



生物多样性 ›› 2025, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (4): 24237. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2024237 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2024237
袁敬毅1, 张旭1, 田镇朋1, 王梓柘1, 高永萍1, 姚迪昭1, 关宏灿2, 李文楷3, 刘婧1,4,5, 张宏1,4,5, 马勤6,1,4,5,*( )
)
收稿日期:2024-06-14
接受日期:2024-09-10
出版日期:2025-04-20
发布日期:2025-04-29
通讯作者:
*E-mail: maqin@nnu.edu.cn
基金资助:
Yuan Jingyi1, Zhang Xu1, Tian Zhenpeng1, Wang Zizhe1, Gao Yongping1, Yao Dizhao1, Guan Hongcan2, Li Wenkai3, Liu Jing1,4,5, Zhang Hong1,4,5, Ma Qin6,1,4,5,*( )
)
Received:2024-06-14
Accepted:2024-09-10
Online:2025-04-20
Published:2025-04-29
Contact:
*E-mail: maqin@nnu.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要: 城市植被的群落组成及结构特征对评估其生长状况和生态功能至关重要。群落内不同树种的数量特征是定量描述植物群落组成结构的基础。但传统的调查方法需要大量人力物力且难以大范围开展, 而单一遥感数据源和方法难以同时提供准确的株数、冠幅和树种信息。为此, 需要探讨多源数据结合的无人机遥感技术在精确获取城市植物群落树种组成和数量特征时的潜力。本研究以庐山风景名胜区的典型城市植被为对象, 分别基于高分辨率可见光影像、激光雷达点云以及两者的结合开展单木分割与树种分类, 对比不同遥感数据源和方法在提取植物群落树种数量特征时的表现。结果表明: (1)采用多源数据结合的方式可以得到最优的单木分割和树种分类精度, 相比于分别使用影像或点云, 单木分割的F值分别提升0.116和0.102, 分类总体精度分别提升12.1%和23.1%; (2)多源数据结合可以更准确地提取群落内树种数量特征的相对关系, 其对各类别树种相对密度和相对盖度的提取误差分别在2.3%和4.8%以内, 而基于单一数据源的方式则对特定树种有明显的高估或低估。本研究证明多源数据结合的方法可以通过同时优化单木探测和树种分类过程, 进而提高城市植物群落树种组成及数量特征提取的精度, 可为开展城市植物群落结构的无人机遥感监测提供理论支持和方法借鉴。
袁敬毅, 张旭, 田镇朋, 王梓柘, 高永萍, 姚迪昭, 关宏灿, 李文楷, 刘婧, 张宏, 马勤 (2025) 结合无人机高分辨率可见光影像和激光雷达点云的城市植物群落树种组成和数量特征提取方法对比. 生物多样性, 33, 24237. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2024237.
Yuan Jingyi, Zhang Xu, Tian Zhenpeng, Wang Zizhe, Gao Yongping, Yao Dizhao, Guan Hongcan, Li Wenkai, Liu Jing, Zhang Hong, Ma Qin (2025) A comparison of methods for extracting tree species composition and quantitative characteristics in urban plant communities using UAV high-resolution RGB imagery and LiDAR point cloud. Biodiversity Science, 33, 24237. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2024237.

图2 庐山市牯岭镇研究区高分辨率可见光影像(a)和归一化数字表面模型以及单木树冠边界(b)
Fig. 2 High-resolution RGB imagery (a) and normalized digital surface model with individual tree canopy boundaries (b) in study area in Guling Town, Lushan City
| 分类方案 Classification schemes | 类别数 Number of categories | 具体类别 Specific categories |
|---|---|---|
| A | 2 | 黄山松 Pinus hwangshanensis |
| 其他树种 Other tree species | ||
| B | 2 | 二球悬铃木 Platanus × acerifolia |
| 其他树种 Other tree species | ||
| C | 2 | 针叶类 Coniferous trees |
