



Biodiv Sci ›› 2019, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (9): 932-942. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2019026 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2019026
• Special Feature: Snow Leopards: Survey, Research and Conservation Status in China • Previous Articles Next Articles
Xiaoyu Li1,#,Lingyun Xiao1,#,Xuchang Liang2,Chen Cheng1,Chen Feng3,Xiang Zhao3,Yanlin Liu4,Xiaoxing Bian2,Bing He5,Changzhi Zhang5,Justine Shanti Alexander6,Rui Xing7,Yahui Huang7,Awangjiumei 8,Xierannima 9,Dazhao Song4,Qiaowen Huang4, 10,Kui Peng11,Hang Yin12,Xinming Lian13,Xin Yang14,Sheng Li1,Xiaogang Shi15,Chuangming Yang16,Zhi Lü1,*( )
)
Received:2019-01-31
Accepted:2019-08-31
Online:2019-09-20
Published:2019-09-25
Contact:
Xiaoyu Li,Lingyun Xiao,Zhi Lü
Xiaoyu Li,Lingyun Xiao,Xuchang Liang,Chen Cheng,Chen Feng,Xiang Zhao,Yanlin Liu,Xiaoxing Bian,Bing He,Changzhi Zhang,Justine Shanti Alexander,Rui Xing,Yahui Huang,Awangjiumei ,Xierannima ,Dazhao Song,Qiaowen Huang, ,Kui Peng,Hang Yin,Xinming Lian,Xin Yang,Sheng Li,Xiaogang Shi,Chuangming Yang,Zhi Lü. Ongoing threats and the current status of snow leopard conservation in China[J]. Biodiv Sci, 2019, 27(9): 932-942.
| 威胁分类 Category of threat | 威胁名称 Threat | 编号 No. | 参考文献 Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| 对雪豹的直接猎杀 或抓捕 Direct killing or capture of snow leopards | 报复性猎杀 In retribution for livestock depredation (RLD) | 1.1 | Oli et al, 1994; Xu et al, 2008; Li et al, 2013; Alexander et al, 2015; Chen et al, 2016; Wild Xinjiang |
| 非法贸易导致的偷猎 Poaching for illegal trade (PIT) | 1.2 | Zhang, 1985; Schaller et al, 1988; Liu, 1993; EIA, 2008, 2012; Peng, 2009; Ma, 2012; Li & Lü, 2014; Maheshwari & Niraj, 2018 | |
| 动物园和博物馆的活体收集 Zoo and museum collection of live animals (ZMC) | 1.3 | Ma, 2012; Shan Shui Conservation Center | |
| 下毒、下套等导致的误杀 Secondary poisoning and trapping (SPT) | 1.4 | Li et al, 2013; Shan Shui Conservation Center | |
| 雪豹疾病 Diseases of snow leopards (DSL) | 1.5 | Fix et al, 1989; Silinski et al, 2003; An, 2016; Ostrowski & Gilbert, 2016; Shan Shui Conservation Center | |
| 栖息地和猎物相关 威胁 Threat about habitats and preys | 栖息地退化 Habitat degradation (HD) | 2.1 | Brown, 2008; Harris, 2010; Wang et al, 2015 |
| 栖息地破碎化 Habitat fragmentation (HF) | 2.2 | World Wide Fund for Nature; Xu et al, 2008; Li, 2012; Wild Xinjiang | |
| 盗猎和误杀导致的猎物种群减少 Prey reduction due to poaching and mistaken killing (PRPMK) | 2.3 | Schaller et al, 1988; Shan Shui Conservation Center | |
| 家畜竞争导致的猎物种群减少 Prey reduction due to competition with livestock (PRCL) | 2.4 | Mishra et al, 2004; Suryawanshi et al, 2010; Xiao, 2017; Wild Xinjiang | |
| 猎物疾病 Diseases of prey (DP) | 2.5 | Fedosenko & Blank, 2001; Dagleish et al, 2007; Wang et al, 2009; Bao et al, 2011; Ostrowski et al, 2011; Ostrowski & Gilbert, 2016; Wild Xinjiang | |
| 政策和认知相关 威胁 Threat about policy and cognition | 普遍认知缺乏导致的政策不当 Improper policy due to lack of cognition (IP) | 3.1 | Li et al, 2017 |
| 政策实施不力 Ineffective implementation of policies (IIP) | 3.2 | Mishra et al, 2003; Chen et al, 2016; Shan Shui Conservation Center | |
| 缺乏跨省(境)合作 Lack of trans-boundary cooperation (LTC) | 3.3 | - | |
| 基层保护部门能力不足 Insufficient capacity of local conservation departments (ICLCD) | 3.4 | - | |
| 当地社区保护动力不足 Lack of conservation incentive among local communities (LCILC) | 3.5 | - | |
| 间接威胁 Indirect threat | 气候变化 Climate change (CC) | 4.1 | IPCC, 2007; Klein et al, 2007; Xue et al, 2009; Vince, 2010; Yu et al, 2010; Forrest et al, 2012; Lovari et al, 2013; Yao et al, 2013; Luo et al, 2015; Aryal et al, 2016; Lehnert et al, 2016; Li et al, 2016; Yang et al, 2018 |
| 人口增长和贫困 Human population growth and poverty (HPGP) | 4.2 | Mishra et al, 2001, 2003; Adams et al, 2004; McShane & Wells, 2004 | |
| 流浪狗袭击雪豹及其猎物 Stray dogs attack snow leopards and their prey (SDA) | 4.3 | Wandeler et al, 1993; Butler et al, 2004; Mingyu Liu (Peking University) | |
| 虫草/药草采挖造成的干扰 Interference caused by cordyceps/herb collection (ICCC) | 4.4 | Shan Shui Conservation Center | |
| 道路建设与旅游开发项目 Road construction and tourism development projects (RCTD) | 4.5 | Wild Xinjiang; Wolong National Nature Reserve | |
| 矿产与水电开发 Mineral exploration and hydropower development (MEHD) | 4.6 | Wingard & Zahler, 2006; Baker et al, 2010; Jackson et al, 2013 |
Table 1 Threat to snow leopard in China
| 威胁分类 Category of threat | 威胁名称 Threat | 编号 No. | 参考文献 Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| 对雪豹的直接猎杀 或抓捕 Direct killing or capture of snow leopards | 报复性猎杀 In retribution for livestock depredation (RLD) | 1.1 | Oli et al, 1994; Xu et al, 2008; Li et al, 2013; Alexander et al, 2015; Chen et al, 2016; Wild Xinjiang |
| 非法贸易导致的偷猎 Poaching for illegal trade (PIT) | 1.2 | Zhang, 1985; Schaller et al, 1988; Liu, 1993; EIA, 2008, 2012; Peng, 2009; Ma, 2012; Li & Lü, 2014; Maheshwari & Niraj, 2018 | |
| 动物园和博物馆的活体收集 Zoo and museum collection of live animals (ZMC) | 1.3 | Ma, 2012; Shan Shui Conservation Center | |
| 下毒、下套等导致的误杀 Secondary poisoning and trapping (SPT) | 1.4 | Li et al, 2013; Shan Shui Conservation Center | |
| 雪豹疾病 Diseases of snow leopards (DSL) | 1.5 | Fix et al, 1989; Silinski et al, 2003; An, 2016; Ostrowski & Gilbert, 2016; Shan Shui Conservation Center | |
| 栖息地和猎物相关 威胁 Threat about habitats and preys | 栖息地退化 Habitat degradation (HD) | 2.1 | Brown, 2008; Harris, 2010; Wang et al, 2015 |
| 栖息地破碎化 Habitat fragmentation (HF) | 2.2 | World Wide Fund for Nature; Xu et al, 2008; Li, 2012; Wild Xinjiang | |
| 盗猎和误杀导致的猎物种群减少 Prey reduction due to poaching and mistaken killing (PRPMK) | 2.3 | Schaller et al, 1988; Shan Shui Conservation Center | |
| 家畜竞争导致的猎物种群减少 Prey reduction due to competition with livestock (PRCL) | 2.4 | Mishra et al, 2004; Suryawanshi et al, 2010; Xiao, 2017; Wild Xinjiang | |
| 猎物疾病 Diseases of prey (DP) | 2.5 | Fedosenko & Blank, 2001; Dagleish et al, 2007; Wang et al, 2009; Bao et al, 2011; Ostrowski et al, 2011; Ostrowski & Gilbert, 2016; Wild Xinjiang | |
| 政策和认知相关 威胁 Threat about policy and cognition | 普遍认知缺乏导致的政策不当 Improper policy due to lack of cognition (IP) | 3.1 | Li et al, 2017 |
| 政策实施不力 Ineffective implementation of policies (IIP) | 3.2 | Mishra et al, 2003; Chen et al, 2016; Shan Shui Conservation Center | |
| 缺乏跨省(境)合作 Lack of trans-boundary cooperation (LTC) | 3.3 | - | |
| 基层保护部门能力不足 Insufficient capacity of local conservation departments (ICLCD) | 3.4 | - | |
| 当地社区保护动力不足 Lack of conservation incentive among local communities (LCILC) | 3.5 | - | |
| 间接威胁 Indirect threat | 气候变化 Climate change (CC) | 4.1 | IPCC, 2007; Klein et al, 2007; Xue et al, 2009; Vince, 2010; Yu et al, 2010; Forrest et al, 2012; Lovari et al, 2013; Yao et al, 2013; Luo et al, 2015; Aryal et al, 2016; Lehnert et al, 2016; Li et al, 2016; Yang et al, 2018 |
| 人口增长和贫困 Human population growth and poverty (HPGP) | 4.2 | Mishra et al, 2001, 2003; Adams et al, 2004; McShane & Wells, 2004 | |
| 流浪狗袭击雪豹及其猎物 Stray dogs attack snow leopards and their prey (SDA) | 4.3 | Wandeler et al, 1993; Butler et al, 2004; Mingyu Liu (Peking University) | |
| 虫草/药草采挖造成的干扰 Interference caused by cordyceps/herb collection (ICCC) | 4.4 | Shan Shui Conservation Center | |
| 道路建设与旅游开发项目 Road construction and tourism development projects (RCTD) | 4.5 | Wild Xinjiang; Wolong National Nature Reserve | |
| 矿产与水电开发 Mineral exploration and hydropower development (MEHD) | 4.6 | Wingard & Zahler, 2006; Baker et al, 2010; Jackson et al, 2013 |
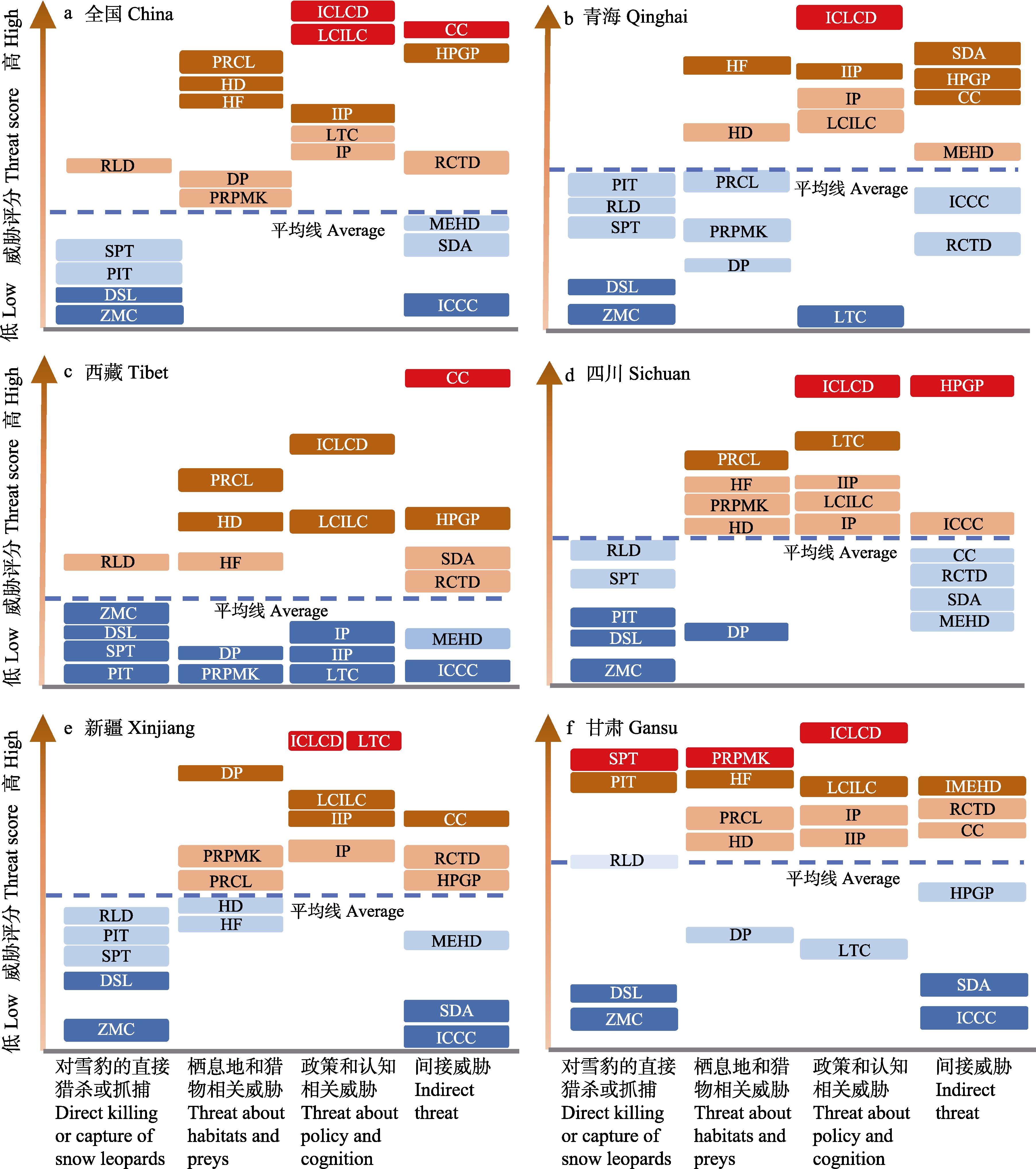
Fig. 1 Rankings of threats to snow leopard at national and provincial level. RLD, In retribution for livestock depredation; PIT, Poaching for illegal trade; ZMC, Zoo and museum collection of live animals; SPT, Secondary poisoning and trapping of snow leopards; DSL, Diseases of snow leopards; HD, Habitat degradation; HF, Habitat fragmentation; PRPMK, Prey reduction due to poaching and mistaken killing; PRCL, Prey reduction due to competition with livestock; DP, Diseases of prey; IP, Improper policy due to lack of cognition; IIP, Ineffective implementation of policies; LTC, Lack of trans-boundary cooperation; ICLCD, Insufficient capacity of local conservation departments; LCILC, Lack of conservation incentive among local communities; CC, Climate change; HPGP, Human population growth and poverty; SDA, Stray dogs attack snow leopards and their prey; ICCC, Interference caused by cordyceps/herb collection; RCTD, Road construction and tourism development projects; MEHD, Mineral exploration and hydropower development.
| 保护行动 Protective actions | 青海 Qinghai | 西藏 Tibet | 四川 Sichuan | 新疆 Xinjiang | 甘肃 Gansu | 全国 China | 应对威胁 Corresponding threat | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 保护地建设<BR/>Development of nature reserves | 保护区监测与反盗猎巡护 Monitoring in conservation area and anti-poaching patrol | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 1.1, 1.2, 1.3, 1.4, 2.3 |
| 保护区能力建设 Capacity building of conservation area | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 3.4 | ||
| 建立新保护地 Establishing new conservation areas | √ | √ | 2.1, 2.2, 3.3, 4.5, 4.6 | |||||
| 在地保护行动<BR/>Local protective actions | 人兽冲突补偿/保险 Compensation/insurance for human-wildlife conflict | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 1.1, 1.4, 3.1, 4.2 |
| 扶贫/生计改善 Poverty alleviation/livelihood improvement | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 1.1, 1.4, 2.1, 2.4, 3.5, 4.2 | |
| 社区/公民志愿者监测与反盗猎巡护 Community/citizen volunteer monitoring and anti-poaching patrol | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 1.1, 1.2, 1.3, 1.4, 2.3, 3.4, 3.5 | ||
| 放牧管理 Grazing management | √ | √ | 2.1, 2.4 | |||||
| 家畜疫病防治 Livestock disease prevention | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 2.5 | |
| 拆除围栏 Fence removal | √ | √ | √ | 2.1, 2.2 | ||||
| 流浪狗管理 Stray dogs ??management | √ | √ | 1.5, 4.3 | |||||
| 虫草/药草采集管理 Cordyceps/herb collection management | √ | √ | 4.4 | |||||
| 社区宣传教育 Community education | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 1.1, 1.2, 1.4, 2.3, 3.2, 3.4, 3.5,4.4 | ||
| 政策与公众推动<BR/>Policy and public promotion | 制定保护规划 Protection planning | √ | √ | √ | 3.1, 3.2 | |||
| 生态补偿 Ecological compensation | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 2.1, 2.4, 3.4, 3.5, 4.2 | |
| 管理开发/发展类项目 Management of development projects | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 2.1, 2.2, 4.5, 4.6 | |
| 政策建议 Policy suggestion | √ | √ | √ | 3.1, 3.2 | ||||
| 公众宣传 Publicity | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 1.2, 3.1 | ||
Table 2 Protective actions and corresponding threat at national and provincial level (Mean of the numbers are shown in Table 1)
| 保护行动 Protective actions | 青海 Qinghai | 西藏 Tibet | 四川 Sichuan | 新疆 Xinjiang | 甘肃 Gansu | 全国 China | 应对威胁 Corresponding threat | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 保护地建设<BR/>Development of nature reserves | 保护区监测与反盗猎巡护 Monitoring in conservation area and anti-poaching patrol | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 1.1, 1.2, 1.3, 1.4, 2.3 |
| 保护区能力建设 Capacity building of conservation area | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 3.4 | ||
| 建立新保护地 Establishing new conservation areas | √ | √ | 2.1, 2.2, 3.3, 4.5, 4.6 | |||||
| 在地保护行动<BR/>Local protective actions | 人兽冲突补偿/保险 Compensation/insurance for human-wildlife conflict | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 1.1, 1.4, 3.1, 4.2 |
| 扶贫/生计改善 Poverty alleviation/livelihood improvement | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 1.1, 1.4, 2.1, 2.4, 3.5, 4.2 | |
| 社区/公民志愿者监测与反盗猎巡护 Community/citizen volunteer monitoring and anti-poaching patrol | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 1.1, 1.2, 1.3, 1.4, 2.3, 3.4, 3.5 | ||
| 放牧管理 Grazing management | √ | √ | 2.1, 2.4 | |||||
| 家畜疫病防治 Livestock disease prevention | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 2.5 | |
| 拆除围栏 Fence removal | √ | √ | √ | 2.1, 2.2 | ||||
| 流浪狗管理 Stray dogs ??management | √ | √ | 1.5, 4.3 | |||||
| 虫草/药草采集管理 Cordyceps/herb collection management | √ | √ | 4.4 | |||||
| 社区宣传教育 Community education | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 1.1, 1.2, 1.4, 2.3, 3.2, 3.4, 3.5,4.4 | ||
| 政策与公众推动<BR/>Policy and public promotion | 制定保护规划 Protection planning | √ | √ | √ | 3.1, 3.2 | |||
| 生态补偿 Ecological compensation | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 2.1, 2.4, 3.4, 3.5, 4.2 | |
| 管理开发/发展类项目 Management of development projects | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 2.1, 2.2, 4.5, 4.6 | |
| 政策建议 Policy suggestion | √ | √ | √ | 3.1, 3.2 | ||||
| 公众宣传 Publicity | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 1.2, 3.1 | ||
| [1] | Adams WM, Aveling R, Brockington D, Dickson B, Elliott J, Hutton J, Roe D, Vira B, Wolmer W ( 2004) Biodiversity conservation and the eradication of poverty. Science, 306, 1146-1149. |
| [2] | Aipanjiguly S, Jacobson SK, Flamm R ( 2003) Conserving manatees: Knowledge, attitudes, and intentions of boaters in Tampa Bay, Florida. Conservation Biology, 17, 1098-1105. |
| [3] | Alexander J, Chen P, Damerell P, Youkui W, Hughes J, Shi K, Riordan P ( 2015) Human wildlife conflict involving large carnivores in Qilianshan, China and the minimal paw-print of snow leopards. Biological Conservation, 187, 1-9. |
| [4] | Aryal A, Shrestha UB, Ji W, Ale SB, Shrestha S, Ingty T, Maraseni T, Cockfield G, Raubenheimer D ( 2016) Predicting the distributions of predator (snow leopard) and prey (blue sheep) under climate change in the Himalaya. Ecology and Evolution, 6, 4065-4075. |
| [5] | Baker MS, Elias N, Guzmán E, Soto-Viruet Y ( 2010) Mineral facilities of Asia and the Pacific. 2010) Mineral facilities of Asia and the Pacific. . (accessed on 2012-11-09 |
| [6] | Bao J, Wang Z, Li L, Wu X, Sang P, Wu G, Ding G, Suo L, Liu C, Wang J, Zhao W, Li J, Qi L ( 2011) Detection and genetic characterization of peste des petits ruminants virus in free-living bharals (Pseudois nayaur) in Tibet, China. Research in Veterinary Science, 90, 238-240. |
| [7] | Brown LR ( 2008) Plan B 3.0: Mobilizing to Save Civilization (substantially revised). WW Norton & Company, New York. |
| [8] | Butler JRA, Du Toit JT, Bingham J ( 2004) Free-ranging domestic dogs (Canis familiaris) as predators and prey in rural Zimbabwe: Threats of competition and disease to large wild carnivores. Biological Conservation, 115, 369-378. |
| [9] | Chen P, Gao Y, Lee AT, Cering LL, Shi K, Clark SG ( 2016) Human-carnivore coexistence in Qomolangma (Mt. Everest) Nature Reserve, China: Patterns and compensation. Biological Conservation, 197, 18-26. |
| [10] | China Forestry Administration ( 2013) China Snow Leopard Conservation Action Plan (Revised Manuscript). |
| [11] | Dagleish MP, Qurban A, Powell RK, Butz D, Woodford MH ( 2007) Fatal Sarcoptes scabiei infection of blue sheep (Pseudois nayaur) in Pakistan. Journal of Wildlife Diseases, 43, 512-517. |
| [12] | Donlan CJ, Wingfield DK, Crowder LB, Wilcox C ( 2010) Using expert opinion surveys to rank threats to endangered species: A case study with sea turtles. Conservation Biology, 24, 1586-1595. |
| [13] | EIA( 2008) Skin Deep: The need for effective enforcement to combat the Asian big cat skin trade.In: The 57th Meeting of the CITES Standing Committee FIC Europe, Brussels. |
| [14] | EIA( 2012) Briefing on snow leopards in illegal trade—Asia’s forgotten cats. In: The 2nd Asian Ministerial Conference on Tiger Conservation, Bhutan. |
| [15] | Fedosenko AK, Blank DA ( 2001) Capra sibirica. Mammal Species, 675, 1-13. |
| [16] | Fix AS, Riordan DP, Hill HT, Gill MA, Evans EB ( 1989) Feline panleukopenia virus and subsequent canine distemper virus infection in two snow leopards (Panthera uncia). Journal of Zoo and Wildlife Medicine, 20, 273-281. |
| [17] | Forrest JL, Wikramanayake E, Shrestha R, Areendran G, Gyeltshen K, Maheshwari A, Mazumdar S, Naidoo R, Thapa GJ, Thapa K ( 2012) Conservation and climate change: Assessing the vulnerability of snow leopard habitat to treeline shift in the Himalaya. Biological Conservation, 150, 129-135. |
| [18] | Harris RB ( 2010) Rangeland degradation on the Qinghai- Tibetan Plateau: A review of the evidence of its magnitude and causes. Journal of Arid Environments, 74, 1-12. |
| [19] | Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) (2007) Climate Change 2007: Synthesis Report. . ( accessed on 2019-01-28) |
| [20] | Jackson RM, Mallon D, Sharma RK, Suryawanshi KS, Mishra C ( 2013) Snow Leopard Survival Strategy. Version 2013.1, Snow Leopard Network, Seattle. |
| [21] | Kerr RA ( 1996) A new way to ask the experts—Rating radioactive waste risks. Science, 274, 913-914. |
| [22] | Klein JA, Harte J, Zhao X ( 2007) Experimental warming, not grazing, decreases rangeland quality on the Tibetan Plateau. Ecological Applications, 17, 541-557. |
| [23] | Lehnert LW, Wesche K, Trachte K, Reudenbach C, Bendix J ( 2016) Climate variability rather than overstocking causes recent large-scale cover changes of Tibetan pastures. Scientific Reports, 6, 24367. |
| [24] | Li J ( 2012) Ecology and Conservation Strategy of Snow Leopard (Panthera uncia) in Sanjiangyuan Area on the Tibetan Plateau. PhD dissertation, Peking University, Beijing. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 李娟 ( 2012) 青藏高原三江源地区雪豹(Panthera uncia)的生态学研究及保护. 博士学位论文, 北京大学, 北京.] | |
| [25] | Li J, Lü Z ( 2014) Snow leopard poaching and trade in China 2000-2013. Biological Conservation, 176, 207-211. |
| [26] | Li J, McCarthy TM, Wang H, Weckworth BV, Schaller GB, Mishra C, Lü Z, Beissinger SR ( 2016) Climate refugia of snow leopards in High Asia. Biological Conservation, 203, 188-196. |
| [27] | Li J, Yin H, Wang D, Jiagong Z, Lü Z ( 2013) Human-snow leopard conflicts in the Sanjiangyuan Region of the Tibetan Plateau. Biological Conservation, 166, 118-123. |
| [28] | Li L, Fassnacht FE, Storch I, Bürgi M ( 2017) Land-use regime shift triggered the recent degradation of alpine pastures in Nyanpo Yutse of the eastern Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Landscape Ecology, 8, 1-17. |
| [29] | Liu WL ( 1993) Brief history about conservation and utilization of wild animals on the Tibetan Plateau. Journal of Tibet University, 8(1), 45-49. (in Chinese) |
| [ 刘务林 ( 1993) 西藏高原人类保护利用野生动物简史. 西藏大学学报, 8(1), 45-49.] | |
| [30] | Lovari S, Ventimiglia M, Minder I ( 2013) Food habits of two leopard species, competition, climate change and upper treeline: A way to the decrease of an endangered species. Ethology Ecology & Evolution, 25, 305-318. |
| [31] | Luo Z, Jiang Z, Tang S ( 2015) Impacts of climate change on distributions and diversity of ungulates on the Tibetan Plateau. Ecological Applications, 25, 24-38. |
| [32] | Ma KP, Qian YQ ( 1998) Biodiversity conservation and its research progress. Chinese Journal of Applied and Environmental Biology, 4, 95-99. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 马克平, 钱迎倩 ( 1998) 生物多样性保护及其研究进展. 应用与环境生物学报, 4, 95-99.] | |
| [33] | Ma M ( 2012) Market prices for the tissues and organs of snow leopards in China. Selevinia, 516, 119-122. |
| [34] | Maheshwari A, Niraj SK ( 2018) Monitoring illegal trade in snow leopards: 2003-2014. Global Ecology and Conservation, 14, e00387. |
| [35] | Martin TG, Kuhnert PM, Mengersen K, Possingham HP ( 2005) The power of expert opinion in ecological models using Bayesian methods: Impact of grazing on birds. Ecological Applications, 15, 266-280. |
| [36] | McCarthy T, Mallon D, Jackson R, Zahler P, McCarthy K ( 2017) Panthera uncia. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2017. . |
| [37] | McShane TO, Wells MP ( 2004) Getting Biodiversity Projects to Work:Towards More Effective Conservation and Development. C olumbia University Press,New York. |
| [38] | Mishra C, Allen P, McCarthy T, Madhusudan MD, Bayarjargal A, Prins HHT ( 2003) The role of incentive programs in conserving the snow leopard. Conservation Biology, 17, 1512-1520. |
| [39] | Mishra C, Prins HHT, Wieren VSE ( 2001) Overstocking in the Trans-Himalayan rangelands of India. Environmental Conservation, 28, 279-283. |
| [40] | Mishra C, Wieren SEV, Ketner P, Heitkonig IMA, Prins HHT ( 2004) Competition between domestic livestock and wild bharal Pseudois nayaur in the Indian Trans-Himalaya. Journal of Applied Ecology, 41, 344-354. |
| [41] | Oli MK, Taylor IR, Rogers ME ( 1994) Snow leopard (Panthera uncia) predation of livestock: An assessment of local perceptions in the Annapurna Conservation Area, Nepal. Biological Conservation, 68, 63-68. |
| [42] | Ostrowski S, Gilbert M ( 2016) Diseases of free-ranging snow leopards and primary prey species. In: Snow Leopard (eds McCarthy T, Mallon D), pp.97-112. Academic Press, London. |
| [43] | Ostrowski S, Thiaucourt F, Amirbekov M, Mahmadshoev A, Manso-Silván L, Dupuy V, Vahobov D, Ziyoev O, Michel S ( 2011) Fatal outbreak of Mycoplasma capricolum pneumonia in endangered markhors. Emerging Infectious Disease, 17, 2338-2341. |
| [44] | Peng JT ( 2009) An investigation on snow leopard resources in Ganzi Prefecture in the Hengduan Mountains on the southeast of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Journal of Sichuan Forestry Science and Technology, 30(1), 57-58, 47. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 彭基泰 ( 2009) 青藏高原东南横断山脉甘孜地区雪豹资源调查研究. 四川林业科技, 30(1), 57-58, 47.] | |
| [45] | Salafsky N, Margoluis R ( 1999) Threat reduction assessment: A practical and cost-effective approach to evaluating conservation and development projects. Conservation Biology, 13, 830-841. |
| [46] | Schaller GB, Junrang R, Mingjiang Q ( 1988) Status of the snow leopard (Panthera uncia) in Qinghai and Gansu provinces, China. Biological Conservation, 45, 179-194. |
| [47] | Silinski S, Robert N, Walzer C ( 2003) Canine distemper and toxoplasmosis in a captive snow leopard (Uncia uncia)—A diagnostic dilemma. Verhandlungsbericht des Symposium uber die Erkrankungen der Zootiere, 41, 107-111. |
| [48] | Suryawanshi KR, Bhatnagar YV, Mishra C ( 2010) Why should a grazer browse? Livestock impact on winter resource use by bharal Pseudois nayaur. Oecologia, 162, 453-462. |
| [49] | Vince G ( 2010) A himalaya village builds artificial glaciers to survive global warming. . (accessed on 2012-09-11) |
| [50] | Wandeler A, Matter H, Kappeler A, Budde A ( 1993) The ecology of dogs and canine rabies: A selective review. Revue Scientifique et Technique (International Office of Epizootics), 12(1), 51-71. |
| [51] | Wang Z, Bao J, Wu X, Liu Y, Li L, Liu C, Suo L, Xie Z, Zhao W, Zhang W, Yang N, Li J, Wang S, Wang J ( 2009) Peste des petits ruminants virus in Tibet, China. Emerging Infectious Disease, 15, 299-301. |
| [52] | Wang P, Lassoie JP, Morreale SJ, Dong S ( 2015) A critical review of socioeconomic and natural factors in ecological degradation on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau, China. The Rangeland Journal, 37, 1-9. |
| [53] | Wingard JR, Zahler P ( 2006) Silent Steppe: The Illegal Wildlife Trade Crisis in Mongolia.. |
| [54] | Xiao LY ( 2017) The Interaction Among Snow Leopards (Panthera uncia), Blue Sheep (Pseudois nayaur) and Livestock in Sanjiangyuan Region. PhD dissertation, Peking University, Beijing. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 肖凌云 ( 2017) 三江源地区雪豹(Panthera uncia)、岩羊(Pseudois nayaur)与家畜的竞争与捕食关系研究. 博士学位论文, 北京大学, 北京.] | |
| [55] | Xu A, Jiang Z, Li C, Guo J, Da S, Cui Q, Yu S, Wu G ( 2008) Status and conservation of the snow leopard Panthera uncia in the Gouli Region, Kunlun Mountains, China. Oryx, 42, 460-463. |
| [56] | Xue X, Guo J, Han B, Sun Q, Liu L ( 2009) The effect of climate warming and permafrost thaw on desertification in the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Geomorphology, 108, 182-190. |
| [57] | Yang Y, Hopping K, Wang G, Chen J, Peng A, Klein JA ( 2018) Permafrost and drought regulate vulnerability of Tibetan Plateau grasslands to warming. Ecosphere, 9, e02233. |
| [58] | Yao T, Wang Y, Liu S, Pu J, Shen Y, Lu A ( 2013) Recent glacial retreat in High Asia in China and its impact on water resource in Northwest China. Science in China, 47, 1065-1075. |
| [59] | Yu H, Luedeling E, Xu J ( 2010) Winter and spring warming result in delayed spring phenology on the Tibetan Plateau . Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences,USA, 107, 22151-22156. |
| [60] | Zhang DM ( 1985) The dynamics of a few animals during the last thirty years in Ili Prefecture, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region . Acta Theriologica Sinica ,5, 56, 66. (in Chinese) |
| [ 张大铭 ( 1985) 新疆伊犁地区近三十年来几种兽类的动态.兽类学报, 5, 56, 66.] |
| [1] | Zhou Zhihua, Jin Xiaohua, Luo Ying, Li Diqiang, Yue Jianbing, Liu Fang, He Tuo, Li Xi, Dong Hui, Luo Peng. Analyses and suggestions on mechanisms of forestry and grassland administrations in China to achieve targets of Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(3): 24487-. |
| [2] | Tian Zhiqi, Su Yang. China’s implementation model of international environmental conventions and its application to the Convention on Biological Diversity—Achieving the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework targets and the role of national parks [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(3): 24593-. |
| [3] | Wei Yi, Yi Ai, Meng Wu, Liming Tian, Tserang Donko Mipam. Soil archaeal community responses to different grazing intensities in the alpine meadows of the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(1): 24339-. |
| [4] | Bangze Li, Shuren Zhang. An updated species checklist and taxonomic synopsis of Cyperaceae in China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(7): 24106-. |
| [5] | Zonggang Hu. China and the United States once planned joint compilation of the Flora of China after the victory in the China’s Resistance War Against Japan [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(6): 24220-. |
| [6] | Qiyu Kuang, Liang Hu. Species diversity and geographical distribution of marine benthic shell-bearing mollusks around Donghai Island and Naozhou Island, Guangdong Province [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(5): 24065-. |
| [7] | Yujie Chi, Xintian Zhang, Zhixuan Tian, Chengshuai Guan, Xinzhi Gu, Zhihui Liu, Zhanbin Wang, Jinjie Wang. Species diversity of powdery mildew fungi (Erysiphaceae) and their host plants in Northeast Asia [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(4): 23443-. |
| [8] | Di Lin, Shuanglin Chen, Que Du, Wenlong Song, Gu Rao, Shuzhen Yan. Investigation of species diversity of myxomycetes in Dabie Mountains [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(2): 23242-. |
| [9] | Jianping Jiang, Bo Cai, Bin Wang, Weitao Chen, Zhixin Wen, Dezhi Zhang, Lulu Sui, Shun Ma, Weibo Wang. New vertebrate species discovered in China in 2023 [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(11): 24327-. |
| [10] | Huanxi Cao, Qingsong Zhou, Arong Luo, Pu Tang, Tingjing Li, Zejian Li, Huayan Chen, Zeqing Niu, Chaodong Zhu. New taxa of extant Hymenoptera in 2023 [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(11): 24319-. |
| [11] | Cheng Du, Jun Liu, Wen Ye, Shuai Liao. 2023 annual report on new taxa and nomenclatural changes for Chinese plants [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(11): 24253-. |
| [12] | Siyuan Xu, Qiqi Lian, Ruixin Zhang, Jiateng Zhao, Xuan Zhou, Lu Zhou, Qin Chen, Ming Bai. The world new taxa of extant Coleoptera in 2023 [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(11): 24307-. |
| [13] | Nuriye Muhetaier, Xiuying Zhang, Subinuer Eli, Houhun Li. Annual report of new taxa for Chinese Lepidoptera in 2023 [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(11): 24428-. |
| [14] | Chen Lin, Qicheng Yang, Yanling Wu, Peng Hou, Bing Zhang, Ding Yang. New taxa of Diptera from China in 2023 [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(11): 24328-. |
| [15] | Yuchen Du, Beimeng Liu, Junfeng Chen, Hao Wang, Yi Xie. Analysis of factors influencing farmers’ protection willingness based on structural equation model: Taking the Hunchun area of Northeast China Tiger and Leopard National Park as an example [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(1): 23155-. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2026 Biodiversity Science
Editorial Office of Biodiversity Science, 20 Nanxincun, Xiangshan, Beijing 100093, China
Tel: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn