



Biodiv Sci ›› 2010, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (3): 251-261. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2010.251 cstr: 32101.14.SP.J.1003.2010.251
• Special Issue • Previous Articles Next Articles
Liang Zhao1,2, Jie Zhang2, Zhijin Liu2, Muqi Xu2, Ming Li2,*( )
)
Received:2009-12-28
Accepted:2010-05-11
Online:2010-05-20
Published:2012-02-08
Contact:
Ming Li
Liang Zhao, Jie Zhang, Zhijin Liu, Muqi Xu, Ming Li. Population genetic structure and demographic history of Neosalanx jordanibased on cytochrome b sequences[J]. Biodiv Sci, 2010, 18(3): 251-261.
| 单倍型 Haplotypes | 长江流域 Yangtze River Basin | 淮河流域 Huaihe River Basin | 合计 Total | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 太湖 Taihu lake | 南漪湖 Nanyihu lake | 鄱阳湖 Poyanghu lake | 洪泽湖 Hongzehu lake | 瓦埠湖 Wabuhu lake | |||
| M01 | 1 | 1 | |||||
| M02 | 1 | 1 | |||||
| M03 | 3 | 3 | |||||
| M04 | 2 | 2 | |||||
| M05 | 1 | 1 | |||||
| M06 | 1 | 1 | |||||
| M07 | 1 | 1 | |||||
| M08 | 1 | 1 | |||||
| M09 | 4 | 4 | |||||
| M10 | 1 | 1 | |||||
| M11 | 1 | 1 | |||||
| M12 | 4 | 15 | 2 | 21 | |||
| M13 | 3 | 3 | |||||
| M14 | 2 | 2 | |||||
| M15 | 1 | 1 | |||||
| M16 | 1 | 1 | 2 | ||||
| M17 | 17 | 23 | 3 | 16 | 21 | 80 | |
| M18 | 3 | 3 | |||||
| 样本量 Sample number | 30 | 25 | 24 | 25 | 25 | 129 | |
Table 1 Distribution and the number of mtDNA Cyt b haplotypes in each population ofNeosalanx jordani
| 单倍型 Haplotypes | 长江流域 Yangtze River Basin | 淮河流域 Huaihe River Basin | 合计 Total | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 太湖 Taihu lake | 南漪湖 Nanyihu lake | 鄱阳湖 Poyanghu lake | 洪泽湖 Hongzehu lake | 瓦埠湖 Wabuhu lake | |||
| M01 | 1 | 1 | |||||
| M02 | 1 | 1 | |||||
| M03 | 3 | 3 | |||||
| M04 | 2 | 2 | |||||
| M05 | 1 | 1 | |||||
| M06 | 1 | 1 | |||||
| M07 | 1 | 1 | |||||
| M08 | 1 | 1 | |||||
| M09 | 4 | 4 | |||||
| M10 | 1 | 1 | |||||
| M11 | 1 | 1 | |||||
| M12 | 4 | 15 | 2 | 21 | |||
| M13 | 3 | 3 | |||||
| M14 | 2 | 2 | |||||
| M15 | 1 | 1 | |||||
| M16 | 1 | 1 | 2 | ||||
| M17 | 17 | 23 | 3 | 16 | 21 | 80 | |
| M18 | 3 | 3 | |||||
| 样本量 Sample number | 30 | 25 | 24 | 25 | 25 | 129 | |
| 种群 Population | 样本量 Number of samples (N) | 单倍型数量 Number of haplotypes (H) | 单倍型多样性 Haplotype diversity (h±SD) | 多态性位点数 Number of polymorphic sites (S) | 核苷酸多样性 Nucleotide diversity (π±SD) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 长江流域 Yangtze River Basin | |||||
| 太湖 Taihu lake | 30 | 8 | 0.664±0.089 | 7 | 0.00077±0.00015 |
| 南漪湖 Nanyihu lake | 25 | 3 | 0.157±0.096 | 5 | 0.00035±0.00022 |
| 鄱阳湖 Poyanghu lake | 24 | 5 | 0.587±0.102 | 5 | 0.00085±0.00019 |
| 小计 Subtotal | 79 | 13 | 0.648±0.049 | 16 | 0.00093±0.00013 |
| 淮河流域 Huaihe River Basin | |||||
| 洪泽湖 Hongzehu lake | 25 | 6 | 0.583±0.109 | 6 | 0.00067±0.00017 |
| 瓦埠湖 Wabuhu lake | 25 | 3 | 0.290±0.109 | 5 | 0.00072±0.00028 |
| 小计 Subtotal | 50 | 7 | 0.449±0.086 | 9 | 0.00071±0.00018 |
| 总体 All samples | 129 | 18 | 0.590±0.047 | 24 | 0.00088±0.00011 |
Table 2 Genetic diversity indices of Neosalanx jordanipopulations
| 种群 Population | 样本量 Number of samples (N) | 单倍型数量 Number of haplotypes (H) | 单倍型多样性 Haplotype diversity (h±SD) | 多态性位点数 Number of polymorphic sites (S) | 核苷酸多样性 Nucleotide diversity (π±SD) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 长江流域 Yangtze River Basin | |||||
| 太湖 Taihu lake | 30 | 8 | 0.664±0.089 | 7 | 0.00077±0.00015 |
| 南漪湖 Nanyihu lake | 25 | 3 | 0.157±0.096 | 5 | 0.00035±0.00022 |
| 鄱阳湖 Poyanghu lake | 24 | 5 | 0.587±0.102 | 5 | 0.00085±0.00019 |
| 小计 Subtotal | 79 | 13 | 0.648±0.049 | 16 | 0.00093±0.00013 |
| 淮河流域 Huaihe River Basin | |||||
| 洪泽湖 Hongzehu lake | 25 | 6 | 0.583±0.109 | 6 | 0.00067±0.00017 |
| 瓦埠湖 Wabuhu lake | 25 | 3 | 0.290±0.109 | 5 | 0.00072±0.00028 |
| 小计 Subtotal | 50 | 7 | 0.449±0.086 | 9 | 0.00071±0.00018 |
| 总体 All samples | 129 | 18 | 0.590±0.047 | 24 | 0.00088±0.00011 |
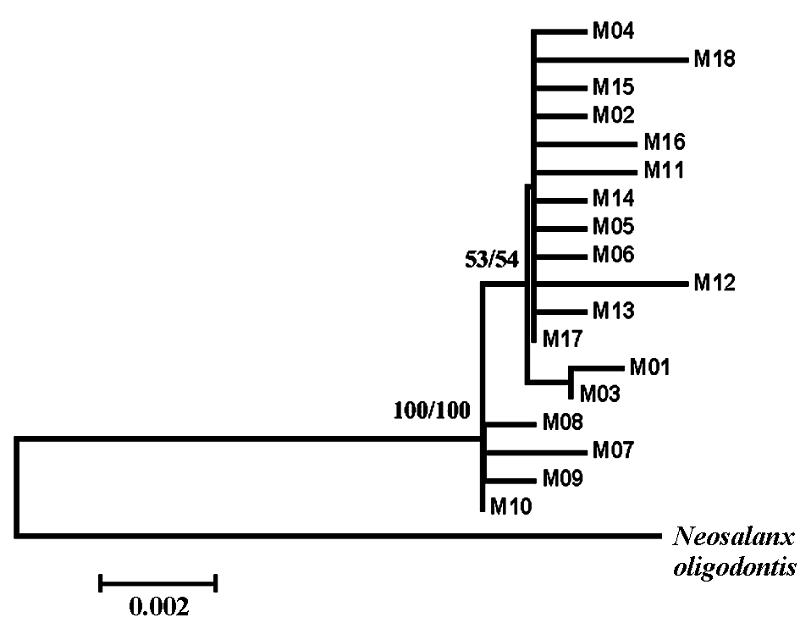
Fig. 1 Neighbor-joining and Maximum-likelihood tree for all 18 haplotypes of Neosalanx jordani and for one outgroup taxa, N. oligodontis. Values indicate bootstrap support for each node.
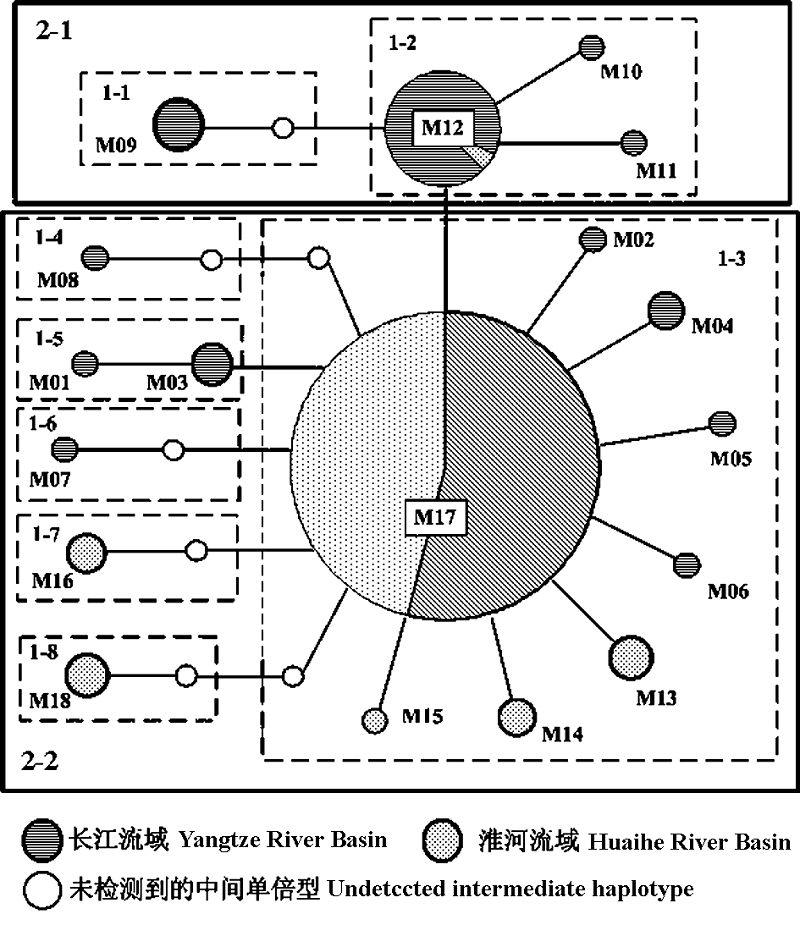
Fig. 2 Minimum spanning network based on statistical parsimony using TCS software. Nodes indicate the haplotypes number and are proportional to the haplotype frequency. White nodes indicate undetected intermediate haplotype. Boxes indicate one-step to two-step nesting levels for the nested clade analysis.
| 变异来源 Source of variation | 自由度 d.f. | 平方和 Sum of squares | 变异组分 Variance components | 变异百分比 % variation | Ф-统计量 Ф-statistics |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 流域间 Among basins | 1 | 4.491 | -0.0292 | -4.40 | ФCT =- 0.04396 |
| 流域内 Within basins | 3 | 18.961 | 0.2269 | 34.17 | ФSC= 0.3273** |
| 种群内 Within populations | 124 | 57.817 | 0.4663 | 70.22 | ФST = 0.2978** |
| 总和 Total | 128 | 81.270 | 0.6640 |
Table 3 Results of AMOVA forNeosalanx jordani mtDNA Cyt b estimation using Ф-statistics
| 变异来源 Source of variation | 自由度 d.f. | 平方和 Sum of squares | 变异组分 Variance components | 变异百分比 % variation | Ф-统计量 Ф-statistics |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 流域间 Among basins | 1 | 4.491 | -0.0292 | -4.40 | ФCT =- 0.04396 |
| 流域内 Within basins | 3 | 18.961 | 0.2269 | 34.17 | ФSC= 0.3273** |
| 种群内 Within populations | 124 | 57.817 | 0.4663 | 70.22 | ФST = 0.2978** |
| 总和 Total | 128 | 81.270 | 0.6640 |
| 嵌套枝 Nested clade | P 值 Pvalue | 内部枝 Interior clades | 枝距离 Clade distance (DC) | 嵌套枝距离 Nested clade distance (DN) | 推断 Inference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clade 1-3 | 0.000 | clade M02 (Tip) | 181.97 | 195.76 | 1-2-11RE-12-13-14 LDC/PF |
| clade M04 (Tip) | 0.00S | 249.12L | |||
| clade M05 (Tip) | 0.00 | 0.00 | |||
| clade M06 (Tip) | 0.00S | 178.79S | |||
| clade M13 (Tip) | 0.00S | 261.54L | |||
| clade M14 (Tip) | 89.68 S | 236.22 L | |||
| clade M15 (Tip) | 17.47S | 130.44S | |||
| clade M17 (Interior) | 19.87S | 194.75 | |||
| I-T | -3.78 | 0.00 | |||
| Clade 2-1 | 0.000 | clade 1-1 (Tip) | 247.12L | 281.70L | 1-2-11RE-12CRE |
| clade 1-2 (Interior) | 54.98S | 106.53S | |||
| I-T | -192.14S | -175.16S | |||
| Clade 2-2 | 0.000 | clade 1-3 (Interior) | 129.83S | 187.67 | 1-2-11RE-12CRE |
| clade 1-4 (Tip) | 44.50S | 176.87 | |||
| clade 1-5 (Tip) | 0.00S | 312.79L | |||
| clade 1-6 (Tip) | 0.00S | 196.43 | |||
| clade 1-7 (Tip) | 41.62S | 173.41 | |||
| clade 1-8 (Tip) | 79.46 | 173.26 | |||
| I-T | 98.96 | 0.96 | |||
| Total cladogram | 0.000 | clade 2-1 (Tip) | 239.66 | 227.23 | 1-2-11RE-12 CRE |
| clade 2-2 (Interior) | 0.00S | 136.82S | |||
| I-T | -241.43L | -1,100.14L |
Table 4 Results of the nested clade analysis of Neosalanx jordani mtDNACyt b haplotypes
| 嵌套枝 Nested clade | P 值 Pvalue | 内部枝 Interior clades | 枝距离 Clade distance (DC) | 嵌套枝距离 Nested clade distance (DN) | 推断 Inference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clade 1-3 | 0.000 | clade M02 (Tip) | 181.97 | 195.76 | 1-2-11RE-12-13-14 LDC/PF |
| clade M04 (Tip) | 0.00S | 249.12L | |||
| clade M05 (Tip) | 0.00 | 0.00 | |||
| clade M06 (Tip) | 0.00S | 178.79S | |||
| clade M13 (Tip) | 0.00S | 261.54L | |||
| clade M14 (Tip) | 89.68 S | 236.22 L | |||
| clade M15 (Tip) | 17.47S | 130.44S | |||
| clade M17 (Interior) | 19.87S | 194.75 | |||
| I-T | -3.78 | 0.00 | |||
| Clade 2-1 | 0.000 | clade 1-1 (Tip) | 247.12L | 281.70L | 1-2-11RE-12CRE |
| clade 1-2 (Interior) | 54.98S | 106.53S | |||
| I-T | -192.14S | -175.16S | |||
| Clade 2-2 | 0.000 | clade 1-3 (Interior) | 129.83S | 187.67 | 1-2-11RE-12CRE |
| clade 1-4 (Tip) | 44.50S | 176.87 | |||
| clade 1-5 (Tip) | 0.00S | 312.79L | |||
| clade 1-6 (Tip) | 0.00S | 196.43 | |||
| clade 1-7 (Tip) | 41.62S | 173.41 | |||
| clade 1-8 (Tip) | 79.46 | 173.26 | |||
| I-T | 98.96 | 0.96 | |||
| Total cladogram | 0.000 | clade 2-1 (Tip) | 239.66 | 227.23 | 1-2-11RE-12 CRE |
| clade 2-2 (Interior) | 0.00S | 136.82S | |||
| I-T | -241.43L | -1,100.14L |
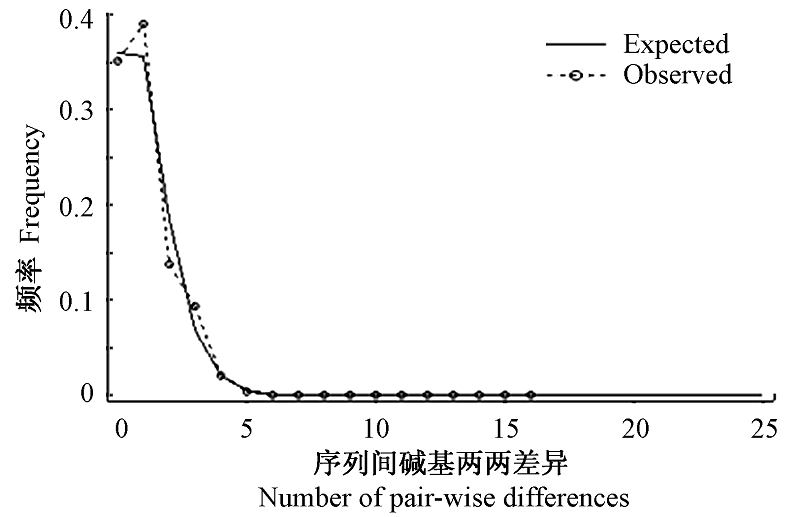
Fig. 4 Observed and expected mismatch distributions showing the frequencies of pair-wise differences. The observed pair-wise difference (dashed line), and the expected mismatch distributions under the sudden expansion model (solid line) ofCyt b.
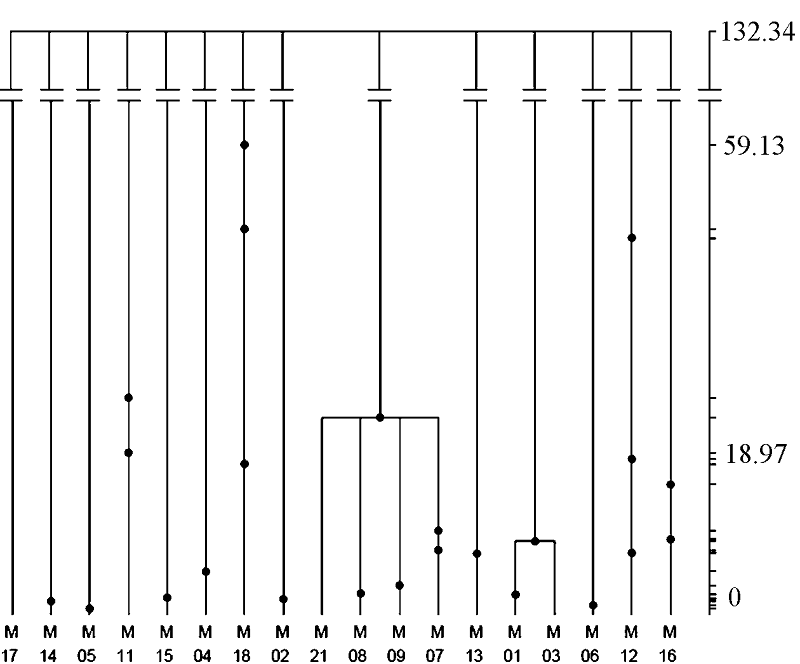
Fig. 5 Gene tree of the Neosalanx jordani mitochondrialCyt bgene. The tree is based on 1,000,000 coalescent simulations. The right coordinate is scaled by absolute coalescent time (kyr), and the dots in the tree shows the ancestral distribution of mutations in the population history.
| [1] | Akaike H (1974) A new look at the statistical model identification. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, AC-19, 716-723. |
| [2] |
Avise JC (1989) A role for molecular genetics in the recognition and conservation of endangered species. Trends in Ecology and Evolution, 4, 279-281.
DOI URL PMID |
| [3] | Avise JC (2000) Phylogeography: the History and Formation of Species. Harvard University Press, Cambridge. |
| [4] |
Bahlo M, Griffiths RC (2000) Inference from gene trees in a subdivided population. Theoretical Population Biology, 57, 79-95.
URL PMID |
| [5] | Beheregaray LB, Ciofi C, Geist D, Gibbs JP, Caccone A, Powell JR (2003) Genes record a prehistoric volcanoe eruption in the Galapagos. Science, 302, 75. |
| [6] |
Buhay JE, Crandall KA (2005) Subterranean phylogeography of freshwater crayfishes shows extensive gene flow and surprisingly large population sizes. Molecular Ecology, 14, 4259-4273.
URL PMID |
| [7] |
Cantatore P, Roberti M, Pesole G, Ludovico A, Milella F, Gadaleta MN, Saccone C (1994) Evolutionary analysis of cytochrome b sequences in some Perciformes: evidence for a slower rate of evolution than in mammals. Journal of Molecular Evolution, 39, 589-597.
URL PMID |
| [8] | Cheng QT (成庆泰), Zheng BS (郑葆珊) (1987) Systematic Synopsis of Chinese Fishes (中国鱼类系统检索). Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [9] |
Clement M, Posada D, Crandall KA (2000) TCS: a computer program to estimate gene genealogies. Molecular Ecology, 9, 1657-1659.
URL PMID |
| [10] | Cook RM, Sinclair A, Stefansson G (1997) Potential collapse of North Sea cod stocks. Nature, 385, 521-522. |
| [11] |
Cortey M, Pla C, García-Marín JL (2004) Historical biogeography of Mediterranean trout. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 33, 831-844.
DOI URL PMID |
| [12] |
Crandall KA, Templeton AR (1993) Empirical tests of some predictions from coalescent theory with applications to intraspecific phylogeny reconstruction. Genetics, 134, 959-969.
URL PMID |
| [13] | Currens KP, Schreck CB, Li WH (1990) Allozyme and morphological divergence of rainbow trout ( Oncorhynchus mykiss) above and below waterfalls in the Deschutes River, Oregon. Copeia, 1990, 730-746. |
| [14] | Emerson BC, Paradis E, Thebaud C (2001) Revealing the demographic histories of species using DNA sequences. Trends in Ecology and Evolution, 16, 707-716. |
| [15] |
Excoffier L, Laval LG, Schneider S (2005) Arlequin ver. 3.0: an integrated software package for population genetics data analysis. Evolutionary Bioinformatics Online, 1, 47-50.
URL PMID |
| [16] | Fang P (1934a) Study on the fishes referring to Salangidae of China. Sinensia, 4, 231-268. |
| [17] | Fang P (1934b) Supplementary notes on the fishes referring to Salangidae of China. Sinensia, 5, 505-511. |
| [18] | Frankham R (1996) Relationship of genetic variation to population size in wildlife. Conservation Biology, 10, 1500-1508. |
| [19] |
Fu YX (1997) Statistical tests of neutrality of mutations against population growth, hitchhiking and background selection. Genetics, 147, 915-925.
URL PMID |
| [20] | Grant WAS, Bowen BW (1998) Shallow population histories in deep evolutionary lineages of marine fishes: insights from sardines and anchovies and lessons for conservation. Journal of Heredity, 89, 415-426. |
| [21] |
Harpending H (1994) Signature of ancient population growth in a low-resolution mitochondrial DNA mismatch distribution. Human Biology, 66, 591-600.
URL PMID |
| [22] |
Hashiguchi Y, Kado T, Kimura S, Tachida H (2006) Comparative phylogeography of two bitterlings, Tanakia lanceolata and T. limbata (Teleostei, Cyprinidae), in Kyushu and adjacent districts of western Japan, based on mitochondrial DNA analysis. Zoological Science, 23, 309-322.
URL PMID |
| [23] | Hynes R, Ferguson A, McCann M (1996) Variation in mitochondrial DNA and post-glacial colonisation of north-west Europe by brown trout ( Salmo trutta L.). Journal of Fish Biology, 48, 54-67. |
| [24] | Ihaka R, Gentleman R (1996) R: a language for data analysis and graphics. Journal of Computational and Graphical Statistics, 5, 299-314. |
| [25] | Inoue JG, Miya M, Tsukamoto K, Nishida M (2000) Complete mitochondrial DNA sequence of the Japanese sardine Sardinops melanostictus. Fisheries Science, 66, 924-932. |
| [26] |
Joy DA, Feng X, Mu J, Furuya T, Chotivanich K, Krettli AU, Ho M, Wang A, White NJ, Suh E, Beerli P, Su XZ (2003) Early origin and recent expansion of Plasmodium falciparum. Science, 300, 318-321.
URL PMID |
| [27] | Kamal MI, Richard AN, Godfrey MH (1996) Spatial patterns of genetic variation generated by different forms of dispersal during range expansion. Heredity, 77, 282-291. |
| [28] |
Kuhner MK, Yamato J, Felsenstein J (1998) Maximum likelihood estimation of population growth rates based on the coalescent. Genetics, 149, 429-434.
URL PMID |
| [29] |
Lambeck K, Esat TM, Potter EK (2002) Links between climate and sea levels for the past three million years. Nature, 419, 199-206.
DOI URL PMID |
| [30] | Li N (李娜), Chen SB (陈少波), Xie QL (谢起浪), Lü JX (吕建新), Guan MX (管敏鑫) (2008) Polymorphisms of mitochondrial Cyt b gene and D-loop region in sweetfish ( Plecoglossus altivelis Temminck et Schlegel) from Zhejiang and Fujian provinces. Hereditas (Beijing) (遗传), 30, 919-925. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [31] |
Mantel N (1967) The detection of disease clustering and a generalized regression approach. Cancer Research, 27, 209-220.
URL PMID |
| [32] | McCusker MR, Parkinson E, Taylor EB (2000) Mitochondrial DNA variation in rainbow trout ( Oncorhynchus mykiss) across its native range: testing biogeographical hypotheses and their relevance to conservation. Molecular Ecology, 9, 2089-2108. |
| [33] |
McGlashan DJ, Hughes JM (2000) Reconciling patterns of genetic variation with stream structure, earth history and biology in the Australian freshwater fish Craterocephalus stercusmuscarum (Atherinidae). Molecular Ecology, 9, 1737-1751.
DOI URL PMID |
| [34] | Moritz C (1994) Applications of mitochondrial DNA analysis in conservation: a critical review. Molecular Ecology, 3, 401-411. |
| [35] | Nelson J (1994) Fishes of the World, 3rd edn. John Wiley and Sons, Inc., New York. |
| [36] | Perdices A, Sayanda D, Coelho MM (2005) Mitochondrial diversity of Opsariichthys bidens (Teleostei, Cyprinidae) in three Chinese drainages. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 37, 920-927. |
| [37] |
Posada D, Crandall KA (1998) MODELTEST: testing the model of DNA substitution. Bioinformatics, 14, 817-818.
DOI URL PMID |
| [38] |
Posada D, Crandall KA (2001) Intraspecific gene genealogies: trees grafting into networks. Trends in Ecology and Evolution, 16, 37-45.
DOI URL PMID |
| [39] |
Posada D, Crandall KA, Templeton AR (2000) GeoDis: a program for the cladistic nested analysis of the geographical distribution of genetic haplotypes. Molecular Ecology, 9, 487-488.
URL PMID |
| [40] |
Pybus OG, Rambaut A, Harvey PH (2000) An integrated framework for the inference of viral population history from reconstructed genealogies. Genetics, 155, 1429-1437.
URL PMID |
| [41] |
Ramos-Onsins SE, Rozas J (2002) Statistical properties of new neutrality tests against population growth. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 19, 2092-2100.
DOI URL PMID |
| [42] |
Riley SPD, Pollinger JP, Sauvajot RM, York EC, Bromley C, Fuller TK, Wayne RK (2006) A southern California freeway is a physical and social barrier to gene flow in carnivores. Molecular Ecology, 15, 1733-1741.
DOI URL PMID |
| [43] |
Rogers AR, Harpending H (1992) Population growth makes waves in the distribution of pairwise genetic differences. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 9, 552-569.
DOI URL PMID |
| [44] |
Rozas J, Sanchez-DelBarrio JC, Messeguer X, Rozas R (2003) DnaSP, DNA polymorphism analyses by the coalescent and other methods. Bioinformatics, 19, 2496-2497.
DOI URL PMID |
| [45] | Sheldon JM, Robert HD, Michael JS (1996) Phylogeny of Pacific salmon and trout based on growth hormone type-2 and mitochondrial NADH dehydrogenase subunit 3 DNA sequences. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, 53, 1165-1176. |
| [46] |
Sigurgislason H, Arnason E (2003) Extent of mitochondrial DNA sequence variation in Atlantic cod from the Faroe Islands: a resolution of gene genealogy. Heredity, 91, 557-564.
DOI URL PMID |
| [47] |
Slatkin M, Hudson RR (1991) Pairwise comparisons of mitochondrial DNA sequences in stable and exponentially growing populations. Genetics, 129, 555-562.
URL PMID |
| [48] | Smith GR (1992) Introgression in fishes: significance for paleontology, cladistics, and evolutionary rates. Systematic Biology, 41, 41-57. |
| [49] |
Strimmer K, Pybus OG (2001) Exploring the demographic history of DNA sequences using the generalized skyline plot. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 18, 2298-2305.
DOI URL PMID |
| [50] | Swofford D (2002) Paup*: Phylogenetic Analysis Using Parsimony (*and Other Methods), Version 4.0b10. Sinauer Associates, Sunderland, Massachusetts. |
| [51] |
Takehana Y, Uchiyama S, Matsuda M, Jeon SR, Sakaizumi M (2004) Geographic variation and diversity of the cytochrome b gene in wild populations of medaka ( Oryzias latipes) from Korea and China. Zoological Science, 21, 483-491.
DOI URL PMID |
| [52] |
Tamura K, Dudley J, Nei M, Kumar S (2007) MEGA4: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis (MEGA) software Version 4.0. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 24, 1596-1599.
URL PMID |
| [53] |
Templeton AR (2004) Statistical phylogeography: methods of evaluating and minimizing inference errors. Molecular Ecology, 13, 789-809.
URL PMID |
| [54] |
Templeton AR, Boerwinkle E, Sing CF (1987) A cladistic analysis of phenotypic associations with haplotypes inferred from restriction endonuclease mapping. I. Basic theory and an analysis of alcohol dehydrogenase activity in Drosophila. Genetics, 117, 343-351.
URL PMID |
| [55] |
Templeton AR, Crandall KA, Sing CF (1992) A cladistic analysis of phenotypic associations with haplotypes inferred from restriction endonuclease mapping and DNA sequence data. III. Cladogram estimation. Genetics, 132, 619-633.
URL PMID |
| [56] |
Templeton AR, Sing CF (1993) A cladistic analysis of phenotypic associations with haplotypes inferred from restriction endonuclease mapping. IV. Nested analyses with cladogram uncertainty and recombination. Genetics, 134, 659-669.
URL PMID |
| [57] | Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Plewniak F, Jeanmougin F, Higgins DG (1997) The CLUSTAL X windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Research, 25, 4876-4882. |
| [58] | Waits L (1989) Mitochondrial DNA phylogeography of the North American brown bear and implications for conservation. Conservation Biology, 13, 408-417. |
| [59] | Wang SM (王苏民), Dou HS (窦鸿身) (1998) The Lakes of China (中国湖泊志). Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [60] | Wang ZS (王忠锁), Fu CZ (傅萃长), Lei GC (雷光春) (2002) Biodiversity of Chinese icefishes (Salangidae) and their conserving strategies. Biodiversity Science (生物多样性), 10, 416-424. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [61] | Ward R, Woodwark M, Skibinski O (1994) A comparison of genetic diversity levels in marine, freshwater and anadromous fishes. Journal of Fish Biology, 44, 213-232. |
| [62] |
Watterson GA (1975) On the number of segregating sites in genetical models without recombination. Theoretical Population Biology, 7, 256-276.
DOI URL PMID |
| [63] |
Whiteley AR, Spruell P, Allendorf FW (2006) Can common species provide valuable information for conservation? Molecular Ecology, 15, 2767-2786.
DOI URL PMID |
| [64] | Xia DQ (夏德全), Cao Y (曹萤), Wu TT (吴婷婷), Yang H (杨弘) (2000) Study on lineages of Protosalanx chinensis, Neosalanx taihuensis and N. oligodontis in Taihu Lake with RAPD technique. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China (中国水产科学), 7, 12-15. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [65] | Xia YZ, Chen YY, Sheng Y (2006) Phylogeographic structure of lenok ( Brachymystax lenok Pallas) (Salmoninae, Salmonidae) populations in water systems of eastern China, inferred from mitochondrial DNA sequences. Zoological Studies, 45, 190-200. |
| [66] | Zhang Y (张颖), Dong S (董仕), Wang Q (王茜), Sun ZR (孙振荣) (2005) The isozyme genetic structures in large icefish ( Protosalanx hyalocranius) and Taihu Lake icefish (Neosalanx taihuensis). Journal of Dalian Fisheries University (大连水产学院学报), 20, 111-115. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [67] | Zhang YL, Qiao XG (1994) Study on phylogeny and zoogeography of fishes of the family Salangidae. Acta Zoologica Taiwanica, 5, 95-115. |
| [68] | Zhao L, Zhang J, Liu Z, Funk S, Wei F, Xu M, Li M (2008) Complex population genetic and demographic history of the Salangid, Neosalanx taihuensis, based on cytochrome b sequences. BMC Evolutionary Biology, 8, 201. |
| [1] | Hong Deng, Zhanyou Zhong, Chunni Kou, Shuli Zhu, Yuefei Li, Yuguo Xia, Zhi Wu, Jie Li, Weitao Chen. Population genetic structure and evolutionary history of Hemibagrus guttatus based on mitochondrial genomes [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(1): 24241-. |
| [2] | Jiachen Wang, Tangjun Xu, Wei Xu, Gaoji Zhang, Yijin You, Honghua Ruan, Hongyi Liu. Impact of urban landscape pattern on the genetic structure of Thereuopoda clunifera population in Nanjing, China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(1): 24251-. |
| [3] | Xianglin Yang, Caiyun Zhao, Junsheng Li, Fangfang Chong, Wenjin Li. Invasive plant species lead to a more clustered community phylogenetic structure: An analysis of herbaceous plants in Guangxi’s national nature reserves [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(11): 24175-. |
| [4] | Weiyue Sun, Jiangping Shu, Yufeng Gu, Morigengaowa, Xiajin Du, Baodong Liu, Yuehong Yan. Conservation genomics analysis revealed the endangered mechanism of Adiantum nelumboides [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2022, 30(7): 21508-. |
| [5] | Yahong Zhang, Huixia Jia, Zhibin Wang, Pei Sun, Demei Cao, Jianjun Hu. Genetic diversity and population structure of Populus yunnanensis [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2019, 27(4): 355-365. |
| [6] | Xingtong Wu, Lu Chen, Minqiu Wang, Yuan Zhang, Xueying Lin, Xinyu Li, Hong Zhou, Yafeng Wen. Population structure and genetic divergence in Firmiana danxiaensis [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2018, 26(11): 1168-1179. |
| [7] | Qingqing Liu, Zhijun Dong. Population genetic structure of Gonionemus vertens based on the mitochondrial COI sequence [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2018, 26(11): 1204-1211. |
| [8] | Rong Li, Hang Sun. Phylofloristics: a case study from Yunnan, China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2017, 25(2): 195-203. |
| [9] | Xiao Luo, Feng Li, Jing Chen, Zhigang Jiang. The taxonomic status of badgers in the Qinghai Lake area and evolutionary history of Meles [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2016, 24(6): 694-700. |
| [10] | Siyuan Ren, Ting Wang, Yan Zhu, Yongzhong Ye, Zhiliang Yuan, Cong Li, Na Pan, Luxin Li. Phylogenetic structure of individuals with different DBH sizes in a deciduous broad-leaved forest community in the temperate-subtropical ecological transition zone, China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2014, 22(5): 574-582. |
| [11] | Min Xiong, Shuang Tian, Zhirong Zhang, Dengmei Fan, Zhiyong Zhang. Population genetic structure and conservation units of Sinomanglietia glauca (Magnoliaceae) [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2014, 22(4): 476-484. |
| [12] | Aihong Yang, Jinju Zhang, Hua Tian, Xiaohong Yao, Hongwen Huang. Microsatellite genetic diversity and fine-scale spatial genetic structure within a natural stand of Liriodendron chinense (Magnoliaceae) in Lanmushan, Duyun City, Guizhou Province [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2014, 22(3): 375-384. |
| [13] | Gangbiao Xu,Yan Liang,Yan Jiang,Xiongsheng Liu,Shangli Hu,Yufei Xiao,Bobo Hao. Genetic diversity and population structure of Bretschneidera sinensis, an endangered species [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2013, 21(6): 723-731. |
| [14] | Deyun Wang,Jie Peng,Yajing Chen,Guosheng Lü,Xiaoping Zhang,Jianwen Shao. Genetic diversity and genetic structure of the rare and endangered species, Primula ranunculoides [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2013, 21(5): 601-609. |
| [15] | Jingjing Li,Jie Zhang,Zimin Hu,Delin Duan. Population genetics and demographic history of red seaweed, Palmaria palmata, from the Canada-northwest Atlantic [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2013, 21(3): 306-314. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2022 Biodiversity Science
Editorial Office of Biodiversity Science, 20 Nanxincun, Xiangshan, Beijing 100093, China
Tel: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn ![]()