



生物多样性 ›› 2024, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (10): 24123. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2024123 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2024123
郝泽周1( ), 张承云2(
), 张承云2( ), 李乐1(
), 李乐1( ), 高丙涛1(
), 高丙涛1( ), 曾伟3, 王淳1, 王梓炫2, 黄万涛2, 张悦2, 裴男才1,*(
), 曾伟3, 王淳1, 王梓炫2, 黄万涛2, 张悦2, 裴男才1,*( )(
)( ), 肖治术4(
), 肖治术4( )
)
收稿日期:2024-03-30
接受日期:2024-08-14
出版日期:2024-10-20
发布日期:2024-09-08
通讯作者:
*E-mail: nancai.pei@gmail.com
基金资助:
Zezhou Hao1( ), Chengyun Zhang2(
), Chengyun Zhang2( ), Le Li1(
), Le Li1( ), Bingtao Gao1(
), Bingtao Gao1( ), Wei Zeng3, Chun Wang1, Zixuan Wang2, Wantao Huang2, Yue Zhang2, Nancai Pei1,*(
), Wei Zeng3, Chun Wang1, Zixuan Wang2, Wantao Huang2, Yue Zhang2, Nancai Pei1,*( )(
)( ), Zhishu Xiao4(
), Zhishu Xiao4( )
)
Received:2024-03-30
Accepted:2024-08-14
Online:2024-10-20
Published:2024-09-08
Contact:
*E-mail: nancai.pei@gmail.com
Supported by:摘要:
在当前城市化快速发展的背景下, 监测与评估城市鸟类多样性是城市生态学研究和生物多样性保护的关键技术。被动声学监测(passive acoustic monitoring, PAM)作为一种利用环境声音评估生物多样性的新兴技术, 能够提供城市鸟类种群的连续动态信息, 为洞察人类活动对生物多样性的影响提供了独特的视角。目前, 中国及全球范围内已经开展了许多基于被动声学监测的生物多样性研究案例。然而, 监测与评价技术的差异直接影响基于被动声学监测的城市鸟类多样性评估的有效性, 制约了城市生物多样性维持机制等科学问题的深入探讨。随着被动声学监测技术的广泛应用, 迫切需要制定一套城市鸟类鸣声被动声学监测与评价技术规范, 推动声学数据的规范化采集与处理, 并构建全国性的城市鸟类声学数据平台, 以高质量的大数据推动城市生态学研究和城市生物多样性保护。本文综述了城市环境下基于被动声学监测评估鸟类多样性的研究案例, 系统地总结了监测方案和评价技术, 梳理了存在的主要问题, 并对未来的研究进行了展望, 旨在为今后城市鸟类多样性被动声学监测与评价的理论研究、调查方案和技术应用提供参考。
郝泽周, 张承云, 李乐, 高丙涛, 曾伟, 王淳, 王梓炫, 黄万涛, 张悦, 裴男才, 肖治术 (2024) 城市鸟类多样性被动声学监测与评价技术应用. 生物多样性, 32, 24123. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2024123.
Zezhou Hao, Chengyun Zhang, Le Li, Bingtao Gao, Wei Zeng, Chun Wang, Zixuan Wang, Wantao Huang, Yue Zhang, Nancai Pei, Zhishu Xiao (2024) Applications of passive acoustic monitoring and evaluation in urban bird research. Biodiversity Science, 32, 24123. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2024123.
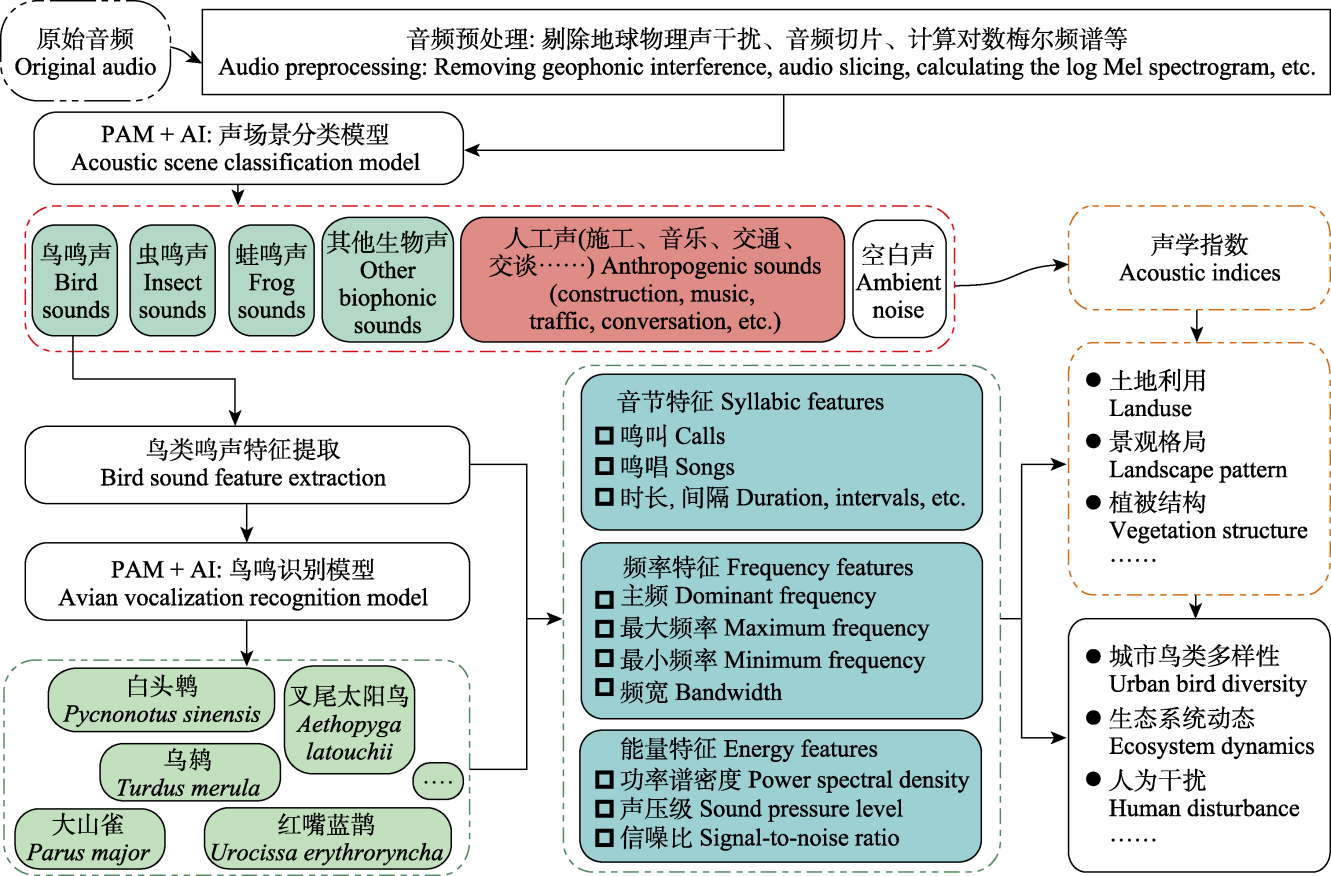
图4 城市鸟类声学数据的分析流程图。PAM: 被动声学监测; AI: 人工智能。
Fig. 4 Flowchart of data analyses on urban bird sounds. PAM, Passive acoustic monitoring; AI, Artificial intelligence.
| 类型 Type | 名称 Name | 基本功能 Basic functions | 网址 Website |
|---|---|---|---|
| 声学指标计算 Acoustic indices calculate | Scikit-maad | 基于Python平台 Based on the Python platform 提供预处理、声学指数和声压级计算模块 Providing preprocessing, acoustic indices and sound pressure level calculation modules 提供多样的音频处理工具集 Providing a diverse set of audio analysis utilities 支持大规模数据处理 Supporting large-scale data processing | |
| seewave | 基于R语言平台 Based on the R language platform 支持音频信号处理和特征提取 Supporting audio signal processing and feature extraction 支持声学指数计算和可视化 Supporting the calculation and visualization of acoustic indices 并未针对大规模数据进行优化 Not optimized for large-scale data | ||
| soundecology | 基于R语言平台 Based on the R language platform 支持声学指数计算 Supporting the calculation of acoustic indices 提供目标信息框选和栅格文件处理功能 Providing the functions of bounding box selection and raster file creation 支持大规模数据处理 Supporting large-scale data processing | ||
| 声场景分类 模型 Acoustic scene classification model | AlexNet | 深度卷积神经网络模型 Deep convolutional neural network model 以语谱图为输入特征 Using spectrogram as input feature 有效提取音频全局特征 Effectively extracting global audio features 适用于多种声音识别任务 Suitable for various sound recognition tasks | |
| GoogleNet | 基于Inception的架构设计 Inception-based architecture design 采用1 × 1卷积核以优化效率 Utilizing 1 × 1 convolutional kernels for efficiency 适配语谱图输入进行音频分析 Adapting spectrogram inputs for audio analysis 轻量级网络, 计算需求低 Lightweight network with low computational demand | ||
| CityNet | 基于卷积神经网络 Based on convolutional neural network CityBioNet: 专注于生物声音的识别 Specialized in recognizing biological sounds CityAnthroNet: 专门识别人为声音 Dedicated to identifying anthropogenic sounds 采用one-vs-one方法优化双模型性能 Using one-vs-one approach to enhance performance of dual models | ||
| 鸟鸣识别模型 Bird song recognition model | BirdNET | 基于CNN模型 Based on the CNN framework 利用大规模的已标记鸟类声音数据进行训练 Trained by using a large dataset of labeled bird sounds 能够处理多种音频格式的输入, 提高模型适用性 Capable of processing multiple audio formats, enhancing model adaptability 具备迁移学习能力 Equipped with transfer learning capabilities 提供了GUI界面, 便于非专业用户使用 Providing a GUI interface, making it user-friendly for non-experts | |
| AudioMAE | 基于Transformer架构 Based on the transformer architecture 利用大规模本地无标签数据完成自监督预训练 Utilizing large-scale local unlabeled data for self-supervised pre-training 有标注数据量要求低 Requiring a low amount of labeled data 支持大规模的音频数据训练 Supporting training with large-scale audio data | ||
| Google Perch | 基于CNN框架 Based on the CNN framework 在大量有标签生物声学数据上进行预训练 Pre-trained on a large amount of labeled bioacoustic data 对目标物种有标签数据的依赖小 Requiring minimal labeled data for the target species 具有迁移学习能力 Possessing transfer learning capabilities |
表1 常用的鸟类鸣声数据处理平台
Table1 Common bird song data processing platforms
| 类型 Type | 名称 Name | 基本功能 Basic functions | 网址 Website |
|---|---|---|---|
| 声学指标计算 Acoustic indices calculate | Scikit-maad | 基于Python平台 Based on the Python platform 提供预处理、声学指数和声压级计算模块 Providing preprocessing, acoustic indices and sound pressure level calculation modules 提供多样的音频处理工具集 Providing a diverse set of audio analysis utilities 支持大规模数据处理 Supporting large-scale data processing | |
| seewave | 基于R语言平台 Based on the R language platform 支持音频信号处理和特征提取 Supporting audio signal processing and feature extraction 支持声学指数计算和可视化 Supporting the calculation and visualization of acoustic indices 并未针对大规模数据进行优化 Not optimized for large-scale data | ||
| soundecology | 基于R语言平台 Based on the R language platform 支持声学指数计算 Supporting the calculation of acoustic indices 提供目标信息框选和栅格文件处理功能 Providing the functions of bounding box selection and raster file creation 支持大规模数据处理 Supporting large-scale data processing | ||
| 声场景分类 模型 Acoustic scene classification model | AlexNet | 深度卷积神经网络模型 Deep convolutional neural network model 以语谱图为输入特征 Using spectrogram as input feature 有效提取音频全局特征 Effectively extracting global audio features 适用于多种声音识别任务 Suitable for various sound recognition tasks | |
| GoogleNet | 基于Inception的架构设计 Inception-based architecture design 采用1 × 1卷积核以优化效率 Utilizing 1 × 1 convolutional kernels for efficiency 适配语谱图输入进行音频分析 Adapting spectrogram inputs for audio analysis 轻量级网络, 计算需求低 Lightweight network with low computational demand | ||
| CityNet | 基于卷积神经网络 Based on convolutional neural network CityBioNet: 专注于生物声音的识别 Specialized in recognizing biological sounds CityAnthroNet: 专门识别人为声音 Dedicated to identifying anthropogenic sounds 采用one-vs-one方法优化双模型性能 Using one-vs-one approach to enhance performance of dual models | ||
| 鸟鸣识别模型 Bird song recognition model | BirdNET | 基于CNN模型 Based on the CNN framework 利用大规模的已标记鸟类声音数据进行训练 Trained by using a large dataset of labeled bird sounds 能够处理多种音频格式的输入, 提高模型适用性 Capable of processing multiple audio formats, enhancing model adaptability 具备迁移学习能力 Equipped with transfer learning capabilities 提供了GUI界面, 便于非专业用户使用 Providing a GUI interface, making it user-friendly for non-experts | |
| AudioMAE | 基于Transformer架构 Based on the transformer architecture 利用大规模本地无标签数据完成自监督预训练 Utilizing large-scale local unlabeled data for self-supervised pre-training 有标注数据量要求低 Requiring a low amount of labeled data 支持大规模的音频数据训练 Supporting training with large-scale audio data | ||
| Google Perch | 基于CNN框架 Based on the CNN framework 在大量有标签生物声学数据上进行预训练 Pre-trained on a large amount of labeled bioacoustic data 对目标物种有标签数据的依赖小 Requiring minimal labeled data for the target species 具有迁移学习能力 Possessing transfer learning capabilities |
| [1] | Abrahams C, Ashington B, Baker E, Bradfer-Lawrence T, Browning E, Carruthers-Jones J, Darby J, Dick J, Eldridge A, Elliott D, Heath B, Howden-Leach P, Johnston A, Lees A, Meyer C, Arana U, Smyth S (2023) Good Practice Guidelines for Long-Term Ecoacoustic Monitoring in the UK. UK Acoustics Network. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/368683386. (accessed on 2023-03-20) |
| [2] | Alcocer I, Lima H, Sugai LSM, Llusia D (2022) Acoustic indices as proxies for biodiversity: A meta-analysis. Biological Reviews, 97, 2209-2236. |
| [3] | Alquezar RD, Macedo RH, Sierro J, Gil D (2020) Lack of consistent responses to aircraft noise in dawn song timing of bird populations near tropical airports. Behavioral Ecology and Sociobiology, 74, 88. |
| [4] | Aodha OM, Martínez Balvanera S, Damstra E, Cooke M, Eichinski P, Browning E, Barataud M, Boughey K, Coles R, Giacomini G, Swiney G, Obrist MK, Parsons S, Sattler T, Jones KE (2022) Towards a general approach for bat echo-location detection and classification. BioRxiv, 520490. |
| [5] |
Arneill GE, Critchley EJ, Wischnewski S, Jessopp MJ, Quinn JL (2020) Acoustic activity across a seabird colony reflects patterns of within-colony flight rather than nest density. Ibis, 162, 416-428.
DOI |
| [6] | Azar JF, Bell BD (2016) Acoustic features within a forest bird community of native and introduced species in New Zealand. Emu - Austral Ornithology, 116, 22-31. |
| [7] | Barber JR, Crooks KR, Fristrup KM (2010) The costs of chronic noise exposure for terrestrial organisms. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 25, 180-189. |
| [8] | Bhakti T, Pena JC, Moura ACM, Pujoni D, Saliba L, Rodrigues M (2024) Urban biodiversity suitability index: Decoding the relationships between cities and birds. Urban Ecosystems, 27, 305-319. |
| [9] | Boncoraglio G, Saino N (2007) Habitat structure and the evolution of bird song: A meta-analysis of the evidence for the acoustic adaptation hypothesis. Functional Ecology, 21, 134-142. |
| [10] | Boullhesen M, Vaira M, Barquez RM, Akmentins MS (2021) Evaluating the efficacy of visual encounter and automated acoustic survey methods in anuran assemblages of the Yungas Andean forests of Argentina. Ecological Indicators, 127, 107750. |
| [11] | Bradfer-Lawrence T, Bunnefeld N, Gardner N, Willis SG, Dent DH (2020) Rapid assessment of avian species richness and abundance using acoustic indices. Ecological Indicators, 115, 106400. |
| [12] | Bradfer-Lawrence T, Desjonqueres C, Eldridge A, Johnston A, Metcalf O (2023) Using acoustic indices in ecology: Guidance on study design, analyses and interpretation. Methods in Ecology and Evolution, 14, 2192-2204. |
| [13] | Brumm H, Slabbekoorn H (2005) Acoustic communication in noise. In: Advances in the Study of Behavior (ed. Slater PJ), pp.151-209. Elsevier, Amsterdam. |
| [14] | Budka M, Jobda M, Szałański P, Piórkowski H (2022) Acoustic approach as an alternative to human-based survey in bird biodiversity monitoring in agricultural meadows. PLoS ONE, 17, e0266557. |
| [15] | Campos-Cerqueira M (2023) Combining passive acoustic monitoring and species distribution models to monitor species responses to climate change. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 153, A25. |
| [16] | Chace JF, Walsh JJ (2006) Urban effects on native avifauna: A review. Landscape and Urban Planning, 74, 46-69. |
| [17] | Chamberlain DE, Cannon AR, Toms MP, Leech DI, Hatchwell BJ, Gaston KJ (2009) Avian productivity in urban landscapes: A review and meta-analysis. Ibis, 151, 1-18. |
| [18] | Chen YX, Rasool MA, Hussain S, Meng S, Yao YP, Wang X, Liu YH (2023) Bird community structure is driven by urbanization level, blue-green infrastructure configuration and precision farming in Taizhou, China. Science of the Total Environment, 859, 160096. |
| [19] | Cohen Y, Nicholson DA, Sanchioni A, Mallaber EK, Skidanova V, Gardner TJ (2022) Automated annotation of birdsong with a neural network that segments spectrograms. eLife, 11, e63853. |
| [20] | Collins MK, Magle SB, Gallo T (2021) Global trends in urban wildlife ecology and conservation. Biological Conservation, 261, 109236. |
| [21] | Darras K, Batáry P, Furnas B, Celis-Murillo A, Van Wilgenburg SL, Mulyani YA, Tscharntke T (2018) Comparing the sampling performance of sound recorders versus point counts in bird surveys: A meta-analysis. Journal of Applied Ecology, 55, 2575-2586. |
| [22] |
DeGregorio BA, Weatherhead PJ, Sperry JH (2014) Power lines, roads, and avian nest survival: Effects on predator identity and predation intensity. Ecology and Evolution, 4, 1589-1600.
DOI PMID |
| [23] | Derryberry EP, Phillips JN, Derryberry GE, Blum MJ, Luther D (2020) Singing in a silent spring: Birds respond to a half-century soundscape reversion during the COVID-19 shutdown. Science, 370, 575-579. |
| [24] | Depraetere M, Pavoine S, Jiguet F, Gasc A, Duvail S, Sueur J (2012) Monitoring animal diversity using acoustic indices: Implementation in a temperate woodland. Ecological Indicators, 13, 46-54. |
| [25] | Dröge S, Martin DA, Andriafanomezantsoa R, Burivalova Z, Fulgence TR, Osen K, Rakotomalala E, Schwab D, Wurz A, Richter T, Kreft H (2021) Listening to a changing landscape: Acoustic indices reflect bird species richness and plot-scale vegetation structure across different land-use types in north-eastern Madagascar. Ecological Indicators, 120, 106929. |
| [26] | Durden JM, Luo JY, Alexander H, Flanagan AM, Grossmann L (2017) Integrating “big data” into aquatic ecology: Challenges and opportunities. Limnology and Oceanography Bulletin, 26, 101-108. |
| [27] | Eldridge A, Casey M, Moscoso P, Peck M (2016) A new method for ecoacoustics? Toward the extraction and evaluation of ecologically-meaningful soundscape components using sparse coding methods. PeerJ, 4, e2108. |
| [28] |
Fairbrass AJ, Firman M, Williams C, Brostow GJ, Titheridge H, Jones KE (2019) CityNet—Deep learning tools for urban ecoacoustic assessment. Methods in Ecology and Evolution, 10, 186-197.
DOI |
| [29] | Fairbrass AJ, Rennert P, Williams C, Titheridge H, Jones KE (2017) Biases of acoustic indices measuring biodiversity in urban areas. Ecological Indicators, 83, 169-177. |
| [30] | Francis CD, Kleist NJ, Ortega CP, Cruz A (2012) Noise pollution alters ecological services:Enhanced pollination and disrupted seed dispersal. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 279, 2727-2735. |
| [31] | French K, Major R, Hely K (2005) Use of native and exotic garden plants by suburban nectarivorous birds. Biological Conservation, 121, 545-559. |
| [32] | Frommolt KH (2017) Information obtained from long-term acoustic recordings: Applying bioacoustic techniques for monitoring wetland birds during breeding season. Journal of Ornithology, 158, 659-668. |
| [33] | Gallardo Cruz KV, Paxton KL, Hart PJ (2021) Temporal changes in songbird vocalizations associated with helicopter noise in Hawai’i’s protected natural areas. Landscape Ecology, 36, 829-843. |
| [34] | Gottesman BL, Olson JC, Yang S, Acevedo-Charry O, Francomano D, Martinez FA, Appeldoorn RS, Mason DM, Weil E, Pijanowski BC (2021) What does resilience sound like? Coral reef and dry forest acoustic communities respond differently to Hurricane Maria. Ecological Indicators, 126, 107635. |
| [35] |
Hagstrum JT, McIsaac HP, Drob DP (2016) Seasonal changes in atmospheric noise levels and the annual variation in pigeon homing performance. Journal of Comparative Physiology A, 202, 413-424.
DOI PMID |
| [36] | Hao ZZ, Wang C, Sun ZK, van den Bosch CK, Zhao DX, Sun BQ, Xu XH, Bian Q, Bai ZT, Wei KY, Zhao YL, Pei NC (2021) Soundscape mapping for spatial-temporal estimate on bird activities in urban forests. Urban Forestry & Urban Greening, 57, 126822. |
| [37] | Hao ZZ, Zhan HS, Zhang CY, Pei NC, Sun B, He JH, Wu RC, Xu XH, Wang C (2022) Assessing the effect of human activities on biophony in urban forests using an automated acoustic scene classification model. Ecological Indicators, 144, 109437. |
| [38] | Hao ZZ, Zhang CY, Li L, Gao BT, Wu RC, Pei NC, Liu Y (2024) Anthropogenic noise and habitat structure shaping dominant frequency of bird sounds along urban gradients. iScience, 27, 109056. |
| [39] | Holgate B, Maggini R, Fuller S (2021) Mapping ecoacoustic hot spots and moments of biodiversity to inform conservation and urban planning. Ecological Indicators, 126, 107627. |
| [40] | Ji T, Zhang YY (2011) Impacts of ambient noise on bird song and adaptation strategies of birds. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 30, 831-836. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [季婷, 张雁云 (2011) 环境噪音对鸟类鸣声的影响及鸟类的适应对策. 生态学杂志, 30, 831-836.] | |
| [41] | Kahl S, Wood CM, Eibl M, Klinck H (2021) BirdNET: A deep learning solution for avian diversity monitoring. Ecological Informatics, 61, 101236. |
| [42] | Krause BL (1987) Bioacoustics, habitat ambience in ecological balance. Whole Earth Review, 57, 14-18. |
| [43] | Lomolino MV (2000) Ecology’s most general, yet protean pattern: The species-area relationship. Journal of Biogeography, 27, 17-26. |
| [44] | Luo LY, Guo ST, Wang M, Qiu HB, Liu ZH (2023) Adaptive noise reduction algorithm based on SPP and NMF for environmental sound event recognition under low-SNR conditions. Wireless Communications and Mobile Computing, 2023, 6582296. |
| [45] | Luther D, Baptista L (2010) Urban noise and the cultural evolution of bird songs. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 277, 469-473. |
| [46] |
Ma KP (2011) Assessing progress of biodiversity conservation with monitoring approach. Biodiversity Science, 19, 125-126. (in Chinese)
DOI |
|
[马克平 (2011) 监测是评估生物多样性保护进展的有效途径. 生物多样性, 19, 125-126.]
DOI |
|
| [47] | MacArthur RH, Wilson EO (1969) The Theory of Island Biogeography. Princeton University Press, Princeton. |
| [48] | McKinney ML (2002) Urbanization, biodiversity, and conservation. BioScience, 52, 883-890. |
| [49] | McPhearson T, Pickett STA, Grimm NB, Niemelä J, Alberti M, Elmqvist T, Weber C, Haase D, Breuste J, Qureshi S (2016) Advancing urban ecology toward a science of cities. BioScience, 66, 198-212. |
| [50] | Mendes S, Colino-Rabanal VJ, Peris SJ (2011) Bird song variations along an urban gradient: The case of the European blackbird (Turdus merula). Landscape and Urban Planning, 99, 51-57. |
| [51] |
Merchant ND, Fristrup KM, Johnson MP, Tyack PL, Witt MJ, Blondel P, Parks SE (2015) Measuring acoustic habitats. Methods in Ecology and Evolution, 6, 257-265.
PMID |
| [52] |
Metcalf OC, Barlow J, Devenish C, Marsden S, Berenguer E, Lees AC (2021) Acoustic indices perform better when applied at ecologically meaningful time and frequency scales. Methods in Ecology and Evolution, 12, 421-431.
DOI |
| [53] | Miller-Rushing AJ, Lloyd-Evans TL, Primack RB, Satzinger P (2008) Bird migration times, climate change, and changing population sizes. Global Change Biology, 14, 1959-1972. |
| [54] | Mockford EJ, Marshall RC (2009) Effects of urban noise on song and response behaviour in great tits. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 276, 2979-2985. |
| [55] | Morales G, Vargas V, Espejo D, Poblete V, Tomasevic JA, Otondo F, Navedo JG (2022) Method for passive acoustic monitoring of bird communities using UMAP and a deep neural network. Ecological Informatics, 72, 101909. |
| [56] |
Moreno-Gómez FN, Bartheld J, Silva-Escobar AA, Briones R, Márquez R, Penna M (2019) Evaluating acoustic indices in the Valdivian rainforest, a biodiversity hotspot in South America. Ecological Indicators, 103, 1-8.
DOI |
| [57] |
Müller J, Mitesser O, Schaefer HM, Seibold S, Busse A, Kriegel P, Rabl D, Gelis R, Arteaga A, Freile J, Leite GA, de Melo TN, LeBien J, Campos-Cerqueira M, Blüthgen N, Tremlett CJ, Böttger D, Feldhaar H, Grella N, Falconí-López A, Donoso DA, Moriniere J, Buřivalová Z (2023) Soundscapes and deep learning enable tracking biodiversity recovery in tropical forests. Nature Communications, 14, 6191.
DOI PMID |
| [58] | Müller S, Gossner MM, Penone C, Jung K, Renner SC, Farina A, Anhäuser L, Ayasse M, Boch S, Haensel F, Heitzmann J, Kleinn C, Magdon P, Perović DJ, Pieretti N, Shaw T, Steckel J, Tschapka M, Vogt J, Westphal C, Scherer-Lorenzen M (2022) Land-use intensity and landscape structure drive the acoustic composition of grasslands. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 328, 107845. |
| [59] | Nemeth E, Pieretti N, Zollinger SA, Geberzahn N, Partecke J, Miranda AC, Brumm H (2013) Bird song and anthropogenic noise:Vocal constraints may explain why birds sing higher-frequency songs in cities. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 280, 20122798. |
| [60] | Pataki DE (2015) Grand challenges in urban ecology. Frontiers in Ecology and Evolution, 3, 57. |
| [61] | Pekin BK, Jung J, Villanueva-Rivera LJ, Pijanowski BC, Ahumada JA (2012) Modeling acoustic diversity using soundscape recordings and LIDAR-derived metrics of vertical forest structure in a neotropical rainforest. Landscape Ecology, 27, 1513-1522. |
| [62] |
Pickett STA, Cadenasso ML, Baker ME, Band LE, Boone CG, Buckley GL, Groffman PM, Grove JM, Irwin EG, Kaushal SS, LaDeau SL, Miller AJ, Nilon CH, Romolini M, Rosi EJ, Swan CM, Szlavecz K (2020) Theoretical perspectives of the Baltimore ecosystem study: Conceptual evolution in a social-ecological research project. BioScience, 70, 297-314.
DOI PMID |
| [63] | Pijanowski BC, Villanueva-Rivera LJ, Dumyahn SL, Farina A, Krause BL, Napoletano BM, Gage SH, Pieretti N (2011) Soundscape ecology: The science of sound in the landscape. BioScience, 61, 203-216. |
| [64] | Quinn CA, Burns P, Gill G, Baligar S, Snyder RL, Salas L, Goetz SJ, Clark ML (2022) Soundscape classification with convolutional neural networks reveals temporal and geographic patterns in ecoacoustic data. Ecological Indicators, 138, 108831. |
| [65] |
Rajan SC, Athira K, Jaishanker R, Sooraj NP, Sarojkumar V (2019) Rapid assessment of biodiversity using acoustic indices. Biodiversity and Conservation, 28, 2371-2383.
DOI |
| [66] |
Rasmussen JH, Stowell D, Briefer EF (2024) Sound evidence for biodiversity monitoring. Science, 385, 138-140.
DOI PMID |
| [67] | Roe P, Eichinski P, Fuller RA, McDonald PG, Schwarzkopf L, Towsey M, Truskinger A, Tucker D, Watson DM (2021) The Australian acoustic observatory. Methods in Ecology and Evolution, 12, 1802-1808. |
| [68] | Ross SR, Friedman NR, Dudley KL, Yoshimura M, Yoshida T, Economo EP (2018) Listening to ecosystems: Data-rich acoustic monitoring through landscape-scale sensor networks. Ecological Research, 33, 135-147. |
| [69] | Sánchez-Giraldo C, Bedoya CL, Morán-Vásquez RA, Isaza CV, Daza JM (2020) Ecoacoustics in the rain: Understanding acoustic indices under the most common geophonic source in tropical rainforests. Remote Sensing in Ecology and Conservation, 6, 248-261. |
| [70] | Sangermano F (2022) Acoustic diversity of forested landscapes: Relationships to habitat structure and anthropogenic pressure. Landscape and Urban Planning, 226, 104508. |
| [71] | Sethi SS, Bick A, Ewers RM, Klinck H, Ramesh V, Tuanmu MN, Coomes DA (2023) Limits to the accurate and generalizable use of soundscapes to monitor biodiversity. Nature Ecology & Evolution, 7, 1373-1378. |
| [72] | Shonfield J, Bayne EM (2017) Autonomous recording units in avian ecological research: Current use and future applications. Avian Conservation and Ecology, 12, art14. |
| [73] | Slabbekoorn H, Peet M (2003) Birds sing at a higher pitch in urban noise. Nature, 424, 267. |
| [74] |
Sugai LSM, Silva TSF, Ribeiro JW, Llusia D (2019) Terrestrial passive acoustic monitoring: Review and perspectives. BioScience, 69, 15-25.
DOI |
| [75] | To AWY, Dingle C, Collins SA (2021) Multiple constraints on urban bird communication: Both abiotic and biotic noise shape songs in cities. Behavioral Ecology: Official Journal of the International Society for Behavioral Ecology, 32, 1042-1053. |
| [76] |
Tolentino VC, Baesse CQ, Melo C (2018) Dominant frequency of songs in tropical bird species is higher in sites with high noise pollution. Environmental Pollution, 235, 983-992.
DOI PMID |
| [77] | Towsey M, Planitz B, Nantes A, Wimmer J, Roe P (2012) A toolbox for animal call recognition. Bioacoustics, 21, 107-125. |
| [78] | Tu HM, Fan MW, Ko JCJ (2020) Different habitat types affect bird richness and evenness. Scientific Reports, 10, 1221. |
| [79] |
Van Doren BM, Horton KG (2018) A continental system for forecasting bird migration. Science, 361, 1115-1118.
DOI PMID |
| [80] | Van Doren BM, Lostanlen V, Cramer A, Salamon J, Dokter A, Kelling S, Bello JP, Farnsworth A (2023) Automated acoustic monitoring captures timing and intensity of bird migration. Journal of Applied Ecology, 60, 433-444. |
| [81] | Warren PS, Katti M, Ermann M, Brazel A (2006) Urban bioacoustics: It’s not just noise. Animal Behaviour, 71, 491-502. |
| [82] | Wood CM, Peery MZ (2022) What does ‘occupancy’ mean in passive acoustic surveys? Ibis, 164, 1295-1300. |
| [83] |
Wu H, Xu XH, Feng XJ, Mi XC, Su YJ, Xiao ZS, Zhu CD, Cao L, Gao X, Song CY, Guo LD, Wu DH, Jiang JP, Shen H, Ma KP (2022) Progress and prospect of China biodiversity monitoring from a global perspective. Biodiversity Science, 30, 22434. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[吴慧, 徐学红, 冯晓娟, 米湘成, 苏艳军, 肖治术, 朱朝东, 曹垒, 高欣, 宋创业, 郭良栋, 吴东辉, 江建平, 沈浩, 马克平 (2022) 全球视角下的中国生物多样性监测进展与展望. 生物多样性, 30, 22434.]
DOI |
|
| [84] |
Xiao ZS, Cui JG, Wang DP, Wang ZT, Luo JH, Xie J (2023) Interdisciplinary development trends of contemporary bioacoustics and the opportunities for China. Biodiversity Science, 31, 22423. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[肖治术, 崔建国, 王代平, 王志陶, 罗金红, 谢捷 (2023) 现代生物声学的学科发展趋势及中国机遇. 生物多样性, 31, 22423.]
DOI |
|
| [85] | Xu ZY, Chen L, Pijanowski BC, Zhao Z (2023) A frequency-dependent acoustic diversity index: A revision to a classic acoustic index for soundscape ecological research. Ecological Indicators, 155, 110940. |
| [86] | Yang J (2020) Big data and the future of urban ecology: From the concept to results. Scientia Sinica (Terrae), 50, 1339-1353. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [杨军 (2020) 大数据与城市生态学的未来: 从概念到结果. 中国科学: 地球科学, 50, 1339-1353.] | |
| [87] | Zhang CY, Jin NT, Xie J, Hao ZZ (2024a) CicadaNet: Deep learning based automatic cicada chorus filtering for improved long-term bird monitoring. Ecological Indicators, 158, 111423. |
| [88] | Zhang CY, Zhan HS, Hao ZZ, Gao XH (2023) Classification of complicated urban forest acoustic scenes with deep learning models. Forests, 14, 206. |
| [89] | Zhang CY, Zhang Y, Zheng XJ, Gao XH, Hao ZZ (2024b) Influence of recording devices and environmental noise on acoustic index scores: Implications for bird sound-based assessments. Ecological Indicators, 159, 111759. |
| [90] |
Zhang J (2017) Biodiversity science and macroecology in the era of big data. Biodiversity Science, 25, 355-363. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[张健 (2017) 大数据时代的生物多样性科学与宏生态学. 生物多样性, 25, 355-363.]
DOI |
|
| [91] |
Zhao Y, Shen XL, Li S, Zhang YY, Peng RH, Ma KP (2020) Progress and outlook for soundscape ecology. Biodiversity Science, 28, 806-820. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[赵莹, 申小莉, 李晟, 张雁云, 彭任华, 马克平 (2020) 声景生态学研究进展和展望. 生物多样性, 28, 806-820.]
DOI |
|
| [92] | Zhao YL, Sheppard S, Sun ZK, Hao ZZ, Jin JL, Bai ZT, Bian Q, Wang C (2022) Soundscapes of urban parks: An innovative approach for ecosystem monitoring and adaptive management. Urban Forestry & Urban Greening, 71, 127555. |
| [1] | 徐欢, 辛凤飞, 施宏亮, 袁琳, 薄顺奇, 赵欣怡, 邓帅涛, 潘婷婷, 余婧, 孙赛赛, 薛程. 生态修复技术集成应用对长江口北支生境与鸟类多样性提升效果评估[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24478-. |
| [2] | 白皓天, 余上, 潘新园, 凌嘉乐, 吴娟, 谢恺琪, 刘阳, 陈学业. AI辅助识别的鸟类被动声学监测在城市湿地公园中的应用[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(8): 24188-. |
| [3] | 王秦韵, 张玉泉, 刘浩, 李明, 刘菲, 赵宁, 陈鹏, 齐敦武, 阙品甲. 成都大熊猫繁育研究基地鸟类多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(8): 24066-. |
| [4] | 段菲, 刘鸣章, 卜红亮, 俞乐, 李晟. 城市化对鸟类群落组成及功能特征的影响——以京津冀地区为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(8): 23473-. |
| [5] | 李乐, 张承云, 裴男才, 高丙涛, 王娜, 李嘉睿, 武瑞琛, 郝泽周. 基于被动声学监测技术的城市绿地景观格局与鸟类多样性关联分析[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(10): 24296-. |
| [6] | 黄万涛, 郝泽周, 张梓欣, 肖治术, 张承云. 被动声学监测设备性能比较及对鸟声识别的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(10): 24273-. |
| [7] | 刘莹莹, 龚立新, 曾皓, 冯江, 董永军, 王磊, 江廷磊. 被动声学监测在蝙蝠研究中的应用[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(10): 24233-. |
| [8] | 陈蕾, 许志勇, 苏菩坤, 赖小甜, 赵兆. 依频声学多样性指数用于人类活动区域的适用能力[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(10): 24286-. |
| [9] | 郭倩茸, 段淑斐, 谢捷, 董雪燕, 肖治术. 鸟声标注技术及其在被动声学监测中的应用[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(10): 24313-. |
| [10] | 谢将剑, 沈忱, 张飞宇, 肖治术. 融合音频及生态位信息的跨地域鸟类物种识别方法[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(10): 24259-. |
| [11] | 殷鲁秦, 王成, 韩文静. 基于取食行为探究北京居民区鸟类的食源特征及多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(5): 22473-. |
| [12] | 申小虎, 朱翔宇, 史洪飞, 王传之. 基于机器学习鸟声识别算法研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(11): 23272-. |
| [13] | 肖治术, 崔建国, 王代平, 王志陶, 罗金红, 谢捷. 现代生物声学的学科发展趋势及中国机遇[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(1): 22423-. |
| [14] | 孙翊斐, 王士政, 冯佳伟, 王天明. 东北虎豹国家公园森林声景的昼夜和季节变化[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(1): 22523-. |
| [15] | 王士政, 孙翊斐, 李珍珍, 舒越, 冯佳伟, 王天明. 鸟类迁徙对图们江下游湿地声景时间格局的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(1): 22337-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn