



Biodiv Sci ›› 2024, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (8): 24131. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2024131 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2024131
• Original Papers • Previous Articles Next Articles
Jiaqi Li1,#( ), Yidi Feng2,#(
), Yidi Feng2,#( ), Lei Wang1, Penyan Pan1, Xiaoru Liu3(
), Lei Wang1, Penyan Pan1, Xiaoru Liu3( ), Xueyang Li2,4(
), Xueyang Li2,4( ), Yihan Wang1,*(
), Yihan Wang1,*( )(
)( ), Fang Wang1,*(
), Fang Wang1,*( )(
)( )
)
Received:2024-04-05
Accepted:2024-07-29
Online:2024-08-20
Published:2024-08-30
Contact:
*E-mail: 21210700093@m.fudan.edu.cn;wfang@fudan.edu.cn
About author:#Co-first authors
Supported by:Jiaqi Li, Yidi Feng, Lei Wang, Penyan Pan, Xiaoru Liu, Xueyang Li, Yihan Wang, Fang Wang. Diet and habitat selection of raccoon dogs (Nyctereutes procyonoides) in Shanghai, a rapidly urbanizing megacity in eastern China[J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(8): 24131.
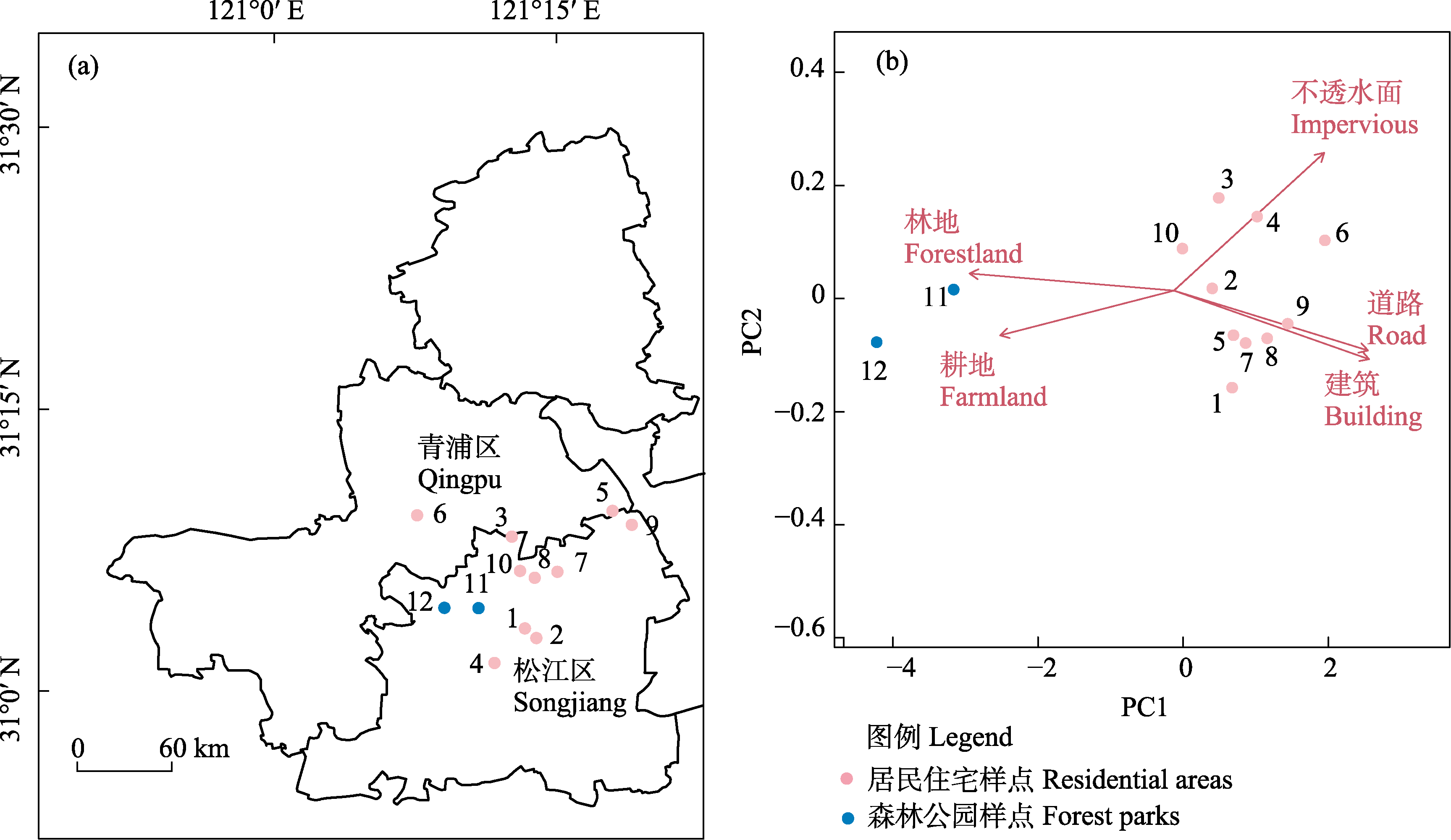
Fig. 1 Distribution of Nyctereutes procyonoides tracking and fecal sample collection site in Shanghai (a) and principal component analysis of land use types of study sites (b). Numbers represent the number of the sites and 1-10 represent residential building sites (1, Gushuiwan; 2, Yushanghai; 3, St. Andrews Manor; 4, Huating; 5, Dahua; 6, Xinqingpu; 7, Tongrun; 8, Milan; 9, Jiucheng; 10, Sheshan); 11-12 represent forest park sites (11, Chenshan; 12, Tianma).
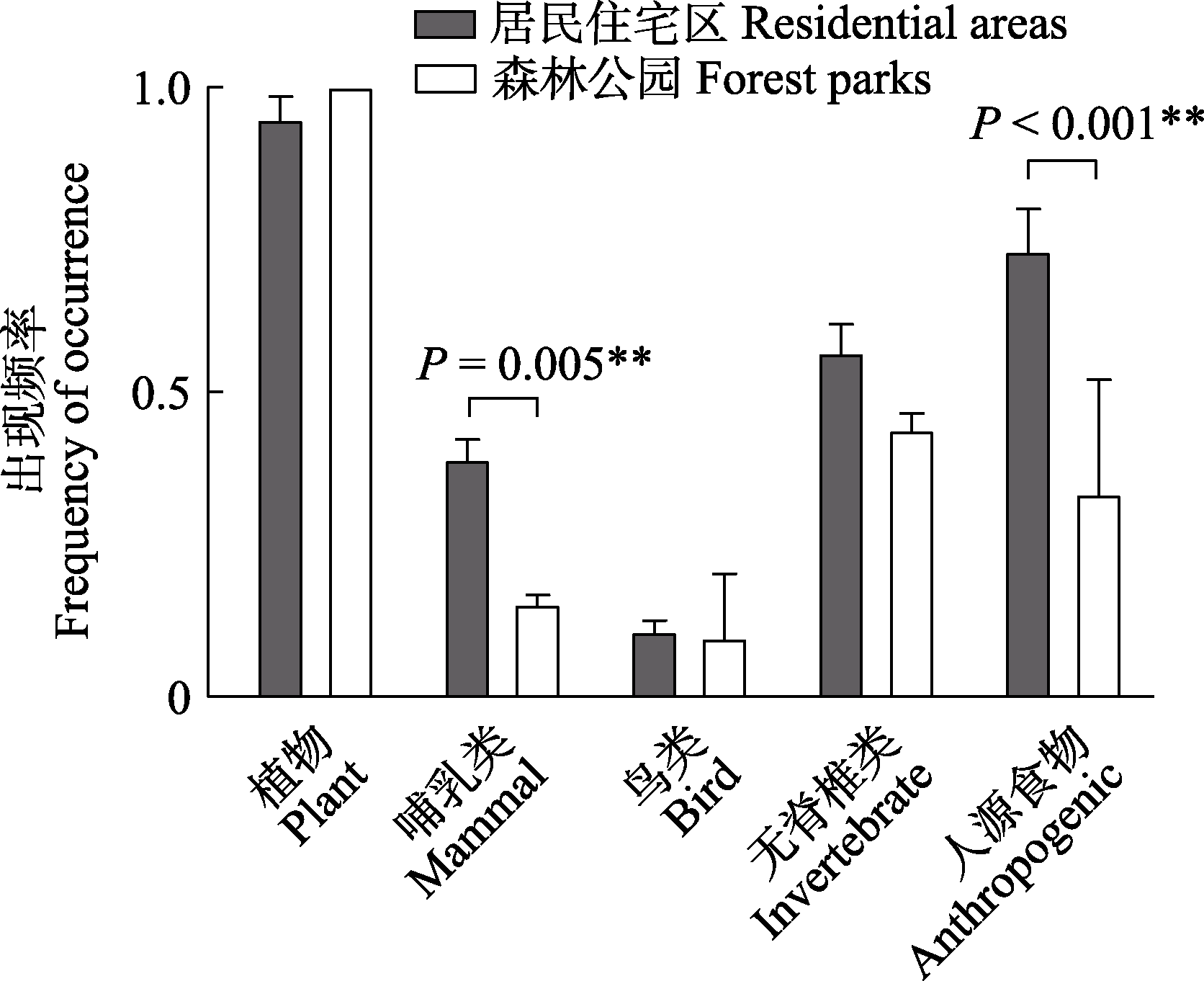
Fig. 2 Frequency and logistic regression results of occurrence of each component of raccoon dog fecal samples in residential buildings and forest parks in Shanghai
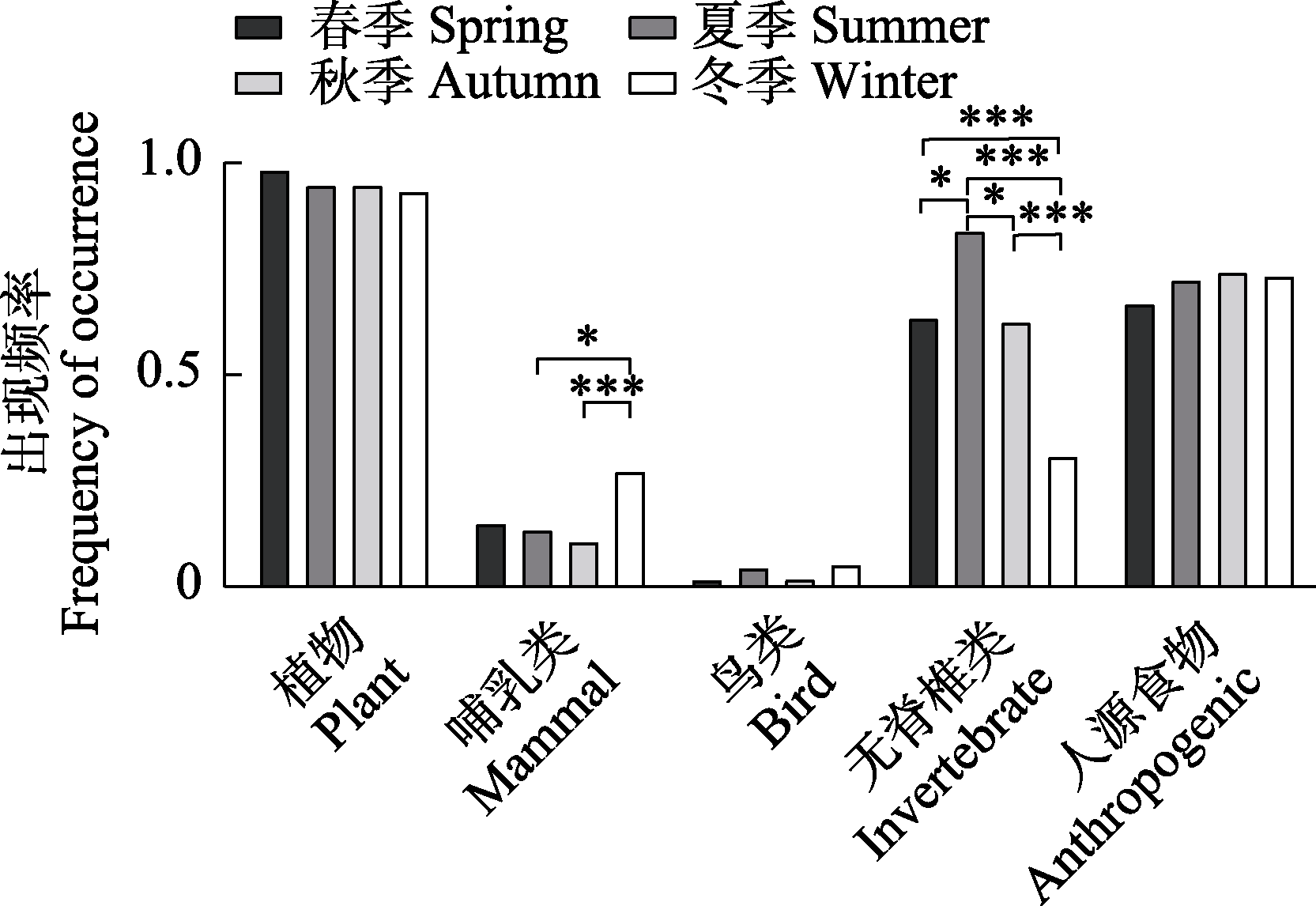
Fig. 3 The frequency and multiple comparisons of each component in fecal samples of raccoon dogs in different seasons in residential areas of Shanghai. Group pairs that had significant difference are marked. * P < 0.05; *** P < 0.001.
| 模型构建 Model formula | 与最佳模型的差值 ΔAIC | AIC 权重 AIC weight |
|---|---|---|
| 居民住宅区 Residential areas | ||
| used ~ dis_w + dis_r + forestland + imprevious + (1 | ID) | 0 | 0.56 |
| used ~ dis_w + dis_r + forestland + building + imprevious + (1 | ID) | 0.487 | 0.44 |
| used ~ dis_w + dis_r + imprevious + (1 | ID) | 10.572 | 0 |
| used ~ dis_w + dis_r + building + imprevious + (1 | ID) | 11.302 | 0 |
| used ~ dis_w + dis_r + forestland + building + (1 | ID) | 25.132 | 0 |
| 森林公园 Forest parks | ||
| used ~ dis_w + dis_r + farmland + forestland + grassland + building + imprevious + bareland + (1 | ID) | 0 | 1.00 |
| used ~ dis_w + dis_r + farmland + forestland + grassland + building + bareland + (1 | ID) | 3.447 | 0 |
| used ~ dis_w + dis_r + forestland + grassland + bareland + (1 | ID) | 3.462 | 0 |
| used ~ dis_w + dis_r + forestland + grassland + imprevious + bareland + (1 | ID) | 3.930 | 0 |
| used ~ dis_r + farmland + forestland + grassland + building + bareland + (1 | ID) | 9.975 | 0 |
Table 1 Summary of generalized linear mixed models of resource selection functions for raccoon dogs in residential areas and forest parks in Shanghai
| 模型构建 Model formula | 与最佳模型的差值 ΔAIC | AIC 权重 AIC weight |
|---|---|---|
| 居民住宅区 Residential areas | ||
| used ~ dis_w + dis_r + forestland + imprevious + (1 | ID) | 0 | 0.56 |
| used ~ dis_w + dis_r + forestland + building + imprevious + (1 | ID) | 0.487 | 0.44 |
| used ~ dis_w + dis_r + imprevious + (1 | ID) | 10.572 | 0 |
| used ~ dis_w + dis_r + building + imprevious + (1 | ID) | 11.302 | 0 |
| used ~ dis_w + dis_r + forestland + building + (1 | ID) | 25.132 | 0 |
| 森林公园 Forest parks | ||
| used ~ dis_w + dis_r + farmland + forestland + grassland + building + imprevious + bareland + (1 | ID) | 0 | 1.00 |
| used ~ dis_w + dis_r + farmland + forestland + grassland + building + bareland + (1 | ID) | 3.447 | 0 |
| used ~ dis_w + dis_r + forestland + grassland + bareland + (1 | ID) | 3.462 | 0 |
| used ~ dis_w + dis_r + forestland + grassland + imprevious + bareland + (1 | ID) | 3.930 | 0 |
| used ~ dis_r + farmland + forestland + grassland + building + bareland + (1 | ID) | 9.975 | 0 |
| 预测变量 Predictor variable | 居民住宅区 Residential areas | 森林公园 Forest parks | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| β系数 β coefficient | 标准误 Standard error | β系数 β coefficient | 标准误 Standard error | |
| 截距 Intercept | -15.304*** | 1.907 | -1.282 | 0.056 |
| 道路接近程度 Proximity to road | -0.138*** | 0.015 | -0.117*** | 0.012 |
| 水源接近程度 Proximity to water | -0.163*** | 0.014 | -0.047*** | 0.013 |
| 林地 Forestland | 0.095*** | 0.023 | 0.397*** | 0.042 |
| 草地 Grassland | 0.401*** | 0.042 | ||
| 建筑 Building | 0.021 | 0.031 | -0.185*** | 0.050 |
| 不透水面 Impervious | -0.203*** | 0.034 | -0.137* | 0.059 |
| 耕地 Farmland | -0.103* | 0.042 | ||
| 裸地 Bareland | 1.796*** | 0.164 | ||
Table 2 Generalized linear mixed model of raccoon dog resource selection function in Shanghai residential areas and forest parks
| 预测变量 Predictor variable | 居民住宅区 Residential areas | 森林公园 Forest parks | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| β系数 β coefficient | 标准误 Standard error | β系数 β coefficient | 标准误 Standard error | |
| 截距 Intercept | -15.304*** | 1.907 | -1.282 | 0.056 |
| 道路接近程度 Proximity to road | -0.138*** | 0.015 | -0.117*** | 0.012 |
| 水源接近程度 Proximity to water | -0.163*** | 0.014 | -0.047*** | 0.013 |
| 林地 Forestland | 0.095*** | 0.023 | 0.397*** | 0.042 |
| 草地 Grassland | 0.401*** | 0.042 | ||
| 建筑 Building | 0.021 | 0.031 | -0.185*** | 0.050 |
| 不透水面 Impervious | -0.203*** | 0.034 | -0.137* | 0.059 |
| 耕地 Farmland | -0.103* | 0.042 | ||
| 裸地 Bareland | 1.796*** | 0.164 | ||
| [1] | Adams CE (2009) Urban Wildlife Management, 2nd edn. CRC Press, Boca Raton. |
| [2] | Adjei IA, Karim R (2016) An application of bootstrapping in logistic regression model. Open Access Library Journal, 3, 1-9. |
| [3] | Anwar MB, Nadeem MS, Kayani AR, Mazhar Q (2011) Is mammalian hair fiber analysis by optical fiber diameter analyzer helpful to identify prey from scats of carnivores? Pakistan Journal of Zoology, 43, 1218-1220. |
| [4] | Bateman PW, Fleming PA (2012) Big city life: Carnivores in urban environments. Journal of Zoology, 287, 1-23. |
| [5] | Blair RB, Launer AE (1997) Butterfly diversity and human land use: Species assemblages along an urban gradient. Biology Conservation, 80, 113-125. |
| [6] | Bozdogan H (1987) Model selection and Akaike’s information criterion (AIC): The general theory and its analytical extensions. Psychometrika, 52, 345-370. |
| [7] | Bozek CK, Prange S, Gehrt SD (2007) The influence of anthropogenic resources on multi-scale habitat selection by raccoons. Urban Ecosystems, 10, 413-425. |
| [8] |
Buonaccorsi JP, Romeo G, Thoresen M (2018) Model-based bootstrapping when correcting for measurement error with application to logistic regression. Biometrics, 74, 135-144.
DOI PMID |
| [9] | Calabrese JM, Fleming CH, Gurarie E (2016) ctmm: An R package for analyzing animal relocation data as a continuous- time stochastic process. Methods in Ecology and Evolution, 7, 1124-1132. |
| [10] | Campbell SJ, Ashley W, Gil-Fernandez M, Newsome TM, Di Giallonardo F, Ortiz-Baez AS, Mahar JE, Towerton AL, Gillings M, Holmes EC, Carthey AJR, Geoghegan JL (2020) Red fox viromes in urban and rural landscapes. Virus Evolution, 6, veaa065. |
| [11] | Cui YY, Xie ZG, Xu X, Chu KL, Jiang WZ, Pei EL, Yuan X, Xu HF (2013) Activity laws and feeding behavior of introduced badgers. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Science, 41, 3407-3409. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [崔勇勇, 谢志刚, 徐循, 褚可龙, 蒋文忠, 裴恩乐, 袁晓, 徐宏发 (2013) 引入狗獾活动规律和取食行为的研究. 安徽农业科学, 41, 3407-3409.] | |
| [12] | Diao YX, Zhao QQ, Weng Y, Huang ZX, Wu YQ, Gu BJ, Zhao Q, Wang F (2022) Predicting current and future species distribution of the raccoon dog (Nyctereutes procyonoides) in Shanghai, China. Landscape and Urban Planning, 228, 104581. |
| [13] | Dong TW, Huang ML, Wei X, Ma S, Yue Q, Liu WL, Zheng JX, Wang G, Ma R, Ding YZ, Bo SQ, Wang ZH (2023) Potential spatial distribution pattern and landscape connectivity of Pelophylax plancyi in Shanghai, China. Biodiversity Science, 31, 22692. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[董廷玮, 黄美玲, 韦旭, 马硕, 岳衢, 刘文丽, 郑佳鑫, 王刚, 马蕊, 丁由中, 薄顺奇, 王正寰 (2023) 上海地区金线侧褶蛙种群的潜在空间分布格局及其景观连通性. 生物多样性, 31, 22692.]
DOI |
|
| [14] |
Dorning J, Harris S (2019) Individual and seasonal variation in contact rate, connectivity and centrality in red fox (Vulpes vulpes) social groups. Scientific Reports, 9, 20095.
DOI PMID |
| [15] | Drygala F, Werner U, Zoller H (2013) Diet composition of the invasive raccoon dog (Nyctereutes procyonoides) and the native red fox (Vulpes vulpes) in northeast Germany. Hystrix, 24, 190-194. |
| [16] | Fischer JD, Cleeton SH, Lyons TP, Miller JR (2012) Urbanization and the predation paradox: The role of trophic dynamics in structuring vertebrate communities. BioScience, 62, 809-818. |
| [17] | Guo XQ, Yu XY, Li ZR, Li ZC, Lü TT, Cao HX, Song HY, Zhao CF (2021) Isolation, identification and VP2 gene sequence analysis of raccoon dog parvovirus RDPV-JL3. Special Wild Economic Animal and Plant Research, 43(5), 13-18. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [郭晓芹, 于小亚, 李滋睿, 李卓宸, 吕甜甜, 曹海旭, 宋海岩, 赵传芳 (2021) 貉细小病毒RDPV-JL3株的分离鉴定及VP2基因序列分析. 特产研究, 43(5), 13-18.] | |
| [18] | Herr J (2008) Ecology and Behaviour of Urban Stone Martens (Martes foina) in Luxembourg. PhD dissertation, University of Sussex, Brighton. |
| [19] | Hubert P, Julliard R, Biagianti S, Poulle ML (2011) Ecological factors driving the higher hedgehog (Erinaceus europeaus) density in an urban area compared to the adjacent rural area. Landscape and Urban Planning, 103, 34-43. |
| [20] | Jia WH (2022) Key points of breeding and management techniques for raccoon dogs during breeding period. Special Economic Animals and Plants, 25(12), 52-59. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [贾文会 (2022) 貉配种期的饲养管理技术要点. 特种经济动植物, 25(12), 52-59.] | |
| [21] | Kirkland GL (1998) Guidelines for the Capture, Handling, and Care of Mammals as approved by the American Society of Mammalogists. Journal of Mammalogy, 79, 1416-1431. |
| [22] | Ladle A, Galpern P, Doyle-Baker P (2018) Measuring the use of green space with urban resource selection functions: An application using smartphone GPS locations. Landscape and Urban Planning, 179, 107-115. |
| [23] | Manly B, McDonald L, Thomas DL, McDonald TL, Erickson WP (2002) Resource Selection by Animals: Statistical Design and Analysis for Field Studies. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht. |
| [24] | McKinney ML (2002) Urbanization, biodiversity, and conservation: The impacts of urbanization on native species are poorly studied, but educating a highly urbanized human population about these impacts can greatly improve species conservation in all ecosystems. BioScience, 52, 883-890. |
| [25] | Mukherjee F, Singh D (2020) Assessing land use-land cover change and its impact on land surface temperature using LANDSAT data: A comparison of two urban areas in India. Earth Systems and Environment, 4, 385-407. |
| [26] | Murray M, Cembrowski A, Latham ADM, Lukasik VM, Pruss S, St Clair CC (2015) Greater consumption of protein-poor anthropogenic food by urban relative to rural coyotes increases diet breadth and potential for human-wildlife conflict. Ecography, 38, 1235-1242. |
| [27] | Murray MH, Becker DJ, Hall RJ, Hernandez SM (2016) Wildlife health and supplemental feeding: A review and management recommendations. Biological Conservation, 204, 163-174. |
| [28] |
Newsome SD, Garbe HM, Wilson EC, Gehrt SD (2015) Individual variation in anthropogenic resource use in an urban carnivore. Oecologia, 178, 115-128.
DOI PMID |
| [29] | Newsome TM, Ballard GA, Crowther MS, Fleming PJS, Dickman CR (2014a) Dietary niche overlap of free-roaming dingoes and domestic dogs: The role of human-provided food. Journal of Mammalogy, 95, 392-403. |
| [30] | Newsome TM, Ballard GA, Fleming PJS, van de Ven R, Story GL, Dickman CR (2014b) Human-resource subsidies alter the dietary preferences of a mammalian top predator. Oecologia, 175, 139-150. |
| [31] | Prange S, Gehrt SD, Wiggers EP (2004) Influences of anthropogenic resources on raccoon (Procyon lotor) movements and spatial distribution. Journal of Mammalogy, 85, 483-490. |
| [32] | Redpath SM, Bhatia S, Young J (2015) Tilting at wildlife: Reconsidering human-wildlife conflict. Oryx, 49, 222-225. |
| [33] | Rodewald AD, Kearns LJ (2011) Shifts in dominant nest predators along a rural-to-urban landscape gradient. The Condor, 113, 899-906. |
| [34] | Šálek M, Drahníková L, Tkadlec E (2015) Changes in home range sizes and population densities of carnivore species along the natural to urban habitat gradient. Mammal Review, 45, 1-14. |
| [35] | Salmerón Gómez R, García Pérez J, López Martín MDM, García CG (2016) Collinearity diagnostic applied in ridge estimation through the variance inflation factor. Journal of Applied Statistics, 43, 1831-1849. |
| [36] | Schulte-Hostedde AI, Mazal Z, Jardine CM, Gagnon J (2018) Enhanced access to anthropogenic food waste is related to hyperglycemia in raccoons (Procyon lotor). Conservation Physiology, 6, coy026. |
| [37] | Tsunoda M, Kaneko Y, Sako T, Koizumi R, Iwasaki K, Mitsuhashi I, Saito MU, Hisano M, Newman C, Macdonald DW, Buesching CD (2019) Human disturbance affects latrine-use patterns of raccoon dogs. The Journal of Wildlife Management, 83, 728-736. |
| [38] | Turner J, Freeman R, Carbone C (2022) Using citizen science to understand and map habitat suitability for a synurbic mammal in an urban landscape: The hedgehog Erinaceus europaeus. Mammal Review, 52, 291-303. |
| [39] | Wang YH, Zhao QQ, Diao YX, Gu BJ, Weng Y, Zhang ZJ, Chen YB, Wang F (2023) Diel activity, habitat utilization, and response to anthropogenic interference of small Indian civets (Viverricula indica) in Shanghai urban areas based on camera trapping. Biodiversity Science, 31, 22294. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[王怡涵, 赵倩倩, 刁奕欣, 顾伯健, 翁悦, 张卓锦, 陈泳滨, 王放 (2023) 基于红外相机调查上海市区小灵猫的活动节律、栖息地利用及其对人类活动的响应. 生物多样性, 31, 22294.]
DOI |
|
| [40] | Wu T, Chu KL, Jiang WZ, Gu GL, Yuan X, Xu HF (2017) Setts habitat features of reintroduced Meles meles after release. Sichuan Journal of Zoology, 36, 94-99. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [吴彤, 褚可龙, 蒋文忠, 顾国林, 袁晓, 徐宏发 (2017) 重引入狗獾释放后定居巢的生境特征. 四川动物, 36, 94-99.] | |
| [41] | Zhang W, Li B, Shu XX, Pei EL, Yuan X, Sun YJ, Wang TH, Wang ZH (2016) Responses of anuran communities to rapid urban growth in Shanghai, China. Urban Forestry & Urban Greening, 20, 365-374. |
| [42] | Zhao QQ, Diao YX, Weng Y, Huang ZX, Gu BJ, Wu Y, Wang YH, Zhao Q, Wang F (2022) Predicting future distributions and dispersal pathways for precautionary management of human-raccoon dog conflicts in metropolitan landscapes. Environmental Research Letters, 17, 104036. |
| [43] | Zhao QQ, Wang YH, Wu LJ, Feng YD, Li YH, Zhang ZJ, Zhao Q, Wang F (2024) A path to human-raccoon dog harmony: Identifying factors influencing the tolerance of urban residents in Shanghai towards a neglected species. People and Nature, 6, 1277-1287. |
| [44] | Zhou XF, Chen H (2018) Impact of urbanization-related land use land cover changes and urban morphology changes on the urban heat island phenomenon. Science of the Total Environment, 635, 1467-1476. |
| [1] | Ma Shangfei, Gong Xin, Shangguan Huayuan, Yao Haifeng, Wang Bin, Li Zhipeng, Sun Xin. Effects of urbanization and different land use types on soil eukaryotic biodiversity [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(3): 24540-. |
| [2] | Zhiqing Hu, Lu Dong. Effects of urbanization on interspecific interactions involving birds [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(8): 24048-. |
| [3] | Fei Duan, Mingzhang Liu, Hongliang Bu, Le Yu, Sheng Li. Effects of urbanization on bird community composition and functional traits: A case study of the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(8): 23473-. |
| [4] | Jiayu Lu, Xiaoyi Shi, Li’an Duo, Tianming Wang, Zhilin Li. Circadian rhythms of urban terrestrial mammals in Tianjin based on camera trapping method [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(8): 23369-. |
| [5] | Jiangtian Geng, Fei Wang, Huabin Zhao. Research progress on the impacts of urbanization on bats in China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(8): 24109-. |
| [6] | Hongyu Niu, Lu Chen, Hengyue Zhao, Gulzar Abdukirim, Hongmao Zhang. Effects of urbanization on animals: From community to individual level [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(8): 23489-. |
| [7] | Quanquan Jin, Ying Xiang, Hua Wang, Xinqiang Xi. Drosophilidae species diversity and parasitism rate in different types of green spaces in Xianlin university town, Nanjing [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(8): 24156-. |
| [8] | Xueyuan Li, Zhixian Sun, Fengzhen Wang, Rui Xi, Yutian Fang, Junyuan Hao, Dong Sheng, Shuya Sun, Yahui Zhao. Impacts of urban development on functional diversity in fish: A case study of Beijing, a megacity [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(8): 24150-. |
| [9] | Mingjun Zhang, Hesheng Wang, Wenbo Yan, Yunnan Fu, Qi Wang, Zhigao Zeng. Diel activity and habitat selection of small Indian civets (Viverricula indica) in Hainan Datian National Nature Reserve [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(6): 23420-. |
| [10] | Tingwei Dong, Meiling Huang, Xu Wei, Shuo Ma, Qu Yue, Wenli Liu, Jiaxin Zheng, Gang Wang, Rui Ma, Youzhong Ding, Shunqi Bo, Zhenghuan Wang. Potential spatial distribution pattern and landscape connectivity of Pelophylax plancyi in Shanghai, China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(8): 22692-. |
| [11] | Jinglong Jiang, Wenbo Yan, Fengcheng Hu, Qi Wang, Wang Sun, Yun Li, Yong Wang. Preliminary examination of the reintroduction of the endangered plant Petrocosmea qinlingensis [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(3): 22520-. |
| [12] | Yihan Wang, Qianqian Zhao, Yixin Diao, Bojian Gu, Yue Weng, Zhuojin Zhang, Yongbin Chen, Fang Wang. Diel activity, habitat utilization, and response to anthropogenic interference of small Indian civets (Viverricula indica) in Shanghai urban areas based on camera trapping [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(2): 22294-. |
| [13] | Tingting Li, Xihong Zhu, Guangnian Wu, Xiao Song, Aichun Xu. Spawning ground microhabitat selection by the Chinhai spiny newt (Echinotriton chinhaiensis) [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(1): 22293-. |
| [14] | Bing Yan, Qing Lu, Song Xia, Junsheng Li. An overview of advances in soil microbial diversity of urban environment [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2022, 30(8): 22186-. |
| [15] | Hualin Yang, Yuehong Cheng, Tianxiang Zhou, Xi Feng, Qiang Hu, Guiquan Zhang, Jian Yang, Jindong Zhang, Bin Wang, Caiquan Zhou. Multi-scale habitat selection of Chinese monal (Lophophorus lhuysii) in Wolong National Nature Reserve, Sichuan [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2022, 30(7): 21535-. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2022 Biodiversity Science
Editorial Office of Biodiversity Science, 20 Nanxincun, Xiangshan, Beijing 100093, China
Tel: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn