



Biodiv Sci ›› 2011, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (2): 127-133. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2011.07290 cstr: 32101.14.SP.J.1003.2011.07290
Special Issue: 中国的森林生物多样性监测
Previous Articles Next Articles
Yue Bin1,2, Wanhui Ye1,*( ), Honglin Cao1, Zhongliang Huang1, Juyu Lian1
), Honglin Cao1, Zhongliang Huang1, Juyu Lian1
Received:2009-12-24
Accepted:2011-01-18
Online:2011-03-20
Published:2011-06-01
Contact:
Wanhui Ye
Yue Bin, Wanhui Ye, Honglin Cao, Zhongliang Huang, Juyu Lian. Seedling distribution in a subtropical evergreen broad-leaved forest plot in the Dinghu Mountain[J]. Biodiv Sci, 2011, 19(2): 127-133.
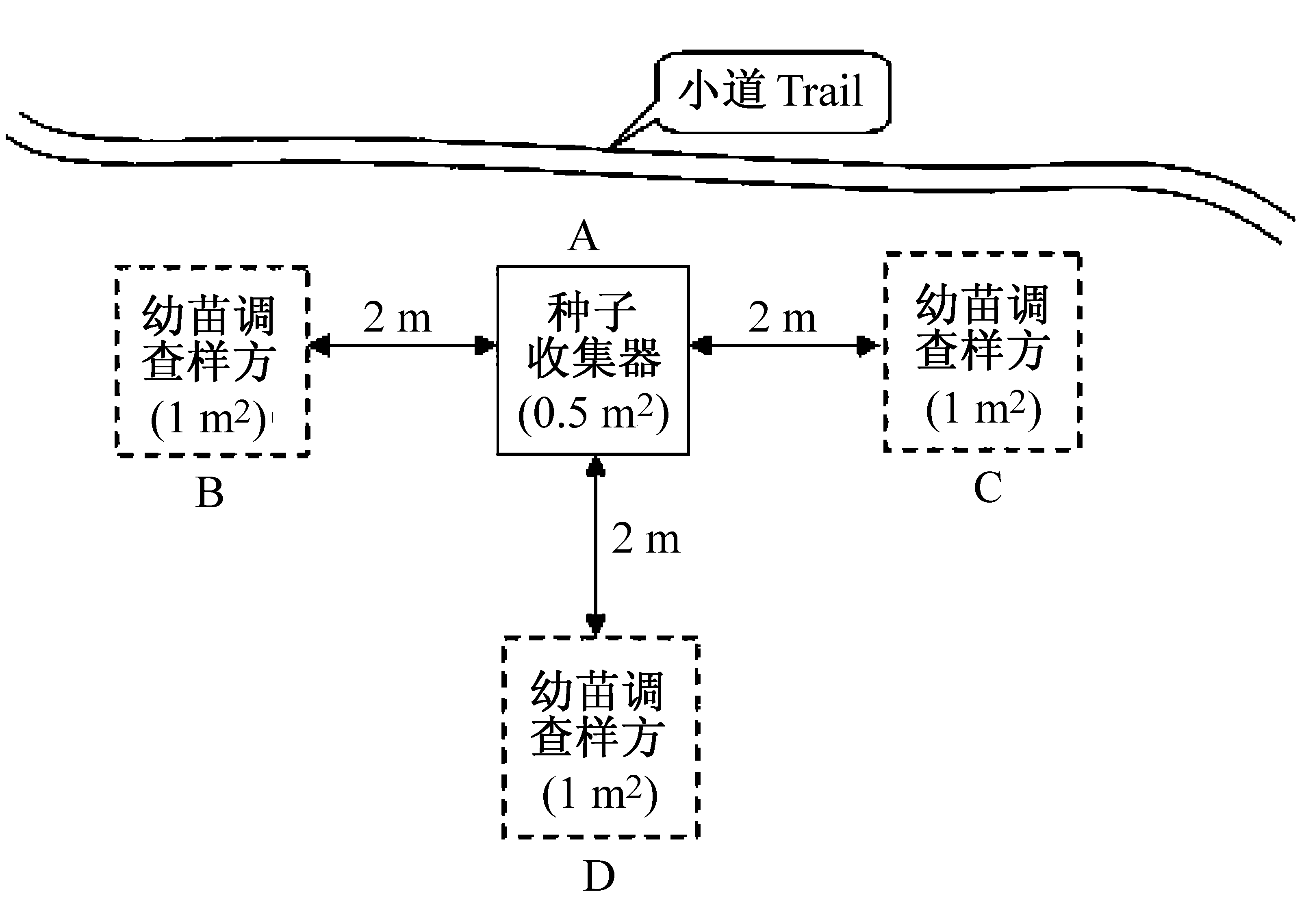
Fig. 1 Arrangement of seedling subplots in the 20-ha Ding- hushan plot. A, Seed trap; B, C, D, Seedling subplots. Three seedling subplots make up a station.
| 树种 Species | 科名 Family | 个体数 No. of individuals | 出现样方数 No. of quadrats present | 光适应性 Adaptation to light |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 灌木 Shrubs | ||||
| 罗伞树 Ardisia quinquegona | 紫金牛科 Myrsinaceae | 70 | 33 | 中生 MST |
| 柏拉木 Blastus cochinchinensis | 野牡丹科 Melastomataceae | 82 | 30 | 耐荫 ST |
| 薄叶胡桐 Calophyllum membranaceum | 藤黄科 Guttiferae | 75 | 42 | 耐荫 ST |
| 山石榴 Catunaregam spinosa | 茜草科 Rubiaceae | 1 | 1 | 中生 MST |
| 毛果巴豆 Croton lachnocarpus | 大戟科 Euphorbiaceae | 13 | 7 | 中生 MST |
| 疏花卫矛 Euonymus laxiflorus | 卫矛科 Celastraceae | 19 | 14 | 中生 MST |
| 黄栀子 Gardenia jasminoides | 茜草科 Rubiaceae | 1 | 1 | 中生 MST |
| 毛冬青 Ilex pubescens | 冬青科 Aquifoliaceae | 1 | 1 | 中生 MST |
| 粗叶木 Lasianthus chinensis | 茜草科 Rubiaceae | 8 | 8 | 中生 MST |
| 柳叶空心花 Maesa salicifolia | 紫金牛科 Myrsinaceae | 32 | 17 | 中生 MST |
| 白背叶 Mallotus apelta | 大戟科 Euphorbiaceae | 15 | 4 | 阳生 LD |
| 毛稔 Melastoma sanguineum | 野牡丹科 Melastomataceae | 6 | 5 | 中生 MST |
| 光叶海桐 Pittosporum glabratum | 海桐花科 Pittosporaceae | 1 | 1 | 耐荫 ST |
| 九节 Psychotria asiatica | 茜草科 Rubiaceae | 21 | 19 | 中生 MST |
| 密毛乌口树 Tarenna mollissima | 茜草科 Rubiaceae | 23 | 17 | 中生 MST |
| 了哥王 Wikstroemia indica | 瑞香科 Thymelaeaceae | 8 | 8 | 阳生 LD |
| 细轴荛花 W. nutans | 瑞香科 Thymelaeaceae | 3 | 3 | 耐荫 ST |
| 乔木 Arbors | ||||
| 肖蒲桃 Acmena acuminatissima | 桃金娘科 Myrtaceae | 29 | 5 | 耐荫 ST |
| 降真香 Acronychia pedunculata | 芸香科 Rutaceae | 3 | 3 | 中生 MST |
| 五月茶 Antidesma bunius | 大戟科 Euphorbiaceae | 7 | 6 | 耐荫 ST |
| 小叶胭脂 Artocarpus styracifolius | 桑科 Moraceae | 22 | 12 | 中生 MST |
| 橄榄 Canarium album | 橄榄科 Burseraceae | 1 | 1 | 中生 MST |
| 竹节树 Carallia brachiata | 红树科 Rhizophoraceae | 17 | 11 | 中生 MST |
| 锥栗 Castanopsis chinensis | 壳斗科 Fagaceae | 6 | 4 | 中生 MST |
| 红皮紫棱 Craibiodendron kwangtungense | 杜鹃花科 Ericaceae | 12 | 10 | 中生 MST |
| 厚壳桂 Cryptocarya chinensis | 樟科 Lauraceae | 32 | 19 | 中生 MST |
| 黄果厚壳桂 C. concinna | 樟科 Lauraceae | 671 | 120 | 中生 MST |
| 黄杞 Engelhardtia roxburghiana | 胡桃科 Juglandaceae | 117 | 15 | 阳生 LD |
| 短序润楠 Machilus breviflora | 樟科 Lauraceae | 24 | 18 | 中生 MST |
| 华润楠 M. chinensis | 樟科 Lauraceae | 54 | 30 | 中生 MST |
| 笔罗子 Meliosma rigida | 清风藤科 Sabiaceae | 1 | 1 | 耐荫 ST |
| 小新木姜 Neolitsea umbrosa | 樟科 Lauraceae | 74 | 42 | 中生 MST |
| 苍叶红豆 Ormosia semicastrata | 蝶形花科 Papilionaceae | 2 | 2 | 耐荫 ST |
| 光叶红豆 O. glaberrima | 蝶形花科 Papilionaceae | 115 | 22 | 中生 MST |
| 半枫荷 Pterospermum heterophyllum | 梧桐科 Sterculiaceae | 1 | 1 | 阳生 LD |
| 臀果木 Pygeum topengii | 蔷薇科 Rosaceae | 10 | 8 | 中生 MST |
| 水石梓 Sarcosperma laurinum | 肉实科 Sarcospermaceae | 3 | 2 | 耐荫 ST |
| 鸭脚木 Schefflera octophylla | 五加科 Araliaceae | 1 | 1 | 中生 MST |
| 假苹婆 Sterculia lanceolata | 梧桐科 Sterculiaceae | 3 | 3 | 中生 MST |
| 红车 Syzygium rehderianum | 桃金娘科 Myrtaceae | 133 | 53 | 中生 MST |
| 子棱蒲桃 S. championii | 桃金娘科 Myrtaceae | 1 | 1 | 中生 MST |
| 黄叶树 Xanthophyllum hainanense | 远志科 Polygalaceae | 7 | 5 | 中生 MST |
| 大叶臭花椒 Zanthoxylum myriacanthum | 芸香科 Rutaceae | 1 | 1 | 中生 MST |
| 小乔木 Subarbors | ||||
| 光叶山黄皮 Aidia canthioides | 茜草科 Rubiaceae | 626 | 96 | 耐荫 ST |
| 酸味子 Antidesma japonicum | 大戟科 Euphorbiaceae | 1 | 1 | 耐荫 ST |
| 云南银柴 Aporosa yunnanensis | 大戟科 Euphorbiaceae | 12 | 9 | 耐荫 ST |
| 亮叶猴耳环 Archidendron lncidum | 含羞草科 Mimosaceae | 6 | 7 | 阳生 LD |
| 大叶土密树 Bridelia fordii | 大戟科 Euphorbiaceae | 1 | 1 | 中生 MST |
| 金叶树 Chrysophyllum lanceolatum | 山榄科 Sapotaceae | 1 | 1 | 耐荫 ST |
| 罗浮柿 Diospyros morrisiana | 柿科 Ebenaceae | 2 | 2 | 中生 MST |
| 狗骨柴 Diplospora dubia | 茜草科 Rubiaceae | 12 | 9 | 中生 MST |
| 三叉苦 Evodia lepta | 芸香科 Rutaceae | 10 | 9 | 阳生 LD |
| 岭南山竹子 Garcinia oblongifolia | 藤黄科 Guttiferae | 4 | 4 | 中生 MST |
| 越南天料木 Homalium cochinchinense | 天料木科 Samydaceae | 9 | 4 | 中生 MST |
| 鼎湖钓樟 Lindera chunii | 樟科 Lauraceae | 7 | 7 | 中生 MST |
| 山钓樟 L. metcalfiana | 樟科 Lauraceae | 28 | 25 | 中生 MST |
| 山苍子 Litsea cubeba | 樟科 Lauraceae | 1 | 1 | 阳生 LD |
| 轮叶木姜 L. verticillata | 樟科 Lauraceae | 14 | 10 | 中生 MST |
| 豺皮樟 L. rotundifolia | 樟科 Lauraceae | 1 | 1 | 阳生 LD |
| 鼎湖血桐 Macaranga sampsoni | 大戟科 Euphorbiaceae | 11 | 2 | 阳生 LD |
| 绒楠 Machilus velutina | 樟科 Lauraceae | 11 | 5 | 中生 MST |
| 谷木 Memecylon ligustrifolium | 野牡丹科 Melastomataceae | 58 | 38 | 耐荫 ST |
| 柬埔新木姜 Neolitsea membranaceum | 樟科 Lauraceae | 3 | 3 | 中生 MST |
| 新木姜 N. aurata | 樟科 Lauraceae | 1 | 1 | 中生 MST |
| 桃叶石楠 Photinia prunifolia | 蔷薇科 Rosaceae | 3 | 2 | 中生 MST |
| 密花树 Rapanea neriifolia | 紫金牛科 Myrsinaceae | 7 | 7 | 中生 MST |
| 鼎湖杜鹃 Rhododendron tinghuense | 杜鹃花科 Ericaceae | 1 | 1 | 耐荫 ST |
| 山黄麻 Trema tomentosa | 榆科 Ulmaceae | 1 | 1 | 阳生 LD |
Table 3 Appendix I Family, number of individuals, number of stations present, adaptation to light, and life forms of the seedling and sapling species
| 树种 Species | 科名 Family | 个体数 No. of individuals | 出现样方数 No. of quadrats present | 光适应性 Adaptation to light |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 灌木 Shrubs | ||||
| 罗伞树 Ardisia quinquegona | 紫金牛科 Myrsinaceae | 70 | 33 | 中生 MST |
| 柏拉木 Blastus cochinchinensis | 野牡丹科 Melastomataceae | 82 | 30 | 耐荫 ST |
| 薄叶胡桐 Calophyllum membranaceum | 藤黄科 Guttiferae | 75 | 42 | 耐荫 ST |
| 山石榴 Catunaregam spinosa | 茜草科 Rubiaceae | 1 | 1 | 中生 MST |
| 毛果巴豆 Croton lachnocarpus | 大戟科 Euphorbiaceae | 13 | 7 | 中生 MST |
| 疏花卫矛 Euonymus laxiflorus | 卫矛科 Celastraceae | 19 | 14 | 中生 MST |
| 黄栀子 Gardenia jasminoides | 茜草科 Rubiaceae | 1 | 1 | 中生 MST |
| 毛冬青 Ilex pubescens | 冬青科 Aquifoliaceae | 1 | 1 | 中生 MST |
| 粗叶木 Lasianthus chinensis | 茜草科 Rubiaceae | 8 | 8 | 中生 MST |
| 柳叶空心花 Maesa salicifolia | 紫金牛科 Myrsinaceae | 32 | 17 | 中生 MST |
| 白背叶 Mallotus apelta | 大戟科 Euphorbiaceae | 15 | 4 | 阳生 LD |
| 毛稔 Melastoma sanguineum | 野牡丹科 Melastomataceae | 6 | 5 | 中生 MST |
| 光叶海桐 Pittosporum glabratum | 海桐花科 Pittosporaceae | 1 | 1 | 耐荫 ST |
| 九节 Psychotria asiatica | 茜草科 Rubiaceae | 21 | 19 | 中生 MST |
| 密毛乌口树 Tarenna mollissima | 茜草科 Rubiaceae | 23 | 17 | 中生 MST |
| 了哥王 Wikstroemia indica | 瑞香科 Thymelaeaceae | 8 | 8 | 阳生 LD |
| 细轴荛花 W. nutans | 瑞香科 Thymelaeaceae | 3 | 3 | 耐荫 ST |
| 乔木 Arbors | ||||
| 肖蒲桃 Acmena acuminatissima | 桃金娘科 Myrtaceae | 29 | 5 | 耐荫 ST |
| 降真香 Acronychia pedunculata | 芸香科 Rutaceae | 3 | 3 | 中生 MST |
| 五月茶 Antidesma bunius | 大戟科 Euphorbiaceae | 7 | 6 | 耐荫 ST |
| 小叶胭脂 Artocarpus styracifolius | 桑科 Moraceae | 22 | 12 | 中生 MST |
| 橄榄 Canarium album | 橄榄科 Burseraceae | 1 | 1 | 中生 MST |
| 竹节树 Carallia brachiata | 红树科 Rhizophoraceae | 17 | 11 | 中生 MST |
| 锥栗 Castanopsis chinensis | 壳斗科 Fagaceae | 6 | 4 | 中生 MST |
| 红皮紫棱 Craibiodendron kwangtungense | 杜鹃花科 Ericaceae | 12 | 10 | 中生 MST |
| 厚壳桂 Cryptocarya chinensis | 樟科 Lauraceae | 32 | 19 | 中生 MST |
| 黄果厚壳桂 C. concinna | 樟科 Lauraceae | 671 | 120 | 中生 MST |
| 黄杞 Engelhardtia roxburghiana | 胡桃科 Juglandaceae | 117 | 15 | 阳生 LD |
| 短序润楠 Machilus breviflora | 樟科 Lauraceae | 24 | 18 | 中生 MST |
| 华润楠 M. chinensis | 樟科 Lauraceae | 54 | 30 | 中生 MST |
| 笔罗子 Meliosma rigida | 清风藤科 Sabiaceae | 1 | 1 | 耐荫 ST |
| 小新木姜 Neolitsea umbrosa | 樟科 Lauraceae | 74 | 42 | 中生 MST |
| 苍叶红豆 Ormosia semicastrata | 蝶形花科 Papilionaceae | 2 | 2 | 耐荫 ST |
| 光叶红豆 O. glaberrima | 蝶形花科 Papilionaceae | 115 | 22 | 中生 MST |
| 半枫荷 Pterospermum heterophyllum | 梧桐科 Sterculiaceae | 1 | 1 | 阳生 LD |
| 臀果木 Pygeum topengii | 蔷薇科 Rosaceae | 10 | 8 | 中生 MST |
| 水石梓 Sarcosperma laurinum | 肉实科 Sarcospermaceae | 3 | 2 | 耐荫 ST |
| 鸭脚木 Schefflera octophylla | 五加科 Araliaceae | 1 | 1 | 中生 MST |
| 假苹婆 Sterculia lanceolata | 梧桐科 Sterculiaceae | 3 | 3 | 中生 MST |
| 红车 Syzygium rehderianum | 桃金娘科 Myrtaceae | 133 | 53 | 中生 MST |
| 子棱蒲桃 S. championii | 桃金娘科 Myrtaceae | 1 | 1 | 中生 MST |
| 黄叶树 Xanthophyllum hainanense | 远志科 Polygalaceae | 7 | 5 | 中生 MST |
| 大叶臭花椒 Zanthoxylum myriacanthum | 芸香科 Rutaceae | 1 | 1 | 中生 MST |
| 小乔木 Subarbors | ||||
| 光叶山黄皮 Aidia canthioides | 茜草科 Rubiaceae | 626 | 96 | 耐荫 ST |
| 酸味子 Antidesma japonicum | 大戟科 Euphorbiaceae | 1 | 1 | 耐荫 ST |
| 云南银柴 Aporosa yunnanensis | 大戟科 Euphorbiaceae | 12 | 9 | 耐荫 ST |
| 亮叶猴耳环 Archidendron lncidum | 含羞草科 Mimosaceae | 6 | 7 | 阳生 LD |
| 大叶土密树 Bridelia fordii | 大戟科 Euphorbiaceae | 1 | 1 | 中生 MST |
| 金叶树 Chrysophyllum lanceolatum | 山榄科 Sapotaceae | 1 | 1 | 耐荫 ST |
| 罗浮柿 Diospyros morrisiana | 柿科 Ebenaceae | 2 | 2 | 中生 MST |
| 狗骨柴 Diplospora dubia | 茜草科 Rubiaceae | 12 | 9 | 中生 MST |
| 三叉苦 Evodia lepta | 芸香科 Rutaceae | 10 | 9 | 阳生 LD |
| 岭南山竹子 Garcinia oblongifolia | 藤黄科 Guttiferae | 4 | 4 | 中生 MST |
| 越南天料木 Homalium cochinchinense | 天料木科 Samydaceae | 9 | 4 | 中生 MST |
| 鼎湖钓樟 Lindera chunii | 樟科 Lauraceae | 7 | 7 | 中生 MST |
| 山钓樟 L. metcalfiana | 樟科 Lauraceae | 28 | 25 | 中生 MST |
| 山苍子 Litsea cubeba | 樟科 Lauraceae | 1 | 1 | 阳生 LD |
| 轮叶木姜 L. verticillata | 樟科 Lauraceae | 14 | 10 | 中生 MST |
| 豺皮樟 L. rotundifolia | 樟科 Lauraceae | 1 | 1 | 阳生 LD |
| 鼎湖血桐 Macaranga sampsoni | 大戟科 Euphorbiaceae | 11 | 2 | 阳生 LD |
| 绒楠 Machilus velutina | 樟科 Lauraceae | 11 | 5 | 中生 MST |
| 谷木 Memecylon ligustrifolium | 野牡丹科 Melastomataceae | 58 | 38 | 耐荫 ST |
| 柬埔新木姜 Neolitsea membranaceum | 樟科 Lauraceae | 3 | 3 | 中生 MST |
| 新木姜 N. aurata | 樟科 Lauraceae | 1 | 1 | 中生 MST |
| 桃叶石楠 Photinia prunifolia | 蔷薇科 Rosaceae | 3 | 2 | 中生 MST |
| 密花树 Rapanea neriifolia | 紫金牛科 Myrsinaceae | 7 | 7 | 中生 MST |
| 鼎湖杜鹃 Rhododendron tinghuense | 杜鹃花科 Ericaceae | 1 | 1 | 耐荫 ST |
| 山黄麻 Trema tomentosa | 榆科 Ulmaceae | 1 | 1 | 阳生 LD |
| 重要值前10位树种 Top ten species by IV | DBH≥1 cm的个体数 No. of individuals (DBH≥1 cm) | 幼苗数目 No. of seedlings |
|---|---|---|
| 锥栗 Castanopsis chinensis | 2,311 | 6 |
| 木荷 Schima superba | 2,296 | 0 |
| 黄杞 Engelhardtia roxburghiana | 737 | 117 |
| 红车 Syzygium rehderianum | 5,990 | 133 |
| 红皮紫棱 Craibiodendron kwangtungense | 3,325 | 12 |
| 光叶山黄皮 Aidia canthioides | 5,996 | 626 |
| 厚壳桂 Cryptocarya chinensis | 2,557 | 32 |
| 黄果厚壳桂 C. concinna | 4,478 | 671 |
| 云南银柴 Aporosa yunnanensis | 3,747 | 12 |
| 罗伞树 Ardisia quinquegona | 3,702 | 70 |
Table 1 Number of individuals with DBH≥1 cm and their seedling numbers recorded in 2008 of the top ten species by importance value (IV) in the 2005 census
| 重要值前10位树种 Top ten species by IV | DBH≥1 cm的个体数 No. of individuals (DBH≥1 cm) | 幼苗数目 No. of seedlings |
|---|---|---|
| 锥栗 Castanopsis chinensis | 2,311 | 6 |
| 木荷 Schima superba | 2,296 | 0 |
| 黄杞 Engelhardtia roxburghiana | 737 | 117 |
| 红车 Syzygium rehderianum | 5,990 | 133 |
| 红皮紫棱 Craibiodendron kwangtungense | 3,325 | 12 |
| 光叶山黄皮 Aidia canthioides | 5,996 | 626 |
| 厚壳桂 Cryptocarya chinensis | 2,557 | 32 |
| 黄果厚壳桂 C. concinna | 4,478 | 671 |
| 云南银柴 Aporosa yunnanensis | 3,747 | 12 |
| 罗伞树 Ardisia quinquegona | 3,702 | 70 |
| 物种 Species | 变量 Variable | 回归系数 Coefficient | 标准误 SE | t值 t-value | P | 调整的R2 Adjusted R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 柏拉木 Blastus cochinchinensis | 凹凸度 Convexity | -0.039 | 0.019 | -2.002 | 0.047* | 0.351 |
| 谷木 Memecylon ligustrifolium | 坡向 Aspect | -0.004 | 0.002 | -2.372 | 0.019* | 0.208 |
| B10 | -0.001 | 0.001 | -2.09 | 0.038* | ||
| N10 | 0.151 | 0.03 | 4.981 | 0.000*** | ||
| 光叶山黄皮 Aidia canthioides | 凹凸度 Convexity | -0.344 | 0.09 | -3.827 | 0.000*** | 0.166 |
| 坡向 Aspect | 0.028 | 0.012 | 2.354 | 0.020* | ||
| B10 | 0.027 | 0.01 | 2.775 | 0.006** | ||
| 红车 Syzygium rehderianum | 坡向 Aspect | 0.016 | 0.007 | 2.385 | 0.018* | 0.085 |
| 华润楠 Machilus chinensis | 凹凸度 Convexity | 0.034 | 0.016 | 2.199 | 0.030* | 0.212 |
| 海拔 Altitude | -0.007 | 0.002 | -3.229 | 0.002** | ||
| B10 | 0.001 | 0 | 3.727 | 0.000*** | ||
| 黄果厚壳桂 Cryptocarya concinna | B10 | 0.012 | 0.003 | 4.093 | 0.000*** | 0.143 |
| 罗伞树 Ardisia quinquegona | 坡向 Aspect | 0.004 | 0.002 | 2.142 | 0.034* | 0.098 |
| N10 | 0.066 | 0.019 | 3.446 | 0.001*** | ||
| 小新木姜 Neolitsea umbrosa | 海拔 Altitude | 0.009 | 0.003 | 3.342 | 0.001** | 0.260 |
Table 2 Results of multiple linear regression analysis on the seedling abundance of eight species against the number of conspecifics within 10 m (N10), the sum of conspecific basal area within 10 m (B10), and the convexity, slope, aspect and altitude of the 20 m × 20 m quadrat in which the station is located. Only significant variables were listed in the table; those nonsignificant variables and intercepts were not listed.
| 物种 Species | 变量 Variable | 回归系数 Coefficient | 标准误 SE | t值 t-value | P | 调整的R2 Adjusted R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 柏拉木 Blastus cochinchinensis | 凹凸度 Convexity | -0.039 | 0.019 | -2.002 | 0.047* | 0.351 |
| 谷木 Memecylon ligustrifolium | 坡向 Aspect | -0.004 | 0.002 | -2.372 | 0.019* | 0.208 |
| B10 | -0.001 | 0.001 | -2.09 | 0.038* | ||
| N10 | 0.151 | 0.03 | 4.981 | 0.000*** | ||
| 光叶山黄皮 Aidia canthioides | 凹凸度 Convexity | -0.344 | 0.09 | -3.827 | 0.000*** | 0.166 |
| 坡向 Aspect | 0.028 | 0.012 | 2.354 | 0.020* | ||
| B10 | 0.027 | 0.01 | 2.775 | 0.006** | ||
| 红车 Syzygium rehderianum | 坡向 Aspect | 0.016 | 0.007 | 2.385 | 0.018* | 0.085 |
| 华润楠 Machilus chinensis | 凹凸度 Convexity | 0.034 | 0.016 | 2.199 | 0.030* | 0.212 |
| 海拔 Altitude | -0.007 | 0.002 | -3.229 | 0.002** | ||
| B10 | 0.001 | 0 | 3.727 | 0.000*** | ||
| 黄果厚壳桂 Cryptocarya concinna | B10 | 0.012 | 0.003 | 4.093 | 0.000*** | 0.143 |
| 罗伞树 Ardisia quinquegona | 坡向 Aspect | 0.004 | 0.002 | 2.142 | 0.034* | 0.098 |
| N10 | 0.066 | 0.019 | 3.446 | 0.001*** | ||
| 小新木姜 Neolitsea umbrosa | 海拔 Altitude | 0.009 | 0.003 | 3.342 | 0.001** | 0.260 |
| [1] | Augspurger CK (1984) Seedling survival of tropical tree species: interactions of dispersal distance, light-gaps, and pathogens. Ecology, 65, 1705-1712. |
| [2] | Connell JH, Tracey JG, Webb LJ (1984) Compensatory recruitment, growth, and mortality as factors maintaining rain forest tree diversity. Ecological Monographs, 54, 141-164. |
| [3] | Deb P, Sundriyal RC (2008) Tree regeneration and seedling survival patterns in old-growth lowland tropical rainforest in Namdapha National Park, north-east India. Forest Ecology and Management, 255, 3995-4006. |
| [4] | Du YJ (杜彦君), Peng SJ (彭闪江), Xu GL (徐国良), Huang ZL (黄忠良) (2006) Analysis of seed death of Castanopsis chinensis in the dispersal process in Dinghushan Biosphere Reserve. Ecology and Environment (生态环境), 15, 1284-1288. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [5] | Du YJ ( 杜彦君), Peng SJ ( 彭闪江), Xu GL ( 徐国良), Huang ZL ( 黄忠良), Huang YJ ( 黄玉佳) (2007) Study of distance-dependence on Castanopsis chinensis seed in coniferous and broad-leaved mixed forest of Dinghushan, China. Acta Phytoecologica Sinica (植物生态学报), 31, 998-1006.( in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [6] |
Gilbert GS, Harms KE, Hammill DN, Hubbell SP (2001) Effects of seedling size, El Niño drought, seedling density, and distance to nearest conspecific adult on 6-year survival of Ocotea whitei seedlings in Panamá. Oecologia, 127, 509-516.
DOI URL PMID |
| [7] | Grubb PJ (1977) The maintenance of species richness in plant communities: the importance of the regeneration niche. Biological Reviews, 52, 107-145. |
| [8] | Harms KE, Condit R, Hubbell SP, Foster RB (2001) Habitat associations of trees and s in a 50-ha neotropical forest plot. Journal of Ecology, 89, 947-959. |
| [9] | Hou JH (侯继华), Ma KP (马克平) (2002) On mechanisms of species coexistence in plant communities. Acta Phytoecologica Sinica (植物生态学报), 26, 1-8. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [10] | Huang ZL (黄忠良), Kong GH (孔国辉), Wei P (魏平) (1998) Plant species diversity dynamics in Dinghu Mountain forests. Chinese Biodiversity (生物多样性), 6, 116-121. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [11] | Kong GH (孔国辉), Ye WH (叶万辉), Huang ZL (黄忠良), Wei P (魏平), Huang YJ (黄玉佳) (1998) Long-term monitoring of the lower tropical evergreen broad-leaved forest in Dinghushan Biosphere Reserve (I). Species composition of Castanopsis chinensis, Cryptocarya concinna community and its contribution. Tropical and tropical Forest Ecosystem (热带亚热带森林生态系统研究), 8, 1-6. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [12] | LePage PT, Canham CD, Coates KD, Bartemucci P (2000) Seed abundance versus strate limitation of seedling recruitment in northern temperate forests of British Columbia. Canadian Journal of Forest Research, 30, 415-427. |
| [13] | Peng SJ (彭闪江), Huang ZL (黄忠良), Zhou GY (周国逸), Zhou XY (周小勇), Zhang C (张池), He WQ (贺握权) (2003) Gap formation characteristics and its effects on sapling composition and diversity in Dinghushan Biosphere Reserve. Journal of Tropical and tropical Botany (热带亚热带植物学报), 11, 229-235. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [14] | Peters HA (2003) Neighbour-regulated mortality, the influence of positive and negative density dependence on tree populations in species-rich tropical forests. Ecology Letters, 6, 757-765. |
| [15] | Qian H (2009) Beta diversity in relation to dispersal ability for vascular plants in North America. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 18, 327-332. |
| [16] |
Queenborough SA, Burslem DFRP, Garwood NC, Valencia R (2007) Neighborhood and community interactions determine the spatial pattern of tropical tree seedling survival. Ecology, 88, 2248-2258.
DOI URL PMID |
| [17] | Ribbens E, Silander JA, Pacala SW (1994) Seedling recruitment in forests: calibrating models to predict patterns of tree seedling dispersion. Ecology, 75, 1794-1806. |
| [18] | Scholl AE, Taylor AH (2006) Regeneration pattern in old- growth red fir-western white pine forests in the northern Sierra Nevada, Lake Tahoe, USA. Forest Ecology and Management, 235, 143-154. |
| [19] | Shi JH (史军辉), Huang ZL (黄忠良), Ouyang XJ (欧阳学军), Zhang C (张池), Li L (李林), Zhou XY (周小勇) (2006a) Composition of vegetation and soil seed bank in low tropical forests and their relationship. Journal of Beijing Forestry University (北京林业大学学报), 28, 22-27. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [20] | Shi JH (史军辉), Huang ZL (黄忠良), Zhou XY (周小勇), Zhang C (张池), Ouyang XJ (欧阳学军), Li L (李林) (2006 b) The regeneration strategies and spatial pattern of woody species in the mixed coniferous and broadleaf forest in Dinghu Mountain. Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Sciences Edition) (南京林业大学学报(自然科学版)), 30, 34-38. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [21] | Uriarte M, Canham CD, Thompson J, Zimmerman JK, Brokaw N (2005) Seedling recruitment in a hurricane-driven tropical forest: light limitation, density-dependence and the spatial distribution of parent trees. Journal of Ecology, 93, 291-304. |
| [22] | Wang Z, Ye W, Cao H, Huang Z, Lian J, Li L, Wei S, Sun IF (2009) Species-topography association in a species-rich tropical forest of China. Basic and Applied Ecology, 10, 648-655. |
| [23] | Wang ZH (王铸豪), He DQ (何道泉), Song SD (宋绍敦), Chen SP (陈树培), Chen DR (陈定如), Tu MZ (屠梦照) (1982) The vegetation of Ding Hu Shan Biosphere Reserve. Tropical and Subtropical Forest Ecosystem (热带亚热带森林生态系统研究), 1, 77-141.(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [24] | Wei SG (魏识广), Li L (李林), Huang ZL (黄忠良), Peng SJ (彭闪江), Shi JH (史军辉) (2005) Study on the dynamic of seed bank of Dinghushan forest soil. Ecology and Environment (生态环境), 14, 917-920. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [25] | Wright SJ, Muller-Landau HC, Calderon O, Hemandez A (2005) Annual and spatial variation in seedfall and seedling recruitment in a neotropical forest. Ecology, 86, 848-860. |
| [26] | Wright SJ, Muller-Landau HC, Condit R, Hubbell SP (2003) Gap-dependent recruitment, realized vital rates, and size distributions of tropical trees. Ecology, 84, 3174-3185. |
| [27] | Xu ZB (徐振邦), Dai LM (代力民), Chen JQ (陈吉泉), Wang Z (王战), Dai HC (戴洪才), Li X (李昕) (2001) Natural regeneration condition in Pinus koraiensis broad-leaved mixed forest. Acta Ecologica Sinica (生态学报), 21, 1413-1420. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [28] | Ye WH (叶万辉), Cao HL (曹洪麟), Huang ZL (黄忠良), Lian JY (练琚愉), Wang ZG (王志高), Li L (李林), Wei SG (魏识广), Wang ZM (王章明) (2008) Community structure of a 20 hm2 lower tropical evergreen broadleaved forest plot in Dinghushan, China. Journal of Plant Ecology Chinese Version (植物生态学报), 32, 274-286. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [29] | Zhang LY (张林艳), Ye WH (叶万辉), Huang ZL (黄忠良) (2006) Assessment of function area design in Dinghushan Biosphere Reserve using landscape ecology principles. Biodiversity Science (生物多样性), 14, 98-106. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [30] | Zhu Y, Mi XC, Ren HB, Ma KP (2010) Density dependence is prevalent in a heterogeneous tropical forest. Oikos, 119, 109-119. |
| [1] | Gong Cuifeng, Wei Wei, Luo Gai, Han Yimin, Wu Pengcheng, He Mengnan, Min Qingyue, Fu Qiang, Chen Peng. Spatial distribution and coexistence of ungulates in Chongzhou Area of Giant Panda National Park [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(3): 24260-. |
| [2] | Rui Qu, Zhenjun Zuo, Youxin Wang, Liangjian Zhang, Zhigang Wu, Xiujuan Qiao, Zhong Wang. The biogeochemical niche based on elementome and its applications in different ecosystems [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(4): 23378-. |
| [3] | Xiaobo Lü, Donghai Li, Xiaobo Yang, Mengwen Zhang. The species coexisted in mangrove communities through niche differentiation of flooding time and salinity [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(3): 23302-. |
| [4] | Guoshan Shi, Feng Liu, Guanghong Cao, Dian Chen, Shangwen Xia, Yun Deng, Bin Wang, Xiaodong Yang, Luxiang Lin. Beta diversity of woody plants in a tropical seasonal rainforest at Xishuangbanna: Roles of space, environment, and forest stand structure [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(12): 24285-. |
| [5] | Congcong Du, Xueyu Feng, Zhilin Chen. The reducing of climate niche differences in the bridgehead effect promotes the invasion of Solenopsis invicta [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(11): 24276-. |
| [6] | Xuejiao Yuan, Yuanyuan Zhang, Yanliang Zhang, Luyi Hu, Weiguo Sang, Zheng Yang, Qi Chen. Investigating the prediction ability of the species distribution model fitted with the historical distribution records of Chromolaena odorata [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(11): 24288-. |
| [7] | Jiangjian Xie, Chen Shen, Feiyu Zhang, Zhishu Xiao. Cross-regional bird species recognition method integrating audio and ecological niche information [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(10): 24259-. |
| [8] | Lixia Han, Yongjian Wang, Xuan Liu. Comparisons between non-native species invasion and native species range expansion [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(1): 23396-. |
| [9] | Zhifa Liu, Xincai Wang, Yuening Gong, Daojian Chen, Qiang Zhang. Diversity and elevational distribution of birds and mammals based on infrared camera monitoring in Guangdong Nanling National Nature Reserve [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(8): 22689-. |
| [10] | Xintong Gong, Fei Chen, Huanhuan Gao, Xinqiang Xi. Larva and adult competition between two Drosophila species and the effects on species coexistence [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(8): 22603-. |
| [11] | Kunming Zhao, Shengbin Chen, Xifu Yang. Investigation of the diversity of mammals and birds and the activity rhythm of dominant species using camera trapping in a fragmented forest in the Dujiangyan region, Sichuan Province [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(6): 22529-. |
| [12] | Buqing Peng, Ling Tao, Jing Li, Ronghui Fan, Shunde Chen, Changkun Fu, Qiong Wang, Keyi Tang. DNA metabarcoding dietary analysis of six sympatric small mammals at the Laojunshan National Nature Reserve, Sichuan Province [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(4): 22474-. |
| [13] | Shusen Fu, Puqing Song, Yuan Li, Yuanyuan Li, Ran Zhang, Hushun Zhang, Rui Wang, Longshan Lin. Trophic levels and trophic niches of fish from the Bering Sea and Chukchi Sea [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(4): 22521-. |
| [14] | Minhao Chen, Chao Zhang, Jiadong Wang, Zhenjie Zhan, Junzhi Chen, Xiaofeng Luan. Distribution and niche overlap of American mink and Eurasian otter in Northeast China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(1): 22289-. |
| [15] | Tingting Li, Xihong Zhu, Guangnian Wu, Xiao Song, Aichun Xu. Spawning ground microhabitat selection by the Chinhai spiny newt (Echinotriton chinhaiensis) [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(1): 22293-. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2022 Biodiversity Science
Editorial Office of Biodiversity Science, 20 Nanxincun, Xiangshan, Beijing 100093, China
Tel: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn ![]()