



生物多样性 ›› 2022, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (11): 22025. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2022025 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2022025
吴墨栩1,2, 安明态1,2,*( ), 田力1,2, 刘锋1,2
), 田力1,2, 刘锋1,2
收稿日期:2022-01-13
接受日期:2022-06-23
出版日期:2022-11-20
发布日期:2022-09-29
通讯作者:
安明态
作者简介: E-mail: gdanmingtai@126.com基金资助:
Moxu Wu1,2, Mingtai An1,2,*( ), Li Tian1,2, Feng Liu1,2
), Li Tian1,2, Feng Liu1,2
Received:2022-01-13
Accepted:2022-06-23
Online:2022-11-20
Published:2022-09-29
Contact:
Mingtai An
摘要:
植物性系统在群落更新、适应性和未来发展中起着重要作用。为了明确喀斯特森林性系统数量特征及其与环境因子的关系, 本研究采用相邻格子法从茂兰白鹇山山脚到山顶连续设置11个垂直样地, 同时采用该方法从山体中部沿同一等高线连续设置21个水平样地, 分析了研究区样地内胸径大于1 cm的木本植物性系统数量特征, 采用独立样本t检验分析了垂直样地与水平样地植物数量与性系统的差异, 采用冗余分析(RDA)探究了性系统数量特征与环境因子的相关性。结果表明: (1)样地内共有木本植物286种14,622株, 其中两性花植物156种(54.5%) 8,235株; 雌雄同株异花植物57种(20.0%) 3,838株; 雌雄异株植物73种(25.5%) 2,549株。垂直方向上, 随着海拔升高雌雄同株异花植物的植株数量显著增加, 两性花植物的物种比例显著下降; 坡位上表现为中坡位植物性系统多样性较低; 水平方向上, 两性花、雌雄同株异花与雌雄异株植物的植株数量、物种比例、性系统多样性指数都无明显规律。(2)雌雄同株异花植物的植株数量和物种比例在垂直样地与水平样地间有显著差异(P < 0.05); 雌雄异株与两性花植物的植株数量与物种比例无显著差异。(3)环境因子对木本植物的性系统数量特征有一定影响, 其中海拔的影响达到极显著水平(P < 0.01), 坡位的影响达到显著水平(P < 0.05)。总体上, 茂兰喀斯特森林木本植物性系统表现出与其他地区不同的丰富性、多样性和复杂性, 但大部分物种种群较小, 其数量分布特征可能是对喀斯特生境异质性适应的结果。
吴墨栩, 安明态, 田力, 刘锋 (2022) 茂兰喀斯特森林木本植物性系统数量特征及其与环境因子的关系. 生物多样性, 30, 22025. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2022025.
Moxu Wu, Mingtai An, Li Tian, Feng Liu (2022) Effects of environmental factors on quantitative characteristics of woody plant sexual system in Maolan karst forest. Biodiversity Science, 30, 22025. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2022025.
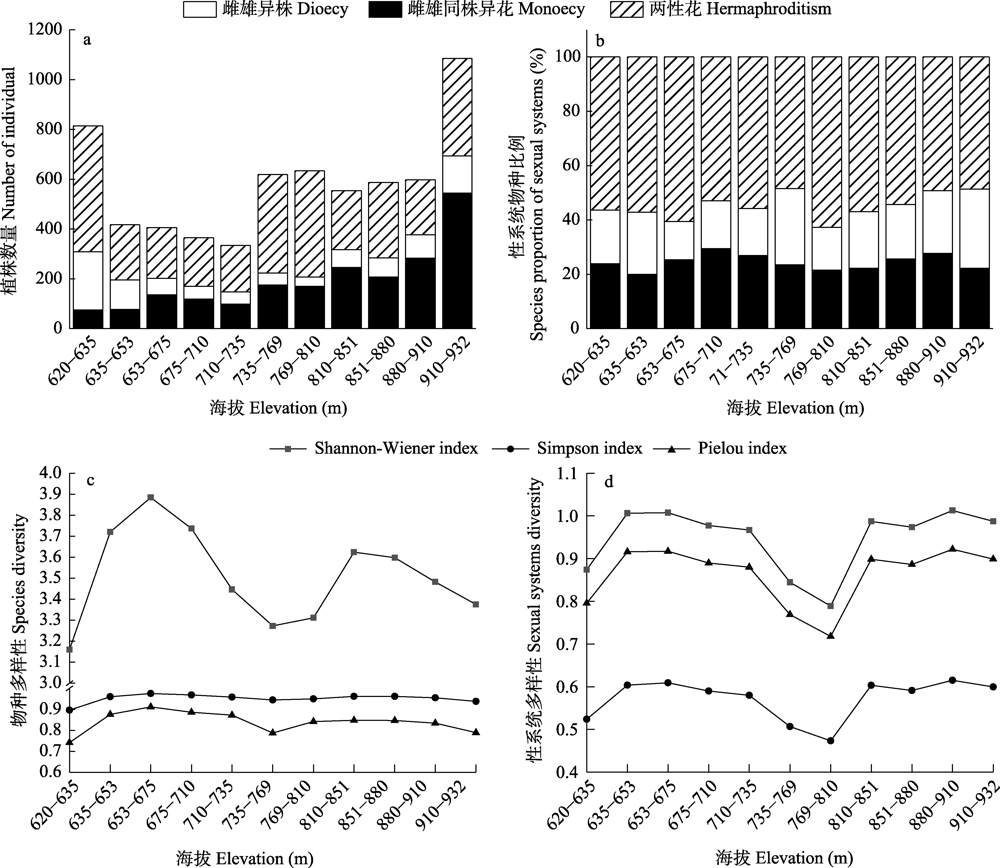
图3 茂兰喀斯特垂直样地植物个体数量(a)、性系统物种比例(b)、物种多样性(c)及性系统多样性(d)的变化
Fig. 3 Variation in plant individual number (a), species proportion of sexual systems (b), diversity of species (c) and sexual systems (d) in vertical plots in Maolan karst forest
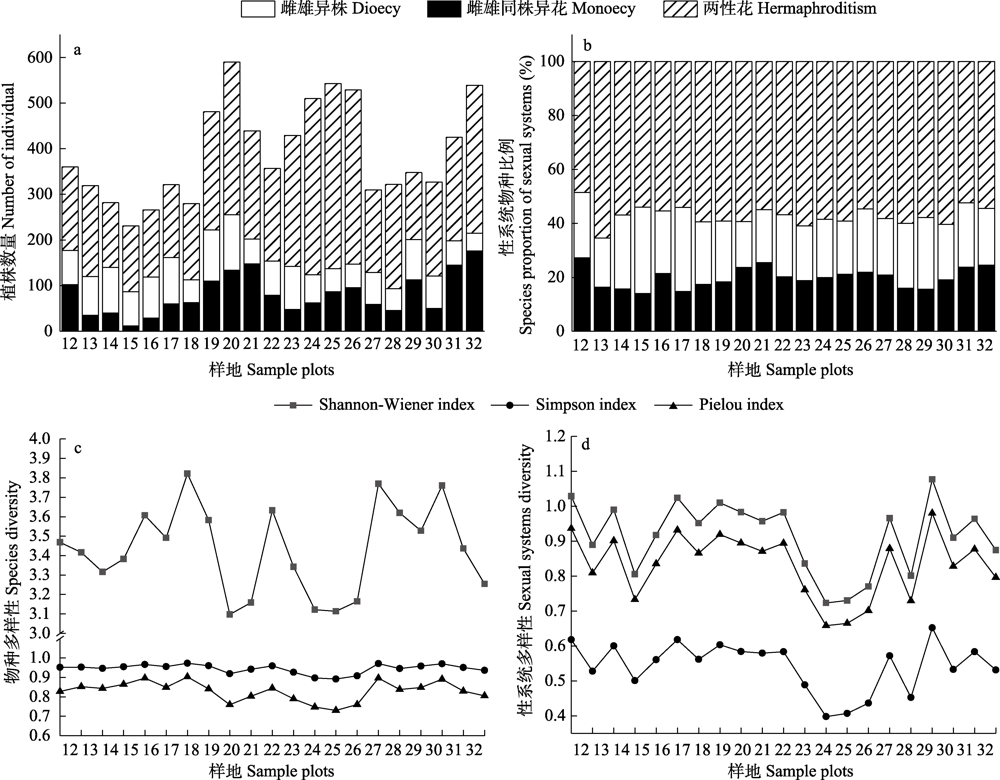
图4 茂兰喀斯特水平样地植物个体数量(a)、性系统物种比例(b)、物种多样性(c)及性系统多样性(d)的变化
Fig. 4 Variation in plant individual number (a), species proportion of sexual systems (b), diversity of species (c) and sexual systems (d) in horizontal plots in Maolan karst forest
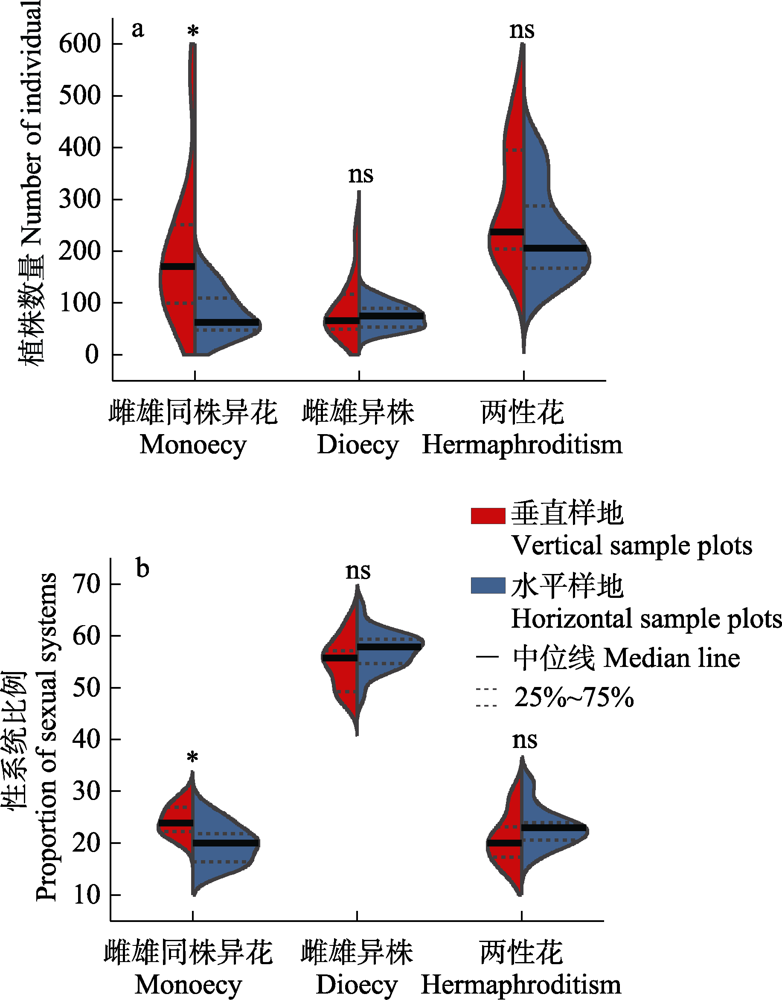
图5 茂兰喀斯特垂直与水平样地性系统的植株数量和比例小提琴图。ns表示垂直样地与水平样地间差异不显著; *表示0.05水平差异显著。
Fig. 5 Violin plots of individual number and proportion of sexual systems in vertical and horizontal plots in Maolan karst forest. ns represents no significant difference between the vertical sample plots and the horizontal sample plots; * represents 0.05 level of significance difference.
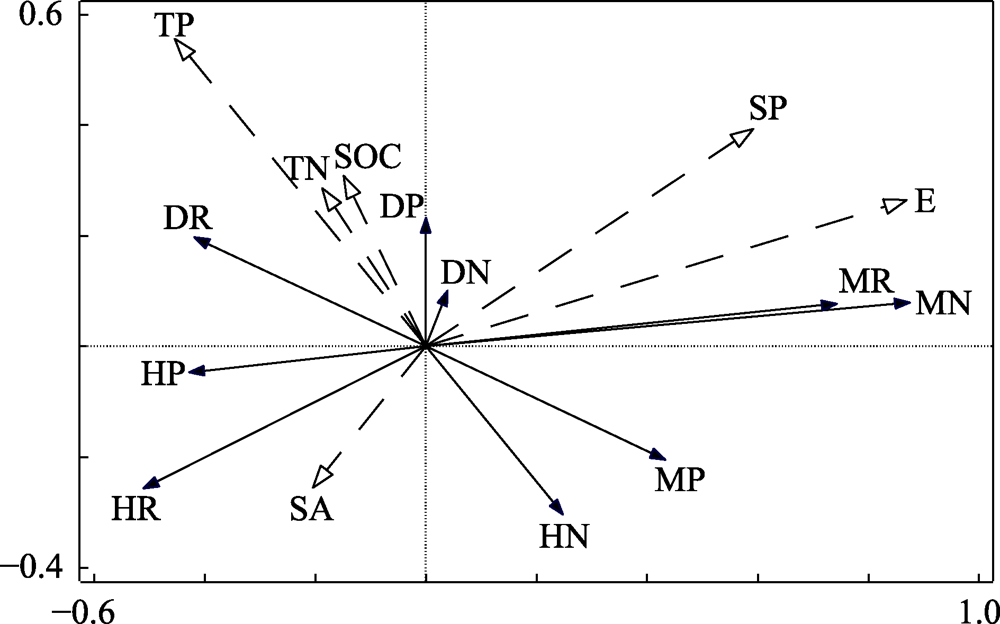
图6 性系统数量特征与环境因子的冗余分析。图中虚线表示环境因子, 实线表示不同性系统的数量特征。E: 海拔; SP: 坡位; SA: 坡向; SOC: 有机碳; TN: 氮; TP: 磷; HN: 两性花植株数量; HP: 两性花物种比例; HR: 两性花相对多度; MN: 雌雄同株异花植株数量; MP: 雌雄同株异花物种比例; MR: 雌雄同株异花相对多度; DN: 雌雄异株植株数量; DP: 雌雄异株物种比例; DR: 雌雄异株相对多度。
Fig. 6 Redundancy analysis of quantitative characteristics between sexual systems and environmental factors. The dotted line in the graph represents the environmental factor, and the solid line represents the quantitative characteristics of the different systems. E: Elevation; SP: Slope position; SA: Slope aspect; SOC: Soil organic carbon; TN: Total nitrogen; TP: Total phosphorus; HN: Number of individual with hermaphroditism; HP: Proportion of hermaphroditism species; HR: Relative abundance of hermaphroditism; MN: Number of individual with monoecy; MP: Proportion of monoecy species; MR: Relative abundance of monoecy; DN: Number of individual with dioecy; DP: Proportion of dioecy species; DR: Relative abundance of dioecy.
| 环境因子 Environmental factors | 重要性 排序 Importance order | 解释量 Explained variance (%) | F | P | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 海拔 Elevation | 1 | 29.9 | 12.8 | 0.002** | |
| 坡位 Slope position | 2 | 9.1 | 4.3 | 0.036* | |
| 土壤有机碳 Soil organic carbon | 3 | 2.0 | 0.9 | 0.348 | |
| 全磷 Total phosphorus | 4 | 1.9 | 0.9 | 0.382 | |
| 坡向 Slope aspect | 5 | 1.2 | 0.6 | 0.574 | |
| 全氮 Total nitrogen | 6 | 0.9 | 0.4 | 0.62 | |
表1 环境因子对性系统的重要性排序及显著性检验结果
Table 1 Results of importance order and significance test level of environmental factors to sexual systems
| 环境因子 Environmental factors | 重要性 排序 Importance order | 解释量 Explained variance (%) | F | P | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 海拔 Elevation | 1 | 29.9 | 12.8 | 0.002** | |
| 坡位 Slope position | 2 | 9.1 | 4.3 | 0.036* | |
| 土壤有机碳 Soil organic carbon | 3 | 2.0 | 0.9 | 0.348 | |
| 全磷 Total phosphorus | 4 | 1.9 | 0.9 | 0.382 | |
| 坡向 Slope aspect | 5 | 1.2 | 0.6 | 0.574 | |
| 全氮 Total nitrogen | 6 | 0.9 | 0.4 | 0.62 | |
| 有机碳 Organic carbon | 全氮 Total nitrogen | 全磷 Total phosphorus | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 海拔 Elevation | 0.210 | 0.049 | ?0.213 |
| 坡位 Slope position | 0.315 | 0.173 | ?0.115 |
| 坡向 Slope aspect | 0.165 | 0.140 | 0.046 |
表2 土壤因子与地形因子的相关性分析
Table 2 Correlation coefficients between soil factors and topography factors
| 有机碳 Organic carbon | 全氮 Total nitrogen | 全磷 Total phosphorus | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 海拔 Elevation | 0.210 | 0.049 | ?0.213 |
| 坡位 Slope position | 0.315 | 0.173 | ?0.115 |
| 坡向 Slope aspect | 0.165 | 0.140 | 0.046 |
| [1] | Case AL, Barrett SCH (2004) Environmental stress and the evolution of dioecy: Wurmbea dioica (Colchicaceae) in Western Australia. Evolutionary Ecology, 18, 145-164. |
| [2] | Chazdon RL, Careaga S, Webb C, Vargas O (2003) Community and phylogenetic structure of reproductive traits of woody species in wet tropical forests. Ecological Monographs, 73, 331-348. |
| [3] | Chen J, Han QQ, Duan BL, Korpelainen H, Li CY (2017) Sex- specific competition differently regulates ecophysiological responses and phytoremediation of Populus cathayana under Pb stress. Plant and Soil, 421, 203-218 |
| [4] | Chen J, Li CY (2014) Sex-specific responses to environmental stresses and sexual competition of dioecious plants. Chinese Journal of Applied and Environmental Biology, 20, 743-750. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [陈娟, 李春阳 (2014) 环境胁迫下雌雄异株植物的性别响应差异及竞争关系. 应用与环境生物学报, 20, 743-750.] | |
| [5] | Chen XS, Li QJ (2008) Sexual systems and ecological correlates in an azonal tropical forests, SW China. Biotropica, 40, 160-167. |
| [6] | Darwin C (1877) The Different Forms of Flowers on Plants of the Same Species. John Murray Press, London. |
| [7] | Dorken ME, Barrett SCH (2003) Life-history differentiation and the maintenance of monoecy and dioecy in Sagittaria latifolia (Alismataceae). Evolution, 57, 1973-1988. |
| [8] |
Etterson JR, Mazer SJ (2016) How climate change affects plants’ sex lives. Science, 353, 32-33.
DOI PMID |
| [9] | Geber MA, Dawson TE, Delph LF (1999) Gender and Sexual Dimorphism in Flowering Plants. Springer, Heidelberg. |
| [10] | Godin VN (2017) Sexual forms and their ecological correlates of flowering plants in Siberia. Russian Journal of Ecology, 48, 433-439. |
| [11] |
Gross CL (2005) A comparison of the sexual systems in the trees from the Australian tropics with other tropical biomes—More monoecy but why? American Journal of Botany, 92, 907-919.
DOI PMID |
| [12] | Guo YL, Wang B, Xiang WS, Ding T, Lu SH, Huang FZ, Wen SJ, Li DX, He YL, Li XK (2016) Responses of spatial pattern of woody plants’ basal area to topographic factors in a tropical karst seasonal rainforest in Nonggang, Guangxi, Southern China. Biodiversity Science, 24, 30-39. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[郭屹立, 王斌, 向悟生, 丁涛, 陆树华, 黄甫昭, 文淑均, 李冬兴, 何运林, 李先琨 (2016) 喀斯特季节性雨林木本植物胸高断面积分布格局及其对地形因子的响应. 生物多样性, 24, 30-39.]
DOI |
|
| [13] | Lai JS, Mi XC, Ren HB, Ma KP (2009) Species-habitat associations change in a subtropical forest of China. Journal of Vegetation Science, 20, 415-423. |
| [14] | Long R, Shang C, Qu S, Zhang ZX (2011) Distribution pattern of plant sexual system diversity in Populus lasiocarpa Oliv. community. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 33(5), 34-41. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [龙茹, 尚策, 曲上, 张志翔 (2011) 大叶杨群落植物性系统多样性的分布格局. 北京林业大学学报, 33(5), 34-41.] | |
| [15] | Ma KP (1994) Methods for measuring biome diversity. I. Methods for measuring α diversity (I). Biodiversity Science, 162-168. (in Chinese) |
| [马克平 (1994) 生物群落多样性的测度方法. I. α多样性的测度方法(上). 生物多样性, 162-168.] | |
| [16] |
Machado IC, Lopes AV, Sazima M (2006) Plant sexual systems and a review of the breeding system studies in the Caatinga, a Brazilian tropical dry forest. Annals of Botany, 97, 277-287.
PMID |
| [17] |
Pickup M, Barrett SCH (2012) Reversal of height dimorphism promotes pollen and seed dispersal in a wind-pollinated dioecious plant. Biology Letters, 8, 245-248.
DOI PMID |
| [18] | Punchi-Manage R, Getzin S, Wiegand T, Kanagaraj R, Savitri Gunatilleke CV, Nimal Gunatilleke IAU, Wiegand K, Huth A (2013) Effects of topography on structuring local species assemblages in a Sri Lankan mixed dipterocarp forest. Journal of Ecology, 101, 149-160. |
| [19] | Qin ST, Long CL, Wu BL (2018) Effects of topographic sites on the community structure and species diversity of karst forest in Maolan, Guizhou Province of southwestern China. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 40(7), 18-26. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [秦随涛, 龙翠玲, 吴邦利 (2018) 地形部位对贵州茂兰喀斯特森林群落结构及物种多样性的影响. 北京林业大学学报, 40(7), 18-26.] | |
| [20] | Ramírez N (2005) Plant sexual systems, dichogamy, and herkogamy in the Venezuelan central plain. Flora, 200, 30-48. |
| [21] | Ramírez N, Brito Y (1990) Reproductive biology of a tropical palm swamp community in the Venezuelan Llanos. American Journal of Botany, 77, 1260-1271. |
| [22] | Réjou-Méchain M, Cheptou PO (2015) High incidence of dioecy in young successional tropical forests. Journal of Ecology, 103, 725-732. |
| [23] | Rogers SR, Eppley SM (2012) Testing the interaction between inter-sexual competition and phosphorus availability in a dioecious grass. Botany, 90, 704-710. |
| [24] | Sim-Sim M, Lopes T, Ruas S, Stech M (2015) Does altitude shape molecular diversity and richness of bryophytes in Madeira’s natural forest? A case study with four bryophyte species at two altitudinal levels. Plant Ecology and Evolution, 148, 171-180. |
| [25] | Song TQ, Peng WX, Du H, Wang KL, Zeng FP (2014) Occurrence, spatial-temporal dynamics and regulation strategies of karst rocky desertification in Southwest China. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 34, 5328-5341. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [宋同清, 彭晚霞, 杜虎, 王克林, 曾馥平 (2014) 中国西南喀斯特石漠化时空演变特征、发生机制与调控对策. 生态学报, 34, 5328-5341.] | |
| [26] | Thomson FJ, Letten AD, Tamme R, Edwards W, Moles AT (2018) Can dispersal investment explain why tall plant species achieve longer dispersal distances than short plant species? New Phytologist, 217, 407-415. |
| [27] | Varga S, Soulsbury CD (2020) Environmental stressors affect sex ratios in sexually dimorphic plant sexual systems. Plant Biology, 22, 890-898. |
| [28] | Wang DL, Yu LF (2005) The quantitative assessment of ecological frangibility in karst area. Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Sciences Edition), 29(6), 23-26. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王德炉, 喻理飞 (2005) 喀斯特环境生态脆弱性数量评价. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 29(6), 23-26.] | |
| [29] | Wang X, Wang GR, Xia FC, Ni CC, Sun Y, Liu BD, Gao W, Zhou HC (2017) Sexual system and ecological links of woody plants in Changbai Mountains, northeastern China. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 39(5), 58-64. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王熊, 王戈戎, 夏富才, 倪成才, 孙越, 刘宝东, 高伟, 周海城 (2017) 长白山木本植物性别系统及其生态关联性. 北京林业大学学报, 39(5), 58-64.] | |
| [30] |
Wang YC, Lin JY, Xu H, Lin MX, Li YD (2019) Numerical characteristics of plant sexual system of the woody plants in the 60 ha plot in the tropical rain forest in Jianfengling, Hainan Island. Biodiversity Science, 27, 297-305. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[王颖灿, 林家怡, 许涵, 林明献, 李意德 (2019) 海南尖峰岭热带山地雨林60 ha大样地木本植物性别系统数量特征. 生物多样性, 27, 297-305.]
DOI |
|
| [31] | Wang YY, Luo A, Lyu T, Dimitrov D, Xu XT, Freckleton RP, Li YQ, Su XY, Li YC, Liu YP, Sandanov D, Li QJ, Hao ZQ, Liu SG, Wang ZH (2021) Global distribution and evolutionary transitions of angiosperm sexual systems. Ecology Letters, 24, 1835-1847. |
| [32] | Wang YY, Lyu T, Luo A, Li YQ, Liu YP, Freckleton RP, Liu SG, Wang ZH (2020a) Spatial patterns and drivers of angiosperm sexual systems in China differ between woody and herbaceous species. Frontiers in Plant Science, 11, 1222. |
| [33] | Wang YY, Lyu T, Shrestha N, Lyu LS, Li YQ, Schmid B, Freckleton RP, Dimitrov D, Liu SG, Hao ZQ, Wang ZH (2020b) Drivers of large-scale geographical variation in sexual systems of woody plants. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 29, 546-557. |
| [34] | Yan LH (2007) Sexual system and environmental adaptability of vines in Hupingshan Mountain, Hunan Province. Journal of Northeast Forestry University, 35(7), 35-36, 39. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [颜立红 (2007) 湖南壶瓶山藤本植物的有性系统及其环境适应性. 东北林业大学学报, 35(7) 35-36, 39.] | |
| [35] | Zhang Q, Niu JM, Buyantuyev A, Han F, Dong JJ, Zhang YN, Kang SRL, Yang Y (2011) Vegetation differentiation and soil effect at different slope locations—A case study of Stipa breviflora grassland in Inner Mongolia, China. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 35, 1167-1181. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[张庆, 牛建明, Buyantuyev A, 韩芳, 董建军, 张艳楠, 康萨如拉, 杨艳 (2011) 不同坡位植被分异及土壤效应——以内蒙古短花针茅草原为例. 植物生态学报, 35, 1167-1181.]
DOI |
|
| [36] | Zhang X, Li JX, Yu XL, Xie ZQ, Xun Y (2015) Spatial patterns of woody species in Rhododendron simsii shrubland at Daweishan, Hunan Province. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 34, 3034-3039. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [张旭, 李家湘, 喻勋林, 谢宗强, 寻院 (2015) 湖南大围山杜鹃灌丛木本植物种群空间格局. 生态学杂志, 34, 3034-3039.] | |
| [37] | Zhu SQ (2003) Study on Karst Forest Ecology (III). Guizhou Science and Technology Press, Guiyang. (in Chinese) |
| [朱守谦 (2003) 喀斯特森林生态研究(III). 贵州科技出版社, 贵阳.] |
| [1] | 袁敬毅, 张旭, 田镇朋, 王梓柘, 高永萍, 姚迪昭, 关宏灿, 李文楷, 刘婧, 张宏, 马勤. 结合无人机高分辨率可见光影像和激光雷达点云的城市植物群落树种组成和数量特征提取方法对比[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24237-. |
| [2] | 宋远昊, 龚吕, 李贲, 胡阳, 李秀珍. 辽河口不同退塘还湿方式对大型底栖动物的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24316-. |
| [3] | 魏诗雨, 宋天骄, 罗佳宜, 张燕, 赵子萱, 茹靖雯, 易华, 林雁冰. 秦岭火地塘针叶林土壤细菌群落的海拔分布格局[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(9): 24180-. |
| [4] | 何花, 谭敦炎, 杨晓琛. 被子植物隐性雌雄异株性系统的多样性、系统演化及进化意义[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(6): 24149-. |
| [5] | 徐凯伦, 陈小荣, 张敏华, 于婉婉, 吴素美, 朱志成, 陈定云, 兰荣光, 董舒, 刘宇. 演替和地形共同影响浙江百山祖森林群落的性系统多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(12): 24338-. |
| [6] | 张雅丽, 张丙昌, 赵康, 李凯凯, 刘燕晋. 毛乌素沙地不同类型生物结皮细菌群落差异及其驱动因子[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(8): 23027-. |
| [7] | 姚仁秀, 陈燕, 吕晓琴, 王江湖, 杨付军, 王晓月. 海拔及环境因子影响杜鹃属植物的表型特征和化学性状[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(2): 22259-. |
| [8] | 王晓凤, 饶杰生, 杨涛, 刘文聪, 田希, 陈稀, 刘其明, 徐衍潇, 张秋雨, 张洪强, 张旭, 欧晓昆, 沈泽昊. 云南鸡足山半湿润常绿阔叶林群落木本植物多样性格局与环境解释[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(11): 23217-. |
| [9] | 闫冰, 陆晴, 夏嵩, 李俊生. 城市土壤微生物多样性研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(8): 22186-. |
| [10] | 汪婷, 周立志. 合肥市小微湿地鸟类多样性的时空格局及其影响因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(7): 21445-. |
| [11] | 王芸芸, 郝占庆. 被子植物性系统的多样性、生态功能及分布规律[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(7): 22065-. |
| [12] | 薛文凯, 孟华旦尚, 王艳红, 朱攀, 德吉, 郭小芳. 纳木措可培养丝状真菌多样性及其与理化因子关系[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(6): 21473-. |
| [13] | 陈燕南, 梁铖, 陈军. 亚热带不同树种组成森林中土壤甲螨群落结构特征: 以江西新岗山为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(12): 22334-. |
| [14] | 施雨含, 任宗昕, 王维嘉, 徐鑫, 刘杰, 赵延会, 王红. 中国-喜马拉雅三种黄耆属植物与其传粉熊蜂的空间分布预测[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(6): 759-769. |
| [15] | 蒋日进,张琳琳,徐开达,李鹏飞,肖祎,樊紫薇. 浙江中南部近岸海域游泳动物功能群特征与多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2019, 27(12): 1330-1338. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn
![]()