



生物多样性 ›› 2010, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (1): 67-75. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2010.067 cstr: 32101.14.SP.J.1003.2010.067
收稿日期:2009-04-09
接受日期:2009-09-24
出版日期:2010-01-20
发布日期:2010-01-20
通讯作者:
赵云龙
作者简介:* E-mail: ylzhao@bio.ecnu.edu.cn基金资助:
Qiang Li, Chuanguang An, Qiang Ma, Linlin Xu, Yunlong Zhao*( )
)
Received:2009-04-09
Accepted:2009-09-24
Online:2010-01-20
Published:2010-01-20
Contact:
Yunlong Zhao
摘要:
为了揭示潮间带潮沟水域浮游动物的多样性, 作者于2008年4-12月在崇明东滩选取6条潮沟共18个站点进行4个季节的浮游动物采样调查。检获到浮游动物44种, 隶属于6个类群, 其中桡足类占绝对优势, 达总种类数的79.5%。分析了浮游动物的种类组成、优势种、群落结构及物种多样性等生态特征参数的季节变化。优势种有9种, 春季以细巧华哲水蚤(Sinocalanus tenellus)优势度最高, 夏季以火腿许水蚤(Schmackeria poplesia)优势度最高, 秋季以火腿许水蚤和中华华哲水蚤(Sinocalanus sinensis)优势度较高, 冬季则以四刺窄腹剑水蚤(Limnoithona etraspina)和中华华哲水蚤的优势度较高。多样性指数显示, Shannon-Wiener指数(H′)值以夏冬季较高, 物种丰富度指数(d)值以夏秋季较高, Pielou均匀度指数(J′)值以冬季最高。与崇明岛附近的长江口北港北支水域已有的研究结果相比, 种类组成差异较大, 仅有6个共有种。浮游动物的生态特征与潮汐关系密切, 涨潮时物种多样性略高于落潮时, 涨潮和落潮时优势种的种类及优势度也均呈现出一定差异。盐度、温度、径流及潮流等环境因素对潮沟浮游动物的时空分布产生了重要影响。
李强, 安传光, 马强, 徐霖林, 赵云龙 (2010) 崇明东滩潮间带潮沟浮游动物的种类组成及多样性. 生物多样性, 18, 67-75. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2010.067.
Qiang Li, Chuanguang An, Qiang Ma, Linlin Xu, Yunlong Zhao (2010) Species composition and diversity of zooplankton in tidal creeks of the Chongming Dongtan intertidal flat. Biodiversity Science, 18, 67-75. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2010.067.
| 类群 Phyla | 春季 Spring | 夏季 Summer | 秋季 Autumn | 冬季 Winter | 全年 Total | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 涨潮 F | 落潮 E | 涨潮 F | 落潮 E | 涨潮 F | 落潮 E | 涨潮 F | 落潮 E | 涨潮 F | 落潮 E | |
| 桡足类 Copepoda | 21 (80.8%) | 21 (80.8%) | 23 (76.7%) | 23 (76.7%) | 27 (75.0%) | 26 (76.5%) | 20 (83.3%) | 19 (82.6%) | 35 (79.5%) | 35 (79.5%) |
| 端足类 Amphipoda | 2 (7.7%) | 2 (7.7%) | 3 (10.0%) | 3 (10.0%) | 3 (8.3%) | 2 (5.9%) | 2 (8.3%) | 2 (8.7%) | 3 (6.8%) | 3 (6.8%) |
| 等足类 Isopoda | 0 | 0 | 1 (3.3%) | 1 (3.3%) | 2 (5.6%) | 2 (5.9%) | 0 | 0 | 2 (4.5%) | 2 (4.5%) |
| 枝角类 Cladoceran | 1 (3.8%) | 1 (3.8%) | 2 (6.7%) | 2 (6.7%) | 2 (5.6%) | 2 (5.9%) | 0 | 0 | 2 (4.5%) | 2 (4.5%) |
| 糠虾类 Mysidacea | 1 (3.8%) | 1 (3.8%) | 1 (3.3%) | 1 (3.3%) | 1 (2.8%) | 1 (2.9%) | 1 (4.2%) | 1 (4.3%) | 1 (2.3%) | 1 (2.3%) |
| 涟虫类 Cumacea | 1 (3.8%) | 1 (3.8%) | 0 | 0 | 1 (2.8%) | 1 (2.9%) | 1 (4.2%) | 1 (4.3%) | 1 (2.3%) | 1 (2.3%) |
| 合计 Total | 26 | 26 | 30 | 30 | 36 | 34 | 24 | 23 | 44 | 44 |
表1 崇明东滩潮间带潮沟浮游动物种类组成及百分比
Table 1 Species composition and percentage of zooplankton in tidal creeks of Chongming Dongtan intertidal flat
| 类群 Phyla | 春季 Spring | 夏季 Summer | 秋季 Autumn | 冬季 Winter | 全年 Total | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 涨潮 F | 落潮 E | 涨潮 F | 落潮 E | 涨潮 F | 落潮 E | 涨潮 F | 落潮 E | 涨潮 F | 落潮 E | |
| 桡足类 Copepoda | 21 (80.8%) | 21 (80.8%) | 23 (76.7%) | 23 (76.7%) | 27 (75.0%) | 26 (76.5%) | 20 (83.3%) | 19 (82.6%) | 35 (79.5%) | 35 (79.5%) |
| 端足类 Amphipoda | 2 (7.7%) | 2 (7.7%) | 3 (10.0%) | 3 (10.0%) | 3 (8.3%) | 2 (5.9%) | 2 (8.3%) | 2 (8.7%) | 3 (6.8%) | 3 (6.8%) |
| 等足类 Isopoda | 0 | 0 | 1 (3.3%) | 1 (3.3%) | 2 (5.6%) | 2 (5.9%) | 0 | 0 | 2 (4.5%) | 2 (4.5%) |
| 枝角类 Cladoceran | 1 (3.8%) | 1 (3.8%) | 2 (6.7%) | 2 (6.7%) | 2 (5.6%) | 2 (5.9%) | 0 | 0 | 2 (4.5%) | 2 (4.5%) |
| 糠虾类 Mysidacea | 1 (3.8%) | 1 (3.8%) | 1 (3.3%) | 1 (3.3%) | 1 (2.8%) | 1 (2.9%) | 1 (4.2%) | 1 (4.3%) | 1 (2.3%) | 1 (2.3%) |
| 涟虫类 Cumacea | 1 (3.8%) | 1 (3.8%) | 0 | 0 | 1 (2.8%) | 1 (2.9%) | 1 (4.2%) | 1 (4.3%) | 1 (2.3%) | 1 (2.3%) |
| 合计 Total | 26 | 26 | 30 | 30 | 36 | 34 | 24 | 23 | 44 | 44 |
| 优势种 Dominant species | 春季 Spring | 夏季 Summer | 秋季 Autumn | 冬季 Winter | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 涨潮 F | 落潮 E | 涨潮 F | 落潮 E | 涨潮 F | 落潮 E | 涨潮 F | 落潮 E | ||||
| 中华华哲水蚤 Sinocalanus sinensis | 0.032 | 0.021 | 0.184 | 0.177 | 0.268 | 0.625 | 0.338 | 0.069 | |||
| 细巧华哲水蚤 S. tenellus | 0.538 | 0.243 | 0.022 | 0.082 | 0.034 | ||||||
| 火腿许水蚤 Schmackeria poplesia | 0.056 | 0.454 | 0.455 | 0.310 | 0.022 | 0.049 | 0.066 | ||||
| 宽足咸水剑水蚤 Halicyclops latus | 0.022 | ||||||||||
| 中华咸水剑水蚤 H. sinensis | 0.043 | 0.049 | 0.050 | 0.080 | 0.031 | ||||||
| 四刺窄腹剑水蚤 Limnoithona etraspina | 0.095 | 0.030 | 0.300 | 0.432 | |||||||
| 湖泊美丽猛水蚤 Nitocra lacustris | 0.029 | ||||||||||
| 三角大吉猛水蚤 Tachidius triangularis | 0.184 | 0.218 | 0.027 | 0.053 | |||||||
| 四刺破足猛水蚤 Mesochra quadrispinosa | 0.122 | 0.081 | 0.043 | 0.036 | |||||||
表2 崇明东滩潮间带潮沟浮游动物优势种及优势度
Table 2 Dominant species and dominance of zooplankton in tidal creeks of Chongming Dongtan intertidal flat
| 优势种 Dominant species | 春季 Spring | 夏季 Summer | 秋季 Autumn | 冬季 Winter | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 涨潮 F | 落潮 E | 涨潮 F | 落潮 E | 涨潮 F | 落潮 E | 涨潮 F | 落潮 E | ||||
| 中华华哲水蚤 Sinocalanus sinensis | 0.032 | 0.021 | 0.184 | 0.177 | 0.268 | 0.625 | 0.338 | 0.069 | |||
| 细巧华哲水蚤 S. tenellus | 0.538 | 0.243 | 0.022 | 0.082 | 0.034 | ||||||
| 火腿许水蚤 Schmackeria poplesia | 0.056 | 0.454 | 0.455 | 0.310 | 0.022 | 0.049 | 0.066 | ||||
| 宽足咸水剑水蚤 Halicyclops latus | 0.022 | ||||||||||
| 中华咸水剑水蚤 H. sinensis | 0.043 | 0.049 | 0.050 | 0.080 | 0.031 | ||||||
| 四刺窄腹剑水蚤 Limnoithona etraspina | 0.095 | 0.030 | 0.300 | 0.432 | |||||||
| 湖泊美丽猛水蚤 Nitocra lacustris | 0.029 | ||||||||||
| 三角大吉猛水蚤 Tachidius triangularis | 0.184 | 0.218 | 0.027 | 0.053 | |||||||
| 四刺破足猛水蚤 Mesochra quadrispinosa | 0.122 | 0.081 | 0.043 | 0.036 | |||||||
| 季节 Season | 潮汐 Tide | S1 | S2 | S3 | S4 | S5 | S6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 春季 Spring | 涨潮 Flood tide | 2.29-3.06 | 1.54-2.07 | 1.53-2.21 | 1.35-1.97 | 1.48-1.83 | 1.46-1.99 |
| 落潮 Ebb tide | 0.75-0.96 | 0.53-0.68 | 0.53-0.77 | 0.54-0.72 | 0.50-0.69 | 0.47-0.63 | |
| 夏季 Summer | 涨潮 Flood tide | 2.37-3.16 | 1.63-2.29 | 1.66-2.30 | 1.48-2.09 | 1.59-1.97 | 1.60-2.07 |
| 落潮 Ebb tide | 0.78-0.99 | 0.56-0.73 | 0.60-0.77 | 0.58-0.71 | 0.60-0.72 | 0.57-0.69 | |
| 秋季 Autumn | 涨潮 Flood tide | 2.31-3.12 | 1.60-2.24 | 1.61-2.26 | 1.45-2.05 | 1.50-1.95 | 1.56-2.03 |
| 落潮 Ebb tide | 0.80-1.01 | 0.55-0.69 | 0.59-0.78 | 0.56-0.73 | 0.59-0.75 | 0.60-0.72 | |
| 冬季 Winter | 涨潮 Flood tide | 2.14-2.98 | 1.47-1.95 | 1.42-2.03 | 1.28-1.85 | 1.34-1.76 | 1.32-1.81 |
| 落潮 Ebb tide | 0.69-0.91 | 0.49-0.65 | 0.46-0.66 | 0.45-0.62 | 0.44-0.55 | 0.44-0.61 |
表3 崇明东滩潮间带潮沟采样站位水深(m)
Table 3 Water depth of sampling stations in tidal creeks of Chongming Dongtan intertidal flat
| 季节 Season | 潮汐 Tide | S1 | S2 | S3 | S4 | S5 | S6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 春季 Spring | 涨潮 Flood tide | 2.29-3.06 | 1.54-2.07 | 1.53-2.21 | 1.35-1.97 | 1.48-1.83 | 1.46-1.99 |
| 落潮 Ebb tide | 0.75-0.96 | 0.53-0.68 | 0.53-0.77 | 0.54-0.72 | 0.50-0.69 | 0.47-0.63 | |
| 夏季 Summer | 涨潮 Flood tide | 2.37-3.16 | 1.63-2.29 | 1.66-2.30 | 1.48-2.09 | 1.59-1.97 | 1.60-2.07 |
| 落潮 Ebb tide | 0.78-0.99 | 0.56-0.73 | 0.60-0.77 | 0.58-0.71 | 0.60-0.72 | 0.57-0.69 | |
| 秋季 Autumn | 涨潮 Flood tide | 2.31-3.12 | 1.60-2.24 | 1.61-2.26 | 1.45-2.05 | 1.50-1.95 | 1.56-2.03 |
| 落潮 Ebb tide | 0.80-1.01 | 0.55-0.69 | 0.59-0.78 | 0.56-0.73 | 0.59-0.75 | 0.60-0.72 | |
| 冬季 Winter | 涨潮 Flood tide | 2.14-2.98 | 1.47-1.95 | 1.42-2.03 | 1.28-1.85 | 1.34-1.76 | 1.32-1.81 |
| 落潮 Ebb tide | 0.69-0.91 | 0.49-0.65 | 0.46-0.66 | 0.45-0.62 | 0.44-0.55 | 0.44-0.61 |
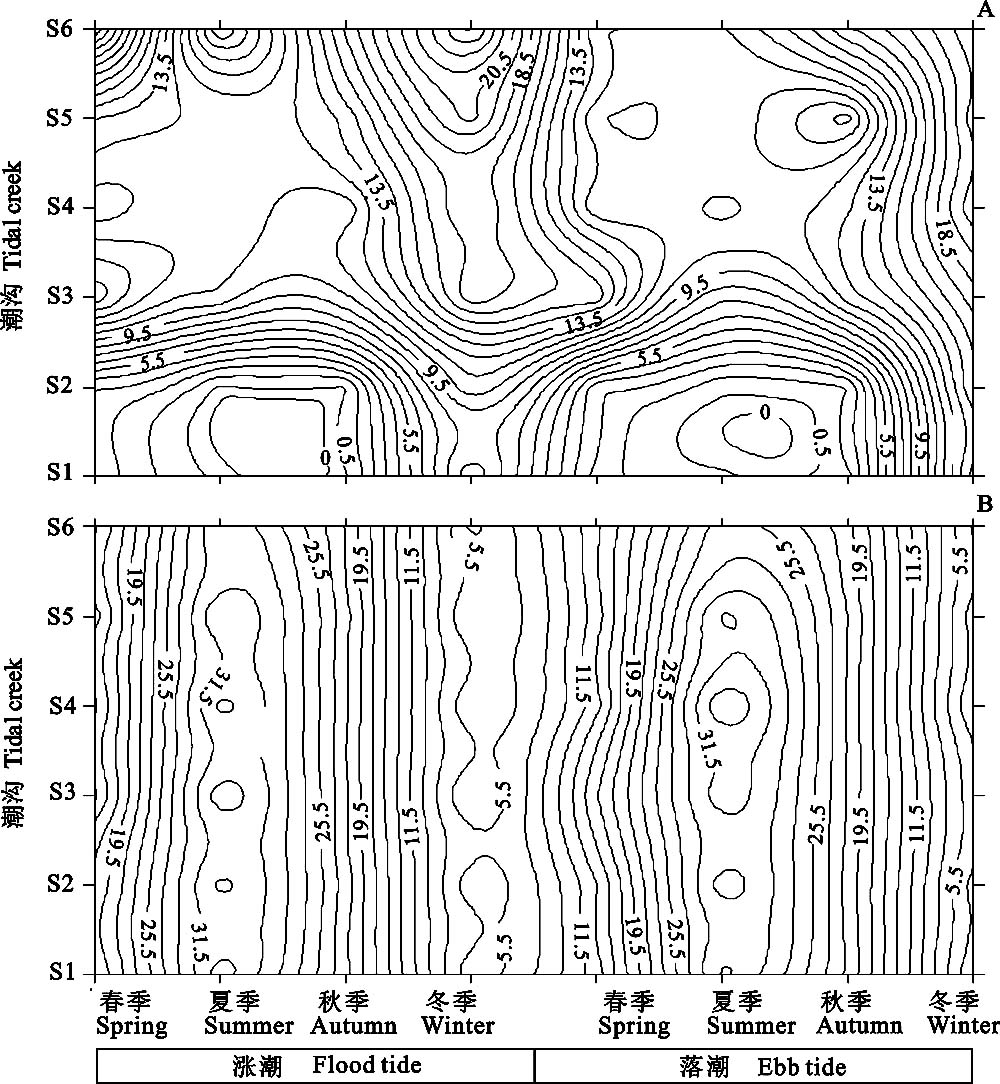
图4 崇明东滩潮间带潮沟表层盐度、温度的时空变化。A: 表层盐度; B: 表层温度。
Fig. 4 Spatial and temporal variations in surface temperature (℃) and salinity in tidal creeks of Chongming Dongtan intertidal flat. A, Surface salinity; B, Surface temperature.
| [1] | Barss MA, Fransz HG (1984) Crazing pressure of copepods on the phytoplankton stock of the central North Sea. Netherland Journal of Sea Research, 18, 120-142. |
| [2] | Chen YQ (陈亚瞿), Xu ZL (徐兆礼), Wang YL (王云龙), Hu FX (胡方西), Han MB (韩明宝), Yan HC (严宏昌) (1995) An ecological study on zooplankton in plume front zone of Changjiang (Yangtze) River estuarine area. Ⅱ. Species composition, community structure and indicator species. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China (中国水产科学), 2(1), 59-63. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [3] | Gao Q (高倩), Xu ZL (徐兆礼), Zhuang P (庄平) (2008) Comparison of mesozooplankton communities in north channel and north branch of Yangtze River Estuary. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology (应用生态学报), 19, 2049-2055. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [4] | Guo PY (郭沛涌), Shen HT (沈焕庭), Liu AC (刘阿成), Wang JH (王金辉), Yang YL (杨元利) (2003) The species composition, community structure and diversity of zooplankton in Changjiang estuary. Acta Ecologica Sinica (生态学报), 23, 892-900. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [5] | Hettler WF (1989) Nekton use of regularly-flooded saltmarsh cordgrass habitat in North Carolina, USA. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 56, 111-118. |
| [6] | Hoss DE, Thayer GW (1993) The importance of habitat to the early life history of estuarine dependent fishes. American Fisheries Society Symposium, 14, 147-158. |
| [7] | Huang JQ (黄加祺), Huang HY (黄辉洋), Xu ZZ (许振祖) (1998) Preliminary study on cultural conditions of Schmackeria poplesia. Journal of Oceanography in Taiwan Strait (台湾海峡), 17(Suppl.), 44-48. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [8] | Ji HH (纪焕红), Ye SF (叶属峰) (2006) Ecological distribution characteristics of zooplankton and its relationship with environmental factors in the Changjiang River estuary. Marine Sciences (海洋科学), 30(6), 23-30. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [9] | Jiang XZ (蒋燮治), Du NS (堵南山) (1979) Fauna Sinica: Freshwater Cladocera (中国动物志: 淡水枝角类). Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [10] | Kwak TJ, Zedler JB (1997) Food web analysis of southern California coastal wetlands using multiple stable isotopes. Oecologia, 110, 262-277. |
| [11] | Likens GE, Bormann FH (1974) Linkages between terrestrial and aquatic ecosystem. BioScience, 24, 447-456. |
| [12] | Lin X (林霞), Li CY (李春月), Lu KH (陆开宏) (2001) The effect of temperature and salinity on the survival of Sinocalanus tenellus. Journal of Ningbo University (Natural Science and Engineering Edition) (宁波大学学报(理工版)), 14, 43-46. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [13] | Ma YA (马云安), Ma ZJ (马志军) (2006) Chongming Dongtan International Importance Wetland (崇明东滩国际重要湿地). China Forestry Publishing House, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [14] | Naiman RJ, Decamps H (1990) The Ecology and Management of Aquatic Terrestrial Ecotones. UNESCO and Parthenon Publish, Paris. |
| [15] | Posey MH, Alphin TD, Cahoon LB, Lindquist DG, Mallin MA, Nevers MB ( 2002) Top-down versus bottom-up limitation in benthic infaunal communities: direct and indirect effects. Estuaries, 25, 999-1014. |
| [16] | Rolland S, Fulton III (1983) Interactive effects of temperature and predation on an estuarine zooplankton community. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology, 72, 67-81. |
| [17] | Ross SW (2003) The relative value of different estuarine nursery areas in North Carolina for transient juvenile marine fishes. Fishery Bulletin, 101, 384-404. |
| [18] | Shen JR (沈嘉瑞) (1979) Fauna Sinica: Freshwater Copepoda (中国动物志: 淡水桡足类). Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [19] | Shu YF (束蕴芳), Han MS (韩茂森) (1992) Marine Plankton of China Illustrata (中国海洋浮游生物图谱). China Ocean Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [20] | State Bureau of Quality and Technical Supervision (国家质量技术监督局) (1998) The Specification for Marine Monitoring (海洋监测规范). GB17378.7. Standards Press of China, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [21] | Tian B (田波), Zhou YX (周云轩), Zhang LQ (张利权), Ma ZJ (马志军), Yang B (杨波), Tang CD (汤臣栋) (2008) A GIS and remote sensing-based analysis of migratory bird habitat suitability for Chongming Dongtan Nature Reserve, Shanghai. Acta Ecologica Sinica (生态学报), 28, 3049-3059. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [22] | Xie DF (谢东风), Fan DD (范代读), Gao S (高抒) (2006) Flat of Chongming Island and its impacts on the sediment distribution. Marine Geology and Quaternary Geology (海洋地质与第四纪地质), 26(2), 9-16. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [23] | Xu HF (徐宏发), Zhao YL (赵云龙) (2005) Scientific Survey on Chongming Dongtan Migratory Birds Nature Reserve of Shanghai (上海市崇明东滩鸟类自然保护区科学考察集). China Forestry Publishing House, Beijing. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [24] | Xu L (徐玲), Li B (李波), Yuan X (袁晓), Xu HF (徐宏发) (2006) The characteristics of the avian community in Chongming Dongtan spring 2003. Chinese Journal of Zoology (动物学杂志), 41(6), 120-126. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [25] | Xu XJ (徐晓军), Wang H (王华), You WH (由文辉), Liu BX (刘宝兴) (2006) A study on the fluctuation of zoobenthic community in Chongming Dongtan’s Spartina alterniflora Loisel. Transactions of Oceanology and Limnology (海洋湖沼通报), (2), 89-95. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [26] | Xu ZM (徐志明) (1985) The eastern flat sedimentation of the Chongming Island. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica (海洋与湖沼), 16, 232-239. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [27] | Xu ZL (徐兆礼), Chen YQ (陈亚瞿) (1989) Aggregated intensity of dominant species of zooplankton in autumn in the East China Sea and Yellow Sea. Chinese Journal of Ecology (生态学杂志), 8(4), 13-15. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [28] | Xu ZL (徐兆礼), Wang YL (王云龙), Chen YQ (陈亚瞿), Hu H (胡辉), Han MB (韩明宝), Li XH (李兴华) (1995) An ecological study on zooplankton in plume front zone of Changjiang (Yangtze) River estuarine area. Ⅲ. Vertical distribution of dominant species. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China (中国水产科学), 2(1), 64-70. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [29] | Xu ZL (徐兆礼), Wang YL (王云龙), Bai XM (白雪梅), Chen YQ (陈亚瞿) (1999) An ecological study on zooplankton in the Changjiang estuary. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China (中国水产科学), 6(5), 55-58. (in Chinese) |
| [30] | Xu ZL (徐兆礼), Hong B (洪波), Zhu MY (朱明远), Chen YQ (陈亚瞿) (2003) Ecological characteristics of zooplankton in frequent HAB areas of the East China Sea in spring. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology (应用生态学报), 14, 1081-1085. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [31] |
Xu ZL (徐兆礼) (2005) Zooplankton in north branch waters of Changjiang Estuary. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology (应用生态学报), 16, 1341-1345. (in Chinese with English abstract)
URL PMID |
| [32] | Yuan XZ (袁兴中), Lu JJ (陆健健) (2001) Preliminary study on macrobenthic community of the creek in the tidal flat of the Changjiang Estuary. Zoological Research (动物学研究), 22, 211-215. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [33] | Zhao P (赵平), Yuan X (袁晓), Tang SX (唐思贤), Wang TH (王天厚) (2003) Species and habitat preference of waterbirds at the eastern end of Chongming Island (Shanghai) in winter. Zoological Research (动物学研究), 24, 387-391. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [34] | Zheng Z (郑重), Li SJ (李少菁), Xu ZZ (许振祖) (1984) Marine Planktology (海洋浮游生物学), pp. 468-494. Ocean Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [35] | Zhou H (周慧), Zhong YK (仲阳康), Zhao P (赵平), Ge ZM (葛振鸣), Wang TH (王天厚) (2005) Niche analysis of wintering waterbirds at the eastern end of Chongming Island (Shanghai). Chinese Journal of Zoology (动物学杂志), 40(1), 59-65. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [1] | 吴晓晴 张美惠 葛苏婷 李漫淑 宋坤 沈国春 达良俊 张健. 上海近自然林重建过程中木本植物物种多样性与地上生物量的时空动态——以闵行区生态岛为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24444-. |
| [2] | 王太, 宋福俊, 张永胜, 娄忠玉, 张艳萍, 杜岩岩. 河西走廊内陆河水系鱼类多样性及资源现状[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24387-. |
| [3] | 张晶晶, 黄文彬, 陈奕廷, 杨泽鹏, 柯伟业, 彭昭杰, 魏世超, 张志伟, 胡怡思, 余文华, 周文良. 广东南澎列岛海洋生态国家级自然保护区造礁石珊瑚多样性及分布特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24424-. |
| [4] | 张明燡, 王晓梅, 郑言鑫, 吴楠, 李东浩, 樊恩源, 李娜, 单秀娟, 于涛, 赵春暖, 李波, 徐帅, 吴玉萍, 任利群. 黄河口典型牡蛎礁分布区资源状况和栖息地功能[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24208-. |
| [5] | 仝淼, 王欢, 张文双, 王超, 宋建潇. 重金属污染土壤中细菌抗生素抗性基因分布特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(3): 24101-. |
| [6] | 尚华丹, 张楚晴, 王梅, 裴文娅, 李国宏, 王鸿斌. 中国杨树害虫物种多样性及其地理分布[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24370-. |
| [7] | 吴昱萱, 王平, 胡晓生, 丁一, 彭甜恬, 植秋滢, 巴德木其其格, 李文杰, 关潇, 李俊生. 呼伦贝尔草地退化现状评估与植被特征变化[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24118-. |
| [8] | 李艳朋, 陈洁, 卢春洋, 许涵. 海南尖峰岭热带山地雨林64 ha次生林动态监测样地群落结构特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24445-. |
| [9] | 陈自宏, 张翼飞, 陈凯, 陈见影, 徐玲. 高黎贡山南段昆虫病原真菌物种多样性及影响因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(1): 24228-. |
| [10] | 谭珂, 宁瑶, 王仁芬, 王晴, 梁丹萍, 辛子兵, 温放. 中国苦苣苔科植物名录与地理分布数据集[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(1): 23275-. |
| [11] | 何泽嵘, 叶鹏, 王舒婷, 关永鑫, 闫淑君, 洪心茹. 中国城市草坪的杂草优势种组成及空间分布[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(1): 24133-. |
| [12] | 韩佳楠, 苏杨, 李霏, 刘君妍, 赵依林, 李琳, 赵建成, 梁红柱, 李敏. 河北省苔藓植物多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(9): 24096-. |
| [13] | 魏诗雨, 宋天骄, 罗佳宜, 张燕, 赵子萱, 茹靖雯, 易华, 林雁冰. 秦岭火地塘针叶林土壤细菌群落的海拔分布格局[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(9): 24180-. |
| [14] | 李东红, 郝媛媛, 甘辉林, 张航, 刘耀猛, 他富源, 胡桂馨. 祁连山北麓中段不同类型草地蝗虫种类及分布[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(9): 24119-. |
| [15] | 牛红玉, 陈璐, 赵恒月, 古丽扎尔·阿不都克力木, 张洪茂. 城市化对动物的影响: 从群落到个体[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(8): 23489-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn