



生物多样性 ›› 2017, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (9): 999-1007. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2017086 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2017086
收稿日期:2017-03-20
接受日期:2017-05-17
出版日期:2017-09-20
发布日期:2017-10-04
通讯作者:
王伟
作者简介:# 共同第一作者
基金资助:
Bing Chen, Fangzheng Liu, Yubo Zhang, Jinhong Du, Wei Wang*( ), Junsheng Li
), Junsheng Li
Received:2017-03-20
Accepted:2017-05-17
Online:2017-09-20
Published:2017-10-04
Contact:
Wang Wei
About author:# Co-first authors
摘要:
对自然保护区的定期评估有助于提升其管理和保护水平。本研究以苍山自然保护区所在的大理市、洱源县、漾濞县3个市/县作为子研究区域, 构建了基于倾向评分配比(propensity score matching)和配对t检验(paired-samples t-test)的保护成效评估技术方案。选取海拔、坡度、与最近居民点的距离、与最近道路的距离4个因子作为环境变量, 通过对每个县单独进行分析, 分别对比了自然保护区晋升国家级时(1995年)与20年后(2015年)其森林覆盖面积的变化, 以此来评估苍山自然保护区的森林保护成效, 并对各环境变量与森林覆盖变化值的关系进行了偏相关分析(partial correlation analysis)。结果表明: 大理市境内苍山自然保护区内的森林覆盖变化值显著高于保护区外部, 且该区段的森林覆盖率最高。洱源县境内苍山自然保护区内、外的森林覆盖变化率均高于其他2个市/县, 且保护区内、外森林覆盖变化值差异不显著。漾濞县境内苍山自然保护区内、外森林覆盖变化率最低, 但其保护区外0-10 km区域的森林覆盖变化值显著高于10 km以外区域, 保护区的存在对其周边0-10 km区域产生了正面的溢出效应 (neighborhood leakage)。海拔、坡度、与最近居民点的距离、与最近道路的距离4个协变量在3个市/县的不同研究区段内均与森林覆盖变化值呈现出了不同程度的相关性。本研究所采用的倾向评分配比法和按照行政区划对自然保护区分区进行评估的方法, 为自然保护区整体保护成效的评价提供了新的技术思路。
陈冰, 刘方正, 张玉波, 杜金鸿, 王伟, 李俊生 (2017) 基于倾向评分配比法评估苍山自然保护区的森林保护成效. 生物多样性, 25, 999-1007. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2017086.
Bing Chen, Fangzheng Liu, Yubo Zhang, Jinhong Du, Wei Wang, Junsheng Li (2017) Assessment of forest conservation in the Cangshan Nature Reserve based on propensity score matching. Biodiversity Science, 25, 999-1007. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2017086.
| 子研究区域 Sub-study area | 1995 | 2015 | 森林覆盖变化值 Forest coverage change (km2) | 森林变化率 Forest change rate | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 森林面积 Forest area (km2) | 森林覆盖率 Forest coverage | 森林面积 Forest area (km2) | 森林覆盖率 Forest coverage | ||||
| 大理市 Dali City | 保护区内 Inside | 166.15 | 78.74% | 168.24 | 79.73% | 2.09 | 1.26% |
| 保护区外 Outside | 284.05 | 28.61% | 320.33 | 32.26% | 36.28 | 12.77% | |
| 洱源县 Eryuan County | 保护区内 Inside | 32.73 | 71.15% | 34.43 | 74.85% | 1.700 | 5.19% |
| 保护区外 Outside | 1004.14 | 38.86% | 1151.36 | 44.56% | 147.22 | 14.66% | |
| 漾濞县 Yangbi County | 保护区内 Inside | 117.26 | 80.32% | 113.98 | 78.07% | -3.28 | -2.80% |
| 保护区外 Outside | 740.91 | 49.26% | 776.95 | 51.66% | 36.04 | 4.86% | |
表1 1995-2015年间大理市、洱源县和漾濞县苍山自然保护区内、外森林覆盖总体情况
Table 1 Overall condition of forest coverage inside and outside of Cangshan Nature Reserve in Dali City, Eryuan County and Yangbi County during 1995-2015
| 子研究区域 Sub-study area | 1995 | 2015 | 森林覆盖变化值 Forest coverage change (km2) | 森林变化率 Forest change rate | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 森林面积 Forest area (km2) | 森林覆盖率 Forest coverage | 森林面积 Forest area (km2) | 森林覆盖率 Forest coverage | ||||
| 大理市 Dali City | 保护区内 Inside | 166.15 | 78.74% | 168.24 | 79.73% | 2.09 | 1.26% |
| 保护区外 Outside | 284.05 | 28.61% | 320.33 | 32.26% | 36.28 | 12.77% | |
| 洱源县 Eryuan County | 保护区内 Inside | 32.73 | 71.15% | 34.43 | 74.85% | 1.700 | 5.19% |
| 保护区外 Outside | 1004.14 | 38.86% | 1151.36 | 44.56% | 147.22 | 14.66% | |
| 漾濞县 Yangbi County | 保护区内 Inside | 117.26 | 80.32% | 113.98 | 78.07% | -3.28 | -2.80% |
| 保护区外 Outside | 740.91 | 49.26% | 776.95 | 51.66% | 36.04 | 4.86% | |
| 研究区段 Survey region | 匹配前 Before matching | 匹配成功 Matched | 未匹配成功 Unmatched | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 对照组 Control | 处理组 Treated | 对照组 Control | 处理组 Treated | 对照组 Control | 处理组 Treated | |
| DA_DB | 336 | 211 | 26 | 26 | 310 | 185 |
| DA_DC | 465 | 211 | 36 | 36 | 429 | 175 |
| DB_DC | 465 | 336 | 232 | 232 | 233 | 104 |
| EA_EB | 428 | 46 | 40 | 40 | 388 | 6 |
| EA_EC | 2,050 | 46 | 45 | 45 | 2,005 | 1 |
| EB_EC | 2,050 | 428 | 414 | 414 | 1,636 | 14 |
| YA_YB | 352 | 146 | 16 | 16 | 336 | 130 |
| YA_YC | 1,152 | 146 | 34 | 34 | 1,118 | 112 |
| YB_YC | 1152 | 352 | 338 | 338 | 814 | 14 |
表2 大理市(D)、洱源县(E)、漾濞县(Y) 3个研究区段间的倾向评分配比结果。A指保护区内; B指保护区外0-10 km; C指保护区10 km以外。表中数值为样本数, 即网格数。
Table 2 Result of propensity score matching of three survey regions in Dali City (D), Eryuan County (E) and Yangbi County (Y). A refers to areas inside Cangshan Nature Reserve; B refers to areas within 10 km outside of Cangshan Nature Reserve; C refers to areas beyond 10 km from Cangshan Nature Reserve. Numbers in the table are sample values, which refers to the number of grids.
| 研究区段 Survey region | 匹配前 Before matching | 匹配成功 Matched | 未匹配成功 Unmatched | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 对照组 Control | 处理组 Treated | 对照组 Control | 处理组 Treated | 对照组 Control | 处理组 Treated | |
| DA_DB | 336 | 211 | 26 | 26 | 310 | 185 |
| DA_DC | 465 | 211 | 36 | 36 | 429 | 175 |
| DB_DC | 465 | 336 | 232 | 232 | 233 | 104 |
| EA_EB | 428 | 46 | 40 | 40 | 388 | 6 |
| EA_EC | 2,050 | 46 | 45 | 45 | 2,005 | 1 |
| EB_EC | 2,050 | 428 | 414 | 414 | 1,636 | 14 |
| YA_YB | 352 | 146 | 16 | 16 | 336 | 130 |
| YA_YC | 1,152 | 146 | 34 | 34 | 1,118 | 112 |
| YB_YC | 1152 | 352 | 338 | 338 | 814 | 14 |
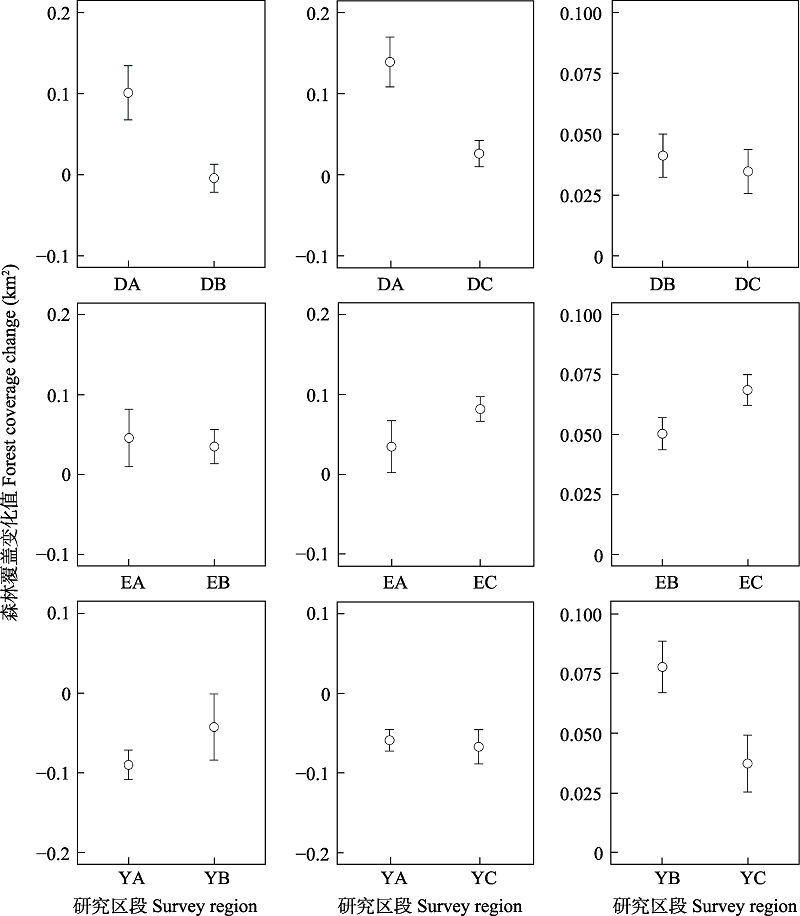
图2 大理市(D)、洱源县(E)、漾濞县(Y)各研究区段1995-2015年森林覆盖变化均值对比(平均值 ± SD)。A指保护区内; B指保护区外0-10 km; C指保护区10 km以外。
Fig. 2 Comparison of forest coverage change during 1995-2015 inside Cangshan Nature Reserve among three survey regions in Dali City (D), Eryuan County (E) and Yangbi County (Y) (mean ± SD). A refers to areas inside Cangshan Nature Reserve; B refers to areas within 10 km outside of Cangshan Nature Reserve; C refers to areas beyond 10km from Cangshan Nature Reserve.
| DA_DB | DA_DC | DB_DC | EA_EB | EA_EC | EB_EC | YA_YB | YA_YC | YB_YC | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| t | 3.553 | 3.187 | 0.535 | 0.246 | -1.359 | -1.943 | -0.970 | 0.283 | 2.772 |
| df | 25 | 35 | 231 | 39 | 44 | 413 | 15 | 33 | 337 |
| P | 0.002* | 0.003* | 0.593 | 0.807 | 0.181 | 0.053 | 0.347 | 0.779 | 0.006* |
表3 大理市(D)、洱源县(E)和漾濞县(Y)各研究区段1995-2015年间森林覆盖变化值配对t检验结果。A指保护区内; B指保护区外0-10 km; C指保护区10 km以外。
Table 3 Results of paired-samples t-test of forest coverage change during 1995-2015 among three survey regions in Dali City (D), Eryuan County (E) and Yangbi County (Y). A refers to areas inside Cangshan Nature Reserve; B refers to areas within 10 km outside of Cangshan Nature Reserve; C refers to areas beyond 10 km from Cangshan Nature Reserve.
| DA_DB | DA_DC | DB_DC | EA_EB | EA_EC | EB_EC | YA_YB | YA_YC | YB_YC | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| t | 3.553 | 3.187 | 0.535 | 0.246 | -1.359 | -1.943 | -0.970 | 0.283 | 2.772 |
| df | 25 | 35 | 231 | 39 | 44 | 413 | 15 | 33 | 337 |
| P | 0.002* | 0.003* | 0.593 | 0.807 | 0.181 | 0.053 | 0.347 | 0.779 | 0.006* |
| [1] |
Andam KS, Ferraro PJ, Pfaff A, Sanchez-Azofeifa GA, Robalino J (2008) Measuring the effectiveness of protected areas networks in reducing deforestation. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 105, 16089-16094.
DOI URL PMID |
| [2] |
Armsworth PR, Daily GC, Kareiva P, Sanchirico JN (2006) Land market feedbacks can undermine biodiversity conservation. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 103, 5403-5408.
DOI URL PMID |
| [3] | Brockington D, Igoe J (2006) Eviction for conservation: a global overview. Conservation and Society, 4, 424-470. |
| [4] |
Bruner AG, Gullison RE, Rice RE, da Fonseca GAB (2001) Effectiveness of parks in protecting tropical biodiversity. Science, 291, 125-128.
DOI URL PMID |
| [5] |
Caro TM, Gardner TA, Stoner C, Fitzherbert EB, Davenport TRB (2009) Assessing the effectiveness of protected areas: paradoxes call for pluralism in evaluating conservation performance. Diversity and Distributions, 15, 178-182.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
Clements T, Suon S, Wilkie DS, Milner-Gulland EJ (2014) Impacts of protected areas on local livelihoods in Cambodia. World Development, 64, S125-S134.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
Coetzee BW, Gaston KJ, Chown SL (2014) Local scale comparisons of biodiversity as a test for global protected area ecological performance: a meta-analysis. PLoS ONE, 9, e105824.
DOI URL PMID |
| [8] |
Ervin J (2003) Rapid assessment of protected area management effectiveness in four countries. BioScience, 53, 833-841.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
Ewers RM, Rodrigues ASL (2008) Estimates of reserve effectiveness are confounded by leakage. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 23, 113-116.
DOI URL PMID |
| [10] |
Gaston KJ, Jackson SF, Cantú-salazar G, Cruz-pi?ón G (2008) The ecological performance of protected areas. Annual Review of Ecology, Evolution, and Systematics, 39, 93-113.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
Gaveau DLA, Epting J, Lyne O, Linkie M, Kumara I, Kanninen M, Leader-Williams N (2009) Evaluating whether protected areas reduce tropical deforestation in Sumatra. Journal of Biogeography, 36, 2165-2175.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
Geldmann J, Barnes M, Coad L, Craigie ID, Hockings M, Burgess ND (2013) Effectiveness of terrestrial protected areas in reducing habitat loss and population declines. Biological Conservation, 161, 230-238.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
Hansen BB, Bowers J (2008) Covariate balance in simple, stratified and clustered comparative studies. Statistical Science, 2, 219-236.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
Hansen BB, Klopfer SO (2006) Optimal full matching and related designs via network flows. Journal of Computational and Graphical Statistics, 15, 609-627.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
Ho DE, Imai K, King G, Stuart EA (2011) MatchIt: nonparametric preprocessing for parametric causal inference. Journal of Statistical Software, 42(8), 3-39.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
Huang FQ, Du CL, Sun MH, Ning B, Luo Y, An SL (2015) Propensity score matching in SPSS. Journal of Southern Medical University, 35, 1597-1601. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[黄福强, 杜春霖, 孙梦辉, 宁冰, 罗颖, 安胜利 (2015) 倾向评分配比在SPSS软件上的实现. 南方医科大学学报, 35, 1597-1601.]
DOI URL |
|
| [17] |
Imbens G (2004) Nonparametric estimation of average treatment effects under exogeneity: a review. Review of Economics and Statistics, 86, 4-29.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
Joppa LN, Pfaff A (2009) High and far: biases in the location of protected areas. PLoS ONE, 4, e8273.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
Joppa LN, Pfaff A (2010) Reassessing the forest impacts of protection: the challenge of nonrandom location and a corrective method. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 1185, 135-149.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
Ma KP (2016) On key issues and possible solutions related to nature reserve management in China. Biodiversity Science, 24, 249-251. (in Chinese)
DOI URL |
|
[马克平 (2016) 当前我国自然保护区管理中存在的问题与对策思考. 生物多样性, 24, 249-251.]
DOI URL |
|
| [21] |
Mas JF (2005) Assessing protected area effectiveness using surrounding (buffer) areas environmentally similar to the target area. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 105, 69-80.
DOI URL PMID |
| [22] |
Nagendra H (2008) Do parks work? Impact of protected areas on land cover clearing. Ambio, 37, 330-337.
DOI URL PMID |
| [23] |
Naughton-Treves L, Holland MB, Brandon K (2005) The role of protected areas in conserving biodiversity and sustaining livelihoods. Annual Review of Environment and Resources, 30, 219-252.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
Nepstad D, Schwartzman S, Bamberger B, Santilli M, Ray D, Schlesinger P, Lefebvre P, Alencar A, Prinz E, Fiske G, Rolla A (2006) Inhibition of Amazon deforestation and fire by parks and indigenous lands. Conservation Biology, 20, 65-73.
DOI URL PMID |
| [25] |
Pouzols FM, Toivonen T, Minin ED, Kukkala AS, Kullberg P, Kuuster? J, Lehtom?ki J, Tenkanen H, Verburg PH, Moilanen A (2014) Global protected area expansion is compromised by projected land-use and parochialism. Nature, 516, 383-386.
DOI URL PMID |
| [26] | Randolph JJ, Falbe K, Manuel AK, Balloun JL (2014) A step-by-step guide to propensity score matching in R. Practical Assessment, Research & Evaluation, 19.. (accessed on 2017-03-06) |
| [27] |
Reese HM, Lillesand TM, Nagel DE, Stewart JS, Goldmann RA, Simmons TE, Chipman JW, Tessar PA (2002) Statewide land cover derived from multiseasonal Landsat TM data: a retrospective of the WISCLAND project. Remote Sensing of Environment, 82, 224-237.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
Ren GP, Young SS, Wang L, Wang W, Long YC, Wu RD, Li JS, Zhu JG, Yu DW (2015) Effectiveness of China’s national forest protection program and nature reserves. Conservation Biology, 29, 1368-1377.
DOI URL PMID |
| [29] |
Shen B (1998) Studies on the resource exploitation and biodiversity conservation in Dali Cangshan-Erhai Nature Reserve. Chinese Biodiversity, 6, 151-156. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[沈兵 (1998) 大理苍洱自然保护区生物多样性保护及其开发利用. 生物多样性, 6, 151-156.]
DOI URL |
|
| [30] | Secretariat of the Convention on Biological Diversity (2014) Global Biodiversity Outlook 4. Montreal, Canada. |
| [31] |
Soares-Filho BS, Nepstad DC, Curran LM, Cerqueira GC, Garcia RA, Ramos CA, Voll E, McDonald A, Lefebvre P, Schlesinger P (2006) Modelling conservation in the Amazon basin. Nature, 440, 520-523.
DOI URL PMID |
| [32] | Sun M (2008) Cangshan Annals. The Nationalities Publishing House of Yunnan, Kunming. (in Chinese) |
| [孙明 (2008) 苍山志. 云南民族出版社, 昆明.] | |
| [33] |
Wang L, Young SS, Wang W, Ren GP, Xiao W, Long YC, Li JS, Zhu JG (2016) Conservation priorities of forest ecosystems with evaluations of connectivity and future threats: implications in the Eastern Himalaya of China. Biological Conservation, 195, 128-135.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
Wang W, Pechacek P, Zhang MX, Xiao NW, Zhu JG, Li JS (2013) Effectiveness of nature reserve system for conserving tropical forests: a statistical evaluation of Hainan Island, China. PLoS ONE, 8, e57561.
DOI URL PMID |
| [35] |
Wang W, Xin LJ, Du JH, Chen B, Liu FZ, Zhang LB, Li JS (2016) Evaluating conservation effectiveness of protected areas: advances and new perspectives. Biodiversity Science, 24, 1177-1188. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[王伟, 辛利娟, 杜金鸿, 陈冰, 刘方正, 张立博, 李俊生 (2016) 自然保护地保护成效评估: 进展与展望. 生物多样性, 24, 1177-1188.]
DOI URL |
|
| [36] |
Wittemyer G, Elsen P, Bean WT, Coleman A, Burton O, Brashares JS (2008) Accelerated human population growth at protected area edges. Science, 321, 123-126.
DOI URL PMID |
| [37] | [武冉 (2011) 我州天保工程一期工程顺利结束. 大理日报.]. (accessed on 2017-03-13) |
| [38] | Xin LJ, Zhu YP, Chen B, Jin YC, Luo JW, Wang W (2015) Effectiveness assessment of Cangshan Nature Reserve of Yunnan Province based on PSR model. Ecological Economy, 31(12), 125-128, 141. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [辛利娟, 朱彦鹏, 陈冰, 靳勇超, 罗建武, 王伟 (2015) 基于PSR模型的云南苍山保护区保护成效研究. 生态经济, 31(12), 125-128, 141.] |
| [1] | 董庆栋, 陈超男, 李艳红, 赵体侠, 孙梓欣, 张哲, 朱连奇. 基于NPP和人类扰动指数评估河南伏牛山地区国家级自然保护区群保护成效与溢出/泄漏效应[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(5): 22503-. |
| [2] | 席辉辉, 王祎晴, 潘跃芝, 许恬, 湛青青, 刘健, 冯秀彦, 龚洵. 中国苏铁属植物资源和保护[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(7): 21495-. |
| [3] | 王伟, 周越, 田瑜, 李俊生. 自然保护地生物多样性保护研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(10): 22459-. |
| [4] | 曹明, 李俊生, 王伟, 夏聚一, 冯春婷, 付刚, 黄文婕, 刘方正. 基于InVEST与倾向评分匹配模型评估秦岭国家级自然保护区水源涵养服务保护成效[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(5): 617-628. |
| [5] | 宋瑞玲, 姚锦仙, 吴恺悦, 张晓川, 吕植, 朱争光, 殷丽洁. 海洋保护区管理与保护成效评估的方法与进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2018, 26(3): 286-294. |
| [6] | 邓舒雨, 董向忠, 马明哲, 臧振华, 徐文婷, 赵常明, 谢宗强, 申国珍. 基于森林碳库动态评估神农架国家级自然保护区的保护成效[J]. 生物多样性, 2018, 26(1): 27-35. |
| [7] | 王翠玲, 臧振华, 邱月, 邓舒雨, 冯朝阳, 谢宗强, 徐文婷, 刘蕾, 陈全胜, 申国珍. 湖北神农架国家级自然保护区森林和川金丝猴栖息地的保护成效[J]. 生物多样性, 2017, 25(5): 504-512. |
| [8] | 王伟, 辛利娟, 杜金鸿, 陈冰, 刘方正, 张立博, 李俊生. 自然保护地保护成效评估: 进展与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2016, 24(10): 1177-1188. |
| [9] | 顾垒, 闻丞, 罗玫, 王昊, 吕植. 中国最受关注濒危物种保护现状快速评价的新方法探讨[J]. 生物多样性, 2015, 23(5): 583-590. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2026 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn
![]()