



生物多样性 ›› 2013, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (1): 90-98. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2013.09106 cstr: 32101.14.SP.J.1003.2013.09106
所属专题: 生物入侵
收稿日期:2012-04-23
接受日期:2012-07-11
出版日期:2013-01-20
发布日期:2013-02-04
通讯作者:
朱耿平,高玉葆
基金资助:
Gengping Zhu*( ), Guoqing Liu, Wenjun Bu, Yubao Gao*(
), Guoqing Liu, Wenjun Bu, Yubao Gao*( )
)
Received:2012-04-23
Accepted:2012-07-11
Online:2013-01-20
Published:2013-02-04
Contact:
Zhu Gengping,Gao Yubao
摘要:
生态位模型是利用物种已知的分布数据和相关环境变量, 根据一定的算法来推算物种的生态需求, 然后将运算结果投射至不同的空间和时间中来预测物种的实际分布和潜在分布。近年来, 该类模型被越来越多地应用在入侵生物学、保护生物学、全球气候变化对物种分布影响以及传染病空间传播的研究中。然而, 由于生态位模型的理论基础未被深入理解, 导致得出入侵物种生态位迁移等不符合实际的结论。作者从生态位与物种分布的关系、生态位模型构建的基本原理以及生态位模型和生态位的关系等方面探讨了生态位模型的理论基础。非生物的气候因素、物种间的相互作用和物种的迁移能力是影响物种分布的3个主要因素, 它们在不同的空间尺度下作用于物种的分布。生态位模型是利用物种分布点所关联的环境变量来模拟物种的分布, 这些分布点本身关联着该物种和其他物种间的相互作用, 因此生态位模型所模拟的是现实生态位(realized niche)或潜在生态位(potential niche), 而不是基础生态位(fundamental niche)。Grinnell生态位和Elton生态位均在生态位模型中得到反映, 这取决于环境变量类型的选择、所采用环境变量的分辨率以及物种自身的迁移能力。生态位模型在生物多样性保护中的应用主要包括物种的生态需求分析、未知物种或种群的探索和发现、自然保护区的选择和设计、物种入侵风险评价、气候变化对物种分布的影响、近缘物种生态位保守性及基于生态位分化的物种界定等方面。
朱耿平, 刘国卿, 卜文俊, 高玉葆 (2013) 生态位模型的基本原理及其在生物多样性保护中的应用. 生物多样性, 21, 90-98. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2013.09106.
Gengping Zhu,Guoqing Liu,Wenjun Bu,Yubao Gao (2013) Ecological niche modeling and its applications in biodiversity conservation. Biodiversity Science, 21, 90-98. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2013.09106.
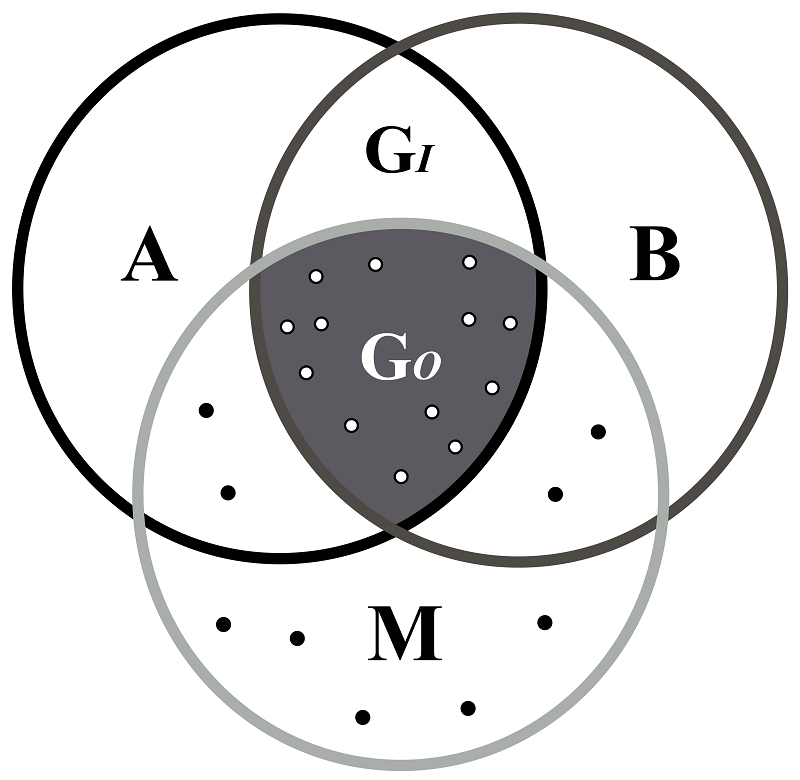
图1 影响物种地理分布的因素修改自(Soberón & Peterson, 2005; Soberón, 2010)。A环表示对物种分布有利的非生物因素(基础生态位), B环表示物种相互作用中对该物种有利的区域, M环表示物种迁移能力范围内的区域, Go为三者的重叠区域(灰色区), 代表物种实际分布区, GI为该物种潜在分布区; 空心点代表源种群(source population), 实心点代表汇种群(sink population)。
Fig. 1 Diagram showing a simplified framework for understanding species distribution adopted from (Soberón & Peterson, 2005; Soberón, 2010). Overlap of the three circles (GO) represents areas of actual distribution, within which environment are favorable (circle A), accessible (circle M), and biologically suitable (circle B) to the species. Area A represents geographic extent of the fundamental ecological niche, and GI represents areas of potential distribution. The open circles represent source populations, whereas the closed circles represent sink populations.
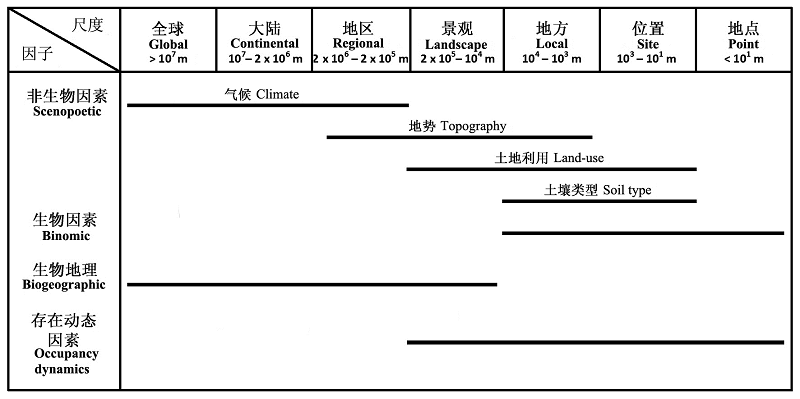
图2 不同影响因素在不同的空间尺度下作用于物种的分布修改自(Pearson & Dawson, 2003; Soberón, 2007, 2010; Hortal et al., 2010)
Fig. 2 Relative importance of factors affecting species distributions across spatial scales adopted from (Pearson & Dawson, 2003; Soberón 2007, 2010; Hortal et al., 2010)
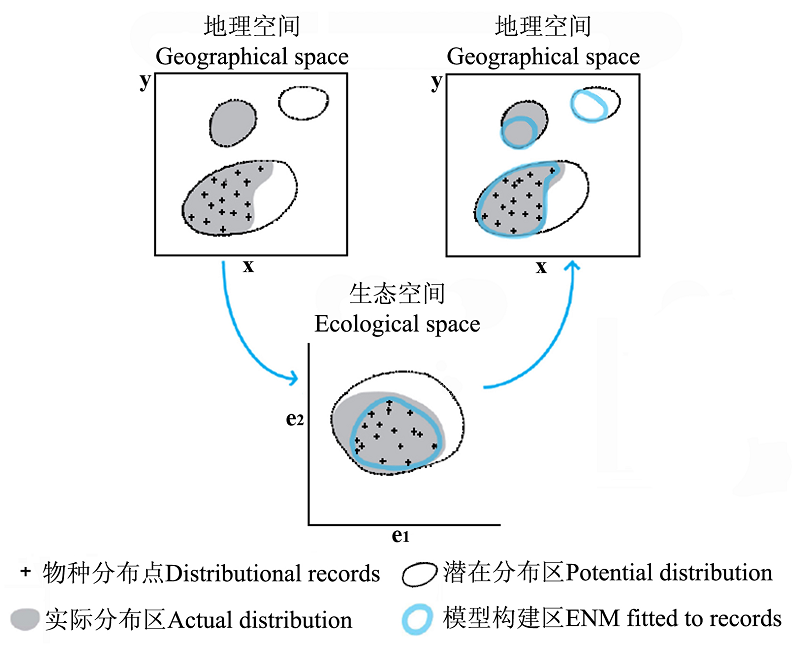
图3 示生态位模型将地理空间和生态空间二者结合引自(Pearson, 2007)
Fig. 3 Ecological niche modeling (ENM) building up the fridge of geographical space and ecological space adopted from (Pearson, 2007)
| 1 | Araújo MB, Peterson AT (2012) Uses and misuses of bioclimatic envelope modelling.Ecology, 93, 1527-1539. |
| 2 | Bourg NA, McShea WJ, Gill DE (2005) Putting a CART before the search: successful habitat prediction for a rare forest herb.Ecology, 86, 2793-2804. |
| 3 | Broennimann O, Treier UA, Müller-Scharer H, Thuiller W, Peterson AT, Guisan A (2007) Evidence of climatic niche shift during biological invasion.Ecology Letters, 10, 701-709. |
| 4 | Brown JH (1995) Macroecology. University of Chicago Press, Chicago. |
| 5 | Colwell RK, Rangel TF (2009) Hutchinson’s duality: the once and future niche. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences,USA, 106, 19651-19658. |
| 6 | Dorji S, Vernes K, Rajaratnam R (2011) Habitat correlates of the red panda in the temperate forests of Bhutan.PLOS ONE, 6, e26483. |
| 7 | Elton CS (1927) Animal Ecology. Sidgwick and Jackson, London. |
| 8 | Etterson JR, Shaw RG (2001) Constraint to adaptive evolution in response to global warming.Science, 294, 151-154. |
| 9 | Gaston KJ (2003) The Structure and Dynamics of Geographic Ranges. Oxford University Press, Oxford. |
| 10 | Grinnell J (1917) The niche-relationships of the California Thrasher.The Auk, 34, 427-433. |
| 11 | Guisan A, Thuiller W (2005) Predicting species distribution: offering more than simple habitat models.Ecology Letters, 8, 993-1009. |
| 12 | Hawlitschek O, Porch N, Hendrich L, Balke M (2011) Ecological niche modelling and nDNA sequencing support a new, morphologically cryptic beetle species unveiled by DNA Barcoding.PLOS ONE, 6, e16662. |
| 13 | Hijmans RJ, Cameron SE, Parra JL, Jones PG, Jarvis A (2005) Very high resolution interpolated climate surfaces for global land areas.International Journal of Climatology, 25, 1965-1978. |
| 14 | Hirzel AH, Hausser J, Chessel D, Perrin N (2002) Ecological-niche factor analysis: how to compute habitat-suitability maps without absence data ?Ecology, 83, 2027-2036. |
| 15 | Holt RD (2003) On the evolutionary ecology of species’ ranges.Evolutionary Ecology Research, 5, 159-178. |
| 16 | Hortal J, Roura-Pascual N, Sanders NJ, Rahbek C (2010) Understanding (insect) species distributions across spatial scales.Ecography, 33, 51-53. |
| 17 | Hutchinson GE (1957) Concluding remarks.Cold Spring Harbor Symposium on Quantitative Biology, 22, 415-427. |
| 18 | Irfan-Ullah M, Amarnath G, Murthy MSR, Peterson AT (2007) Mapping the geographic distribution of Aglaia bourdillonii Gamble (Meliaceae), an endemic and threatened plant, using ecological niche modeling.Plant Conservation and Biodiversity, 16, 1917-1925. |
| 19 | Jackson ST, Overpeck JT (2000) Responses of plant populations and communities to environmental changes of the late Quaternary.Paleobiology, 26, 194-220. |
| 20 | Leaché AD, Koo MS, Spencer CL, Papenfuss TJ, Fisher RN, McGuire JA (2009) Quantifying ecological, morphological, and genetic variation to delimit species in the coast horned lizard species complex (Phrynosoma). Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 106, 12418-12423. |
| 21 | Luoto M, Heikkinen RK, Pöyry J, Saarinen K (2006) Determinants of the biogeographical distribution of butterflies in boreal regions.Journal of Biogeography, 33, 1764-1778. |
| 22 | Mackey BG, Lindenmayer DB (2001) Towards a hierarchical framework for modelling the spatial distribution of animals.Journal of Biogeography, 28, 1147-1166. |
| 23 | McCormack JE, Zellmer AJ, Knowles LL (2010) Does niche divergence accompany allopatric divergence in Aphelocoma jays as predicted under ecological speciation? Insights from tests with niche models.Evolution, 64, 1231-1244. |
| 24 | Medley KA (2010) Niche shifts during the global invasion of the Asian tiger mosquito, Aedes albopictus Skuse (Culicidae), revealed by reciprocal distribution models.Global Ecology and Biogeography, 19, 122-133. |
| 25 | Menon S, Choudhury BI, Khan ML, Peterson AT (2010) Ecological niche modeling and local knowledge predict new populations of Gymnocladus assamicus, a critically endangered tree species.Endangered Species Research, 11, 175-181. |
| 26 | Owens HL, Bentley AC, Peterson AT (2011) Predicting suitable environments and potential occurrences for coelacanths (Latimeria spp.).Biodiversity and Conservation, 21, 577-587. |
| 27 | Pearson RG (2007) Species’ distribution modeling for conservation educators and practitioners. Synthesis. American Museum of Natural History.. |
| 28 | Pearson RG, Dawson TP (2003) Predicting the impacts of climate change on the distribution of species: are bioclimate envelope models useful ?Global Ecology and Biogeography, 12, 361-371. |
| 29 | Peterson AT (2011) Ecological niche conservatism: a time-structured review of evidence.Journal of Biogeography, 38, 817-827. |
| 30 | Peterson AT, Nakazawa Y (2008) Environmental data sets matter in ecological niche modelling: an example with Solenopsis invicta and Solenopsis richteri.Global Ecology and Biogeography, 17, 135-144. |
| 31 | Peterson AT, Navarro-Sigüenza AG (2009) Making biodiversity discovery more efficient: an exploratory test using Mexican birds.Zootaxa, 2246, 58-66. |
| 32 | Peterson AT, Ortega-Huerta MA, Bartley J, Sánchez-Cordero V, Soberón J, Buddemeier RH, Stockwell DRB (2002) Future projections for Mexican faunas under global climate change scenarios. Nature, 416, 626-629. |
| 33 | Peterson AT, Soberón J (2012) Integrating fundamental concepts of ecology, biogeography, and sampling into effective ecological niche modeling and species distribution modeling.Plant Biosystems, 146, 789-796. |
| 34 | Peterson AT, Soberón J, Pearson RG, Anderson RP, Nakamura M, Martínez-Meyer E, Araújo MB (2011) Ecological Niches and Geographical Distributions. Princeton University Press, New Jersey. |
| 35 | Peterson AT, Soberón J, Sánchez-Cordero V (1999) Conservatism of ecological niches in evolutionary time.Science, 285, 1265-1267. |
| 36 | Petitpierre B, Kueffer C, Broennimann O, Randin C, Daehler C, Guisan A (2012) Climatic niche shifts are rare among terrestrial plant invaders.Science, 335, 1344-1348. |
| 37 | Pulliam HR (2000) On the relationship between niche and distribution.Ecology Letters, 3, 349-361. |
| 38 | Raxworthy CJ, Ingram CM, Rabibisoa N, Pearson RG (2007) Applications of ecological niche modeling for species delimitation: a review and empirical evaluation using day geckos (Phelsuma) from Madagascar.Systematic Biology, 56, 907-923. |
| 39 | Raxworthy CJ, Martínez-Meyer E, Horning N, Nussbaum RA, Schneider GE, Ortega-Huerta MA, Peterson AT (2003) Predicting distributions of known and unknown reptile species in Madagascar.Nature, 426, 837-841. |
| 40 | Rissler LJ, Apodaca JJ (2007) Adding more ecology into species delimitation: ecological niche models and phylogeography help define cryptic species in the Black Salamander (Aneides flavipunctatus).Systematic Biology, 56, 924-942. |
| 41 | Robinson LM, Elith J, Hobday AJ, Pearson RG, Kendall BE, Possingham HP, Richardson AJ (2011) Pushing the limits in marine species distribution modelling: lessons from the land present challenges and opportunities.Global Ecology and Biogeography, 20, 789-802. |
| 42 | Rödder D, Lötters S (2009) Niche shift versus niche conservatism? Climatic characteristics of the native and invasive ranges of the Mediterranean house gecko (Hemidactylus turcicus).Global Ecology and Biogeography, 18, 674-687. |
| 43 | Saupe E, Barve V, Myers C, Soberón J, Barve N, Hensz C, Peterson AT, Owens HL, Lira-Noriega A (2012) Variation in niche and distribution model performance: the need for a priori assessment of key causal factors.Ecological Modelling, 237, 11-22. |
| 44 | Sillero N (2011) What does ecological modelling model? A proposed classification of ecological niche models based on their underlying methods.Ecological Modelling, 222, 1343-1346. |
| 45 | Soberón J (2007) Grinnellian and Eltonian niches and geographic distributions of species.Ecology Letters, 10, 1115-1123. |
| 46 | Soberón J, Peterson AT (2005) Interpretation of models of fundamental ecological niches and species' distributional areas.Biodiversity Informatics, 2, 1-10. |
| 47 | Soberón JM (2010) Niche and area of distribution modeling: a population ecology perspective.Ecography, 33, 159-167. |
| 48 | Svenning JC, Skov F (2004) Limited filling of the potential range in European tree species.Ecology Letters, 7, 565-573. |
| 49 | Thuiller W, Lavorel S, Araújo MB, Sykes MT, Prentice IC (2005) Climate change threats to plant diversity in Europe.Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 102, 8245-8250. |
| 50 | Warren DL (2012) In defense of niche modeling.Trends in Ecology and Evolution, 27, 497-500. |
| 51 | Warren DL, Glor RE, Turelli M (2008) Environmental niche equivalency versus conservatism: quantitative approaches to niche evolution.Evolution, 62, 2868-2883. |
| 52 | Warren DL, Glor RE, Turelli M (2010) ENMTools: a toolbox for comparative studies of environmental niche models.Ecography, 33, 607-611. |
| 53 | Whittaker RJ, Araújo MB, Jepson P, Ladle RJ, Watson JEM, Willis KJ (2005) Conservation biogeography: assessment and prospect.Diversity and Distributions, 11, 3-23. |
| 54 | Willis KJ, Whittaker RJ (2002) Species diversity―scale matters.Science, 295, 1245-1248. |
| 55 | Wiens JJ, Graham CH (2005) Niche conservatism: integrating evolution, ecology, and conservation biology.Annual Review of Ecology, Evolution, and Systematics, 36, 519-539. |
| 56 | Zhou WW, Wen Y, Fu JZ, Xu YB, Jin JQ, Ding L, Min MS, Che J, Zhang YP (2012) Speciation in the Rana chensinensis species complex and its relationship to the uplift of the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau.Molecular Ecology, 21, 960-973. |
| 57 | Zhu G, Bu W, Gao Y, Liu G (2012a) Potential geographic distribution of Brown Marmorated Stink Bug invasion (Halyomorpha halys).PLOS ONE, 7, e31246. |
| 58 | |
| 59 | Zhu GP, Petersen MJ, Bu WJ (2012b) Selecting biological meaningful environmental dimensions of low discrepancy among ranges to predict potential distribution of bean plataspid invasion.PLOS ONE, 7, e46247. |
| 60 | Zhu L, Sun OJ, Sang WG, Li ZY, Ma KP (2007) Predicting the spatial distribution of an invasive plant species (Eupatorium adenophorum) in China.Landscape Ecology, 22, 1143-1154. |
| [1] | 刘志发, 王新财, 龚粤宁, 陈道剑, 张强. 基于红外相机监测的广东南岭国家级自然保护区鸟兽多样性及其垂直分布特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(8): 22689-. |
| [2] | 杨华林, 程跃红, 周天祥, 冯茜, 胡强, 张贵权, 杨建, 张晋东, 王彬, 周材权. 四川卧龙国家级自然保护区多空间尺度下绿尾虹雉的生境选择[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(7): 21535-. |
| [3] | 王然, 乔慧捷. 生态位模型在流行病学中的应用[J]. 生物多样性, 2020, 28(5): 579-586. |
| [4] | 范靖宇, 李汉芃, 杨琢, 朱耿平. 基于本土最优模型模拟入侵物种水盾草在中国的潜在分布[J]. 生物多样性, 2019, 27(2): 140-148. |
| [5] | 庄鸿飞, 张殷波, 王伟, 任月恒, 刘方正, 杜金鸿, 周越. 基于最大熵模型的不同尺度物种分布概率优化热点分析: 以红色木莲为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2018, 26(9): 931-940. |
| [6] | 王波, 黄勇, 李家堂, 戴强, 王跃招, 杨道德. 西南喀斯特地貌区两栖动物丰富度分布格局与环境因子的关系[J]. 生物多样性, 2018, 26(9): 941-950. |
| [7] | 丁晨晨, 胡一鸣, 李春旺, 蒋志刚. 印度野牛在中国的分布及其栖息地适宜性分析[J]. 生物多样性, 2018, 26(9): 951-961. |
| [8] | 周中一, 刘冉, 时书纳, 苏艳军, 李文楷, 郭庆华. 基于激光雷达数据的物种分布模拟: 以美国加州内华达山脉南部区域食鱼貂分布模拟为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2018, 26(8): 878-891. |
| [9] | 高梅香, 林琳, 常亮, 孙新, 刘冬, 吴东辉. 土壤动物群落空间格局和构建机制研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2018, 26(10): 1034-1050. |
| [10] | 叶俊伟, 袁永革, 蔡荔, 王晓娟. 中国东北温带针阔混交林植物物种的谱系地理研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2017, 25(12): 1339-1349. |
| [11] | 谭珊珊, 王忍忍, 龚筱羚, 蔡佳瑶, 沈国春. 群落物种及结构多样性对森林地上生物量的影响及其尺度效应: 以巴拿马BCI样地为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2017, 25(10): 1054-1064. |
| [12] | 方晓峰, 杨庆松, 刘何铭, 马遵平, 董舒, 曹烨, 袁铭皎, 费希旸, 孙小颖, 王希华. 天童常绿阔叶林中常绿与落叶物种的物种多度分布格局[J]. 生物多样性, 2016, 24(6): 629-638. |
| [13] | 朱耿平, 乔慧捷. Maxent模型复杂度对物种潜在分布区预测的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2016, 24(10): 1189-1196. |
| [14] | 崔相艳, 王文娟, 杨小强, 李述, 秦声远, 戎俊. 基于生态位模型预测野生油茶的潜在分布[J]. 生物多样性, 2016, 24(10): 1117-1128. |
| [15] | 任思远, 王婷, 祝燕, 叶永忠, 李聪, 潘娜, 叶永忠. 暖温带-北亚热带过渡带落叶阔叶林群落不同径级系统发育结构的变化[J]. 生物多样性, 2014, 22(5): 574-582. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn