



Biodiv Sci ›› 2022, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (11): 22209. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2022209 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2022209
Special Issue: 青藏高原生物多样性与生态安全
• Reviews • Previous Articles Next Articles
Abudusaimaiti Maierdiyali1,2, Yun Wang2,*( ), Shuangcheng Tao2, Yaping Kong2, Hao Wang1, Zhi Lü1,*(
), Shuangcheng Tao2, Yaping Kong2, Hao Wang1, Zhi Lü1,*( )
)
Received:2022-04-21
Accepted:2022-09-05
Online:2022-11-20
Published:2022-11-21
Contact:
Yun Wang,Zhi Lü
Abudusaimaiti Maierdiyali, Yun Wang, Shuangcheng Tao, Yaping Kong, Hao Wang, Zhi Lü. Research status and challenges of road impacts on wildlife in China[J]. Biodiv Sci, 2022, 30(11): 22209.
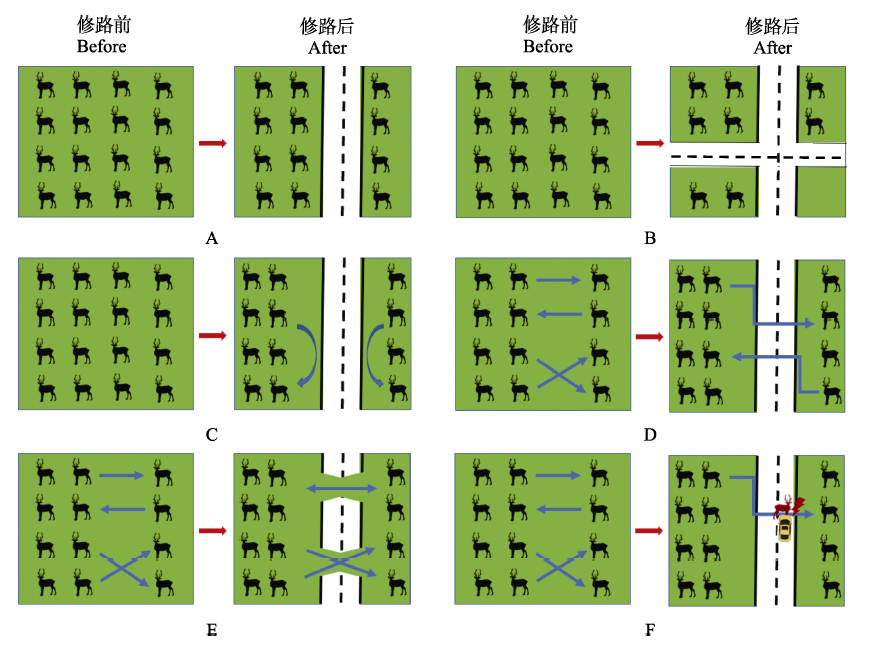
Fig. 1 A diagram of the impact of road on wildlife. The red arrows show the changes before and after the road was built, and the blue arrows show the movement of the wildlife. A, Road construction causes habitat loss and decrease of wildlife population; B, The network of road causes habitat fragmentation; C, Road disturbance causes wildlife to keep a distance from the road; D, Road affect migration route of wildlife; E, Wildlife use crossing structures; F, Wildlife cross roads might cause roadkill.
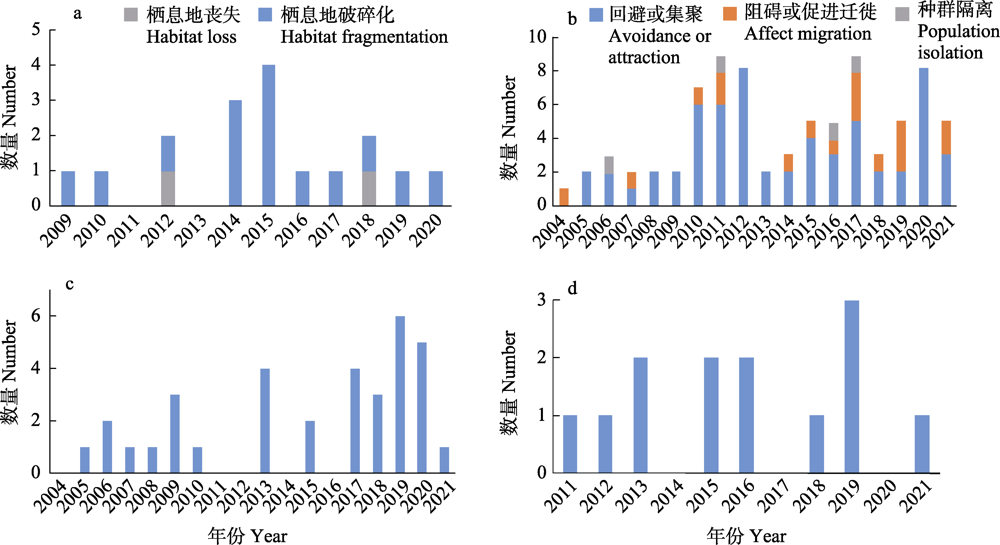
Fig. 3 Annual distribution of published articles on wildlife and road. a, Impact on habitat; b, Impact on animal behavior; c, Wildlife crossing structures; d, Roadkill.
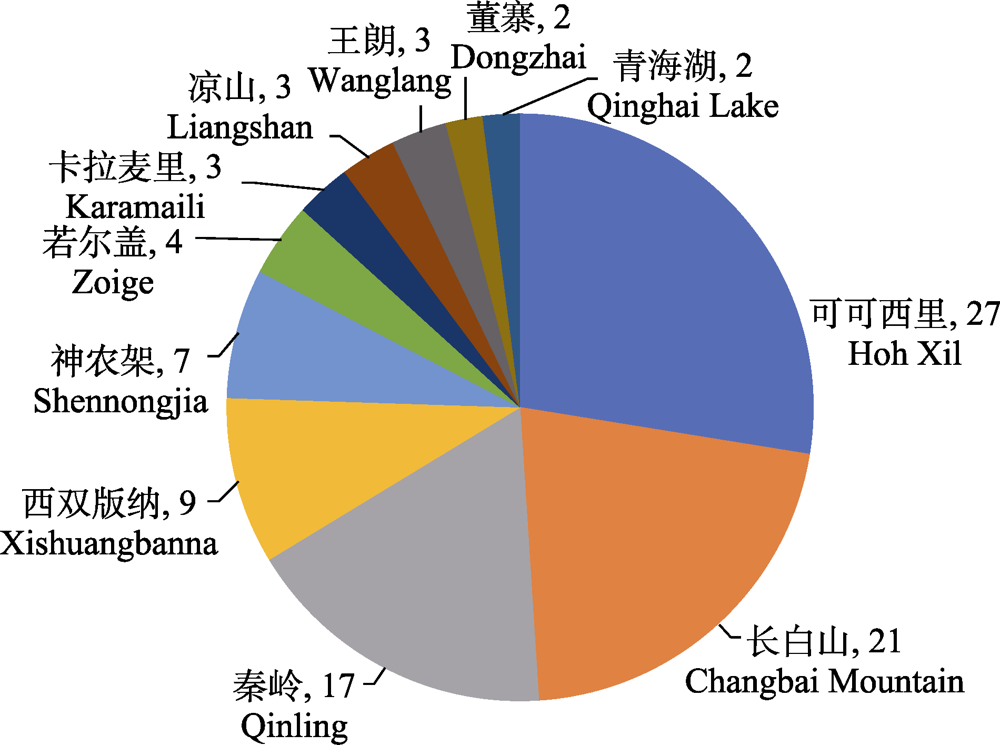
Fig. 4 Research area distribution of published articles on wildlife and road. The number of research area associated with only one article is large, so they’re not shown in this figure.
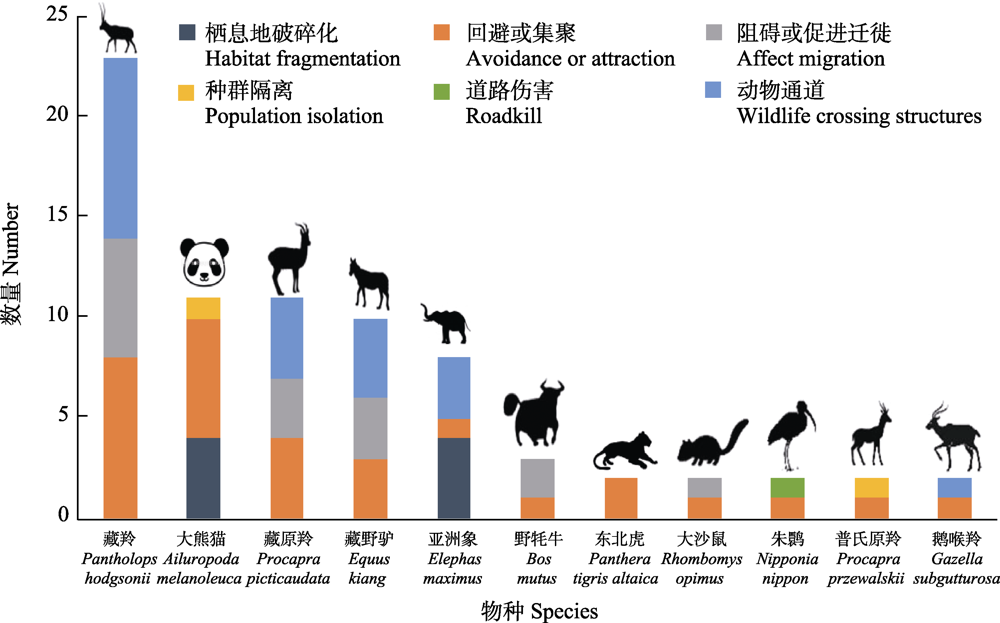
Fig. 5 Focal species distribution of published articles on wildlife and road. The number of focal species associated with only one article is large, so they’re not shown in this figure.
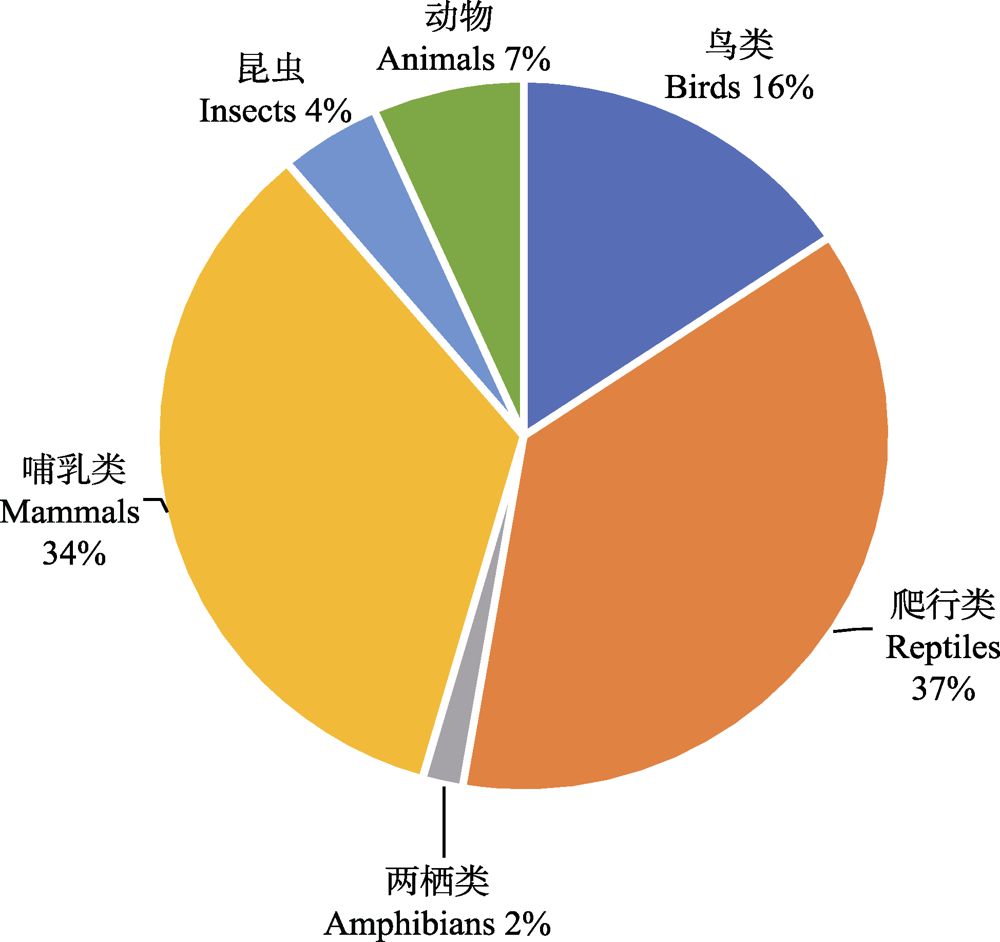
Fig. 7 The distribution of taxon of roadkill recorded from Sina Microblog data. Mammals and reptiles have the most records, birds also have some records, insects and amphibians have fewer records. There are 7% records that didn’t point out species and used “animal” to replace them.
| [1] |
Berger J, Beckmann JP (2010) Sexual predators, energy development, and conservation in greater Yellowstone. Conservation Biology, 24, 891-896.
DOI PMID |
| [2] | Bu QS, Dong GQ, He CS, Li DL (2013) Eco-environmental impact post-assessment of Qinghai-Tibet Railway from Golmud to Lhasa in operation. Railway Energy Saving & Environmental Protection & Occupational Safety and Health, (3), 111-115. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [步青松, 董贵奇, 何财松, 李德良 (2013) 青藏铁路格尔木至拉萨段运营期生态环境影响后评价. 铁路节能环保与安全卫生, (3), 111-115.] | |
| [3] | Buho H, Jiang Z, Liu C, Yoshida T, Mahamut H, Kaneko M, Asakawa M, Motokawa M, Kaji K, Wu X, Otaishi N, Ganzorig S, Masuda R (2011) Preliminary study on migration pattern of the Tibetan antelope (Pantholops hodgsonii) based on satellite tracking. Advances in Space Research, 48, 43-48. |
| [4] |
Carter N, Killion A, Easter T, Brandt J, Ford A (2020) Road development in Asia: Assessing the range-wide risks to tigers. Science Advances, 6, 9619.
DOI PMID |
| [5] | Ceia-Hasse A, Borda-de-Água L, Grilo C, Pereira HM (2017) Global exposure of carnivores to roads. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 26, 592-600. |
| [6] | Chen JD, Kong YP, Chen JY (2017) Science and Practice of Green Road in China. China Communication Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [陈济丁, 孔亚平, 陈建业 (2017) 绿色公路建设理论与实践. 人民交通出版社, 北京.] | |
| [7] | Chen XL, Shi XX, Cui BJ, Zheng ZH (2017) Impact of expressway reconstruction and extension project on habitat for reed-white-crowned pheasants and design of wildlife channel. Environment and Development, 29, 9-10, 12. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [陈兴龙, 史晓雪, 崔宝军, 郑志华 (2017) 高速公路改扩建工程对白冠长尾雉栖息地的影响分析及野生动物通道设计. 环境与发展, 29, 9-10, 12.] | |
| [8] | Cheng HF, Zhu Y, Cai Q, Yang Z, Feng T, Zhang HF (2015) The effective monitoring of wildlife corridor along Donghetai-Liangfengya Highway in Guanyinshan Nature Reserve of Shaanxi. Shaanxi Forest Science and Technology, (6), 19-23. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [成鸿飞, 朱云, 蔡琼, 杨钊, 封托, 张洪峰 (2015) 陕西观音山国家级自然保护区东凉公路动物通道有效性监测. 陕西林业科技, (6), 19-23.] | |
| [9] | Chyn K, Lin TE, Chen YK, Chen CY, Fitzgerald LA (2019) The magnitude of roadkill in Taiwan: Patterns and consequences revealed by citizen science. Biological Conservation, 237, 317-326. |
| [10] | Clauzel C, Deng XQ, Wu GS, Giraudoux P, Li L (2015) Assessing the impact of road developments on connectivity across multiple scales: Application to Yunnan snub-nosed monkey conservation. Biological Conservation, 192, 207-217. |
| [11] | Cui JF, Chen WW, Newman C, Han WW, Buesching CD, MacDonald DW, Xie ZQ, Zhou YB (2018) Roads disrupt rodent scatter-hoarding seed-dispersal services: Implication for forest regeneration. Perspectives in Plant Ecology, Evolution and Systematics, 34, 102-108. |
| [12] | Dai JH, Dai Q, Zhang M, Zhang JD, Li C, Liu B, Liu ZJ, Wang YZ (2005) Habitat selection of three amphibians (Rana kukunoris, Nanorana pleskei, Bufo minshanicus) during summer-autumn in Zoige Wetland National Nature Reserve. Zoological Research, 26, 263-271. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [戴建洪, 戴强, 张明, 张晋东, 李成, 刘兵, 刘志军, 王跃招 (2005) 若尔盖湿地国家自然保护区三种无尾两栖类夏秋季生境选择. 动物学研究, 26, 263-271.] | |
| [13] | Dai Q, Wang YZ (2011) Effect of road on the distribution of amphibians in Wetland area—Test with model-averaged prediction. Polish Journal of Ecology, 59, 381-389. |
| [14] |
Dai Q, Yuan ZP, Zhang JD, Yang Y, Zhang M, Zhang Q, Gu HJ, Liu ZJ, Jian Y, Wang YZ (2006) Road and road construction effects on habitat use of small mammals and birds in Zoige alpine wetland. Biodiversity Science, 14, 121-127. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[戴强, 袁佐平, 张晋东, 杨勇, 张明, 张强, 顾海军, 刘志君, 蹇依, 王跃招 (2006) 道路及道路施工对若尔盖高寒湿地小型兽类及鸟类生境利用的影响. 生物多样性, 14, 121-127.]
DOI |
|
| [15] | David ML, Fritts SH, Radde GL, Paul WJ (1988) Wolf distribution and road density in Minnesota. Wildlife Society Bulletin, 16, 85-87. |
| [16] | Denneboom D, Bar-Massada A, Shwartz A (2021) Factors affecting usage of crossing structures by wildlife—A systematic review and meta-analysis. Science of the Total Environment, 777, 146061. |
| [17] | Ding H, Jin YH, Cui JG, Zhao LS, Piao ZJ (2008) Review on ranges of ecological road-effect zones. Journal of Zhejiang Forestry College, 25, 810-816. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [丁宏, 金永焕, 崔建国, 赵林森, 朴正吉 (2008) 道路的生态学影响域范围研究进展. 浙江林学院学报, 25, 810-816.] | |
| [18] | Dong YX, Liu LM, Zhan C (2018) Distribution characteristics and impact analysis of wild conservation animals in Daxin-Longzhou highway area. Western China Communications Science & Technology, (6), 182-185. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [董云霞, 刘路明, 詹诚 (2018) 大新至龙州公路路域野生保护动物分布特征及影响分析. 西部交通科技, (6), 182-185.] | |
| [19] | Feng T, Wu XM, Zhang HF (2019) Distribution of ungulate in different grades of highway and influential factors concerned in Qinling Mountains. Shaanxi Forest Science and Technology, (5), 1-6. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [封托, 吴晓民, 张洪峰 (2019) 秦岭不同等级公路周边有蹄类动物分布规律及影响因素研究. 陕西林业科技, (5), 1-6.] | |
| [20] | Feng T, Zhang HF, Wu XM (2013) Utilization of wildlife underpasses on Qinghai-Tibetan Railway during the operation. Shaanxi Forest Science and Technology, (6), 42-45. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [封托, 张洪峰, 吴晓民 (2013) 青藏铁路运营期野生动物通道利用状况初探. 陕西林业科技, (6), 42-45.] | |
| [21] | Forman RTT, Alexander LE (1998) Roads and their major ecological effects. Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics, 29, 207-231. |
| [22] | Forman RTT (2003) Road Ecology:Science and Solutions. Island Press, Washington, DC. |
| [23] | Ge C, Li ZQ, Li J, Huang C (2011) The effects on birds of human encroachment on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Transportation Research Part D: Transport and Environment, 16, 604-606. |
| [24] | Gloyne CC, Clevenger AP (2001) Cougar puma concolor use of wildlife crossing structures on the Trans-Canada highway in Banff National Park, Alberta. Wildlife Biology, 7, 117-124. |
| [25] | Gong MH, Hou M, Lin C, Song YL, Ouyang ZY (2012) The quantitative assessing of trail impacts on giant panda activity based on field track points and GIS. Biodiversity Science, 20, 420-426. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[龚明昊, 侯盟, 蔺琛, 宋延龄, 欧阳志云 (2012) 基于野外痕迹点和GIS技术定量评估步道对大熊猫活动的影响. 生物多样性, 20, 420-426.]
DOI |
|
| [26] | Gong MH, Ouyang ZY, Song YL (2014) Route selection based on wildlife habitat cost and GIS: The Yiziyakou passage of Sichuan 306 Road within giant panda habitat as a case study. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 34, 5627-5634. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [龚明昊, 欧阳志云, 宋延龄 (2014) 基于野生动物栖息地成本和GIS技术的道路选线——以大熊猫栖息地内四川306省道椅子垭口段为例. 生态学报, 34, 5627-5634.] | |
| [27] | Gong MH, Ouyang ZY, Xu WH, Song YL, Dai B (2015) The location of wildlife corridors under the impact of road disturbance: Case study of a giant panda conservation corridor. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 35, 3447-3453. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [龚明昊, 欧阳志云, 徐卫华, 宋延龄, 戴波 (2015) 道路影响下野生动物廊道的选址——以大熊猫保护廊道为例. 生态学报, 35, 3447-3453.] | |
| [28] | Grilo C, Borda-de-Água L, Beja P, Goolsby E, Soanes K, Roux A, Koroleva E, Ferreira FZ, Gagné SA, Wang Y, González-Suárez M, Meyer C (2021) Conservation threats from roadkill in the global road network. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 30, 2200-2210. |
| [29] | Grilo C, Koroleva E, Andrášik R, Bíl M, González-Suárez M (2020) Roadkill risk and population vulnerability in European birds and mammals. Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment, 18, 323-328. |
| [30] | Gu HJ, Dai Q, Wang Q, Wang YZ (2011) Factors contributing to amphibian road mortality in a wetland. Current Zoology, 57, 768-774. |
| [31] | Guan L, Wang Y, Chen B, Wang J, Xu JJ, Zheng HM, Zhao K (2020) Activity rhythm of Asian elephants at wild elephant valley section of Simao-Xiaomengyang expressway. Transport Research, 6(4), 52-59. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [关磊, 王云, 陈兵, 王冀, 徐景江, 郑宏民, 赵琨 (2020) 思小高速公路野象谷段路域亚洲象活动规律. 交通运输研究, 6(4), 52-59.] | |
| [32] |
He K, Dai Q, Gu XH, Zhang ZJ, Zhou J, Qi DW, Gu XD, Yang XY, Zhang W, Yang B, Yang ZS (2019) Effects of roads on giant panda distribution: A mountain range scale evaluation. Scientific Reports, 9, 1110.
DOI PMID |
| [33] | Hou X, Zhang HF, Wang J, Wu XM, Gao MZ, Gu MC (2011) Research progress of wildlife protection measures in highway construction. Transportation Construction & Management, (4), 102-103. (in Chinese) |
| [侯祥, 张洪峰, 王静, 吴晓民, 高美真, 顾明臣 (2011) 公路建设中野生动物保护措施的研究进展. 交通建设与管理, (4), 102-103.] | |
| [34] | Hu H, Tang JQ, Wang Y, Zhang HF, Lin YC, Su LN, Liu Y, Zhang W, Wang C, Wu D, Wu XM (2020) Evaluating bird collision risk of a high-speed railway for the crested ibis. Transportation Research Part D: Transport and Environment, 87, 102533. |
| [35] | Huang C, Li XY, Khanal L, Jiang XL (2019) Habitat suitability and connectivity inform a co-management policy of protected area network for Asian elephants in China. PeerJ, 7, e6791. |
| [36] |
Ibisch PL, Hoffmann MT, Kreft S, Pe’er G, Kati V, Biber-Freudenberger L, DellaSala DA, Vale MM, Hobson PR, Selva N (2016) A global map of roadless areas and their conservation status. Science, 354, 1423-1427.
PMID |
| [37] | Ji SN, Jiang ZG, Li LL, Li CW, Zhang YJ, Ren S, Ping XG, Cui SP, Chu HJ (2017) Impact of different road types on small mammals in Mt. Kalamaili Nature Reserve. Transportation Research Part D: Transport and Environment, 50, 223-233. |
| [38] | Jiang GS, Sun HY, Lang JM, Yang LJ, Li C, Lyet A, Long B, Miquelle DG, Zhang CZ, Aramilev S, Ma JZ, Zhang MH (2014) Effects of environmental and anthropogenic drivers on Amur tiger distribution in northeastern China. Ecological Research, 29, 801-813. |
| [39] | Kang DW, Wang R, Yang HW, Duan LJ, Li JQ (2015) Habitat use by giant pandas (Ailuropoda melanoleuca) in relation to roads in the Wanglang Nature Reserve, People’s Republic of China. Canadian Journal of Zoology, 92, 715-719. |
| [40] | Kang DW, Zhao ZJ, Chen XY, Lin YC, Wang XR, Li JQ (2020) Evaluating the effects of roads on giant panda habitat at two scales in a typical nature reserve. Science of the Total Environment, 710, 136351. |
| [41] | Kong YP, Wang Y, Guan L (2013) Road wildlife ecology research in China. Procedia-Social and Behavioral Sciences, 96, 1191-1197. |
| [42] | Kong YP, Wang Y, Zhang F (2011) Review on road-effect zone of wildlife. Sichuan Journal of Zoology, 30, 986-991, 1021. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [孔亚平, 王云, 张峰 (2011) 道路建设对野生动物的影响域研究进展. 四川动物, 30, 986-991, 1021.] | |
| [43] | Lan JY, Wang Y, Guan L, Chen JD, Kong YP, Piao MJ, Zhu HQ (2017) Distribution character and diversity of ungulates along Qinghai to Tibet highway and railway. Chinese Journal of Wildlife, 38, 341-346. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [兰家宇, 王云, 关磊, 陈济丁, 孔亚平, 朴敏娟, 朱洪强 (2017) 青藏公路和铁路(昆仑山口-五道梁段)有蹄类动物群落结构和多样性分布特征. 野生动物学报, 38, 341-346.] | |
| [44] | Lan JY, Wang Y, Guan L, Zhou HP, Kong YP (2020) Experimental study on the crossing behavior of highway culverts by amphibians in Changbai Mountain. Highway Engineering, 45(3), 95-98. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [兰家宇, 王云, 关磊, 周红萍, 孔亚平 (2020) 长白山区两栖类动物对公路涵洞穿越行为的试验研究. 公路工程, 45(3), 95-98.] | |
| [45] | Li B, Ma WC, Chen JR, Xue W, Zhang K, Luan XF (2012) Influence of highway construction on avian community. Sichuan Journal of Zoology, 31, 834-840, 847. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [李斌, 马武昌, 陈建荣, 薛伟, 张可, 栾晓峰 (2012) 韶赣高速公路(粤境段)建设对路域生态系统鸟类群落的影响. 四川动物, 31, 834-840, 847.] | |
| [46] | Li BB, Liao SY, Shi DY, Liu JM, Jiang SY, Zhu L, Lu MY, Shao YW, Gong WJ (2021) National Bird-building Collision Survey Report. https://env.dukekunshan.edu.cn/zh-hans/news. (accessed on 2022-06-23) |
| [47] | Li CW, Jiang ZG, Feng ZJ, Yang XB, Yang J, Chen LW (2009) Effects of highway traffic on diurnal activity of the critically endangered Przewalski’s gazelle. Wildlife Research, 36, 379-385. |
| [48] | Li J, Cong J, Liu X, Zhou YY, Wang XL, Li GL, Li DQ (2015) Effect of tourist roads on mammal activity in Shennongjia National Nature Reserve based on the trap technique of infrared cameras. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 34, 2195-2200. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [李佳, 丛静, 刘晓, 周芸芸, 王秀磊, 李广良, 李迪强 (2015) 基于红外相机技术调查神农架旅游公路对兽类活动的影响. 生态学杂志, 34, 2195-2200.] | |
| [49] | Li LB, Wang Y, Guan L, Zhu GH, Li N, Kong YP, Zhu HQ (2019) Monitoring of wildlife crossing structures along Beijing-Xinjiang Expressway (Linbai section). Sichuan Journal of Zoology, 38, 92-98. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [李灵贝, 王云, 关磊, 朱广河, 李娜, 孔亚平, 朱洪强 (2019) 京新高速公路(临白段)野生动物通道监测研究. 四川动物, 38, 92-98.] | |
| [50] |
Li SC, Xu YQ, Zhou QF, Wang L (2004) Statistical analysis on the relationship between road network and ecosystem fragmentation in China. Progress in Geography, 23, 78-85, 110. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
| [李双成, 许月卿, 周巧富, 王磊 (2004) 中国道路网与生态系统破碎化关系统计分析. 地理科学进展, 23, 78-85, 110.] | |
| [51] | Li TA, Shilling F, Thorne J, Li FM, Schott H, Boynton R, Berry AM (2010) Fragmentation of China’s landscape by roads and urban areas. Landscape Ecology, 25, 839-853. |
| [52] | Li YH, Hu YM, Li XZ, Xiao DN (2003) A review on road ecology. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 14, 447-452. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [李月辉, 胡远满, 李秀珍, 肖笃宁 (2003) 道路生态研究进展. 应用生态学报, 14, 447-452.] | |
| [53] | Li YH, Wu W, Xiong ZP, Hu YM, Chang Y, Xiao DN (2014) Effects of forest roads on habitat pattern for sables in Da Hinggan Mountains, Northeasten China. Chinese Geographical Science, 24, 587-598. |
| [54] | Li YQ, Xing SH, Liu SQ, Luo AD, Cui GF (2013) Designing method of terrestrial wildlife path. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 35(6), 137-143. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [李玉强, 邢韶华, 刘生强, 罗爱东, 崔国发 (2013) 陆生野生动物通道设计方法. 北京林业大学学报, 35(6), 137-143.] | |
| [55] | Li YZ, Zhou TJ, Jiang HB (2008) Utilization effect of wildlife passages in Golmud-Lhasa section of Qinghai-Tibet Railway. China Railway Science, 29, 127-131. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [李耀增, 周铁军, 姜海波 (2008) 青藏铁路格拉段野生动物通道利用效果. 中国铁道科学, 29, 127-131.] | |
| [56] | Li ZL, Kang AL, Gu JY, Xue YG, Ren Y, Zhu ZW, Liu PQ, Ma JZ, Jiang GS (2017) Effects of human disturbance on vegetation, prey and Amur tigers in Hunchun Nature Reserve, China. Ecological Modelling, 353, 28-36. |
| [57] | Li ZQ, Ge C, Li J, Li YK, Xu AC, Zhou KX, Xue DY (2010) Ground-dwelling birds near the Qinghai-Tibet highway and railway. Transportation Research Part D: Transport and Environment, 15, 525-528. |
| [58] | Lian XM, Li XX, Zhou DX, Yan PS (2012) Avoidance distance from Qinghai-Tibet Highway in sympatric Tibetan antelope and gazelle. Transportation Research Part D: Transport and Environment, 17, 585-587. |
| [59] | Lian XM, Zhang TZ, Cao YC, Su JP, Thirgood S (2011) Road proximity and traffic flow perceived as potential predation risks: Evidence from the Tibetan antelope in the Kekexili National Nature Reserve, China. Wildlife Research, 38, 141-146. |
| [60] | Liu G, Gong MH, Guan TP, Chen LM, Li HX, Zhang Y, Zhou TY (2016) A framework to evaluate impacts of tourism on giant pandas: A case study in Tangjiahe National Nature Reserve. Chinese Journal of Zoology, 51, 724-733. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [刘刚, 龚明昊, 官天培, 谌利民, 李惠鑫, 张翼, 周天元 (2016) 生态旅游对大熊猫影响评价方法研究——以四川唐家河国家级自然保护区为例. 动物学杂志, 51, 724-733.] | |
| [61] | Liu H, Deng Y, Li RN, Chen F (2018) Analysis and protection measures of the impact of Simao-Lancang Expressway on the habitat of Asian elephants. Technology of Highway and Transport, 34(5), 132-138. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [刘煌, 邓玉, 李瑞年, 陈芳 (2018) 思茅-澜沧高速公路对亚洲象栖息地影响分析及保护措施. 公路交通技术, 34(5), 132-138.] | |
| [62] | Liu LM, Liu XH, Jin XL, Wang ZC, Gong MH (2017) Research on the change of giant pandas’ spatial utilization and road impacts in the Qinling Mountains. Acta Theriologica Sinica, 37, 215-225. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [刘兰妹, 刘雪华, 金学林, 王志臣, 龚明昊 (2017) 秦岭地区大熊猫种群空间利用消长状态以及道路影响研究. 兽类学报, 37, 215-225.] | |
| [63] | Liu P, Dai J, Cao DF, Li ZH, Zhang L (2016) Habitat suitability assessment for Asian elephant in Pu’er prefecture in the Yunnan Province of China. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 36, 4163-4170. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [刘鹏, 代娟, 曹大藩, 李志宏, 张立 (2016) 普洱市亚洲象栖息地适宜度评价. 生态学报, 36, 4163-4170.] | |
| [64] | Liu SL, Deng L, Chen LD, Li JR, Dong SK, Zhao HD (2014) Landscape network approach to assess ecological impacts of road projects on biological conservation. Chinese Geographical Science, 24, 5-14. |
| [65] | Liu SL, Dong YH, Cheng FY, Zhang YQ, Hou XY, Dong SK, Coxixo A (2017) Effects of road network on Asian elephant habitat and connectivity between the nature reserves in Xishuangbanna, Southwest China. Journal for Nature Conservation, 38, 11-20. |
| [66] | Luo YM, Wang ZC, Wang C, Piao ZJ, Li Z, Huang LY, Zhang R, Sui YC (2015) Survey and conservation of amphibian populations losses in roadside of Changbai Mountain. Journal of Beihua University (Natural Science), 16, 108-112. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [罗玉梅, 王卓聪, 王超, 朴正吉, 李卓, 黄利亚, 张睿, 睢亚橙 (2015) 长白山路域两栖类动物损失调查及保护. 北华大学学报(自然科学版), 16, 108-112.] | |
| [67] | Ma YT, Tian LH, Zeng ZG, Wu XT, Shao JB, Wang JF, Yu ZC (2007) The influence of road on the diffusion by golden takin between east and west Niubeiliang Nature Reserve. Journal of Shaanxi Normal University (Natural Science), 35, 112-115. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [麻应太, 田联会, 曾治高, 吴逊涛, 邵建斌, 王俊峰, 于占成 (2007) 210国道对牛背梁保护区羚牛东西扩散影响的研究(Ⅰ)——210国道两侧羚牛东西扩散特征. 陕西师范大学学报(自然科学版), 35, 112-115.] | |
| [68] | Mao WB, Duan CQ (2009) Road Ecology. China Communication Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [毛文碧, 段昌群 (2009) 公路路域生态学. 人民交通出版社, 北京.] | |
| [69] | Niu HY, Peng C, Chen ZW, Wang ZY, Zhang HM (2021) Country roads as barriers to rodent-mediated seed dispersal in a warm-temperate forest: Implications for forest fragmentation. European Journal of Forest Research, 140, 477-488. |
| [70] |
Pan WJ, Lin L, Luo AD, Zhang L (2009) Corridor use by Asian elephants. Integrative Zoology, 4, 220-231.
DOI PMID |
| [71] | Piao ZJ, Jin YH, Li SL, Wang C, Piao JH, Luo YM, Wang ZC, Sui YC (2012) Mammal mortality caused by highways in the Changbai Mountain National Nature Reserve of Jilin Province, China. Acta Theriologica Sinica, 32, 124-129. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [朴正吉, 金永焕, 李善龙, 王超, 朴金花, 罗玉梅, 王卓聪, 睢亚橙 (2012) 长白山自然保护区兽类道路交通致死的初步分析. 兽类学报, 32, 124-129.] | |
| [72] | Piao ZJ, Wang Y, Wang C, Wang ZC, Luo YM, Jin YH, Sui YC (2016) Preliminary report of bird road kills in the Changbai Mountain Nature Reserve in China. North-Western Journal of Zoology, 12, 178-183. |
| [73] | Prather JW, Dodd NL, Dickson BG, Hampton HM, Xu YG, Aumack EN, Sisk TD (2006) Landscape models to predict the influence of forest structure on tassel-eared squirrel populations. Journal of Wildlife Management, 70, 723-731. |
| [74] | Qiu L, Feng ZJ (2004) Effects of traffic during daytime and other human activities on the migration of Tibetan antelope along the Qinghai-Tibet Highway, Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Acta Zoologica Sinica, 50, 669-674. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [裘丽, 冯祚建 (2004) 青藏公路沿线白昼交通运输等人类活动对藏羚羊迁徙的影响. 动物学报, 50, 669-674.] | |
| [75] | Ren XT, Shen G, Wang ZL, Lu JQ (2011) Effects of road and grazing on spatiotemporal distribution of Brandt’s vole population in Xilin Gol Grassland of Inner Mongolia. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 30, 2245-2249. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [任修涛, 沈果, 王振龙, 路纪琪 (2011) 道路和放牧对锡林郭勒草原布氏田鼠种群时空分布的影响. 生态学杂志, 30, 2245-2249.] | |
| [76] | Riitters KH, Wickham JD (2003) How far to the nearest road? Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment, 1, 125-129. |
| [77] |
Riley SPD, Serieys LEK, Pollinger JP, Sikich JA, Dalbeck L, Wayne RK, Ernest HB (2014) Individual behaviors dominate the dynamics of an urban mountain lion population isolated by roads. Current Biology, 24, 1989-1994.
DOI PMID |
| [78] | Ru H (2018) Impact of traffic noise on Tibetan antelopes: A preliminary experiment on the Qinghai-Tibet Highway in China. Applied Ecology and Environmental Research, 16, 2923-2932. |
| [79] | Ru H, Xu JL, Jiang SF (2022) Experimental observation and analysis of traffic impact on Tibetan antelopes on the Qinghai-Tibet Highway. Advances in Civil Engineering, 2022, 1226781. |
| [80] | Shilling FM, Waetjen DP (2015) Wildlife-vehicle collision hotspots at US highway extents: Scale and data source effects. Nature Conservation. 11, 41-60. |
| [81] | Sun Y, Dong L, Zhang YY, Zheng GM, Browne S (2009) Is a forest road a barrier for the Vulnerable Cabot’s Tragopan Tragopan caboti in Wuyishan, Jiangxi, China? Oryx, 43, 614-617. |
| [82] | Thatte P, Joshi A, Vaidyanathan S, Landguth E, Ramakrishnan U (2018) Maintaining tiger connectivity and minimizing extinction into the next century: Insights from landscape genetics and spatially-explicit simulations. Biological Conservation, 218, 181-191. |
| [83] | Torres AR (2016) The road to improvement in obsessive-compulsive disorder. The Lancet Psychiatry, 3, 695-697. |
| [84] | van der Ree R, Smith DJ, Grilo C (2015) Handbook of Road Ecology. John Wiley & Sons, Ltd, Oxford. |
| [85] | van Dyke FG, Brocke RH, Shaw HG, Ackerman BB, Hemker TP, Lindzey FG (1986) Reactions of mountain lions to logging and human activity. Journal of Wildlife Management, 50, 95-102. |
| [86] | Waetjen DP, Shilling FM (2017) Large extent volunteer roadkill and wildlife observation systems as sources of reliable data. Frontiers in Ecology and Evolution, 5, 89. |
| [87] | Wang C, Wang ZC, Luo YM, Huang NW, Huang LY, Zhang R, Zou CS, Piao ZJ, Niu LJ (2016) Road mortality characteristic analysis of reptiles in Changbai Mountain National Nature Reserve. Sichuan Journal of Zoology, 35, 123-128. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王超, 王卓聪, 罗玉梅, 黄乃伟, 黄利亚, 张睿, 邹长胜, 朴正吉, 牛丽君 (2016) 长白山国家级自然保护区爬行动物道路致死特征的初步分析. 四川动物, 35, 123-128.] | |
| [88] | Wang HP, Li TA (2009) The newly research overview of the application of road ecology in animal and plant. Western China Communications Science & Technology, (11), 107-116. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王化平, 李太安 (2009) 道路生态学在植物和动物方面的研究动态综述. 西部交通科技, (11), 107-116.] | |
| [89] | Wang MY, Ji SN, Chen C, Xu WX, Han L, Yang WK (2020) Effects of road on diurnal group pattern and vigilance behavior in goitered gazelle. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 39, 937-943. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [汪沐阳, 吉晟男, 陈晨, 徐文轩, 韩雷, 杨维康 (2020) 道路交通对鹅喉羚昼间集群特征和警戒行为的影响. 生态学杂志, 39, 937-943.] | |
| [90] | Wang MY, Ji SN, Shao CL, Xu WX, Chen C, Yang WK (2021) Effects of road type on the distribution of great gerbil in the Kalamaili Mountain Ungulate Nature Reserve, China. Sichuan Journal of Zoology, 40, 1-7. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [汪沐阳, 吉晟男, 邵长亮, 徐文轩, 陈晨, 杨维康 (2021) 不同类型道路对卡拉麦里山有蹄类野生动物自然保护区大沙鼠分布的影响. 四川动物, 40, 1-7.] | |
| [91] | Wang Y, Piao ZJ, Li QL, Kong YP, Chen JD, Liu L, Zhao SY (2010) Research on yellow weasels’ roadside activities along Changbaishan Mountain Tourist Highway in Jilin Province. Sichuan Journal of Zoology, 29, 166-169. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王云, 朴正吉, 李麒麟, 孔亚平, 陈济丁, 刘龙, 赵世元 (2010) 黄鼬在吉林环长白山旅游公路路域活动的调查研究. 四川动物, 29, 166-169.] | |
| [92] | Wang Y, Chen JD, Tao SC, Wang MM, Wang XY, Asif S (2012) Wildlife protection along the Karakorum Highway in Khunjerab National Park. Pakistan Journal of Zoology, 44, 1452-1457. |
| [93] | Wang Y, Piao ZJ, Guan L, Kong YP (2013) Influence of Ring Changbai Mountain Scenic Highway on wildlife. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 32, 425-435. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王云, 朴正吉, 关磊, 孔亚平 (2013) 环长白山旅游公路对野生动物的影响. 生态学杂志, 32, 425-435.] | |
| [94] | Wang Y, Piao Z, Guan L, Wang X, Kong YP, Chen JD (2013) Road mortalities of vertebrate species on Ring Changbai Mountain Scenic Highway, Jilin Province, China. North-Western Journal of Zoology, 9, 399-409. |
| [95] | Wang Y, Piao ZJ, Guan L, Kong YP (2014) A review for methods of studying road wildlife ecology. Sichuan Journal of Zoology, 33, 778-784. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王云, 朴正吉, 关磊, 孔亚平 (2014) 公路路域动物生态学研究方法综述. 四川动物, 33, 778-784.] | |
| [96] | Wang Y, Guan L, Piao ZJ, Kong YP (2016) Barrier effect of Ring Changbai Mountain Scenic Highway on middle and large sized mammals. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 35, 2152-2158. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王云, 关磊, 朴正吉, 孔亚平 (2016) 环长白山旅游公路对中大型兽类的阻隔作用. 生态学杂志, 35, 2152-2158.] | |
| [97] | Wang Y, Guan L, Chen JD, Kong YP, Si L, Shah A (2017a) The overlapping impact of Qinghai-Tibet highway and railway on ungulates. Pakistan Journal of Zoology, 49, 1507-1510. |
| [98] | Wang Y, Guan L, Chen JD, Kong YP, Zhang W (2017a) Study on design parameters of wildlife passage in Golmud-Lhasa section of Qinghai-Tibet Expressway. Journal of Highway and Transportation Research and Development, 34, 146-152. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王云, 关磊, 陈济丁, 孔亚平, 张伟 (2017a) 青藏高速公路格拉段野生动物通道设计参数研究. 公路交通科技, 34, 146-152.] | |
| [99] | Wang Y, Guan L, Piao ZJ, Wang ZC, Kong YP (2017b) Monitoring wildlife crossing structures along highways in Changbai Mountain, China. Transportation Research Part D: Transport and Environment, 50, 119-128. |
| [100] | Wang Y, Zhou HP, Wang YD, Guan L, Kong YP (2017b) Methods of designing amphibian corridors crossing highway. Transport Research, 3(4), 16-21. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王云, 周红萍, 王玉滴, 关磊, 孔亚平 (2017b) 公路两栖类动物通道设置方法研究. 交通运输研究, 3(4), 16-21.] | |
| [101] | Wang Y, Guan L, Chen JD, Kong YP (2018) Influences on mammals frequency of use of small bridges and culverts along the Qinghai-Tibet Railway, China. Ecological Research, 33, 879-887. |
| [102] | Wang Y, Guan L, Zhou HP, Wang YD, Kong YP (2018) Study on the setting method of highway mammal passage. Highway, 63(4), 253-257. (in Chinese) |
| [王云, 关磊, 周红萍, 王玉滴, 孔亚平 (2018) 公路哺乳动物通道设置方法的研究. 公路, 63(4), 253-257.] | |
| [103] |
Wang Y, Lan JY, Zhou HP, Guan L, Wang YD, Han YS, Qu JP, Shah SA, Kong YP (2019) Investigating the effectiveness of road-related mitigation measures under semi-controlled conditions: A case study on Asian amphibians. Asian Herpetological Research, 10, 62-68.
DOI |
| [104] | Wang Y, Yang YG, Shi GQ, Wang ZC, Piao ZJ, Zhang LL, Cao GH, Zhou HP, Tao SC, Kong YP (2021a) Influence of roadkill on amphibian population quantity stability in Changbai Mountain Nature Reserve. Transport Research, 7(6), 106-114. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王云, 杨艳刚, 史国强, 王卓聪, 朴正吉, 张伶俐, 曹广华, 周红萍, 陶双成, 孔亚平 (2021a) 长白山自然保护区公路致死影响下两栖类动物数量稳定性风险评价. 交通运输研究, 7(6), 106-114.] | |
| [105] | Wang Y, Guan L, Du LX, Qu JP, Wang MY, Han YS, Yang YG, Zhou HP, Kong YP (2021b) Overlapping barrier and avoidance effects of the Qinghai-Tibet highway and railway on four typical ungulates on the Tibetan Plateau. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 40, 1091-1097. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王云, 关磊, 杜丽侠, 曲家鹏, 王明月, 韩用顺, 杨艳刚, 周红萍, 孔亚平 (2021b) 青藏公路和铁路对青藏高原四种典型有蹄类动物的叠加阻隔和回避影响. 生态学杂志, 40, 1091-1097.] | |
| [106] | Wang Y, Qu JP, Han YS, Du LX, Wang MY, Yang YG, Cao GH, Tao SC, Kong YP (2022) Impacts of linear transport infrastructure on terrestrial vertebrate species and conservation in China. Global Ecology and Conservation, 38, e02207. |
| [107] | Wang ZC, Wang Y, Wang C, Luo YM, Huang LY, Zhang R, Tai ZJ, Piao ZJ (2015) Traffic death of amphibian on tourism highway in Changbai Mountain National Nature Reserve. Chinese Journal of Zoology, 50, 866-874. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王卓聪, 王云, 王超, 罗玉梅, 黄利亚, 张睿, 邰志娟, 朴正吉 (2015) 长白山国家级自然保护区两栖类动物道路致死特征分析. 动物学杂志, 50, 866-874.] | |
| [108] | Wu M, Chen J, Zhao CC, Zhai R, Su YQ, Zheng JX, Hu XS (2020) Site selection of animal passage on Quanzhou-Sanming Expressway: A case study of Neofelis nebulosa. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 40, 2360-2366. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [吴旻, 陈瑾, 赵超超, 翟瑞, 苏雨秋, 郑金兴, 胡喜生 (2020) 泉三高速公路动物通道选址研究——以云豹为例. 生态学报, 40, 2360-2366.] | |
| [109] | Wu XM, Gao MZ, Li QL, Gu MC, Zhang HF, Ji Z (2009) Behavior adaptation and protection of Tibetan antelope migration to Qinghai-Tibet Highway. Transportation Construction & Management, (9), 113-116. (in Chinese) |
| [吴晓民, 高美真, 李麒麟, 顾明臣, 张洪峰, 姬周 (2009) 藏羚迁徙对青藏公路的行为适应与保护. 交通建设与管理, (9), 113-116.] | |
| [110] | Wu XT, Shao JB, Ma Y, Wang XF (2011) The effect of 210 National Highway on the migration and diffusion of the wild animals in Niubeiliang Nature Reserve. Shaanxi Forest Science and Technology, (2), 24-27. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [吴逊涛, 邵建斌, 马宇, 王西峰 (2011) 210国道对牛背梁保护区野生动物迁移扩散的影响. 陕西林业科技, (2), 24-27.] | |
| [111] | Wu Y (2016) Review of road works influence on wildlife and conservation measures. Railway Energy Saving & Environmental Protection & Occupational Safety and Health, 6(5), 227-229. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [吴杨 (2016) 道路工程对野生动物影响及保护措施研究进展. 铁路节能环保与安全卫生, 6(5), 227-229.] | |
| [112] | Wu ZY, Du YB, Xu G, Zhu GP (2020) Spatial distribution and suitability analysis of Equus kiang along G 219 National Road—Case study of road section from Zhongba to Gaer. Journal of Tianjin Normal University (Natural Science Edition), 40(3), 18-21, 47. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [吴自有, 杜元宝, 许刚, 朱耿平 (2020) G219国道沿线西藏野驴的空间分布及其适生性分析——以仲巴至噶尔段为例. 天津师范大学学报(自然科学版), 40(3), 18-21, 47.] | |
| [113] | Xia L, Yang QS, Li ZC, Wu YH, Feng ZJ (2007) The effect of the Qinghai-Tibet Railway on the migration of Tibetan antelope Pantholops hodgsonii in Hoh-xil National Nature Reserve, China. Oryx, 41, 352-357. |
| [114] | Xia L, Yang QS, Li ZC, Wu YH, Liang MY (2005) Disturbance of transportation facilities to seasonal migration of Tibetan antelopes in Hoh-xil National Nature Reserve. Sichuan Journal of Zoology, 24(2), (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [夏霖, 杨奇森, 李增超, 武永华, 梁孟元(2005) 交通设施对可可西里藏羚季节性迁移的影响. 四川动物, 151.] | |
| [115] | Xu F, Yang WK, Xu WX, Xia CJ, Liao HH, Blank D (2013) The effects of the Taklimakan Desert Highway on endemic birds Podoces biddulphi. Transportation Research Part D: Transport and Environment, 20, 12-14. |
| [116] | Xu WJ, Huang QY, Stabach J, Buho H, Leimgruber P (2019) Railway underpass location affects migration distance in Tibetan antelope (Pantholops hodgsonii). PLoS ONE, 14, e0211798. |
| [117] | Yang SM, Huai HY, Zhang YL, Yin BF, Zhou L, Wei WH (2006) Effects of railway traffic on the community structure of rodents in warm steppe along the Qinghai-Tibet Railway. Acta Theriologica Sinica, 26, 267-273. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [杨生妹, 淮虎银, 张镱锂, 殷宝法, 周乐, 魏万红 (2006) 青藏铁路温性草原区铁路运营对啮齿动物群落结构的影响. 兽类学报, 26, 267-273.] | |
| [118] | Yin BF, Huai HY, Zhang YL, Zhou L, Wei WH (2006) Influence of Qinghai-Tibetan railway and highway on wild animal’s activity. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 26, 3917-3923. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [殷宝法, 淮虎银, 张镱锂, 周乐, 魏万红 (2006) 青藏铁路、公路对野生动物活动的影响. 生态学报, 26, 3917-3923.] | |
| [119] | Yu H, Song SY, Liu JZ, Li S, Zhang L, Wang DJ, Luo SJ (2017) Effects of the Qinghai-Tibet Railway on the landscape genetics of the endangered Przewalski’s gazelle (Procapra przewalskii). Scientific Reports, 7, 17983. |
| [120] | Zeng ZG, Li JS, Yan WB, Fan JT, Cui FJ, Song YL (2009) Impact of Yangxian-Taibai Highway on the movement of giant panda in the Qinling Mountains and its habitat protection. Journal of Northwest Forestry University, 24(6), 88-93. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [曾治高, 李俊生, 颜文博, 范俊韬, 崔芳洁, 宋延龄 (2009) 洋太公路对秦岭大熊猫活动及其栖息地保护的影响. 西北林学院学报, 24(6), 88-93.] | |
| [121] | Zhang B (2019) Study on the design of highway wildlife passage in Northwest China. Journal of Highway Communication Technology (Application Technology version), 15, 318-320. (in Chinese) |
| [张斌 (2019) 西北干旱区公路野生动物通道设计研究. 公路交通科技(应用技术版), 15, 318-320.] | |
| [122] | Zhang B, Tang JQ, Wang Y, Zhang HF, Wu D, Xu G, Lin Y, Wu XM (2019) Designing wildlife crossing structures for ungulates in a desert landscape: A case study in China. Transportation Research Part D: Transport and Environment, 77, 50-62. |
| [123] | Zhang HF, Feng T, Ji MZ, Kong F, Wu XM (2009) Monitoring study on the utilization of Qinghai-Tibet Railway bridges by plateau wildlife such as Tibetan antelope. Bulletin of Biology, 44(10), 8-10. (in Chinese) |
| [张洪峰, 封托, 姬明周, 孔飞, 吴晓民 (2009) 青藏铁路小桥被藏羚羊等高原野生动物利用的监测研究. 生物学通报, 44(10), 8-10.] | |
| [124] | Zhang L, Dong T, Xu WH, Ouyang ZY (2015) Assessment of habitat fragmentation caused by traffic networks and identifying key affected areas to facilitate rare wildlife conservation in China. Wildlife Research, 42, 266-279. |
| [125] | Zhang WY, Shu GC, Li YL, Xiong S, Liang CP, Li C (2018) Daytime driving decreases amphibian roadkill. PeerJ, 6, e5385. |
| [126] | Zhang XF, Guo F, Peng AH, Dong SK, Chen DQ, Wen L (2019) Monitoring of wildlife crossings in section of Hatengtaohai Nature Reserve along Beijing-Xinjiang Expressway. Chinese Journal of Wildlife, 40, 848-854. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [张相锋, 郭锋, 彭阿辉, 董世魁, 陈冬勤, 温璐 (2019) 京新高速公路哈腾套海保护区段野生动物通道监测研究. 野生动物学报, 40, 848-854.] | |
| [127] | Zhao LH (2019) Study on the protective measures for Asian crested ibis along Xi’an-Chengdu High-speed Railway. Railway Standard Design, 63, 174-177. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [赵留辉 (2019) 西安至成都高速铁路朱鹮防护措施研究. 铁道标准设计. 63, 174-177.] | |
| [128] | Zhou B, Liu JM, Liang W (2020) Breeding in a noisy world: Attraction to urban arterial roads and preference for nest-sites by the scaly-breasted munia (Lonchura punctulata). Global Ecology and Conservation, 22, e00987. |
| [129] | Zhou L, Yin BF, Yang SM, Huai HY, Li SP, Zhang YL, Wei WH (2006) Effects of Qinghai-Tibet Highway on genetic differentiation of plateau pika (Ochotona curzoniae). Acta Ecologica Sinica, 26, 3572-3577. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [周乐, 殷宝法, 杨生妹, 淮虎银, 李世平, 张镱锂, 魏万红 (2006) 青藏公路对高原鼠兔种内遗传分化的影响. 生态学报, 26, 3572-3577.] | |
| [130] | Zhou YB, Buesching CD, Newman C, Kaneko Y, Xie ZQ, MacDonald DW (2013) Balancing the benefits of ecotourism and development: The effects of visitor trail-use on mammals in a protected area in rapidly developing China. Biological Conservation, 165, 18-24. |
| [131] |
Zhu LF, Zhang SN, Gu XD, Wei FW (2011) Significant genetic boundaries and spatial dynamics of giant pandas occupying fragmented habitat across Southwest China. Molecular Ecology, 20, 1122-1132.
DOI PMID |
| [132] | Zong YG, Zhou SY, Peng P, Liu C, Guo RH, Chen HC (2003) Perspective of road ecology development. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 23, 2396-2405. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [宗跃光, 周尚意, 彭萍, 刘超, 郭瑞华, 陈红春 (2003) 道路生态学研究进展. 生态学报, 23, 2396-2405.] |
| [1] | Yan Kang Jing Gan Linlin Yu Chenjing He Jingbin Wu Liqing Zhang. Design pattern and network development of urban microhabitat based on natural-based solutions (NbS): A case study of habitat gardens in Changning District, Shanghai [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 24528-. |
| [2] | Huan Xu, Fengfei Xin, Hongliang Shi, Lin Yuan, Shunqi Bo, Xinyi Zhao, Shuaitao Deng, Tingting Pan, Jing Yu, Saisai Sun, Cheng Xue. Evaluation of effects of integrated ecological restoration technology on habitat and bird diversity improvement in the northern branch of Yangtze River Estuary [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 24478-. |
| [3] | Mingyi Zhang, Xiaomei Wang, Yanxin Zheng, Nan Wu, Donghao Li, Enyuan Fan, Na Li, Xiujuan Shan, Tao Yu, Chunnuan Zhao, Bo Li, Shuai Xu, Yuping Wu, Liqun Ren. Resource status and habitat function of typical oyster reef areas in the Yellow River Estuary [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 24208-. |
| [4] | Fei Duan, Mingzhang Liu, Hongliang Bu, Le Yu, Sheng Li. Effects of urbanization on bird community composition and functional traits: A case study of the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(8): 23473-. |
| [5] | Rongfei Su, Ruishan Chen, Linlin Yu, Jingbin Wu, Yan Kang. Biodiversity in community habitat gardens in Changning District, Shanghai based on camera trapping [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(8): 24068-. |
| [6] | Jiaqi Li, Yidi Feng, Lei Wang, Penyan Pan, Xiaoru Liu, Xueyang Li, Yihan Wang, Fang Wang. Diet and habitat selection of raccoon dogs (Nyctereutes procyonoides) in Shanghai, a rapidly urbanizing megacity in eastern China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(8): 24131-. |
| [7] | Yiyun Gu, Jiaqi Xue, Jinhui Gao, Xinyi Xie, Ming Wei, Jinyu Lei, Cheng Wen. A public science data-based regional bird diversity assessment method [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(7): 24080-. |
| [8] | Mingjun Zhang, Hesheng Wang, Wenbo Yan, Yunnan Fu, Qi Wang, Zhigao Zeng. Diel activity and habitat selection of small Indian civets (Viverricula indica) in Hainan Datian National Nature Reserve [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(6): 23420-. |
| [9] | Peng Wang, Jiarong Sui, Xinyao Ding, Weizhong Wang, Xueqian Cao, Haipeng Zhao, Yanping Wang. Nested distribution patterns of bird assemblages and their influencing factors in Zhengzhou urban parks [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(3): 23359-. |
| [10] | Naipeng Zhang, Hongru Liang, Yan Zhang, Chao Sun, Yong Chen, Lulu Wang, Jiangbao Xia, FangLei Gao. Effects of soil type and groundwater depth on spatial differentiation of typical salt marsh plant communities in the Yellow River Delta [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(2): 23370-. |
| [11] | Haolin Wang, Huaisheng Zhang, Jianqiang Zhu, Zhongyi Chen, Yulin Ke, Tao Yang, Hui Chen. Research progress of diet composition and its research methods for Père David’s deer [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(1): 23057-. |
| [12] | Churan Zhang, Shengfa Li, Fengchang Li, Zhizhong Tang, Huiyan Liu, Lihong Wang, Rong Gu, Yun Deng, Zhiming Zhang, Luxiang Lin. Habitat association and community classification of woody plants in the 20 ha forest dynamics plot of subtropical semi-humid evergreen broad-leaved forest in the Jizu Mountains, Yunnan [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(1): 23393-. |
| [13] | Cailian Liu, Xiong Zhang, Enyuan Fan, Songlin Wang, Yan Jiang, Baian Lin, Lu Fang, Yuqiang Li, Lebin Liu, Min Liu. Species diversity, ecological characteristics and conservation measures of seahorses (Hippocampus) in China’s waters [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(1): 23282-. |
| [14] | Shuhan Yang, He Wang, Lei Chen, Yingfei Liao, Guang Yan, Yining Wu, Hongfei Zou. Effects of heterogeneous habitat on soil nematode community characteristics in the Songnen Plain [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(1): 23295-. |
| [15] | Minghui Wang, Zhaoquan Chen, Shuaifeng Li, Xiaobo Huang, Xuedong Lang, Zihan Hu, Ruiguang Shang, Wande Liu. Spatial pattern of dominant species with different seed dispersal modes in a monsoon evergreen broad-leaved forest in Pu’er, Yunnan Province [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(9): 23147-. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2026 Biodiversity Science
Editorial Office of Biodiversity Science, 20 Nanxincun, Xiangshan, Beijing 100093, China
Tel: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn