



生物多样性 ›› 2024, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (4): 23435. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2023435 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2023435
王永财1, 万华伟2, 高吉喜2,*( ), 胡卓玮1,*(
), 胡卓玮1,*( ), 孙晨曦2, 吕娜2, 张志如2
), 孙晨曦2, 吕娜2, 张志如2
收稿日期:2023-11-15
接受日期:2024-03-30
出版日期:2024-04-20
发布日期:2024-05-17
通讯作者:
* E-mail: 基金资助:
Yongcai Wang1, Huawei Wan2, Jixi Gao2,*( ), Zhuowei Hu1,*(
), Zhuowei Hu1,*( ), Chenxi Sun2, Na Lü2, Zhiru Zhang2
), Chenxi Sun2, Na Lü2, Zhiru Zhang2
Received:2023-11-15
Accepted:2024-03-30
Online:2024-04-20
Published:2024-05-17
Contact:
* E-mail: 摘要:
草地植物的分类识别是开展草地资源调查和生物多样性监测的基础, 计算机视觉和深度学习技术的快速发展为植物分类识别提供了技术条件, 但目前缺乏专门针对草地植物识别的数据集和模型。本研究建立了我国北方831种常见天然草地植物的图像数据集, 基于卷积神经网络(convolutional neural network, CNN)和视觉Transformers (vision transformers, ViT)这两个最先进的图像分类架构进行模型训练, 以获取草地植物识别模型, 并从模型识别精度、识别速度和大小等方面评估了Eva-02、ResNet-RS、MobileNetV3和MobileViTv2 4个模型的性能。从模型识别精度方面来看, Eva-02、MobileViTv2、ResNet_RS和MobileNetV3在测试集的Top1准确率分别为96.78%、94.29%、95.57%和91.53%, Top5准确率分别为99.17%、98.93%、98.79%和97.56%。从模型大小和识别速度来看, MobileNetV3的参数量最小, 识别速度最快, 其次为MobileViTv2, 可用于移动端部署, 而Eva-02参数量最大, 检测速度最慢。与Pl@ntNet、花伴侣、百度识图植物识别效果的比较表明, 本研究训练得到的4个植物识别模型可以识别的天然草地植物物种数量最多, 识别准确率最高, 均优于这3个识别系统。
王永财, 万华伟, 高吉喜, 胡卓玮, 孙晨曦, 吕娜, 张志如 (2024) 基于深度学习的我国北方常见天然草地植物识别. 生物多样性, 32, 23435. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2023435.
Yongcai Wang, Huawei Wan, Jixi Gao, Zhuowei Hu, Chenxi Sun, Na Lü, Zhiru Zhang (2024) Identification of common native grassland plants in northern China using deep learning. Biodiversity Science, 32, 23435. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2023435.
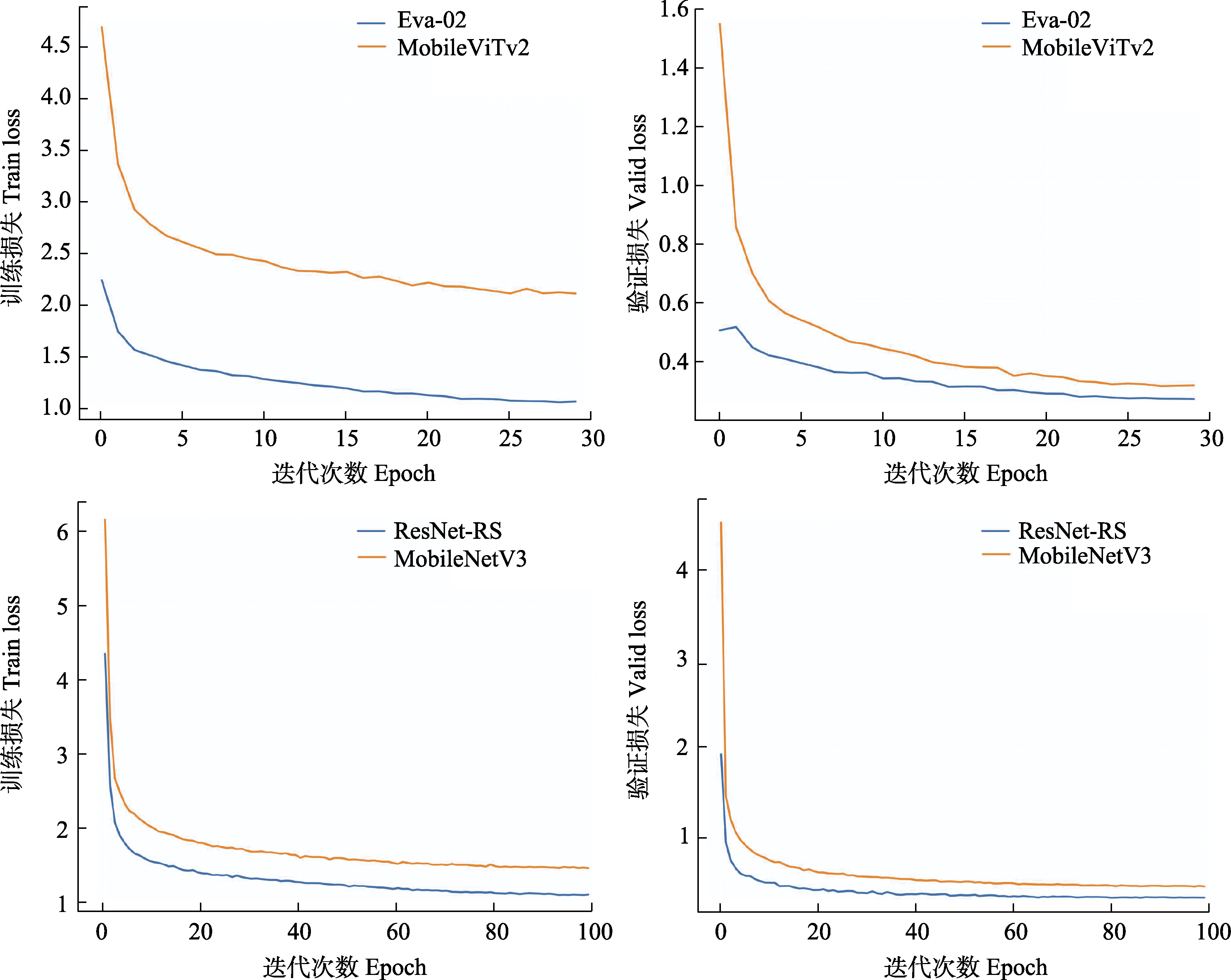
图2 Eva-02、MobileViTv2、ResNet-RS和MobileNetV3 4个模型在训练和验证集上的损失变化
Fig. 2 Loss variation on the training and validation datasets for all four models of Eva-02, MobileViTv2, ResNet-RS, and MobileNetV3

图3 Eva-02、MobileViTv2、ResNet-RS和MobileNetV3 4个模型在验证集上的Top1和Top5准确率变化
Fig. 3 The Top1 and Top5 accuracy variation on the validation dataset for all four models of Eva-02, MobileViTv2, ResNet-RS, and MobileNetV3
| 模型 Model | 测试集 Test | 验证集 Valid | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Top1 (%) | Top5 (%) | Top1 (%) | Top5 (%) | |
| Eva-02 | 96.78 | 99.17 | 96.25 | 99.11 |
| MobileViTv2 | 94.29 | 98.93 | 93.97 | 98.83 |
| ResNet-RS | 95.57 | 98.79 | 95.34 | 98.78 |
| MobileNetV3 | 91.53 | 97.56 | 91.30 | 97.85 |
表1 Eva-02、MobileViTv2、ResNet-RS和MobileNetV3 4个模型识别精度
Table 1 The recognition accuracy for all four models of Eva-02, MobileViTv2, ResNet-RS, and MobileNetV3
| 模型 Model | 测试集 Test | 验证集 Valid | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Top1 (%) | Top5 (%) | Top1 (%) | Top5 (%) | |
| Eva-02 | 96.78 | 99.17 | 96.25 | 99.11 |
| MobileViTv2 | 94.29 | 98.93 | 93.97 | 98.83 |
| ResNet-RS | 95.57 | 98.79 | 95.34 | 98.78 |
| MobileNetV3 | 91.53 | 97.56 | 91.30 | 97.85 |
| 模型 Model | 参数量 Params (M) | 裁剪大小 Crop size | 每秒浮点运 算次数 Flops | 每秒样本数 Samples/s |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Eva-02 | 303.78 | 448,448 | 310.15 G | 29.62 |
| MobileViTv2 | 18.40 | 384,384 | 16.09 G | 197.14 |
| ResNet-RS | 93.21 | 256,256 | 20.26 G | 84.62 |
| MobileNetV3 | 4.17 | 256,256 | 280.44 M | 200.12 |
表2 Eva-02、MobileViTv2、ResNet-RS和MobileNetV3 4个模型参数大小及推理性能
Table 2 The parameter size and inference performance for all four models of Eva-02, MobileViTv2, ResNet-RS, and MobileNetV3
| 模型 Model | 参数量 Params (M) | 裁剪大小 Crop size | 每秒浮点运 算次数 Flops | 每秒样本数 Samples/s |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Eva-02 | 303.78 | 448,448 | 310.15 G | 29.62 |
| MobileViTv2 | 18.40 | 384,384 | 16.09 G | 197.14 |
| ResNet-RS | 93.21 | 256,256 | 20.26 G | 84.62 |
| MobileNetV3 | 4.17 | 256,256 | 280.44 M | 200.12 |

图4 Eva-02、MobileViTv2、ResNet-RS和MobileNetV3 4个模型在Top1和Top5达到90%以上识别精度的物种数
Fig. 4 The number of species with recognition accuracy exceeding 90% in both Top1 and Top5 for all four models of Eva-02, MobileViTv2, ResNet-RS, and MobileNetV3
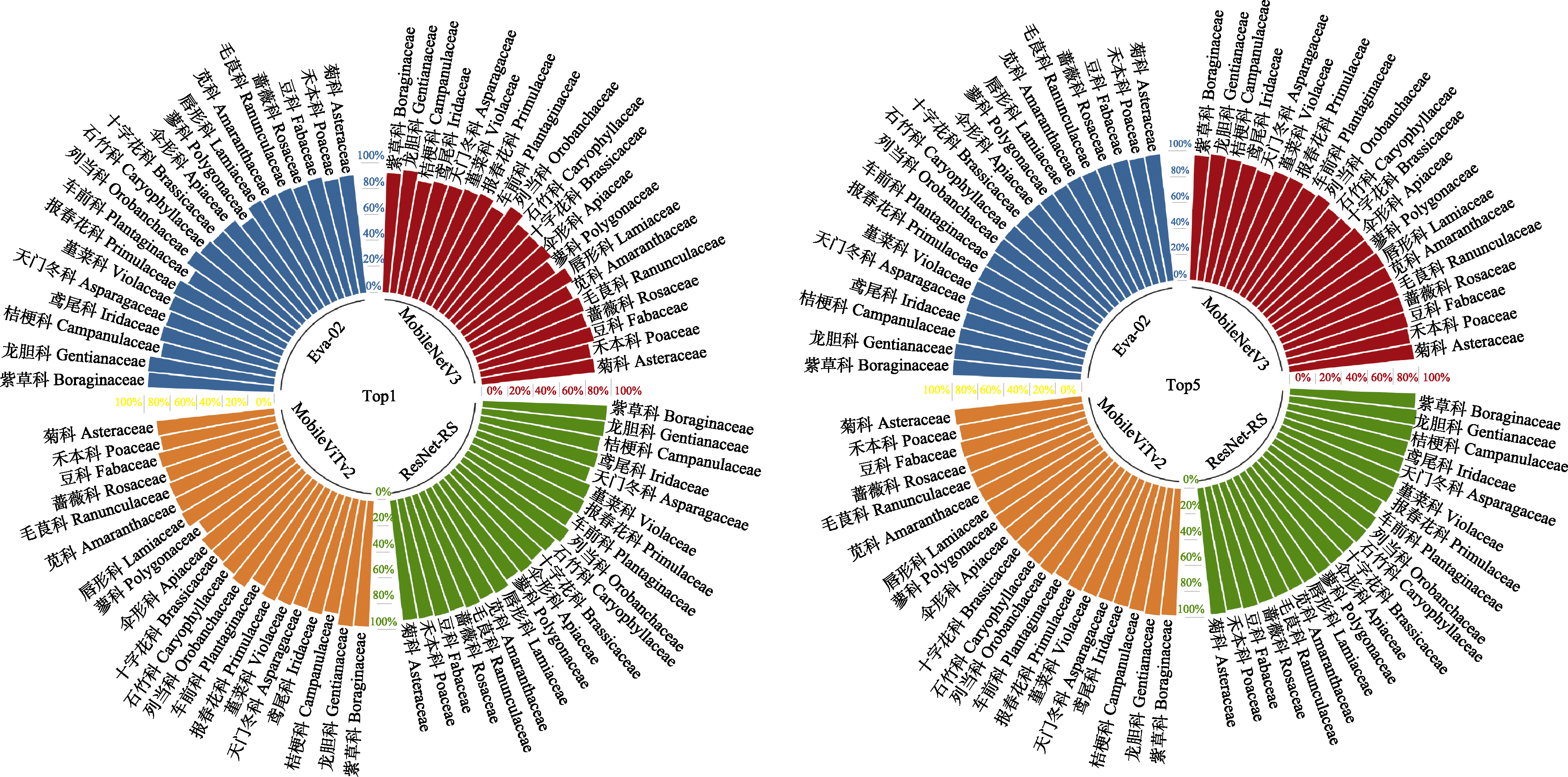
图5 Eva-02、MobileViTv2、ResNet-RS和MobileNetV3 4个模型对不同科植物物种的识别准确率
Fig. 5 The recognition accuracy of plant species from different families for all four models of Eva-02, MobileViTv2, ResNet-RS, and MobileNetV3
| 模型 Model | 识别植物种类 Recognized plant species | Top1 (%) | Top5 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pl@ntNet | 207 | 15.14 | 26.51 |
| 百度识图 Baidu-Shitu | 509 | 56.12 | 73.59 |
| 花伴侣 HuaBanLv | 569 | 41.08 | 62.87 |
表3 3种植物识别系统在测试数据集上的识别结果
Table 3 The recognition results of three plant identification systems on the test dataset
| 模型 Model | 识别植物种类 Recognized plant species | Top1 (%) | Top5 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pl@ntNet | 207 | 15.14 | 26.51 |
| 百度识图 Baidu-Shitu | 509 | 56.12 | 73.59 |
| 花伴侣 HuaBanLv | 569 | 41.08 | 62.87 |
| [1] | Alzubaidi L, Zhang JL, Humaidi AJ, Al-Dujaili A, Duan Y, Al-Shamma O, Santamaría J, Fadhel MA, Al-Amidie M, Farhan L (2021) Review of deep learning: Concepts, CNN architectures, challenges, applications, future directions. Journal of Big Data, 8, 1-74. |
| [2] | Belhumeur PN, Chen DZ, Feiner S, Jacobs DW, Kress WJ, Ling HB, Lopez I, Ramamoorthi R, Sheorey S, White S, Zhang L (2008) Searching the world’s herbaria:A system for visual identification of plant species. In: European Conference on Computer Vision (eds Forsyth D, Torr P, Zisserman A), pp. 116-129. Springer, Berlin. |
| [3] | Bello I, Fedus W, Du XZ, Cubuk ED, Srinivas A, Lin TY, Shlens J, Zoph B (2021) Revisiting ResNets: Improved training and scaling strategies. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 34, 22614-22627. |
| [4] | Buslaev A, Iglovikov VI, Khvedchenya E, Parinov A, Druzhinin M, Kalinin AA (2020) Albumentations: Fast and flexible image augmentations. Information, 11, 125. |
| [5] | Chytrý M, Schaminée JHJ, Schwabe A (2011) Vegetation survey: A new focus for Applied Vegetation Science. Applied Vegetation Science, 14, 435-439. |
| [6] | Donahue J, Jia YQ, Vinyals O, Hoffman J, Zhang N, Tzeng E, Darrell T (2014) DeCAF: A deep convolutional activation feature for generic visual recognition. Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on International Conference on Machine Learning, 32, 647-655. |
| [7] | Elhariri E, El-Bendary N, Hassanien AE (2014) Plant classification system based on leaf features. In: 2014 9th International Conference on Computer Engineering & Systems (ICCES), pp. 271-276. IEEE, Cairo, Egypt. |
| [8] | Fang YX, Sun Q, Wang XG, Huang TJ, Wang XL, Cao Y (2023) Eva-02: A visual representation for neon genesis. ArXiv, doi: 2303.11331. |
| [9] | Garcin C, Joly A, Bonnet P, Lombardo JC, Affouard A, Chouet M, Salmon J (2021) Pl@ntNet-300K:A plant image dataset with high label ambiguity and a long-tailed distribution. In: NeurIPS 2021—35th Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Online. |
| [10] | Gao HY, Gao XH, Feng QS, Li WL, Lu Z, Liang TG (2020) Approach to plant species identification in natural grasslands based on deep learning. Pratacultural Science, 37, 1931-1939. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [高宏元, 高新华, 冯琦胜, 李文龙, 鲁征, 梁天刚 (2020) 基于深度学习的天然草地植物物种识别方法. 草业科学, 37, 1931-1939.] | |
| [11] | Goëau H, Bonnet P, Joly A (2022) Overview of PlantCLEF 2022:Image-based plant identification at global scale. In: Conference and Labs of the Evaluation Forum (CLEF) (Working Notes), pp. 1916-1928. Bologna, Italy. |
| [12] | Goëau H, Joly A, Bonnet P, Selmi S, Molino JF, Barthélémy D, Boujemaa N (2014) LifeCLEF plant identification task 2014. In: Conference and Labs of the Evaluation Forum (CLEF), pp. 598-615. Sheffield, UK. |
| [13] | Gyires-Tóth BP, Osváth M, Papp D, Szűcs G (2019) Deep learning for plant classification and content-based image retrieval. Cybernetics and Information Technologies, 19, 88-100. |
| [14] | Han K, Wang Y, Chen H, Chen X, Guo J, Liu Z, Tang Y, Xiao A, Xu C, Yang Z, Zhang Y, Tao D (2022) A survey on vision transformer. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 45, 87-110. |
| [15] | Hart AG, Bosley H, Hooper C, Perry J, Sellors-Moore J, Moore O, Goodenough AE (2023) Assessing the accuracy of free automated plant identification applications. People and Nature, 5, 929-937. |
| [16] | Howard A, Sandler M, Chu G, Chen LC, Chen B, Tan M, Wang W, Zhu Y, Pang R, Vasudevan V, Le Q, Adam H (2019) Searching for MobileNetv3. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF international conference on computer vision, pp. 1314-1324. |
| [17] | Joly A, Bonnet P, Goëau H, Barbe J, Selmi S, Champ J, Dufour-Kowalski S, Affouard A, Carré J, Molino JF, Boujemaa N, Barthélémy D (2016) A look inside the Pl@ntNet experience: The good, the bias and the hope. Multimedia Systems, 22, 751-766. |
| [18] | Joly A, Goëau H, Glotin H, Spampinato C, Bonnet P, Vellinga WP, Planque R, Rauber A, Fisher B, Müller H (2014) LifeCLEF:Multimedia life species identification. In: Environmental Multimedia Retrieval, pp. 7-13. Sheffield, UK. |
| [19] | Joly A, Goëau H, Kahl S, Picek L, Lorieul T, Cole E, Šulc M (2022) LifeCLEF 2022 teaser: An evaluation of machine- learning based species identification and species distribution predictio. In: European Conference on Information Retrieval, pp. 390-399. Springer International Publishing, Cham. |
| [20] |
Kong JX, Zhang ZC, Zhang J (2019) Classification and identification of plant species based on multi-source remote sensing data: Research progress and prospect. Biodiversity Science, 27, 796-812. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[孔嘉鑫, 张昭臣, 张健 (2019) 基于多源遥感数据的植物物种分类与识别: 研究进展与展望. 生物多样性, 27, 796-812.]
DOI |
|
| [21] | Kumar N, Belhumeur PN, Biswas A, Jacobs DW, Kress WJ, Lopez IC, Soares JV (2012) Leafsnap: A computer vision system for automatic plant species identification, pp. 502-516. Springer, Berlin. |
| [22] | Lewkowycz A (2021) How to decay your learning rate. arXiv, doi: 2103.12682. |
| [23] | Li M (2018) “flower partners”: A new medium of knowledge service in the era of artificial intelligence. Publishing Reference, (8), 23-24. (in Chinese) |
| [李敏 (2018) “花伴侣”:人工智能时代知识服务的新媒介. 出版参考, (8), 23-24.] | |
| [24] | Mehta S, Rastegari M (2022) Separable self-attention for mobile vision transformers. arXiv, doi: 2206.02680. |
| [25] | Munisami T, Ramsurn M, Kishnah S, Pudaruth S (2015) Plant leaf recognition using shape features and colour histogram with K-nearest neighbour classifiers. Procedia Computer Science, 58, 740-747. |
| [26] | Parr CS, Wilson MN, Leary MP, Schulz KS, Lans MK, Walley ML, Corrigan Jr MRJ (2014) The Encyclopedia of Life v2: Providing global access to knowledge about life on earth. Biodiversity Data Journal, 2, e1079. |
| [27] | Picek L, Šulc M, Matas J, Heilmann-Clausen J, Jeppesen TS, Lind E (2022a) Automatic fungi recognition: Deep learning meets mycology. Sensors, 22, 633. |
| [28] | Picek L, Šulc M, Patel Y, Matas J (2022b) Plant recognition by AI: Deep neural nets, transformers, and kNN in deep embeddings. Frontiers in Plant Science, 13, 787527. |
| [29] | Prasad S, Kudiri KM, Tripathi RC (2011) Relative sub-image based features for leaf recognition using support vector machine. In:Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference on Communication, Computing & Security, 343-346. |
| [30] | Rahman A, Khanom A (2013) Taxonomic and ethno-medicinal study of species from Moraceae (mulberry) family in Bangladesh Flora. Research in Plant Sciences, 1(3), 53-57. |
| [31] | Robertson T, Döring M, Guralnick R, Bloom D, Wieczorek J, Braak K, Desmet P (2014) The GBIF integrated publishing toolkit: Facilitating the efficient publishing of biodiversity data on the internet. PLoS ONE, 9, e102623. |
| [32] | Rzanny M, Wittich HC, Mäder P, Deggelmann A, Boho D, Wäldchen J (2022) Image-based automated recognition of 31 Poaceae species: The most relevant perspectives. Frontiers in Plant Science, 12, 804140. |
| [33] | Shalev-Shwartz S, Ben-David S (2014) Understanding Machine Learning:From Theory to Algorithms. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge. |
| [34] | Sharif Razavian A, Azizpour H, Sullivan J, Carlsson S (2014) CNN features off-the-shelf: An astounding baseline for recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition workshops, pp. 806-813. |
| [35] | Simonyan K, Zisserman A (2014) Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv, doi: 1409.1556. |
| [36] | Song G, Wang Q (2023) Species classification from hyperspectral leaf information using machine learning approaches. Ecological Informatics, 76, 102141. |
| [37] | Sun Y, Liu Y, Wang G, Zhang H (2017) Deep learning for plant identification in natural environment. Computational Intelligence and Neuroscience, 2017, 2-4. |
| [38] |
Šulc M, Matas J (2017) Fine-grained recognition of plants from images. Plant Methods, 13, 115.
DOI PMID |
| [39] | Szegedy C, Liu W, Jia Y, Sermanet P, Reed S, Anguelov D, Rabinovich A (2014) Going deeper with convolutions. arXiv, doi: 1409.4842v1. |
| [40] | Van Horn G, Mac Aodha O, Song Y, Cui Y, Sun C, Shepard A, Belongie S (2018) The iNaturalist Species Classification and Detection Dataset-Supplementary Material. Reptilia, 32, 1-3. |
| [41] | Wang JX (2019) Research on the communication effect of “Huajian” article on shape-color App based on “5W” communication mode. Audio-Visual, 142(2), 131-132. (in Chinese) |
| [王加希 (2019) 基于“5W”传播模式对形色App “花间”文章传播效果的探究. 视听, 142(2), 131-132.] | |
| [42] | Wäldchen J, Mäder P (2018) Machine learning for image based species identification. Methods in Ecology and Evolution, 9, 2216-2225. |
| [43] |
Xu ZH, Liu SY, Zhao Y, Tu WQ, Chang ZF, Zhang ET, Guo J, Zheng D, Geng J, Gu GY, Guo CP, Guo LL, Wang J, Xu CY, Peng C, Yang T, Cui MQ, Sun WC, Zhang JT, Liu HT, Ba CQ, Wang HQ, Jia JC, Wu JZ, Xiao C, Ma KP (2020) Evaluation of the identification ability of eight commonly used plant identification application softwares in China. Biodiversity Science, 28, 524-533. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[许展慧, 刘诗尧, 赵莹, 涂文琴, 常诏峰, 张恩涛, 郭靖, 郑迪, 耿鋆, 顾高营, 郭淳鹏, 郭璐璐, 王静, 徐春阳, 彭钏, 杨腾, 崔梦琪, 孙伟成, 张剑坛, 刘皓天, 巴超群, 王鹤琪, 贾竞超, 武金洲, 肖翠, 马克平 (2020) 国内8款常用植物识别软件的识别能力评价. 生物多样性, 28, 524-533.]
DOI |
|
| [44] | Zhang S, Huang W, Huang YA, Zhang C (2020) Plant species recognition methods using leaf image: Overview. Neurocomputing, 408, 246-272. |
| [1] | 谢淦, 宣晶, 付其迪, 魏泽, 薛凯, 雒海瑞, 高吉喜, 李敏. 草地植物多样性无人机调查的物种智能识别模型构建[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24236-. |
| [2] | 吴昱萱, 王平, 胡晓生, 丁一, 彭甜恬, 植秋滢, 巴德木其其格, 李文杰, 关潇, 李俊生. 呼伦贝尔草地退化现状评估与植被特征变化[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24118-. |
| [3] | 李东红, 郝媛媛, 甘辉林, 张航, 刘耀猛, 他富源, 胡桂馨. 祁连山北麓中段不同类型草地蝗虫种类及分布[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(9): 24119-. |
| [4] | 万凤鸣, 万华伟, 张志如, 高吉喜, 孙晨曦, 王永财. 草地植物多样性无人机调查的应用潜力[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(3): 23381-. |
| [5] | 黄万涛, 郝泽周, 张梓欣, 肖治术, 张承云. 被动声学监测设备性能比较及对鸟声识别的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(10): 24273-. |
| [6] | 谢将剑, 沈忱, 张飞宇, 肖治术. 融合音频及生态位信息的跨地域鸟类物种识别方法[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(10): 24259-. |
| [7] | 罗正明, 刘晋仙, 张变华, 周妍英, 郝爱华, 杨凯, 柴宝峰. 不同退化阶段亚高山草甸土壤原生生物群落多样性特征及驱动因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(8): 23136-. |
| [8] | 蔡建民, 何培宇, 杨智鹏, 李露莹, 赵启军, 潘帆. 基于深度特征融合的鸟鸣识别方法及其可解释性分析[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(7): 23087-. |
| [9] | 赵秋杰, 郭辉军, 孟广涛, 钟明川, 尹俊, 刘倬橙, 李品荣, 陈力, 陶毅, 秋生, 王红, 赵延会. 放牧对蜜蜂的影响及其生态修复建议[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(5): 23037-. |
| [10] | 黄雨菲, 路春燕, 贾明明, 王自立, 苏越, 苏艳琳. 基于无人机影像与面向对象-深度学习的滨海湿地植物物种分类[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(3): 22411-. |
| [11] | 申小虎, 朱翔宇, 史洪飞, 王传之. 基于机器学习鸟声识别算法研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(11): 23272-. |
| [12] | 徐岩, 张聪伶, 降瑞娇, 王子斐, 朱梦晨, 沈国春. 无人机高光谱影像与冠层树种多样性监测[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(5): 647-660. |
| [13] | 许展慧, 刘诗尧, 赵莹, 涂文琴, 常诏峰, 张恩涛, 郭靖, 郑迪, 耿鋆, 顾高营, 郭淳鹏, 郭璐璐, 王静, 徐春阳, 彭钏, 杨腾, 崔梦琪, 孙伟成, 张剑坛, 刘皓天, 巴超群, 王鹤琪, 贾竞超, 武金洲, 肖翠, 马克平. 国内8款常用植物识别软件的识别能力评价[J]. 生物多样性, 2020, 28(4): 524-533. |
| [14] | 张中华, 周华坤, 赵新全, 姚步青, 马真, 董全民, 张振华, 王文颖, 杨元武. 青藏高原高寒草地生物多样性与生态系统功能的关系[J]. 生物多样性, 2018, 26(2): 111-129. |
| [15] | 宋瑞玲, 王昊, 张迪, 吕植, 朱子云, 张璐, 刘炎林, 才文公保, 吴岚. 基于MODIS-EVI评估三江源高寒草地的保护成效[J]. 生物多样性, 2018, 26(2): 149-157. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2026 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn
![]()