



Biodiv Sci ›› 2024, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (1): 23155. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2023155 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2023155
• Original Papers: Biosafety and Nature Conservation • Previous Articles Next Articles
Yuchen Du, Beimeng Liu, Junfeng Chen, Hao Wang, Yi Xie*( )
)
Received:2023-05-19
Accepted:2023-11-24
Online:2024-01-20
Published:2023-11-29
Contact:
*E-mail: yixie@bjfu.edu.cn
Yuchen Du, Beimeng Liu, Junfeng Chen, Hao Wang, Yi Xie. Analysis of factors influencing farmers’ protection willingness based on structural equation model: Taking the Hunchun area of Northeast China Tiger and Leopard National Park as an example[J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(1): 23155.
| Box 1 变量定义与说明 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 变量类型 | 变量名称 | 变量定义与赋值 | |
| 被解释 变量 | 保护 意愿WILL | (W1)参与保护的意愿(1 = 非常不愿意, 2 = 不愿意, 3 = 一般, 4 = 愿意, 5 = 非常愿意); (W2)参与国家公园日常巡护(制止盗猎、盗挖等)工作的意愿(1 = 非常不愿意, 2 = 不愿意, 3 = 一般, 4 = 愿意, 5 = 非常愿意); (W3)参与国家公园生态保护修复工作的意愿(1 = 非常不愿意, 2 = 不愿意, 3 = 一般, 4 = 愿意, 5 = 非常愿意); (W4)参与国家公园科普教育工作的意愿(1 = 非常不愿意, 2 = 不愿意, 3 = 一般, 4 = 愿意, 5 = 非常愿意) | |
| 解释变量 | 态度 Att | 价值评价 Att1 | (A1)保护东北虎豹非常重要(1 = 非常不同意, 2 = 不同意, 3 = 一般, 4 = 同意, 5 = 非常同意); (A2)保护植物资源非常重要(1 = 非常不同意, 2 = 不同意, 3 = 一般, 4 = 同意, 5 = 非常同意); (A3)保护周边环境非常重要(1 = 非常不同意, 2 = 不同意, 3 = 一般, 4 = 同意, 5 = 非常同意) |
| 经验性评价Att2 | (A4)可以提高地区知名度(1 = 非常不同意, 2 = 不同意, 3 = 一般, 4 = 同意, 5 = 非常同意); (A5)可以改善社区基础设施(1 = 非常不同意, 2 = 不同意, 3 = 一般, 4 = 同意, 5 = 非常同意); (A6)可以提高居民环保意识(1 = 非常不同意, 2 = 不同意, 3 = 一般, 4 = 同意, 5 = 非常同意) | ||
| 产生结果 Att3 | (A7)可以改善社区基础设施(1 = 非常不同意, 2 = 不同意, 3 = 一般, 4 = 同意, 5 = 非常同意); (A8)可以提高经济收入(1 = 非常不同意, 2 = 不同意, 3 = 一般, 4 = 同意, 5 = 非常同意); (A9)可以增加就业机会(1 = 非常不同意, 2 = 不同意, 3 = 一般, 4 = 同意, 5 = 非常同意) | ||
| 规范 Nor | 个人规范 Nor1 | (N1)我有责任参与(1 = 非常不同意, 2 = 不同意, 3 = 一般, 4 = 同意, 5 = 非常同意); (N2)参与符合我的道德原则(1 = 非常不同意, 2 = 不同意, 3 = 一般, 4 = 同意, 5 = 非常同意); (N3)如果不参与保护, 我会感到自责(1 = 非常不同意, 2 = 不同意, 3 = 一般, 4 = 同意, 5 = 非常同意) | |
| 命令性规范Nor2 | (N4)家人认为我应该参与(1 = 非常不同意, 2 = 不同意, 3 = 一般, 4 = 同意, 5 = 非常同意); (N5)其他村民认为我应该参与(1 = 非常不同意, 2 = 不同意, 3 = 一般, 4 = 同意, 5 = 非常同意); (N6)政府政策要求我参与(1 = 非常不同意, 2 = 不同意, 3 = 一般, 4 = 同意, 5 = 非常同意) | ||
| 描述性规范Nor3 | (N7)家人参与程度(1 = 很低, 2 = 低, 3 = 一般, 4 = 高, 5 = 很高); (N8)其他村民参与程度(1 = 很低, 2 = 低, 3 = 一般, 4 = 高, 5 = 很高); (N9)村干部参与程度(1 = 很低, 2 = 低, 3 = 一般, 4 = 高, 5 = 很高) | ||
| 知觉行为控制 Pbc | (P1)有足够时间参与(1 = 非常不同意, 2 = 不同意, 3 = 一般, 4 = 同意, 5 = 非常同意); (P2)有足够经济能力参与(1 = 非常不同意, 2 = 不同意, 3 = 一般, 4 = 同意, 5 = 非常同意); (P3)有足够专业技能参与(1 = 非常不同意, 2 = 不同意, 3 = 一般, 4 = 同意, 5 = 非常同意) | ||
| 控制变量 | 年龄 Age | 实际年龄 | |
| 受教育程度 Edu | 1 = 小学及以下, 2 = 初中、中专、技校, 3 = 职高、高中, 4 = 大专、本科, 5 = 硕士及以上 | ||
| 性别 Gen | 0 = 女, 1 = 男 | ||
| 家庭年收入 Inc | 实际收入 | ||
| Box 1 变量定义与说明 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 变量类型 | 变量名称 | 变量定义与赋值 | |
| 被解释 变量 | 保护 意愿WILL | (W1)参与保护的意愿(1 = 非常不愿意, 2 = 不愿意, 3 = 一般, 4 = 愿意, 5 = 非常愿意); (W2)参与国家公园日常巡护(制止盗猎、盗挖等)工作的意愿(1 = 非常不愿意, 2 = 不愿意, 3 = 一般, 4 = 愿意, 5 = 非常愿意); (W3)参与国家公园生态保护修复工作的意愿(1 = 非常不愿意, 2 = 不愿意, 3 = 一般, 4 = 愿意, 5 = 非常愿意); (W4)参与国家公园科普教育工作的意愿(1 = 非常不愿意, 2 = 不愿意, 3 = 一般, 4 = 愿意, 5 = 非常愿意) | |
| 解释变量 | 态度 Att | 价值评价 Att1 | (A1)保护东北虎豹非常重要(1 = 非常不同意, 2 = 不同意, 3 = 一般, 4 = 同意, 5 = 非常同意); (A2)保护植物资源非常重要(1 = 非常不同意, 2 = 不同意, 3 = 一般, 4 = 同意, 5 = 非常同意); (A3)保护周边环境非常重要(1 = 非常不同意, 2 = 不同意, 3 = 一般, 4 = 同意, 5 = 非常同意) |
| 经验性评价Att2 | (A4)可以提高地区知名度(1 = 非常不同意, 2 = 不同意, 3 = 一般, 4 = 同意, 5 = 非常同意); (A5)可以改善社区基础设施(1 = 非常不同意, 2 = 不同意, 3 = 一般, 4 = 同意, 5 = 非常同意); (A6)可以提高居民环保意识(1 = 非常不同意, 2 = 不同意, 3 = 一般, 4 = 同意, 5 = 非常同意) | ||
| 产生结果 Att3 | (A7)可以改善社区基础设施(1 = 非常不同意, 2 = 不同意, 3 = 一般, 4 = 同意, 5 = 非常同意); (A8)可以提高经济收入(1 = 非常不同意, 2 = 不同意, 3 = 一般, 4 = 同意, 5 = 非常同意); (A9)可以增加就业机会(1 = 非常不同意, 2 = 不同意, 3 = 一般, 4 = 同意, 5 = 非常同意) | ||
| 规范 Nor | 个人规范 Nor1 | (N1)我有责任参与(1 = 非常不同意, 2 = 不同意, 3 = 一般, 4 = 同意, 5 = 非常同意); (N2)参与符合我的道德原则(1 = 非常不同意, 2 = 不同意, 3 = 一般, 4 = 同意, 5 = 非常同意); (N3)如果不参与保护, 我会感到自责(1 = 非常不同意, 2 = 不同意, 3 = 一般, 4 = 同意, 5 = 非常同意) | |
| 命令性规范Nor2 | (N4)家人认为我应该参与(1 = 非常不同意, 2 = 不同意, 3 = 一般, 4 = 同意, 5 = 非常同意); (N5)其他村民认为我应该参与(1 = 非常不同意, 2 = 不同意, 3 = 一般, 4 = 同意, 5 = 非常同意); (N6)政府政策要求我参与(1 = 非常不同意, 2 = 不同意, 3 = 一般, 4 = 同意, 5 = 非常同意) | ||
| 描述性规范Nor3 | (N7)家人参与程度(1 = 很低, 2 = 低, 3 = 一般, 4 = 高, 5 = 很高); (N8)其他村民参与程度(1 = 很低, 2 = 低, 3 = 一般, 4 = 高, 5 = 很高); (N9)村干部参与程度(1 = 很低, 2 = 低, 3 = 一般, 4 = 高, 5 = 很高) | ||
| 知觉行为控制 Pbc | (P1)有足够时间参与(1 = 非常不同意, 2 = 不同意, 3 = 一般, 4 = 同意, 5 = 非常同意); (P2)有足够经济能力参与(1 = 非常不同意, 2 = 不同意, 3 = 一般, 4 = 同意, 5 = 非常同意); (P3)有足够专业技能参与(1 = 非常不同意, 2 = 不同意, 3 = 一般, 4 = 同意, 5 = 非常同意) | ||
| 控制变量 | 年龄 Age | 实际年龄 | |
| 受教育程度 Edu | 1 = 小学及以下, 2 = 初中、中专、技校, 3 = 职高、高中, 4 = 大专、本科, 5 = 硕士及以上 | ||
| 性别 Gen | 0 = 女, 1 = 男 | ||
| 家庭年收入 Inc | 实际收入 | ||
| 克隆巴赫系数Cronbach’s alpha index | 组合信度 CR | 平均方差提取值 AVE | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 态度 Att | 0.838 | 0.868 | 0.548 |
| 规范 Nor | 0.876 | 0.831 | 0.569 |
| 知觉行为控制 Pbc | 0.773 | 0.782 | 0.554 |
| 保护意愿 WILL | 0.962 | 0.919 | 0.744 |
Table 1 The results of reliability and average variance extracted
| 克隆巴赫系数Cronbach’s alpha index | 组合信度 CR | 平均方差提取值 AVE | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 态度 Att | 0.838 | 0.868 | 0.548 |
| 规范 Nor | 0.876 | 0.831 | 0.569 |
| 知觉行为控制 Pbc | 0.773 | 0.782 | 0.554 |
| 保护意愿 WILL | 0.962 | 0.919 | 0.744 |
| 保护意愿WILL | 态度 Att | 规范 Nor | 知觉行为控制 Pbc | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 保护意 WILL | 0.863 | |||
| 态度 Att | 0.509*** | 0.669 | ||
| 规范 Nor | 0.633*** | 0.569*** | 0.607 | |
| 知觉行为控制Pbc | 0.584*** | 0.476*** | 0.594*** | 0.744 |
Table 2 The results of discriminant validity
| 保护意愿WILL | 态度 Att | 规范 Nor | 知觉行为控制 Pbc | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 保护意 WILL | 0.863 | |||
| 态度 Att | 0.509*** | 0.669 | ||
| 规范 Nor | 0.633*** | 0.569*** | 0.607 | |
| 知觉行为控制Pbc | 0.584*** | 0.476*** | 0.594*** | 0.744 |
| 拟合指标 Fit indicators | 绝对拟合度指标 Absolute goodness-of-fit indices | 相对拟合度指标 Relative goodness-of-fit indices | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 近似误差均方根RMSEA | 标准化均方根残差SRMR | 拟合优度指数GFI | 塔克·刘易斯指数TLI | 比较性拟合指标CFI | 规范拟合指标NFI | 成长拟合指标IFI | |
| 评价标准Criterion | < 0.10 | < 0.08 | > 0.90 | > 0.90 | > 0.90 | > 0.90 | > 0.90 |
| 模型结果Results | 0.078 | 0.072 | 0.910 | 0.929 | 0.918 | 0.904 | 0.918 |
Table 3 Confirmatory analysis fitting indicators
| 拟合指标 Fit indicators | 绝对拟合度指标 Absolute goodness-of-fit indices | 相对拟合度指标 Relative goodness-of-fit indices | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 近似误差均方根RMSEA | 标准化均方根残差SRMR | 拟合优度指数GFI | 塔克·刘易斯指数TLI | 比较性拟合指标CFI | 规范拟合指标NFI | 成长拟合指标IFI | |
| 评价标准Criterion | < 0.10 | < 0.08 | > 0.90 | > 0.90 | > 0.90 | > 0.90 | > 0.90 |
| 模型结果Results | 0.078 | 0.072 | 0.910 | 0.929 | 0.918 | 0.904 | 0.918 |
| 估计值 Estimate | 估计值标准误 SE | 临界值 CR | 假设 H | 检验结果 Results | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 态度 Att | 0.259*** | 0.744 | 3.489 | H1 | 接受Accept |
| 规范 Nor | 0.210*** | 0.681 | 3.086 | H2 | 接受Accept |
| 知觉行为控制Pbc | 0.379*** | 0.438 | 8.667 | H3 | 接受Accept |
| 年龄 Age | 0.022*** | 0.004 | 5.817 | ||
| 受教育程度 Edu | 0.020 | 0.026 | 0.757 | ||
| 家庭年收入 Inc | 0.006* | 0.052 | 1.240 | ||
| 性别 Gen | 0.251 | 0.086 | 2.931 |
Table 4 Summary of hypotheses testing results
| 估计值 Estimate | 估计值标准误 SE | 临界值 CR | 假设 H | 检验结果 Results | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 态度 Att | 0.259*** | 0.744 | 3.489 | H1 | 接受Accept |
| 规范 Nor | 0.210*** | 0.681 | 3.086 | H2 | 接受Accept |
| 知觉行为控制Pbc | 0.379*** | 0.438 | 8.667 | H3 | 接受Accept |
| 年龄 Age | 0.022*** | 0.004 | 5.817 | ||
| 受教育程度 Edu | 0.020 | 0.026 | 0.757 | ||
| 家庭年收入 Inc | 0.006* | 0.052 | 1.240 | ||
| 性别 Gen | 0.251 | 0.086 | 2.931 |
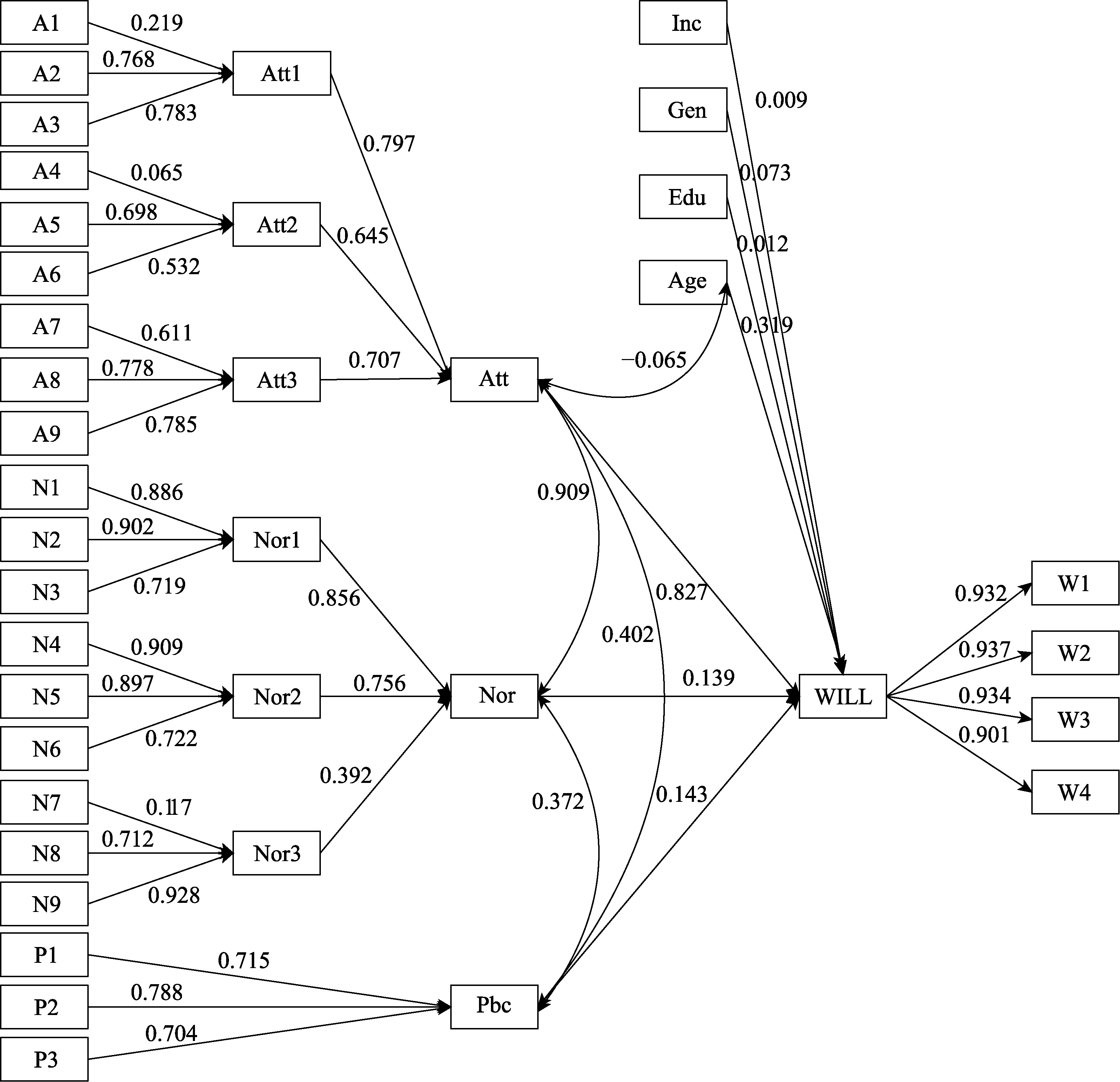
Fig. 2 Structural model of the predict willingness for farmers in the Northeast China Tiger and Leopard National Park (Abbreviations in the figure can be found in Box 1)
| [1] | Ajzen I (1985) From Intentions to Actions: A Theory of Planned Behavior. Springer, Heidelberg. |
| [2] |
Ajzen I (1991) The theory of planned behavior. Organizational Behavior and Human Decision Processes, 50, 179-211.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
Bruskotter J T, Wilson R S (2014) Determining where the wild things will be: Using psychological theory to find tolerance for large carnivores. Conservation Letters, 7, 158-165.
DOI URL |
| [4] | Castilho LC, De Vleeschouwer KM, Milner-Gulland EJ, Schiavetti A (2018) Attitudes and behaviors of rural residents toward different motivations for hunting and deforestation in protected areas of the northeastern Atlantic Forest, Brazil. Tropical Conservation Science, 11, 1-14. |
| [5] | Cheng KM (2006) Characteristics and application of structural equation model. Statistics and Decision, (10), 22-25. (in Chinese) |
| [程开明 (2006) 结构方程模型的特点及应用. 统计与决策, (10), 22-25.] | |
| [6] | Cialdini RB, Kallgren CA, Reno RR (1991) A focus theory of normative conduct, a theoretical refinement and reevaluation of the role of norms in human behavior. Advances in Experimental Social Psychology, 24, 201-234. |
| [7] | Cui XL, Cai YY, Zhang AL (2011) Farmers’ willingness to protect farmland ecological environment and influencing factors. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation, 31(5), 125-130. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [崔新蕾, 蔡银莺, 张安录 (2011) 农户参与保护农田生态环境意愿的影响因素实证分析. 水土保持通报, 31(5), 125-130.] | |
| [8] | Cui Y, Zhao K, He J (2019) Analysis of willingness and behavior of different types of farmer for protecting cultivated land based on theory of planned behavior. Journal of Henan Agricultural University, 53, 638-646, 652. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [崔悦, 赵凯, 贺婧 (2019) 基于计划行为理论不同类型农户耕地保护意愿和行为分析. 河南农业大学学报, 53, 638-646, 652.] | |
| [9] |
Davies J, Foxall GR, Pallister J (2002) Beyond the intention-behaviour mythology: An integrated model of recycling. Marketing Theory, 2, 29-113.
DOI URL |
| [10] | Deng ZT, Mao Y, Liang B (2013) Analysis of influencing factor on protection intention of residents participating in historic and cultural town—A case study of Xindian Town, Hubei Province. Resource Development & Market, 29, 1213-1215, 1212. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [邓祖涛, 毛焱, 梁滨 (2013) 居民参与历史文化名镇保护意愿的影响因素分析——来自湖北省新店镇的调查数据. 资源开发与市场, 29, 1213-1215, 1212.] | |
| [11] | Geng ST, Zhang HX (2022) Community participation models in national park construction: Realistic dilemmas and practical approaches. Journal of Southeast University (Philosophy and Social Science), 24(5), 70-77, 147. (in Chinese) |
| [耿松涛, 张鸿霞 (2022) 国家公园建设中社区参与模式: 现实困境与实践进路. 东南大学学报(哲学社会科学版), 24(5), 70-77, 147.] | |
| [12] |
Guo B, Zhang L, Li Y (2019) Research on the path of residents’ willingness to upgrade by installing elevators in old residential quarters based on safety precautions. Safety Science, 118, 389-396.
DOI URL |
| [13] | Guo XR, Wen YL (2012) Analysis on factors influencing peasant households’ protection awareness of Crested Ibises. Issues of Forestry Economics, 32, 444-449. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [郭向荣, 温亚利 (2012) 保护区农户朱鹮保护意愿的影响因素分析. 林业经济问题, 32, 444-449.] | |
| [14] | Huang Y, Yang J, Qin YT, Shi YN, Wen YL (2021) The willingness of tourists to protect the ecological forest under the context of forest tourism. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 57(10), 145-156. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [黄元, 杨洁, 秦悦婷, 石亚男, 温亚利 (2021) 森林旅游背景下游客的生态公益林保护行为意愿. 林业科学, 57(10), 145-156.] | |
| [15] |
Kotchen MJ, Reiling SD (2000) Environmental attitudes, motivations, and contingent valuation of nonuse values: A case study involving endangered species. Ecological Economics, 32, 93-107.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
Kraft P, Rise J, Sutton S, Røysamb E (2005) Perceived difficulty in the theory of planned behaviour: Perceived behavioural control or affective attitude? British Journal of Social Psychology, 44, 479-496.
DOI PMID |
| [17] | Kuang FY, Chen MQ, Lu YF, Weng ZL (2017) The impact of farmers’ livelihood capital on the willingness of cultivated land protection: Based on the investigation data from 587 farmer in Jiangxi Province. China Land Science, 31(2), 58-66. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [邝佛缘, 陈美球, 鲁燕飞, 翁贞林 (2017) 生计资本对农户耕地保护意愿的影响分析——以江西省587份问卷为例. 中国土地科学, 31(2), 58-66.] | |
| [18] | Li HM, Wang SH, Li RJ, Ren MX (2022) Community participation in the construction of national parks: A case study of Sanjiangyuan National Park. Journal of Tropical Biology, 13, 185-194. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [李惠梅, 王诗涵, 李荣杰, 任明迅 (2022) 国家公园建设的社区参与现状——以三江源国家公园为例. 热带生物学报, 13, 185-194.] | |
| [19] |
Li HM, Zhang AL, Wang S, Zhang X, Yang HZ, Zhuo MC (2013) Herdsmen’s willingness to participate in ecological protection in Sanjiangyuan region, China. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 33, 5943-5951. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
| [李惠梅, 张安录, 王珊, 张雄, 杨海镇, 卓玛措 (2013) 三江源牧户参与草地生态保护的意愿. 生态学报, 33, 5943-5951.] | |
| [20] | Li L, Wang YC, Ma RF, Ye CY, Chen F, Liu WS (2016) Analysis of influence factor and effect on protection intention of resident in ancient villages based on structural equation model. World Sci-Tech Research & Development, 38, 634-641. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [李玲, 王益澄, 马仁锋, 叶持跃, 陈芳, 刘文生 (2016) 基于结构方程模型的古村居民保护意愿影响因素及效应研究. 世界科技研究与发展, 38, 634-641.] | |
| [21] | Liu F (2016) Habitat Evaluation and Potential Corridor Analysis of Wild Amur Tiger Habitat in Hunchun, Jilin Province. PhD dissertation, Beijing Forestry University, Beijing. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [刘芳 (2016) 吉林珲春野生东北虎栖息地生境评价与潜在廊道分析. 博士学位论文, 北京林业大学, 北京.] | |
| [22] | Liu MP, Nan L, Li XQ, Zhao LJ (2019) Research on the impact of environmental literacy on farmers’ ecological protection behavior in farmland: Based on 1023 household survey data from Shaanxi, Shanxi, Gansu, Anhui, and Jiangsu provinces. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 33(2), 53-59. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [刘妙品, 南灵, 李晓庆, 赵连杰 (2019) 环境素养对农户农田生态保护行为的影响研究——基于陕、晋、甘、皖、苏五省1023份农户调查数据. 干旱区资源与环境, 33(2), 53-59.] | |
| [23] | Luo C (2010) Analysis of factors influencing consumers’ willingness to pay for safe food: Based on the framework of planned behavior theory. China Rural Survey, (6), 22-34. (in Chinese) |
| [罗丞 (2010) 消费者对安全食品支付意愿的影响因素分析——基于计划行为理论框架. 中国农村观察, (6), 22-34.] | |
| [24] |
Mai YJ, Wen ZL (2013) Exploratory structural equation modeling (ESEM): An integration of EFA and CFA. Advances in Psychological Science, 21, 934-939. (in Chinese)
DOI |
|
[麦玉娇, 温忠麟 (2013) 探索性结构方程建模(ESEM), EFA和CFA的整合. 心理科学进展, 21, 934-939.]
DOI |
|
| [25] |
Ru X, Qin H, Wang S (2019) Young people’s behaviour intentions towards reducing PM2.5 in China: Extending the theory of planned behaviour. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 141, 99-108.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
Schoenau M, Mueller M (2017) What affects our urban travel behavior? A GPS-based evaluation of internal and external determinants of sustainable mobility in Stuttgart (Germany). Transportation Research Part F: Traffic Psychology and Behaviour, 48, 61-73.
DOI URL |
| [27] | Schwartz SH (1977) Normative influences on altruism. Advances in Experimental Social Psychology, 10, 221-279. |
| [28] | Shi P, Yu J (2019) Research on the willingness and influencing factors of relocated farmers in poverty alleviation through relocation: An explanatory framework based on planned behavior theory. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 33(1), 38-43. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [时鹏, 余劲 (2019) 易地扶贫搬迁农户意愿及影响因素研究——一个基于计划行为理论的解释架构. 干旱区资源与环境, 33(1), 38-43.] | |
| [29] | Song WF, Li GP, Yang YL (2018) Analysis of farmers’ willingness to be compensated for ecological protection and its influencing factors: Based on research data from 660 households around Shaanxi National Nature Reserve. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 32(3), 63-69. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [宋文飞, 李国平, 杨永莲 (2018) 农民生态保护受偿意愿及其影响因素分析——基于陕西国家级自然保护区周边660户农户的调研数据. 干旱区资源与环境, 32(3), 63-69.] | |
| [30] | Su HH, Li JM (2019) Research on the path of community co-construction in the pilot system of Sanjiangyuan National Park. Qinghai Social Sciences, (3), 109-118. (in Chinese) |
| [苏海红, 李婧梅 (2019) 三江源国家公园体制试点中社区共建的路径研究. 青海社会科学, (3), 109-118.] | |
| [31] | Su SY, Zhou YX, Cai WX (2020) Analysis of farmers’ willingness to participate and its influencing factors in rural domestic sewage treatment: Based on survey data from 16 cities in Shandong Province. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 34(10), 71-77. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [苏淑仪, 周玉玺, 蔡威熙 (2020) 农村生活污水治理中农户参与意愿及其影响因素分析——基于山东16地市的调研数据. 干旱区资源与环境, 34(10), 71-77.] | |
| [32] | Sun T, Ou MH (2020) A study on the willingness to organize rural residential areas under the framework of planned behavior theory. Journal of Huazhong Agricultural University (Social Sciences Edition), 146(2), 118-126, 168. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [孙涛, 欧名豪 (2020) 计划行为理论框架下农村居民点整理意愿研究. 华中农业大学学报(社会科学版), 146(2), 118-126, 168.] | |
| [33] | Tian ML, Hao RJ, Li ZX, Zhou Y, Kou YY, Zhang WZ (2021) Influence system of the willingness of residents to participate in the construction of national park system—Taking Shennongjia National Park as an example. Forestry Economics, 43(4), 30-44. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [田美玲, 郝瑞君, 李子欣, 周永, 寇圆圆, 张文洲 (2021) 居民参与国家公园体制建设意愿的影响机制——以神农架国家公园为例. 林业经济, 43(4), 30-44.] | |
| [34] | Tsi EA, Ajaga N, Wiegleb G, Mühlenberg (2008) The willingness to pay (WTP) for the conservation of wild animals: Case of the Derby Eland (Taurotragus derbianus gigas) and the African wild dog (Lycaon pictus) in North Cameroon. African Journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 2, 51-58. |
| [35] | Wang CR, Han XP, Zhang JZ (2013) Analysis of social capital in rural environmental governance. Journal of Northeast Normal University (Philosophy and Social Sciences), (3), 217-219. (in Chinese) |
| [王春荣, 韩喜平, 张俊哲 (2013) 农村环境治理中的社会资本探析. 东北师大学报(哲学社会科学版), (3), 217-219.] | |
| [36] |
Wossink GAA, van Wenum JH (2003) Biodiversity conservation by farmers: Analysis of actual and contingent participation. European Review of Agricultural Economics, 30, 461-485.
DOI URL |
| [37] | Xiao Y, Yin K (2020) Research on the impact of farmers’ ecological risk perception on their willingness to participate in protection in rural tourism development. Chinese Journal of Agricultural Resources and Regional Planning, 41(4), 243-249. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [肖轶, 尹珂 (2020) 乡村旅游开发中农户生态风险认知对其参与保护意愿的影响研究. 中国农业资源与区划, 41(4), 243-249.] | |
| [38] | Xie Y, Wen YL (2005) The application of participatory developmental theory to natural protection. Forestry Survey and Planning, (6), 81-83. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [谢屹, 温亚利 (2005) 浅谈参与式发展理论在自然保护中的运用. 林业调查规划, (6), 81-83.] | |
| [39] | Yan Y (2014) A review on the origins and development of the theory of planned behavior. Chinese Journal of Journalism & Communication, 36(7), 113-129. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [闫岩 (2014) 计划行为理论的产生、发展和评述. 国际新闻界, 36(7), 113-129.] | |
| [40] | Yang S, Lei XY, Zhao GP (2021) The impact of social capital in Qinling National Park communities on farmers’ willingness to participate in ecological environment protection. Journal of Statistics and Information, 36(12), 71-79. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [杨朔, 雷小雨, 赵国平 (2021) 秦岭国家公园社区社会资本对农户参与生态环境保护意愿的影响. 统计与信息论坛, 36(12), 71-79.] | |
| [41] | Yang SY, Yang L, Li YZ, Xie CF (2021) Analyzing the impacts of virtual social network and income on farmers’ willingness to pay for rural environmental governance based on a survey data in Fujian, Henan, and Sichuan. Research of Agricultural Modernization, 42, 451-461. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [杨思宇, 杨龙, 李羿枝, 谢昌凡 (2021) 虚拟社会网络、收入状况与农户环境治理支付意愿——基于闽豫川农户调研数据. 农业现代化研究, 42, 451-461.] | |
| [42] | Zhang J, Li SP, Guo YN (2019) Study on the influencing factors of farmers’ environmental behavior based on the protection motivation theory. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 33(5), 8-13. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [张娇, 李世平, 郭悦楠 (2019) 基于保护动机理论的农户亲环境行为影响因素研究——以秸秆处理为例. 干旱区资源与环境, 33(5), 8-13.] | |
| [43] | Zhang JM, Liu TC, Liu W (2011) Analysis of influencing factors of civic charitable donation based on theory of planned behavior—Data from Liaoning Province. Soft Science, 25(8), 71-77. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [张进美, 刘天翠, 刘武 (2011) 基于计划行为理论的公民慈善捐赠行为影响因素分析——以辽宁省数据为例. 软科学, 25(8), 71-77.] | |
| [44] |
Zhang JY, Zhang YJ (2017) On public participation in the construction of national parks. Biodiversity Science, 25, 80-87. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[张婧雅, 张玉钧 (2017) 论国家公园建设的公众参与. 生物多样性, 25, 80-87.]
DOI |
|
| [45] |
Zhang XY, Hu YX, Zhang ZY, Fu YH, Xie Y (2021) Chinese public willingness of international wildlife conservation: A case study of African elephant. Biodiversity Science, 29, 1358-1368. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[张馨予, 胡宇轩, 张忠义, 傅钰涵, 谢屹 (2021) 中国公众的国际野生动物保护意愿调查: 以非洲象为例. 生物多样性, 29, 1358-1368.]
DOI |
|
| [46] | Zhao W, Zhou H, Yang GQ, Li JY (2016) Farmers’ transformation between willingness and behavior of post land consolidation supervision and maintenance: A case study of Dengzhou, Henan Province. China Land Science, 30(3), 55-62. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [赵微, 周惠, 杨钢桥, 李金玉 (2016) 农民参与农地整理项目建后管护的意愿与行为转化研究: 以河南邓州的调查为例. 中国土地科学, 30(3), 55-62.] | |
| [47] | Zhou LP, Su H, Deng QZ, Weng ZL, Fu LL (2014) Study on the influencing factors of peasant households’ intention on participating in water user association from perspective of the planned behavior theory—An empirical analysis based on structural equation modeling. Guangdong Agricultural Sciences, 41(6), 231-236. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [周利平, 苏红, 邓群钊, 翁贞林, 付莲莲 (2014) 计划行为理论视角下农户参与用水协会意愿影响因素研究——基于结构方程模型的实证分析. 广东农业科学, 41(6), 231-236.] |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2026 Biodiversity Science
Editorial Office of Biodiversity Science, 20 Nanxincun, Xiangshan, Beijing 100093, China
Tel: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn