



Biodiv Sci ›› 2021, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (12): 1687-1699. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2021141 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2021141
Special Issue: 土壤生物与土壤健康
• Reviews • Previous Articles Next Articles
Dong Dai1,2, Hua Xing1,2, Jiarong Yang1,2, Yajing Liu1,2, Huanman Cai3, Yu Liu1,2,4,*( )
)
Received:2021-04-14
Accepted:2021-07-20
Online:2021-12-20
Published:2021-11-12
Contact:
Yu Liu
Dong Dai, Hua Xing, Jiarong Yang, Yajing Liu, Huanman Cai, Yu Liu. Advances in mechanisms of rare species maintenance and plant-soil feedback in plant communities[J]. Biodiv Sci, 2021, 29(12): 1687-1699.
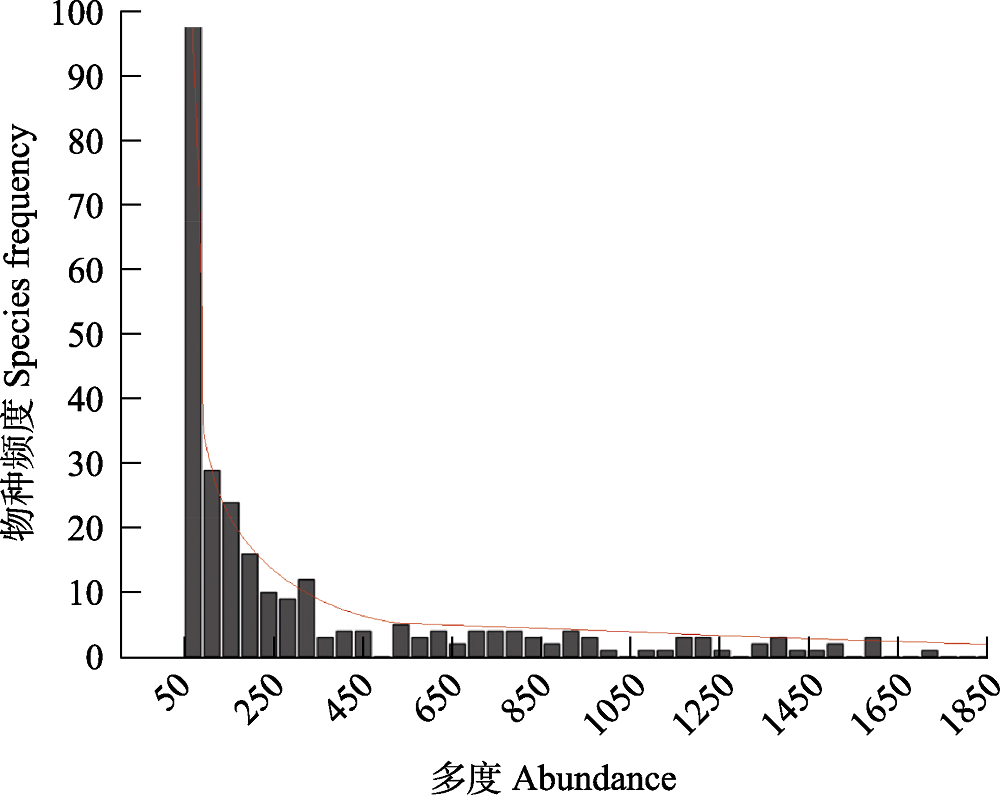
Fig. 1 The relationship between tree species frequency and species abundance in Barro Colorado Island (BCI) 50 ha tropical forest dynamics plot. The curve is the trend line. Width of each bar represents abundance span for 50 (e.g. the fist bar for the abundance from 1 to 50; the abundance is not complete due to the limitation of the picture size).
| [1] |
Adler PB, HilleRisLambers J, Levine JM (2007) A niche for neutrality. Ecology Letters, 10, 95-104.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
Ai D, Chu CJ, Ellwood MDF, Hou R, Wang G (2013) Migration and niche partitioning simultaneously increase species richness and rarity. Ecological Modelling, 258, 33-39.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
Augspurger CK (1984) Seedling survival of tropical tree species: Interactions of dispersal distance, light-gaps, and pathogens. Ecology, 65, 1705-1712.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
Augspurger CK, Kelly CK (1984) Pathogen mortality of tropical tree seedlings: Experimental studies of the effects of dispersal distance, seedling density, and light conditions. Oecologia, 61, 211-217.
DOI PMID |
| [5] |
Bachelot B, Kobe RK (2013) Rare species advantage? Richness of damage types due to natural enemies increases with species abundance in a wet tropical forest. Journal of Ecology, 101, 846-856.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
Bachelot B, Kobe RK, Vriesendorp C (2015) Negative density- dependent mortality varies over time in a wet tropical forest, advantaging rare species, common species, or no species. Oecologia, 179, 853-861.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
Bachelot B, Uriarte M, McGuire KL, Thompson J, Zimmerman J (2017) Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal diversity and natural enemies promote coexistence of tropical tree species. Ecology, 98, 712-720.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
Bagchi R, Gallery RE, Gripenberg S, Gurr SJ, Narayan L, Addis CE, Freckleton RP, Lewis OT (2014) Pathogens and insect herbivores drive rainforest plant diversity and composition. Nature, 506, 85-88.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
Balzergue C, Puech-Pagès V, Bécard G, Rochange SF (2011) The regulation of arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiosis by phosphate in pea involves early and systemic signalling events. Journal of Experimental Botany, 62, 1049-1060.
DOI PMID |
| [10] |
Bayandala, Masaka K, Seiwa K (2017) Leaf diseases drive the Janzen-Connell mechanism regardless of light conditions: A 3-year field study. Oecologia, 183, 191-199.
DOI PMID |
| [11] |
Bell T, Freckleton RP, Lewis OT (2006) Plant pathogens drive density-dependent seedling mortality in a tropical tree. Ecology Letters, 9, 569-574.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
Bellard C, Bertelsmeier C, Leadley P, Thuiller W, Courchamp F (2012) Impacts of climate change on the future of biodiversity. Ecology Letters, 15, 365-377.
DOI PMID |
| [13] |
Bever JD (1999) Dynamics within mutualism and the maintenance of diversity: Inference from a model of interguild frequency dependence. Ecology Letters, 2, 52-61.
DOI URL |
| [14] | Bever JD (2002) Negative feedback within a mutualism:Host-specific growth of mycorrhizal fungi reduces plant benefit. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 269, 2595-2601. |
| [15] |
Branscheid A, Sieh D, Pant BD, May P, Devers EA, Elkrog A, Schauser L, Scheible WR, Krajinski F (2010) Expression pattern suggests a role of MiR399 in the regulation of the cellular response to local Pi increase during arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiosis. Molecular Plant Microbe Interactions, 23, 915-926.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
Brown JH (1984) On the relationship between abundance and distribution of species. The American Naturalist, 124, 255- 279.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
Brundrett MC (2009) Mycorrhizal associations and other means of nutrition of vascular plants: Understanding the global diversity of host plants by resolving conflicting information and developing reliable means of diagnosis. Plant and Soil, 320, 37-77.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
Cameron DD, Neal AL, van Wees SCM, Ton J (2013) Mycorrhiza-induced resistance: More than the sum of its parts? Trends in Plant Science, 18, 539-545.
DOI PMID |
| [19] |
Caughley G (1994) Directions in conservation biology. Journal of Animal Ecology, 63, 215-244.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
Chapman ASA, Tunnicliffe V, Bates AE (2018) Both rare and common species make unique contributions to functional diversity in an ecosystem unaffected by human activities. Diversity and Distributions, 24, 568-578.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
Chen L, Swenson NG, Ji NN, Mi XC, Ren HB, Guo LD, Ma KP (2019) Differential soil fungus accumulation and density dependence of trees in a subtropical forest. Science, 366, 124-128.
DOI PMID |
| [22] |
Chesson P (2000) Mechanisms of maintenance of species diversity. Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics, 31, 343-366.
DOI URL |
| [23] | Chesson P (2008) Quantifying and testing species coexistence mechanisms. In: Unity in Diversity: Reflections on Ecology after the Legacy of Ramon Margalef (eds Valladares F, Camacho A, Elosegui A, Gracia C, Estrada M, Senar JC, Gili JM), pp. 119-164. BBVA, Bilbao, Spain. |
| [24] |
Chu CJ, Wang YS, Liu Y, Jiang L, He FL (2017) Advances in species coexistence theory. Biodiversity Science, 25, 345-354. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[ 储诚进, 王酉石, 刘宇, 蒋林, 何芳良 (2017) 物种共存理论研究进展. 生物多样性, 25, 345-354.]
DOI |
|
| [25] |
Comita LS, Muller-Landau HC, Aguilar S, Hubbell SP (2010) Asymmetric density dependence shapes species abundances in a tropical tree community. Science, 329, 330-332.
DOI PMID |
| [26] | Connell JH (1971) On the role of natural enemies in preventing competitive exclusion in some marine animals and in rain forest trees. In: Dynamics of Populations (eds Boer PJD, Gradwell GR), pp. 298-312. Center for Agriculture Publishing and Documentation, Wageningen. |
| [27] |
Connell JH, Tracey JG, Webb LJ (1984) Compensatory recruitment, growth, and mortality as factors maintaining rain forest tree diversity. Ecological Monographs, 54, 141-164.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
Corrales A, Mangan SA, Turner BL, Dalling JW (2016) An ectomycorrhizal nitrogen economy facilitates monodominance in a neotropical forest. Ecology Letters, 19, 383-392.
DOI PMID |
| [29] |
Cortois R, Schröder-Georgi T, Weigelt A, van der Putten WH, De Deyn GB (2016) Plant-soil feedbacks: Role of plant functional group and plant traits. Journal of Ecology, 104, 1608-1617.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
Dawson W, Fischer M, van Kleunen M (2012) Common and rare plant species respond differently to fertilisation and competition, whether they are alien or native. Ecology Letters, 15, 873-880.
DOI PMID |
| [31] |
Eissenstat DM (1992) Costs and benefits of constructing roots of small diameter. Journal of Plant Nutrition, 15, 763-782.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
Enquist BJ, Feng X, Boyle B, Maitner B, Newman EA, Jørgensen PM, Roehrdanz PR, Thiers BM, Burger JR, Corlett RT, Couvreur TLP, Dauby G, Donoghue JC, Foden W, Lovett JC, Marquet PA, Merow C, Midgley G, Morueta-Holme N, Neves DM, Oliveira-Filho AT, Kraft NJB, Park DS, Peet RK, Pillet M, Serra-Diaz JM, Sandel B, Schildhauer M, Šímová I, Violle C, Wieringa JJ, Wiser SK, Hannah L, Svenning JC, McGill BJ (2019) The commonness of rarity: Global and future distribution of rarity across land plants. Science Advances, 5, eaaz0414.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
Forrister DL, Endara MJ, Younkin GC, Coley PD, Kursar TA (2019) Herbivores as drivers of negative density dependence in tropical forest saplings. Science, 363, 1213-1216.
DOI PMID |
| [34] |
Gaston KJ, Blackburn TM, Lawton JH (1997) Interspecific abundance-range size relationships: An appraisal of mechanisms. Journal of Animal Ecology, 66, 579-601.
DOI URL |
| [35] |
Grainger TN, Levine JM, Gilbert B (2019) The invasion criterion: A common currency for ecological research. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 34, 925-935.
DOI URL |
| [36] |
Grinnell J (1917) The niche-relationships of the California thrasher. The Auk, 34, 427-433.
DOI URL |
| [37] |
Guo DL, Xia MX, Wei X, Chang WJ, Liu Y, Wang ZQ (2008) Anatomical traits associated with absorption and mycorrhizal colonization are linked to root branch order in twenty-three Chinese temperate tree species. New Phytologist, 180, 673-683.
DOI URL |
| [38] |
Gustafson DJ, Casper BB (2004) Nutrient addition affects AM fungal performance and expression of plant/fungal feedback in three serpentine grasses. Plant and Soil, 259, 9-17.
DOI URL |
| [39] | Harnik PG, Simpson C, Payne JL (2012) Long-term differences in extinction risk among the seven forms of rarity. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 279, 4969-4976. |
| [40] |
Hart TB, Hart JA, Murphy PG (1989) Monodominant and species-rich forests of the humid tropics: Causes for their co-occurrence. The American Naturalist, 133, 613-633.
DOI URL |
| [41] |
He FL (2009) Price of prosperity: Economic development and biological conservation in China. Journal of Applied Ecology, 46, 511-515.
DOI URL |
| [42] |
Ho MD, Rosas JC, Brown KM, Lynch JP (2005) Root architectural tradeoffs for water and phosphorus acquisition. Functional Plant Biology, 32, 737-748.
DOI URL |
| [43] | Hubbell SP, Foster RB (1986) Canopy gaps and the dynamics of a Neotropical forest. In: Plant Ecology (ed.ed. Crawley MJ), pp. 77-96. Blackwell, Oxford. |
| [44] |
Hyatt LA, Rosenberg MS, Howard TG, Bole G, Fang W, Anastasia J, Brown K, Grella R, Hinman K, Kurdziel JP, Gurevitch J (2003) The distance dependence prediction of the Janzen-Connell hypothesis: A meta-analysis. Oikos, 103, 590-602.
DOI URL |
| [45] |
in’t Zandt D, van den Brink A, de Kroon H, Visser EJW (2019) Plant-soil feedback is shut down when nutrients come to town. Plant and Soil, 439, 541-551.
DOI |
| [46] |
Jain M, Flynn DFB, Prager CM, Hart GM, DeVan CM, Ahrestani FS, Palmer MI, Bunker DE, Knops JMH, Jouseau CF, Naeem S (2014) The importance of rare species: A trait-based assessment of rare species contributions to functional diversity and possible ecosystem function in tall-grass prairies. Ecology and Evolution, 4, 104-112.
DOI URL |
| [47] |
Janzen DH (1970) Herbivores and the number of tree species in tropical forests. The American Naturalist, 104, 501-528.
DOI URL |
| [48] |
Jia SH, Wang XG, Yuan ZQ, Lin F, Ye J, Lin GG, Hao ZQ, Bagchi R (2020) Tree species traits affect which natural enemies drive the Janzen-Connell effect in a temperate forest. Nature Communications, 11, 286.
DOI URL |
| [49] |
Johnson DJ, Beaulieu WT, Bever JD, Clay K (2012) Conspecific negative density dependence and forest diversity. Science, 336, 904-907.
DOI PMID |
| [50] |
Jung SC, Martinez-Medina A, Lopez-Raez JA, Pozo MJ (2012) Mycorrhiza-induced resistance and priming of plant defenses. Journal of Chemical Ecology, 38, 651-664.
DOI URL |
| [51] |
Keane RM, Crawley MJ (2002) Exotic plant invasions and the enemy release hypothesis. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 17, 164-170.
DOI URL |
| [52] |
Kempel A, Rindisbacher A, Fischer M, Allan E (2018) Plant soil feedback strength in relation to large-scale plant rarity and phylogenetic relatedness. Ecology, 99, 597-606.
DOI PMID |
| [53] |
Klironomos JN (2002) Feedback with soil biota contributes to plant rarity and invasiveness in communities. Nature, 417, 67-70.
DOI URL |
| [54] |
Klironomos JN (2003) Variation in plant response to native and exotic arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. Ecology, 84, 2292- 2301.
DOI URL |
| [55] |
Kobae Y, Ohmori Y, Saito C, Yano K, Ohtomo R, Fujiwara T (2016) Phosphate treatment strongly inhibits new arbuscule development but not the maintenance of arbuscule in mycorrhizal rice roots. Plant Physiology, 171, 566-579.
DOI URL |
| [56] |
Kos M, Veendrick J, Bezemer TM (2013) Local variation in conspecific plant density influences plant-soil feedback in a natural grassland. Basic and Applied Ecology, 14, 506-514.
DOI URL |
| [57] |
Kramer-Walter KR, Bellingham PJ, Millar TR, Smissen RD, Richardson SJ, Laughlin DC (2016) Root traits are multidimensional: Specific root length is independent from root tissue density and the plant economic spectrum. Journal of Ecology, 104, 1299-1310.
DOI URL |
| [58] |
Laliberté E, Lambers H, Burgess TI, Wright SJ (2015) Phosphorus limitation, soil-borne pathogens and the coexistence of plant species in hyperdiverse forests and shrublands. New Phytologist, 206, 507-521.
DOI PMID |
| [59] |
Laliberté E, Turner BL, Costes T, Pearse SJ, Wyrwoll KH, Zemunik G, Lambers H (2012) Experimental assessment of nutrient limitation along a 2-million-year dune chronosequence in the south-western Australia biodiversity hotspot. Journal of Ecology, 100, 631-642.
DOI URL |
| [60] | Le Bagousse-Pinguet Y, Gross N, Saiz H, Maestre FT, Ruiz S, Dacal M, Asensio S, Ochoa V, Gozalo B, Cornelissen JHC, Deschamps L, García C, Maire V, Milla R, Salinas N, Wang JT, Singh BK, García-Palacios P (2021) Functional rarity and evenness are key facets of biodiversity to boost multifunctionality. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 118, e2019355118. |
| [61] |
Leimu R, Mutikainen P, Koricheva J, Fischer M (2006) How general are positive relationships between plant population size, fitness and genetic variation? Journal of Ecology, 94, 942-952.
DOI URL |
| [62] | Leitão RP, Zuanon J, Villéger S, Williams SE, Baraloto C, Fortunel C, Mendonça FP, Mouillot D (2016) Rare species contribute disproportionately to the functional structure of species assemblages. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 283, 20160084. |
| [63] |
Li RB, Yu SX, Wang YF, Staehelin C, Zang RG (2009) Distance-dependent effects of soil-derived biota on seedling survival of the tropical tree legume Ormosia semicastrata. Journal of Vegetation Science, 20, 527-534.
DOI URL |
| [64] |
Liang MX, Liu XB, Etienne RS, Huang FM, Wang YF, Yu SX (2015) Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi counteract the Janzen- Connell effect of soil pathogens. Ecology, 96, 562-574.
DOI URL |
| [65] |
Liang MX, Liu XB, Gilbert GS, Zheng Y, Luo S, Huang FM, Yu SX (2016) Adult trees cause density-dependent mortality in conspecific seedlings by regulating the frequency of pathogenic soil fungi. Ecology Letters, 19, 1448-1456.
DOI URL |
| [66] |
Liu Y, Yu SX, Xie ZP, Staehelin C (2012) Analysis of a negative plant-soil feedback in a subtropical monsoon forest. Journal of Ecology, 100, 1019-1028.
DOI URL |
| [67] |
Liu Y, Fang SQ, Chesson P, He FL (2015) The effect of soil-borne pathogens depends on the abundance of host tree species. Nature Communications, 6, 10017.
DOI PMID |
| [68] |
Liu Y, He FL (2019) Incorporating the disease triangle framework for testing the effect of soil-borne pathogens on tree species diversity. Functional Ecology, 33, 1211-1222.
DOI |
| [69] |
Lloyd KM, Lee WG, Wilson JB (2002) Competitive abilities of rare and common plants: Comparisons using Acaena (Rosaceae) and Chionochloa (Poaceae) from New Zealand. Conservation Biology, 16, 975-985.
DOI URL |
| [70] |
Lynch JP, Ho MD (2005) Rhizoeconomics: Carbon costs of phosphorus acquisition. Plant and Soil, 269, 45-56.
DOI URL |
| [71] |
MacArthur R, Levins R (1967) The limiting similarity, convergence, and divergence of coexisting species. The American Naturalist, 101, 377-385.
DOI URL |
| [72] | MacArthur R (1972) Geographical Ecology. Princeton University Press, Princeton. |
| [73] | MacDougall AS, Rillig MC, Klironomos JN (2011) Weak conspecific feedbacks and exotic dominance in a species- rich savannah. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 278, 2939-2945. |
| [74] |
Mangan SA, Herre EA, Bever JD (2010a) Specificity between Neotropical tree seedlings and their fungal mutualists leads to plant-soil feedback. Ecology, 91, 2594-2603.
DOI URL |
| [75] |
Mangan SA, Schnitzer SA, Herre EA, Mack KML, Valencia MC, Sanchez EI, Bever JD (2010b) Negative plant-soil feedback predicts tree-species relative abundance in a tropical forest. Nature, 466, 752-755.
DOI URL |
| [76] |
Marden JH, Mangan SA, Peterson MP, Wafula E, Fescemyer HW, Der JP, dePamphilis CW, Comita LS (2017) Ecological genomics of tropical trees: How local population size and allelic diversity of resistance genes relate to immune responses, cosusceptibility to pathogens, and negative density dependence. Molecular Ecology, 26, 2498- 2513.
DOI PMID |
| [77] |
Maron JL, Laney Smith A, Ortega YK, Pearson DE, Callaway RM (2016) Negative plant-soil feedbacks increase with plant abundance, and are unchanged by competition. Ecology, 97, 2055-2063.
DOI PMID |
| [78] |
Marx DH (1972) Ectomycorrhizae as biological deterrents to pathogenic root infections. Annual Review of Phytopathology, 10, 429-454.
PMID |
| [79] |
McCormack ML, Dickie IA, Eissenstat DM, Fahey TJ, Fernandez CW, Guo DL, Helmisaari HS, Hobbie EA, Iversen CM, Jackson RB, Leppälammi-Kujansuu J, Norby RJ, Phillips RP, Pregitzer KS, Pritchard SG, Rewald B, Zadworny M (2015) Redefining fine roots improves understanding of below-ground contributions to terrestrial biosphere processes. New Phytologist, 207, 505-518.
DOI PMID |
| [80] |
McGuire KL (2007) Common ectomycorrhizal networks may maintain monodominance in a tropical rain forest. Ecology, 88, 567-574.
PMID |
| [81] |
Mi XC, Sun ZH, Song YF, Liu XJ, Yang J, Wu JJ, Ci XQ, Li J, Lin LX, Cao M, Ma KP (2021) Rare tree species have narrow environmental but not functional niches. Functional Ecology, 35, 511-520.
DOI URL |
| [82] | Mi XC, Swenson NG, Valencia R, Kress WJ, Erickson DL, Pérez ÁJ, Ren HB, Su SH, Gunatilleke N, Gunatilleke S, Hao ZQ, Ye WH, Cao M, Suresh HS, Dattaraja HS, Sukumar R, Ma KP (2012) The contribution of rare species to community phylogenetic diversity across a global network of forest plots. The American Naturalist, 180, E17-E30. |
| [83] |
Newsham KK, Fitter AH, Watkinson AR (1995) Arbuscular mycorrhiza protect an annual grass from root pathogenic fungi in the field. Journal of Ecology, 83, 991-1000.
DOI URL |
| [84] |
Packer A, Clay K (2000) Soil pathogens and spatial patterns of seedling mortality in a temperate tree. Nature, 404, 278-281.
DOI URL |
| [85] |
Parker IM, Saunders M, Bontrager M, Weitz AP, Hendricks R, Magarey R, Suiter K, Gilbert GS (2015) Phylogenetic structure and host abundance drive disease pressure in communities. Nature, 520, 542-544.
DOI URL |
| [86] |
Petermann JS, Fergus AJF, Turnbull LA, Schmid B (2008) Janzen-Connell effects are widespread and strong enough to maintain diversity in grasslands. Ecology, 89, 2399-2406.
PMID |
| [87] |
Pimm SL, Jones HL, Diamond J (1988) On the risk of extinction. The American Naturalist, 132, 757-785.
DOI URL |
| [88] |
Pimm SL, Russell GJ, Gittleman JL, Brooks TM (1995) The future of biodiversity. Science, 269, 347-350.
PMID |
| [89] |
Plassard C, Dell B (2010) Phosphorus nutrition of mycorrhizal trees. Tree Physiology, 30, 1129-1139.
DOI PMID |
| [90] |
Porter SS, Sachs JL (2020) Agriculture and the disruption of plant-microbial symbiosis. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 35, 426-439.
DOI URL |
| [91] |
Pregitzer KS (2002) Fine roots of trees-A new perspective. New Phytologist, 154, 267-270.
DOI PMID |
| [92] |
Preston FW (1962) The canonical distribution of commonness and rarity: Part I. Ecology, 43, 185-215.
DOI URL |
| [93] | Rabinowitz D (1981) Seven forms of rarity. In:The Biological Aspects of Rare Plant Conservation (ed.ed. Synge H), pp.205-217. John Wiley & Sons, Chichester. |
| [94] |
Regus JU, Wendlandt CE, Bantay RM, Gano-Cohen KA, Gleason NJ, Hollowell AC, O’Neill MR, Shahin KK, Sachs JL (2017) Nitrogen deposition decreases the benefits of symbiosis in a native legume. Plant and Soil, 414, 159-170.
DOI URL |
| [95] |
Reich PB (2014) The world-wide ‘fast-slow’ plant economics spectrum: A traits manifesto. Journal of Ecology, 102, 275-301.
DOI URL |
| [96] |
Rousseau JVD, Sylvia DM, Fox AJ (1994) Contribution of ectomycorrhiza to the potential nutrient-absorbing surface of pine. New Phytologist, 128, 639-644.
DOI URL |
| [97] |
Schroeder JW, Dobson A, Mangan SA, Petticord DF, Herre EA (2020) Mutualist and pathogen traits interact to affect plant community structure in a spatially explicit model. Nature Communications, 11, 2204.
DOI PMID |
| [98] |
Schroeder JW, Martin JT, Angulo DF, Barbosa JM, Perea R, Arias-Del Razo I, Sebastián-González E, Dirzo R (2018) Community composition and diversity of Neotropical root- associated fungi in common and rare trees. Biotropica, 50, 694-703.
DOI URL |
| [99] |
Siepielski AM, McPeek MA (2010) On the evidence for species coexistence: A critique of the coexistence program. Ecology, 91, 3153-3164.
PMID |
| [100] |
Smith MD, Knapp AK (2003) Dominant species maintain ecosystem function with non-random species loss. Ecology Letters, 6, 509-517.
DOI URL |
| [101] | Smith SE, Read DJ (1997) Mycorrhizal Symbioses. Academic Press, London. |
| [102] |
Stump SM, Marden JH, Beckman NG, Mangan SA, Comita LS (2020) Resistance genes affect how pathogens maintain plant abundance and diversity. The American Naturalist, 196, 472-486.
DOI URL |
| [103] |
Umaña MN, Zhang CC, Cao M, Lin LX, Swenson NG (2015) Commonness, rarity, and intraspecific variation in traits and performance in tropical tree seedlings. Ecology Letters, 18, 1329-1337.
DOI URL |
| [104] |
van de Voorde TFJ, van der Putten WH, Bezemer TM (2012) The importance of plant-soil interactions, soil nutrients, and plant life history traits for the temporal dynamics of Jacobaea vulgaris in a chronosequence of old-fields. Oikos, 121, 1251-1262.
DOI URL |
| [105] |
van der Heijden MGA, Boller T, Wiemken A, Sanders IR (1998) Different arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal species are potential determinants of plant community structure. Ecology, 79, 2082-2091.
DOI URL |
| [106] |
Vermeij GJ, Grosberg RK (2018) Rarity and persistence. Ecology Letters, 21, 3-8.
DOI PMID |
| [107] |
Wehner J, Antunes PM, Powell JR, Mazukatow J, Rillig MC (2010) Plant pathogen protection by arbuscular mycorrhizas: A role for fungal diversity? Pedobiologia, 53, 197-201.
DOI URL |
| [108] | Xi XQ, Yang YHS, Tylianakis JM, Yang SH, Dong YR, Sun SC (2020) Asymmetric interactions of seed-predation network contribute to rare-species advantage. Ecology, 101, e03050. |
| [109] |
Yenni G, Adler PB, Morgan Ernest SK (2012) Strong self- limitation promotes the persistence of rare species. Ecology, 93, 456-461.
DOI URL |
| [110] |
Yenni G, Adler PB, Morgan Ernest SK (2017) Do persistent rare species experience stronger negative frequency dependence than common species? Global Ecology and Biogeography, 26, 513-523.
DOI URL |
| [111] |
Yu WB, Li SP (2020) Modern coexistence theory as a framework for invasion ecology. Biodiversity Science, 28, 1362-1375. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
| [ 于文波, 黎绍鹏 (2020) 基于现代物种共存理论的入侵生态学概念框架. 生物多样性, 28, 1362-1375.] | |
| [112] |
Zemunik G, Turner BL, Lambers H, Laliberté E (2015) Diversity of plant nutrient-acquisition strategies increases during long-term ecosystem development. Nature Plants, 1, 15050.
DOI URL |
| [113] |
Zhang ZJ, van Kleunen M (2019) Common alien plants are more competitive than rare natives but not than common natives. Ecology Letters, 22, 1378-1386.
DOI URL |
| [114] |
Zhu Y, Mi XC, Ma KP (2009) A mechanism of plant species coexistence: The negative density-dependent hypothesis. Biodiversity Science, 17, 594-604. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[ 祝燕, 米湘成, 马克平 (2009) 植物群落物种共存机制: 负密度制约假说. 生物多样性, 17, 594-604.]
DOI |
| [1] | Weiqiang Xu, Qiang Su. Exploring the interplay of fractal model and species abundance distribution: A case study of shellfish and insect [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(4): 23410-. |
| [2] | Rongjiang Zhao, Jihua Wu, Weiming He, Caiyun Zhao, Bo Zhou, Bo Li, Qiang Yang. Soil biodiversity and exotic plant invasions: Progress and perspectives [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(11): 24243-. |
| [3] | Shiyun Shen, Yuanfei Pan, Liru Chen, Yanli Tu, Xiaoyun Pan. Plant-soil feedbacks differ between native and introduced populations of Alternanthera philoxeroides [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(3): 22436-. |
| [4] | Yingda Wu, Xiaowu Man, Yuan Yuan, Yucheng Dai. Species diversity, distribution and composition of polypores occurring in botanical gardens in China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2022, 30(7): 22213-. |
| [5] | Danqi She, Xiting Zhang, Lu Xiao, Zhaoliang Zhong, Huimei Wang, Wenjie Wang. Plant beta diversity and its influence factors in the Liangshui National Nature Reserve in the central region of the Xiaoxing’an Mountains [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2022, 30(3): 21274-. |
| [6] | Jiapeng Kang, Lu Han, Chunhui Feng, Haizhen Wang. Species abundance distribution in two riparian forests under contrasting environmental regimes in the Tarim Desert [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2021, 29(7): 875-886. |
| [7] | Minxia Liu, Quandi Li, Xiaoxuan Jiang, Sujuan Xia, Xiaoning Nan, Yaya Zhang, Bowen Li. Contribution of rare species to species diversity and species abundance distribution pattern in the Gannan subalpine meadow [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2020, 28(2): 107-116. |
| [8] | Hui Ding, Yanming Fang, Xinhu Yang, Fayin Yuan, Liheng He, Jianfei Yao, Jun Wu, Bin Chi, Yao Li, Shuifei Chen, Tingting Chen, Haigen Xu. Community characteristics of a subtropical evergreen broad-leaved forest in Huangshan, Anhui Province, East China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2016, 24(8): 875-887. |
| [9] | Xiaofeng Fang, Qingsong Yang, Heming Liu, Zunping Ma, Shu Dong, Ye Cao, Mingjiao Yuan, Xiyang Fei, Xiaoying Sun, Xihua Wang. Distribution of species abundance of evergreen and deciduous woody plants in the evergreen broad-leaved forests at Tiantong, Zhejiang [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2016, 24(6): 629-638. |
| [10] | Gexi Xu, Zuomin Shi, Jingchao Tang, Han Xu, Huai Yang, Shirong Liu, Yide Li, Mingxian Lin. Effects of species abundance and size classes on assessing community phylogenetic structure: a case study in Jianfengling tropical montane rainforest [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2016, 24(6): 617-628. |
| [11] | Yin Guo, Yunquan Wang, Lei Chen, Xiangcheng Mi, Haibao Ren, Shengwen Chen, Jianhua Chen. Comparing tree seedling composition and distribution patterns under different sampling intensities in the 24 ha Gutianshan forest dynamics plot [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2016, 24(10): 1093-1104. |
| [12] | Heming Liu, Qingsong Yang, Xiaofeng Fang, Zunping Ma, Guochun Shen, Zhiguo Zhang, Zhanghua Wang, Xihua Wang. Influences on gap species richness in a subtropical evergreen broad- leaved forest [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2015, 23(2): 149-156. |
| [13] | Kechang Niu, Yining Liu, Zehao Shen, Fangliang He, Jingyun Fang. Community assembly: the relative importance of neutral theory and niche theory [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2009, 17(6): 579-593. |
| [14] | Yinggui Dai, Min Li. Fish resources around Fanjing Mountain, Guizhou [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2006, 14(1): 55-64. |
| [15] | JIA Feng-Long, LIANG Ge-Qiu, CHEN Zhen-Yao, PANG Hong, XIE Wei-Cai, CHEN Li-Er, YE Gui-Dong. Species diversity of beetles of Mt.Wutongshan [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2000, 08(2): 169-171. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2022 Biodiversity Science
Editorial Office of Biodiversity Science, 20 Nanxincun, Xiangshan, Beijing 100093, China
Tel: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn ![]()