



Biodiv Sci ›› 2025, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (2): 24445. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2024445 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2024445
• Original Papers: Plant Diversity • Previous Articles Next Articles
Li Yanpeng( ), Chen Jie(
), Chen Jie( ), Lu Chunyang(
), Lu Chunyang( ), Xu Han*(
), Xu Han*( )(
)( )
)
Received:2024-10-13
Accepted:2025-01-02
Online:2025-02-20
Published:2025-03-17
Contact:
*E-mail: ywfj@163.com
Supported by:Li Yanpeng, Chen Jie, Lu Chunyang, Xu Han. Community characteristics of a 64-ha secondary forest dynamics plot in a tropical montane rainforest in Jianfengling, Hainan[J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(2): 24445.
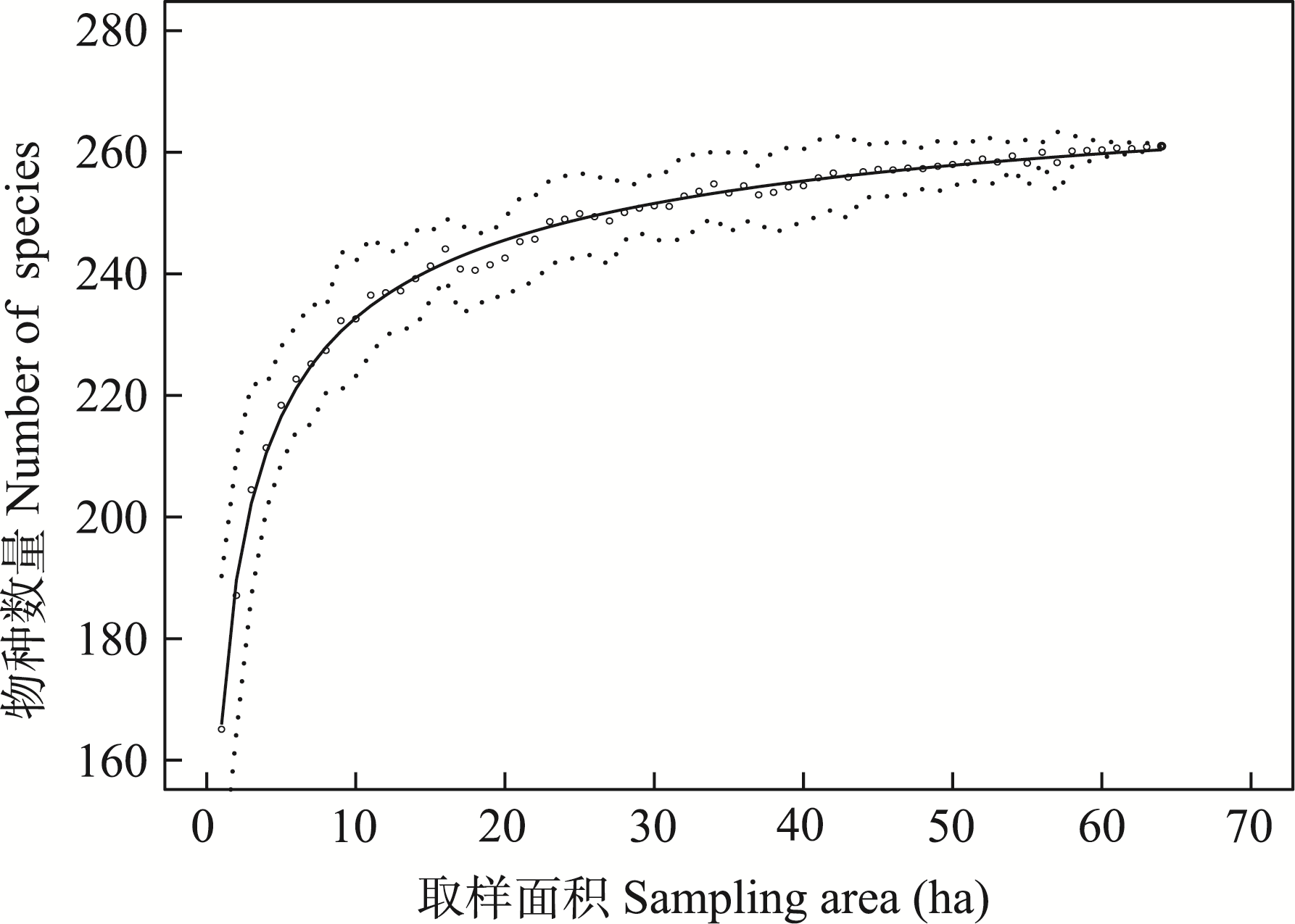
Fig. 2 Species-area relationship curve of woody plants in the 64-ha secondary forest dynamics plot in a tropical montane rainforest in Jianfengling, Hainan. The envelopes are the 95% confidence interval.
| 物种 Species | 相对胸高断面积 Relative basal area (%) | 相对多度 Relative abundance (%) | 相对频度 Relative frequency (%) | 重要值 Importance value (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 米槠 Castanopsis carlesii | 9.52 | 4.20 | 1.47 | 5.07 |
| 白颜树 Gironniera subaequalis | 4.72 | 4.56 | 2.09 | 3.79 |
| 海南韶子 Nephelium topengii | 3.58 | 3.29 | 1.88 | 2.92 |
| 厚壳桂 Cryptocarya chinensis | 2.25 | 3.54 | 1.78 | 2.52 |
| 红柯 Lithocarpus fenzelianus | 4.26 | 1.46 | 1.23 | 2.31 |
| 黧蒴锥 Castanopsis fissa | 4.09 | 1.57 | 0.87 | 2.18 |
| 毛果柯 Lithocarpus pseudovestitus | 3.64 | 1.22 | 1.21 | 2.02 |
| 薄叶山矾 Symplocos anomala | 1.35 | 3.15 | 1.49 | 2.00 |
| 大叶蒲葵 Livistona saribus | 3.41 | 0.86 | 1.03 | 1.77 |
| 山油柑 Acronychia pedunculata | 1.17 | 2.02 | 1.49 | 1.56 |
| 阴香 Cinnamomum burmanni | 1.02 | 1.74 | 1.39 | 1.38 |
| 黄叶树 Xanthophyllum hainanense | 1.77 | 1.22 | 1.05 | 1.35 |
| 鹅掌柴 Heptapleurum heptaphyllum | 1.41 | 1.28 | 1.34 | 1.34 |
| 木荷 Schima superba | 1.50 | 1.39 | 1.10 | 1.33 |
| 北油丹 Alseodaphne hainanensis | 1.24 | 1.39 | 1.36 | 1.33 |
| 腺叶山矾 Symplocos adenophylla | 0.75 | 1.85 | 1.33 | 1.31 |
| 硬壳桂 Cryptocarya chingii | 0.78 | 1.77 | 1.36 | 1.30 |
| 黄杞 Engelhardia roxburghiana | 1.80 | 0.87 | 1.01 | 1.23 |
| 木姜叶柯 Lithocarpus litseifolius | 1.67 | 0.90 | 0.99 | 1.19 |
| 双瓣木犀 Osmanthus didymopetalus | 1.20 | 1.24 | 1.08 | 1.17 |
| 九节 Psychotria asiatica | 0.39 | 1.84 | 1.25 | 1.16 |
| 橄榄 Canarium album | 1.01 | 1.12 | 1.28 | 1.14 |
| 托盘青冈 Quercus patelliformis | 1.40 | 0.79 | 0.95 | 1.05 |
| 多瓣核果茶 Pyrenaria multisepala | 0.73 | 1.10 | 1.29 | 1.04 |
| 其他 Others | 45.35 | 55.62 | 68.67 | 56.55 |
| 合计 Total | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 |
Table 1 Dominant species composition of woody plants in the 64-ha secondary forest dynamics plot in a tropical montane rainforest in Jianfengling, Hainan
| 物种 Species | 相对胸高断面积 Relative basal area (%) | 相对多度 Relative abundance (%) | 相对频度 Relative frequency (%) | 重要值 Importance value (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 米槠 Castanopsis carlesii | 9.52 | 4.20 | 1.47 | 5.07 |
| 白颜树 Gironniera subaequalis | 4.72 | 4.56 | 2.09 | 3.79 |
| 海南韶子 Nephelium topengii | 3.58 | 3.29 | 1.88 | 2.92 |
| 厚壳桂 Cryptocarya chinensis | 2.25 | 3.54 | 1.78 | 2.52 |
| 红柯 Lithocarpus fenzelianus | 4.26 | 1.46 | 1.23 | 2.31 |
| 黧蒴锥 Castanopsis fissa | 4.09 | 1.57 | 0.87 | 2.18 |
| 毛果柯 Lithocarpus pseudovestitus | 3.64 | 1.22 | 1.21 | 2.02 |
| 薄叶山矾 Symplocos anomala | 1.35 | 3.15 | 1.49 | 2.00 |
| 大叶蒲葵 Livistona saribus | 3.41 | 0.86 | 1.03 | 1.77 |
| 山油柑 Acronychia pedunculata | 1.17 | 2.02 | 1.49 | 1.56 |
| 阴香 Cinnamomum burmanni | 1.02 | 1.74 | 1.39 | 1.38 |
| 黄叶树 Xanthophyllum hainanense | 1.77 | 1.22 | 1.05 | 1.35 |
| 鹅掌柴 Heptapleurum heptaphyllum | 1.41 | 1.28 | 1.34 | 1.34 |
| 木荷 Schima superba | 1.50 | 1.39 | 1.10 | 1.33 |
| 北油丹 Alseodaphne hainanensis | 1.24 | 1.39 | 1.36 | 1.33 |
| 腺叶山矾 Symplocos adenophylla | 0.75 | 1.85 | 1.33 | 1.31 |
| 硬壳桂 Cryptocarya chingii | 0.78 | 1.77 | 1.36 | 1.30 |
| 黄杞 Engelhardia roxburghiana | 1.80 | 0.87 | 1.01 | 1.23 |
| 木姜叶柯 Lithocarpus litseifolius | 1.67 | 0.90 | 0.99 | 1.19 |
| 双瓣木犀 Osmanthus didymopetalus | 1.20 | 1.24 | 1.08 | 1.17 |
| 九节 Psychotria asiatica | 0.39 | 1.84 | 1.25 | 1.16 |
| 橄榄 Canarium album | 1.01 | 1.12 | 1.28 | 1.14 |
| 托盘青冈 Quercus patelliformis | 1.40 | 0.79 | 0.95 | 1.05 |
| 多瓣核果茶 Pyrenaria multisepala | 0.73 | 1.10 | 1.29 | 1.04 |
| 其他 Others | 45.35 | 55.62 | 68.67 | 56.55 |
| 合计 Total | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 |
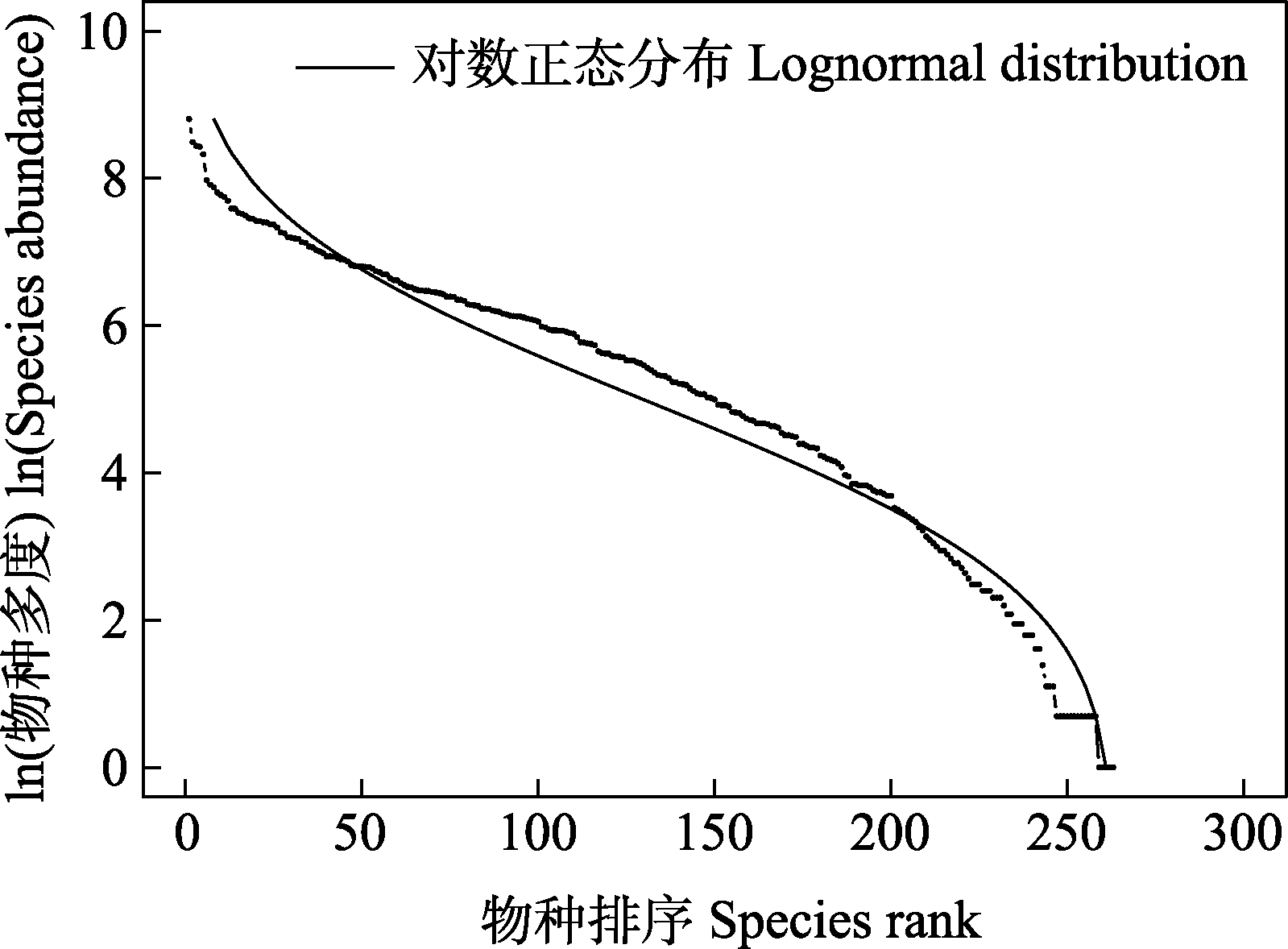
Fig. 3 The species abundance distribution of woody plants in the 64-ha secondary forest dynamics plot in a tropical montane rainforest in Jianfengling, Hainan
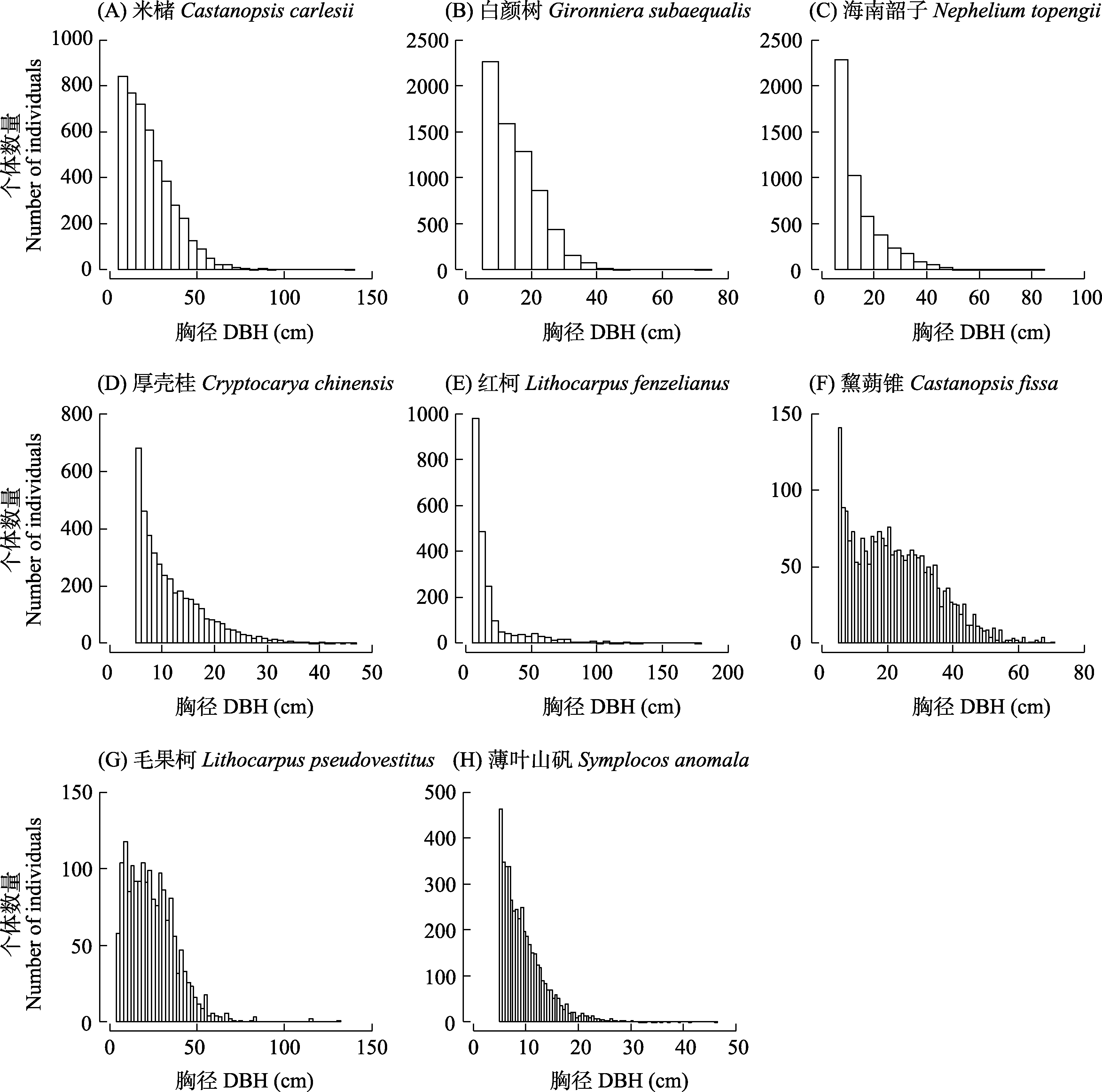
Fig. 5 DBH class structures of the top eight dominant species in the 64-ha secondary forest dynamics plot in a tropical montane rainforest in Jianfengling, Hainan
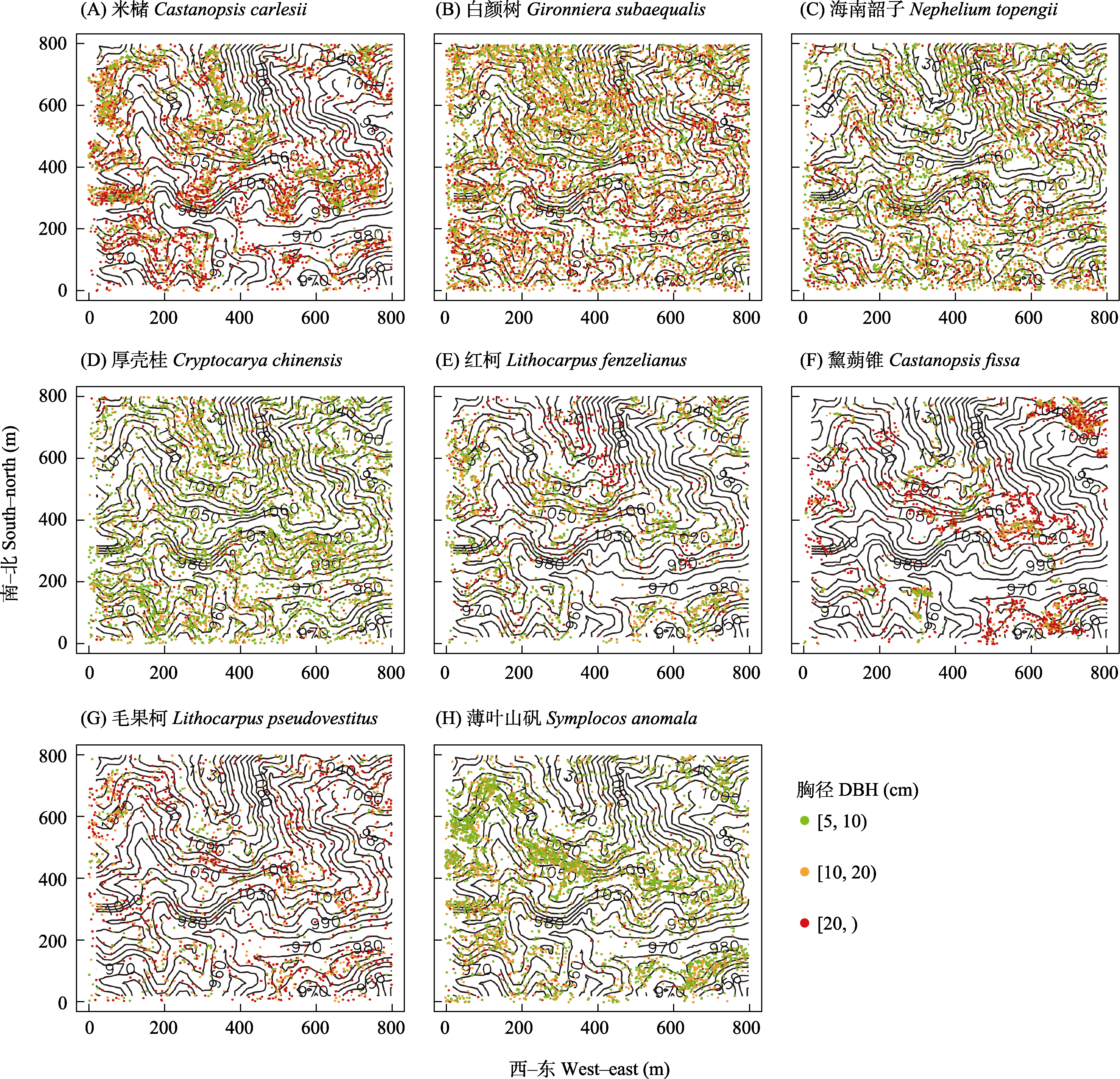
Fig. 6 Spatial distribution map of eight dominant species in the 64-ha secondary forest dynamics plot in a tropical montane rainforest in Jianfengling, Hainan
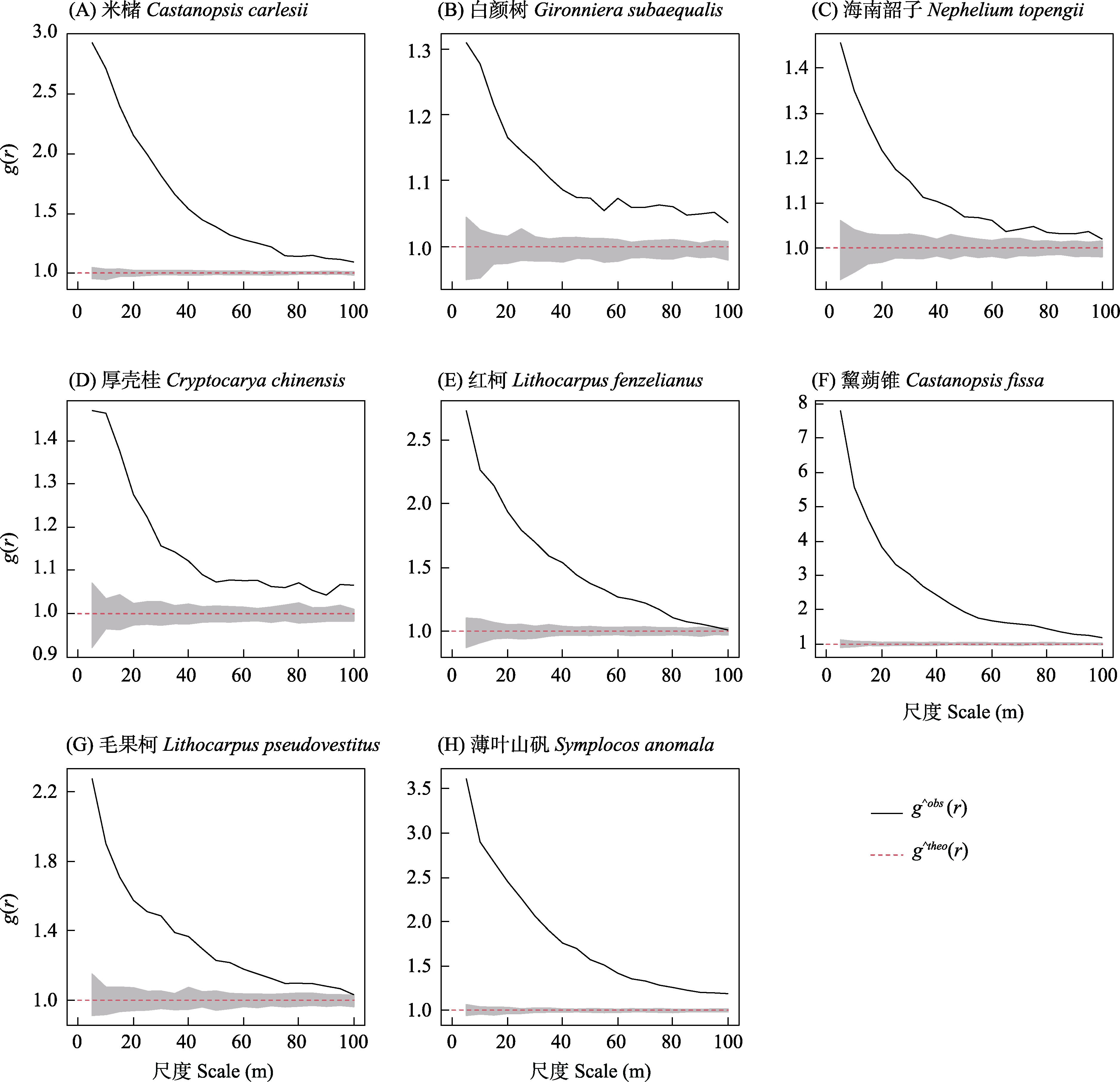
Fig. 7 Spatial distribution pattern of eight dominant species under complete spatial randomness null model in the 64-ha secondary forest dynamics plot in a tropical montane rainforest in Jianfengling, Hainan. g^obs(r), Observed value of g(r); g^theo(r), Theoretical value of g(r); the envelopes are the 99% confidence interval.
| [1] | Akima H, Gebhardt A (2022) akima: Interpolation of Irregularly and Regularly Spaced Data. R package version 0.6-3.4. https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=akima. (accessed on 2023-07-18) |
| [2] |
Avolio ML, Forrestel EJ, Chang CC, La Pierre KJ, Burghardt KT, Smith MD (2019) Demystifying dominant species. New Phytologist, 223, 1106-1126.
DOI PMID |
| [3] | Baddeley A, Turner R (2005) spatstat: An R package for analyzing spatial point patterns. Journal of Statistical Software, 12(6), 1-42. |
| [4] | Cao M, Zhu H, Wang H, Lan GY, Hu YH, Zhou SS, Deng XB, Cui JY (2008) Xishuangbanna Tropical Seasonal Rainforest Dynamics Plot:Tree Distribution Maps, Diameter Tables and Species Documentation. Yunnan Science and Technology Press, Kunming. |
| [5] | Chen K, Burgess KS, He FL, Yang XY, Gao LM, Li DZ (2022) Seed traits and phylogeny explain plants’ geographic distribution. Biogeosciences, 19, 4801-4810. |
| [6] | Condit R (1998) Tropical Forest Census Plots: Methods and Results from Barro Colorado Island, Panama and a Comparison with Other Plots. Springer, Berlin. |
| [7] | Elias F, Ferreira J, Lennox GD, Berenguer E, Ferreira S, Schwartz G, de Oliveira Melo L, Reis Júnior DN, Nascimento RO, Ferreira FN, Espirito-Santo F, Smith CC, Barlow J (2020) Assessing the growth and climate sensitivity of secondary forests in highly deforested Amazonian landscapes. Ecology, 101, e02954. |
| [8] | Fang JY, Li YD, Zhu B, Liu GH, Zhou GY (2004) Community structures and species richness in the montane rain forest of Jianfengling, Hainan Island, China. Biodiversity Science, 12, 29-43. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[ 方精云, 李意德, 朱彪, 刘国华, 周光益 (2004) 海南岛尖峰岭山地雨林的群落结构、物种多样性以及在世界雨林中的地位. 生物多样性, 12, 29-43.]
DOI |
|
| [9] | Godefroid S, Phartyal SS, Koedam N (2006) Depth distribution and composition of seed banks under different tree layers in a managed temperate forest ecosystem. Acta Oecologica, 29, 283-292. |
| [10] |
Gong HD, Yang GP, Lu ZY, Liu YH (2011) Diversity and spatial distribution patterns of trees in an evergreen broad-leaved forest in the Ailao Mountains, Yunnan. Biodiversity Science, 19, 143-150. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[ 巩合德, 杨国平, 鲁志云, 刘玉洪 (2011) 哀牢山常绿阔叶林树种多样性及空间分布格局. 生物多样性, 19, 143-150.]
DOI |
|
| [11] |
Guo ZW, Zheng JM (2017) Predicting modes of seed dispersal using plant life history traits. Biodiversity Science, 25, 966-971. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[ 郭志文, 郑景明 (2017) 用植物生活史性状预测种子扩散方式. 生物多样性, 25, 966-971.]
DOI |
|
| [12] | Li JQ, Niu SK, Liu YH (2010) Forest Ecology, 2nd edn. Higher Education Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 李俊清, 牛树奎, 刘艳红 (2010) 森林生态学(第二版). 高等教育出版社, 北京.] | |
| [13] | Li YD (1995) Biodiversity of tropical forest and its protection strategies in Hainan Island, China. Forest Research, 8, 455-461. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 李意德 (1995) 海南岛热带森林的变迁及生物多样性的保护对策. 林业科学研究, 8, 455-461.] | |
| [14] | Li YD, Chen BF, Zhou GY (2002) Tropical Forests and Biodiversity Protection on Hainan Island, China. China Forestry Publishing House, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 李意德, 陈步峰, 周光益 (2002) 中国海南岛热带森林及其生物多样性保护研究. 中国林业出版社, 北京.] | |
| [15] |
Li YP, Xu H, Li YD, Luo TS, Chen DX, Zhou Z, Lin MX, Yang H (2016) Scale-dependent spatial patterns of species diversity in the tropical montane rain forest in Jianfengling, Hainan Island, China. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 40, 861-870. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[ 李艳朋, 许涵, 李意德, 骆土寿, 陈德祥, 周璋, 林明献, 杨怀 (2016) 海南尖峰岭热带山地雨林物种多样性空间分布格局的尺度效应. 植物生态学报, 40, 861-870.]
DOI |
|
| [16] | Liang S, Xu H, Lin JY, Li YD, Lin MX (2014) Spatial distribution pattern of the dominant species Gironniera subaequalis in tropical montane rainforest of Jianfengling, Hainan Island, China. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 38, 1273-1282. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 梁爽, 许涵, 林家怡, 李意德, 林明献 (2014) 尖峰岭热带山地雨林优势树种白颜树空间分布格局. 植物生态学报, 38, 1273-1282.] | |
| [17] | Liu SR, Pang Y, Zhang HR, Wang B, Ye B, Jiang ZP, Xie HS, Niu XD, Wang DJ, Ding Y, Wu SR, Song QF, Wang XH, Zhang C (2021) Evaluation indicator system and method designed for Natural Forest Protection Program of China. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 41, 5067-5079. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 刘世荣, 庞勇, 张会儒, 王兵, 叶兵, 江泽平, 谢和生, 牛晓栋, 王登举, 丁易, 吴水荣, 宋庆丰, 王晓慧, 张超 (2021) 中国天然林资源保护工程综合评价指标体系与评估方法. 生态学报, 41, 5067-5079.] | |
| [18] |
Liu XL, Wu YG, Zhang MH, Chen XR, Zhu ZC, Chen DY, Dong S, Li BH, Ding BY, Liu Y (2024) Community composition and structure of a 25-ha forest dynamics plot of subtropical forest in Baishanzu, Zhejiang Province. Biodiversity Science, 32, 23294. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
| [ 刘啸林, 吴友贵, 张敏华, 陈小荣, 朱志成, 陈定云, 董舒, 李步杭, 丁炳扬, 刘宇 (2024) 浙江百山祖25 ha亚热带森林动态监测样地群落组成与结构特征. 生物多样性, 32, 23294.] | |
| [19] | Losos EC, Leigh EG (2004) Tropical Forest Diversity and Dynamism:Findings from a Large-scale Plot Network. University of Chicago Press, Chicago. |
| [20] | Luo W, Li YP, Xu H, Qin WH, Liu DY, Mo SQ (2023) Characteristics of suitable communities of Hopea hainanensis, a Wild Plant with Extremely Small Populations in National Park of Hainan Tropical Rainforest. Forest Resources Management, (4), 98-106. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 罗文, 李艳朋, 许涵, 秦文豪, 刘大业, 莫世琴 (2023) 海南热带雨林国家公园极小种群野生植物坡垒适生群落特征研究. 林业资源管理, (4), 98-106.] | |
| [21] |
Makoto K, Wilson SD (2019) When and where does dispersal limitation matter in primary succession? Journal of Ecology, 107, 559-565.
DOI |
| [22] | Ma KP, Huang JH, Yu SL, Chen LZ (1995) Plant community diversity in Dongling Mountain, Beijing, China. II. Species richness, evenness and species diversities. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 15, 268-277. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 马克平, 黄建辉, 于顺利, 陈灵芝 (1995) 北京东灵山地区植物群落多样性的研究. II. 丰富度、均匀度和物种多样性. 生态学报, 15, 268-277.] | |
| [23] | Oberleitner F, Egger C, Oberdorfer S, Dullinger S, Wanek W, Hietz P (2021) Recovery of aboveground biomass, species richness and composition in tropical secondary forests in SW Costa Rica. Forest Ecology and Management, 479, 118580. |
| [24] | Oksanen J, Blanchet F, Kindt R, Legendre P, Minchin P, O’Hara R, Simpson G, Solymos P, Stevens M, Wagner H (2013) vegan: Community Ecology Package. R package version 2.0-10. https://cran.r-project.org/src/contrib/Archive/vegan/. (accessed on 2023-07-18) |
| [25] | Pan YD, Birdsey RA, Fang JY, Houghton R, Kauppi PE, Kurz WA, Phillips OL, Shvidenko A, Lewis SL, Canadell JG, Ciais P, Jackson RB, Pacala SW, David McGuire A, Piao SL, Rautiainen A, Sitch S, Hayes D (2011) A large and persistent carbon sink in the world’s forests. Science, 333, 988-993. |
| [26] | Poorter L, Bongers F, Aide TM, Zambrano AMA, Balvanera P, Becknell JM, Boukili V, Brancalion PHS, Broadbent EN, Chazdon RL, Craven D, de Almeida-Cortez JS, Cabral GAL, de Jong BHJ, Denslow JS, Dent DH, DeWalt SJ, Dupuy JM, Durán SM, Espírito-Santo MM, Fandino MC, César RG, Hall JS, Hernandez-Stefanoni JL, Jakovac CC, Junqueira AB, Kennard D, Letcher SG, Licona JC, Lohbeck M, Marín-Spiotta E, Martínez-Ramos M, Massoca P, Meave JA, Mesquita R, Mora F, Muñoz R, Muscarella R, Nunes YRF, Ochoa-Gaona S, de Oliveira AA, Orihuela-Belmonte E, Peña-Claros M, Pérez-García EA, Piotto D, Powers JS, Rodríguez-Velázquez J, Romero-Pérez IE, Ruíz J, Saldarriaga JG, Sanchez-Azofeifa A, Schwartz NB, Steininger MK, Swenson NG, Toledo M, Uriarte M, van Breugel M, van der Wal H, Veloso MDM, Vester HFM, Vicentini A, Vieira ICG, Bentos TV, Bruce Williamson G, Rozendaal DMA (2016) Biomass resilience of Neotropical secondary forests. Nature, 530, 211-214. |
| [27] |
Poorter L, Craven D, Jakovac CC, van der Sande MT, Amissah L, Bongers F, Chazdon RL, Farrior CE, Kambach S, Meave JA, Muñoz R, Norden N, Rüger N, van Breugel M, Zambrano AMA, Amani B, Andrade JL, Brancalion PHS, Broadbent EN, de Foresta H, Dent DH, Derroire G, DeWalt SJ, Dupuy JM, Durán SM, Fantini AC, Finegan B, Hernández-Jaramillo A, Hernández-Stefanoni JL, Hietz P, Junqueira AB, N’Dja JK, Letcher SG, Lohbeck M, López-Camacho R, Martínez-Ramos M, Melo FPL, Mora F, Müller SC, N’Guessan AE, Oberleitner F, Ortiz-Malavassi E, Pérez-García EA, Pinho BX, Piotto D, Powers JS, Rodríguez-Buriticá S, Rozendaal DMA, Ruíz J, Tabarelli M, Teixeira HM, de Sá Barretto Sampaio EV, van der Wal H, Villa PM, Fernandes GW, Santos BA, Aguilar-Cano J, de Almeida-Cortez JS, Alvarez-Davila E, Arreola-Villa F, Balvanera P, Becknell JM, Cabral GAL, Castellanos-Castro C, de Jong BHJ, Nieto JE, Espírito-Santo MM, Fandino MC, García H, García-Villalobos D, Hall JS, Idárraga A, Jiménez-Montoya J, Kennard D, Marín-Spiotta E, Mesquita R, Nunes YRF, Ochoa-Gaona S, Peña-Claros M, Pérez-Cárdenas N, Rodríguez-Velázquez J, Villanueva LS, Schwartz NB, Steininger MK, Veloso MDM, Vester HFM, Vieira ICG, Bruce Williamson G, Zanini K, Hérault B (2021) Multidimensional tropical forest recovery. Science, 374, 1370-1376.
DOI PMID |
| [28] | R Core Team (2017) R, A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna. https://www.r-project.org/. (accessed on 2023-07-18) |
| [29] | Rozendaal DMA, Bongers F, Mitchell Aide T, Alvarez-Dávila E, Ascarrunz N, Balvanera P, Becknell JM, Bentos TV, Brancalion PHS, Cabral GAL, Calvo-Rodriguez S, Chave J, César RG, Chazdon RL, Condit R, Dallinga JS, de Almeida-Cortez JS, de Jong B, de Oliveira A, Denslow JS, Dent DH, DeWalt SJ, Dupuy JM, Durán SM, Dutrieux LP, Espírito-Santo MM, Fandino MC, Wilson Fernandes G, Finegan B, García H, Gonzalez N, Moser VG, Hall JS, Hernández-Stefanoni JL, Hubbell S, Jakovac CC, Hernández AJ, Junqueira AB, Kennard D, Larpin D, Letcher SG, Licona JC, Lebrija-Trejos E, Marín-Spiotta E, Martínez-Ramos M, Massoca PES, Meave JA, Mesquita RCG, Mora F, Müller SC, Muñoz R, de Oliveira Neto SN, Norden N, Nunes YRF, Ochoa-Gaona S, Ortiz-Malavassi E, Ostertag R, Peña-Claros M, Pérez-García EA, Piotto D, Powers JS, Aguilar-Cano J, Rodriguez-Buritica S, Rodríguez-Velázquez J, Romero-Romero MA, Ruíz J, Sanchez-Azofeifa A, de Almeida AS, Silver WL, Schwartz NB, Thomas WW, Toledo M, Uriarte M, de Sá Sampaio EV, van Breugel M, van der Wal H, Martins SV, Veloso MDM, Vester HFM, Vicentini A, Vieira ICG, Villa P, Bruce Williamson G, Zanini KJ, Zimmerman J, Poorter L (2019) Biodiversity recovery of Neotropical secondary forests. Science Advances, 5, eaau3114. |
| [30] | Situ SJ (1987) Study on Land Development in the History of Hainan Island. Hainan People’s Press, Haikou. (in Chinese) |
| [ 司徒尚纪 (1987) 海南岛历史上土地开发的研究. 海南人民出版社, 海口.] | |
| [31] | Song YC (2016) Vegetation Ecology, 2nd edn. Higher Education Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 宋永昌 (2016) 植被生态学(第二版). 高等教育出版社, 北京.] | |
| [32] | The Biodiversity Committee of Chinese Academy of Sciences (2024) Catalogue of Life China 2024 Annual Checklist, Beijing. http://www.sp2000.org.cn/CoLChina. (accessed on 2024-12-31) |
| [33] | Thomson FJ, Moles AT, Auld TD, Ramp D, Ren SQ, Kingsford RT (2010) Chasing the unknown: Predicting seed dispersal mechanisms from plant traits. Journal of Ecology, 98, 1310-1318. |
| [34] | Tian LX, Ding Y, Zang RG (2022) Advances in tree species diversity and aboveground biomass recovery dynamics in tropical secondary forests. Terrestrial Ecosystem and Conservation, 2(6), 88-96. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 田立新, 丁易, 臧润国 (2022) 热带次生林树种多样性和地上生物量恢复动态的研究进展. 陆地生态系统与保护学报, 2(6), 88-96.] | |
| [35] | Wang JM, Xu H, Li YD, Lin MX, Zhou Z, Luo TS, Chen DX (2018) Effects of topographic heterogeneity on community structure and diversity of woody plants in Jianfengling tropical montane rainforest. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 54(1), 1-11. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 王家鸣, 许涵, 李意德, 林明献, 周璋, 骆土寿, 陈德祥 (2018) 地形异质性对尖峰岭热带山地雨林木本植物群落结构及多样性的影响. 林业科学, 54(1), 1-11.] | |
| [36] | Wang YH, Li SF, Lang XD, Huang XB, Liu WD, Xu CH, Su JR (2020) Effects of topographic heterogeneity on species diversity in a monsoon evergreen broadleaved forest in Puʼer, Yunnan, China. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 44, 1015-1027. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 王艳红, 李帅锋, 郎学东, 黄小波, 刘万德, 徐崇华, 苏建荣 (2020) 地形异质性对云南普洱季风常绿阔叶林物种多样性的影响. 植物生态学报, 44, 1015-1027.] | |
| [37] |
Wiegand T, Gunatilleke S, Gunatilleke N, Okuda T (2007) Analyzing the spatial structure of a Sri Lankan tree species with multiple scales of clustering. Ecology, 88, 3088-3102.
PMID |
| [38] | Wiegand T, Moloney KA (2004) Rings, circles, and null-models for point pattern analysis in ecology. Oikos, 104, 209-229. |
| [39] | Xu H, Li YD, Lin MX, Wu JH, Luo TS, Zhou Z, Chen DX, Yang H, Li GJ, Liu SR (2015a) Community characteristics of a 60 ha dynamics plot in the tropical montane rain forest in Jianfengling, Hainan Island. Biodiversity Science, 23, 192-201. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 许涵, 李意德, 林明献, 吴建辉, 骆土寿, 周璋, 陈德祥, 杨怀, 李广建, 刘世荣 (2015a) 海南尖峰岭热带山地雨林60 ha动态监测样地群落结构特征. 生物多样性, 23, 192-201.] | |
| [40] | Xu H, Li YD, Liu SR, Zang RG, He FL, Spence JR (2015) Partial recovery of a tropical rain forest a half-century after clear-cut and selective logging. Journal of Applied Ecology, 52, 1044-1052. |
| [41] | Xu H, Li YD, Luo TS, Chen DX, Lin MX, Wu JH, Li YP, Yang H, Zhou Z (2015b) Jianfengling Tropical Mountain Rain Forest Dynamic Plot:Community Characteristic, Tree Species and Their Distribution Patterns. China Forestry Publishing House, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 许涵, 李意德, 骆土寿, 陈德祥, 林明献, 吴建辉, 李艳朋, 杨怀, 周璋 (2015b) 海南尖峰岭热带山地雨林——群落特征、树种及其分布格局. 中国林业出版社, 北京.] | |
| [42] | Xu H, Li YP, Li YD, Hong XJ, Zhou Z, Luo TS, Chen J, Lin MX, Zhang B (2021) Study history and discussion on classification of the tropical forest vegetation types in China. Guihaia, 41, 1595-1604. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 许涵, 李艳朋, 李意德, 洪小江, 周璋, 骆土寿, 陈洁, 林明献, 张斌 (2021) 中国热带森林植被类型研究历史和划分探讨. 广西植物, 41, 1595-1604.] | |
| [43] | Xue Y, Liang JZ, Su SF, Yao XL, Wang XY, Lin ZP, Xue YW (2020) Changes of vegetation and soil nutrient in different forests after logging ban in tropical coastal area of Hainan Island. Chinese Journal of Tropical Crops, 41, 1273-1278. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[ 薛杨, 梁居智, 宿少锋, 姚小兰, 王小燕, 林之盼, 薛雁文 (2020) 海南岛不同类型滨海林地禁伐后的植被与土壤养分变化. 热带作物学报, 41, 1273-1278.]
DOI |
|
| [44] | Ye WH, Cao HL, Huang ZL, Lian JY, Wang ZG, Li L, Wei SG, Wang ZM (2008) Community structure of a 20 hm2 lower subtropical evergreen broadleaved forest plot in Dinghushan, China. Journal of Plant Ecology (Chinese Version), 32, 274-286. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[ 叶万辉, 曹洪麟, 黄忠良, 练琚愉, 王志高, 李林, 魏识广, 王章明 (2008) 鼎湖山南亚热带常绿阔叶林20公顷样地群落特征研究. 植物生态学报, 32, 274-286.]
DOI |
|
| [45] | Zeng QB, Li YD, Chen BF (1997) Research and Management of Tropical Forest Ecosystem. China Forestry Publishing House, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 曾庆波, 李意德, 陈步峰 (1997) 热带森林生态系统研究与管理. 中国林业出版社, 北京.] | |
| [46] | Zhang JT (1998) Analysis of spatial point pattern for plant species. Acta Phytoecologica Sinica, 22, 344-349. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 张金屯 (1998) 植物种群空间分布的点格局分析. 植物生态学报, 22, 344-349.] | |
| [47] | Zhang SW, Li JH, Yang XB, Li DH, Huang Y, Du CY, Shang NY (2024) The spatial distribution pattern of Chunia bucklandioides in Jianfengling area of Hainan Tropical Rainforest National Park. Forest and Grassland Resources Research, (2), 17-25. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 张顺卫, 李婧涵, 杨小波, 李东海, 黄耀, 杜春雁, 商乃演 (2024) 海南热带雨林国家公园尖峰岭片区山铜材种群空间分布格局. 林草资源研究, (2), 17-25.] | |
| [48] |
Zhong L, Chang-Yang CH, Lu P, Gu XP, Lei ZP, Cai YB, Zheng FD, Sun IF, Yu MJ (2015) Community structure and species composition of the secondary evergreen broad- leaved forest: The analyses for a 9 ha forest dynamics plot in Wuyanling Nature Reserve, Zhejiang Province, East China. Biodiversity Science, 23, 619-629. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[ 仲磊, 张杨家豪, 卢品, 顾雪萍, 雷祖培, 蔡延奔, 郑方东, 孙义方, 于明坚 (2015) 次生常绿阔叶林的群落结构与物种组成: 基于浙江乌岩岭9 ha森林动态样地. 生物多样性, 23, 619-629.]
DOI |
|
| [49] | Zhu H (2018) A sketch for classification of tropical forest vegetation in Yunnan. Guihaia, 38, 984-1004. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 朱华 (2018) 云南热带森林植被分类纲要. 广西植物, 38, 984-1004.] |
| [1] | Mingyi Zhang, Xiaomei Wang, Yanxin Zheng, Nan Wu, Donghao Li, Enyuan Fan, Na Li, Xiujuan Shan, Tao Yu, Chunnuan Zhao, Bo Li, Shuai Xu, Yuping Wu, Liqun Ren. Resource status and habitat function of typical oyster reef areas in the Yellow River Estuary [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 24208-. |
| [2] | Tong Miao, Wang Huan, Zhang Wenshuang, Wang Chao, Song Jianxiao. Distribution characteristics of antibiotic resistance genes in soil bacterial communities exposed to heavy metal pollution [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(3): 24101-. |
| [3] | Jia Zhenni, Zhang Yicen, Du Yanjun, Ren Haibao. Influences of disturbances on successional dynamics of species diversity in mid- subtropical forests [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(2): 24078-. |
| [4] | Shiyu Wei, Tianjiao Song, Jiayi Luo, Yan Zhang, Zixuan Zhao, Jingwen Ru, Hua Yi, Yanbing Lin. Altitudinal distribution patterns of soil bacterial communities in the Huoditang coniferous forests of the Qinling Mountains [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(9): 24180-. |
| [5] | Yongqiang Shi, Qingshan Luan, Xiujuan Shan, Chao Wei, Yongsong Zhao, Cece Sun, Xianshi Jin. Annual changes in zooplankton biodiversity in the southern waters of Changdao [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(7): 23428-. |
| [6] | Yanmei Ni, Li Chen, Zhiyuan Dong, Debin Sun, Baoquan Li, Xumin Wang, Linlin Chen. Community structure of macrobenthos and ecological health evaluation in the restoration area of the Yellow River Delta wetland [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(3): 23303-. |
| [7] | Jiaxin Wei, Zhiguo Jiang, Linsen Yang, Huanhuan Xiong, Jiaojiao Jin, Fanglin Luo, Jiehua Li, Hao Wu, Yaozhan Xu, Xiujuan Qiao, Xinzeng Wei, Hui Yao, Huiliang Yu, Jingyuan Yang, Mingxi Jiang. Community composition and structure in a 25 ha mid-subtropical mountain deciduous broad-leaved forest dynamics plot in Shennongjia, Hubei, China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(3): 23338-. |
| [8] | Xiaolin Liu, Yougui Wu, Minhua Zhang, Xiaorong Chen, Zhicheng Zhu, Dingyun Chen, Shu Dong, Buhang Li, Bingyang Ding, Yu Liu. Community composition and structure of a 25-ha forest dynamics plot of subtropical forest in Baishanzu, Zhejiang Province [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(2): 23294-. |
| [9] | Fangfang Wu, Na Liu, Chunmei He, Zuoqiang Yuan, Zhanqing Hao, Qiulong Yin. Elevational gradient pattern of woody plant community structure and diversity in the Qinling Mountains [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(12): 24239-. |
| [10] | Kailun Xu, Xiaorong Chen, Minhua Zhang, Wanwan Yu, Sumei Wu, Zhicheng Zhu, Dingyun Chen, Rongguang Lan, Shu Dong, Yu Liu. Succession and topography jointly influence the diversity of plant sexual systems in the Baishanzu forest community [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(12): 24338-. |
| [11] | Hang Shan, Zupei Lei, Fangdong Zheng, Boliang Wei, Lei Zhong, Mingjian Yu. Dynamic changes in the community of a secondary evergreen broad-leaved forest in Wuyanling, Zhejiang Province from 2013 to 2023 [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(12): 24372-. |
| [12] | Jiayi Feng, Juyu Lian, Yujun Feng, Dongxu Zhang, Honglin Cao, Wanhui Ye. Effects of vertical stratification on community structure and functions in a subtropical, evergreen broad-leaved forest in the Dinghushan National Nature Reserve [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(12): 24306-. |
| [13] | Xingyu Wang, Jinghui Meng, Siyuan Ren, Yan Zhu. Relationship between biodiversity and aboveground biomass in the warm temperate deciduous broad-leaved forest of Donglingshan, Beijing [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(12): 24230-. |
| [14] | Qingqing Du, Siyuan Ren, Nicole Tsz Shun Yuan, Yan Zhu. Factors affecting the productivity of sapling and adult trees in the warm temperate deciduous broad-leaved forest of Donglingshan, Beijing [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(12): 24284-. |
| [15] | Junhan Huang, Fandong Yu, Yuxiang Wang, Zhe Huang, Mingsi Zhang, Miao Fang, Lu Shu, Meng Xu, Hui Wei, Xuejie Wang, Dang’en Gu, Si Luo. The current status of invasive fish and their interrelationships with environmental factors in the middle and lower reaches of the Huadi River [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(11): 24249-. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2022 Biodiversity Science
Editorial Office of Biodiversity Science, 20 Nanxincun, Xiangshan, Beijing 100093, China
Tel: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn ![]()