘦尾简角水蚤 P. tenuicauda | + | + | ||
| 纺锤水蚤科 Acartiidae 太平洋纺锤水蚤 Acartia pacifica | + | + | + | |
| 刺尾纺锤水蚤 A. spinicauda | + | |||
| 红纺锤水蚤 A. erythraea | + | + | + | |
| 小纺锤水蚤 A. negligens | + | |||
| 歪水蚤科 Tortanidae 钳形歪水蚤 Tortanus forcipatus | + | + | + | + |
| 瘦歪水蚤 T. gracilis | + | |||
| 长腹剑水蚤科 Oithonidae 瘦长腹剑水蚤 Oithona tenuis | + | |||
| 短角长腹剑水蚤 O. brevicornis | + | + | ||
| 细长腹剑水蚤 O. attenuata | + | |||
| 大眼剑水蚤科 Corycaeidae 大眼剑水蚤一种 Corycaeus sp. | + | + | ||
| 叶剑水蚤科 Sapphirinidae 黑点叶剑水蚤 Sapphirina nigromaculata | + | |||
| 叶剑水蚤一种 Sapphirina sp. | + | |||
| 桨剑水蚤一种 Copilia sp. | + | |||
| 长猛水蚤科 Ectinosomatidae 挪威小星猛水蚤 Microsetella norvegica | + | |||
| 怪水蚤科 Monstrillidae 怪水蚤一种 Monstrilla sp. | + |
附表1 昌江沿岸水域浮游桡足类种类名录
Table S1 Species checklist of planktonic copepods in Changjiang coastal waters off Hainan Island
| 物种 Taxa | 秋季 Autumn | 冬季 Winter | 春季 Spring | 夏季 Summer |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 哲水蚤科 Calanidae 微刺哲水蚤 Canthocalanus pauper | + | + | + | + |
| 普通波水蚤 Undinula vulgaris | + | + | + | + |
| 真哲水蚤科 Eucalanidae 强次真哲水蚤 Eucalanus crassua | + | + | ||
| 亚强次真哲水蚤 Subeucalanus subcrassus | + | + | + | + |
| 拟哲水蚤科 Paracalanidae 驼背隆哲水蚤 Acrocalanus gibber | + | + | ||
| 微驼隆哲水蚤 A. gracilis | + | |||
| 厦门矮隆哲水蚤 Bestiola amoyensis | + | |||
| 小拟哲水蚤 Paracalanus parvus | + | + | ||
| 宽水蚤科 Temoridae 锥形宽水蚤 Temora turbinata | + | + | + | + |
| 异尾宽水蚤 T. discaudata | + | + | + | |
| 柱形宽水蚤 T. stylifera | + | + | ||
| 胸刺水蚤科 Centropagidae 瘦尾胸刺水蚤 Centropages tenuiremis | + | + | + | + |
| 叉胸刺水蚤 C. furcatus | + | |||
| 背针胸刺水蚤 C. dorsispinatus | + | |||
| 奥氏胸刺水蚤 C. orsinii | + | |||
| 真刺水蚤科 Euchaetidae 精致真刺水蚤 Euchaeta concinna | + | + | + | + |
| 光水蚤科 Lucicutiidae 黄角光水蚤 Lucicutia flavicornis 卵形光水蚤 L. ovalis | + | + + | + | |
| 厚壳水蚤科 Scolecithricidae 绿齿厚壳水蚤 Scolecithrix nicobarica | + | + | + | |
| 平头水蚤科 Candaciidae 伯氏平头水蚤 Candacia bradyi | + | + | ||
| 平头水蚤一种 Candacia. sp. | + | |||
| 角水蚤科 Pontellidae 汤氏长足水蚤 Calanopia thompsoni | + | + | ||
| 椭形长足水蚤 C. elliptica | + | + | + | |
| 双刺唇角水蚤 Labidocera bipinnata | + | + | + | + |
| 小唇角水蚤 L. minuta | + | + | + | + |
| 真刺唇角水蚤 L. euchaeta | + | |||
| 科氏唇角水蚤 L. kroyeri | + | |||
| 扩指简角水蚤 Pontellopsis inflatodigitata | + | + | ||
| 瘦尾简角水蚤 P. tenuicauda | + | + | ||
| 纺锤水蚤科 Acartiidae 太平洋纺锤水蚤 Acartia pacifica | + | + | + | |
| 刺尾纺锤水蚤 A. spinicauda | + | |||
| 红纺锤水蚤 A. erythraea | + | + | + | |
| 小纺锤水蚤 A. negligens | + | |||
| 歪水蚤科 Tortanidae 钳形歪水蚤 Tortanus forcipatus | + | + | + | + |
| 瘦歪水蚤 T. gracilis | + | |||
| 长腹剑水蚤科 Oithonidae 瘦长腹剑水蚤 Oithona tenuis | + | |||
| 短角长腹剑水蚤 O. brevicornis | + | + | ||
| 细长腹剑水蚤 O. attenuata | + | |||
| 大眼剑水蚤科 Corycaeidae 大眼剑水蚤一种 Corycaeus sp. | + | + | ||
| 叶剑水蚤科 Sapphirinidae 黑点叶剑水蚤 Sapphirina nigromaculata | + | |||
| 叶剑水蚤一种 Sapphirina sp. | + | |||
| 桨剑水蚤一种 Copilia sp. | + | |||
| 长猛水蚤科 Ectinosomatidae 挪威小星猛水蚤 Microsetella norvegica | + | |||
| 怪水蚤科 Monstrillidae 怪水蚤一种 Monstrilla sp. | + |
| [1] | Chen QC (陈清潮), Chen YQ (陈亚瞿), Hu YZ (胡雅竹) (1980) Preliminary study on the plankton communities in the southern Yellow Sea and the East China Sea.Acta Oceanologica Sinica(海洋学报), 2, 149-157. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [2] | Guo DH (郭东晖), Huang JQ (黄加祺), Li SJ (李少菁), Xu ZZ (许振祖) (2008) Ecological studies on zooplankton in Beibu Gulf during summer and winter. III. Copepods. In: A Collection of Papers of Marine Science in Beibu Gulf, Vol.1 (北部湾海洋科学研究论文集, 第一辑), pp. 243-248. China Ocean Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [3] | Huang JQ (黄加祺), Zheng Z (郑重) (1986) Effects of temperature and salinity on survival rate of copepods of Xiamen port.Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica(海洋与湖沼), 17, 161-167. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [4] | Huang ZG (黄宗国), Lin M (林茂) (2012) The Living Species in China’s Seas (中国海洋物种多样性). China Ocean Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [5] | Li SJ (李少菁), Huang JQ (黄加祺), Guo DH (郭东晖), Xu ZZ (许振祖), Chen G (陈钢) (2006) Study on ecology of marine plankton in Taiwan Strait, China.Journal of Xiamen University (Natural Science)(厦门大学学报 (自然科学版)), 45(S2), 25-31. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [6] | Liao XL (廖秀丽), Du FY (杜飞雁), Li CH (李纯厚) (2011) Species composition and diversity of planktonic copepods in Beibu Gulf during El Nino /La Nina.South China Fisheries Science(南方水产科学), 7(5), 1-8. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [7] | Lin LM (林利民), Xu F (许峰), Lin J (林君) (1998) Effects of various salinities to growth and development of Acartia spinicauda.Journal of Oceanography in Taiwan Strait(台湾海峡), 17(S1), 53-55. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [8] | Lin YS (林元烧), Li S (李松) (1984) A preliminary study on the life cycle of Calanus sinicus (Brodsky) in Xiamen harbour. Journal of Xiamen University (Natural Science) (厦门大学学报 (自然科学版)), 23, 111-117. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [9] | Liu GX, Xu DH (2009) Effects of calanoid copepod Schmackeria poplesia as a live food on the growth, survival and fatty acid composition of larvae and juveniles of Japanese flounder, Paralichthys olivaceus.Oceanic and Coastal Sea Research, 8, 359-365. |
| [10] | Pan FW (潘非斐), Cao WQ (曹文清), Lin YS (林元烧), Zheng LM (郑连明), Yang WD (杨位迪) (2011) Spatio-temporal variability of copepod composition in the eastern Beibu Gulf. In: A Collection of Papers of Marine Science in Beibu Gulf, Vol.3 (北部湾海洋科学研究论文集, 第三辑), pp. 36-54. China Ocean Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [11] | Pielou EC (1966) The measurement of diversity in different types of biological collections. Journal of Theoretical Biology, 13, 131-144. |
| [12] | Rezai H, Yusoff FM, Arshad A, Ross O (2005) Spatial and temporal variations in calanoid copepod distribution in the straits of Malacca.Hydrobiologia, 537, 157-167. |
| [13] | Shannon CE, Weaver W (1949) The Mathematical Theory of Communication . University of Illinois Press, Urbana. |
| [14] | Shimode S, Toda T, Kikuchi T (2006) Spatio-temporal changes in diversity and community structure of planktonic copepods in Sagami Bay.Marine Biology, 148, 581-597. |
| [15] | Wang F (王芳) (2000) Strategic concept review and development of marine resources and environment conditions in Beibu Gulf.Resources and Industries (资源•产业), 2, 37-41. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [17] | Wang R (王荣), Gao SW (高尚武), Wang K (王克), Zuo T (左涛) (2007) Zooplankton indication of the Yellow Sea warm current in winter.Journal of Fisheries of China(水产学报), 27(Suppl.), 39-48. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [18] | Wang R (王荣), Zhang HY (张鸿雁), Wang K (王克), Zuo T (左涛) (2002) Function performed by small copepods in marine ecosystem.Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica(海洋与湖沼), 33, 453-460. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [19] | Wang Y (王雨), Lin M (林茂), Chen XQ (陈兴群), Lin GM (林更铭) (2012) Annual variation on phytoplankton in coastal waters of western Hainan Island and related affecting factors.Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica(水生生物学报), 36, 724-733. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [20] | Xu DH (徐东晖) (2010) The Effects of Natural and Anthropogenic Factors on the Physiology of Some Dominant Copepods in the Yellow Sea and East China Sea (自然和人为因子对黄、东海几种桡足类优势种生理活动的影响). PhD dissertation, Ocean University of China, Qingdao. (in Chinese) |
| [21] | Xu ZL (徐兆礼) (2006) Ecological characters of the Eucalanus subcrassus population in the East China Sea.Acta Ecologica Sinica(生态学报), 26, 1151-1158. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [22] | Xu ZL (徐兆礼), Chen YQ (陈亚瞿) (1989) Aggregated intensity of dominant species of zooplankton in autumn in the East China Sea and Yellow Sea.Chinese Journal of Ecology(生态学杂志), 8(4), 13-15. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [23] | Xu ZL, Gao Q (2011) Optimal salinity for dominant copepods in the East China Sea, determined using a yield density model.Chinese Journal of Oceanology and Limnology, 29, 514-523. |
| [24] | Zhang DJ, Li SJ, Wang GZ, Guo DH (2011) Impacts of CO2-driven seawater acidification on survival, egg production rate and hatching success of four marine copepods. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 30(6), 86-94. |
| [25] | Zhao ZM (赵志模), Zhou XY (周新远) (1984)An Introduction to Ecology (生态学引论). Scientific and Technical Documentation Press, Chongqing. (in Chinese) |
| [26] | Zheng Z (郑重), Li SJ (李少菁), Xu ZZ (许振祖) (1984) Marine Planktology (海洋浮游生物学). China Ocean Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [27] | Zheng Z (郑重), Li SJ (李少菁), Lian GS (连光山) (1992) The Marine Copepod Biology (海洋桡足类生物学). Xiamen University Press, Xiamen. (in Chinese) |
| [1] | 宋远昊, 龚吕, 李贲, 胡阳, 李秀珍. 辽河口不同退塘还湿方式对大型底栖动物的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24316-. |
| [2] | 魏诗雨, 宋天骄, 罗佳宜, 张燕, 赵子萱, 茹靖雯, 易华, 林雁冰. 秦岭火地塘针叶林土壤细菌群落的海拔分布格局[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(9): 24180-. |
| [3] | 张雅丽, 张丙昌, 赵康, 李凯凯, 刘燕晋. 毛乌素沙地不同类型生物结皮细菌群落差异及其驱动因子[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(8): 23027-. |
| [4] | 姚仁秀, 陈燕, 吕晓琴, 王江湖, 杨付军, 王晓月. 海拔及环境因子影响杜鹃属植物的表型特征和化学性状[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(2): 22259-. |
| [5] | 王晓凤, 饶杰生, 杨涛, 刘文聪, 田希, 陈稀, 刘其明, 徐衍潇, 张秋雨, 张洪强, 张旭, 欧晓昆, 沈泽昊. 云南鸡足山半湿润常绿阔叶林群落木本植物多样性格局与环境解释[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(11): 23217-. |
| [6] | 闫冰, 陆晴, 夏嵩, 李俊生. 城市土壤微生物多样性研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(8): 22186-. |
| [7] | 汪婷, 周立志. 合肥市小微湿地鸟类多样性的时空格局及其影响因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(7): 21445-. |
| [8] | 薛文凯, 孟华旦尚, 王艳红, 朱攀, 德吉, 郭小芳. 纳木措可培养丝状真菌多样性及其与理化因子关系[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(6): 21473-. |
| [9] | 陈燕南, 梁铖, 陈军. 亚热带不同树种组成森林中土壤甲螨群落结构特征: 以江西新岗山为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(12): 22334-. |
| [10] | 吴墨栩, 安明态, 田力, 刘锋. 茂兰喀斯特森林木本植物性系统数量特征及其与环境因子的关系[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(11): 22025-. |
| [11] | 施雨含, 任宗昕, 王维嘉, 徐鑫, 刘杰, 赵延会, 王红. 中国-喜马拉雅三种黄耆属植物与其传粉熊蜂的空间分布预测[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(6): 759-769. |
| [12] | 张家真, 高春蕾, 李艳, 孙萍, 王宗灵. 江阴港口外来船舶压载舱沉积物中甲藻包囊种类及组成[J]. 生物多样性, 2020, 28(2): 144-154. |
| [13] | 蒋日进,张琳琳,徐开达,李鹏飞,肖祎,樊紫薇. 浙江中南部近岸海域游泳动物功能群特征与多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2019, 27(12): 1330-1338. |
| [14] | 李雪晴, 孙赫英, 何德奎, 陈毅峰. 澜沧江-湄公河中上游淡水鱼类多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2019, 27(10): 1090-1100. |
| [15] | 吴初平, 韩文娟, 江波, 刘博文, 袁位高, 沈爱华, 黄玉洁, 朱锦茹. 浙江定海次生林内物种丰富度与生物量和生产力关系的环境依赖性[J]. 生物多样性, 2018, 26(6): 545-553. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn