



生物多样性 ›› 2022, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (12): 22222. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2022222 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2022222
所属专题: 土壤生物与土壤健康
刘笑彤1,2, 田艺佳1,2, 刘汉文1,2, 梁翠影1, 姜思维1, 梁文举1,3, 张晓珂1,3,*( )
)
收稿日期:2022-04-25
接受日期:2022-07-06
出版日期:2022-12-20
发布日期:2022-09-21
通讯作者:
*E-mail: zxk@iae.ac.cn
基金资助:
Xiaotong Liu1,2, Yijia Tian1,2, Hanwen Liu1,2, Cuiying Liang1, Siwei Jiang1, Wenju Liang1,3, Xiaoke Zhang1,3,*( )
)
Received:2022-04-25
Accepted:2022-07-06
Online:2022-12-20
Published:2022-09-21
Contact:
*E-mail: zxk@iae.ac.cn
摘要:
下辽河平原农田生态系统在管理过程中频繁的耕作、施肥以及农用化学品施用等引发了一系列问题, 如土壤退化、耕地数量减少以及生产力下降等, 不可避免地对土壤生物健康产生影响。为探究农田土壤人工管理对土壤生物群落动态的影响, 本研究在辽宁沈阳农田生态系统国家野外科学观测研究站开展了农田土壤线虫群落组成的季节变化研究, 对4个季节农田和废弃农田(对照)的土壤线虫群落组成、多度以及多样性等进行了比较分析。研究结果表明, 土壤线虫总多度在废弃农田中显著高于农田, 但季节间差异不显著。季节变化主要显著影响了自由生活线虫的多度, 其在9月达到最高; 季节变化也显著影响了属的数量, 其在非生长季的11月最低。与废弃农田相比, 农田管理显著降低了杂食捕食线虫和食真菌线虫的多度, 土壤食物网结构相对稳定; 而废弃的农田更易受到季节波动的影响, 土壤食物网也受到一定的干扰。
刘笑彤, 田艺佳, 刘汉文, 梁翠影, 姜思维, 梁文举, 张晓珂 (2022) 下辽河平原农田土壤线虫群落组成的季节变化. 生物多样性, 30, 22222. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2022222.
Xiaotong Liu, Yijia Tian, Hanwen Liu, Cuiying Liang, Siwei Jiang, Wenju Liang, Xiaoke Zhang (2022) Seasonal variation in cropland soil nematode community composition in the lower reaches of Liaohe Plain. Biodiversity Science, 30, 22222. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2022222.
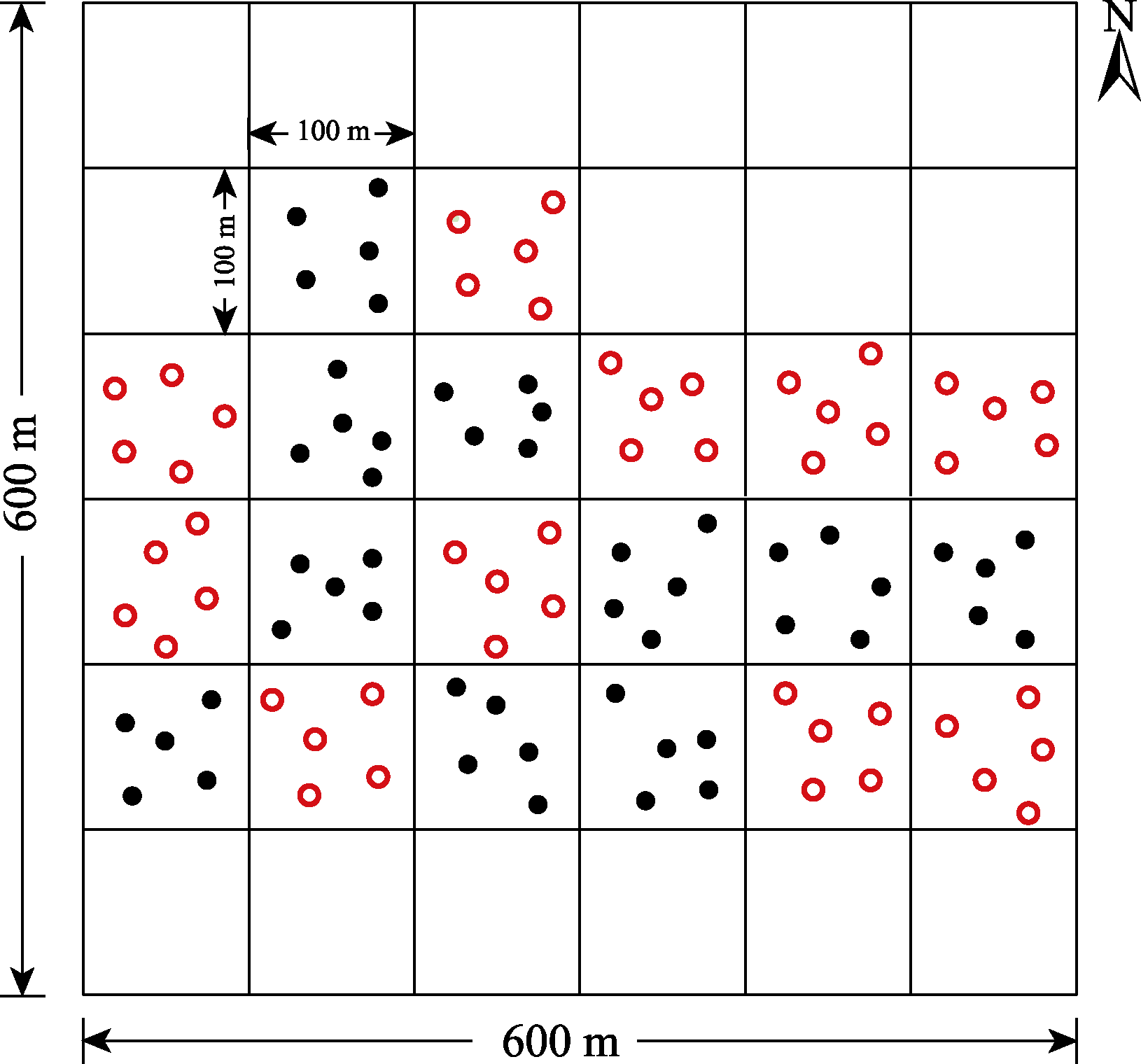
图1 研究区采样位置示意图。实心圆点代表农田采样区, 红色空心圆点代表废弃农田采样区。
Fig. 1 Diagram of sampling locations in the experiment area. Solid points represent cropland sampling areas. Red hollow points represent abandoned cropland sampling areas.
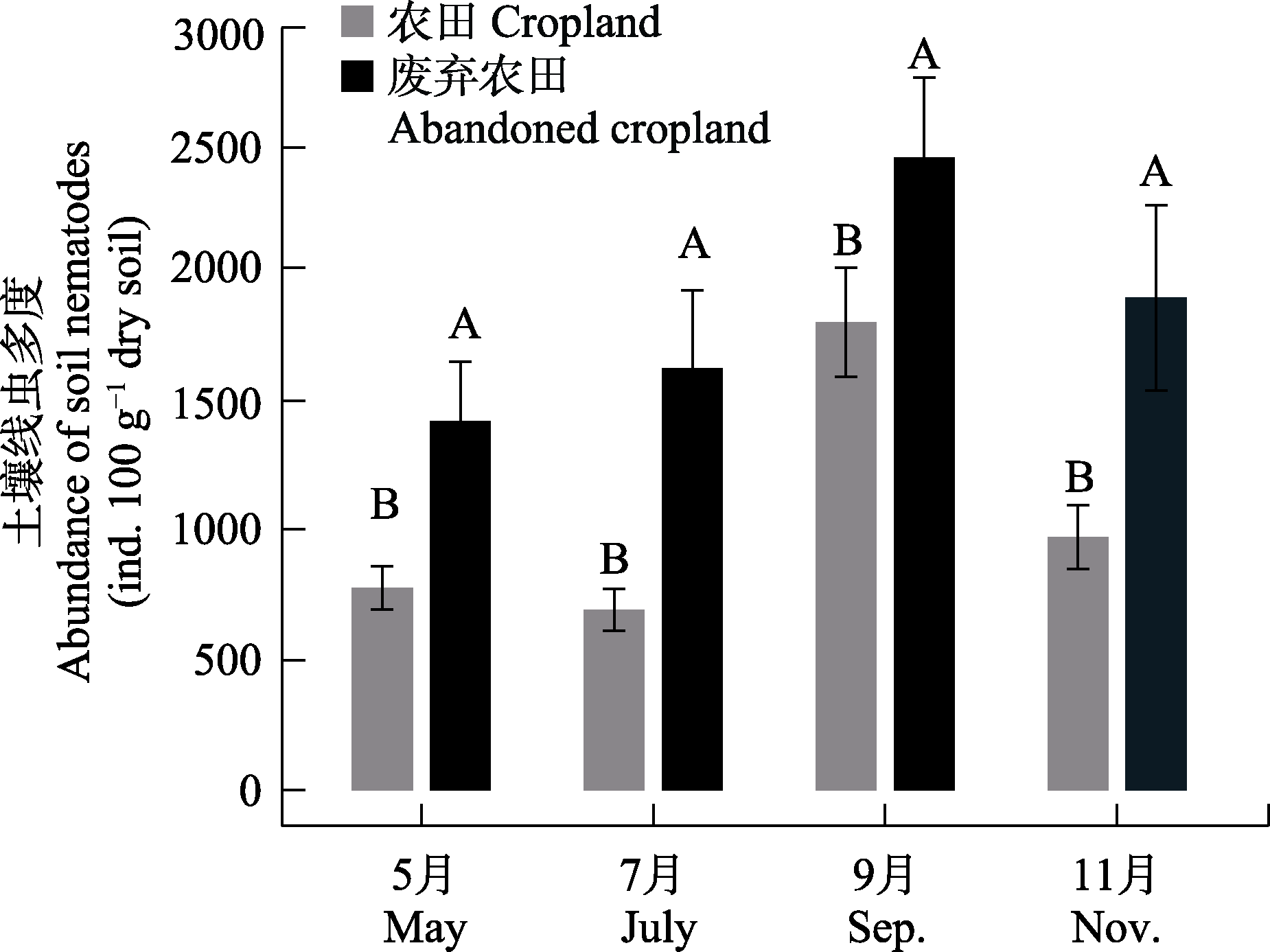
图2 土壤线虫多度的季节变化。不同大写字母代表两种土地利用方式间存在显著差异。
Fig. 2 Seasonal variation of the nematode abundance. Different capital letters indicate that there were significant differences between the cropland and abandoned cropland.
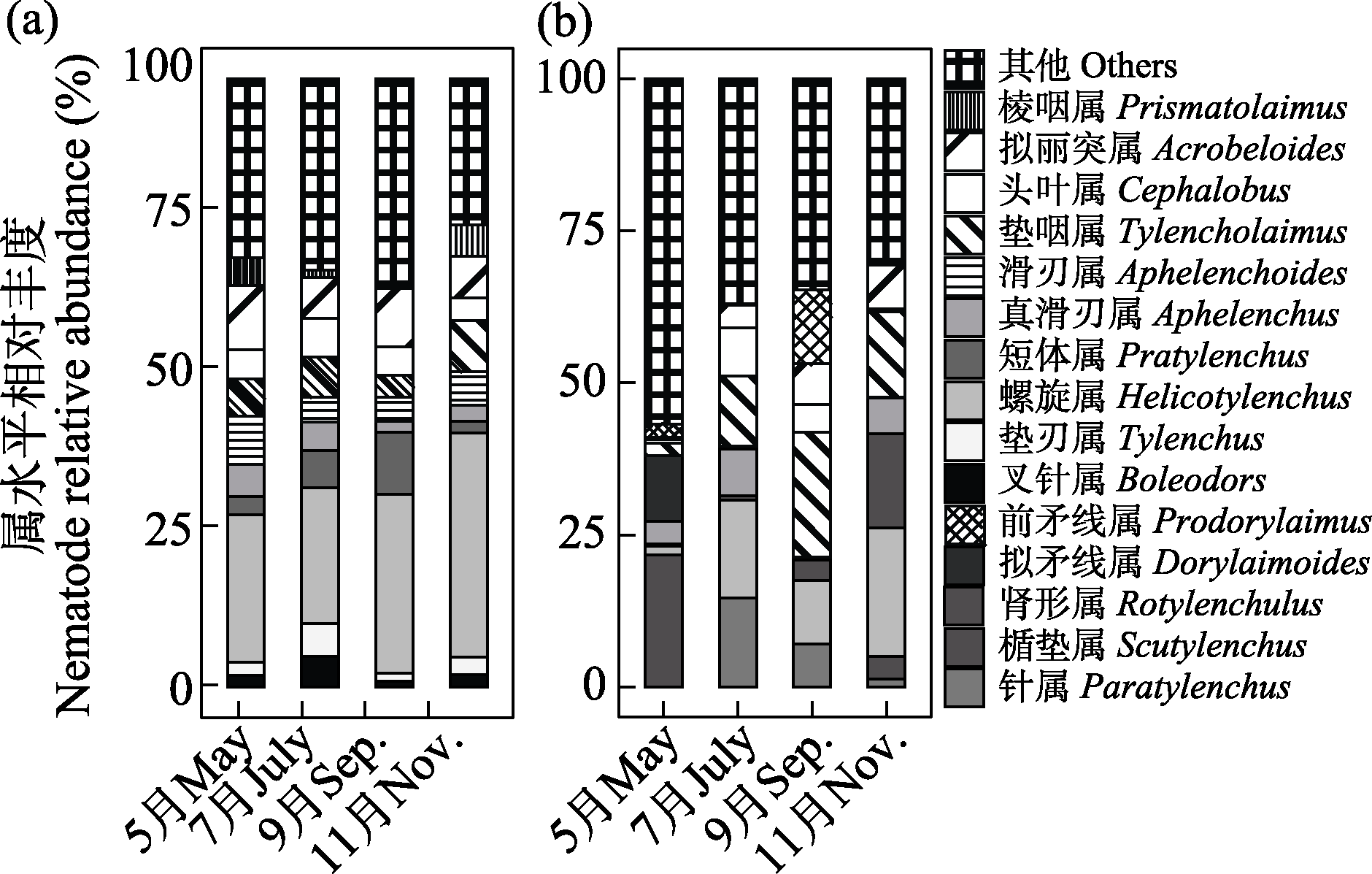
图3 不同季节农田(a)和废弃农田(b)土壤线虫属相对丰度(%) (只列出相对丰度前10的线虫属)。(a)农田, (b)废弃农田。
Fig. 3 Relative abundance (%) of top 10 soil nematode genera at different seasons. (a) Cropland, (b) Abandoned cropland.
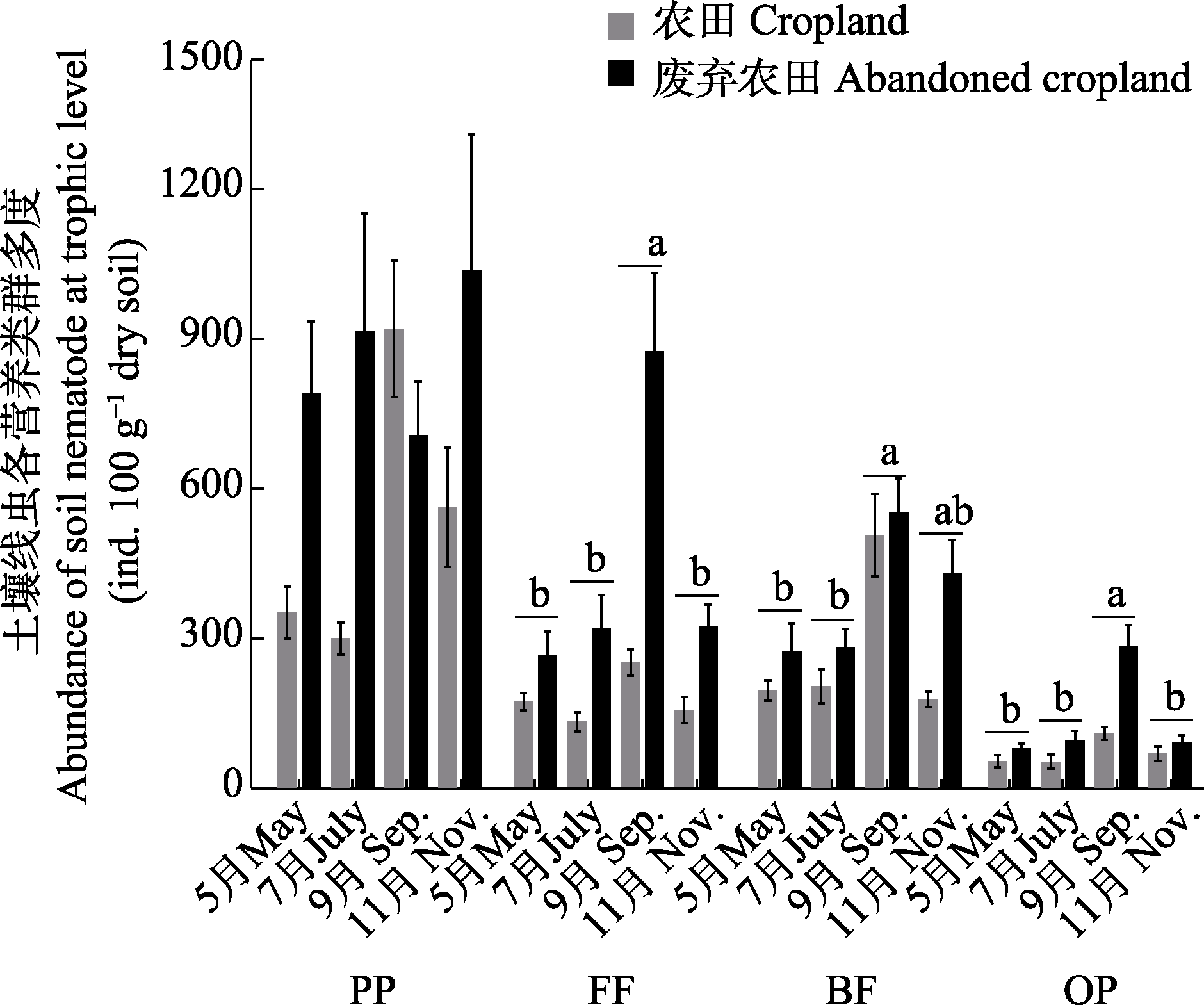
图4 不同土地利用方式土壤线虫4个营养类群多度的季节变化。PP: 植物寄生线虫; FF: 食真菌性线虫; BF: 食细菌性线虫; OP: 杂食捕食线虫。不同小写字母表示不同季节间有显著性差异。
Fig. 4 Seasonal variation in the abundance of soil nematode trophic groups. PP, Plant-parasites; FF, Fungivores; BF, Bacterivores; OP, Omnivores-predators. Different lowercase letters indicate that there were significant differences in different seasons.
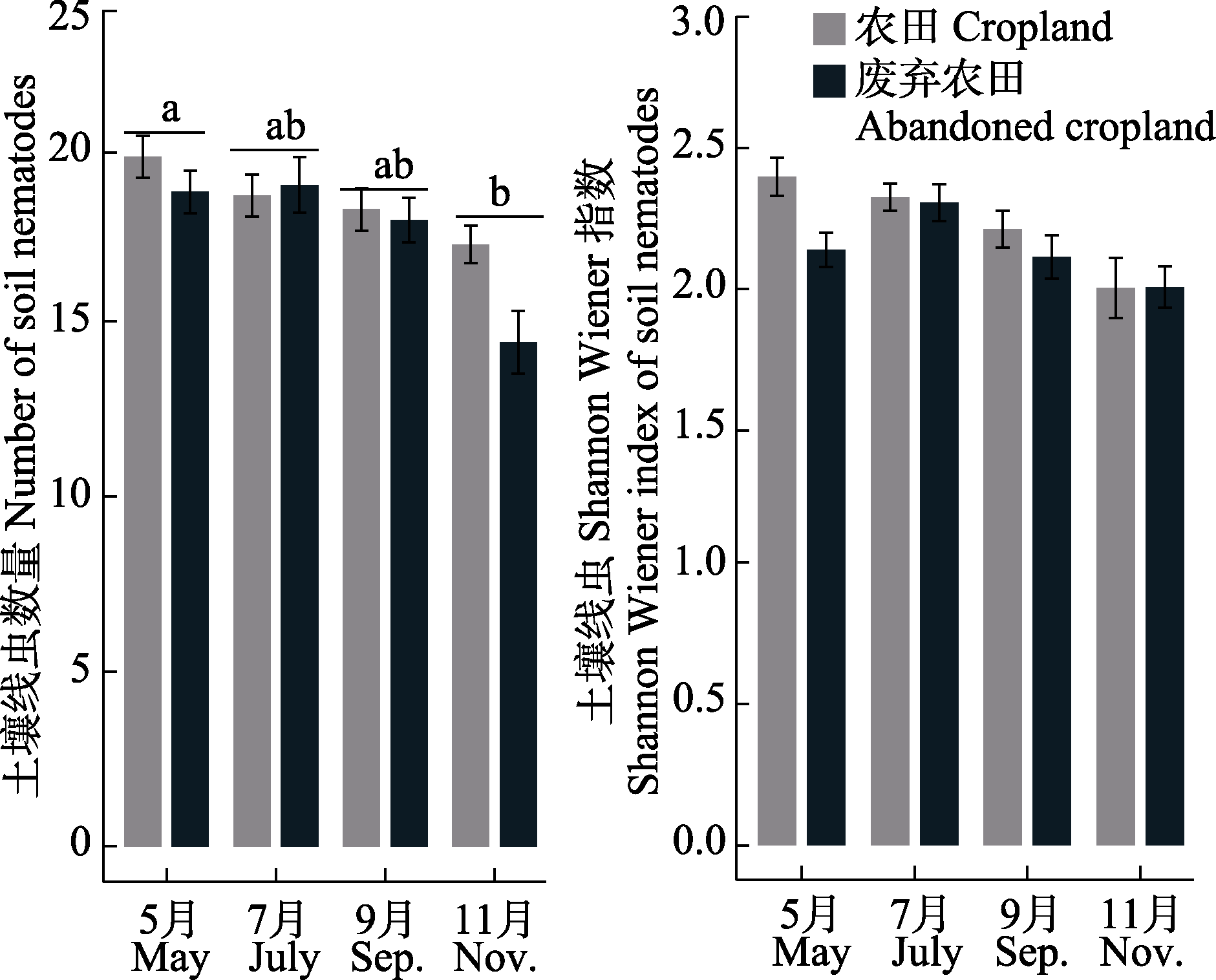
图5 土壤线虫α多样性指数的季节变化。不同小写字母表示不同季节间有显著性差异。
Fig. 5 Seasonal variation in the alpha diversity of soil nematodes. Different lowercase letters indicate that there were significant differences in different seasons.
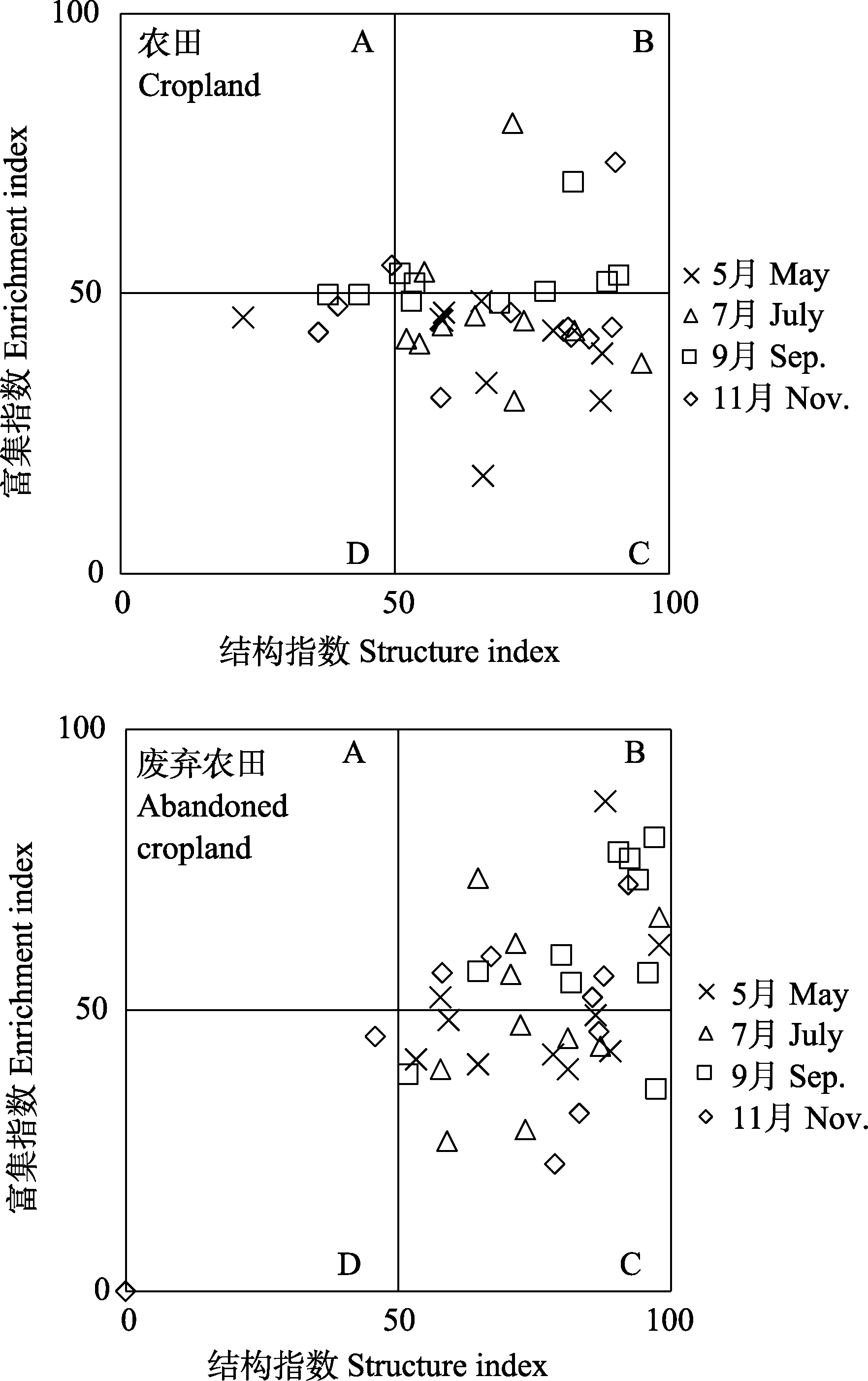
图6 土壤线虫区系分析。A: A象限; B: B象限; C: C象限; D: D象限。
Fig. 6 Results of soil nematode faunal analysis. A, Quadrant A; B, Quadrant B; C, Quadrant C; D, Quadrant D.
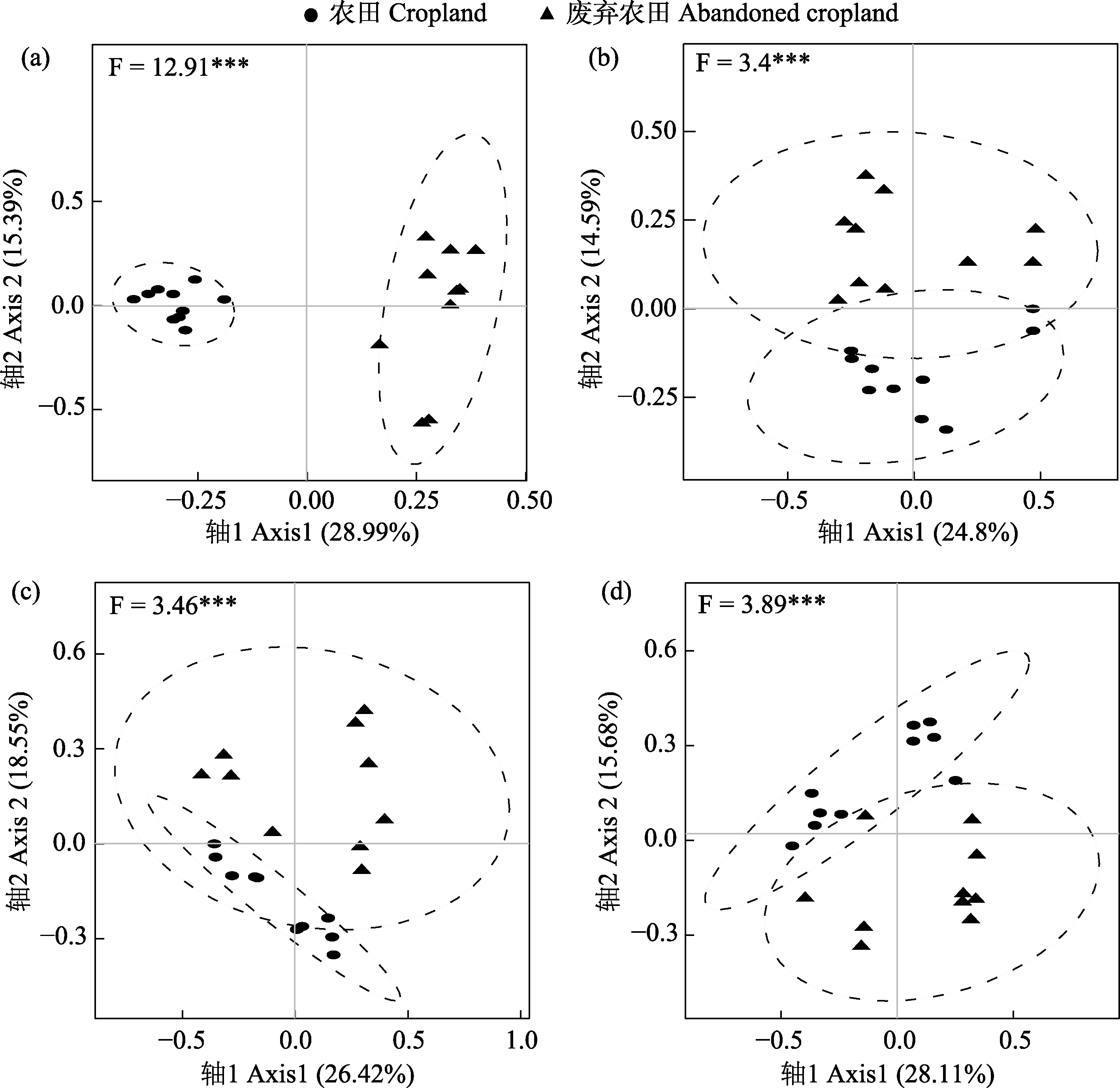
图7 不同季节土壤线虫群落主坐标分析。(a) 5月; (b) 7月; (c) 9月; (d) 11月。
Fig. 7 Principal coordinate analysis of soil nematode communities among different seasons. (a) May; (b) July; (c) September; (d) November. ***, P < 0.001.
| [1] |
Bakonyi G, Nagy P, Kovács-Láng E, Kovács E, Barabás S, Répási V, Seres A (2007) Soil nematode community structure as affected by temperature and moisture in a temperate semiarid shrubland. Applied Soil Ecology, 37, 31-40.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
Bardgett RD, van der Putten WH(2014) Belowground biodiversity and ecosystem functioning. Nature, 515, 505-511.
DOI URL |
| [3] | Bernard GC, Egnin M, Bonsi C (2017) The impact of plant-parasitic nematodes on agriculture and methods of control. Nematology-Concepts, Diagnosis and Control, 10, 121-151. |
| [4] |
Blankinship JC, Niklaus PA, Hungate BA (2011) A meta-analysis of responses of soil biota to global change. Oecologia, 165, 553-565.
DOI PMID |
| [5] |
Bongers T, Ferris H (1999) Nematode community structure as a bioindicator in environmental monitoring. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 14, 224-228.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
Bongiorno G, Bodenhausen N, Bünemann EK, Brussaard L, Geisen S, Mäder P, Quist CW, Walser JC, de Goede RGM(2019) Reduced tillage, but not organic matter input, increased nematode diversity and food web stability in European long-term field experiments. Molecular Ecology, 28, 4987-5005.
DOI PMID |
| [7] |
Bünemann EK, Bongiorno G, Bai ZG, Creamer RE, de Deyn G, de Goede R, Fleskens L, Geissen V, Kuyper TW, Mäder P, Pulleman M, Sukkel W, van Groenigen JW, Brussaard L (2018) Soil quality—A critical review. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 120, 105-125.
DOI URL |
| [8] | Chen L, Liu JL, Gu JC, Wang ZQ (2011) Seasonal dynamics of soil nematodes in Fraxinus mandshurica and Larix gmelinii plantations. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 47, 69-77. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 陈利, 刘金梁, 谷加存, 王政权 (2011) 水曲柳和落叶松人工林土壤线虫密度的季节动态. 林业科学, 47, 69-77.] | |
| [9] |
Costa D, Freitas H, Sousa JP (2013) Influence of seasons and land-use practices on soil microbial activity and metabolic diversity in the “Montado ecosystem”. European Journal of Soil Biology, 59, 22-30.
DOI URL |
| [10] | Du XF, Li YB, Liu F, Su XL, Li Q (2018) Structure and ecological functions of soil micro-food web. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 29, 403-411. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[ 杜晓芳, 李英滨, 刘芳, 宿晓琳, 李琪 (2018) 土壤微食物网结构与生态功能. 应用生态学报, 29, 403-411.]
DOI |
|
| [11] |
Fan KK, Delgado-Baquerizo M, Guo XS, Wang DZ, Zhu YG, Chu HY (2020) Microbial resistance promotes plant production in a four-decade nutrient fertilization experiment. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 141, 107679.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
Ferris H, Bongers T, de Goede RGM(2001) A framework for soil food web diagnostics: Extension of the nematode faunal analysis concept. Applied Soil Ecology, 18, 13-29.
DOI URL |
| [13] | Ferris H, Sánchez-Moreno S, Brennan EB (2012) Structure, functions and interguild relationships of the soil nematode assemblage in organic vegetable production. Applied Soil Ecology, 61, 16-25. |
| [14] |
Ferris H, Venette RC, Scow KM (2004) Soil management to enhance bacterivore and fungivore nematode populations and their nitrogen mineralisation function. Applied Soil Ecology, 25, 19-35.
DOI URL |
| [15] | Girgan C, du Preez G, Marais M, Swart A, Fourie H (2020) Nematodes and the effect of seasonality in grassland habitats of South Africa. Journal of Nematology, 52, e2020-e2118. |
| [16] |
Kandji ST, Ogol CKPO, Albrecht A (2002) Influence of some agroforestry practices on the temporal structures of nematodes in western Kenya. European Journal of Soil Biology, 38, 197-203.
DOI URL |
| [17] | Lazarova SS, de Goede RGM, Peneva VK, Bongers T (2004) Spatial patterns of variation in the composition and structure of nematode communities in relation to different microhabitats: A case study of Quercus dalechampii Ten. forest. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 36, 701-712. |
| [18] | Li HX, Liu MQ, Hu F, Chen XY, He YQ (2002) Nematode abundance under different vegetations restored on degraded red soil. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 22, 1882-1889. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 李辉信, 刘满强, 胡锋, 陈小云, 何圆球 (2002) 不同植被恢复方式下红壤线虫数量特征. 生态学报, 22, 1882-1889.] | |
| [19] |
Li Q, Liang WJ, Ou W (2007) Responses of nematode communities to land use in an aquic brown soil. Biodiversity Science, 15, 172-179. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[ 李琪, 梁文举, 欧伟 (2007) 潮棕壤线虫群落对土地利用方式的响应. 生物多样性, 15, 172-179.]
DOI |
|
| [20] |
Li XP, Zhu HM, Geisen S, Bellard C, Hu F, Li HX, Chen XY, Liu MQ (2020) Agriculture erases climate constraints on soil nematode communities across large spatial scales. Global Change Biology, 26, 919-930.
DOI PMID |
| [21] | Li ZP, Wei ZF, Yang XD (2016) Seasonal variations of soil nematode community at different secondary succession stages of evergreen broad-leaved forests in Ailao Mountain. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 35, 3023-3031. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 李志鹏, 韦祖粉, 杨效东 (2016) 哀牢山常绿阔叶林不同演替阶段土壤线虫群落的季节变化特征. 生态学杂志, 35, 3023-3031.] | |
| [22] |
Liang W, Lavian I, Steinberger Y (2001) Effect of agricultural management on nematode communities in a Mediterranean agroecosystem. Journal of Nematology, 33, 208-213.
PMID |
| [23] |
Liang WJ, Lou YL, Li Q, Zhong S, Zhang XK, Wang JK (2009) Nematode faunal response to long-term application of nitrogen fertilizer and organic manure in Northeast China. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 41, 883-890.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
Lu CY, Wang HY, Chen HH, Yuan L, Ma J, Shi Y, Zhang XD, He HB, Chen X (2018) Effects of N fertilization and maize straw on the transformation and fate of labeled (15NH4)2SO4 among three continuous crop cultivations. Agricultural Water Management, 208, 275-283.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
Ma HK, Bai GY, Sun Y, Kostenko O, Zhu X, Lin S, Ruan WB, Zhao NX, Bezemer TM (2016) Opposing effects of nitrogen and water addition on soil bacterial and fungal communities in the Inner Mongolia steppe: A field experiment. Applied Soil Ecology, 108, 128-135.
DOI URL |
| [26] | Ma JY, Ma Y, Yang BB, Zhao Y, Shen ZB, Li DP, Jia HT, Zhu XP (2021) The characteristic of soil nematodes communities under different land use types in Chaiwopu Lake Wetland. Journal of Xinjiang Agricultural University, 44, 313-323. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 马嘉昱, 马越, 杨贝贝, 赵一, 申志博, 李典鹏, 贾宏涛, 朱新萍 (2021) 柴窝堡湖湿地不同土地利用方式对土壤线虫群落的影响. 新疆农业大学学报, 44, 313-323.] | |
| [27] |
Neher DA (2001) Role of nematodes in soil health and their use as indicators. Journal of Nematology, 33, 161-168.
PMID |
| [28] | Pan FJ, Xu YL, Li CJ, Han XH, Liu W (2008) Seasonal trend of main plant-parasitic nematodes in soybean rhizosphere under different rotation systems. Soybean Science, 27, 997-1002. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 潘凤娟, 许艳丽, 李春杰, 韩新华, 刘伟 (2008) 大豆不同轮作系统主要植物线虫季节动态. 大豆科学, 27, 997-1002.] | |
| [29] |
Porazinska DL, McSorley R, Duncan LW, Graham JH, Wheaton TA, Parsons LR (1998) Nematode community composition under various irrigation schemes in a citrus soil ecosystem. Journal of Nematology, 30, 170-178.
PMID |
| [30] | Qi ZM, Wang KY, Zhang YB, Xie YH (2009) The seasonal changes of soil microbes and enzymatic activities under subalpine timberline ecotone in western Sichuan. Journal of Southwest China Normal University (Natural Science Edition), 34, 49-54. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 齐泽民, 王开运, 张远彬, 谢玉华 (2009) 川西亚高山林线交错带土壤微生物类群及酶活性季节动态. 西南师范大学学报(自然科学版), 34, 49-54.] | |
| [31] |
Ruan WB, Sang Y, Chen Q, Zhu X, Lin S, Gao YB (2012) The response of soil nematode community to nitrogen, water, and grazing history in the Inner Mongolian Steppe, China. Ecosystems, 15, 1121-1133.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
Sikandar A, Khanum TA, Wang YY (2021) Biodiversity and community analysis of plant-parasitic and free-living nematodes associated with maize and other rotational crops from Punjab, Pakistan. Life, 11, 1426.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
Simmons BL, Coleman DC (2008) Microbial community response to transition from conventional to conservation tillage in cotton fields. Applied Soil Ecology, 40, 518-528.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
van den Hoogen J, Geisen S, Routh D, Ferris H, Traunspurger W, Wardle DA, de Goede RGM, Adams BJ, Ahmad W, Andriuzzi WS, Bardgett RD, Bonkowski M, Campos-Herrera R, Cares JE, Caruso T, de Brito Caixeta L, Chen XY, Costa SR, Creamer R, Mauro da Cunha Castro J, Dam M, Djigal D, Escuer M, Griffiths BS, Gutiérrez C, Hohberg K, Kalinkina D, Kardol P, Kergunteuil A, Korthals G, Krashevska V, Kudrin AA, Li Q, Liang WJ, Magilton M, Marais M, Martín JAR, Matveeva E, Mayad EH, Mulder C, Mullin P, Neilson R, Nguyen TAD, Nielsen UN, Okada H, Rius JEP, Pan KW, Peneva V, Pellissier L, Carlos Pereira da Silva J, Pitteloud C, Powers TO, Powers K, Quist CW, Rasmann S, Moreno SS, Scheu S, Setälä H, Sushchuk A, Tiunov AV, Trap J, van der Putten W, Vestergård M, Villenave C, Waeyenberge L, Wall DH, Wilschut R, Wright DG, Yang JI, Crowther TW(2019) Soil nematode abundance and functional group composition at a global scale. Nature, 572, 194-198.
DOI URL |
| [35] | Wang W, Guo JX, Zhang BT (2003) Seasonal dynamics of environmental factors and decomposition rate of litter in Leymus chinensis community in Songnen grassland in Northeast China. Acta Pratacultural Science, 12, 47-52. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 王娓, 郭继勋, 张保田 (2003) 东北松嫩草地羊草群落环境因素与凋落物分解季节动态. 草业学报, 12, 47-52.] | |
| [36] |
Wilschut RA, Geisen S (2021) Nematodes as drivers of plant performance in natural systems. Trends in Plant Science, 26, 237-247.
DOI PMID |
| [37] |
Yeates GW (2003) Nematodes as soil indicators: Functional and biodiversity aspects. Biology and Fertility of Soils, 37, 199-210.
DOI URL |
| [38] |
Yeates GW, Bongers T (1999) Nematode diversity in agroecosystems. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 74, 113-135.
DOI URL |
| [39] | Yeates GW, Wardle DA (1996) Nematodes as predators and prey: Relationships to biological control and soil processes. Pedobiologia, 40, 43-50. |
| [40] | Zhang XK, Liang WJ, Li Q (2013) Forest Soil Nematodes in Changbai Mountain—Morphology and Distribution. China Agricultural Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 张晓珂, 梁文举, 李琪 (2013) 长白山森林土壤线虫——形态分类与分布格局. 中国农业出版社, 北京.] |
| [1] | 刘志禹, 吉鑫, 隋国辉, 杨定, 李轩昆. 北京首都国际机场野牛草与杂草草坪无脊椎动物多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24456-. |
| [2] | 李华亮, 张明军, 张熙斌, 谭荣, 李诗川, 冯尔辉, 林雪云, 陈珉, 颜文博, 曾治高. 海南东寨港国家级自然保护区两栖类群落组成及影响因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24350-. |
| [3] | 李蓉姣, 董江海, 郑文芳, 刘入源, 赵立娟, 高瑞贺. 关帝山不同海拔杨桦混交林土壤动物多样性特征及其影响因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(9): 24070-. |
| [4] | 姚祝, 魏雪, 马金豪, 任晓, 王玉英, 胡雷, 吴鹏飞. 气候暖湿化对高寒草甸土壤线虫群落的短期影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(5): 23483-. |
| [5] | 陈哲涵, 尹进, 叶吉, 刘冬伟, 毛子昆, 房帅, 蔺菲, 王绪高. 增温对东北温带次生林草本群落季节动态的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(5): 23059-. |
| [6] | 周欣扬, 王誉陶, 李建平. 黄土高原典型草原植物群落组成对降水变化的响应[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(3): 22118-. |
| [7] | 王朝雅, 李金涛, 刘畅, 王波, 苗白鸽, 彭艳琼. 西双版纳热带植物园蝴蝶多样性稳定的年际变化及幼虫与植物的互作网络结构[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(12): 23305-. |
| [8] | 刘金花, 李风, 田桃, 肖海峰. 土壤细菌和线虫对热带雨林优势植物凋落物特性和多样性的响应[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(11): 23276-. |
| [9] | 张超, 李娟, 程海云, 段家充, 潘昭. 秦岭西段地区蝴蝶群落多样性与环境因子相关性[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(1): 22272-. |
| [10] | 孙翌昕, 李英滨, 李玉辉, 李冰, 杜晓芳, 李琪. 高通量测序技术在线虫多样性研究中的应用[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(12): 22266-. |
| [11] | 陈燕南, 梁铖, 陈军. 亚热带不同树种组成森林中土壤甲螨群落结构特征: 以江西新岗山为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(12): 22334-. |
| [12] | 高洁, 李德浩, 姜海波, 邓光怡, 张超凡, 何春光, 孙鹏. 白鹤利用农田作为中转取食生境的原因[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(11): 22093-. |
| [13] | 任淯, 陶胜利, 胡天宇, 杨海涛, 关宏灿, 苏艳军, 程凯, 陈梦玺, 万华伟, 郭庆华. 中国生物多样性核心监测指标遥感产品体系构建与思考[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(10): 22530-. |
| [14] | 高梅香, 刘启龙, 朱家祺, 赵博宇, 杜嘉, 吴东辉. 中国农田土壤动物长期监测样地科学调查监测的实施方法[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(1): 21265-. |
| [15] | 段美春, 覃如霞, 张宏斌, 陈宝雄, 金彬, 张松泊, 任少鹏, 金树权, 朱升海, 华家宁, 刘云慧, 宇振荣. 农田节肢动物不同取样方法的综合比较[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(4): 477-487. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2026 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn
![]()