



生物多样性 ›› 2023, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (10): 23079. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2023079 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2023079
• 研究报告: 动物多样性 • 下一篇
收稿日期:2023-03-19
接受日期:2023-08-23
出版日期:2023-10-20
发布日期:2023-09-18
通讯作者:
*E-mail: wushibao@163.com
基金资助:
Fuhua Zhang, Fei Xi, Xinrui Tang, Peng Cen, Shibao Wu( )
)
Received:2023-03-19
Accepted:2023-08-23
Online:2023-10-20
Published:2023-09-18
Contact:
*E-mail: wushibao@163.com
摘要:
中国是穿山甲(Manis spp.)肉及甲片的主要消费区域之一。针对穿山甲不同形式产品的非法贸易和消费特点制定差异化、精准的保护对策, 对于穿山甲物种保护具有重要的促进作用。然而, 目前缺乏分别对穿山甲的肉或甲片开展非法贸易和消费特点的研究。本研究通过使用关键词“穿山甲”检索2022年1月11日之前在中国裁判文书网和网络媒体上报道的穿山甲肉的非法贸易案例, 对其涉及区域、贸易网络特征及贸易方式等进行了研究。结果发现, 穿山甲肉的贸易和消费主要集中在中国南方地区; 这些肉主要是由东南亚地区输入我国, 少量可能来自查获地。防城港、保山以及德宏是穿山甲肉非法贸易入境的主要陆路通道, 而广东和福建的港口和小码头是主要的海运通道。国内防城港、广州和昆明是穿山甲非法贸易网络上的关键城市。本研究的结果可能会受到2013年之前裁判文书网相应案件收录不全以及越久远的网络报道案例丢失越多的数据偏差的影响。根据本研究结果, 我们建议: 加强中国广西、云南边境口岸以及广东、福建港口、小码头等的货物走私检查和监察力度, 提高防城港、广州、保山和德宏出境车辆货物检查率, 在中国南方和北方采取差异化的穿山甲保护公众教育措施, 同时呼吁东南亚国家加强野生动物保护立法、执法力度和公众教育等措施, 是有效遏制中国大陆穿山甲肉非法贸易和消费的手段。本研究对于中国的穿山甲物种保护具有较大的实践意义。
张富华, 席菲, 汤芯蕊, 岑鹏, 吴诗宝 (2023) 穿山甲肉在中国大陆的非法贸易网络及对其实施关键干预措施的启示. 生物多样性, 31, 23079. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2023079.
Fuhua Zhang, Fei Xi, Xinrui Tang, Peng Cen, Shibao Wu (2023) The illegal trade network of pangolin meat in Chinese mainland and its implications for the implementation of key interventions. Biodiversity Science, 31, 23079. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2023079.
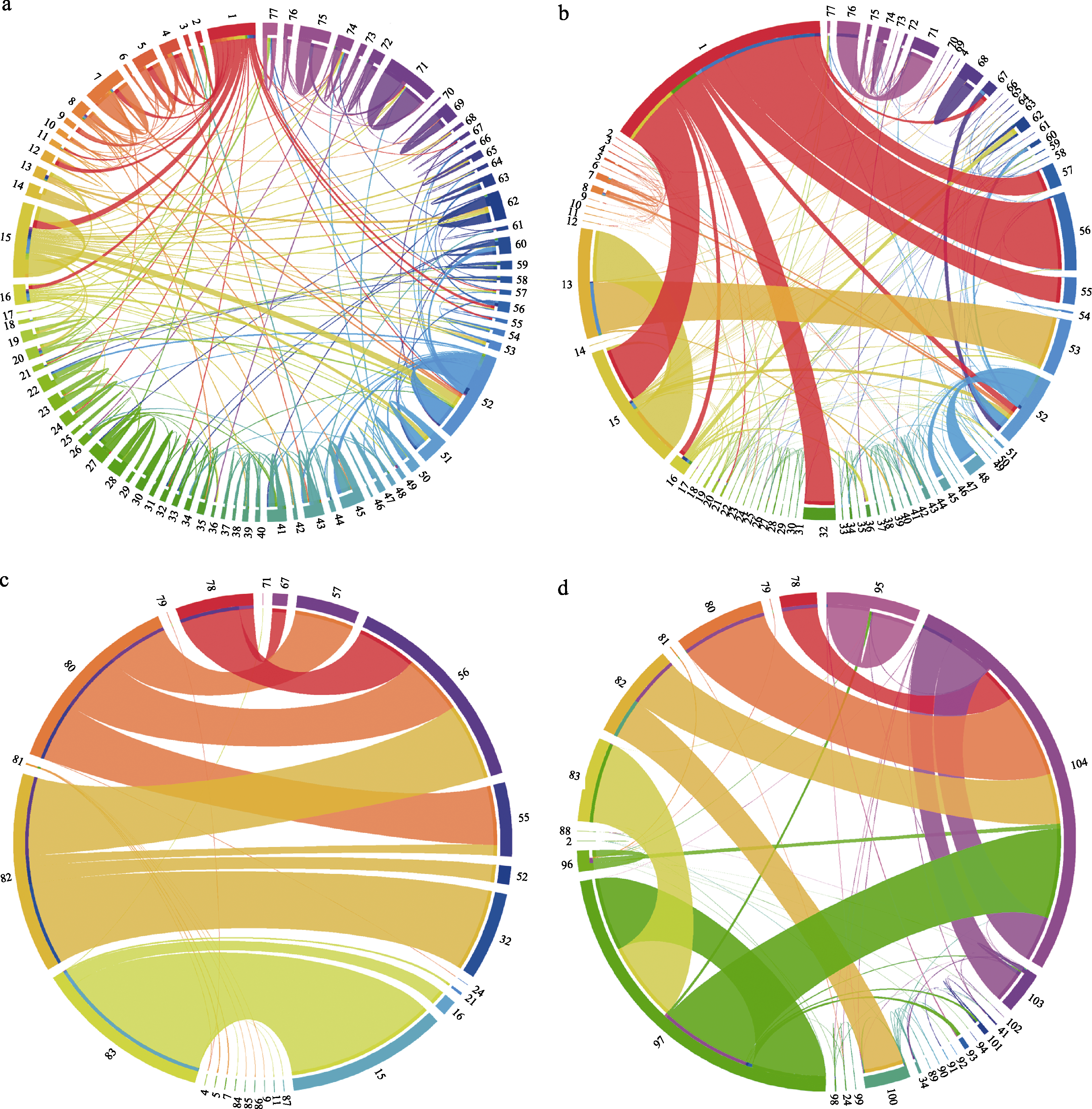
图3 2001?2021年间在中国境内缉获的不同地区间穿山甲肉相关的非法贸易环状图。(a)查获的不同区域间穿山甲肉非法贸易案件数量; (b)查获的由境外输入的中国大陆不同城市及大陆境内不同城市间非法贸易的穿山甲个体数量; (c)查获的不同国家输入中国大陆不同城市非法贸易的穿山甲个体数量; (d)查获的不同国家与中国大陆各省及大陆各省之间进行非法贸易的穿山甲个体数量。连接带与边缘彩色环条之间的间隙表示进口, 边缘彩色环条与相同颜色的连接带表示出口, 填充两者之间间隙的彩色环条代表货物出口的目的地, 连接带的宽度表示非法贸易案件数量(a)或个体数量(b, c和d)。图中各数字代表城市如下: 1. 国外; 2. 重庆; 3. 六盘水、绵阳、成都、攀枝花; 4. 西双版纳; 5. 保山; 6. 楚雄; 7. 德宏; 8. 昆明; 9. 普洱; 10. 曲靖; 11. 文山; 12. 丽江、怒江、大理、红河、临沧; 13. 北海; 14. 崇左; 15. 防城港; 16. 广西未知城市、梧州、贺州、百色; 17. 桂林; 18. 柳州; 19. 南宁; 20. 钦州; 21. 玉林; 22. 赣州; 23. 鹰潭、南昌、抚州、上饶、吉安、九江; 24. 海南; 25. 荆州、恩施; 26. 福建未知城市、莆田、南平; 27. 福州; 28. 龙岩; 29. 宁德; 30. 泉州; 31. 三明; 32. 厦门; 33. 漳州; 34. 北京; 35. 山东未知、西安、吉林、石家庄、青岛; 36. 郑州; 37. 常州; 38. 苏州、泰州; 39. 南京; 40. 无锡; 41. 上海; 42. 阜阳、宣城、芜湖; 43. 长沙; 44. 郴州; 45. 衡阳; 46. 怀化; 47. 湖南未知城市、湘西、永州; 48. 益阳; 49. 株洲; 50. 东莞; 51. 佛山; 52. 广州; 53. 广东未知城市、潮州、汕头、汕尾; 54. 河源; 55. 惠州; 56. 江门; 57. 揭阳; 58. 茂名; 59. 梅州; 60. 清远; 61. 韶关; 62. 深圳; 63. 阳江; 64. 云浮; 65. 湛江; 66. 肇庆; 67. 中山; 68. 珠海; 69. 杭州; 70. 嘉兴; 71. 金华; 72. 丽水; 73. 宁波; 74. 衢州; 75. 绍兴; 76. 台州; 77. 温州; 78. 印度尼西亚; 79. 老挝; 80. 马来西亚; 81. 缅甸; 82. 国外未知; 83. 越南; 84. 红河; 85. 临沧; 86. 怒江; 87. 百色; 88. 四川; 89. 吉林; 90. 山东; 91. 河北; 92. 陕西; 93. 河南; 94. 贵州; 95. 浙江; 96. 云南; 97. 广西; 98. 江西; 99. 湖北; 100. 福建; 101. 江苏; 102. 安徽; 103. 湖南; 104. 广东。
Fig. 3 A circular map of the illegal trade in pangolin meat between different regions seized in China from 2001 to 2021. (a) The number of seized incidences in pangolin meat between regions; (b) Number of seized individuals in pangolin meat between regions; (c) Number of individuals illegally traded into different cities of Chinese mainland from different countries; (d) Number of individuals in illegal trade between different provinces in China and between different provinces in China and other countries. The gap between the connection band and the edge colored ring bar represents the import, the edge colored ring bar and the same color connection band indicates the exit, and the colored ring bar filling the gap between the two represents the destination of the goods export. The width of the connection band indicates the number of seized incidences (a) or individuals (b, c and d). The numbers in the figure represent the cities as follow: 1. Abroad; 2. Chongqing; 3. Liupanshui, Mianyang, Chengdu, Panzhihua; 4. Xishuangbanna; 5. Baoshan; 6. Chuxiong; 7. Dehong; 8. Kunming; 9. Pu’er; 10. Qujing; 11. Wenshan; 12. Lijiang, Nujiang, Dali, Honghe, Lincang; 13. Beihai; 14. Chongzuo; 15. Fangchenggang; 16. Unknown cities in Guangxi, Wuzhou, Hezhou, Baise; 17. Guilin; 18. Liuzhou; 19. Nanning; 20. Qinzhou; 21. Yulin; 22. Ganzhou; 23. Yingtan, Nanchang, Fuzhou (Jiangxi), Shangrao, Ji’an, Jiujiang; 24. Hainan; 25. Jingzhou, Enshi; 26. Unknown cities in Fujian, Putian, Nanping; 27. Fuzhou (Fujian); 28. Longyan; 29. Ningde; 30. Quanzhou; 31. Sanming; 32. Xiamen; 33, Zhangzhou; 34. Beijing; 35. Unknown cities in Shandong, Xi’an, Jilin, Shijiazhuang, Qingdao; 36. Zhengzhou; 37. Changzhou; 38. Suzhou, Taizhou (Jiangsu); 39. Nanjing; 40. Wuxi; 41. Shanghai; 42. Fuyang, Xuancheng, Wuhu; 43. Changsha; 44. Chenzhou; 45. Hengyang; 46. Huaihua; 47. Unknown cities in Hunan, Xiangxi, Yongzhou; 48. Yiyang; 49. Zhuzhou; 50. Dongguan; 51. Foshan; 52. Guangzhou; 53. Unknown cities in Guangdong, Chaozhou, Shantou, Shanwei; 54. Heyuan; 55. Huizhou; 56. Jiangmen; 57. Jieyang; 58. Maoming; 59. Meizhou; 60. Qingyuan; 61. Shaoguan; 62. Shenzhen; 63. Yangjiang; 64. Yunfu; 65. Zhanjiang; 66. Zhaoqing; 67. Zhongshan; 68. Zhuhai; 69. Hangzhou; 70. Jiaxing; 71. Jinhua; 72. Lishui; 73. Ningbo; 74. Quzhou; 75. Shaoxing; 76. Taizhou (Zhejiang); 77. Wenzhou; 78. Indonesia; 79. Laos; 80. Malaysia; 81. Myanmar; 82. Abroad unknown; 83. Vietnam; 84. Honghe; 85. Lincang; 86. Nujiang ; 87. Baise; 88. Sichuan; 89. Jilin; 90. Shandong; 91. Hebei; 92. Shaanxi; 93. Henan; 94. Guizhou; 95. Zhejiang; 96. Yunnan; 97. Guangxi; 98. Jiangxi; 99. Hubei; 100. Fujian; 101. Jiangsu; 102. Anhui; 103. Hunan; 104. Guangdong.
| 序号 No. | 总贸易量中介值 Betw. (ind.) | 贸易个体来源 Borgatti’s source betw. (ind.) | 贸易个体去向 Borgatti’s destination betw. (ind.) | 总案件量中介值 Betw. (inc) | 贸易案件来源 Borgatti’s source betw. (inc.) | 贸易案件去向 Borgatti’s destination betw. (inc.) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 广州 Guangzhou | 广州 Guangzhou | 广州 Guangzhou | 广州 Guangzhou | 广州 Guangzhou | 广州 Guangzhou |
| 2 | 防城港 Fangchenggang | 防城港 Fangchenggang | 防城港 Fangchenggang | 衢州 Quzhou | 防城港 Fangchenggang | 佛山 Foshan |
| 3 | 金华 Jinhua | 衢州 Quzhou | 金华 Jinhua | 昆明 Kunming | 衢州 Quzhou | 昆明 Kunming |
| 4 | 昆明 Kunming | 北海 Beihai | 昆明 Kunming | 上海 Shanghai | 上海 Shanghai | 深圳 Shenzhen |
| 5 | 衢州 Quzhou | 昆明 Kunming | 深圳 Shenzhen | 佛山 Foshan | 长沙 Changsha | 衢州 Quzhou |
表1 不同城市穿山甲肉的非法贸易中缉获个体数量和案件数量的中介中心性
Table 1 Betweenness centrality of the number of seized individuals and incidences in the illegal trade of pangolin meat in different cities
| 序号 No. | 总贸易量中介值 Betw. (ind.) | 贸易个体来源 Borgatti’s source betw. (ind.) | 贸易个体去向 Borgatti’s destination betw. (ind.) | 总案件量中介值 Betw. (inc) | 贸易案件来源 Borgatti’s source betw. (inc.) | 贸易案件去向 Borgatti’s destination betw. (inc.) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 广州 Guangzhou | 广州 Guangzhou | 广州 Guangzhou | 广州 Guangzhou | 广州 Guangzhou | 广州 Guangzhou |
| 2 | 防城港 Fangchenggang | 防城港 Fangchenggang | 防城港 Fangchenggang | 衢州 Quzhou | 防城港 Fangchenggang | 佛山 Foshan |
| 3 | 金华 Jinhua | 衢州 Quzhou | 金华 Jinhua | 昆明 Kunming | 衢州 Quzhou | 昆明 Kunming |
| 4 | 昆明 Kunming | 北海 Beihai | 昆明 Kunming | 上海 Shanghai | 上海 Shanghai | 深圳 Shenzhen |
| 5 | 衢州 Quzhou | 昆明 Kunming | 深圳 Shenzhen | 佛山 Foshan | 长沙 Changsha | 衢州 Quzhou |
| 序号 No. | 总贸易量 Degree value (ind.) | 输入数量 Indegree value (ind.) | 输出数量 Outdegree value (ind.) | 总案件数量 Degree value (inc.) | 输入案件量 Indegree value (inc.) | 输出案件量 Outdegree value (inc.) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 防城港 Fangchenggang | 江门 Jiangmen | 防城港 Fangchenggang | 广州 Guangzhou | 广州 Guangzhou | 防城港 Fangchenggang |
| 2 | 北海 Beihai | 防城港 Fangchenggang | 北海 Beihai | 防城港 Fangchenggang | 佛山 Foshan | 广州 Guangzhou |
| 3 | 江门 Jiangmen | 北海 Beihai | 广州 Guangzhou | 德宏 Dehong | 防城港 Fangchenggang | 德宏 Dehong |
| 4 | 广州 Guangzhou | 厦门 Xiamen | 台州 Taizhou | 昆明 Kunming | 保山 Baoshan | 长沙 Changsha |
| 5 | 厦门 Xiamen | 惠州 Huizhou | 中山 Zhongshan | 佛山 Foshan | 衡阳 Hengyang | 昆明 Kunming |
表2 不同城市穿山甲肉的非法贸易中缉获个体数量和案件数量的度中心性
Table 2 Degree centrality of the number of seized individuals and incidences in the illegal trade of pangolin meat in different cities
| 序号 No. | 总贸易量 Degree value (ind.) | 输入数量 Indegree value (ind.) | 输出数量 Outdegree value (ind.) | 总案件数量 Degree value (inc.) | 输入案件量 Indegree value (inc.) | 输出案件量 Outdegree value (inc.) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 防城港 Fangchenggang | 江门 Jiangmen | 防城港 Fangchenggang | 广州 Guangzhou | 广州 Guangzhou | 防城港 Fangchenggang |
| 2 | 北海 Beihai | 防城港 Fangchenggang | 北海 Beihai | 防城港 Fangchenggang | 佛山 Foshan | 广州 Guangzhou |
| 3 | 江门 Jiangmen | 北海 Beihai | 广州 Guangzhou | 德宏 Dehong | 防城港 Fangchenggang | 德宏 Dehong |
| 4 | 广州 Guangzhou | 厦门 Xiamen | 台州 Taizhou | 昆明 Kunming | 保山 Baoshan | 长沙 Changsha |
| 5 | 厦门 Xiamen | 惠州 Huizhou | 中山 Zhongshan | 佛山 Foshan | 衡阳 Hengyang | 昆明 Kunming |
| 分组 No. | 关键节点 Key players | 破碎化指数 Fragmentation index |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 中国上海 China’s Shanghai | 0.394 |
| 2 | 中国福州、上海 China’s Fuzhou, Shanghai | 0.46 |
| 3 | 中国长沙、广州、昆明 China’s Changsha, Guangzhou, Kunming | 0.511 |
| 4 | 中国防城港、广州、深圳、广西未知城市 China’s Fangchenggang, Guangzhou, Shenzhen, unknown cities in Guangxi | 0.546 |
| 5 | 中国防城港、广州、深圳、广西未知城市; 越南 China’s Fangchenggang, Guangzhou, Shenzhen, unknown cities in Guangxi; Vietnam | 0.583 |
| 6 | 中国防城港、福州、广州、上海、广西未知城市; 越南 China’s Fangchenggang, Fuzhou, Guangzhou, Shanghai, unknown cities in Guangxi; Vietnam | 0.771 |
| 7 | 中国长沙、防城港、广州、昆明、衢州、深圳、广西未知城市 China’s Changsha, Fangchenggang, Guangzhou, Kunming, Quzhou, Shenzhen, unknown cities in Guangxi | 0.886 |
| 8 | 中国长沙、防城港、福州、广州、上海、昆明、广西未知城市; 越南 China’s Changsha, Fangchenggang, Fuzhou, Guangzhou, Shanghai, Kunming, unknown cities in Guangxi; Vietnam | 0.923 |
| 9 | 中国长沙、防城港、广州、昆明、上海、深圳、广西未知城市; 越南; 马来西亚 China’s Changsha, Fangchenggang, Guangzhou, Kunming, Shanghai, Shenzhen, unknown cities in Guangxi; Vietnam; Malaysia | 0.943 |
| 10 | 中国长沙、防城港、广州、昆明、上海、深圳、广西未知城市; 越南; 马来西亚; 缅甸 China’s Changsha, Fangchenggang, Guangzhou, Kunming, Shanghai, Shenzhen, unknown cities in Guangxi; Vietnam; Malaysia; Myanmar | 0.953 |
表3 去掉或隔离1?10个城市组成的一组节点对穿山甲肉非法贸易网络的破坏情况
Table 3 Removal or isolation of the destruction of the illegal trade network of pangolin meat by a group of nodes composed of 1 to 10 cities
| 分组 No. | 关键节点 Key players | 破碎化指数 Fragmentation index |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 中国上海 China’s Shanghai | 0.394 |
| 2 | 中国福州、上海 China’s Fuzhou, Shanghai | 0.46 |
| 3 | 中国长沙、广州、昆明 China’s Changsha, Guangzhou, Kunming | 0.511 |
| 4 | 中国防城港、广州、深圳、广西未知城市 China’s Fangchenggang, Guangzhou, Shenzhen, unknown cities in Guangxi | 0.546 |
| 5 | 中国防城港、广州、深圳、广西未知城市; 越南 China’s Fangchenggang, Guangzhou, Shenzhen, unknown cities in Guangxi; Vietnam | 0.583 |
| 6 | 中国防城港、福州、广州、上海、广西未知城市; 越南 China’s Fangchenggang, Fuzhou, Guangzhou, Shanghai, unknown cities in Guangxi; Vietnam | 0.771 |
| 7 | 中国长沙、防城港、广州、昆明、衢州、深圳、广西未知城市 China’s Changsha, Fangchenggang, Guangzhou, Kunming, Quzhou, Shenzhen, unknown cities in Guangxi | 0.886 |
| 8 | 中国长沙、防城港、福州、广州、上海、昆明、广西未知城市; 越南 China’s Changsha, Fangchenggang, Fuzhou, Guangzhou, Shanghai, Kunming, unknown cities in Guangxi; Vietnam | 0.923 |
| 9 | 中国长沙、防城港、广州、昆明、上海、深圳、广西未知城市; 越南; 马来西亚 China’s Changsha, Fangchenggang, Guangzhou, Kunming, Shanghai, Shenzhen, unknown cities in Guangxi; Vietnam; Malaysia | 0.943 |
| 10 | 中国长沙、防城港、广州、昆明、上海、深圳、广西未知城市; 越南; 马来西亚; 缅甸 China’s Changsha, Fangchenggang, Guangzhou, Kunming, Shanghai, Shenzhen, unknown cities in Guangxi; Vietnam; Malaysia; Myanmar | 0.953 |
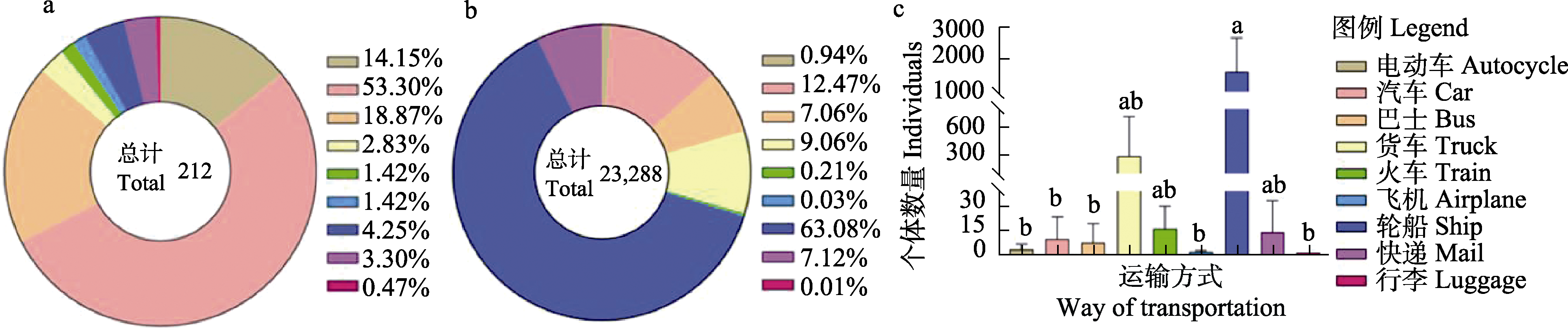
图4 穿山甲肉非法贸易中使用的不同运输方式。(a)查获的使用不同运输方式非法贸易的次数; (b)通过不同运输方式非法贸易的穿山甲个体总数; (c)通过不同运输方式平均每次非法贸易的穿山甲个体数量以及差异(平均值 ± 标准差)。在图(c)中, 相同字母表示二者之间差异不显著, 不同字母代表差异显著。
Fig. 4 Different ways of transportation used in the illegal trade of pangolin meat. (a) Frequency of different modes of transportation; (b) The total volume of transportation and; (c) Volume of single transportation mode (mean ± SD). In Fig. (c), there are no significant differences between those labeled with the same letter and those with different letters represent a significant difference.
| [1] | Allen GM (1938) The Mammals of China and Mongolia (Part 1). The American Museum of Natural History, New York. |
| [2] | Borgatti SP (2014) Key Player Program. http://www.analytictech.com/keyplayer/keyplayer.htm. (accessed on 2021-04-15) |
| [3] | Broad S, Mulliken T, Roe D (2014) The nature and extent of legal and illegal trade in wildlife. In: The Trade in Wildlife: Regulation for Conservation (ed. Oldfield S), pp. 25-44. Routledge, London. |
| [4] | Burgess G, Olmedo A, Cerissimo D, Waterman C (2020) Changing consumer behavior for pangolin products. In: Pangolins: Science, Society and Conservation (eds Challender DWS, Nash HC, Waterman C), pp. 349-366. Academic Press, London. |
| [5] | Butts CT (2010) sna: Tools for Social Network Analysis. R package version 2.2-0. |
| [6] | Challender DWS, Waterman C, Baillie JEM (2014a) Scaling up Pangolin Conservation. IUCN SSC Pangolin Specialist Group Conservation Action Plan, Zoological Society of London, London. |
| [7] | Challender DWS, Nguyen VT, Shepherd C, Krishnasamy K, Wang A, Lee B, Panjang E, Fletcher L, Heng S, Seah HMJ, Olsson A, Nguyen TTA, Nguyen VQ, Chung Y (2014b) Manis javanica. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Version 2014. 3. https://www.iucnredlist.org. (accessed on 2015-05-08) |
| [8] |
Challender DWS, Harrop SR, MacMillan DC (2015) Understanding markets to conserve trade-threatened species in CITES. Biological Conservation, 187, 249-259.
DOI URL |
| [9] | Challender DWS, Baillie J, Waterman C, Pietersen D, Nash H, Wicker L, Parker K, Thomson P, Nguyen TV, Hywood L, Shepherd C (2016) On scaling up pangolin conservation. TRAFFIC Bulletin, 28, 19-21. |
| [10] | Challender DWS, Heinrich S, Shepherd CR, Katsis LKD (2020) International trade and trafficking in pangolins, 1900-2019. In: Pangolins: Science, Society and Conservation (eds Challender DWS, Nash HC, Waterman C), pp. 259-276. Academic Press, London. |
| [11] |
Cheng W, Xing S, Bonebrake TC (2017) Recent pangolin seizures in China reveal priority areas for intervention. Conservation Letters, 10, 757-764.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
Emogor CA, Ingram DJ, Coad L, Worthington TA, Dunn A, Imong I, Balmford A (2021) The scale of Nigeria’s involvement in the trans-national illegal pangolin trade: Temporal and spatial patterns and the effectiveness of wildlife trade regulations. Biological Conservation, 264, 109365.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
Heinrich S, Wittmann TA, Prowse TAA, Ross JV, Delean S, Shepherd CR, Cassey P (2016) Where did all the pangolins go? International CITES trade in pangolin species. Global Ecology and Conservation, 8, 241-253.
DOI URL |
| [14] | Heinrich S, Wittman TA, Ross JV, Shepherd CR, Challender DWS, Cassey P (2017) The global trafficking of pangolins: A comprehensive summary of seizures and trafficking routes from 2010-2015. TRAFFIC, Southeast Asia Regional Office, Petaling Jaya, Selangor, Malaysia. |
| [15] | Heinrich S, Ross JV, Cassey P (2019) Of cowboys, fish and pangolins: US trade in exotic leather. Conservation Science and Practice, 1, e75. |
| [16] | Huang XQ, Newman C, Buesching CD, Shao ML, Ye YC, Liu S, MacDonald DW, Zhou ZM (2021) Prosecution records reveal pangolin trading networks in China, 2014-2019. Zoological Research, 42, 666-670. |
| [17] | Ingram DJ, Cronin DT, Challender DWS, Venditti DM, Gonder MK (2019) Characterising trafficking and trade of pangolins in the Gulf of Guinea. Global Ecology and Conservation, 17, e00576. |
| [18] | IUCN SSC Pangolin Specialist Group (2019) Pangolin. https://pangolinsg.org/pangolins/. (accessed on 2022-04-05) |
| [19] | IUCN (2014) Eating Pangolins to Extinction. http://www.iucnredlist.org/news/eating-pangolins-to-extinction. (accessed on 2014-08-05) |
| [20] |
Mendiratta U, Sheel V, Singh S (2017) Enforcement seizures reveals large-scale illegal trade in India’s tortoise and freshwater turtles. Biological Conservation, 207, 100-105.
DOI URL |
| [21] | Mozer A, Prost S (2023) An introduction to illegal wildlife trade and its effects on biodiversity and society. Forensic Science International: Animals and Enviroments, 3, 100064. |
| [22] | Nellemann C, Henriksen R, Kreilhuber A, Stewart D, Kotsovou M, Raxter P, Mrema E, Barrat S (2016) The Rise of Environmental Crime—A Growing Threat to Natural Resources, Peace, Development and Security. United Nations Environment and Development Forum (UNED), Norwegian Center for Global Analyses, http://www.unep.org/resources/report/rise-environmental-crime-growing-threat-natural-resources-peace-development-and. (accessed on 2021-05-17) |
| [23] | Omifolaji JK, Hughes AC, Ibrahim AS, Zhou J, Zhang S, Ikyaagba ET, Luan X (2022) Dissecting the illegal pangolin trade in China: An insight from seizures data reports. Nature Conservation, 45, 17-38. |
| [24] | Patel NG, Rorres C, Joly DO, Brownstein JS, Boston R, Levy MZ, Smith G (2015) Quantitative methods of identifying the key nodes in the illegal wildlife trade network. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 112, 7948-7953. |
| [25] | R Core Development Team (2014) R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. |
| [26] | Riski P (2015) Customs officials seize 455 pangolins hidden in crates of fish in Indonesia. https://news.mongabay.com/2015/07/customs-officials-seize-455-pangolins-hidden-in-crates-of-fish-in-indonesia/. (accessed on 2023-02-05) |
| [27] | Schoppe S, Katsis LKD, Alvarado D, Acosta-Lagrada L (2020) Philippine pangolin Manis culionensis (de Elera, 1915). In: Pangolins: Science, Society and Conservation (eds Challender DWS, Nash HC, Waterman C), pp. 109-122. Academic Press, London. |
| [28] |
Sulaiman MH, Azmi WA, Hassan M, Chong JL (2017) Current updates on the morphological measurements of the Malayan pangolin (Manis javanica). Folia Zoologica, 66, 262-266.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
Wang Y, Turvey ST, Leader-Williams N (2020) Knowledge and attitudes about the use of pangolin scale products in Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) within China. People and Nature, 2, 903-912.
DOI URL |
| [30] | Wang RH (1985) Need to protect rare wild animals—Pangolins. Sichuan Environment, (2), 78-79. (in Chinese) |
| [王荣怀 (1985) 要保护稀有野生动物——穿山甲. 四川环境, (2), 78-79.] | |
| [31] | Wu SB, Liu NF, Zhang YM, Ma GZ (2004a) Assessment of threatened status of Chinese pangolin. Chinese Journal of Applied and Environmental Biology, 10, 456-461. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [吴诗宝, 刘廼发, 张迎梅, 马广智 (2004a) 中国穿山甲受危状况评估. 应用与环境生物学报, 10, 456-461.] | |
| [32] | Wu SB, Liu NF, Zhang YN, Ma GZ (2004b) Physical measurement and comparison for two species of pangolin. Acta Theriologica Sinica, 24, 361-364. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [吴诗宝, 刘廼发, 张迎梅, 马广智 (2004b) 两种穿山甲外形量衡度的测定及比较. 兽类学报, 24, 361-364.] | |
| [33] | Wu SB, Ma GZ, Liao QX, Lu KH (2005) Studies of Conservation Biology on Chinese Pangolin (Manis pentadactyla). China Forestry Publishing House, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [吴诗宝, 马广智, 廖庆祥, 卢开和 (2005) 中国穿山甲(Manis pentadactyla)保护生物学研究. 中国林业出版社, 北京.] | |
| [34] | Wyatt T (2013) Wildlife Trafficking: A Deconstruction of the Crime, the Victims, and the Offenders. Palgrave Macmillan. London. |
| [35] | Xing S, Bonebrake TC, Cheng W, Zhang M, Ades G, Shaw D, Zhou Y (2020) Meat and medicine:Historic and contemporary use in Asia. In: Pangolins: Science, Society and Conservation (eds Challender DWS, Nash HC, Waterman C), pp. 227-239. Academic Press, London. |
| [36] | Xu J, Yee E, Zhang K (2019) The Pangolin Reports: Trafficked to Extinction. https://globalstory.pangolinreports.com/#lede. (accessed on 2022-04-05) |
| [37] | Yang L, Zou JJ, Zhang FH, Su C, Ma GZ, Wu SB (2010) Estimation of number of individuals of Malayan pangolin with number of their scales. Chinese Journal of Wildlife, 31(4), 180-181. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [杨立, 邹洁建, 张富华, 苏超, 马广智, 吴诗宝 (2010) 用鳞片估计马来穿山甲个体数量. 野生动物, 31(4), 180-181.] | |
| [38] | Yu DY, Gao EH, Lin YH, Qin XY (2001) The status and countermeasures for protection of Chinese pangolin. Journal of Northeast Forestry University, 29(2), 79-82. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [遇达祎, 郜二虎, 林英华, 秦秀云 (2001) 中国穿山甲的现状与保护对策. 东北林业大学学报, 29(2), 79-82.] | |
| [39] |
Zhang M, Gouveia A, Qin T, Quan R, Nijman V (2017) Illegal pangolin trade in northernmost Myanmar and its links to India and China. Global Ecology and Conservation, 10, 23-31.
DOI URL |
| [40] |
Zhang F, Yu Y, Wu S, Mahmood A, Yu J, Min Y (2020) Reducing pangolin demand by understanding motivations for human consumption in Guangdong, China. Frontiers in Ecology and Evolution, 8, 574161.
DOI URL |
| [41] | Zhang F, Wang W, Mahmood A, Wu S, Li J, Xu N (2021) Observations of Chinese pangolins (Manis pentadactyla) in mainland China. Global Ecology and Conservation, 26, e01460. |
| [42] | Zhang F, Wu S, Cen P (2022a) The past, present and future of the pangolin in mainland China. Global Ecology and Conservation, 33, e01995. |
| [43] | Zhang F, Tang X, Cen P, Wu S (2022b) Illegal Trade of Pangolins Meat in China [Data set]. Zenodo, https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6809243. |
| [44] |
Zhou ZM, Zhou Y, Newman C, MacDonald DW (2014) Scaling up pangolin protection in China. Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment, 12(2), 97-98.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 袁智勇, 陈进民, 吴云鹤, 李先琦, 车静. 云南省两栖类物种名录修订[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(4): 21470-. |
| [2] | 王剀, 吕植桐, 王健, 齐硕, 车静. 云南省爬行动物名录和地理区划更新[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(4): 21326-. |
| [3] | 张馨予, 胡宇轩, 张忠义, 傅钰涵, 谢屹. 中国公众的国际野生动物保护意愿调查: 以非洲象为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(10): 1358-1368. |
| [4] | 梁智健, 胡佳贝, 胡思帆, 赵晶晶, 周凯文, 焦运波, 黄程, 何霞, 温嘉恩, 李立姝, 华方圆, 李添明. 多学科视角下的野生动物消费需求和消费行为研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2020, 28(5): 606-620. |
| [5] | 吕忠梅, 陈真亮. 《野生动物保护法》再修订: 背景、争点与建议[J]. 生物多样性, 2020, 28(5): 550-557. |
| [6] | 曾岩, 平晓鸽, 魏辅文. “野生动物”的概念框架和术语定义[J]. 生物多样性, 2020, 28(5): 541-549. |
| [7] | 余小林, 周友兵, 徐文婷, 谢宗强. 保护地旅游公路的野生动物通道设计原则与技术参数[J]. 生物多样性, 2015, 23(6): 824-829. |
| [8] | 李晟, 王大军, 肖治术, 李欣海, 王天明, 冯利民, 王云. 红外相机技术在我国野生动物研究与保护中的应用与前景[J]. 生物多样性, 2014, 22(6): 685-695. |
| [9] | 樊祥国, 周宇晶, 刘宝祥, 冯庚菲, 樊恩源. 《濒危野生动植物种国际贸易公约》中有关水生生物物种的提案和对策研究[J]. 生物多样性, 2008, 16(5): 516-524. |
| [10] | 冉景丞, 陈会明, 陈正仁, 余登利, 玉屏. 茂兰自然保护区内捕猎现状与野生动物保护[J]. 生物多样性, 2001, 09(4): 482-486. |
| [11] | 王静波, 胡长龙, 徐宏发. 线粒体DNA(mtDNA多态性在动物保护生物学中的应用[J]. 生物多样性, 2001, 09(2): 181-187. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn