



生物多样性 ›› 2018, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (8): 819-827. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2018052 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2018052
李爱农1,*( ), 尹高飞1, 张正健1,2, 谭剑波1,2, 南希1, 马克平3, 郭庆华3
), 尹高飞1, 张正健1,2, 谭剑波1,2, 南希1, 马克平3, 郭庆华3
收稿日期:2018-02-11
接受日期:2018-06-24
出版日期:2018-08-20
发布日期:2018-09-27
通讯作者:
李爱农
作者简介:# 共同第一作者
基金资助:
Ainong Li1,*( ), Gaofei Yin1, Zhengjian Zhang1,2, Jianbo Tan1,2, Xi Nan1, Keping Ma3, Qinghua Guo3
), Gaofei Yin1, Zhengjian Zhang1,2, Jianbo Tan1,2, Xi Nan1, Keping Ma3, Qinghua Guo3
Received:2018-02-11
Accepted:2018-06-24
Online:2018-08-20
Published:2018-09-27
Contact:
Li Ainong
About author:# Co-first authors
摘要:
科学制定生物多样性保护和恢复政策, 需要空间上连续、时间上高频的物种和生境分布以及物种迁移信息支持, 遥感是目前能满足该要求的有效技术手段。近年来, 遥感平台和载荷技术高速发展, 综合多平台、多尺度、多模式遥感技术, 开展基于站点的星空地一体化遥感观测试验, 可以对地表进行时空多维度、立体连续观测, 为生物多样性遥感监测提供了新的契机。本文总结了使用遥感技术监测生物多样性的主要方法, 回顾了典型的星空地一体化遥感观测试验。综述以往研究发现, 一方面, 现有遥感试验还缺少对生物多样性直接监测指标的观测, 另一方面, 生物多样性遥感监测方法也缺少星空地多维立体观测平台的支撑, 亟需加强两者的融合, 开展基于站点的生物多样性星空地一体化遥感监测研究。以设于我国四川王朗大熊猫国家级自然保护区内的王朗山地生态遥感综合观测试验站为例, 展示了星空地一体化遥感综合观测试验平台在生物多样性监测中的应用潜力。星空地一体化遥感观测可以提供物种和生境的综合定量信息, 与生态模型有机结合, 可以刻画生物多样性的时空格局与动态过程, 有助于挖掘过程机理, 提高生物多样性监测的信息化水平。
李爱农, 尹高飞, 张正健, 谭剑波, 南希, 马克平, 郭庆华 (2018) 基于站点的生物多样性星空地一体化遥感监测. 生物多样性, 26, 819-827. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2018052.
Ainong Li, Gaofei Yin, Zhengjian Zhang, Jianbo Tan, Xi Nan, Keping Ma, Qinghua Guo (2018) Space-air-field integrated biodiversity monitoring based on experimental station. Biodiversity Science, 26, 819-827. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2018052.
| 方法 Method | 传感器 Sensor | 空间分辨率 Spatial resolution | 光谱分辨 Spectral resolution | 监测内容 Monitoring contents | 参考文献 Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 直接法 Direct approaches | |||||
| 天基遥感 Space-based | IKONOS Quickbird WorldView-2 吉林一号 Jilin-1 | 1-4 m 0.6-2.4 m 0.5 m, 2 m 0.72-2.88 m | 4波段 4 bands 4波段 4 bands 8波段 8 bands 4波段 4 bands | 冠层、物种信息 Canopy and species information | |
| ADS40 AHS-160 CASI Lidar | 0.2 m 2.4 m 1 m | 4波段 4 bands 63波段 63 bands 288波段 288 bands | |||
| 地基遥感 Ground-based | 红外相机 Infrared camera 视频监控 Video monitoring 声景监控 Soundscape | 可见光、红外 Visible, infrared 可见光、红外 Visible and infrared | 物种活动场景 The behavior of species | ||
| 间接法 Indirect approaches | |||||
| 景观指数法 Landscape index | TM/ETM + HJ MODIS EO-1 Hyperion ASTER Sentinel-2 MSI SPOT CBERS-04 | 30-120 m 30-100 m 250-1 km 30 m 15 m, 30 m, 90 m 10 m, 20 m, 60 m 1.5 m, 6 m, 1 km 5-80 m | 7-9波段 7-9 bands 4波段 4 bands 36波段 36 bands 220波段 220 bands 14波段 14 bands 13波段 13 bands 4-6波段 4-6 bands 12波段 12 bands | 土地分类 Land cover classification | |
| 遥感指数法 Satellite index | 多样性指数 Biodiversity index | ||||
| 光谱变异性指数法 Spectral heterogeneity index | 光谱异质性指数 Spectral heterogeneity index | ||||
| 模型模拟法 Model simulation | TRMM/TMI FY-3C/VIRR | 5-72 km 1 km | 5波段 5 bands 10波段 10 bands | 物种分布 Species distribution | |
表1 生物多样性遥感监测的主要方法
Table 1 Main methods of remote sensing for biodiversity monitoring
| 方法 Method | 传感器 Sensor | 空间分辨率 Spatial resolution | 光谱分辨 Spectral resolution | 监测内容 Monitoring contents | 参考文献 Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 直接法 Direct approaches | |||||
| 天基遥感 Space-based | IKONOS Quickbird WorldView-2 吉林一号 Jilin-1 | 1-4 m 0.6-2.4 m 0.5 m, 2 m 0.72-2.88 m | 4波段 4 bands 4波段 4 bands 8波段 8 bands 4波段 4 bands | 冠层、物种信息 Canopy and species information | |
| ADS40 AHS-160 CASI Lidar | 0.2 m 2.4 m 1 m | 4波段 4 bands 63波段 63 bands 288波段 288 bands | |||
| 地基遥感 Ground-based | 红外相机 Infrared camera 视频监控 Video monitoring 声景监控 Soundscape | 可见光、红外 Visible, infrared 可见光、红外 Visible and infrared | 物种活动场景 The behavior of species | ||
| 间接法 Indirect approaches | |||||
| 景观指数法 Landscape index | TM/ETM + HJ MODIS EO-1 Hyperion ASTER Sentinel-2 MSI SPOT CBERS-04 | 30-120 m 30-100 m 250-1 km 30 m 15 m, 30 m, 90 m 10 m, 20 m, 60 m 1.5 m, 6 m, 1 km 5-80 m | 7-9波段 7-9 bands 4波段 4 bands 36波段 36 bands 220波段 220 bands 14波段 14 bands 13波段 13 bands 4-6波段 4-6 bands 12波段 12 bands | 土地分类 Land cover classification | |
| 遥感指数法 Satellite index | 多样性指数 Biodiversity index | ||||
| 光谱变异性指数法 Spectral heterogeneity index | 光谱异质性指数 Spectral heterogeneity index | ||||
| 模型模拟法 Model simulation | TRMM/TMI FY-3C/VIRR | 5-72 km 1 km | 5波段 5 bands 10波段 10 bands | 物种分布 Species distribution | |
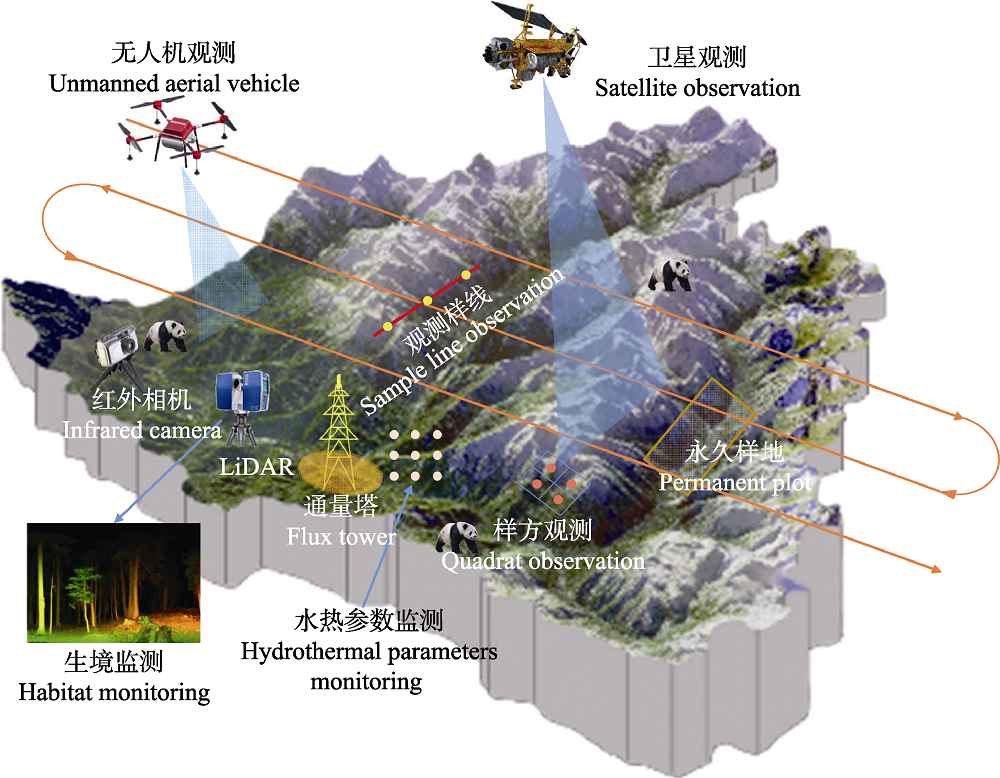
图1 基于站点的星空地一体化王朗山地生态遥感综合观测试验站生物多样性监测概念设计
Fig. 1 The concepted design of biodiversity monitoring at Wanglang integrated observation and experiment station based on space-air-field integrated remote sensing observation
| [1] | Bejarano S, Mumby PJ, Sotheran I (2010) Predicting structural complexity of reefs and fish abundance using acoustic remote sensing (RoxAnn). Marine Biology, 158, 489-504. |
| [2] | Belluco E, Camuffo M, Ferrari S, Modenese L, Silvestri S, Marani A, Marani M (2006) Mapping salt-marsh vegetation by multispectral and hyper-spectral remote sensing. Remote Sensing of Environment, 105, 54-67. |
| [3] | Burton A, Neilson E, Moreira D, Ladle A, Steenweg R, Fisher J, Bayne E, Boutin S, Stephens P (2015) Wildlife camera trapping: A review and recommendations for linking surveys to ecological processes. Journal of Applied Ecology, 52, 675-685. |
| [4] | Bush A, Sollmann R, Wilting A, Bohmann K, Cole B, Balzter H, Martius C, Zlinszky A (2017) Connecting earth observation to high-throughput biodiversity data. Nature Ecology & Evolution, 1, 176. |
| [5] | Cardinale J, Duffy J, Gonzalez A, Hooper D, Perrings C, Venail P, Narwani A, Mace G, Tilman D, Wardle D (2012) Biodiversity loss and its impact on humanity. Nature, 486, 59-67. |
| [6] | Carlson K, Asner G, Hughes R, Ostertag RM (2007) Hyperspectral remote sensing of canopy biodiversity in Hawaiian lowland rainforests. Ecosystems, 10, 536-549. |
| [7] | Ceballos G, Ehrlich P, Barnosky A, García A, Pringle R, Palmer T (2015) Accelerated modern human-induced species losses: Entering the sixth mass extinction. Science Advances, 1, e1400253. |
| [8] | Cheng GD, Li X (2015) Integrated research methods in watershed science. Science China: Earth Sciences, 58, 1159-1168. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [程国栋, 李新 (2015) 流域科学及其集成研究方法. 中国科学: 地球科学, 58, 1159-1168.] | |
| [9] | Cohen WB, Maiersperger TK, Turner DP, Ritts WD, Pflugmacher D, Kennedy RE, Kirschbaum A, Running SW, Costa M, Gower ST (2006) MODIS land cover and LAI collection 4 product quality across nine sites in the western hemisphere. IEEE Transactions in Geosciences and Remote Sensing, 44, 1843-1857. |
| [10] | Delalieux S, Somers B, Haest B, Spanhove T, Borre V, Mucher C (2012) Heathland conservation status mapping through integration hyperspectral mixture analysis and decision tree classifiers. Remote Sensing of Environment, 126, 222-231. |
| [11] | Fang H, Liang S, Hoogenboom G (2011) Integration of MODIS LAI and vegetation index products CSM-CERES-Maize model for corn yield estimation. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 32, 1039-1065. |
| [12] | Foody GM, Cutler M (2006) Mapping the species richness and composition of tropical forests from remotely sensed data with neural networks. Ecological Modelling, 195, 37-42. |
| [13] | Forman R, Godron M (1986) Landscape Ecology. John Wiley & Sons, New York. |
| [14] | Forzieri G, Tanteri L, Moser G, Catani F (2013) Mapping natural and urban environments using airborne multi-sensor ADS40-MIVIS-LiDAR synergies. International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation, 23, 313-323. |
| [15] | Gillespie T (2005) Predicting woody-plant species richness in tropical dry forests: A case study from South Florida, USA. Ecological Applications, 15, 27-37. |
| [16] | Gould WA, Walker MD (1997) Landscape-scale patterns in plant species richness along an arctic river. Canadian Journal of Botany, 75, 1748-1765. |
| [17] | Guo QH, Liu J, Li YM, Zhai QP, Wang YC, Wu FF, Hu TY, Wan HW, Liu HM, Shen WM (2016) A near-surface remote sensing platform for biodiversity monitoring: Perspectives and prospects. Biodiversity Science, 24, 1249-1266. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [郭庆华, 刘瑾, 李玉美, 翟秋萍, 王永财, 吴芳芳, 胡天宇, 万华伟, 刘慧明, 申文明 (2016) 生物多样性近地面遥感监测: 应用现状与前景展望. 生物多样性, 24, 1249-1266.] | |
| [18] | Guyon D, Guillot M, Vitasse Y, Cardot H, Hagolle O, Dezon S, Wigneron J (2011) Monitoring elevation variations in leaf phenology of deciduous broadleaf forests from SPOT/VEGETATION time-series. Remote Sensing of Environment, 115, 615-627. |
| [19] | Herrmann I, Pimstein A, Karnieli A (2011) LAI assessment of wheat and potato crops by VENlS and Sentinel-2 bands. Remote Sensing of Environment, 115, 2141-2151. |
| [20] | Hooper D, Chapin I, Ewel J, Hector A, Inchausti P, Lavorel S, Lawton J, Lodge D, Loreau M, Naeem S (2005) Effects of biodiversity on ecosystem functioning: A consensus of current knowledge. Ecological Monographs, 75, 3-35. |
| [21] | Hu HD, Li XY, Du YF, Zheng HF, Du BX, He XY (2012) Research advances in biodiversity remote sensing monitoring. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 31, 1591-1596. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [胡海德, 李小玉, 杜宇飞, 郑海峰, 都本绪, 何兴元 (2012) 生物多样性遥感监测方法研究进展. 生态学杂志, 31, 1591-1596.] | |
| [22] | Hu TY, Wang NN, Zhao XQ, Mi XC, Guo QH, Ma KP (2018) Advances in biodiversity observation network. Journal of Remote Sensing, 22, 708-711. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [胡天宇, 王宁宁, 赵晓倩, 米湘成, 郭庆华, 马克平 (2018) 生物多样性监测网络建设进展. 遥感学报, 22, 708-711.] | |
| [23] | Jiang ZG, Ma KP (2009) Status, challenges and strategy in Conservation Biology. Biodiversity Science, 17, 107-116. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [蒋志刚, 马克平 (2009) 保护生物学的现状、挑战和对策. 生物多样性, 17, 107-116.] | |
| [24] | Jin R, Li X, Ma MG (2017) Key methods and experiment verification for the validation of quantitative remote sensing products. Advances in Earth Science, 32, 630-642. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [晋锐, 李新, 马明国 (2017) 陆地定量遥感产品的真实性检验关键技术与试验验证. 地球科学进展, 32, 630-642.] | |
| [25] | Keith DA, Rodríguez J, Rodríguez-Clark KM, Nicholson E, Aapala K, Alonso Al, Asmussen M, Bachman S, Basset A, Barrow EG (2013) Scientific foundations for an IUCN Red List of Ecosystems. PLoS ONE, 8, e62111. |
| [26] | Li BV, Pimm S, Li S, Zhao L, Luo C (2017) Free-ranging livestock threaten the long-term survival of giant pandas. Biological Conservation, 216, 18-25. |
| [27] | Li X, Cheng G, Liu S (2013) Heihe watershed allied telemetry experimental research (HiWATER): Scientific objectives and experimental design. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 94, 1145-1160. |
| [28] | Li X, Li X, Li Z (2009) Watershed allied telemetry experimental research. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 114. |
| [29] | Ma KP (2016) Hot topics for biodiversity science. Biodiversity Science, 24, 1-2. (in Chinese) |
| [马克平 (2016) 生物多样性科学的热点问题. 生物多样性, 24, 1-2.] | |
| [30] | Ma KP, Qian YQ (1998) biodiversity conservation and its research progress. Chinese Journal of Applied and Environmental Biology, 4, 95-99. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [马克平, 钱迎倩 (1998) 生物多样性保护及其研究进展. 应用与环境生物学报, 4, 95-99.] | |
| [31] | Myers N, Mittermeier RA, Mittermeier CG, Fonseca D, Kent J (2000) Biodiversity hotspots for conservation priorities. Nature, 403, 853-858. |
| [32] | Nagendra H (2001) Using remote sensing to assess biodiversity. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 22, 2377-2400. |
| [33] | Oindo BO, Skidmore A (2002) Interannual variability of NDVI and species richness in Kenya. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 23, 285-298. |
| [34] | Palmer MW, Earls PG, Hoagland BW, White PS, Wohlgemuth T (2002) Quantitative tools for perfecting species lists. Environmetrics, 13, 121-137. |
| [35] | Petrou ZI, Kosmidou V, Manakos I, Stathaki T, Adamo M, Tarantino C (2014) A rule-based classification methodology to handle uncertainty in habitat mapping employing evidential reasoning and fuzzy logic. Pattern Recognition Letters, 48, 24-33. |
| [36] | Petrou ZI, Manakos I, Stathaki T (2015) Remote sensing for biodiversity monitoring: A review of methods for biodiversity indicator extraction and assessment of progress towards international targets. Biodiversity and Conservation, 24, 2333-2363. |
| [37] | Phillips SJ, Dudík M (2008) Modeling of species distributions with MaxEnt: New extensions and a comprehensive evaluation. Ecography, 31, 161-175. |
| [38] | Pimm SL, Jenkins CN, Abell R, Brooks TM, Gittleman JL, Joppa LN, Raven PH, Roberts CM, Sexton J (2014) The biodiversity of species and their rates of extinction, distribution, and protection. Science, 344, 1246752. |
| [39] | Pu R, Bell S, Levy KH, Meyer C (2010) Mapping detailed seagrass habitats using satellite imagery. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Honolulu, USA, pp. 1-4. |
| [40] | Reiche M, Funk R, Zhang Z, Hoffmann C, Reiche J, Wehrhan M (2012) Application of satellite remote sensing for mapping wind erosion risk and dust emission-deposition in Inner Mongolia grassland, China. Grassland Science, 58, 8-19. |
| [41] | Rocchini D (2007) Effects of spatial and spectral resolution in estimating ecosystem α-diversity by satellite imagery. Remote Sensing of Environment, 111, 423-434. |
| [42] | Rocchini D, Chiarucci A (2004) Testing the spectral variation hypothesis by using satellite multispectral images. Acta Oecologica, 26, 117-120. |
| [43] | Saatchi S, Buermann W, Mori S, Smith TB (2008) Modeling distribution of Amazonian tree species and diversity using remote sensing measurements. Remote Sensing of Environment, 112, 2000-2017. |
| [44] | Sellers P, Hall F, Margolis H (1995) The boreal ecosystem-atmosphere study (BOREAS): An overview and early results from the 1994 field year. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 76, 1549-1577. |
| [45] | Sellers PJ, Hall FG, Kelly (1997) BOREAS in 1997: Experiment overview, scientific results, and future directions. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 102, 28731-28769. |
| [46] | Soberon J, Nakamura M (2009) Niches and distributional areas: Concepts, methods, and assumptions. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 106, 19644-19650. |
| [47] | Tan J, Li A, Lei G, Bian J, Chen G, Ma K (2017) Preliminary assessment of ecosystem risk based on IUCN criteria in a hierarchy of spatial domains: A case study in Southwestern China. Biological Conservation, 215, 152-161. |
| [48] | Tan JB, Li AN, Lei GB, Chen GK, Ma KP (2017) Research advances and challenges in the IUCN Red List of Ecosystems. Biodiversity Science, 25, 453-463. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [谭剑波李爱农, 雷光斌, 陈国科, 马克平 (2017) IUCN生态系统红色名录研究进展. 生物多样性, 25, 453-463.] | |
| [49] | Towsey M, Wimmer J, Williamson I, Roe P (2014) The use of acoustic indices to determine avian species richness in audio-recordings of the environment. Ecological Informatics, 21, 110-119. |
| [50] | Turner DP, Ritts WD, Cohen WB, Maeirsperger TK, Gower ST, Kirschbaum A, Running SW, Zhao M, Wofsy SC, Dunn AL, Law BE, Campbell JC, Oechel WC, Kwon HJ, Meyers TP, Small EE, Kurc SA, Gamon JA (2005) Site-level evaluation of satellite-based global terrestrial gross primary production and net primary production monitoring. Global Change Biology, 11, 666-684. |
| [51] | Turner W, Spector S, Gardiner N, Fladeland M, Sterling E, Steininger M (2003) Remote sensing for biodiversity science and conservation. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 18, 306-314. |
| [52] | Wang KY (2004) Processes of Subalpine Forest Ecosystems in the West of Sichuan. Sichuan Science and Technology Press, Chengdu. |
| [王开运 (2004) 川西亚高山森林群落生态系统过程. 四川科学技术出版社, 成都.] | |
| [53] | Wang X, Wang Q, Wu C (2012) A method coupled with remote sensing data to evaluate non-point source pollution in the Xin’anjiang catchment of China. Science of the Total Environment, 430, 132-143. |
| [54] | Wei YC, Wu BF, Zhang XW, Du X (2008) Advances in remote sensing research for biodiversity monitoring. Advances in Earth Science, 23, 924-931. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [魏彦昌, 吴炳方, 张喜旺, 杜鑫 (2008) 生物多样性遥感研究进展. 地球科学进展, 23, 924-931.] | |
| [55] | Wulder MA, White JC, Coops NC, Butson CR (2008) Multi-temporal analysis of high spatial resolution imagery for disturbance monitoring. Remote Sensing of Environment, 112, 2729-2740. |
| [56] | Wythers KR, Reich PB, Turner DP (2003) Predicting leaf area index from scaling principles: Corroboration and consequences. Tree Physiology, 23, 1171-1179. |
| [57] | Xiao ZS, Li XH, Jiang GS (2014) Applications of camera trapping to wildlife surveys in China. Biodiversity Science, 22, 683-684. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [肖治术, 李欣海, 姜广顺 (2014) 红外相机技术在我国野生动物监测研究中的应用. 生物多样性, 22, 683-684.] | |
| [58] | Yin GF, Li AN, Verger A (2017) Spatiotemporally representative and cost-efficient sampling design for validation activities in Wanglang Experimental Site. Remote Sensing, 9, 1217. |
| [59] | Zainuddin M, Kiyofuji H, Saitoh K, Saitoh SI (2006) Using multi-sensor satellite remote sensing and catch data to detect ocean hot spots for albacore (Thunnus alalunga) in the northwestern North Pacific. Deep-Sea Research II, 53, 419-431. |
| [60] | Zhang LB, Cui SP, Huang YJ, Chen DQ, Qiao HJ, Li CW, Jiang ZG (2014) Infrared camera traps in wildlife research and monitoring in China: Issues and insights. Biodiversity Science, 22, 696-703. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [张履冰, 崔绍朋, 黄元骏, 陈代强, 乔慧捷, 李春旺, 蒋志刚 (2014) 红外相机技术在我国野生动物监测中的应用: 问题与限制. 生物多样性, 22, 696-703.] | |
| [61] | Zhang Y, Liu QH, Tan LF, Huang HG, Ni WJ, Yin TG, Qin WH, Sun GQ (2017) A 3-D joint simulation platform for multiband remote sensing. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 10, 4763-4778. |
| [62] | Zhong L, Gong P, Biging GS (2014) Efficient corn and soybean mapping with temporal extendability: A multi-year experiment using Landsat imagery. Remote Sensing of Environment, 140, 1-13. |
| [63] | Zhu C, Fang Y, Zhou KX, Mu SJ, Jiang JL (2015) IUCN red list of ecosystems: A new tool for biodiversity conservation. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 35, 2826-2836. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [朱超, 方颖, 周可新, 穆少杰, 蒋金亮 (2015) 生态系统红色名录: 一种新的生物多样性保护工具. 生态学报, 35, 2826-2836.] |
| [1] | 干靓 刘巷序 鲁雪茗 岳星. 全球生物多样性热点地区大城市的保护政策与优化方向[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24529-. |
| [2] | 曾子轩 杨锐 黄越 陈路遥. 清华大学校园鸟类多样性特征与环境关联[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24373-. |
| [3] | 臧明月, 刘立, 马月, 徐徐, 胡飞龙, 卢晓强, 李佳琦, 于赐刚, 刘燕. 《昆明-蒙特利尔全球生物多样性框架》下的中国城市生物多样性保护[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24482-. |
| [4] | 祝晓雨, 王晨灏, 王忠君, 张玉钧. 城市绿地生物多样性研究进展与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 25027-. |
| [5] | 袁琳, 王思琦, 侯静轩. 大都市地区的自然留野:趋势与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24481-. |
| [6] | 胡敏, 李彬彬, Coraline Goron. 只绿是不够的: 一个生物多样性友好的城市公园管理框架[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24483-. |
| [7] | 王欣, 鲍风宇. 基于鸟类多样性提升的南滇池国家湿地公园生态修复效果分析[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24531-. |
| [8] | 明玥, 郝培尧, 谭铃千, 郑曦. 基于城市绿色高质量发展理念的中国城市生物多样性保护与提升研究[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24524-. |
| [9] | 谢淦, 宣晶, 付其迪, 魏泽, 薛凯, 雒海瑞, 高吉喜, 李敏. 草地植物多样性无人机调查的物种智能识别模型构建[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24236-. |
| [10] | 褚晓琳, 张全国. 演化速率假说的实验验证研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 25019-. |
| [11] | 宋威, 程才, 王嘉伟, 吴纪华. 土壤微生物对植物多样性–生态系统功能关系的调控作用[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24579-. |
| [12] | 卢晓强, 董姗姗, 马月, 徐徐, 邱凤, 臧明月, 万雅琼, 李孪鑫, 于赐刚, 刘燕. 前沿技术在生物多样性研究中的应用现状、挑战与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24440-. |
| [13] | 农荞伊, 曹军, 程文达, 彭艳琼. 不同方法对蜜蜂总科昆虫资源与多样性监测效果的比较[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 25057-. |
| [14] | 郭雨桐, 李素萃, 王智, 解焱, 杨雪, 周广金, 尤春赫, 朱萨宁, 高吉喜. 全国自然保护地对国家重点保护野生物种的覆盖度及其分布状况[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(3): 24423-. |
| [15] | 赵维洋, 王伟, 马冰然. 其他有效的区域保护措施(OECMs)研究进展与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(3): 24525-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn