



Biodiv Sci ›› 2012, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (5): 551-558. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2012.08118 cstr: 32101.14.SP.J.1003.2012.08118
Special Issue: 创刊20周年纪念专刊; 生物入侵
• Editorial • Previous Articles Next Articles
Jianzhang Ma*( ), Ke Rong, Kun Cheng
), Ke Rong, Kun Cheng
Received:2012-05-22
Accepted:2012-08-07
Online:2012-09-20
Published:2012-09-07
Contact:
Jianzhang Ma
Jianzhang Ma, Ke Rong, Kun Cheng. Research and practice on biodiversity in situ conservation in China: progress and prospect[J]. Biodiv Sci, 2012, 20(5): 551-558.
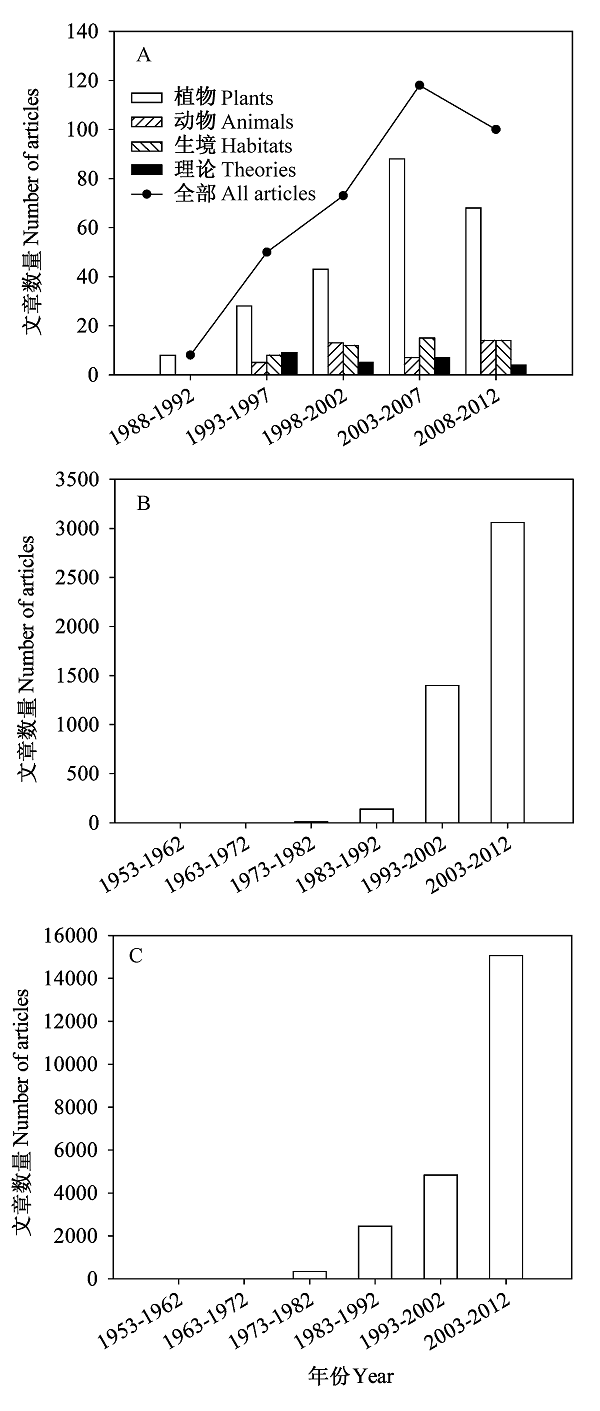
Fig. 1 Publishing trends of in situ conservation research in China. A, Retrieval result used “就地保护” as a keyword in the CNKI Database. B, Retrieval result used “in situ conservation” as a keyword in the Google Scholar. C, Retrieval result used “自然保护区” as a keyword in the CNKI Database
| [1] | An S, Li H, Guan B, Zhou C, Wang Z, Deng Z, Zhi Y, Liu Y, Xu C, Fang S, Jiang J, Li H (2007) China’s natural wetlands: past problems, current status, and future fhallenges. AMBIO: A Journal of the Human Environment, 36, 335-342. |
| [2] | Balmford A, Green RE, Jenkins M (2003) Measuring the changing state of nature. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 18, 326-330. |
| [3] |
Bani L, Massimino D, Bottoni L, Massa R (2006) A multiscale method for selecting indicator species and priority conservation areas: a case study for broadleaved forests in Lombardy, Italy. Conservation Biology, 20, 512-526.
URL PMID |
| [4] | Chen SB (陈圣宾), Jiang GM (蒋高明), Gao JX (高吉喜), Li YG (李永庚), Su D (苏德) (2008) Review of indicators system developing for biodiversity monitoring. Acta Ecologica Sinica (生态学报), 28, 5123-5132. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [5] |
Chen GK (陈国科), Ma KP (马克平) (2012) Criteria and methods for assessing the threat status of ecosystem. Biodiversity Science (生物多样性), 20, 66-75. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
| [6] | Chen TH (陈廷辉) (2011) Game of Interests on Legislation of Natural Reserves. Journal of Beijing Forestry University (social sciences)(北京林业大学学报(社会科学版)), 10, 10-16. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [7] | Chen YH (陈雅涵), Tang ZY (唐志尧), Fang JY (方精云) (2009) Distribution of nature reserves and status of biodiversity protection in China. Biodiversity Science (生物多样性), 17, 664-674. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [8] | Deng YN (邓亚妮), Cheng X (成晓), Jiao Y (焦瑜), Chen GJ (陈贵菊) (2009) Bioecological characteristics and endanger- ment mechanisms of Neocheiropteris palmatopedata, an endangered plant endemic to China. Biodiversity Science (生物多样性), 17, 62-68. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [9] | Fazey I, Fischer J, Lindenmayer DB (2005) What do conservation biologists publish? Biological Conservation, 124, 63-73. |
| [10] | Han NY (韩念勇) (2000) A policy study on sustainable management for China’s nature reserves. Journal of Natural Resources (自然资源学报), 15, 201-207. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [11] |
Hector A, Bagchi R (2007) Biodiversity and ecosystem multifunctionality. Nature, 448, 188-190.
DOI URL PMID |
| [12] | Hooper DU, Chapin FS, Ewel JJ, Hector A, Inchausti P, Lavorel S, Lawton JH, Lodge DM, Loreau M, Naeem S, Schmid B, Setala H, Symstad AJ, Vandermeer J, Wardle DA (2005) Effects of biodiversity on ecosystem functioning: a consensus of current knowledge. Ecological Monographs, 75, 3-35. |
| [13] | Hu Y (胡涌), Zhang QX (张启翔) (1998) Discussion on the theoretical problems of forest parks, also on the relationship among nature reserves, scenery spots and famous sites, and forest parks. Journal of Beijing Forestry University (北京林业大学学报), 20, 52-60. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [14] |
Huang H (2011) Plant diversity and conservation in China: planning a strategic bioresource for a sustainable future. Botanical Journal of the Linnean Society, 166, 282-300.
URL PMID |
| [15] | Jiang LJ (姜立军), Miao H (苗鸿), Ouyang ZY (欧阳志云) (2006) An investigation of factors that influence the effects of management of protected areas. Acta Ecologica Sinica (生态学报), 26, 3775-3781. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [16] | Jiang ZG (蒋志刚) (2005) On the upper limit of the area of the strictly protected nature reserves in China. Acta Ecologica Sinica (生态学报), 25, 1205-1212. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [17] | Jiang ZG (蒋志刚), Ge S (葛颂) (2005) Exploring the mechanism of species endangerment and conservation strategy in the Yangtze River drainage. Biodiversity Science (生物多样性), 13, 367-375. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [18] | Lei YB (类延宝), Xiao HF (肖海峰), Feng YL (冯玉龙) (2010) Impacts of alien plant invasions on biodiversity and evolutionary responses of native species. Biodiversity Science (生物多样性), 18, 620-630. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [19] |
Levine JM, HilleRisLambers J (2009) The importance of niches for the maintenance of species diversity. Nature, 461, 254-257.
URL PMID |
| [20] | Li YM (李延梅), Niu D (牛栋), Zhang ZQ (张志强), Qu JS (曲建升) (2009) Review of international scientific programmes and frontiers of biodiversity research. Acta Ecologica Sinica (生态学报), 29, 2115-2123. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [21] |
Li W (2004) Degradation and restoration of forest ecosystems in China. Forest Ecology and Management, 201, 33-41.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
Liu HL (刘海龙), Pan YW (潘运伟) (2010) The spatial distribution of geoparks of China and suggestions on geological conservation network. Journal of Natural Resources (自然资源学报), 25, 1480-1488. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
| [23] |
Liu J, Diamond J (2005) China’s environment in a globalizing world. Nature, 435, 1179-1186.
DOI URL PMID |
| [24] |
Liu J, Ouyang Z, Pimm SL, Raven PH, Wang X, Miao H, Han N (2003) Protecting China’s biodiversity. Science, 300, 1240-1241.
DOI URL PMID |
| [25] | Liu J, Raven PH (2010) China’s environmental challenges and implications for the world. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology, 40, 823-851. |
| [26] | Liu Y (刘洋), Lü YH (吕一河) (2008) The economic impact of tourism on local residents in Wolong Nature Reserve. Biodiversity Science (生物多样性), 16, 68-74. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [27] | López-Pujol J, Zhang FM, Ge S (2006) Plant biodiversity in China: richly varied, endangered, and in need of conservation. Biodiversity and Conservation, 15, 3983-4026. |
| [28] | López-Pujol J, Zhao AM (2004) China: a rich flora needed of urgent conservation. Orsis, 19, 49-89. |
| [29] |
Loreau M, Naeem S, Inchausti P, Bengtsson J, Grime J, Hector A, Hooper D, Huston M, Raffaelli D, Schmid B (2001) Biodiversity and ecosystem functioning: current knowledge and future challenges. Science, 294, 804-808.
DOI URL PMID |
| [30] | Lü YH (吕一河), Chen LD (陈利顶), Fu BJ (傅伯杰), Xu JY (徐建英) (2004) Protected area management based on game theory. Biodiversity Science (生物多样性), 12, 546-552. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [31] | Ma KP (马克平) (2011) Assessing progress of biodiversity conservation with monitoring approach. Biodiversity Science (生物多样性), 19, 125-126. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [32] | Ma KP (马克平) (2012) A mini review on the advancement in biodiversity research in China in 2011. Biodiversity Science (生物多样性), 20, 1-2. (in Chinese) |
| [33] | Ma JZ (马建章), Cheng K (程鲲) (2008) Impacts of ecotourism on wildlife in nature reserves: monitoring and management. Acta Ecologica Sinica (生态学报), 28, 2818-2827. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [34] | Ministry of Environmental Protection, People’s Republic of China (MEP, 中华人民共和国环境保护部) (2008) China’s fourth national report on implementation of the convention on biological diversity. Available at http://www.cbd.int/countries/profile.shtml?country=cn. |
| [35] |
Myers N, Knoll AH (2001) The biotic crisis and the future of evolution. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 98, 5389.
DOI URL |
| [36] |
Ozaki K, Isono M, Kawahara T, Lida S, Kudo T, Fukuyama K (2006) A mechanistic approach to evaluation of umbrella species as conservation surrogates. Conservation Biology, 20, 1507-1515.
DOI URL PMID |
| [37] |
Pereira HM, Leadley PW, Proença V, Alkemade R, Scharlemann JPW, Fernandez-Manjarrés JF, Araújo MB, Balvanera P, Biggs R, Cheung WWL (2010) Scenarios for global biodiversity in the 21st century. Science, 330, 1496-1501.
URL PMID |
| [38] |
Qin WH (秦卫华), Jiang MK (蒋明康), Xu WG (徐网谷), He ZH (贺昭和) (2012) Assessment of in situ conservation of 1,334 native orchids in China. Biodiversity Science (生物多样性), 20, 177-183. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
| [39] | Quan J (权佳), Ouyang ZY (欧阳志云), Xu WH (徐卫华), Miao H (苗鸿) (2010) Comparison and applications of methodologies for management effectiveness assessment of protected areas. Biodiversity Science (生物多样性), 18, 90-99. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [40] |
Rands MRW, Adams WM, Bennun L, Butchart SHM, Clements A, Coomes D, Entwistle A, Hodge I, Kapos V, Scharlemann JPW (2010) Biodiversity conservation: challenges beyond 2010. Science, 329, 1298-1303.
DOI URL PMID |
| [41] | Rong K (戎可), Ma JZ (马建章), Zhao D (赵丹), Wu QM (吴庆明) (2008) The establishment and application of area evaluation model for China’s nature reserves. Acta Ecologica Sinica (生态学报), 28, 2738-2745. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [42] |
Sang W, Ma K, Axmacher JC (2011) Securing a future for China’s wild plant resources. BioScience, 61, 720-725.
DOI URL |
| [43] | Tang XP (唐小平) (2005) Analysis of the current situation of China’s nature reserve network and a draft plan for its optimization. Biodiversity Science (生物多样性), 13, 81-88. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [44] | Tang Z, Wang Z, Zheng C, Fang J (2006) Biodiversity in China’s mountains. Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment, 4, 347-352. |
| [45] | Wang B (王兵), Cui XH (崔向慧), Yang FW (杨锋伟) (2004) Chinese forest ecosystem research network (CFERN) and its development. Chinese Journal of Ecology (生态学杂志), 23, 84-91. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [46] | Wang G, Innes J, Wu S, Krzyzanowski J, Yin Y, Dai S, Zhang X, Liu S (2012) National park development in China: conservation or commercialization? AMBIO: A Journal of the Human Environment, 41, 247-261. |
| [47] | Wang XP (王献溥) (1989) 2nd Botanic Gardens Conservation International Conference. Plants (植物杂志), (5), 46. (in Chinese) |
| [48] | Wang XP (王献溥), Yu SL (于顺利), Wang ZS (王宗帅) (2009) On “basic implication of ecosystem approach” and its application in effective management of protected areas. Chinese Journal of Wildlife (野生动物), 30, 326-330. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [49] | Wang XZ (王学志), Xu WH (徐卫华), Ouyang ZY (欧阳志云), Liu JG (刘建国), Xiao Y (肖燚), Chen YP (陈佑平), Zhao LJ (赵联军), Huang JZ (黄俊忠) (2008) The application of Ecological-Niche factor analysis in giant pandas (Ailuropoda melanoleuca) habitat assessment. Acta Ecologica Sinica (生态学报), 28, 821-828. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [50] | Wang Y, Chen S, Ding P (2011) Testing multiple assembly rule models in avian communities on islands of an inundated lake, Zhejiang Province, China. Journal of Biogeography, 38, 1330-1344. |
| [51] |
Wu B (吴波), Zhu CQ (朱春全), Li DQ (李迪强), Dong K (董珂), Wang XL (王秀磊), Shi PL (石培礼) (2006) Setting biodiversity conservation priorities in the forests of the upper Yangtze ecoregion based on ecoregion conservation methodology. Biodiversity Science (生物多样性), 14, 87-97. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
| [52] |
Wu R, Zhang S, Yu DW, Zhao P, Li X, Wang L, Yu Q, Ma J, Chen A, Long Y (2011) Effectiveness of China’s nature reserves in representing ecological diversity. Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment, 9, 383-389.
DOI URL |
| [53] |
Xiao DN (肖笃宁), Chen WB (陈文波), Guo FL (郭福良) (2002) On the basic concepts and contents of ecological security. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology (应用生态学报), 13, 354-358. (in Chinese with English abstract)
URL PMID |
| [54] | Xu H, Tang X, Liu J, Ding H, Wu J, Zhang M, Yang Q, Cai L, Zhao H, Liu Y (2009) China’s progress toward the significant reduction of the rate of biodiversity loss. BioScience, 59, 843-852. |
| [55] | Xu H, Wang S, Xue D (1999) Biodiversity conservation in China: legislation, plans and measures. Biodiversity and Conservation, 8, 819-837. |
| [56] | Yip J, Corlett R, Dudgeon D (2004) A fine-scale gap analysis of the existing protected area system in Hong Kong, China. Biodiversity and Conservation, 13, 943-957. |
| [57] | Yu GZ (于广志), Jiang ZG (蒋志刚) (2003) Buffer zones: pattern, function and design principles. Biodiversity Science (生物多样性), 11, 256-261. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [58] | Yuan H (苑虎), Zhang YB (张殷波), Qin HN (覃海宁), Liu Y (刘燕), Yu M (喻梅) (2009) The in situ conservation of state key protected wild plants in national nature reserves in China. Biodiversity Science (生物多样性), 17, 280-287. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [59] |
Zhai TQ (翟天庆), Li XH (李欣海) (2012) Climate change induced potential range shift of the crested ibis based on ensemble models. Acta Ecologica Sinica (生态学报), 32, 2361-2370. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
| [60] | Zhang CZ (张常智), Zhang MH (张明海) (2011) Population status and dynamic trends of Amur tiger’s prey in Eastern Wandashan mountain, Heilongjiang Province. Acta Ecologica Sinica (生态学报), 31, 6481-6487. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [61] | Zhang JL (张金良), Li HF (李焕芳), Huang FG (黄方国) (2000) Community co-management: a new model for nature reserve management. Biodiversity Science (生物多样性), 8, 347-350. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [62] | Zheng Y, Zhang H, Niu Z, Gong P (2012) Protection efficacy of national wetland reserves in China. Chinese Science Bulletin, 57, 1116-1134. |
| [63] | Zhong L, Deng J, Xiang B (2008) Tourism development and the tourism area life-cycle model: a case study of Zhangjiajie National Forest Park, China. Tourism Management, 29, 841-856. |
| [64] | Environment Protection Leading Group of the State Council (国务院环境保护领导小组办公室) (1980) Summary on world conservation strategy. Journal of Natural Resources (自然资源学报), (2), 67-69. (in Chinese) |
| [1] | Jing Gan Xiangxu Liu Xueming Lu Xing Yue. China's Large Cities in Global Biodiversity Hotspots: Conservation Policies and Optimization Directions [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 24529-. |
| [2] | Zixuan Zeng Rui Yang Yue Huang Luyao Chen. Characteristics of bird diversity and environmental relationships in Tsinghua University campus [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 24373-. |
| [3] | Mingyue Zang, Li Liu, Yue Ma, Xu Xu, Feilong Hu, Xiaoqiang Lu, Jiaqi Li, Cigang Yu, Yan Liu. China’s urban biodiversity conservation under the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 24482-. |
| [4] | Xiaoyu Zhu, Chenhao Wang, Zhongjun Wang, Yujun Zhang. Research progress and prospect of urban green space biodiversity [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 25027-. |
| [5] | Lin Yuan, Siqi Wang, Jingxuan Hou. “Leaving space for wildness” in metropolitan region: Trends and prospects [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 24481-. |
| [6] | Min Hu, Binbin Li, Coraline Goron. Green is not enough: A management framework for urban biodiversity-friendly parks [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 24483-. |
| [7] | Xin Wang, Femgyu Bao. Analysis of the ecological restoration effect of South Dianchi National Wetland Park based on the enhancement of bird diversity [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 24531-. |
| [8] | Yue Ming, Peiyao Hao, Lingqian Tan, Xi Zheng. A study on urban biodiversity conservation and enhancement in china based on the concept of green and high-quality development of cities [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 24524-. |
| [9] | Gan Xie, Jing Xuan, Qidi Fu, Ze Wei, Kai Xue, Hairui Luo, Jixi Gao, Min Li. Establishing an intelligent identification model for unmanned aerial vehicle surveys of grassland plant diversity [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 24236-. |
| [10] | Xiaolin Chu, Quanguo Zhang. A review of experimental evidence for the evolutionary speed hypothesis [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 25019-. |
| [11] | Jingjing Zhang, Wenbin Huang, Yiting Chen, Zepeng Yang, Weiye Ke, Zhaojie Peng, Shichao Wei, Zhiwei Zhang, Yisi Hu, Wenhua Yu, Wenliang Zhou. Reef-building coral diversity and distribution characteristics in the National Nature Reserve for Marine Ecology of Guangdong Nanpeng Islands [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 24424-. |
| [12] | Zhiyu Liu, Xin Ji, Guohui Sui, Ding Yang, Xuankun Li. Invertebrate diversity in buffalo grass and weedy lawns at Beijing Capital International Airport [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 24456-. |
| [13] | Xiaoqiang Lu, Shanshan Dong, Yue Ma, Xu Xu, Feng Qiu, Mingyue Zang, Yaqiong Wan, Luanxin Li, Cigang Yu, Yan Liu. Current status, challenges, and prospects of frontier technologies in biodiversity conservation applications [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 24440-. |
| [14] | Qiaoyi Nong, Jun Cao, Wenda Cheng, Yanqiong Peng. Comparative study of monitoring methods for Apoidea resources and diversity [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 25057-. |
| [15] | Guo Yutong, Li Sucui, Wang Zhi, Xie Yan, Yang Xue, Zhou Guangjin, You Chunhe, Zhu Saning, Gao Jixi. Coverage and distribution of national key protected wild species in China’s nature reserves [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(3): 24423-. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2022 Biodiversity Science
Editorial Office of Biodiversity Science, 20 Nanxincun, Xiangshan, Beijing 100093, China
Tel: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn ![]()