| 阔叶类 Broadleaf trees | ||
| D | 3 | 优势针叶类 Dominant coniferous trees |
| 优势阔叶类 Dominant broadleaf trees | ||
| 其他类 Other tree species | ||
| E | 5 | 优势针叶类 Dominant coniferous trees |
| 优势阔叶类 Dominant broadleaf trees | ||
| 伴生针叶类 Companion coniferous trees | ||
| 伴生阔叶类 Companion broadleaf trees | ||
| 其他类 Other tree species | ||
| F | 11 | 黄山松 Pinus hwangshanensis |
| 日本柳杉 Cryptomeria japonica | ||
| 二球悬铃木 Platanus × acerifolia | ||
| 日本扁柏 Chamaecyparis obtusa | ||
| 金钱松 Pseudolarix amabilis | ||
| 鹅掌楸 Liriodendron chinense | ||
| 灯台树 Cornus controversa | ||
| 鸡爪槭 Acer palmatum | ||
| 山樱花 Prunus serrulata | ||
| 偶见针叶类 Occasional coniferous trees | ||
| 偶见阔叶类 Occasional broadleaf trees |
表1 树种分类方案
Table 1 Tree species classification schemes
| 分类方案 Classification schemes | 类别数 Number of categories | 具体类别 Specific categories |
|---|---|---|
| A | 2 | 黄山松 Pinus hwangshanensis |
| 其他树种 Other tree species | ||
| B | 2 | 二球悬铃木 Platanus × acerifolia |
| 其他树种 Other tree species | ||
| C | 2 | 针叶类 Coniferous trees |
| 阔叶类 Broadleaf trees | ||
| D | 3 | 优势针叶类 Dominant coniferous trees |
| 优势阔叶类 Dominant broadleaf trees | ||
| 其他类 Other tree species | ||
| E | 5 | 优势针叶类 Dominant coniferous trees |
| 优势阔叶类 Dominant broadleaf trees | ||
| 伴生针叶类 Companion coniferous trees | ||
| 伴生阔叶类 Companion broadleaf trees | ||
| 其他类 Other tree species | ||
| F | 11 | 黄山松 Pinus hwangshanensis |
| 日本柳杉 Cryptomeria japonica | ||
| 二球悬铃木 Platanus × acerifolia | ||
| 日本扁柏 Chamaecyparis obtusa | ||
| 金钱松 Pseudolarix amabilis | ||
| 鹅掌楸 Liriodendron chinense | ||
| 灯台树 Cornus controversa | ||
| 鸡爪槭 Acer palmatum | ||
| 山樱花 Prunus serrulata | ||
| 偶见针叶类 Occasional coniferous trees | ||
| 偶见阔叶类 Occasional broadleaf trees |
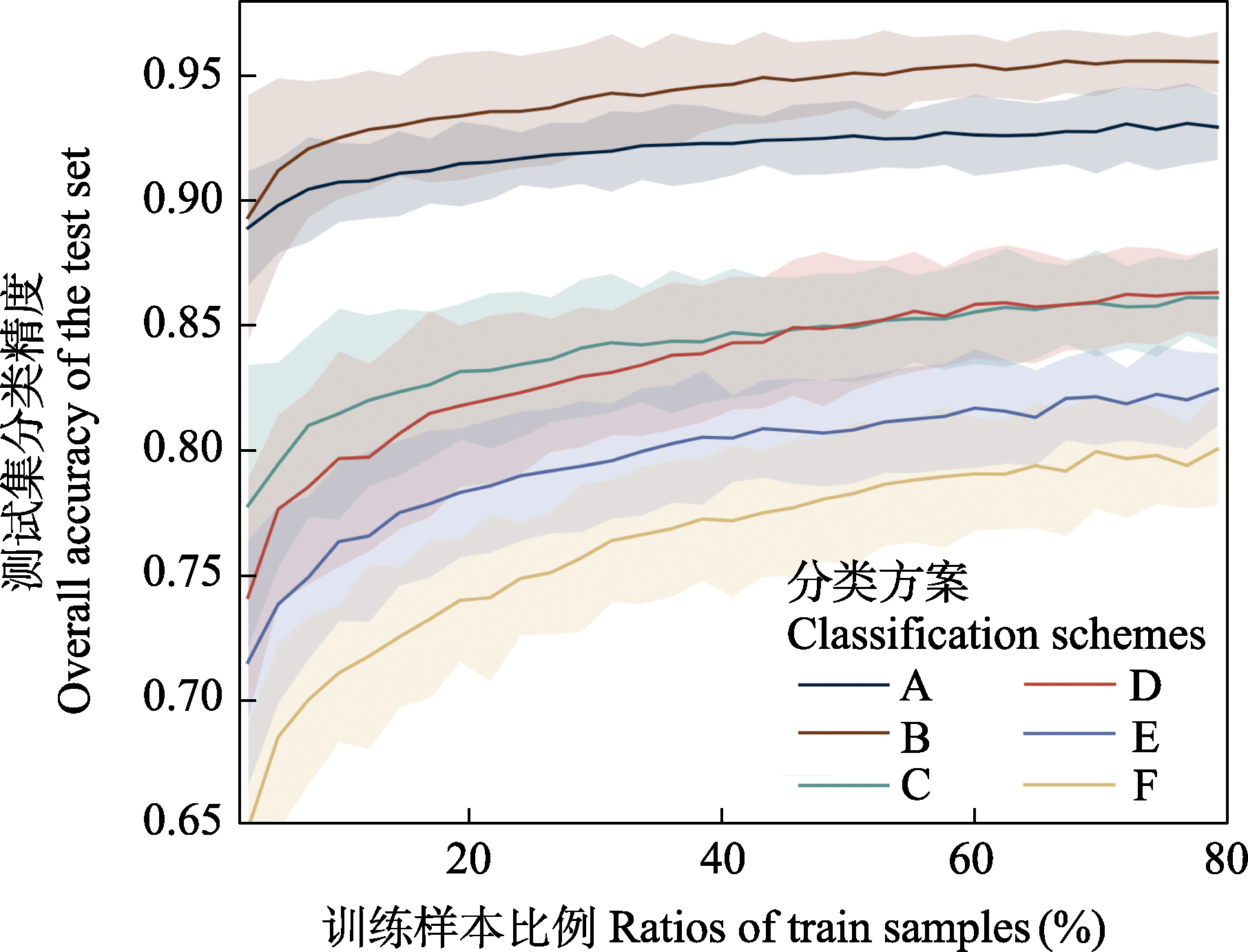
图3 不同分类方案(详见表1)中分类精度(均值与95%置信区间)和训练样本比例的关系
Fig. 3 Relationship between classification accuracies (mean value with 95% confidence interval) and the ratios of training samples in different classification schemes (see Table 1)
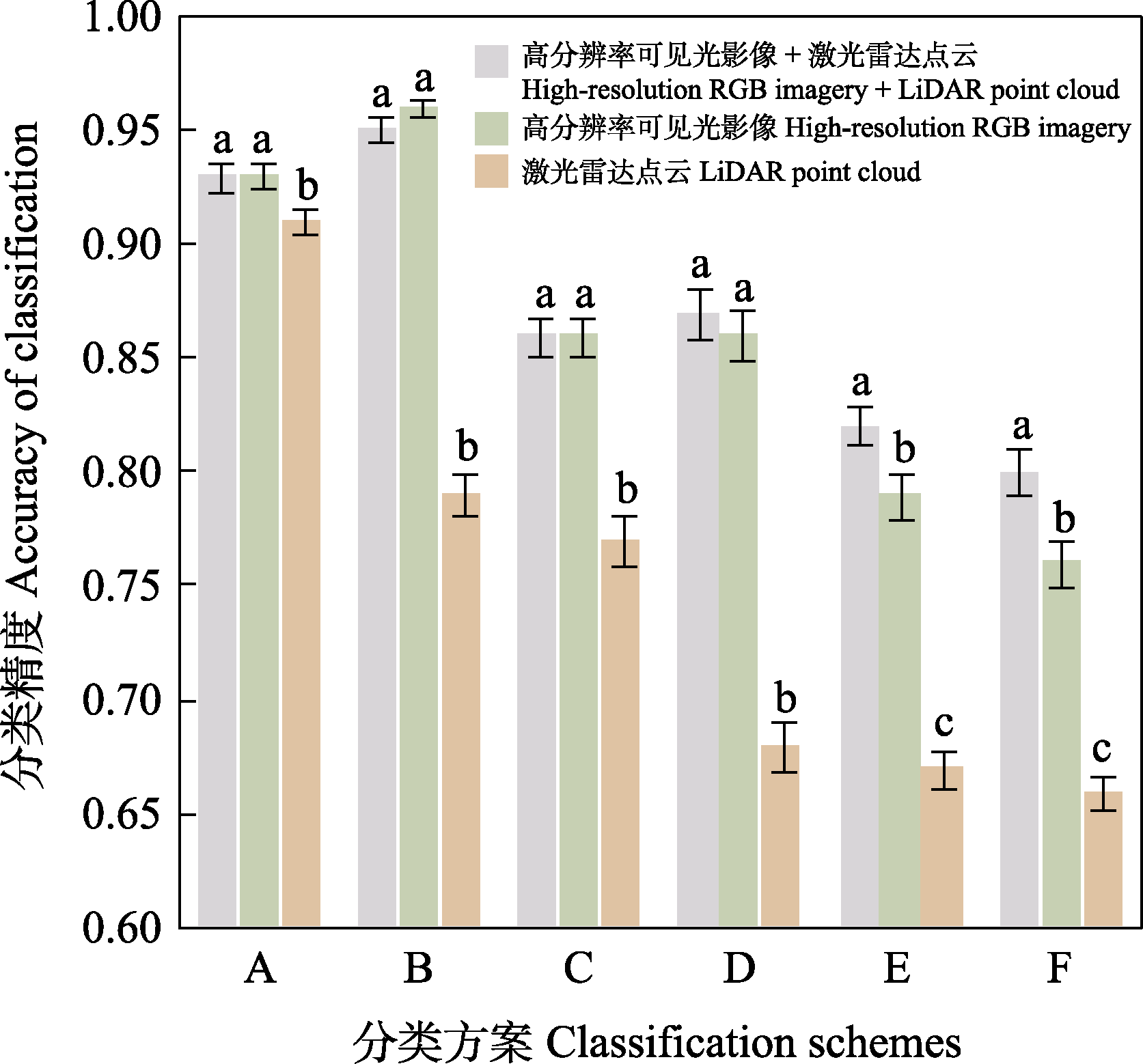
图4 不同分类方案(详见表1)中特征选择对分类精度(平均值 ± 标准差)的影响。不同小写字母代表不同分类特征在P < 0.01水平差异显著。
Fig. 4 Influence of feature selection on classification accuracies (mean ± SD) in different classification schemes (see Table 1). Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between classification features at P < 0.01.
