



生物多样性 ›› 2023, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (4): 22477. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2022477 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2022477
所属专题: 土壤生物与土壤健康
魏庐潞1,2, 徐婷婷3, 李媛媛4, 艾喆4, 马飞1,2,*( )
)
收稿日期:2022-08-10
接受日期:2022-11-08
出版日期:2023-04-20
发布日期:2023-04-20
通讯作者:
*E-mail: 基金资助:
Lulu Wei1,2, Tingting Xu3, Yuanyuan Li4, Zhe Ai4, Fei Ma1,2,*( )
)
Received:2022-08-10
Accepted:2022-11-08
Online:2023-04-20
Published:2023-04-20
Contact:
*E-mail: 摘要:
环境和遗传分化共同影响植物的功能性状, 进而能够通过根系分泌物影响根际微生物。本研究利用同质园试验, 通过高通量测序技术, 基于固氮酶基因nifH的同源性, 分析同质园栽培的不同种源小叶锦鸡儿(Caragana microphylla)、中间锦鸡儿(C. liouana)和荒漠锦鸡儿(C. roborovskyi)根际土壤固氮菌多样性, 并探究其与种源地气候及同质园土壤属性的关系。结果表明, 3种锦鸡儿植物根际土壤固氮菌隶属6门9纲18目21科33属72种, 其中变形菌门、疣微菌门和蓝细菌门为优势门, 优势属为中慢生根瘤菌属(Mesorhizobium)、固氮氢自养单胞菌属(Azohydromonas)和慢生根瘤菌属(Bradyrhizobium)。3种锦鸡儿根际土壤固氮菌α多样性种间差异不显著, 但中间锦鸡儿和荒漠锦鸡儿根际土壤固氮菌的α多样性存在显著的种内差异(P < 0.05), 小叶锦鸡儿和荒漠锦鸡儿根际土壤固氮菌群落结构存在显著的种内差异(P < 0.05)。冗余分析表明同质园土壤pH和种源地年均温分别是影响3种锦鸡儿根际土壤固氮菌多样性和群落结构变化的主要因子, 说明3种锦鸡儿属植物根际土壤固氮菌群落多样性受同质园环境与遗传分化的共同调控。本研究结果为锦鸡儿属植物的生态适应机制和引种栽培提供理论依据和数据支持。
魏庐潞, 徐婷婷, 李媛媛, 艾喆, 马飞 (2023) 同质园环境和遗传分化影响锦鸡儿属植物根际土壤固氮菌多样性和群落结构. 生物多样性, 31, 22477. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2022477.
Lulu Wei, Tingting Xu, Yuanyuan Li, Zhe Ai, Fei Ma (2023) The common garden environment and genetic differentiation jointly influence the diversity and community structure of nitrogen-fixing bacteria in the rhizosphere soil of three Caragana species. Biodiversity Science, 31, 22477. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2022477.
| 样点 Site | 东经 Longitude (E) | 北纬 Latitude (N) | 海拔 ALT (m) | 年均温 MAT (℃) | 年均降水量 MAP (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CM1 | 119.15° | 42.98° | 626 | 6.23 | 326.76 |
| CM2 | 121.88° | 44.03° | 1,178 | 6.68 | 331.43 |
| CM3 | 114.33° | 42.07° | 1,419 | 2.51 | 325.42 |
| CL1 | 110.28° | 39.33° | 1,285 | 7.34 | 382.46 |
| CL2 | 110.15° | 39.21° | 1,257 | 7.19 | 379.92 |
| CL3 | 107.67° | 38.85° | 1,344 | 7.42 | 225.23 |
| CR1 | 100.69° | 38.48° | 2,295 | 1.71 | 190.10 |
| CR2 | 103.15° | 36.88° | 2,314 | 5.38 | 303.75 |
| CR3 | 101.36° | 38.58° | 2,032 | 3.92 | 158.89 |
表1 小叶锦鸡儿(CM)、中间锦鸡儿(CL)和荒漠锦鸡儿(CR)不同种源地的地理和气候因子信息
Table 1 Geographical and climatic information of different sampling sites collecting seeds of Caragana microphylla (CM), C. liouana (CL), and C. roborovskyi (CR). ALT, Altitude; MAT, Mean annual temperature; MAP, Mean annual precipitation.
| 样点 Site | 东经 Longitude (E) | 北纬 Latitude (N) | 海拔 ALT (m) | 年均温 MAT (℃) | 年均降水量 MAP (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CM1 | 119.15° | 42.98° | 626 | 6.23 | 326.76 |
| CM2 | 121.88° | 44.03° | 1,178 | 6.68 | 331.43 |
| CM3 | 114.33° | 42.07° | 1,419 | 2.51 | 325.42 |
| CL1 | 110.28° | 39.33° | 1,285 | 7.34 | 382.46 |
| CL2 | 110.15° | 39.21° | 1,257 | 7.19 | 379.92 |
| CL3 | 107.67° | 38.85° | 1,344 | 7.42 | 225.23 |
| CR1 | 100.69° | 38.48° | 2,295 | 1.71 | 190.10 |
| CR2 | 103.15° | 36.88° | 2,314 | 5.38 | 303.75 |
| CR3 | 101.36° | 38.58° | 2,032 | 3.92 | 158.89 |
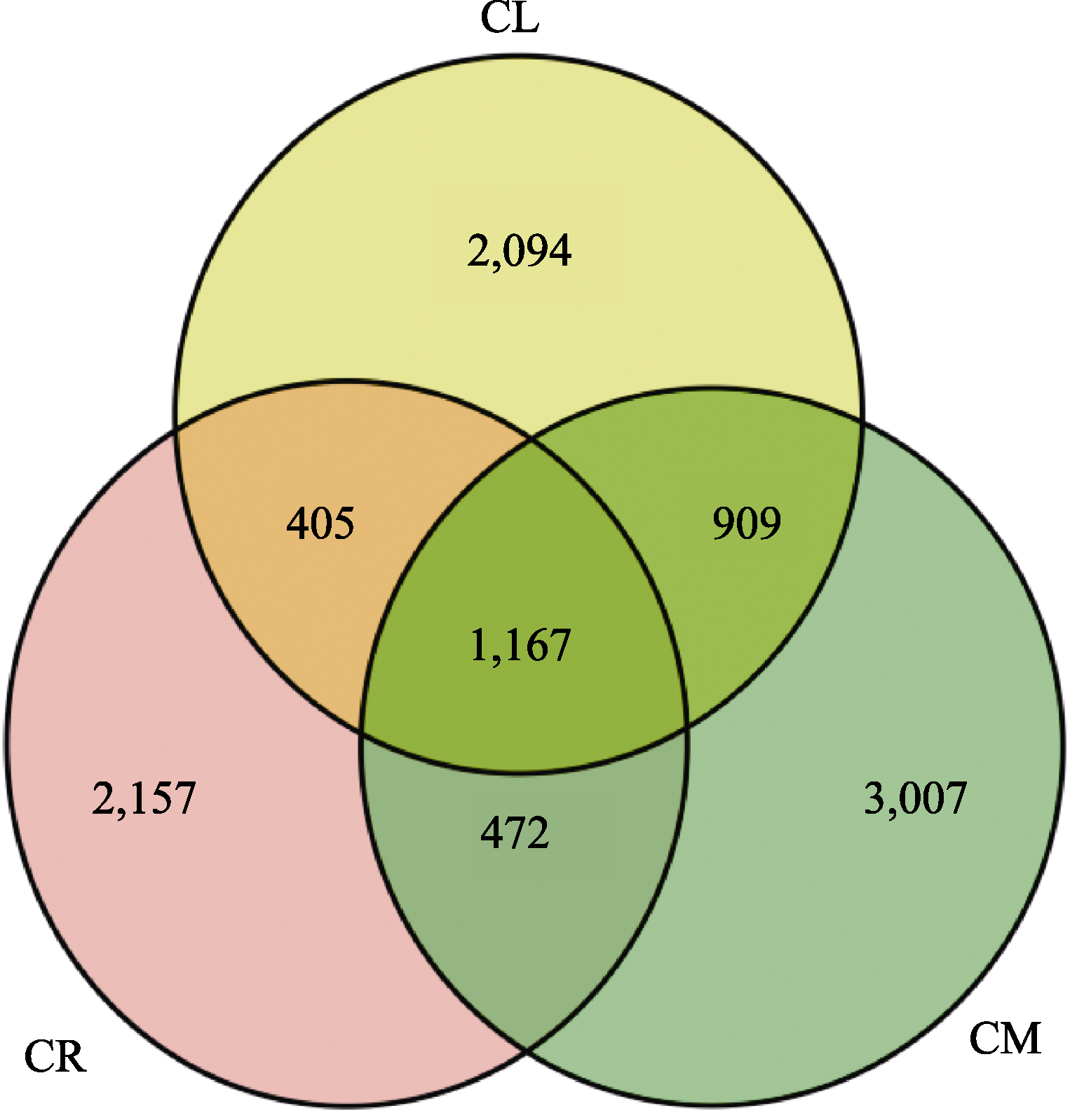
图1 小叶锦鸡儿(CM)、中间锦鸡儿(CL)和荒漠锦鸡儿(CR)根际土壤固氮菌OTUs分布Venn图
Fig. 1 Venn diagrams of rhizosphere soil nitrogen-fixing bacteria OTUs of Caragana microphylla (CM), C. liouana (CL), and C. roborovskyi (CR)
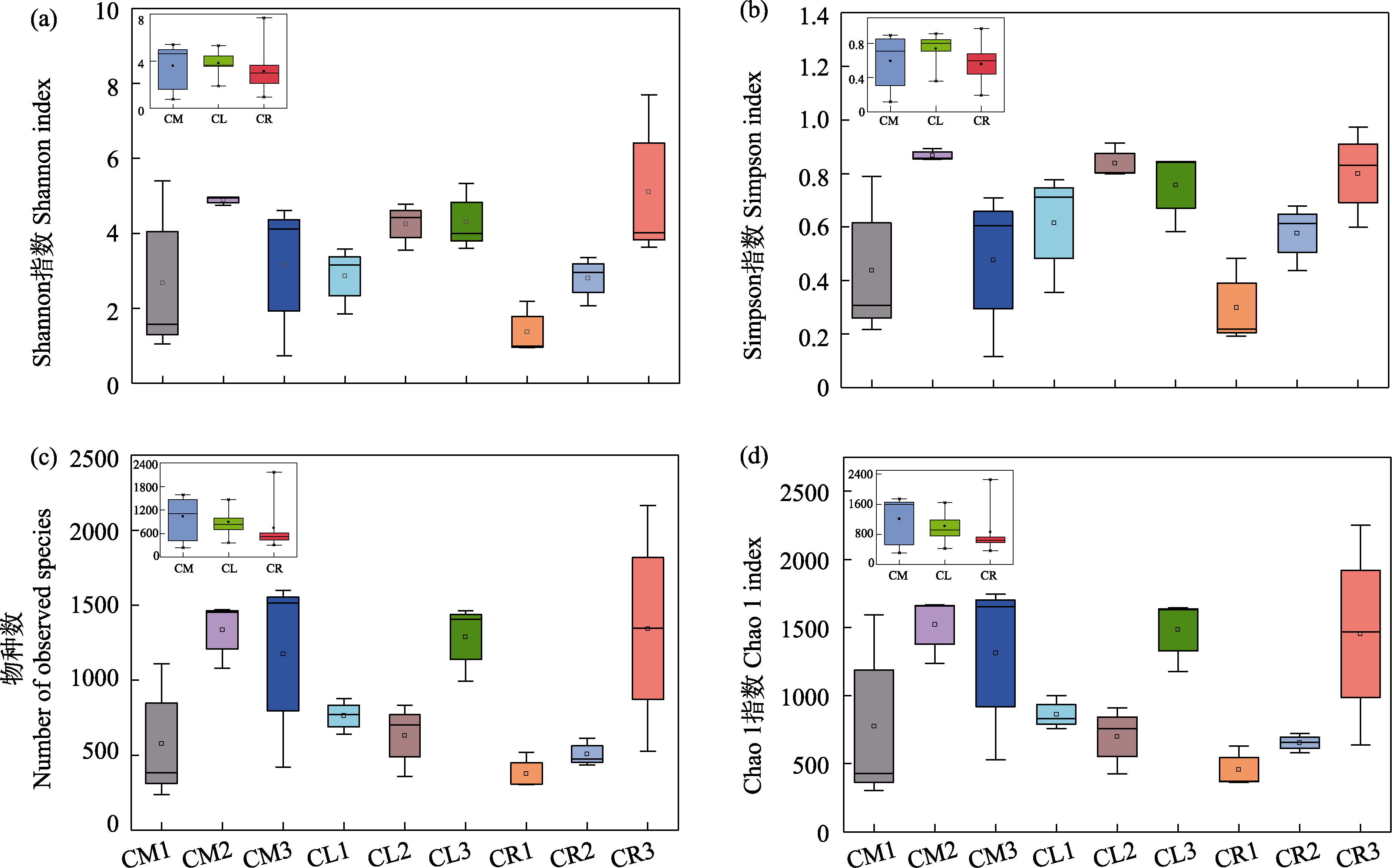
图2 小叶锦鸡儿(CM)、中间锦鸡儿(CL)和荒漠锦鸡儿(CR)根际土壤固氮菌α多样性指数。a: Shannon指数; b: Simpson指数; c: 物种数; d: Chao 1指数。嵌合图代表小叶锦鸡儿、中间锦鸡儿和荒漠锦鸡儿根际土壤固氮菌α多样性指数差异比较。
Fig. 2 α diversity index of rhizosphere soil nitrogen-fixing bacteria of Caragana microphylla (CM), C. liouana (CL), and C. roborovskyi (CR). a, Shannon index; b, Simpson index; c, Observed species; d, Chao 1 index. The chimeric plot represents a comparison of the α diversity indices of nitrogen-fixing bacteria in the rhizosphere soil of Caragana microphylla (CM), C. liouana (CL), and C. roborovskyi (CR).
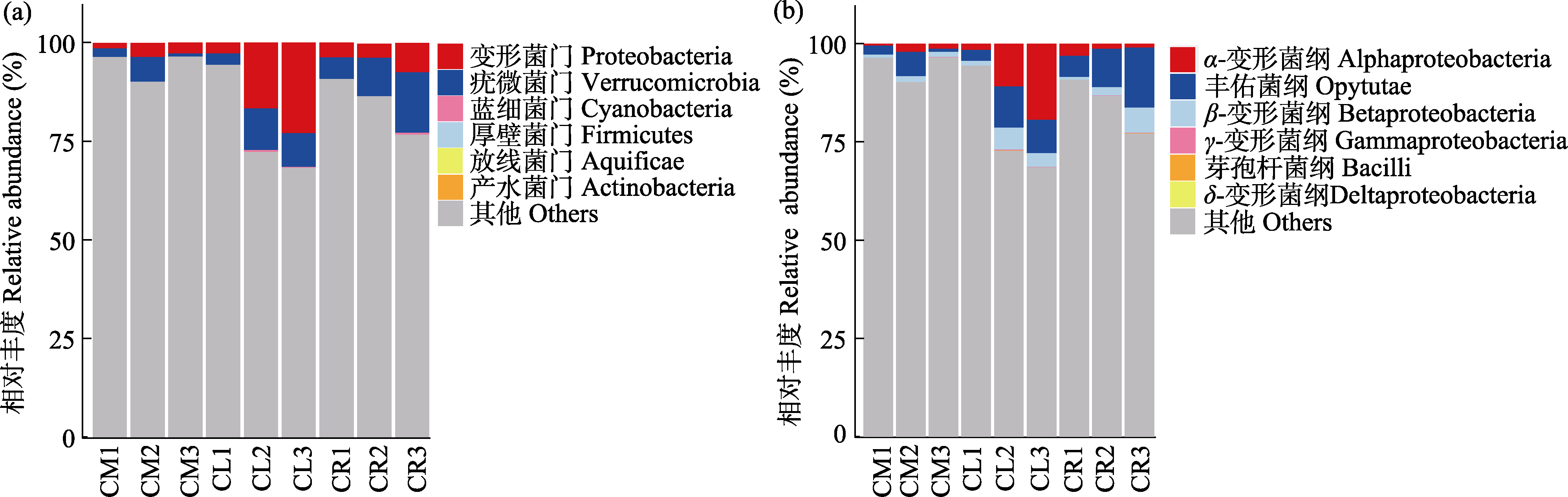
图3 门水平(a)和纲水平(b)小叶锦鸡儿(CM)、中间锦鸡儿(CL)和荒漠锦鸡儿(CR)根际土壤固氮菌优势群落分布
Fig. 3 Distribution of dominant communities of rhizosphere soil nitrogen-fixing bacteria at the phylum (a) and class (b) levels of Caragana microphylla (CM), C. liouana (CL), and C. roborovskyi (CR)
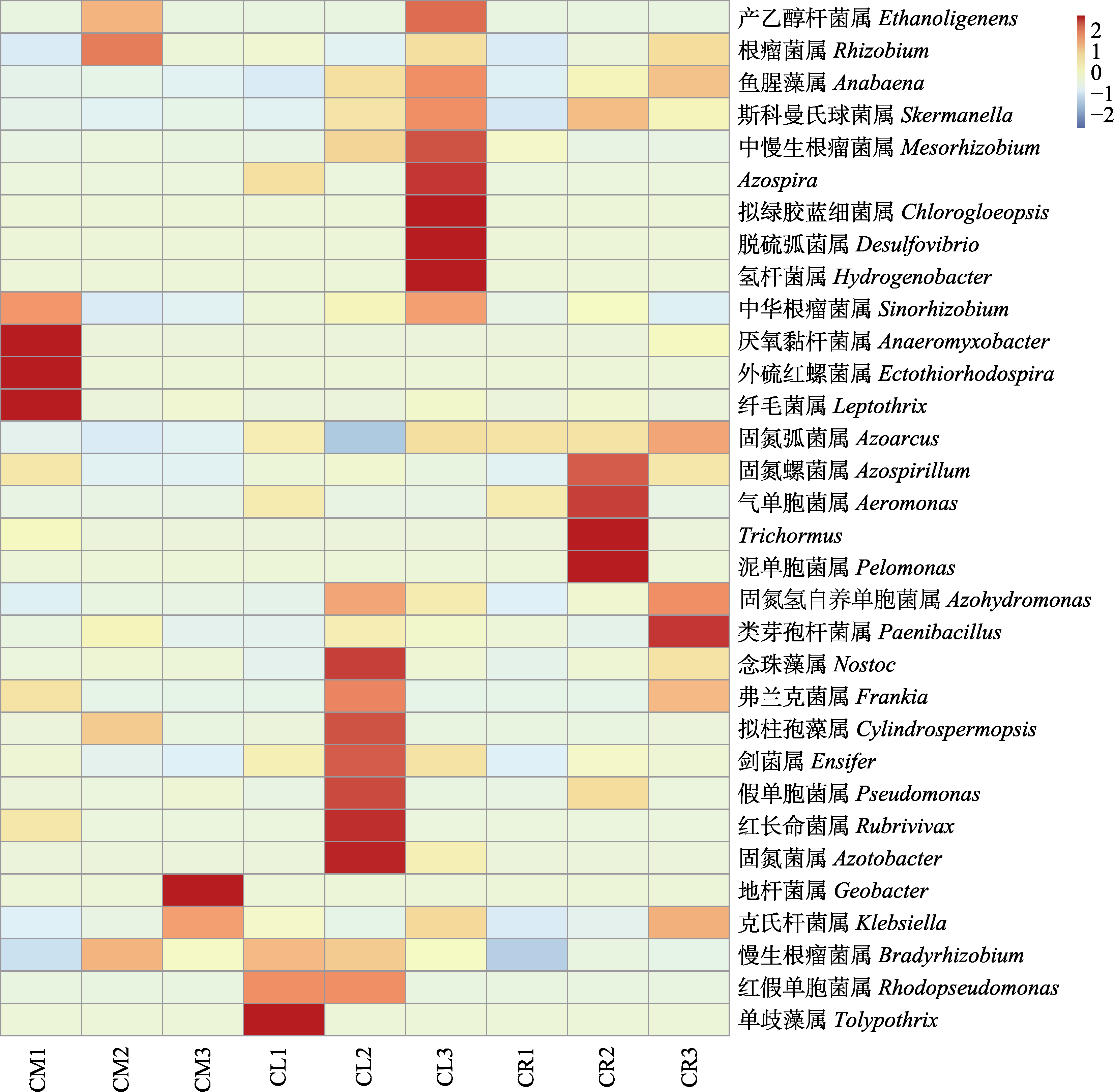
图4 属水平上小叶锦鸡儿(CM)、中间锦鸡儿(CL)和荒漠锦鸡儿(CR)根际土壤固氮菌群落结构热图
Fig. 4 Heatmap of rhizosphere soil nitrogen-fixing bacterial community structures of Caragana microphylla (CM), C. liouana (CL), and C. roborovskyi (CR) at the genus level
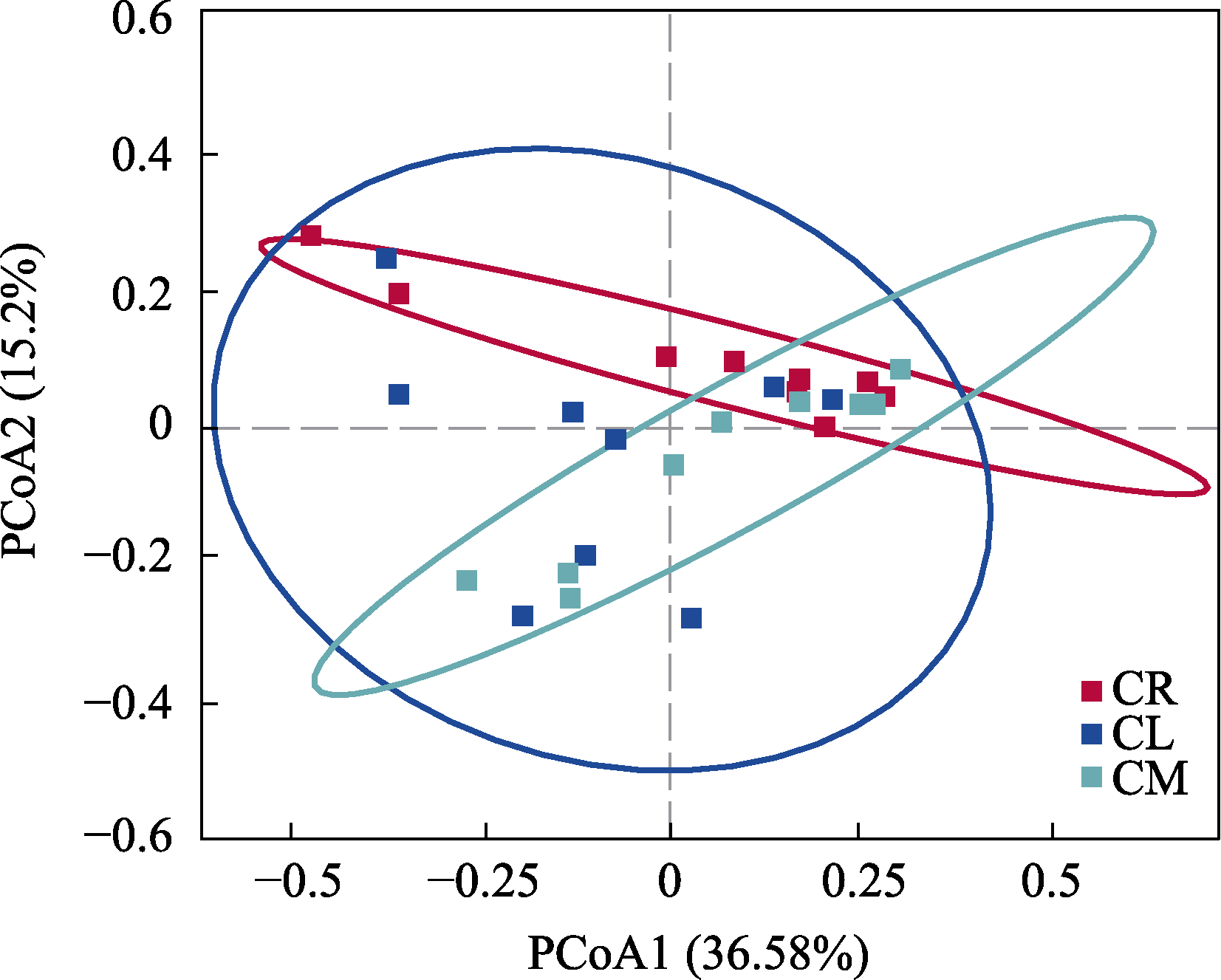
图5 小叶锦鸡儿(CM)、中间锦鸡儿(CL)和荒漠锦鸡儿(CR)根际土壤固氮菌群落结构的主坐标分析(PCoA)
Fig. 5 Principal coordinate analysis (PCoA) of rhizosphere soil nitrogen-fixing bacteria community composition of Caragana microphylla (CM), C. liouana (CL), and C. roborovskyi (CR)
| 优势类群 Dominant group | pH | 有机碳 SOC | 全氮 TN | 全磷 TP | 电导率 EC | 海拔 ALT | 年均降水量 MAP | 年均温 MAT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 门水平 Phylum level | ||||||||
| 变形菌门 Proteobacteria | ?0.316 | 0.197 | 0.118 | 0.228 | ?0.041 | ?0.053 | ?0.113 | 0.279 |
| 疣微菌门 Verrucomicrobia | ?0.458* | 0.129 | ?0.01 | 0.601** | 0.197 | 0.234 | ?0.24 | 0.047 |
| 蓝细菌门 Cyanobacteria | 0.192 | ?0.384* | ?0.317 | ?0.188 | ?0.19 | 0.134 | ?0.102 | 0.098 |
| 纲水平 Class level | ||||||||
| α-变形菌纲 Alphaproteobacteria | ?0.345 | 0.325 | 0.214 | 0.14 | ?0.009 | ?0.086 | ?0.063 | 0.253 |
| 丰佑菌纲 Opitutae | ?0.458* | 0.129 | ?0.01 | 0.601** | 0.197 | 0.234 | ?0.24 | 0.047 |
| β-变形菌纲 Betaproteobacteria | 0.055 | ?0.356 | ?0.271 | 0.286 | ?0.09 | 0.097 | ?0.165 | 0.101 |
| γ-变形菌纲 Gammaproteobacteria | 0.169 | ?0.336 | ?0.222 | ?0.036 | ?0.417* | ?0.047 | 0.140 | 0.147 |
| 属水平 Genus level | ||||||||
| 中慢生根瘤菌属 Mesorhizobium | ?0.374 | 0.351 | 0.237 | 0.154 | 0.030 | ?0.074 | ?0.084 | 0.216 |
| 固氮氢自养单胞菌属Azohydromonas | 0.050 | ?0.359 | ?0.261 | 0.287 | ?0.089 | 0.086 | ?0.149 | 0.105 |
| 慢生根瘤菌属 Bradyrhizobium | 0.303 | ?0.365 | ?0.299 | ?0.232 | ?0.487** | ?0.250 | 0.416* | 0.406* |
| 斯科曼氏球菌属 Skermanella | 0.317 | ?0.127 | ?0.158 | 0.031 | ?0.236 | 0.146 | ?0.139 | 0.279 |
| 念珠藻属 Nostoc | 0.217 | ?0.486* | ?0.391* | ?0.337 | ?0.208 | ?0.037 | 0.087 | 0.127 |
表2 环境因子与固氮菌群落类群不同分类水平的相关性分析。pH: 土壤pH; EC: 土壤电导率; TN: 土壤全氮; TP: 土壤全磷; SOC: 土壤有机碳; ALT: 海拔; MT: 年均温; MAP: 年均降水量。
Table 2 Correlation analysis of environmental factors with different taxonomic levels of nitrogen-fixing bacterial communities. * P < 0.05; ** P < 0.01. SOC, Soil organic carbon; TN, Total nitrogen; TP, Total phosphorus; EC, Electrical conductivity; ALT, Altitude; MAP, Mean annual precipitation; MAT, Mean annual temperature.
| 优势类群 Dominant group | pH | 有机碳 SOC | 全氮 TN | 全磷 TP | 电导率 EC | 海拔 ALT | 年均降水量 MAP | 年均温 MAT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 门水平 Phylum level | ||||||||
| 变形菌门 Proteobacteria | ?0.316 | 0.197 | 0.118 | 0.228 | ?0.041 | ?0.053 | ?0.113 | 0.279 |
| 疣微菌门 Verrucomicrobia | ?0.458* | 0.129 | ?0.01 | 0.601** | 0.197 | 0.234 | ?0.24 | 0.047 |
| 蓝细菌门 Cyanobacteria | 0.192 | ?0.384* | ?0.317 | ?0.188 | ?0.19 | 0.134 | ?0.102 | 0.098 |
| 纲水平 Class level | ||||||||
| α-变形菌纲 Alphaproteobacteria | ?0.345 | 0.325 | 0.214 | 0.14 | ?0.009 | ?0.086 | ?0.063 | 0.253 |
| 丰佑菌纲 Opitutae | ?0.458* | 0.129 | ?0.01 | 0.601** | 0.197 | 0.234 | ?0.24 | 0.047 |
| β-变形菌纲 Betaproteobacteria | 0.055 | ?0.356 | ?0.271 | 0.286 | ?0.09 | 0.097 | ?0.165 | 0.101 |
| γ-变形菌纲 Gammaproteobacteria | 0.169 | ?0.336 | ?0.222 | ?0.036 | ?0.417* | ?0.047 | 0.140 | 0.147 |
| 属水平 Genus level | ||||||||
| 中慢生根瘤菌属 Mesorhizobium | ?0.374 | 0.351 | 0.237 | 0.154 | 0.030 | ?0.074 | ?0.084 | 0.216 |
| 固氮氢自养单胞菌属Azohydromonas | 0.050 | ?0.359 | ?0.261 | 0.287 | ?0.089 | 0.086 | ?0.149 | 0.105 |
| 慢生根瘤菌属 Bradyrhizobium | 0.303 | ?0.365 | ?0.299 | ?0.232 | ?0.487** | ?0.250 | 0.416* | 0.406* |
| 斯科曼氏球菌属 Skermanella | 0.317 | ?0.127 | ?0.158 | 0.031 | ?0.236 | 0.146 | ?0.139 | 0.279 |
| 念珠藻属 Nostoc | 0.217 | ?0.486* | ?0.391* | ?0.337 | ?0.208 | ?0.037 | 0.087 | 0.127 |
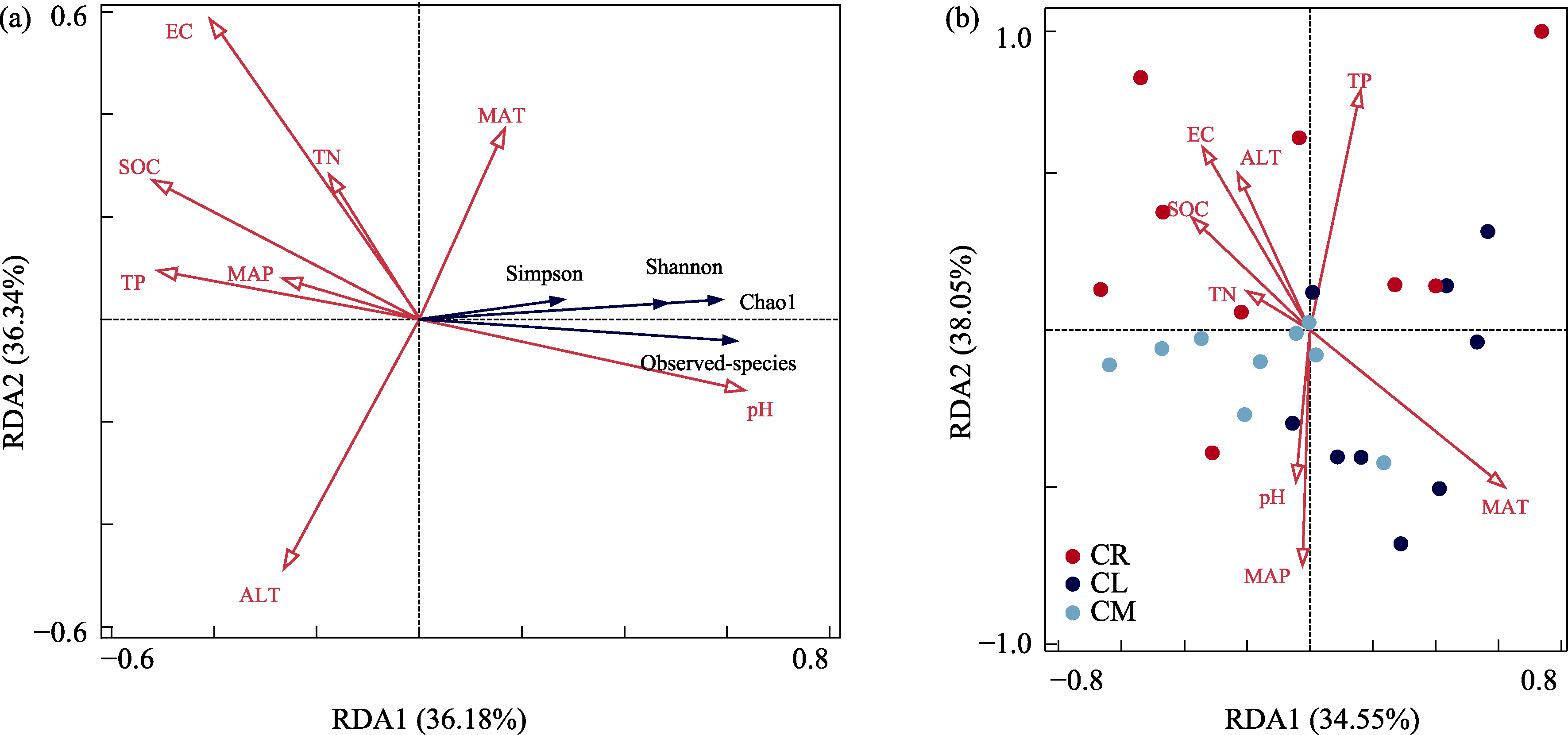
图6 小叶锦鸡儿(CM)、中间锦鸡儿(CL)和荒漠锦鸡儿(CR)根际土壤固氮菌多样性(a)和群落结构与环境因子的冗余分析(b)。缩写全称见表2。
Fig. 6 Redundancy analysis of environmental factors on diversity (a) and composition (b) of rhizosphere soil nitrogen-fixing bacteria community of Caragana microphylla (CM), C. liouana (CL), and C. roborovskyi (CR). Full names of abbreviations see Table 2.
| α多样性 α diversity | 群落结构 Community structure | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 环境因子 Environmental factor | 解释度 Explains (%) | P | 环境因子 Environmental factor | 解释度 Explains (%) | P |
| pH | 14.5 | 0.048 | 年均温 MAT | 14.2 | 0.036 |
| 全氮 TN | 5.9 | 0.182 | 全磷 TP | 8.3 | 0.072 |
| 海拔 ALT | 6.1 | 0.196 | 年均降水量 MAP | 7.8 | 0.108 |
| 年均降水量 MAP | 5.4 | 0.238 | 有机碳 SOC | 5.6 | 0.158 |
| 全磷 TP | 2.2 | 0.438 | 电导率 EC | 2.2 | 0.490 |
| 电导率 EC | 2 | 0.454 | 海拔 ALT | 2 | 0.498 |
| 年均温 MAT | 0.2 | 0.848 | pH | 1.8 | 0.544 |
| 有机碳 SOC | < 0.1 | 0.902 | 全氮 TN | 0.7 | 0.838 |
表3 环境因子对小叶锦鸡儿(CM)、中间锦鸡儿(CL)和荒漠锦鸡儿(CR)土壤固氮菌多样性和群落结构的影响。缩写全称见表2。
Table 3 Effects of environmental factors on diversity and composition of rhizosphere soil nitrogen-fixing bacterial community of Caraganamicrophylla (CM), C. liouana (CL), and C. roborovskyi (CR). Full names of abbreviations see Table 2.
| α多样性 α diversity | 群落结构 Community structure | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 环境因子 Environmental factor | 解释度 Explains (%) | P | 环境因子 Environmental factor | 解释度 Explains (%) | P |
| pH | 14.5 | 0.048 | 年均温 MAT | 14.2 | 0.036 |
| 全氮 TN | 5.9 | 0.182 | 全磷 TP | 8.3 | 0.072 |
| 海拔 ALT | 6.1 | 0.196 | 年均降水量 MAP | 7.8 | 0.108 |
| 年均降水量 MAP | 5.4 | 0.238 | 有机碳 SOC | 5.6 | 0.158 |
| 全磷 TP | 2.2 | 0.438 | 电导率 EC | 2.2 | 0.490 |
| 电导率 EC | 2 | 0.454 | 海拔 ALT | 2 | 0.498 |
| 年均温 MAT | 0.2 | 0.848 | pH | 1.8 | 0.544 |
| 有机碳 SOC | < 0.1 | 0.902 | 全氮 TN | 0.7 | 0.838 |
| [1] |
Abdelfattah A, Wisniewski M, Schena L, Tack A (2021) Experimental evidence of microbial inheritance in plants and transmission routes from seed to phyllosphere and root. Environmental Microbiology, 23, 2199-2214.
DOI PMID |
| [2] |
Albaugh TJ, Fox TR, Maier CA, Campoe OC, Rubilar RA, Cook RL, Raymond JE, Alvares CA, Stape JL (2018) A common garden experiment examining light use efficiency and heat sum to explain growth differences in native and exotic Pinus taeda. Forest Ecology and Management, 425, 35-44.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
Baker KL, Langenheder S, Nicol GW, Ricketts D, Killham K, Campbell CD, Prosser JI (2009) Environmental and spatial characterisation of bacterial community composition in soil to inform sampling strategies. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 41, 2292-2298.
DOI URL |
| [4] | Bao SD (2000) Soil Agrochemical Analysis. China Agriculture Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 鲍士旦 (2000) 土壤农化分析. 中国农业出版社, 北京.] | |
| [5] |
Berendsen RL, Pieterse CMJ, Bakker PAHM (2012) The rhizosphere microbiome and plant health. Trends in Plant Science, 17, 478-486.
DOI PMID |
| [6] |
Bowen JL, Kearns PJ, Byrnes JEK, Wigginton S, Allen WJ, Greenwood M, Tran K, Yu J, Cronin JT, Meyerson LA (2017) Lineage overwhelms environmental conditions in determining rhizosphere bacterial community structure in a cosmopolitan invasive plant. Nature Communications, 8, 433.
DOI PMID |
| [7] |
Che RX, Deng YC, Wang F, Wang WJ, Xu ZH, Hao YB, Xue K, Zhang B, Tang L, Zhou HK, Cui XY (2018) Autotrophic and symbiotic diazotrophs dominate nitrogen-fixing communities in Tibetan grassland soils. Science of the Total Environment, 639, 997-1006.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
Delgado-Baquerizo M, Fry EL, Eldridge DJ, de Vries FT, Manning P, Hamonts K, Kattge J, Boenisch G, Singh BK, Bardgett RD (2018) Plant attributes explain the distribution of soil microbial communities in two contrasting regions of the globe. New Phytologist, 219, 574-587.
DOI PMID |
| [9] |
Geng LL, Shao GX, Ben R, Wang ML, Sun XX, Shu CL, Zhang J (2018) Subterranean infestation by Holotrichia parallela larvae is associated with changes in the peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.) rhizosphere microbiome. Microbiological Research, 211, 13-20.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
Guo HY, Gao YB, Ma CC, Ren AZ, Wu JB, Wang YH (2008) Genetic diversity and genetic relationship of Caragana microphylla, Caragana davazamcii and Caragana korshinskii in Inner Mongolia Plateau. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 28, 3729-3736. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
| [ 郭宏宇, 高玉葆, 马成仓, 任安芝, 吴建波, 王银华 (2008) 内蒙古高原小叶锦鸡儿(Caragana microphylla)、中间锦鸡儿(C. davazamcii)和柠条锦鸡儿(C. korshinskii)的遗传多样性及遗传关系. 生态学报, 28, 3729-3736.] | |
| [11] |
Haas BJ, Gevers D, Earl AM, Feldgarden M, Ward DV, Giannoukos G, Ciulla D, Tabbaa D, Highlander SK, Sodergren E, Methé B, DeSantis TZ, Consortium HM, Petrosino JF, Knight R, Birren BW (2011) Chimeric 16S rRNA sequence formation and detection in Sanger and 454-pyrosequenced PCR amplicons. Genome Research, 21, 494-504.
DOI PMID |
| [12] |
Hu XJ, Liu JJ, Zhu P, Wei D, Jin J, Liu XB, Wang GH (2018) Long-term manure addition reduces diversity and changes community structure of diazotrophs in a neutral black soil of northeast China. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 18, 2053-2062.
DOI |
| [13] |
Jason R, Siefert JL, Staples CR, Blankenship RE (2004) The Natural History of Nitrogen Fixation. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 21, 541-554.
PMID |
| [14] |
Ji RX, Yu X, Chang Y, Shen C, Bai XQ, Xia XL, Yin WL, Liu C (2020) Geographical provenance variation of leaf anatomical structure of Caryopteris mongholica and its significance in response to environmental changes. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 44, 277-286. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[ 纪若璇, 于笑, 常远, 沈超, 白雪卡, 夏新莉, 尹伟伦, 刘超 (2020) 蒙古莸叶片解剖结构的地理种源变异及其对环境变化响应的意义. 植物生态学报, 44, 277-286.]
DOI |
|
| [15] | Li YY, Xu TT, Ai Z, Ma F (2021) Fungal community diversity and driving factors in rhizosphere soil of Caragana species across semi-arid regions, China. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 32, 4289-4297. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[ 李媛媛, 徐婷婷, 艾喆, 马飞 (2021) 半干旱区锦鸡儿属植物根际土壤真菌群落多样性及驱动因素. 应用生态学报, 32, 4289-4297.]
DOI |
|
| [16] | Li YY, Xu TT, Ai Z, Wei LL, Ma F (2022) Differences in bacterial community structure in rhizosphere soil of three Caragana species and its driving factors in a common garden experiment, China. Environmental Science, 43, 3854-3864. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 李媛媛, 徐婷婷, 艾喆, 魏庐潞, 马飞 (2022) 同质环境下不同锦鸡儿属植物根际土壤细菌群落结构差异及其影响因素. 环境科学, 43, 3854-3864.] | |
| [17] |
Lin YX, Ye GP, Liu DY, Ledgard S, Luo JF, Fan JB, Yuan JJ, Chen ZM, Ding WX (2018) Long-term application of lime or pig manure rather than plant residues suppressed diazotroph abundance and diversity and altered community structure in an acidic Ultisol. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 123, 218-228.
DOI URL |
| [18] | Liu S, Wang JG, Ci ZL, Bai SL, Shao DH (2012) AMF diversity in Caragana in different habitats of Oerhtossu Plateau, China. Journal of Inner Mongolia Agricultural University (Natural Science Edition), 33(4), 74-80. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 刘声, 王琚钢, 慈忠玲, 白淑兰, 邵东华 (2012) 鄂尔多斯高原不同生境锦鸡儿属植物AMF多样性. 内蒙古农业大学学报, 33(4), 74-80.] | |
| [19] |
Lladó S, Jiménez N, Viñas M, Solanas AM (2009) Microbial populations related to PAH biodegradation in an aged biostimulated creosote-contaminated soil. Biodegradation, 20, 593-601.
DOI PMID |
| [20] | Ma F, Xu TT, Li M, Liu JL, Wang J, Zhao LX, Wang HJ, Na XF (2017) Effect of plantation of Caragana species on soil properties and bacterial community dynamics in saline-alkali soil. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 37, 1872-1880. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 马飞, 徐婷婷, 李明, 刘吉利, 王静, 赵聆希, 王贺瑾, 纳小凡 (2017) 锦鸡儿植物对盐碱地土壤理化性质和细菌群落的影响. 西北植物学报, 37, 1872-1880.] | |
| [21] | Ma RP, Dai XL, Liu GY, Xie YC, Gao XL, Gao X (2021) Effects of fertilizer patterns on the potential nitrogen fixation rate and community structure of asymbiotic diazotroph in highland barley fields on the Tibetan Plateau. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 29, 1692-1703. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 马瑞萍, 戴相林, 刘国一, 谢永春, 高小丽, 高雪 (2021) 施肥模式对青稞田土壤潜在固氮速率和自生固氮微生物群落结构的影响. 中国生态农业学报, 29, 1692-1703.] | |
| [22] | Ma XY, Liu LL, Yin MQ, Song HJ, Zhu PC, Yu XN, Du N, Wang RQ, Guo WH (2021) Variation in plant functional traits of Phragmites australis based on field investigation and common garden experiment. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 41, 3755-3764. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 马香艳, 刘乐乐, 尹美淇, 宋慧佳, 朱鹏程, 于晓娜, 杜宁, 王仁卿, 郭卫华 (2021) 基于野外调查和同质种植园实验的芦苇植物功能性状变异研究. 生态学报, 41, 3755-3764.] | |
| [23] |
Na XF, Xu TT, Li M, Zhou ZN, Ma SL, Wang J, He J, Jiao BZ, Ma F (2018) Variations of bacterial community diversity within the rhizosphere of three phylogenetically related perennial shrub plant species across environmental gradients. Frontiers in Microbiology, 9, 709.
DOI PMID |
| [24] | Nie G, Chen WM, Wei GH (2014) Genetic diversity of rhizobia isolated from shrubby and herbaceous legumes in Shenmu arid area, China. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 25, 1674-1680. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 聂刚, 陈卫民, 韦革宏 (2014) 神木地区耐旱灌木和草本豆科植物根瘤菌遗传多样性. 应用生态学报, 25, 1674-1680.] | |
| [25] | Peiffer JA, Spor A, Koren O, Jin Z, Tringe SG, Dangl JL, Buckler ES, Ley RE (2013) Diversity and heritability of the maize rhizosphere microbiome under field conditions. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the USA, 110, 6548-6553. |
| [26] | Quast C, Pruesse E, Yilmaz P, Gerken J, Schweer T, Yarza P, Peplies J, Glöckner FO (2013) The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: Improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Research, 41, D590-D596. |
| [27] |
Rösch C, Mergel A, Bothe H (2002) Biodiversity of denitrifying and dinitrogen-fixing bacteria in an acid forest soil. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 68, 3818-3829.
DOI PMID |
| [28] | Vitousek P, Cassman K, Cleveland C, Crews T, Field C, Grimm N, Howarth R, Marino R, Martinelli L, Rastetter E, Sprent J (2002) Towards an ecological understanding of biological nitrogen fixation. Biogeochemistry, 57/58, 1-45. |
| [29] | Wang CC, Zhong QL, Cheng DL, Yu H, Xu CB (2019) Relationship between the leaf functional traits of Zenia insignis and the provenance environments in common gardens during the introduction period. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 39, 4892-4899. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 王楚楚, 钟全林, 程栋梁, 余华, 徐朝斌 (2019) 引种期同质园翅荚木主要叶功能性状与种源地环境关系. 生态学报, 39, 4892-4899.] | |
| [30] |
Wang J, Bao JT, Li XR, Liu YB (2016) Molecular ecology of nifH genes and transcripts along a chronosequence in revegetated areas of the Tengger Desert. Microbial Ecology, 71, 150-163.
DOI PMID |
| [31] |
Wang JM, Wang Y, He NP, Ye ZQ, Chen C, Zang RG, Feng YM, Lu Q, Li JW (2020) Plant functional traits regulate soil bacterial diversity across temperate deserts. Science of the Total Environment, 715, 136976.
DOI URL |
| [32] | Wang L, Wang J, Zhang AJ, Zhang H, Zhang YC (2020) Effects of long-term organic fertilization on soil diazotrophic community structure and diversity under wheat-sweet potato rotation system. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 40, 5771-5782. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 王磊, 王静, 张爱君, 张辉, 张永春 (2020) 小麦-甘薯轮作长期增施有机肥对碱性土壤固氮菌群落结构及多样性的影响. 生态学报, 40, 5771-5782.] | |
| [33] |
Wang Q, Garrity GM, Tiedje JM, Cole JR (2007) Naive Bayesian classifier for rapid assignment of rRNA sequences into the new bacterial taxonomy. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 73, 5261-5267.
DOI PMID |
| [34] | Wang YS, Li CN, Kou YP, Wang JJ, Tu B, Li H, Li XZ, Wang CT, Yao MJ (2017) Soil pH is a major driver of soil diazotrophic community assembly in Qinghai-Tibet alpine meadows. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 115, 547-555. |
| [35] | Wang YS, Li CN, Shen ZH, Rui JP, Jin DC, Li JB, Li XZ (2019) Community assemblage of free-living diazotrophs along the elevational gradient of Mount Gongga. Soil Ecology Letters, 1, 136-146. |
| [36] | Wang ZM, Li CH, Ma QL, Li QX, Wei YR, Zhao J, Yu JL, Xi NNG (2021) Moisture, salinity and pH co-driving spatial heterogeneity of Verrucomicrobial populations in Xilin River landscape, China. Acta Microbiologica Sinica, 61, 1728-1742. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 王泽铭, 李传虹, 马巧丽, 李千雪, 魏亚茹, 赵吉, 于景丽, 希尼尼根 (2021) 湿度盐度pH协同驱动锡林河景观疣微菌群空间异质性. 微生物学报, 61, 1728-1742.] | |
| [37] |
Xu B, Sun GL, Wang XM, Lu JW, Wang IJ, Wang Z (2017) Population genetic structure is shaped by historical, geographic, and environmental factors in the leguminous shrub Caragana microphylla on the Inner Mongolia Plateau of China. BMC Plant Biology, 17, 200.
DOI URL |
| [38] |
Xu YD, Zhang W, Zhong ZK, Guo SJ, Han XH, Yang GH, Ren CJ, Chen ZX, Dai YY, Qiao WJ (2019) Vegetation restoration alters the diversity and community composition of soil nitrogen-fixing microorganisms in the loess hilly region of China. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 83, 1378-1386.
DOI URL |
| [39] | Yang YD, Feng XM, Hu YG, Ren CZ, Zeng ZH (2017) Effects of legume-oat intercropping on abundance and community structure of soil N2-fixing bacteria. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 28, 957-965. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[ 杨亚东, 冯晓敏, 胡跃高, 任长忠, 曾昭海 (2017) 豆科作物间作燕麦对土壤固氮微生物丰度和群落结构的影响. 应用生态学报, 28, 957-965.]
DOI |
|
| [40] | Zhang C, Liu GB, Xue S, Wang GL (2016) Soil bacterial community dynamics reflect changes in plant community and soil properties during the secondary succession of abandoned farmland in the Loess Plateau. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 97, 40-49. |
| [41] |
Zhang P, Li XR, Zhang ZS, Pan YX, Liu YM, Su JQ (2012) Nitrogen fixation potential of biological soil crusts in southeast edge of Tengger Desert, Northwest China. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 23, 2157-2164. (in Chinese with English abstract)
PMID |
|
[ 张鹏, 李新荣, 张志山, 潘艳霞, 刘艳梅, 苏洁琼 (2012) 腾格里沙漠东南缘生物土壤结皮的固氮潜力. 应用生态学报, 23, 2157-2164.]
PMID |
|
| [42] |
Zhang TH, Su YZ, Cui JY, Zhang ZH, Chang XX (2006) A leguminous shrub (Caragana microphylla) in semiarid sandy soils of North China. Pedosphere, 16, 319-325.
DOI URL |
| [43] | Zhang YT, Jiang D, Tang J, Luo YF, Liang YM, Shah MMR, Jin P, Daroch M (2019) Isolation and characterization of two thermophilic Leptolyngbyaceae strains isolated from Huizhou area, China. Microbiology China, 46, 481-493. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 张艳婷, 江东, 唐杰, 雒义凡, 梁园梅, Shah MMR, 金鹏, Daroch M (2019) 两株采自惠州的细鞘丝藻亚科(Leptolyngbyaceae)嗜热蓝细菌的分离鉴定及细胞组分分析. 微生物学通报, 46, 481-493.] | |
| [44] | Zhang YX, Liu F, Duan N, Xu J, Chen HL, Zhang G (2014) Study on drought resistance of 4 species of Caragana, China. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 30, 25-29. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 章尧想, 刘芳, 段娜, 徐军, 陈海玲, 张格 (2014) 4种锦鸡儿属(Caragana)植物抗旱性研究. 中国农学通报, 30, 25-29.] | |
| [45] | Zhao H, Zhou YC (2020) Characteristics of structure and abundance of the nitrogen-fixing bacterial community in Pinus massoniana soil developed from different parent rocks. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 40, 6189-6201. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 赵辉, 周运超 (2020) 不同母岩发育马尾松土壤固氮菌群落结构和丰度特征. 生态学报, 40, 6189-6201.] | |
| [46] | Zhou ZY, Yu MH, Ding GD, Gao GL, He YY (2020) Diversity of bacterial communities in the rhizocompartments of Caragana in the Mu Us Desert. Journal of Desert Research, 40, 128-137. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[ 周子渊, 于明含, 丁国栋, 高广磊, 何莹莹 (2020) 毛乌素沙地锦鸡儿(Caragana)根系微域细菌群落多样性特征. 中国沙漠, 40, 128-137.]
DOI |
| [1] | 胡正艳, 郑全晶, 母其勇, 杜志强, 刘琳, 星耀武, 韩廷申. 不同纬度高蔊菜的交配系统和繁殖保障[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(6): 712-721. |
| [2] | 刘丽平, 宋瑞凤, 张馥, 张秀香, 彭桂香, 谭志远. 高秆野生稻内生固氮细菌多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2020, 28(8): 1018-1025. |
| [3] | 徐艳琴, 蔡婉珍, 胡生福, 黄小虎, 葛菲, 王瑛. 箭叶淫羊藿同质园栽培居群非腺毛多样性及其分类学启示[J]. 生物多样性, 2013, 21(2): 185-196. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn