



生物多样性 ›› 2011, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (4): 424-431. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2011.08325 cstr: 32101.14.SP.J.1003.2011.08325
所属专题: 生物入侵
高末1,2, 胡仁勇2, 陈贤兴2, 李伟成3, 丁炳扬2,*( )
)
收稿日期:2010-12-27
接受日期:2011-03-09
出版日期:2011-07-20
发布日期:2011-07-29
通讯作者:
丁炳扬
作者简介:* E-mail: dby@wzu.edu.cn基金资助:
Mo Gao1,2, Renyong Hu2, Xianxing Chen2, Weicheng Li3, Bingyang Ding2,*( )
)
Received:2010-12-27
Accepted:2011-03-09
Online:2011-07-20
Published:2011-07-29
Contact:
Bingyang Ding
摘要:
分析自然因子和人为活动对入侵植物分布的影响, 有助于预测外来植物的入侵。本研究采用路线踏查和样地调查相结合的方法, 对温州地区外来入侵植物的组成和分布进行3次调查, 同时记录样地土壤类型、地形、人为干扰等环境因子。使用典范对应分析(canonical correspondence analysis)进行排序, 分析外来植物的分布与环境因子之间的相关性以及不同因子对物种分布的影响; 利用方差分析比较外来入侵植物物种数和多度在不同地点间的差异, 及造成这种差异的主要影响因子。结果表明: (1)目前温州市外来入侵植物共64种, 隶属于28科51属; 从生活型上来看, 以一、二年生双子叶植物为主, 占70%以上, 原产地以美洲为主, 占68.8%。(2)各个区县间的物种分布存在显著差异(P = 0.000), 以乐清市的种类最多, 有51种, 其次是苍南县(43种), 最少的为洞头县(有27种)。(3)典范对应分析结果显示, 温州地区外来入侵植物分布格局主要受交通频度、聚居程度和地形的影响。(4)广布种和常见种的分布受到各个环境因子的影响差别不大, 而局限种和散布种的分布则明显受交通频度、地形两个因子的制约。(5)成功入侵的植物, 在侵入阶段更多的受人为活动的影响, 定居阶段则是环境因子起更大作用, 最后是否成功扩散并对入侵地造成危害则主要由植物自身的生物学特性决定。
高末, 胡仁勇, 陈贤兴, 李伟成, 丁炳扬 (2011) 干扰、地形和土壤对温州入侵植物分布的影响. 生物多样性, 19, 424-431. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2011.08325.
Mo Gao, Renyong Hu, Xianxing Chen, Weicheng Li, Bingyang Ding (2011) Effects of disturbance, topography, and soil conditions on the distribution of invasive plants in Wenzhou. Biodiversity Science, 19, 424-431. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2011.08325.
| 环境因子 Environmental factor | 量化标准 Quantification standard |
|---|---|
| F1: 土壤含水量 F1: Soil water content (%) | 1=很干燥, 2=干燥, 3=湿润, 4=很潮湿, 5=水淹没 1=Very arid, 2=Arid, 3=Damp, 4=Very damp, 5=Flush |
| F2: 土壤含沙量 F2: Sand content of soil | 1=粘土, 2=黄壤土, 3=红壤土, 4=壤土, 5=沙壤土, 6=砂土, 7=砾石 1=Clay, 2=Yellow soil, 3=Red soil, 4=Loan, 5=Sandy soil, 6=Sand, 7=Cobble stone |
| F3: 地形 F3: Landform | 1=山地, 2=丘陵坡地, 3=丘陵平地, 4=平原缓坡地, 5=平原平地 1=Mountains, 2=Hilly upland, 3=Hilly land, 4= Slope terra, 5=Plain |
| F4: 交通频度 F4: Traffic frequency | 1=极低, 2=农村小道, 3=乡镇公路, 4=城郊要道, 5=交通枢纽 1=Seldom, 2=Path, 3= Town road, 4= Suburban main road, 5=Pivot hub of communications |
| F5: 聚居程度 F5: Settlement degree | 1=人烟稀少, 2=农村, 3=乡镇, 4=城郊, 5=繁华区域 1=Sparsely populated, 2=Village, 3=Town, 4=Suburb, 5=Prosperous area |
| F6: 土地利用类型 F6: Land use types | 1=水田, 2=旱地, 3=有林地, 4=疏林地和灌丛, 5=园地, 6=水域, 7=城镇用地, 8=乡村用地, 9=荒地 1=Paddy field, 2=Arid farmland, 3=Woodland, 4=Sparse woodland, 5=Field, 6=Lake regions, 7= Town land use, 8=Village land use, 9=Wasteland |
表1 环境因子半量化、属性和等级数据的量化标准
Table 1 Half quantification, attribute and rank data quantification standard of environmental factors
| 环境因子 Environmental factor | 量化标准 Quantification standard |
|---|---|
| F1: 土壤含水量 F1: Soil water content (%) | 1=很干燥, 2=干燥, 3=湿润, 4=很潮湿, 5=水淹没 1=Very arid, 2=Arid, 3=Damp, 4=Very damp, 5=Flush |
| F2: 土壤含沙量 F2: Sand content of soil | 1=粘土, 2=黄壤土, 3=红壤土, 4=壤土, 5=沙壤土, 6=砂土, 7=砾石 1=Clay, 2=Yellow soil, 3=Red soil, 4=Loan, 5=Sandy soil, 6=Sand, 7=Cobble stone |
| F3: 地形 F3: Landform | 1=山地, 2=丘陵坡地, 3=丘陵平地, 4=平原缓坡地, 5=平原平地 1=Mountains, 2=Hilly upland, 3=Hilly land, 4= Slope terra, 5=Plain |
| F4: 交通频度 F4: Traffic frequency | 1=极低, 2=农村小道, 3=乡镇公路, 4=城郊要道, 5=交通枢纽 1=Seldom, 2=Path, 3= Town road, 4= Suburban main road, 5=Pivot hub of communications |
| F5: 聚居程度 F5: Settlement degree | 1=人烟稀少, 2=农村, 3=乡镇, 4=城郊, 5=繁华区域 1=Sparsely populated, 2=Village, 3=Town, 4=Suburb, 5=Prosperous area |
| F6: 土地利用类型 F6: Land use types | 1=水田, 2=旱地, 3=有林地, 4=疏林地和灌丛, 5=园地, 6=水域, 7=城镇用地, 8=乡村用地, 9=荒地 1=Paddy field, 2=Arid farmland, 3=Woodland, 4=Sparse woodland, 5=Field, 6=Lake regions, 7= Town land use, 8=Village land use, 9=Wasteland |
| 编号 No. | 种名 Species | 原产地 Original place | 生活型/生活习性 Life form/Habit | 分布类型 Distributional types |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 喜旱莲子草 Alternanthera philoxeroides | 南美洲 South America | 草本/多年生 Herb/Perennial | 广布型 E |
| 2 | 苏门白酒草 Conyza sumatrensis | 南美洲 South America | 草本/二年生 Herb/Biennial | 广布型 E |
| 3 | 钻形紫菀 Aster sublatus | 北美洲 North America | 草本/一年生 Herb/Annual | 广布型 E |
| 4 | 土荆芥 Chenopodium ambrosioides | 中、南美洲 Central, South America | 草本/一年生 Herb/Annual | 广布型 E |
| 5 | 美洲商陆 Phytolcca americana | 北美洲 North America | 草本/多年生 Herb/Perennial | 广布型 E |
| 6 | 野茼蒿 Crassocephalum crepidioides | 热带美洲 Tropical America | 草本/一年生 Herb/Annual | 广布型 E |
| 7 | 小蓬草 Conyza canadensis | 北美洲 North America | 草本/一年生 Herb/Annual | 广布型 E |
| 8 | 北美独行菜 Lepidium virginicum | 美洲 America | 草本/一年或多年生 Herb/Annual or perennial | 广布型 E |
| 9 | 大狼把草 Bidens frondosa | 北美洲 North America | 草本/一年生 Herb/Annual | 广布型 E |
| 10 | 藿香蓟 Ageratum conyzoides | 中、南美洲 Central, South America | 草本/一年生 Herb/Annual | 广布型 E |
| 11 | 鬼针草 Bidens pilosa | 热带美洲 Tropical America | 草本/一年生 Herb/Annual | 广布型 E |
| 12 | 一年蓬 Erigeron annuus | 北美洲 North America | 草本/二年生 Herb/Biennial | 广布型 E |
| 13 | 刺苋 Amaranthus spinosus | 热带美洲 Tropical America | 草本/一年生 Herb/Annual | 广布型 E |
| 14 | 裸柱菊 Soliva anthemifolia | 南美洲 South America | 草本/一年生 Herb/Annual | 常见型 C |
| 15 | 阿拉伯婆婆纳 Veronica persica | 西亚至伊朗 West Asia to Iran | 草本/二年生 Herb/Biennial | 常见型 C |
| 16 | 野老鹳草 Geranium carolinianum | 美洲 America | 草本/一年生 Herb/Annual | 常见型 C |
| 17 | 红花酢浆草 Oxalis corymbosa | 热带美洲 Tropical America | 草本/多年生 Herb/Perennial | 常见型 C |
| 18 | 臭荠 Coronopus didymus | 南美洲 South America | 草本/一年或二年生 Herb/Annual or biennial | 常见型 C |
| 19 | 紫茉莉 Mirabilis jalapa | 美洲 America | 草本/一或多年生 Herb/Annual or perennial | 常见型 C |
| 20 | 细枝落葵薯 Anredera cordifolia | 南美洲 South America | 草本/多年生 Herb/Perennial | 常见型 C |
| 21 | 圆叶牵牛 Pharbitis purpurea | 热带美洲 Tropical America | 草本/一年生 Herb/Annual | 常见型 C |
| 22 | 直立婆婆纳 Veronica arvensis | 欧洲 Europe | 草本/二年生 Herb/Biennial | 常见型 C |
| 23 | 田菁 Sesbania cannabina | 热带亚洲、大洋洲 Tropical Asia, Oceania | 草本/一年生 Herb/ Annual | 局限型 L |
| 24 | 铺地黍 Panicum repens | 南美洲 South America | 草本/多年生 Herb/Perennial | 局限型 L |
| 25 | 飞扬草 Euphorbia hirta | 热带美洲 Tropical America | 草本/一年生 Herb/Annual | 局限型 L |
| 26 | 牛茄子 Solanum capsicoides | 巴西 Brazil | 草本/一年生 Herb/Annual | 局限型 L |
| 27 | 草木樨 Melilotus officinalis | 欧洲 Europe | 草本/二年生 Herb/Biennial | 局限型 L |
| 28 | 凤眼莲 Eichornia crassipes | 巴西 Brazil | 草本/一年生 Herb/Annual | 局限型 L |
| 29 | 互花米草 Spartina alterniflora | 北美洲 North America | 草本/多年生 Herb/Perennial | 局限型 L |
| 30 | 豚草 Ambrosia artemisiifolia | 北美洲 North America | 草本/一年生 Herb/Annual | 局限型 L |
| 31 | 小叶冷水花 Pilea microphylla | 南美洲 South America | 草本/一年生 Herb/Annual | 局限型 L |
| 32 | 皱果苋 Amaranthus viridis | 热带美洲 Tropical America | 草本/一年生 Herb/Annual | 零散分布型 M |
| 33 | 斑地锦 Euphorbia maculata | 北美洲 North America | 草本/一年生 Herb/Annual | 零散分布型 M |
| 34 | 细叶芹 Apium leptophyllum | 美洲 America | 草本/一年生 Herb/Annual | 零散分布型 M |
| 35 | 睫毛牛膝菊 Galinsoga ciliata | 南美洲 South America | 草本/一年生 Herb/Annual | 零散分布型 M |
| 36 | 土人参 Talinum paniculatum | 南美洲 South America | 草本/一年或多年生 Herb/Annual or perennial | 零散分布型 M |
| 37 | 假酸浆 Nicandra physaloides | 南美洲 South America | 草本/一年生 Herb/Annual | 零散分布型 M |
| 38 | 三裂叶薯 Ipomoea triloba | 热带美洲 Tropical America | 草本/一年生 Herb/Annual | 零散分布型 M |
| 39 | 北美车前 Plantago virginica | 北美洲 North America | 草本/一年生 Herb/Annual | 偶见型 R |
| 40 | 菊芋 Halianthus tuberosus | 北美洲 North America | 草本/多年生 Herb/Perennial | 偶见型 R |
| 41 | 野燕麦 Avena fatua | 地中海地区 Mediterranean region | 草本/一年生 Herb/Annual | 偶见型 R |
| 42 | 婆婆纳 Veronica polita | 西亚 West Asia | 草本/二年生 Herb/Biennial | 偶见型 R |
| 43 | 野塘蒿 Conyza bonariensis | 南美洲 South America | 草本/二年生 Herb/Biennial | 偶见型 R |
| 44 | 凤尾兰 Yucca gloriosa | 北美洲 North America | 常绿灌木 Evergreen shrub | 偶见型 R |
| 45 | 加拿大一枝黄花 Solidago canadensis | 北美洲 North America | 草本/多年生 Herb/Perennial | 偶见型 R |
| 46 | 反枝苋 Amaranthus retroflexus | 美洲 America | 草本/一年生 Herb/Annual | 偶见型 R |
| 47 | 仙人掌 Opuntia stricta var. dillenii | 墨西哥 Mexico | 灌木/多年生 Shrub/Perennial | 偶见型 R |
| 48 | 大花金鸡菊 Coreopsis glandiflora | 北美洲 North America | 草本/一年生 Herb/Annual | 偶见型 R |
| 49 | 黑荆树 Acacia mearnsii | 大洋洲 Oceania | 常绿乔木 Evergreen tree | 偶见型 R |
| 50 | 野胡萝卜 Daucus carota | 欧洲 Europe | 草本/二年生 Herb/Biennial | 偶见型 R |
| 51 | 绿荆树 Acacia dealbata | 大洋洲 Oceania | 常绿乔木 Evergreen tree | 偶见型 R |
| 52 | 草胡椒 Peperomia pellucida | 热带美洲 Tropical America | 草本/一年生 Herb/Annual | 偶见型 R |
| 53 | 大漂 Pistia stratiotes | 巴西 Brazil | 草本/一年生 Herb/Annual | 偶见型 R |
| 54 | 苦槛蓝 Myoporum bontioides | 台湾 Taiwan, China | 常绿灌木 Evergreen shrub | 偶见型 R |
| 55 | 阔叶丰花草 Spermacoce latifolia | 南美洲 South America | 草本/一年生 Herb/Annual | 偶见型 R |
| 56 | 丝毛雀稗 Paspalum urvillei | 南美洲 South America | 草本/一年生 Herb/Annual | 偶见型 R |
| 57 | 北美水茄 Solanum carolinense | 北美洲 North America | 灌木/一年生 Shrub/Annual | 偶见型 R |
| 58 | 蓖麻 Ricinus communis | 非洲东北部 Northeast Africa | 草本/一年生 Herb/Annual | 偶见型 R |
附录I 本文涉及的温州58种外来入侵植物的名称、生活习性和分布类型
Appendix I The scientific name, habit and distributional types of 58 invasive plant species in Wenzhou City
| 编号 No. | 种名 Species | 原产地 Original place | 生活型/生活习性 Life form/Habit | 分布类型 Distributional types |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 喜旱莲子草 Alternanthera philoxeroides | 南美洲 South America | 草本/多年生 Herb/Perennial | 广布型 E |
| 2 | 苏门白酒草 Conyza sumatrensis | 南美洲 South America | 草本/二年生 Herb/Biennial | 广布型 E |
| 3 | 钻形紫菀 Aster sublatus | 北美洲 North America | 草本/一年生 Herb/Annual | 广布型 E |
| 4 | 土荆芥 Chenopodium ambrosioides | 中、南美洲 Central, South America | 草本/一年生 Herb/Annual | 广布型 E |
| 5 | 美洲商陆 Phytolcca americana | 北美洲 North America | 草本/多年生 Herb/Perennial | 广布型 E |
| 6 | 野茼蒿 Crassocephalum crepidioides | 热带美洲 Tropical America | 草本/一年生 Herb/Annual | 广布型 E |
| 7 | 小蓬草 Conyza canadensis | 北美洲 North America | 草本/一年生 Herb/Annual | 广布型 E |
| 8 | 北美独行菜 Lepidium virginicum | 美洲 America | 草本/一年或多年生 Herb/Annual or perennial | 广布型 E |
| 9 | 大狼把草 Bidens frondosa | 北美洲 North America | 草本/一年生 Herb/Annual | 广布型 E |
| 10 | 藿香蓟 Ageratum conyzoides | 中、南美洲 Central, South America | 草本/一年生 Herb/Annual | 广布型 E |
| 11 | 鬼针草 Bidens pilosa | 热带美洲 Tropical America | 草本/一年生 Herb/Annual | 广布型 E |
| 12 | 一年蓬 Erigeron annuus | 北美洲 North America | 草本/二年生 Herb/Biennial | 广布型 E |
| 13 | 刺苋 Amaranthus spinosus | 热带美洲 Tropical America | 草本/一年生 Herb/Annual | 广布型 E |
| 14 | 裸柱菊 Soliva anthemifolia | 南美洲 South America | 草本/一年生 Herb/Annual | 常见型 C |
| 15 | 阿拉伯婆婆纳 Veronica persica | 西亚至伊朗 West Asia to Iran | 草本/二年生 Herb/Biennial | 常见型 C |
| 16 | 野老鹳草 Geranium carolinianum | 美洲 America | 草本/一年生 Herb/Annual | 常见型 C |
| 17 | 红花酢浆草 Oxalis corymbosa | 热带美洲 Tropical America | 草本/多年生 Herb/Perennial | 常见型 C |
| 18 | 臭荠 Coronopus didymus | 南美洲 South America | 草本/一年或二年生 Herb/Annual or biennial | 常见型 C |
| 19 | 紫茉莉 Mirabilis jalapa | 美洲 America | 草本/一或多年生 Herb/Annual or perennial | 常见型 C |
| 20 | 细枝落葵薯 Anredera cordifolia | 南美洲 South America | 草本/多年生 Herb/Perennial | 常见型 C |
| 21 | 圆叶牵牛 Pharbitis purpurea | 热带美洲 Tropical America | 草本/一年生 Herb/Annual | 常见型 C |
| 22 | 直立婆婆纳 Veronica arvensis | 欧洲 Europe | 草本/二年生 Herb/Biennial | 常见型 C |
| 23 | 田菁 Sesbania cannabina | 热带亚洲、大洋洲 Tropical Asia, Oceania | 草本/一年生 Herb/ Annual | 局限型 L |
| 24 | 铺地黍 Panicum repens | 南美洲 South America | 草本/多年生 Herb/Perennial | 局限型 L |
| 25 | 飞扬草 Euphorbia hirta | 热带美洲 Tropical America | 草本/一年生 Herb/Annual | 局限型 L |
| 26 | 牛茄子 Solanum capsicoides | 巴西 Brazil | 草本/一年生 Herb/Annual | 局限型 L |
| 27 | 草木樨 Melilotus officinalis | 欧洲 Europe | 草本/二年生 Herb/Biennial | 局限型 L |
| 28 | 凤眼莲 Eichornia crassipes | 巴西 Brazil | 草本/一年生 Herb/Annual | 局限型 L |
| 29 | 互花米草 Spartina alterniflora | 北美洲 North America | 草本/多年生 Herb/Perennial | 局限型 L |
| 30 | 豚草 Ambrosia artemisiifolia | 北美洲 North America | 草本/一年生 Herb/Annual | 局限型 L |
| 31 | 小叶冷水花 Pilea microphylla | 南美洲 South America | 草本/一年生 Herb/Annual | 局限型 L |
| 32 | 皱果苋 Amaranthus viridis | 热带美洲 Tropical America | 草本/一年生 Herb/Annual | 零散分布型 M |
| 33 | 斑地锦 Euphorbia maculata | 北美洲 North America | 草本/一年生 Herb/Annual | 零散分布型 M |
| 34 | 细叶芹 Apium leptophyllum | 美洲 America | 草本/一年生 Herb/Annual | 零散分布型 M |
| 35 | 睫毛牛膝菊 Galinsoga ciliata | 南美洲 South America | 草本/一年生 Herb/Annual | 零散分布型 M |
| 36 | 土人参 Talinum paniculatum | 南美洲 South America | 草本/一年或多年生 Herb/Annual or perennial | 零散分布型 M |
| 37 | 假酸浆 Nicandra physaloides | 南美洲 South America | 草本/一年生 Herb/Annual | 零散分布型 M |
| 38 | 三裂叶薯 Ipomoea triloba | 热带美洲 Tropical America | 草本/一年生 Herb/Annual | 零散分布型 M |
| 39 | 北美车前 Plantago virginica | 北美洲 North America | 草本/一年生 Herb/Annual | 偶见型 R |
| 40 | 菊芋 Halianthus tuberosus | 北美洲 North America | 草本/多年生 Herb/Perennial | 偶见型 R |
| 41 | 野燕麦 Avena fatua | 地中海地区 Mediterranean region | 草本/一年生 Herb/Annual | 偶见型 R |
| 42 | 婆婆纳 Veronica polita | 西亚 West Asia | 草本/二年生 Herb/Biennial | 偶见型 R |
| 43 | 野塘蒿 Conyza bonariensis | 南美洲 South America | 草本/二年生 Herb/Biennial | 偶见型 R |
| 44 | 凤尾兰 Yucca gloriosa | 北美洲 North America | 常绿灌木 Evergreen shrub | 偶见型 R |
| 45 | 加拿大一枝黄花 Solidago canadensis | 北美洲 North America | 草本/多年生 Herb/Perennial | 偶见型 R |
| 46 | 反枝苋 Amaranthus retroflexus | 美洲 America | 草本/一年生 Herb/Annual | 偶见型 R |
| 47 | 仙人掌 Opuntia stricta var. dillenii | 墨西哥 Mexico | 灌木/多年生 Shrub/Perennial | 偶见型 R |
| 48 | 大花金鸡菊 Coreopsis glandiflora | 北美洲 North America | 草本/一年生 Herb/Annual | 偶见型 R |
| 49 | 黑荆树 Acacia mearnsii | 大洋洲 Oceania | 常绿乔木 Evergreen tree | 偶见型 R |
| 50 | 野胡萝卜 Daucus carota | 欧洲 Europe | 草本/二年生 Herb/Biennial | 偶见型 R |
| 51 | 绿荆树 Acacia dealbata | 大洋洲 Oceania | 常绿乔木 Evergreen tree | 偶见型 R |
| 52 | 草胡椒 Peperomia pellucida | 热带美洲 Tropical America | 草本/一年生 Herb/Annual | 偶见型 R |
| 53 | 大漂 Pistia stratiotes | 巴西 Brazil | 草本/一年生 Herb/Annual | 偶见型 R |
| 54 | 苦槛蓝 Myoporum bontioides | 台湾 Taiwan, China | 常绿灌木 Evergreen shrub | 偶见型 R |
| 55 | 阔叶丰花草 Spermacoce latifolia | 南美洲 South America | 草本/一年生 Herb/Annual | 偶见型 R |
| 56 | 丝毛雀稗 Paspalum urvillei | 南美洲 South America | 草本/一年生 Herb/Annual | 偶见型 R |
| 57 | 北美水茄 Solanum carolinense | 北美洲 North America | 灌木/一年生 Shrub/Annual | 偶见型 R |
| 58 | 蓖麻 Ricinus communis | 非洲东北部 Northeast Africa | 草本/一年生 Herb/Annual | 偶见型 R |
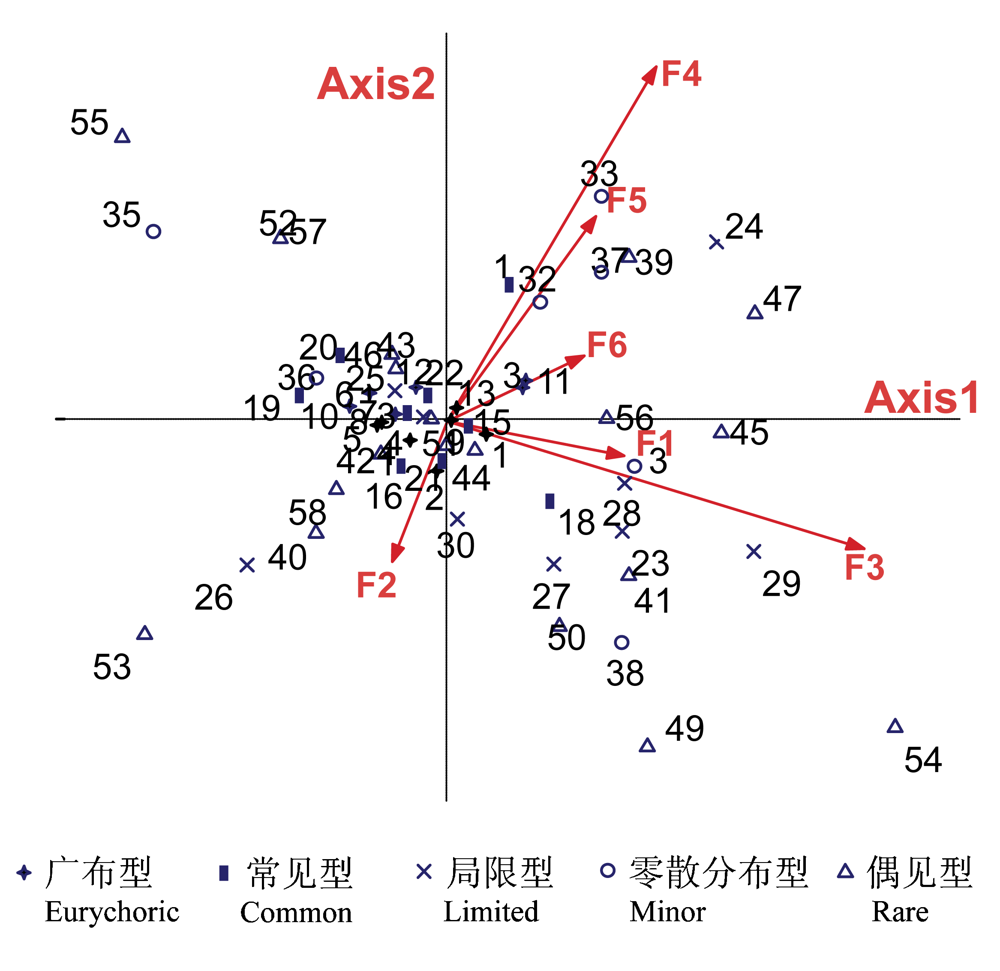
图2 温州入侵植物分布与环境因子间关系的CCA排序图。图中箭头表示环境因子, 箭头连线的长短表示物种分布与环境因子相关性的大小, 箭头所处的象限表示环境因子与排序轴之间相关性的正负。物种1-58见附录I, 环境因子F1至F6见表1。
Fig. 2 CCA ordination diagram of correlation between the distribution of invasive plants and environmental factors in Wenzhou. See Appendix I for details of species 1-58, and environmental factors F1- F6 are the same as in Table 1.
| 项目 Item | CCA axes | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Axis 1 | Axis 2 | Axis 3 | Axis 4 | |
| 特征值 Eigen value | 0.112** | 0.072** | 0.04 | 0.035 |
| 物种-环境相关性 Species-environment correlations | 0.668 | 0.606 | 0.452 | 0.441 |
| 物种方差累计贡献率 Cumulative percentage variance of species data (%) | 1.6 | 2.7 | 3.3 | 3.8 |
| 物种-环境关系方差累计贡献率 Cumulative percentage variance of species-environment relationship (%) | 34.6 | 56.9 | 69.3 | 80.1 |
表2 CCA排序特征值和入侵物种与环境的相关性
Table 2 Eigen values and correlations between species axes and environmental axes from CCA ordination
| 项目 Item | CCA axes | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Axis 1 | Axis 2 | Axis 3 | Axis 4 | |
| 特征值 Eigen value | 0.112** | 0.072** | 0.04 | 0.035 |
| 物种-环境相关性 Species-environment correlations | 0.668 | 0.606 | 0.452 | 0.441 |
| 物种方差累计贡献率 Cumulative percentage variance of species data (%) | 1.6 | 2.7 | 3.3 | 3.8 |
| 物种-环境关系方差累计贡献率 Cumulative percentage variance of species-environment relationship (%) | 34.6 | 56.9 | 69.3 | 80.1 |
| 项目 Item | CCA axes | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Axis 1 | Axis 2 | Axis 3 | Axis 4 | ||||||
| 广布型、常见型 Eurychoric and common species | |||||||||
| 特征值 Eigen value | 0.11 | 0.06 | 0.037 | 0.034 | |||||
| 物种-环境相关性 Species-environment correlations | 0.636 | 0.503 | 0.425 | 0.388 | |||||
| 物种方差累计贡献率 Cumulative percentage variance of species data (%) | 2.7 | 4.2 | 5.1 | 6 | |||||
| 物种-环境关系方差累计贡献率 Cumulative percentage variance of species-environment relationship (%) | 40.7 | 63.1 | 76.6 | 89 | |||||
| 散布型、局限型、偶见型 Limited, minor and rare species | |||||||||
| 特征值 Eigen value | 0.504** | 0.489** | 0.267** | 0.24** | |||||
| 物种-环境相关性 Species-environment correlations | 0.758 | 0.784 | 0.619 | 0.551 | |||||
| 物种方差累计贡献率 Cumulative percentage variance of species data (%) | 2.3 | 4.5 | 5.7 | 6.8 | |||||
| 物种-环境关系方差累计贡献率 Cumulative percentage variance of species-environment relationship (%) | 26.4 | 52.1 | 66.1 | 78.7 | |||||
表3 不同分布频度外来植物的CCA排序特征值和物种与环境的相关性
Table 3 Eigen values and correlations between species and environmental axes from CCA ordination for invading species in Wenzhou
| 项目 Item | CCA axes | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Axis 1 | Axis 2 | Axis 3 | Axis 4 | ||||||
| 广布型、常见型 Eurychoric and common species | |||||||||
| 特征值 Eigen value | 0.11 | 0.06 | 0.037 | 0.034 | |||||
| 物种-环境相关性 Species-environment correlations | 0.636 | 0.503 | 0.425 | 0.388 | |||||
| 物种方差累计贡献率 Cumulative percentage variance of species data (%) | 2.7 | 4.2 | 5.1 | 6 | |||||
| 物种-环境关系方差累计贡献率 Cumulative percentage variance of species-environment relationship (%) | 40.7 | 63.1 | 76.6 | 89 | |||||
| 散布型、局限型、偶见型 Limited, minor and rare species | |||||||||
| 特征值 Eigen value | 0.504** | 0.489** | 0.267** | 0.24** | |||||
| 物种-环境相关性 Species-environment correlations | 0.758 | 0.784 | 0.619 | 0.551 | |||||
| 物种方差累计贡献率 Cumulative percentage variance of species data (%) | 2.3 | 4.5 | 5.7 | 6.8 | |||||
| 物种-环境关系方差累计贡献率 Cumulative percentage variance of species-environment relationship (%) | 26.4 | 52.1 | 66.1 | 78.7 | |||||
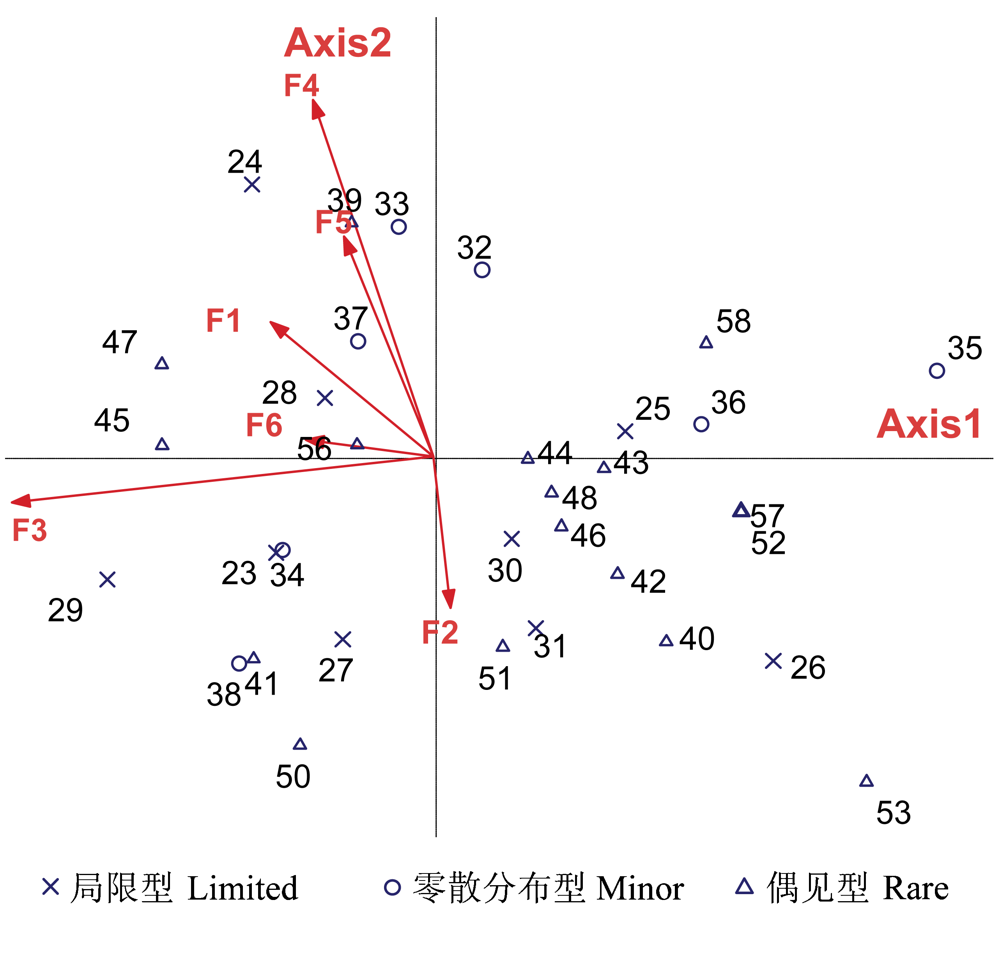
图3 零散分布型、局限型、偶见型分布与环境因子间关系的CCA排序图。图中箭头表示环境因子, 箭头连线的长短表示物种分布与环境因子相关性的大小, 箭头所处的象限表示环境因子与排序轴之间相关性的正负。物种1-58见附录I, 环境因子F1- F6 见表1。
Fig. 3 CCA ordination diagram of correlation between disposition and environment factors limited species, minor species and rare species. See Appendix I for details of species 1-58. Environmental factors F1-F6 are the same as in Table 1.
| [1] | Belote RT, Jones HR, Hood MS (2008) Diversity-invasibility across an experimental disturbance gradient in Appalachian forests. Ecology, 89, 183-192. |
| [2] | Chen ZW (陈志伟), Yang JP (杨京平), Wang RZ (王荣洲), Shang HW (商晗武) (2009) Spatial distribution pattern of Solidago canadensis in Zhejiang Province and its relationship with anthropogenic activities. Acta Ecologica Sinica (生态学报), 29, 120-128. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [3] | Chen XY (陈小永), Wang HY (王海燕), Ding BY (丁炳扬), Mei XM (梅笑漫) (2006) The species and habitat characteristics of exotic weeds in Hangzhou. Bulletin of Botanical Research (植物研究), 26, 243-249. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [4] | Cleland EE, Smith MD, Andelman CB, Bowles C, Carney KM, Horner-Devine MC, Drake JM, Emery SM, Gramling JM, Vandermast DB (2004) Invasion in space and time: non-native species richness and relative abundance respond to interannual variation in productivity and diversity. Ecology Letters, 7, 947-957. |
| [5] | Davis MA, Grime JP, Thompson K (2000) Fluctuating resources in plant communities: a general theory of invasibility. Journal of Ecology, 88, 528-534. |
| [6] | Dong M (董梅), Lu JZ (陆建忠), Zhang WJ (张文驹), Chen JK (陈家宽), Li B (李博) (2006) Canada goldenrod (Solidago canadensis): an invasive alien weed rapidly spreading in China. Acta Phytotaxonomica Sinica (植物分类学报), 44, 72-85. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [7] | Dukes JS (2001) Biodiversity and invasibility in grassland microcosms. Oecologia, 126, 563-568. |
| [8] | Editorial Committee of Forests of Wenzhou (温州市林业志编纂委员会) (2004) Forests in Wenzhou (温州市林业志). Zhonghua Shuju, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [9] | Feng JM (冯建孟), Xu CD (徐成东) (2009) Spatial distribution pattern of alien plants in Yunnan Province and its relationship with environmental factors and human activities. Journal of Southwest University (Natural Science Edition) (西南大学学报(自然科学版)), 31, 78-83. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [10] | Fu DG (付登高), Yan K (阎凯), Li B (李博), Han JB (韩金保), Hou XL (侯秀丽), Duan CQ (段昌群) (2010) Distribution pattern and related habitat factors of invasive plant Eupatorium adenophorum along the roadsides in central Yunnan Province, China. Chinese Journal of Ecology (生态学杂志), 29, 566-571. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [11] | Herben T, Mandák B, Bímová K, Münzbergová Z (2004) Invasibility and species richness of a community: a neutral model and a survey of published data. Ecology, 85, 3223-3233. |
| [12] | Hierro JL, Villareal D, Eren Ö, Graham JM, Callaway RM (2006) Disturbance facilitates invasion: the effects are stronger abroad than at home. The American Naturalist, 168, 144-156. |
| [13] | Kolar CS, Lodge DM (2001) Predicting invaders-response. Trends in Ecology and Evolution, 16, 546. |
| [14] | Li B (李博), Xu BS (徐炳声), Chen JK (陈家宽) (2001) Perspectives on general trends of plant invasions with special reference to alien weed flora of Shanghai. Biodiversity Science (生物多样性), 9, 446-457. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [15] | Li GY (李根有), Jin SH (金水虎), Yuan JG (袁建国) (2006) Species, characteristics and control measures of injurious plants in Zhejiang Province. Journal of Zhejiang Forestry College (浙江林学院学报), 23, 614-624. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [16] | Liu J (刘建) (2005) The Distribution Pattern and Characteristics of the Invasive Plant Species in China (中国入侵植物分布格局和特性分析). PhD dissertation, Shandong University, Shandong. (in Chinese with English Summary) |
| [17] | Liu J (刘建), Li JM (李钧敏), Yu H (余华), He WM (何维明), Yu FH (于飞海), Sang WG (桑卫国), Liu GF (刘国方), Dong M (董鸣) (2010) The relationship between functional traits and invasiveness of alien plants. Biodiversity Science (生物多样性), 18, 569-576. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [18] | Rejmanek M, Richardson DM (1996) What attributes make some plant species more invasive? Ecology, 77, 1655-1661. |
| [19] | Renne IJ, Tracy BF, Colonna IA (2006) Shifts in grassland invasibility: effects of soil resources, disturbance, composition, and invader size. Ecology, 87, 2264-2277. |
| [20] | Sang WG (桑卫国), Zhu L (朱丽), Ma KP (马克平) (2006) Issues, phenomena and study emphasis of alien species invasion in China. Advances in Earth Science (地球科学进展), 21, 305-312. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [21] | Shea K, Chesson P (2002) Community ecology theory as a framework for biological invasions. Trends in Ecology and Evolution, 17, 170-176. |
| [22] | Shi SZ (石胜璋), Tian MJ (田茂洁), Liu YC (刘玉成) (2004) Investigation and study on the alien invasive plants in Chongqing. Journal of Southwest China Normal University (Natural Science) (西南师范大学学报(自然科学版)), 29, 863-866. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [23] | Symstad A (2000) A test of the effects of functional group richness and composition on grassland invisibility. Ecology, 81, 99-109. |
| [24] | Von Holle B, Simberloff D (2005) Ecological resistance to biological invasion overwhelmed by propagule pressure. Ecology, 86, 3212-3218. |
| [25] | Weber E, Sun SG, Li B (2008) Invasive alien plants in China: diversity and ecological insights. Biological Invasions, 10, 1411-1429. |
| [26] | Wu SH, Sun HT, Teng YC, Rejmánek M, Chaw SM, Yang TYA, Hsieh CF (2010) Patterns of plant invasions in China: taxonomic, biogeographic, climatic approaches and anthropogenic effects. Biological Invasions, 12, 2179-2206. |
| [27] | Wu XW (吴晓雯), Luo J (罗晶), Chen JK (陈家宽), Li B (李博) (2006) Spatial patterns of invasive alien plants in China and its relationship with environmental and anthropological factors. Journal of Plant Ecology (Chinese version) (植物生态学报), 30, 576-584. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [28] | Zhang S (张帅), Guo SL (郭水良), Guan M (管铭), Yin LP (印丽萍), Zhang RX (张若轩) (2010) Diversity differentiation of invasive plants at a regional scale in China and its influencing factors: according to analyses on the data from 74 regions. Acta Ecologica Sinica (生态学报), 30, 4241-4256. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [29] | Zhu SX (朱世新), Qin HN (覃海宁), Chen YL (陈艺林) (2005) Alien species of Compositae in China. Guihaia (广西植物), 25, 69-76. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [1] | 李艳朋, 陈洁, 卢春洋, 许涵. 海南尖峰岭热带山地雨林64 ha次生林动态监测样地群落结构特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24445-. |
| [2] | 宋远昊, 龚吕, 李贲, 胡阳, 李秀珍. 辽河口不同退塘还湿方式对大型底栖动物的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24316-. |
| [3] | 魏诗雨, 宋天骄, 罗佳宜, 张燕, 赵子萱, 茹靖雯, 易华, 林雁冰. 秦岭火地塘针叶林土壤细菌群落的海拔分布格局[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(9): 24180-. |
| [4] | 郑博瀚, 陈鑫瑶, 倪健. 中国维管植物生长型和生活型数据集[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(7): 23468-. |
| [5] | 吴相獐, 雷富民, 单壹壹, 于晶. 上海城市公园苔藓植物多样性分布格局及其环境影响因子[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(2): 23364-. |
| [6] | 张雅丽, 张丙昌, 赵康, 李凯凯, 刘燕晋. 毛乌素沙地不同类型生物结皮细菌群落差异及其驱动因子[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(8): 23027-. |
| [7] | 杨俊毅, 关潇, 李俊生, 刘晶晶, 郝颢晶, 王槐睿. 乌江流域生物多样性与生态系统服务的空间格局及相互关系[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(7): 23061-. |
| [8] | 肖俞, 李宇然, 段禾祥, 任正涛, 冯圣碧, 姜志诚, 李家华, 张品, 胡金明, 耿宇鹏. 高黎贡山外来植物入侵现状及管控建议[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(5): 23011-. |
| [9] | 谢艳秋, 黄晖, 王春晓, 何雅琴, 江怡萱, 刘子琳, 邓传远, 郑郁善. 福建海岛滨海特有植物种-面积关系及物种丰富度决定因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(5): 22345-. |
| [10] | 姚仁秀, 陈燕, 吕晓琴, 王江湖, 杨付军, 王晓月. 海拔及环境因子影响杜鹃属植物的表型特征和化学性状[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(2): 22259-. |
| [11] | 王晓凤, 饶杰生, 杨涛, 刘文聪, 田希, 陈稀, 刘其明, 徐衍潇, 张秋雨, 张洪强, 张旭, 欧晓昆, 沈泽昊. 云南鸡足山半湿润常绿阔叶林群落木本植物多样性格局与环境解释[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(11): 23217-. |
| [12] | 崔夏, 刘全儒, 吴超然, 何宇飞, 马金双. 京津冀外来入侵植物[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(8): 21497-. |
| [13] | 闫冰, 陆晴, 夏嵩, 李俊生. 城市土壤微生物多样性研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(8): 22186-. |
| [14] | 汪婷, 周立志. 合肥市小微湿地鸟类多样性的时空格局及其影响因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(7): 21445-. |
| [15] | 李正飞, 蒋小明, 王军, 孟星亮, 张君倩, 谢志才. 雅鲁藏布江中下游底栖动物物种多样性及其影响因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(6): 21431-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2026 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn
![]()