| 树种 Tree species | 生活型 Life form | 多度 Abundance | 相对密度 Relative density (%) | 树冠面积 Canopy area (m2) | 相对盖度 Relative coverage (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 黄山松 Pinus hwangshanensis | ECT | 152 | 24.3 | 3,105.5 | 12.1 |
| 日本柳杉 Cryptomeria japonica | ECT | 149 | 23.8 | 4,063.4 | 15.9 |
| 二球悬铃木 Platanus × acerifolia | DBT | 92 | 14.7 | 11,545.1 | 45.1 |
| 日本扁柏 Chamaecyparis obtusa | ECT | 79 | 12.6 | 1,847.1 | 7.2 |
| 金钱松 Pseudolarix amabilis | DCT | 17 | 2.7 | 348.5 | 1.4 |
| 鹅掌楸 Liriodendron chinense | DBT | 13 | 2.1 | 793.9 | 3.1 |
| 灯台树 Cornus controversa | DBT | 14 | 2.2 | 652.2 | 2.5 |
| 鸡爪槭 Acer palmatum | DBT | 11 | 1.8 | 216.1 | 0.8 |
| 山樱花 Prunus serrulata | DBT | 11 | 1.8 | 185.6 | 0.7 |
| 其他针叶树 Other coniferous trees | 17 | 2.7 | 523.8 | 2.0 | |
| 其他阔叶树 Other broadleaf trees | 70 | 11.2 | 2,321.7 | 9.1 | |
| 总计 Total | 625 | 100.0 | 25,602.9 | 100.0 |
表2 研究区群落主要树种数量特征
Table 2 Quantitative characteristics of main tree species in the community in the study area
| 树种 Tree species | 生活型 Life form | 多度 Abundance | 相对密度 Relative density (%) | 树冠面积 Canopy area (m2) | 相对盖度 Relative coverage (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 黄山松 Pinus hwangshanensis | ECT | 152 | 24.3 | 3,105.5 | 12.1 |
| 日本柳杉 Cryptomeria japonica | ECT | 149 | 23.8 | 4,063.4 | 15.9 |
| 二球悬铃木 Platanus × acerifolia | DBT | 92 | 14.7 | 11,545.1 | 45.1 |
| 日本扁柏 Chamaecyparis obtusa | ECT | 79 | 12.6 | 1,847.1 | 7.2 |
| 金钱松 Pseudolarix amabilis | DCT | 17 | 2.7 | 348.5 | 1.4 |
| 鹅掌楸 Liriodendron chinense | DBT | 13 | 2.1 | 793.9 | 3.1 |
| 灯台树 Cornus controversa | DBT | 14 | 2.2 | 652.2 | 2.5 |
| 鸡爪槭 Acer palmatum | DBT | 11 | 1.8 | 216.1 | 0.8 |
| 山樱花 Prunus serrulata | DBT | 11 | 1.8 | 185.6 | 0.7 |
| 其他针叶树 Other coniferous trees | 17 | 2.7 | 523.8 | 2.0 | |
| 其他阔叶树 Other broadleaf trees | 70 | 11.2 | 2,321.7 | 9.1 | |
| 总计 Total | 625 | 100.0 | 25,602.9 | 100.0 |
| 数据 Database | 方法 Methods | 正确分割 True positive | 过分割 False positive | 欠分割 False negative | 召回率 Recall | 精确率 Precision | F值 F-score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 高分辨率可见光影像 High-resolution RGB imagery | 多尺度分割 Multi-scale segmentation | 349 | 300 | 178 | 0.662 | 0.538 | 0.594 |
| 激光雷达点云 LiDAR point cloud | 点云分割 Point cloud segmentation | 343 | 259 | 184 | 0.651 | 0.570 | 0.608 |
| 高分辨率可见光影像 + 激光雷达点云 High-resolution RGB imagery + LiDAR point cloud | 单木分割优化 Optimized individual tree segmentation | 337 | 85 | 190 | 0.639 | 0.799 | 0.710 |
表3 基于不同数据和方法的单木分割精度
Table 3 Accuracy of individual tree detection based on different databases and methods
| 数据 Database | 方法 Methods | 正确分割 True positive | 过分割 False positive | 欠分割 False negative | 召回率 Recall | 精确率 Precision | F值 F-score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 高分辨率可见光影像 High-resolution RGB imagery | 多尺度分割 Multi-scale segmentation | 349 | 300 | 178 | 0.662 | 0.538 | 0.594 |
| 激光雷达点云 LiDAR point cloud | 点云分割 Point cloud segmentation | 343 | 259 | 184 | 0.651 | 0.570 | 0.608 |
| 高分辨率可见光影像 + 激光雷达点云 High-resolution RGB imagery + LiDAR point cloud | 单木分割优化 Optimized individual tree segmentation | 337 | 85 | 190 | 0.639 | 0.799 | 0.710 |
| 数据 Database | 方法 Methods | 类别 Categories | 生产者精度 Producer’s accuracy (%) | 用户精度 User’s accuracy (%) | 总体精度 Overall accuracy (%) | Kappa系数 Kappa coefficient |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 高分辨率可见光影像 High-resolution RGB imagery | 面向对象分类 Object-oriented classification | 优势针叶类 Dominant coniferous trees | 61.7 | 78.4 | 74.6 | 0.608 |
| 优势阔叶类 Dominant broadleaf trees | 85.0 | 91.1 | ||||
| 其他类 Other tree species | 73.9 | 45.9 | ||||
| 激光雷达点云 LiDAR point cloud | 面向单木点云分类 Point-cloud-oriented classification | 优势针叶类 Dominant coniferous trees | 75.0 | 55.9 | 63.6 | 0.443 |
| 优势阔叶类 Dominant broadleaf trees | 64.4 | 74.4 | ||||
| 其他类 Other tree species | 46.9 | 65.2 | ||||
| 高分辨率可见光影像 + 激光雷达点云 High-resolution RGB imagery + LiDAR point cloud | 面向种子点分类 Seed-point-oriented classification | 优势针叶类 Dominant coniferous trees | 83.1 | 81.7 | 86.7 | 0.783 |
| 优势阔叶类 Dominant broadleaf trees | 87.3 | 99.2 | ||||
| 其他类 Other tree species | 88.9 | 68.6 |
表4 基于不同数据和方法的树种分类精度
Table 4 Accuracy of tree species classification based on different databases and methods
| 数据 Database | 方法 Methods | 类别 Categories | 生产者精度 Producer’s accuracy (%) | 用户精度 User’s accuracy (%) | 总体精度 Overall accuracy (%) | Kappa系数 Kappa coefficient |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 高分辨率可见光影像 High-resolution RGB imagery | 面向对象分类 Object-oriented classification | 优势针叶类 Dominant coniferous trees | 61.7 | 78.4 | 74.6 | 0.608 |
| 优势阔叶类 Dominant broadleaf trees | 85.0 | 91.1 | ||||
| 其他类 Other tree species | 73.9 | 45.9 | ||||
| 激光雷达点云 LiDAR point cloud | 面向单木点云分类 Point-cloud-oriented classification | 优势针叶类 Dominant coniferous trees | 75.0 | 55.9 | 63.6 | 0.443 |
| 优势阔叶类 Dominant broadleaf trees | 64.4 | 74.4 | ||||
| 其他类 Other tree species | 46.9 | 65.2 | ||||
| 高分辨率可见光影像 + 激光雷达点云 High-resolution RGB imagery + LiDAR point cloud | 面向种子点分类 Seed-point-oriented classification | 优势针叶类 Dominant coniferous trees | 83.1 | 81.7 | 86.7 | 0.783 |
| 优势阔叶类 Dominant broadleaf trees | 87.3 | 99.2 | ||||
| 其他类 Other tree species | 88.9 | 68.6 |
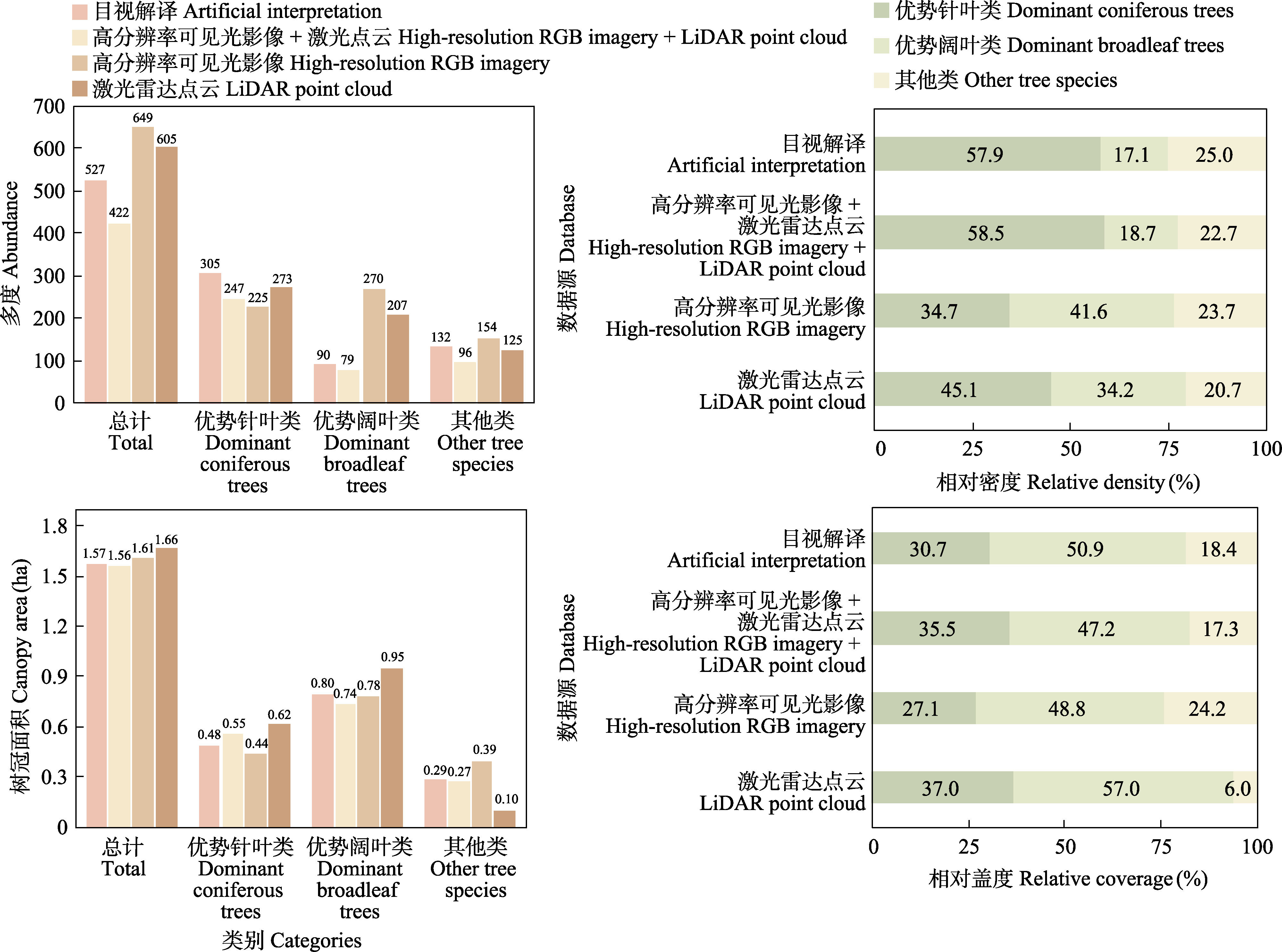
图5 基于不同遥感数据源的群落树种数量特征提取结果
Fig. 5 Results of the quantitative characteristics of tree species in the community extracted by different remote sensing databases
| 研究区域 Study region | 树种/类别数量 No. of species/ categories | 数据源 Databases | 分类精度 Classification accuracy | 参考文献 Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 森林 Forest | 7 | 可见光影像 RGB imagery | 79.0 | 滕文秀等, |
| 城市 Urban | 9 | 可见光影像 RGB imagery | 92.4 | 陈逊龙等, |
| 城市 Urban | 2 | 激光雷达点云 LiDAR point cloud | 83.8 | Cetin & Yastikli, |
| 森林 Forest | 2 | 激光雷达点云 LiDAR point cloud | 86.7 | 刘茂华等, |
| 城市 Urban | 10 | 可见光影像和激光雷达点云 RGB imagery and LiDAR point cloud | 74.1 | Wu et al, |
| 城市 Urban | 15 | 激光雷达点云和高光谱影像 LiDAR point cloud and hyperspectral imagery | 70.0 | Liu et al, |
| 森林 Forest | 18 | 可见光影像、激光雷达点云和高光谱影像 RGB imagery, LiDAR point cloud, and hyperspectral imagery | 91.8 | Qin et al, |
表5 部分已有的树种分类研究
Table 5 Examples on tree species classification in previous studies
| 研究区域 Study region | 树种/类别数量 No. of species/ categories | 数据源 Databases | 分类精度 Classification accuracy | 参考文献 Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 森林 Forest | 7 | 可见光影像 RGB imagery | 79.0 | 滕文秀等, |
| 城市 Urban | 9 | 可见光影像 RGB imagery | 92.4 | 陈逊龙等, |
| 城市 Urban | 2 | 激光雷达点云 LiDAR point cloud | 83.8 | Cetin & Yastikli, |
| 森林 Forest | 2 | 激光雷达点云 LiDAR point cloud | 86.7 | 刘茂华等, |
| 城市 Urban | 10 | 可见光影像和激光雷达点云 RGB imagery and LiDAR point cloud | 74.1 | Wu et al, |
| 城市 Urban | 15 | 激光雷达点云和高光谱影像 LiDAR point cloud and hyperspectral imagery | 70.0 | Liu et al, |
| 森林 Forest | 18 | 可见光影像、激光雷达点云和高光谱影像 RGB imagery, LiDAR point cloud, and hyperspectral imagery | 91.8 | Qin et al, |
| [1] | Alonzo M, Bookhagen B, Roberts DA (2014) Urban tree species mapping using hyperspectral and lidar data fusion. Remote Sensing of Environment, 148, 70-83. |
| [2] | Aronson MF, Lepczyk CA, Evans KL, Goddard MA, Lerman SB, MacIvor JS, Nilon CH, Vargo T (2017) Biodiversity in the city: Key challenges for urban green space management. Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment, 15, 189-196. |
| [3] | Cao YJ, Ball JGC, Coomes DA, Steinmeier L, Knapp N, Wilkes P, Disney M, Calders K, Burt A, Lin Y, Jackson TD (2023) Benchmarking airborne laser scanning tree segmentation algorithms in broadleaf forests shows high accuracy only for canopy trees. International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation, 123, 103490. |
| [4] | Cetin Z, Yastikli N (2022) The use of machine learning algorithms in urban tree species classification. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information, 11, 226. |
| [5] | Chen J, Liu SY, Song CC, Zhao JJ (2019) The estimation of sampling area and the missing plants curves in urban vegetation survey. Ecological Science, 38(2), 25-30. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [陈静, 刘时彦, 宋晨晨, 赵娟娟 (2019) 城市植被调查的取样面积推算与遗漏植物曲线. 生态科学, 38(2), 25-30.] | |
| [6] | Chen XL, Sun YM, Guo SJ, Duan YK, Tang AQ, Ye ZX, Zhang HX (2024) Urban tree species classification by UAV visible light imagery and OBIA-RF model. Journal of Northeast Forestry University, 52(3), 48-59. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [陈逊龙, 孙一铭, 郭仕杰, 段煜柯, 唐桉琦, 叶章熙, 张厚喜 (2024) 应用无人机可见光影像和面向对象的随机森林模型对城市树种分类. 东北林业大学学报, 52(3), 48-59.] | |
| [7] | Chen XW, Wang RR, Shi W, Li XT, Zhu XH, Wang XY (2023) An individual tree segmentation method that combines LiDAR data and spectral imagery. Forests, 14, 1009. |
| [8] | Chen YL, Fang SB, Sun M, Liu ZP, Pan LH, Mo WH, Chen C (2022) Mangrove growth monitoring based on camera visible images—A case study on typical mangroves in Guangxi. Frontiers in Earth Science, 9, 771753. |
| [9] | Escobedo FJ, Giannico V, Jim CY, Sanesi G, Lafortezza R (2019) Urban forests, ecosystem services, green infrastructure and nature-based solutions: Nexus or evolving metaphors? Urban Forestry & Urban Greening, 37, 3-12. |
| [10] | Fang JY, Shen ZH, Tang ZY, Wang ZH (2004) The protocol for the survey plan for plant species diversity of China’s mountains. Biodiversity Science, 12, 5-9. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[方精云, 沈泽昊, 唐志尧, 王志恒 (2004) “中国山地植物物种多样性调查计划”及若干技术规范. 生物多样性, 12, 5-9.]
DOI |
|
| [11] |
Fang JY, Wang XP, Shen ZH, Tang ZY, He JS, Yu D, Jiang Y, Wang ZH, Zheng CY, Zhu JL, Guo ZD (2009) Methods and protocols for plant community inventory. Biodiversity Science, 17, 533-548. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[方精云, 王襄平, 沈泽昊, 唐志尧, 贺金生, 于丹, 江源, 王志恒, 郑成洋, 朱江玲, 郭兆迪 (2009) 植物群落清查的主要内容、方法和技术规范. 生物多样性, 17, 533-548.]
DOI |
|
| [12] | Farajelahi B, Eya FF, Arefi H (2023) Forest modeling and inventory estimation using LiDAR data. ISPRS Annals of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences, X-4/W1-2022, 159-164. |
| [13] | Fassnacht FE, Latifi H, Stereńczak K, Modzelewska A, Lefsky M, Waser LT, Straub C, Ghosh A (2016) Review of studies on tree species classification from remotely sensed data. Remote Sensing of Environment, 186, 64-87. |
| [14] | Ferreira MP, Martins GB, da Silva Ribeiro R, da Veiga VF Jr, da Silva Rocha Paz I, de Siqueira MF, Kurtz BC (2024) Estimating aboveground biomass of tropical urban forests with UAV-borne hyperspectral and LiDAR data. Urban Forestry & Urban Greening, 96, 128362. |
| [15] | Gao S, Shen X, Dai JS, Cao L (2018) Tree species classification in urban forests based on LiDAR point cloud segmentation and hyperspectral metrics extraction. Remote Sensing Technology and Application, 33, 1073-1083. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [皋厦, 申鑫, 代劲松, 曹林 (2018) 结合LiDAR单木分割和高光谱特征提取的城市森林树种分类. 遥感技术与应用, 33, 1073-1083.] | |
| [16] | Ghosh A, Fassnacht FE, Joshi PK, Koch B (2014) A framework for mapping tree species combining hyperspectral and LiDAR data: Role of selected classifiers and sensor across three spatial scales. International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation, 26, 49-63. |
| [17] | Gitelson AA, Kaufman YJ, Stark R, Rundquist D (2002) Novel algorithms for remote estimation of vegetation fraction. Remote Sensing of Environment, 80, 76-87. |
| [18] | Grabska E, Hostert P, Pflugmacher D, Ostapowicz K (2019) Forest stand species mapping using the Sentinel-2 time series. Remote Sensing, 11, 1197. |
| [19] |
Guo QH, Hu TY, Liu J, Jin SC, Xiao Q, Yang GJ, Gao XL, Xu Q, Xie PH, Peng CG, Yan L (2021) Advances in light weight unmanned aerial vehicle remote sensing and major industrial applications. Progress in Geography, 40, 1550-1569. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[郭庆华, 胡天宇, 刘瑾, 金时超, 肖青, 杨贵军, 高显连, 许强, 谢品华, 彭炽刚, 闫利 (2021) 轻小型无人机遥感及其行业应用进展. 地理科学进展, 40, 1550-1569.]
DOI |
|
| [20] | Guo QH, Li WK, Yu H, Alvarez O (2010) Effects of topographic variability and LiDAR sampling density on several DEM interpolation methods. Photogrammetric Engineering & Remote Sensing, 76, 701-712. |
| [21] | Hu BX, Li JL, Jing LH, Judah A (2014) Improving the efficiency and accuracy of individual tree crown delineation from high-density LiDAR data. International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation, 26, 145-155. |
| [22] | Hu TY, Zhao D, Zeng Y, Guo QH, He HL (2023) Advances in multi-source data fusion for ecosystem assessment. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 43, 542-553. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [胡天宇, 赵旦, 曾源, 郭庆华, 何洪林 (2023) 面向生态系统评估的多源数据融合体系. 生态学报, 43, 542-553.] | |
| [23] | Hui ZY, Cheng PG, Yang BS, Zhou GQ (2022) Multi-level self-adaptive individual tree detection for coniferous forest using airborne LiDAR. International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation, 114, 103028. |
| [24] | Khosravipour A, Skidmore AK, Wang TJ, Isenburg M, Khoshelham K (2015) Effect of slope on treetop detection using a LiDAR Canopy Height Model. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 104, 44-52. |
| [25] | Larsen M, Eriksson M, Descombes X, Perrin G, Brandtberg T, Gougeon FA (2011) Comparison of six individual tree crown detection algorithms evaluated under varying forest conditions. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 32, 5827-5852. |
| [26] | Li FR (2019) Forest Mensuration,4th edn. China Forestry Publishing House, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [李凤日 (2019) 测树学(第4版). 中国林业出版社, 北京.] | |
| [27] | Li WK, Guo QH, Jakubowski MK, Kelly M (2012) A new method for segmenting individual trees from the Lidar point cloud. Photogrammetric Engineering & Remote Sensing, 78, 75-84. |
| [28] | Li X, Chen WY, Sanesi G, Lafortezza R (2019) Remote sensing in urban forestry: Recent applications and future directions. Remote Sensing, 11, 1144. |
| [29] | Lisiewicz M, Kamińska A, Kraszewski B, Stereńczak K (2022) Correcting the results of CHM-based individual tree detection algorithms to improve their accuracy and reliability. Remote Sensing, 14, 1822. |
| [30] | Liu LX, Coops NC, Aven NW, Pang Y (2017) Mapping urban tree species using integrated airborne hyperspectral and LiDAR remote sensing data. Remote Sensing of Environment, 200, 170-182. |
| [31] | Liu MH, Han ZW, Chen YM, Liu ZJ, Han YS (2022) Tree species classification of airborne LiDAR data based on 3D deep learning. Journal of National University of Defense Technology, 44(2), 123-130. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [刘茂华, 韩梓威, 陈一鸣, 刘正军, 韩颜顺 (2022) 机载激光雷达数据的三维深度学习树种分类. 国防科技大学学报, 44(2), 123-130.] | |
| [32] |
Liu XL, Wu YG, Zhang MH, Chen XR, Zhu ZC, Chen DY, Dong S, Li BH, Ding BY, Liu Y (2024) Community composition and structure of a 25-ha forest dynamics plot of subtropical forest in Baishanzu, Zhejiang Province. Biodiversity Science, 32, 23294. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
| [刘啸林, 吴友贵, 张敏华, 陈小荣, 朱志成, 陈定云, 董舒, 李步杭, 丁炳扬, 刘宇 (2024) 浙江百山祖25 ha亚热带森林动态监测样地群落组成与结构特征. 生物多样性, 32, 23294.] | |
| [33] | Ma JW, Xia D, Wang YK, Niu XX, Jiang S, Liu ZY, Guo HX (2022) A comprehensive comparison among metaheuristics (MHs) for geohazard modeling using machine learning: Insights from a case study of landslide displacement prediction. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 114, 105150. |
| [34] | Ma KS, Chen ZX, Fu LY, Tian WL, Jiang FG, Yi J, Du Z, Sun H (2022) Performance and sensitivity of individual tree segmentation methods for UAV-LiDAR in multiple forest types. Remote Sensing, 14, 298. |
| [35] | Ma Q, Lin J, Ju Y, Li WK, Liang L, Guo QH (2023) Individual structure mapping over six million trees for New York City USA. Scientific Data, 10, 102. |
| [36] | Maschler J, Atzberger C, Immitzer M (2018) Individual tree crown segmentation and classification of 13 tree species using airborne hyperspectral data. Remote Sensing, 10, 1218. |
| [37] | Mäyrä J, Keski-Saari S, Kivinen S, Tanhuanpää T, Hurskainen P, Kullberg P, Poikolainen L, Viinikka A, Tuominen S, Kumpula T, Vihervaara P (2021) Tree species classification from airborne hyperspectral and LiDAR data using 3D convolutional neural networks. Remote Sensing of Environment, 256, 112322. |
| [38] | Meyer GE, Mehta T, Kocher MF, Mortensen DA, Samal A (1998) Textural imaging and discriminant analysis for distinguishing weeds for spot spraying. Transactions of the ASAE, 41, 1189-1197. |
| [39] | Meyer GE, Neto JC (2008) Verification of color vegetation indices for automated crop imaging applications. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture, 63, 282-293. |
| [40] | Michałowska M, Rapiński J (2021) A review of tree species classification based on airborne LiDAR data and applied classifiers. Remote Sensing, 13, 353. |
| [41] | Mitchell MGE, Wu D, Johansen K, Maron M, McAlpine C, Rhodes JR (2016) Landscape structure influences urban vegetation vertical structure. Journal of Applied Ecology, 53, 1477-1488. |
| [42] | Mohan M, Silva CA, Klauberg C, Jat P, Catts G, Cardil A, Hudak AT, Dia M (2017) Individual tree detection from unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) derived canopy height model in an open canopy mixed conifer forest. Forests, 8, 340. |
| [43] | Nevalainen O, Honkavaara E, Tuominen S, Viljanen N, Hakala T, Yu XW, Hyyppä J, Saari H, Pölönen I, Imai NN, Tommaselli AMG (2017) Individual tree detection and classification with UAV-based photogrammetric point clouds and hyperspectral imaging. Remote Sensing, 9, 185. |
| [44] | Nie S, Wang C, Xi XH, Luo SZ, Zhu XX, Li GY, Liu H, Tian JY, Zhang S (2019) Assessing the impacts of various factors on treetop detection using LiDAR-derived canopy height models. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 57, 10099-10115. |
| [45] | Niu CJ, Lou AR, Sun RY, Li QF (2015) Foundations in Ecology,3rd edn. Higher Education Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [牛翠娟, 娄安如, 孙儒泳, 李庆芬 (2015) 基础生态学(第三版). 高等教育出版社, 北京.] | |
| [46] |
Peng DH, Gui ZP, Wang DH, Ma YC, Huang ZC, Zhou Y, Wu HY (2022) Clustering by measuring local direction centrality for data with heterogeneous density and weak connectivity. Nature Communications, 13, 5455.
DOI PMID |
| [47] | Pu YH, Xu DD, Wang HB, Li X, Xu X (2023) A new strategy for individual tree detection and segmentation from leaf-on and leaf-off UAV-LiDAR point clouds based on automatic detection of seed points. Remote Sensing, 15, 1619. |
| [48] | Qin HM, Zhou WQ, Yao Y, Wang WM (2022) Individual tree segmentation and tree species classification in subtropical broadleaf forests using UAV-based LiDAR, hyperspectral, and ultrahigh-resolution RGB data. Remote Sensing of Environment, 280, 113143. |
| [49] |
Rao JS, Yang T, Tian X, Liu WC, Wang XF, Qian HJ, Shen ZH (2023) Vertical structural characteristics of a semi-humid evergreen broad-leaved forest and common tree species based on a portable backpack LiDAR. Biodiversity Science, 31, 23216. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[饶杰生, 杨涛, 田希, 刘文聪, 王晓凤, 钱恒君, 沈泽昊 (2023) 基于背包LiDAR的半湿润常绿阔叶林及其常见树种的垂直结构特征. 生物多样性, 31, 23216.]
DOI |
|
| [50] | Roussel JR, Auty D, Coops NC, Tompalski P, Goodbody TRH, Meador AS, Bourdon JF, de Boissieu F, Achim A (2020) lidR: An R package for analysis of airborne laser scanning (ALS) data. Remote Sensing of Environment, 251, 112061. |
| [51] | Saponaro M, Agapiou A, Hadjimitsis DG, Tarantino E (2021) Influence of spatial resolution for vegetation indices’ extraction using visible bands from unmanned aerial vehicles’ orthomosaics datasets. Remote Sensing, 13, 3238. |
| [52] | Schiefer F, Kattenborn T, Frick A, Frey J, Schall P, Koch B, Schmidtlein S (2020) Mapping forest tree species in high resolution UAV-based RGB-imagery by means of convolutional neural networks. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 170, 205-215. |
| [53] | Secord J, Zakhor A (2007) Tree detection in urban regions using aerial LiDAR and image data. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 4, 196-200. |
| [54] | Seiferling I, Naik N, Ratti C, Proulx R (2017) Green streets—Quantifying and mapping urban trees with street-level imagery and computer vision. Landscape and Urban Planning, 165, 93-101. |
| [55] | Shen X, Cao L (2017) Tree-species classification in subtropical forests using airborne hyperspectral and LiDAR data. Remote Sensing, 9, 1180. |
| [56] | Shi YF, Wang TJ, Skidmore AK, Heurich M (2020) Improving LiDAR-based tree species mapping in Central European mixed forests using multi-temporal digital aerial colour- infrared photographs. International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation, 84, 101970. |
| [57] | Sun ZF, Zhang XL, Li NW (2019) Comparison of individual tree crown extraction method and suitability of airborne and spaceborne high-resolution remote sensing images. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 41(11), 66-75. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [孙振峰, 张晓丽, 李霓雯 (2019) 机载与星载高分遥感影像单木树冠分割方法和适宜性对比. 北京林业大学学报, 41(11), 66-75.] | |
| [58] |
Teng WX, Wang N, Shi HH, Xu ZY (2019) Tree species classification of high resolution image combining with object-oriented and deep feature. Bulletin of Surveying and Mapping, (4), 38-42. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[滕文秀, 王妮, 施慧慧, 许振宇 (2019) 结合面向对象和深度特征的高分影像树种分类. 测绘通报, (4), 38-42.]
DOI |
|
| [59] | The Biodiversity Committee of Chinese Academy of Sciences (2024) Catalogue of Life China: 2024 Annual Checklist, Beijing, China. |
| [60] | Verrelst J, Schaepman ME, Koetz B, Kneubühler M (2008) Angular sensitivity analysis of vegetation indices derived from CHRIS/PROBA data. Remote Sensing of Environment, 112, 2341-2353. |
| [61] | Walker JJ, de Beurs KM, Wynne RH (2014) Dryland vegetation phenology across an elevation gradient in Arizona, USA, investigated with fused MODIS and Landsat data. Remote Sensing of Environment, 144, 85-97. |
| [62] | Wang BS (1998) Urban vegetation and urban vegetology. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Sunyatseni, 37(4), 10-13. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王伯荪 (1998) 城市植被与城市植被学. 中山大学学报(自然科学版), 37(4), 10-13.] | |
| [63] | Wang JJ, Jiang LC, Xin SD, Wang YZ, He P, Yan YF (2023) Two new methods applied to crown width additive models: A case study for three tree species in Northeastern China. Annals of Forest Science, 80, 11. |
| [64] | Wang XQ, Wang MM, Wang SQ, Wu YD (2015) Extraction of vegetation information from visible unmanned aerial vehicle images. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 31(5), 152-159. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [汪小钦, 王苗苗, 王绍强, 吴云东 (2015) 基于可见光波段无人机遥感的植被信息提取. 农业工程学报, 31(5), 152-159.] | |
| [65] | Wu JR, Man QX, Yang XM, Dong PL, Ma XT, Liu CH, Han CY (2024) Fine classification of urban tree species based on UAV-based RGB imagery and LiDAR data. Forests, 15, 390. |
| [66] | Wu XQ, Shen X, Cao L, Wang GB, Cao FL (2019) Assessment of individual tree detection and canopy cover estimation using unmanned aerial vehicle based light detection and ranging (UAV-LiDAR) data in planted forests. Remote Sensing, 11, 908. |
| [67] | Xu X, Liu LY, Han P, Gong XQ, Zhang Q (2022) Accuracy of vegetation indices in assessing different grades of grassland desertification from UAV. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19, 16793. |
| [68] | Xue JH (2006) Forest Ecology. China Forestry Publishing House, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [薛建辉 (2006) 森林生态学. 中国林业出版社, 北京.] | |
| [69] | Yao DJ, Yang J, Zhan XJ (2014) Feature selection algorithm based on random forest. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 44(1), 137-141. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [姚登举, 杨静, 詹晓娟 (2014) 基于随机森林的特征选择算法. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 44(1), 137-141.] | |
| [70] | Yao Y, Qin HM, Zhang ZM, Wang WM, Zhou WQ (2022) The classification of subtropical forest tree species based on UAV multi-source remote sensing data. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 42, 3666-3677. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [姚扬, 秦海明, 张志明, 王伟民, 周伟奇 (2022) 基于无人机多源遥感数据的亚热带森林树种分类. 生态学报, 42, 3666-3677.] | |
| [71] | Yu J, Lei L, Li ZH (2024) Individual tree segmentation based on seed points detected by an adaptive crown shaped algorithm using UAV-LiDAR data. Remote Sensing, 16, 825. |
| [72] | Yun T, Jiang K, Li GC, Eichhorn MP, Fan JC, Liu FZ, Chen BQ, An F, Cao L (2021) Individual tree crown segmentation from airborne LiDAR data using a novel Gaussian filter and energy function minimization-based approach. Remote Sensing of Environment, 256, 112307. |
| [73] |
Zhang CR, Li SF, Li FC, Tang ZZ, Liu HY, Wang LH, Gu R, Deng Y, Zhang ZM, Lin LX (2024) Habitat association and community classification of woody plants in the 20 ha forest dynamics plot of subtropical semi-humid evergreen broad-leaved forest in the Jizu Mountains, Yunnan. Biodiversity Science, 32, 23393. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
| [张楚然, 李生发, 李逢昌, 唐志忠, 刘辉燕, 王丽红, 顾荣, 邓云, 张志明, 林露湘 (2024) 云南鸡足山亚热带半湿润常绿阔叶林20 ha动态监测样地木本植物生境关联与群落数量分类. 生物多样性, 32, 23393.] | |
| [74] | Zhang WM, Qi JB, Wan P, Wang HT, Xie DH, Wang XY, Yan GJ (2016) An easy-to-use airborne LiDAR data filtering method based on cloth simulation. Remote Sensing, 8, 501. |
| [75] | Zhao ZH, Jiang G, Li YS (2023) A novel method for digital orthophoto generation from top view constrained dense matching. Remote Sensing, 15, 177. |
| [76] | Zhou L, Li XJ, Zhang B, Xuan J, Gong YL, Tan C, Huang HG, Du HQ (2022) Estimating 3D green volume and aboveground biomass of urban forest trees by UAV-Lidar. Remote Sensing, 14, 5211. |
| [1] | 张浩斌, 肖路, 刘艳杰. 夜间灯光对外来入侵植物和本地植物群落多样性和生长的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24553-. |
| [2] | 刘咏华, 童光蓉, 余航远, 王宁宁, 任海保, 陈磊, 马克平, 米湘成. 钱江源-百山祖国家公园候选区钱江源园区冠层三维结构及光谱特征对人为干扰的响应[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24174-. |
| [3] | 黄雨菲, 路春燕, 贾明明, 王自立, 苏越, 苏艳琳. 基于无人机影像与面向对象-深度学习的滨海湿地植物物种分类[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(3): 22411-. |
| [4] | 杨欣, 姚志良, 王彬, 温韩东, 邓云, 曹敏, 张志明, 谭正洪, 林露湘. 亚热带常绿阔叶林林分结构对物种组成变异的驱动作用: 从局域到区域尺度[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(2): 22139-. |
| [5] | 饶杰生, 杨涛, 田希, 刘文聪, 王晓凤, 钱恒君, 沈泽昊. 基于背包LiDAR的半湿润常绿阔叶林及其常见树种的垂直结构特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(11): 23216-. |
| [6] | 吴墨栩, 安明态, 田力, 刘锋. 茂兰喀斯特森林木本植物性系统数量特征及其与环境因子的关系[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(11): 22025-. |
| [7] | 张昭臣, 胡健波, 杨庆松, 练琚愉, 李步杭, 王希华, 叶万辉, 张健. 中国亚热带4个森林动态监测样地无人机可见光遥感影像数据集[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(9): 1181-1185. |
| [8] | 徐岩, 张聪伶, 降瑞娇, 王子斐, 朱梦晨, 沈国春. 无人机高光谱影像与冠层树种多样性监测[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(5): 647-660. |
| [9] | 周中一, 刘冉, 时书纳, 苏艳军, 李文楷, 郭庆华. 基于激光雷达数据的物种分布模拟: 以美国加州内华达山脉南部区域食鱼貂分布模拟为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2018, 26(8): 878-891. |
| [10] | 郭庆华, 胡天宇, 姜媛茜, 金时超, 王瑞, 关宏灿, 杨秋丽, 李玉美, 吴芳芳, 翟秋萍, 刘瑾, 苏艳军. 遥感在生物多样性研究中的应用进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2018, 26(8): 789-806. |
| [11] | 郭庆华, 吴芳芳, 胡天宇, 陈琳海, 刘瑾, 赵晓倩, 高上, 庞树鑫. 无人机在生物多样性遥感监测中的应用现状与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2016, 24(11): 1267-1278. |
| [12] | 郭庆华, 刘瑾, 李玉美, 翟秋萍, 王永财, 吴芳芳, 胡天宇, 万华伟, 刘慧明, 申文明. 生物多样性近地面遥感监测: 应用现状与前景展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2016, 24(11): 1249-1266. |
| [13] | 袁素芬, 唐海萍. 新疆准噶尔荒漠短命植物群落特征及其水热适应性[J]. 生物多样性, 2010, 18(4): 346-354. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn