



Biodiv Sci ›› 2017, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (8): 840-846. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2017130 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2017130
• Original Papers: Animal Diversity • Previous Articles Next Articles
Fei Li1, Xi Zheng1, Huarong Zhang2, Jianhuan Yang1, Bosco Pui Lok Chan1,*( )
)
Received:2017-05-02
Accepted:2017-06-15
Online:2017-08-20
Published:2017-08-31
Contact:
Pui Lok Chan Bosco
Fei Li, Xi Zheng, Huarong Zhang, Jianhuan Yang, Bosco Pui Lok Chan. The current status and conservation of otters on the coastal islands of Zhuhai, Guangdong Province, China[J]. Biodiv Sci, 2017, 25(8): 840-846.
| 面积 Area (km2) | 最高海拔 Highest elevation (m) | 有效被访者数量 No. of effective respondents | 样线 Transect line | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 数量 No. | 总长度 Total length (m) | ||||
| 三灶岛 Sanzao Is. | 78.00 | 307 | 7 | 8 | 4,263 |
| 横琴岛 Hengqin Is. | 47.00 | 458 | 16 | 15 | 26,217 |
| 高栏岛 Gaolan Is. | 34.20 | 428 | 8 | 3 | 2,180 |
| 淇澳岛 Qi’ao Is. | 15.92 | 185 | 6 | 5 | 5,980 |
| 荷包岛 Hebao Is. | 12.00 | 386 | 4 | 3 | 4,335 |
| 大杧岛 Damang Is. | 5.20 | 268 | 2 | 1 | 532 |
| 三角山岛 Sanjiaoshan Is. | 0.82 | 142 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 横洲 Hengzhou Is. | 0.70 | 113 | 0 | 3 | 2,293 |
| 獭洲 Tazhou Is. | 0.12 | 84 | 0 | 1 | 395 |
| 交杯岛 Jiaobei Is. | 0.08 | 47 | 0 | 2 | 199 |
| 总计 Total | 43 | 41 | 46,394 | ||
Table 1 Basic information of otter survey sites in Zhuhai City, Guangdong Province, China
| 面积 Area (km2) | 最高海拔 Highest elevation (m) | 有效被访者数量 No. of effective respondents | 样线 Transect line | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 数量 No. | 总长度 Total length (m) | ||||
| 三灶岛 Sanzao Is. | 78.00 | 307 | 7 | 8 | 4,263 |
| 横琴岛 Hengqin Is. | 47.00 | 458 | 16 | 15 | 26,217 |
| 高栏岛 Gaolan Is. | 34.20 | 428 | 8 | 3 | 2,180 |
| 淇澳岛 Qi’ao Is. | 15.92 | 185 | 6 | 5 | 5,980 |
| 荷包岛 Hebao Is. | 12.00 | 386 | 4 | 3 | 4,335 |
| 大杧岛 Damang Is. | 5.20 | 268 | 2 | 1 | 532 |
| 三角山岛 Sanjiaoshan Is. | 0.82 | 142 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 横洲 Hengzhou Is. | 0.70 | 113 | 0 | 3 | 2,293 |
| 獭洲 Tazhou Is. | 0.12 | 84 | 0 | 1 | 395 |
| 交杯岛 Jiaobei Is. | 0.08 | 47 | 0 | 2 | 199 |
| 总计 Total | 43 | 41 | 46,394 | ||
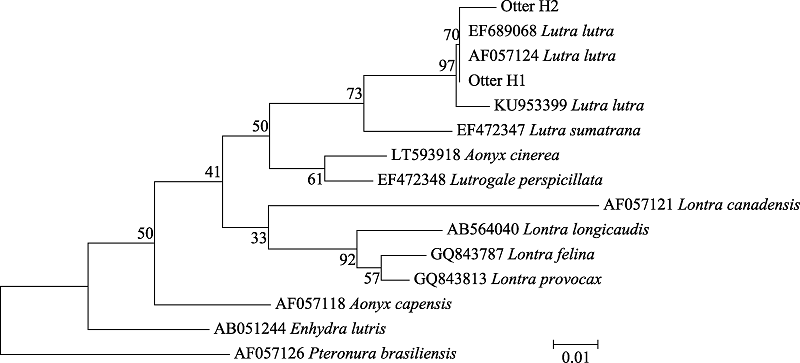
Fig. 3 NJtree showing the phylogenetic relationships among spraint samples and 11 otter species using partial Cyt b fragment (Otter H1 and Otter H2 represent Zhuhai samples)
| 1 | [珠海市地方志编委会 (1987) 珠海市海岛志.]. (accessed on 2017-04-24 |
| 2 | Galletta AM (2013) Mastering the Semi-Structured Interview and Beyond. New York University Press, New York. |
| 3 | Gao YT (1987) Fauna Sinica: Mammalia, Vol. 8: Carnivora. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [高耀亭 (1987) 中国动物志兽纲第八卷食肉目. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| 4 | Huang YJ, Cui SP, Li N, Li CW, Jiang ZG (2017) Invasion and potential impacts of the first alien carnivore in China: American minks (Neovison vison) in Altai region, Xinjiang. Chinese Science Bulletin, 62, 279-288. (in Chinese) |
| [黄元骏, 崔绍朋, 李娜, 李春旺, 蒋志刚 (2017) 外来食肉类北美水貂在新疆阿勒泰地区的入侵及潜在影响探讨. 科学通报, 62, 279-288.] | |
| 5 | Jiang ZG, Jiang JP, Wang YZ, Zhang E, Zhang YY, Li LL, Xie F, Cai B, Cao L, Zheng GM, Dong L, Zhang ZW, Ding P, Luo ZH, Ding CQ, Ma ZJ, Tang SH, Cao WX, Li CW, Hu HJ, Ma Y, Wu Y, Wang YX, Zhou KY, Liu SY, Chen YY, Li JT, Feng ZJ, Wang Y, Wang B, Li C, Song XL, Cai L, Zang CX, Zeng Y, Meng ZB, Fang HX, Ping XG (2016) Red List of China’s Vertebrates. Biodiversity Science, 24, 500-551. (in Chinese and in English) |
| [蒋志刚, 江建平, 王跃招, 张鹗, 张雁云, 李立立, 谢锋, 蔡波, 曹亮, 郑光美, 董路, 张正旺, 丁平, 罗振华, 丁长青, 马志军, 汤宋华, 曹文宣, 李春旺, 胡慧建, 马勇, 吴毅, 王应祥, 周开亚, 刘少英, 陈跃英, 李家堂, 冯祚建, 王燕, 王斌, 李成, 宋雪琳, 蔡蕾, 臧春鑫, 曾岩, 孟智斌, 方红霞, 平晓鸽 (2016) 中国脊椎动物红色名录. 生物多样性, 24, 500-551.] | |
| 6 | Kruuk H (2006) Otters Ecology, Behaviour and Conservation. Oxford University Press, Oxford. |
| 7 | Lau MWN, Fellowes JR, Chan BPL (2010) Carnivores (Mammalia: Carnivora) in South China: a status review with notes on the commercial trade. Mammal Review, 40, 247-292. |
| 8 | Li F, Chan BPL (2017) Past and present: the status and distribution of otters (Carnivora: Lutrinae) in China. Oryx, published online, doi: . |
| 9 | Madisha MT, Ponsonby D, Schwaibold U, Kotzé A, Jansen R, Brettschneider H, Dalton DL (2015) Differentiation of two South African otter species (Aonyx capensis and Lutra maculicollis) from spraint based on partial Cyt b primer sets. Global Ecology and Conservation, 4, 8-13. |
| 10 | Xu LH (1984) Species of otters in China and the conservation of their natural resources. Wildlife, 6(1), 9-11. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [徐龙辉 (1984) 中国水獭种类及资源保护. 野生动物, 6(1), 9-11.] | |
| 11 | Zhang R, Yang L, Laguardia A, Jiang Z, Huang M, Lü J, Ren YH, Zhang W, Luan XF (2016) Historical distribution of the otter (Lutra lutra) in north-east China according to historical records (1950-2014). Aquatic Conservation: Marine and Freshwater Ecosystems, 606, 602-606. |
| 12 | Zhang RZ (1997) Distribution of Mammalian Species in China. China Forestry Publishing House, Beijing. |
| [张荣祖 (1997) 中国哺乳动物分布. 中国林业出版社, 北京.] | |
| 13 | Zhao YL (2010) The remote sensing dynamic monitoring of the evolution of shoreline and mangrove wetlands in the Zhujiang River estuary in the past 30 years. Remote Sensing for Land & Resources, 86(Suppl.), 178-184. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [赵玉灵 (2010) 珠江口地区近30年海岸线与红树林湿地遥感动态监测. 国土资源遥感, 86(增刊), 178-184.] | |
| 14 | Zou FS, Ye GF (2016) The Checklist and Distribution of Terrestrial Vertebrates of Guangdong Province. Guangdong Science and Technology Press, Guangzhou. (in Chinese) |
| [邹发生, 叶冠锋 (2016) 广东陆生脊椎动物分布名录. 广东科技出版社, 广州.] |
| [1] | Murong Yi, Ping Lu, Yong Peng, Yong Tang, Jiuheng Xu, Haoping Yin, Luyang Zhang, Xiaodong Weng, Mingxiao Di, Juan Lei, Chenqi Lu, Rujun Cao, Nianhua Dai, Deyang Zhan, Mei Tong, Zhiming Lou, Yonggang Ding, Jing Chai, Jing Che. Population status and habitat of Critically Endangered Jiangxi giant salamander (Andrias jiangxiensis) [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 24145-. |
| [2] | Motong Li, Tuo He, Wei Li, Jing Liao, Yan Zeng. Regulating international trade in wild fauna and flora: An analysis of CITES terminology [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 24545-. |
| [3] | Tuo He, Yan Zeng, Yafang Yin, Kun Zhang, Liangchen Yuan, Hui Dong, Zhihua Zhou. Consolidating the scientific foundation for global wild plant conservation and sustainable trade—Comments on the 27th Meeting of the Plants Committee of CITES [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(9): 24390-. |
| [4] | Jinfeng Chen, Xinjing Wu, Hai Lin, Guofa Cui. A comparative analysis of the List of State Key Protected Wild Animals and other wildlife protection lists [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(6): 22639-. |
| [5] | Minhao Chen, Chao Zhang, Jiadong Wang, Zhenjie Zhan, Junzhi Chen, Xiaofeng Luan. Distribution and niche overlap of American mink and Eurasian otter in Northeast China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(1): 22289-. |
| [6] | Yanyan Liu, Chang Liu, Xiaoxin Wei. Current status of taxonomy, systematics and conservation of the white pines in China and adjacent regions [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2022, 30(2): 21344-. |
| [7] | Chao Zhang, Minhao Chen, Li Yang, Hongfei Zhuang, Shuhong Wu, Zhenjie Zhan, Jiadong Wang, Xiaofeng Luan. Distribution pattern and identification of conservation priority areas of the otter in Northeast China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2022, 30(1): 21157-. |
| [8] | Xuesong Han, Zhengyi Dong, Ge Zhao, Xiang Zhao, Xiangying Shi, Zhi Lü, Hongqi Li. Using surveillance cameras to analyze the activity pattern of the Eurasian otters (Lutra lutra) and the efficiency of camera trap monitoring [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2021, 29(6): 770-779. |
| [9] | Jiang Zhigang. China’s key protected species lists, their criteria and management [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2019, 27(6): 698-703. |
| [10] | Xiping Zhou, Zhen Li, Peifang Wu, Xi Wu, Yixin Chen, Kangge Liu, Dongyan Liu, Yujue Wang, Yueqi Wang. The structure of macrobenthic community in Pearl River Estuary [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2019, 27(10): 1112-1121. |
| [11] | Jianmin Chu, Yifu Li, Lei Zhang, Bin Li, Mingyuan Gao, Xiaoqian Tang, Jianwei Ni, Xinqiao Xu. Potential distribution range and conservation strategies for the endangered species Amygdalus pedunculata [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2017, 25(8): 799-806. |
| [12] | Jun Chen. Challenges regarding the necessity of voucher specimens for naming a new animal species: the Code, species conservation and the digital age [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2017, 25(11): 1239-1245. |
| [13] | Wenzhong Yang, Zhenyong Xiang, Shanshan Zhang, Hongmei Kang, Fuqiang Shi. Plant species with extremely small populations (PSESP) and their significance in China’s national plant conservation strategy [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2015, 23(3): 419-425. |
| [14] | ZHANG Da-Yong, LEI Guang-Chun, ILKKA HANSKI, . Metapopulation dynamics: theory and applications [J]. Biodiv Sci, 1999, 07(2): 81-90. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2022 Biodiversity Science
Editorial Office of Biodiversity Science, 20 Nanxincun, Xiangshan, Beijing 100093, China
Tel: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn ![]()